Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 14
Enhanced growth and differentiation of myoblast cells grown on E-jet 3D printed platforms
Authors Chen H, Zhong J, Wang J, Huang R, Qiao X, Wang H, Tan Z
Received 6 November 2018
Accepted for publication 8 January 2019
Published 4 February 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 937—950
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S193624
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Haoxiang Chen,* Juchang Zhong,* Jian Wang, Ruiying Huang, Xiaoyin Qiao, Honghui Wang, Zhikai Tan
College of Biology, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan 410082, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Background: Skeletal muscle tissue engineering often involves the prefabrication of muscle tissues in vitro by differentiation and maturation of muscle precursor cells on a platform which provides an environment that facilitates the myogenic differentiation of the seeded cells.
Methods: Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) 3D printed scaffolds, which simulate the highly complex structure of extracellular matrix (ECM), were fabricated by E-jet 3D printing in this study. The scaffolds were used as platforms, providing environment that aids in growth, differentiation and other properties of C2C12 myoblast cells.
Results: The C2C12 myoblast cells grown on the PLGA 3D printed platforms had enhanced cell adhesion and proliferation. Moreover, the platforms were able to induce myogenic differentiation of the myoblast cells by promoting the formation of myotubes and up-regulating the expressions of myogenic genes (MyHC and MyOG).
Conclusion: The fabricated 3D printed platforms have excellent biocompatibility, thereby can potentially be used as functional cell culture platforms in skeletal tissue engineering and regeneration.
Keywords: myoblast, myogenic differentiation, 3D printing, 3D cell culture, skeletal muscle regeneration
Introduction
Skeletal muscles, which play important roles in generating physical movement, can be easily injured. Preventing and controlling skeletal muscle injury as well as speeding up and improving the healing process of muscle is a challenge in the field of sports medicine.1 The injured muscles are generally self-repaired through degeneration, repair, and tissue plasticity,2 or are traditionally treated by ice compress and surgical rehabilitation, which, however, have low efficiency.3 Moreover, the original function of muscles cannot be completely restored after treatments, which is easy to cause secondary injuries.4
Tissue engineering is an important field within the discipline of regenerative medicine and is a central means of tissue regeneration.3,5 Skeletal muscle regeneration often involves the prefabrication of muscle tissues in vitro by differentiation and maturation of muscle precursor cells on a scaffold which provides an environment that facilitates myogenic differentiation of the cultured cells.6 To improve the efficiency of myogenic differentiation, the properties of the scaffolds, such as spatial arrangement, porosity, and biocompatibility, need to be optimized. An in situ observation has shown that the tissues are enclosed by highly aligned basement membranes that comprise of numerous extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins and well-organized fibers with tissue-specific functions.7 With an appropriate scale, ECM in tissues such as nerve (10–15 μm), skin (60–120 μm), and muscle (50–300 μm) can be achieved.8 The alignments and orientations of these proteins, which can be reticulated, unidirectional, and disordered, can influence the function of cells that interact with them.9,10 Structure of scaffolds can provide a track for the cells within engineered tissues such as blood vessels, muscle, and skin.11
Three-dimensional (3D) culture technology has become a hot research topic in cell culture.12 It uses various methods and materials to provide a 3D environment for cell growth.13 Researchers have applied the 3D cell culture system in skeletal muscle tissue regeneration and discovered that it greatly improves the treatment efficacy.14,15 The 3D environment plays an important role in proliferation, differentiation, and fusion of skeletal muscle cells during repair; it not only provides a physical support for cell growth, but also delivers nutrients to cells.15 The differentiation and growth of skeletal muscle cells grown in 3D cell culture system have been shown to be similar to those grown in vivo.16–19 Therefore, numerous studies have focused on the fabrication of artificial scaffolds for using as promising biomimetic substrates. Techniques that have been used for such fabrication include microfabrication,20 selective laser sintering,21 phase separation,22 stereolithography,23 electrospinning,24 fused filament fabrication,25 and 3D printing.26–29
In this work, 3D culture systems were fabricated to culture myoblast cells, and their effects on skeletal muscle regeneration were demonstrated. The electrohydrodynamic jet (E-jet) 3D printing is a novel printing technique that has been utilized to fabricate a wide range of biomaterial scaffolds with precisely controlled geometry.30,31 We developed a variety of tissue engineering platforms using E-jet 3D printing.32 Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA), which has high biocompatibility, was used as the polymer to construct the fibrous scaffolds.33 The 3D printed scaffolds were able to control cell behaviors and provide appropriate 3D microenvironments for cells, and are thus suitable for clinical treatments of skeletal muscle injury.
Materials and methods
Materials
PLGA (obtained from Dai Gang, Beijing Shi, China; molecular weight [Mw] =5×105 Da, L-lactide/glycolide ratio =75:25) was used as the scaffold polymer. N,N-dimethylformamide ([DMF]; obtained from the Chinese Medicine Group, SINOPHARM, Beijing, China) was used as the solvent. DMEM and horse serum (HS) were purchased from Hyclone (Logan, UT, USA). Penicillin (100 units/mL), streptomycin (100 mg/mL), and trypsin-EDTA solution were purchased from Beyotime (Shanghai, China). FBS, ammonium persulfate, and PBS were purchased from Grand Biological Technology Co., Ltd (Shijiazhuang, China). Specific primary antibodies for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), myosin heavy chain (MyHC), and myogenin (MyOG) were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA, USA). Secondary antibodies (horseradish peroxidase [HRP]-conjugated anti-rabbit or anti-mouse) were purchased from TransGene Biotech (Beijing, China). An ECL-plus kit was purchased from Advansta (MenloPark, CA, USA). Nonfat milk was purchased from Difco (Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Triton X-100, tetramethylethylenediamine, and N,N-methylene bisacrylamide were obtained from Sigma (Shanghai, China). Alexa Fluor 568-Phalloidin and ProLong Gold Antifade Reagent, paraformaldehyde, and DAPI were purchased from Biotopped Science & Technology Co. Ltd. (Beijing, China).
Fabrication of cell culture platforms
The fabrication of various fibrillar structures that can provide suitable 3D environments for cell culture was carried out using a customized E-jet 3D printing system according to the previously reported method.31 The 3D printing system is composed of a 3D (X, Y, and Z axes) precision stage, a feeding system for the printing solution, a light source, an optical observation system, and a high-voltage power supply (Figure 1A). PLGA was dissolved in DMF to a concentration of 10% (w/v) and stirred for 10 hours until the solution became homogeneous. The resultant PLGA solution was then added into a 5 mL printing syringe and the flow rate was set to 0.1 mL/h. After applying a suitable voltage (2.6–3.0 kV) to the nozzle, filaments with controllable sizes were created as a consequence of varying forces applied to the printing solution when it was ejected. The distance between the needle and the substrate was set to 2 mm. Finally, by moving the substrate through different paths, different cell culture platforms were printed (Figure 1). The PLGA films were also fabricated by casting PLGA solution onto a superflat polytetrafluoroethylene plate at room temperature.
Cell culture
C2C12 myoblast cells, a cell line model widely used to study skeletal muscle regeneration, were purchased from Type Culture Collection of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). The cells were cultured in DMEM medium (Hyclone) supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin at 37°C in an incubator saturated with 5% CO2. During differentiation experiment, the differentiation medium containing DMEM and 2% HS was used.
Prior to cell seeding, the scaffolds (3×3×1.5 mm) were sterilized by soaking in 75% (v/v) ethanol for 24 hours and irradiating under ultraviolet light (800 mW) for 2 hours. After that, the scaffolds were rinsed three times with DMEM medium and then placed in a 12-well culture plate, in which cells were cultured at a cell density of 5.0×104 cells per well (the cells should uniformly grow on the scaffolds). Subsequently, the plate was incubated in a 37°C incubator saturated with 5% CO2. Cell spheroids were produced by mixing the cell suspension (5.0×106 cells/mL) and sodium alginate (2%, w/v) with prewarmed calcium chloride solution (1.5% [w/v]). The resultant cell droplets were then incubated at 37°C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 for 24 hours; as a result, spheroids with an average diameter of 3 mm were obtained. Flat PLGA films were used as a control.
Cell viability assay
Viability of cells grown on different cell culture platforms (PLGA films [control], spheroids, or 3D printed scaffolds) was evaluated. The cells were cultured for 7 days and were then harvested. The spheroids were rinsed with PBS and dissolved in sodium citrate. Following incubation at room temperature for 2 minutes, the solution was centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 5 minutes and the cell pellet was obtained (the supernatant was discarded). The 3D scaffolds and PLGA films were rinsed with PBS (the washing solution was collected) and were then digested with pancreatic enzyme for 15 minutes; after that, the reaction was terminated by adding 10% FBS (in culture medium). The digestion solution and the washing solution (that was previously collected) were mixed and centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 5 minutes and the pellet was collected.
Viability of cells grown in different culture platforms was evaluated using calcein-AM (stains live cells; Sigma-Aldrich Co., St Louis, MO, USA) and propidium iodide (PI) (stains dead cells; Sigma-Aldrich). After staining, the cells were diluted in assay buffer and were then observed under a fluorescence microscope (TI-S; Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The cell death rate was calculated by the following equation:
|
Characterization of cell growth
C2C12 cells were cultured on different cell culture platforms (PLGA films [control], spheroids, or 3D printed scaffolds) for up to 7 days. The concentrations of glucose and lactic acid in the culture medium were measured using glucose and lactic acid kits (Jiancheng, Nanjing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For the analysis of apoptosis, 300 μL of cell suspension (5×106 cells/mL) was mixed with 5 μL of Annexin-V and PI staining solution (Sigma-Aldrich). After 15 minutes of incubation in the dark at room temperature, the stained cells were quantified using a fluorescence-activated cell sorting flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA).
Cell proliferation rate was assessed by means of DNA, collagen, and calcium contents. The scaffolds with attached cells were digested with 1 mL of papain solution (125 mg/mL papain in 0.1 M sodium phosphate containing 5 mM Na2-EDTA and 5 mM cysteine-HCl, pH 6.5) at 60°C for 16 hours. A control using only the papain solution was also run in parallel. The contents of DNA, collagen, and calcium were determined using DNA, collagen, and calcium kits (TaKaRa, Kusatsu, Japan), respectively.
Cell adhesion and proliferation
The adhesion and proliferation of C2C12 cells on various 3D printed scaffolds were examined by vinculin staining, MTT assays, and DNA quantification. After the scaffolds were sterilized, C2C12 cells were seeded at a density of 5.0×104 cells/mL onto different 3D scaffolds with different filament gaps (30, 50, 100, 150, and 200 μm), and PLGA film was used as a control. After 4 hours of cell culture, the cells were observed under a microscope, in which eight to ten fields were randomly selected and the number of cells was counted. The number of cells in the control was set as 100%.
For the MTT assay, C2C12 cells were grown on scaffolds in a 24-well culture plate. At the end of the cell culture period, 100 μL of MTT solution (5 mg/mL; Sigma-Aldrich) was added to each well and then incubated at 37°C under 5% CO2 atmosphere for 4 hours. After that, the liquid was replaced with 650 μL of dimethyl sulfoxide (Chinese Medicine Group) and the plate was shaken at room temperature for 15 minutes. The optical density at 490 nm was then measured using a microplate reader (Benchmark Plus; Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA, USA).
Immunofluorescence microscopy
C2C12 cells were seeded either on the 3D scaffolds or PLGA films and grown for 24 hours. After the culture medium was replaced with differentiation medium, the cells were allowed to grow for an additional 9 days, between which the medium was replaced with fresh differentiation medium every 2 days. Immunofluorescence staining was performed to visualize the myogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells. The cultured C2C12 cells were fixed in 4% (w/v) formaldehyde for 15 minutes, and after rinsing with PBS, they were permeabilized with 0.1% (v/v) Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich) for 10 minutes. After that, 200 μL of 100 nM phalloidin was added and then incubated at room temperature in the dark for 45 minutes. Subsequently, 200 μL of 100 nM DAPI was added (to stain nucleus) and incubated for 15 minutes. The stained samples were visualized under a fluorescence microscope (TI-S; Nikon Corporation).
Western blotting
Cells cultured on different cell culture platforms were harvested and then rinsed with ice-cold PBS (pH 7.4). After that, the cells were lysed on ice with ice-cold lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 100 μg/mL phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride) for 30 minutes. The lysates were centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes at 4°C and the protein concentration was then measured. Following this, proteins of equivalent quantities (40–100 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE using 10% polyacrylamide gel; they were transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) and then blocked with 5% nonfat milk at room temperature for 1 hour. The membranes were subsequently incubated with primary antibodies (MyOG [rabbit anti-mouse; 1:1,000], MyHC [rabbit anti-mouse; 1:1,000], and GADPH [rabbit anti-mouse; 1:1,000]) at 4°C overnight. The binding of secondary antibody (HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit or anti-mouse) to primary antibodies was visualized on an Odyssey TM Infrared Imager (LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, NE, USA).
Quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR)
The total RNA of each sample was extracted using Trizol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. One milligram of RNA was used for the synthesis of cDNA using a reverse transcription reagent kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). qRT-PCR was carried out on 7500 Fast Real-time PCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific), operated using the following thermal cycles: 1 cycle of 95°C for 30 seconds, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 seconds, and 1 cycle of 60°C for 1 minute. The myogenic differentiation was assessed through two different myogenic genes, MyOG and MyHC, along with a housekeeping gene GAPDH. Primers suitable for qRT-PCR were purchased from GeneCopoeia (Guangzhou, China) (Table 1). The gene expression levels of the samples were normalized to the expression level of housekeeping gene GAPDH.
  | Table 1 Sequences of primers used in qRT-PCR |
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using Tukey’s honestly significant difference. Each experiment was repeated at least five times, and all results were presented as mean ± SD. P-value of <0.05 (P<0.05) was considered significant.
Results
Characteristics of cell culture platforms
Various cell culture platforms were fabricated using E-jet 3D printing to simulate highly complex structures of ECM in the human body. Figure 1 shows the schematic diagrams of the instrument set-up and the 3D printed cell culture scaffolds. Both the monolayer and multilayer PLGA-based scaffolds were printed directly onto the substrate (Figure 1B and D). The fibrillar structure of the scaffolds, which was controlled and designed by software, was observed under a microscope. As confirmed by scanning electron microscopy imaging (Figure 1D), the multilayer PLGA-based scaffolds have well-controlled and uniform anisotropic architecture, demonstrating that the E-jet 3D printing is a reliable tool for fabricating cell culture platforms with defined structures.
Characterization of cell growth
C2C12 cells were cultured on PLGA film, spheroids, and 3D printed multilayer scaffolds for 7 days. The cell viability experiment indicated that the cells cultured on the 3D printed scaffold had a significantly higher survival rate than control (Figure 2A and B). The concentrations of glucose, glycogen, and lactic acid in the culture media, which can indicate the proliferation of C2C12 cells, were measured. Glucose concentration in the culture medium for cells grown on the 3D printed scaffold was lower than that for cells grown on PLGA film (Figure 2C). Conversely, glycogen concentration (Figure 2D) and lactic acid concentration (Figure 2E) in the culture medium for cells grown on the 3D printed scaffold were greater than those for cells grown on PLGA film. These indicate that the metabolism of cells cultured on the 3D printed scaffolds is greater than that of cells cultured on PLGA films or spheroids.
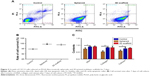
The results from flow cytometry also showed that 3D cultured cells had lower apoptotic rate than those cultured on PLGA films, indicating that these cells have better cell growth (Figure 3A and B). Compared with those grown on spheroid, the cells grown on 3D printed scaffolds have controlled morphology, which can affect their behaviors.31 Additionally, the 3D printed scaffolds also are significantly superior for large-scale cell culture.34,35 The contents of DNA, collagen, and calcium, which were measured at day 7 of the cell culture, for the cells cultured on the 3D printed scaffolds were higher than those for the cells cultured on PLGA film and spheroids. This demonstrates that cells cultured on the 3D printed scaffolds have higher proliferation rate (Figure 3C). These results indicate that the 3D printed scaffolds can improve the growth and proliferation of C2C12 cells, suggesting that they can mimic the physiological environment of the ECM.
Effects of 3D printed scaffolds with different fibrillar gaps on cell adhesion and proliferation
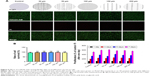
The effects of 3D printed scaffolds with varying fibrillar gaps (30, 50, 100, 150, and 200 μm) on cell adhesion and proliferation of C2C12 cells were investigated. PLGA film was used as a control. The adhesions of C2C12 cells onto different monolayer scaffolds were significantly different (Figure 4). After 4 hours of cell culture, the adhesions of cells onto scaffolds with 50 and 100 μm gaps were much higher than those onto scaffolds with other gap sizes (Figure 4B). This indicates that the fibrillar gap sizes can affect cell adhesion. Analysis of cell survival rates after 7 days of cell culture indicated that while cells grown on 3D printed scaffolds had higher survival rate than those grown on PLGA films (Figure 5), the fibrillar gaps had no significant effects on cell proliferation (Figure 5B and C).
Effects of 3D printed scaffolds with different fibrillar gaps on cell differentiation
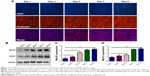
Myogenic differentiation plays a critical role in skeletal muscle regeneration; thus, the levels of MyOG and MyHC proteins, which are highly expressed during myogenic differentiation, were observed. The effects of 3D printed scaffolds with various fibrillar gaps on the differentiation of C2C12 cells were determined. Cells were immunofluorescence stained (nuclei and F-actin) and visualized, and protein and gene expression levels of MyHC and MyOG were monitored using Western blotting and qRT-PCR. The immunofluorescence staining indicated that, after 5 days of cell culture, the amount of myotubes observed in cells grown on the scaffolds was higher than that in cells grown on PLGA film (control), as shown in Figure 6A. However, the amount of myotubes varied among different scaffolds; cells grown on scaffolds with 50 μm fibrillar gaps had the highest differentiation rate. The Western blot results (Figure 6B) further showed that the expression levels of MyHC and MyOG proteins by C2C12 cells grown on the scaffolds with 50 μm fibrillar gaps were much higher than those by cells grown on scaffolds with other fibrillar gaps. Moreover, qRT-PCR results (Figure 6C and D) indicated that the expression levels of MyOG and MyHC genes in C2C12 cells grown on the scaffold with 50 μm fibrillar gaps were higher than those in cells grown on scaffolds with other fibrillar gaps. These observations show that the 3D printed scaffolds with 50 μm fibrillar gaps can promote the differentiation of C2C12 cells; therefore, they were subsequently used in differentiation experiment.
C2C12 cells were cultured on the 3D printed scaffolds with 50 μm fibrillar gaps for 9 days. The observations showed that the number of cells and the amount of myotubes increased with time (Figure 7A). The results from Western blot and qRT-PCR further showed that the expression levels of MyHC and MyOG, at both protein and gene levels, in C2C12 cells also increased with time (Figure 7B–D). This demonstrates that the 3D printed scaffolds with 50 μm fibrillar gaps can promote cell differentiation.
Effects of multilayer scaffolds on cell infiltration
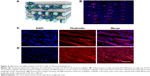
The infiltration and differentiation of C2C12 cells grown on the multilayer 3D printed scaffolds were investigated after 7 days of cell culture. The diagram illustrating how the cells were grown is shown in Figure 8A. Cell nuclei and F-actin were stained and visualized under a fluorescence microscope. The fluorescence image showed that C2C12 cells were able to infiltrate into the multilayer 3D-printed scaffolds and grow in all directions (Figure 8B). Additionally, after 48 hours of cell culture, the images (Figure 8C and D) further showed that cells grew without abnormal cell morphology, indicating that scaffolds can provide an environment that is suitable for cell differentiation and proliferation. Some intertwining cells were also observed in ECM.
Taken together, as indicated by the enhanced expression levels (both mRNA and protein levels) of myogenic markers, the formation of myotubes in C2C12 cells grown on 3D printed scaffolds was enhanced. This suggests that the 3D printed scaffolds may promote myogenic differentiation, which is an important process in skeletal muscle regeneration.
Discussion
Myotube formation is crucial for repair of muscular functions. Biomaterials that can enhance the differentiation of myoblast cells into myotubes are, therefore, highly desirable. In traditional skeletal muscle tissue engineering, myoblast cells and modified scaffolds are used to fabricate muscle tissues in vitro. Biocompatibility, biodegradability, and formation of polar parallel myotubes are the key factors determining the success of tissue-repaired transplantation.3,36 Studies have shown that orderly arranged 3D scaffolds can promote cell adhesion and proliferation.37 Ideal scaffolds should provide environments that are suitable for cell proliferation, differentiation, alignment, orientation, and migration during the reparation of tissue damages.38 This study used 3D printed platforms to promote myogenesis, a process necessary for muscle repair. The platforms were fabricated from biocompatible and biodegradable materials that simulate highly complex structures of ECM, and their effects on differentiation of C2C12 myoblast cells were observed.
The 3D cell environment plays a crucial role in cell growth in vivo;39 thus, accurate replication of such an environment can improve the reliability of in vitro 3D tissue models. We demonstrated that cell cultures carried out in 3D systems are different from those carried out in traditional two-dimensional (2D) systems. Our results showed that cells cultured on 3D printed scaffolds had significantly higher survival rate than those grown on 2D PLGA films. The concentrations of glucose, glycogen, and lactic acid are associated with cell proliferation and differentiation. The concentration of glucose in the culture medium for cells grown on 3D printed scaffolds was lower than that in the culture medium for cells grown on PLGA films (control). The concentrations of glycogen and lactic acid in the culture medium for cells grown on 3D printed scaffolds were increased compared with those for control, indicating that the metabolism of cells grown on the 3D printed scaffolds is higher than that of control cells. In addition, cells cultured on 3D printed scaffolds grew at a faster rate than those cultured on 2D films. It is possible that limited space in the 2D environment may inhibit cell growth, thus causing cell apoptosis,40,41 as was confirmed by flow cytometric analysis. The 3D printed scaffolds provide 3D space that can result in greater cell survival rate.42 Cells cultured in traditional 2D environments have different rates of proliferation and metabolism as well as different cell morphology compared with those of cells grown in vivo.43–45 The interactions between 2D-cultured cells are also different from those between cells grown in 3D environment.46,47
The evaluation of adhesion and growth of C2C12 cells grown on 3D printed scaffolds with varying fibrillar gaps showed that the fibrillar gaps affected cell adhesion. Cells grown for 4 hours on the 3D printed scaffolds with 50 and 100 μm fibrillar gaps had the highest adhesion rates, indicating that these fibrillar gaps are suitable for the adhesion of skeletal muscle cells. Sizes of skeletal muscle nucleus are generally 20–40 μm;48,49 it is likely that the fibrillar gap of 30 μm is too narrow for cell growth, while that of 100 μm is too large, and the proportion of attached to unattached cells decreased as the pore size increased.50 Moreover, the differentiation of C2C12 was highest on the 3D printed scaffolds with a fibrillar gap of 50 μm. Immunofluorescence staining also showed that myotubes had the highest density with more uniform arrangements. Ideal 3D scaffolds can effectively promote the initial attachment and proliferation of C2C12 cells. Studies have reported that improved adhesion or proliferation of myoblasts promotes differentiation due to confluence effect.51,52 These findings show that the 3D culture system can not only enhance cell adhesion and proliferation, but also help in myogenic differentiation.
Genes encoding MyHC and MyOG are highly expressed during myogenic differentiation; thus, they are used as the gene markers of C2C12 myotubes differentiation.33,36,53 Our Western blot and qRT-PCR results showed that the expression levels of MyHC and MyOG in C2C12 cells cultured on 3D printed scaffolds increased with culture time, demonstrating that the cells have good differentiation. Suitable multilayer 3D scaffolds are more conducive to the proliferation and migration of cells.54 These scaffolds can strongly influence the polarity of cells through a process called “contact guidance”.55,56 It is important that cells can penetrate into the scaffolds, whereby they differentiate and proliferate; thus, the scaffolds play an important role in the formation of skeletal muscle tissues. Although the developed 3D printed scaffolds could not completely mimic the structure and functions of a native cell microenvironment, their transplantation into the wounded skeletal muscle may aid in a better repair of muscle damages. Altogether, our results demonstrate that the developed 3D printed scaffolds are biocompatible and may be used as biomimetic platforms to promote cell differentiation, adhesion, and proliferation.
Conclusion
In this work, the 3D printed scaffolds, which simulate highly complex structures of ECM, were fabricated by E-jet 3D printing. The scaffolds were used as cell culture platforms for the culture of C2C12 myoblast cells. The results showed that the 3D printed platforms with suitable fibrillar gaps (50 μm) could enhance cell adhesion and proliferation. Moreover, they could induce the myogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblast cells by promoting myotubes formation and upregulating the expression of myogenic genes (MyHC and MyOG). The findings suggest that the 3D printed scaffolds have excellent biocompatibility and can potentially be used as biofunctional cell culture platforms for skeletal tissue engineering and regeneration.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 31600782), the Science and Technology Research and Development Foundation of Shenzhen (No JCYJ20170818112151323), and the Hunan University (No 53112102).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Zhang C, Wang C, Li Y, et al. Complement C3a signaling facilitates skeletal muscle regeneration by regulating monocyte function and trafficking. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):2078. | ||
Gilmore KJ, Kita M, Han Y, et al. Skeletal muscle cell proliferation and differentiation on polypyrrole substrates doped with extracellular matrix components. Biomaterials. 2009;30(29):5292–5304. | ||
Ma D, Wang Y, Dai W. Silk fibroin-based biomaterials for musculoskeletal tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;89:456–469. | ||
Bach AD, Beier JP, Stern-Staeter J, Horch RE. Skeletal muscle tissue engineering. J Cell Mol Med. 2004;8(4):413–422. | ||
Wang X, Ding B, Li B. Biomimetic electrospun nanofibrous structures for tissue engineering. Mater Today (Kidlington). 2013;16(6):229–241. | ||
Gilmore KJ, Kita M, Han Y, et al. Skeletal muscle cell proliferation and differentiation on polypyrrole substrates doped with extracellular matrix components. Biomaterials. 2009;30(29):5292–5304. | ||
Kim DH, Provenzano PP, Smith CL, Levchenko A. Matrix nanotopography as a regulator of cell function. J Cell Biol. 2012;197(3):351–360. | ||
Kim HN, Jiao A, Hwang NS, et al. Nanotopography-guided tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(4):536–558. | ||
Ghanian MH, Farzaneh Z, Barzin J, et al. Nanotopographical control of human embryonic stem cell differentiation into definitive endoderm. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(11):3539–3553. | ||
Cha C, Liechty WB, Khademhosseini A, Peppas NA. Designing biomaterials to direct stem cell fate. ACS Nano. 2012;6(11):9353–9358. | ||
Kim HN, Hong Y, Kim MS, Kim SM, Suh KY. Effect of orientation and density of nanotopography in dermal wound healing. Biomaterials. 2012;33(34):8782–8792. | ||
Kim MS, Lee B, Kim HN, et al. 3D tissue formation by stacking detachable cell sheets formed on nanofiber mesh. Biofabrication. 2017;9(1):015029. | ||
Mirabella T, Macarthur JW, Cheng D, et al. 3D-printed vascular networks direct therapeutic angiogenesis in ischaemia. Nat Biomed Eng. 2017;1(6):0083. | ||
Raman R, Cvetkovic C, Bashir R. A modular approach to the design, fabrication, and characterization of muscle-powered biological machines. Nat Protoc. 2017;12(3):519–533. | ||
Rao L, Qian Y, Khodabukus A, Ribar T, Bursac N. Engineering human pluripotent stem cells into a functional skeletal muscle tissue. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):126. | ||
Corona BT, Machingal MA, Criswell T, et al. Further development of a tissue engineered muscle repair construct in vitro for enhanced functional recovery following implantation in vivo in a murine model of volumetric muscle loss injury. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(11–12):1213–1228. | ||
Corona BT, Ward CL, Baker HB, Walters TJ, Christ GJ. Implantation of in vitro tissue engineered muscle repair constructs and bladder acellular matrices partially restore in vivo skeletal muscle function in a rat model of volumetric muscle loss injury. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(3–4):705. | ||
Corona BT, Wu X, Ward CL, Mcdaniel JS, Rathbone CR, Walters TJ. The promotion of a functional fibrosis in skeletal muscle with volumetric muscle loss injury following the transplantation of muscle-ECM. Biomaterials. 2013;34(13):3324–3335. | ||
Diekjürgen D, Grainger DW. Polysaccharide matrices used in 3D in vitro cell culture systems. Biomaterials. 2017;141:96–115. | ||
Pholpabu P, Kustra S, Wu H, Balasubramanian A, Bettinger CJ. Lithography-free fabrication of reconfigurable substrate topography for contact guidance. Biomaterials. 2015;39(39):164–172. | ||
Wiria FE, Leong KF, Chua CK, Liu Y. Poly-epsilon-caprolactone/hydroxyapatite for tissue engineering scaffold fabrication via selective laser sintering. Acta Biomater. 2007;3(1):1–12. | ||
Ma PX, Zhang R. Synthetic nano-scale fibrous extracellular matrix. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;46(1):60–72. | ||
Melchels FPW, Bertoldi K, Gabbrielli R, Velders AH, Feijen J, Grijpma DW. Mathematically defined tissue engineering scaffold architectures prepared by stereolithography. Biomaterials. 2010;31(27):6909–6916. | ||
Tan Z, Wang H, Gao X, Liu T, Tan Y. Composite vascular grafts with high cell infiltration by co-electrospinning. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;67:369–377. | ||
Seyednejad H, Gawlitta D, Dhert WJ, van Nostrum CF, Vermonden T, Hennink WE. Preparation and characterization of a three-dimensional printed scaffold based on a functionalized polyester for bone tissue engineering applications. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(5):1999–2006. | ||
Venugopal J, Ramakrishna S. Biocompatible nanofiber matrices for the engineering of a dermal substitute for skin regeneration. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(5–6):847–854. | ||
Hung KC, Tseng CS, Dai LG, Hsu SH. Water-based polyurethane 3D printed scaffolds with controlled release function for customized cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2016;83:156–168. | ||
Olubamiji AD, Izadifar Z, Si JL, Cooper DM, Eames BF, Chen DX. Modulating mechanical behaviour of 3D-printed cartilage-mimetic PCL scaffolds: influence of molecular weight and pore geometry. Biofabrication. 2016;8(2):025020. | ||
Zhang YS, Arneri A, Bersini S, et al. Bioprinting 3D microfibrous scaffolds for engineering endothelialized myocardium and heart-on-a-chip. Biomaterials. 2016;110:45–59. | ||
Visser J, Melchels FP, Jeon JE, et al. Reinforcement of hydrogels using three-dimensionally printed microfibres. Nat Commun. 2015;6(1):6933. | ||
Liu T, Huang R, Zhong J, Yang Y, Tan Z, Tan W. Control of cell proliferation in E-jet 3D-printed scaffolds for tissue engineering applications: the influence of the cell alignment angle. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(20):3728–3738. | ||
Huang R, Gao X, Wang J, et al. Triple-layer vascular grafts fabricated by combined E-Jet 3D printing and electrospinning. Ann Biomed Eng. 2018;46(9):1254–1266. | ||
Shin YC, Lee JH, Jin L, et al. Stimulated myoblast differentiation on graphene oxide-impregnated PLGA-collagen hybrid fibre matrices. J Nanobiotechnology. 2015;13(1):21. | ||
Montgomery M, Ahadian S, Davenport Huyer L, et al. Flexible shape-memory scaffold for minimally invasive delivery of functional tissues. Nat Mater. 2017;16(10):1038–1046. | ||
Petersen A, Princ A, Korus G, et al. A biomaterial with a channel-like pore architecture induces endochondral healing of bone defects. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4430. | ||
Ge J, Liu K, Niu W, et al. Gold and gold-silver alloy nanoparticles enhance the myogenic differentiation of myoblasts through p38 MAPK signaling pathway and promote in vivo skeletal muscle regeneration. Biomaterials. 2018;175:19–29. | ||
Tan Z, Liu T, Zhong J, Yang Y, Tan W. Control of cell growth on 3D-printed cell culture platforms for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(12):3281–3292. | ||
Chew SY, Mi R, Hoke A, Leong KW. The effect of the alignment of electrospun fibrous scaffolds on Schwann cell maturation. Biomaterials. 2008;29(6):653–661. | ||
Brancato V, Garziano A, Gioiella F, et al. 3D is not enough: building up a cell instructive microenvironment for tumoral stroma microtissues. Acta Biomater. 2017;47:1–13. | ||
Levine EM, Becker Y, Boone CW, Eagle H. Contact inhibition, macromolecular synthesis, and polyribosomes in cultured human diploid fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965;53(2):350–356. | ||
Nam-Gyun Kim EK, Chen X, Gumbiner BM. E-cadherin mediates contact inhibition of proliferation through Hippo signaling-pathway components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:11930–11935. | ||
Storch K, Eke I, Borgmann K, et al. Three-dimensional cell growth confers radioresistance by chromatin density modification. Cancer Res. 2010;70(10):3925–3934. | ||
Du C, Cui FZ, Zhu XD, de Groot K, de GK. Three-dimensional nano-HAp/collagen matrix loading with osteogenic cells in organ culture. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;44(4):407–415. | ||
Baker BA, Pine PS, Chatterjee K, et al. Ontology analysis of global gene expression differences of human bone marrow stromal cells cultured on 3D scaffolds or 2D films. Biomaterials. 2014;35(25):6716–6726. | ||
de La Puente P, Muz B, Gilson RC, et al. 3D tissue-engineered bone marrow as a novel model to study pathophysiology and drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Biomaterials. 2015;73:70–84. | ||
Rahimi M, Zarnani AH, Mobini S, Khorasani S, Darzi M, Kazemnejad S. Comparative effectiveness of three-dimensional scaffold, differentiation media and co-culture with native cardiomyocytes to trigger in vitro cardiogenic differentiation of menstrual blood and bone marrow stem cells. Biologicals. 2018;54:13–21. | ||
Lampe KJ, Heilshorn SC. Building stem cell niches from the molecule up through engineered peptide materials. Neurosci Lett. 2012;519(2):138–146. | ||
Gavriilidis C, Laredj L, Solinhac R, et al. The MTM1-UBQLN2-HSP complex mediates degradation of misfolded intermediate filaments in skeletal muscle. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(2):198–210. | ||
Sullivan B. Effects of obesity and resistance exercise on the regulation of skeletal muscle fiber size [dissertation]. West Lafayette, IN: Purdue University; 2017. | ||
O’Brien FJ, Harley BA, Yannas IV, Gibson LJ. The effect of pore size on cell adhesion in collagen-GAG scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2005;26(4):433–441. | ||
Shin YC, Lee JH, Jin L, et al. Stimulated myoblast differentiation on graphene oxide-impregnated PLGA-collagen hybrid fibre matrices. J Nanobiotechnology. 2015;13(1):21. | ||
Buckingham M. How the community effect orchestrates muscle differentiation. Bioessays. 2003;25(1):13–16. | ||
Xie M, Wang L, Guo B, Wang Z, Chen YE, Ma PX. Ductile electroactive biodegradable hyperbranched polylactide copolymers enhancing myoblast differentiation. Biomaterials. 2015;71:158–167. | ||
Liu T, Huang R, Zhong J, Yang Y, Tan Z, Tan W. Control of cell proliferation in E-jet 3D-printed scaffolds for tissue engineering applications: the influence of the cell alignment angle. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(20):3728–3738. | ||
Dunn GA, Ebendal T. Contact guidance on oriented collagen gels. Exp Cell Res. 1978;111(2):475–479. | ||
Clark P, Connolly P, Curtis AS, Dow JA, Wilkinson CD. Cell guidance by ultrafine topography in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1991;99(Pt 1):73. |
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.