Back to Journals » Vascular Health and Risk Management » Volume 17
Endovascular Treatment for Critical Limb Ischemia in Type II Diabetes Mellitus Involving Femoropopliteal and Infrapopliteal Segments: Revascularization Strategy
Authors Al-Zoubi NA , Shatnawi NJ, Bakkar L , Al-Sabah M
Received 22 December 2020
Accepted for publication 19 February 2021
Published 4 March 2021 Volume 2021:17 Pages 69—76
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/VHRM.S298435
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Pietro Scicchitano
Nabil A Al-Zoubi, Nawaf J Shatnawi, Lujain Bakkar, Mohammad Al-Sabah
Department of Surgery, Vascular Surgery, Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid, 22110, Jordan
Correspondence: Nabil A Al-Zoubi
Department of Surgery, Vascular Surgery, Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid 22110, Jordan
Tel +962795774637
Email [email protected]
Purpose: To determine if further endovascular infrapopliteal angioplasty in combination with femoropopliteal revascularization improves the clinical outcomes regarding major amputation rate, rate of secondary interventions, and mortality in diabetic type-II patients presented with critical lower limb ischemia (CLI).
Patients and Methods: This is a retrospective study in which all type-II diabetic patients with CLI at King Abdullah University Hospital between October 2015 and September 2019 were identified. Patients with concomitant femoropopliteal and infrapopliteal vessels atherosclerotic lesions (total occlusion or more than 50% stenosis) who received successful endovascular treatment were included. Patients were divided into 2 groups. Group-I included patients treated for femoropopliteal segment alone, while Group-II included patients treated for both femoropopliteal and infrapopliteal segments. The outcomes of the two groups were compared regarding major amputation rate, rate of secondary interventions, and mortality. In addition, demographic data, atherosclerotic lesions distributions and cardiovascular risk factors were also collected and analyzed.
Results: In all, 90 patients (65 males and 25 females) with a mean age of 67.5± 12 years were included. In Group-I; 44 patients (48.9%) were included (36 males and 8 females) with a mean age of 67± 12 years. In group-II; 46 patients (51.1%) were included (29 males and 17 females) with a mean age of 68± 13 years. The major amputation rate was higher and statistically significant in Group-I (38.6% vs 17.4%, p-value = 0.034). However, the secondary interventions and the mortality rates showed no statistically significant differences (56.8% vs 39.1%, p-value = 0.139) and (22.7% vs 28.3%, p-value = 0.632), respectively.
Conclusion: Endovascular infrapopliteal angioplasty in combination with femoropopliteal revascularization in diabetic type-II patients with CLI improves the clinical outcome regarding major amputation rate. However, there were no significant differences regarding the rate of secondary interventions and the mortality rate.
Keywords: femoropopliteal, crural vessels, endovascular therapy
Introduction
The incidence of PAD has been increasing, along with the increase in patients with risk factors for atherosclerosis, especially diabetes mellitus (DM), obesity, hypertension (HTN), dyslipidemia, chronic kidney disease (CKD) and smoking.1–3 There is a strong association between DM and PAD.4 More than 25% of diabetic patients develop CLI during their lifetime,5 and more than 50% of patients with CLI are diabetics.4 CLI in DM carry a poor prognosis with amputation rates up to 30% and mortality up to 25% after 1 year.6,7 The pathophysiologic mechanisms of vascular disease in the presence of DM are multifactorial and include: inflammation, endothelial cell dysfunction, smooth muscle cell migration, altered platelet function and hyper-coagulability, which eventually lead to atherosclerosis which is the main cause of PAD.3,4 The diagnosis of PAD in patients with DM is often delayed because of the presence of neuropathy, as PAD-related symptoms go unnoticed until more severe critical limb ischemia (CLI) symptoms develop.8 The anatomical distribution of PAD is different in the diabetic and non-diabetic populations.7 PAD in diabetic patients is characterized by calcified, distal (infrapopliteal arteries), symmetrical, multi-segmental with a higher percentage of occlusions than stenosis, which can also affect the collateral vessels.7,9 However, age, HTN, and smoking are associated with proximal (aortoiliac and femoropopliteal) atherosclerotic lesions more than DM.10 CLI is unlikely to be related to isolated SFA lesions; usually, femoropopliteal involvement combined with aortoiliac or infrapopliteal disease is found, especially in patients with multiple risk factors (DM, HTN, dyslipidemia, smoking).11,12
The involvement of distal limb vessels in diabetic CLI limits the potential for collateral vessel development and reducing options for revascularization which increase the amputation rate to more than 20-fold.13 Successful revascularization reduces the major amputation rate in diabetic patients presenting with CLI.9 Revascularization may be surgical through bypass or endovascular technique.14 Outcomes of aortoiliac segment angioplasty and stenting in patients with diabetes have been reported in some studies to be similar to non-diabetic patients.13 In contrast, the long-term patency rates after femoropopliteal segment angioplasty are lower in diabetic than in nondiabetic patients, however, the long-term patency rates of infrapopliteal segment angioplasty are low in diabetic and nondiabetic patients but may be sufficient in the short term to facilitate healing of foot ulcers.13 Although open surgical bypass has been shown to have excellent results in patients with diabetes and PAD, contemporary management of CLI has gradually favored the use of minimally invasive endovascular techniques.8 However, it is difficult to provide guidelines with respect to selection of patients for infrapopliteal angioplasty in combination with angioplasty of the SFA or popliteal artery.15 Moreover, when indicated, the decision to revascularize the femoropopliteal segment alone or to proceed for additional infrapopliteal vessels with an endovascular approach is imperative and based on clinical experience. Therefore, the aim of this study is to assess if further infrapopliteal angioplasty after femoropopliteal revascularization improves the clinical outcomes regarding major amputation rate, rate of secondary interventions, and mortality in diabetic patients with CLI.
Patients and Methods
This study was approved by the Ethics Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Jordan University of Science and Technology (JUST) and King Abdullah University Hospital (KAUH). Patient informed consent was not required due to the de-identified data without breach of confidentiality, and that this study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. It is a retrospective, single center study in which all type-II diabetic patients with the diagnosis of CLI (with Rutherford category IV and V) at KAUH between October 2015 and September 2019 were identified using computerized medical records. CLI was defined as any patient with rest pain or tissue loss.16,17 Only patients with concomitant femoropopliteal and infrapopliteal vessels atherosclerotic lesions (total occlusion or more than 50% stenosis) who received technically successful endovascular treatment were included. Successful treatment was defined as technically successful opening of the targeted vessels and increase in ABI more than 0.15. Selected patients were divided into two groups. Group-I included patients treated for femoropopliteal segment alone, while Group-II included patients treated for both femoropopliteal and infrapopliteal segments at the same time. The clinical outcomes of the two groups were compared regarding major amputation rate (amputation above the ankle), rate of secondary interventions, and mortality. In addition, demographic data and patients’ characteristics involving age, sex, atherosclerotic lesions distribution, cardiovascular risk factors, body mass index (BMI), wound ischemia foot infection (WIFI) stage, global anatomic staging system (GLASS) stage and ABI were also collected and analyzed. Endovascular treatment was performed by ante-grade approach using ipsilateral common femoral artery (CFA) or retrograde using contralateral CFA and cross-over technique. The decision to perform femoropopliteal segment alone or to proceed to infrapopliteal vessels was judgmental and depend on the operator assessments of the degree of collateralization below the knee. SPSS version 22 was used for the analysis. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Unpaired Student’s t-test was used to compare the means, and the chi-square test was used to compare the proportions. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
The total number of type-II diabetic patients with CLI who had femoropopliteal and infrapopliteal lesions and received successful endovascular treatment was 90 patients (65 males and 25 females) with a mean age of 67.5±12 years. The patient demographics and cardiovascular risk factors are shown in Table 1. Hypertension, smoking, hyperlipidemia, chronic renal insufficiency, ischemic heart diseases were present in 67.8%, 37.8%, 56.7%, 17.8% and 34.4% of the patients, respectively. The average follow-up period was 13.3 ± 2.37 months. The arterial segments involved in the study group were; posterior tibial artery (68.8%), SFA (64.4%), popliteal artery (61.0%), anterior tibial artery (45.6%) and peroneal artery (25.6%). The most common arterial segment successfully managed by endovascular treatment was SFA (63.0%) followed by popliteal artery (60.0%), posterior tibial artery (35.6%), anterior tibial artery (16.0%), and peroneal artery (4.4%). Atherosclerotic lesions types (narrowing or occlusion) and distribution are shown in Table 2.
 |
Table 1 Demographic Data and Patients’ Characteristics. Results are Presented as the Mean ± Standard Deviation |
 |
Table 2 Atherosclerotic Lesions Types, Distribution and Rate of Intervention |
In Group-I, 44 patients (48.9%) were included (36 males and 8 females) with a mean age of 67±12 years. Of them, 27 patients (61.4%) had no major amputation and 17 patients (38.6%) had major amputations, 34 patients (77.3%) had no death and 10 patients (22.7%) had death, and 19 patients (43.2%) had no secondary interventions and 25 patients (56.8%) had secondary interventions. In group-II, 46 patients (51.1%) were included (29 males and 17 females) with a mean age of 68±12 years. Of them, 38 patients (82.6%) had no major amputations and 8 patients (17.4%) had major amputations, 33 patients (71.7%) had no death and 13 patients (28.3%) had death, and 28 patients (60.9%) had no secondary interventions and 18 patients (39.1%) had secondary interventions.
When comparing the two groups, the major amputation rate was higher and statistically significant in Group-I (38.6% vs 17.4%, p-value = 0.034). However, the secondary interventions and the mortality rates showed no statistically significant differences (56.8% vs 39.1%, p-value = 0.139) and (22.7% vs 28.3%, p-value = 0.632), respectively, this is shown in Table 3. Kaplan-Meier cures for each outcome are shown in Figure 1.
 |
Table 3 Comparison Between Group-I and Group-II |
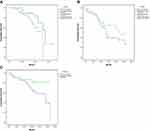 |
Figure 1 Comparison of outcomes among the two groups. (A) Major amputation, (B) mortality, and (C) secondary interventions. |
Discussion
This study indicates that the prevalence of PAD is more common in males than females, even in this subgroup of patients with CLI and DM. The average age in both groups was similar. The traditional cardiovascular risk factors (HTN, smoking, hyperlipidemia, chronic renal insufficiency, ischemic heart disease), BMI, HbA1c, ambulation status of the patients, WIFI stage, GLASS stage, inflammatory mediators (ESR, CRP, MPV) were homogeneous in our study population and there were no statistically significant differences between the two groups. Anatomical distributions of atherosclerotic lesions in our data showed predilection for distal involvements which conform with what have been published in the literature in diabetic patients.18
In our institution, lower extremity endovascular treatment is performed by either vascular surgeons or interventional radiologists. Absence of management guidelines regarding whether to proceed for further infra-popliteal angioplasty after femoropopliteal revascularization or not in diabetic type-II patients with CLI, has led to a nihilistic approach towards revascularization, consequently leading to two different practices. First, to treat the femoropopliteal segment alone. Second to treat both the femoropopliteal and infrapopliteal segments at the same time. Proponents of the treatment of both femoropopliteal and infrapopliteal have several justifications. First, this provides a direct foot revascularization with respect to the angiosome concept. Second, the possibility to revascularize more than one infrapopliteal artery which ensure more blood flow to the foot which is associated with better wound healing rates but not with better limb salvages as concluded by Biagioni RB et al.19 Third, assessments of infrapopliteal collaterals after successful femoropopliteal revascularization is highly subjective. Fourth, this approach gives more satisfactory feeling to the operator as he performed the maximum for the patient. In contrast, proponents of the more conservative approach by treating only the femoropopliteal segment have also some justifications. First, infrapopliteal angioplasty is a critical procedure because of the small diameter and length of the treated vessels, both of which have a tendency towards a high re-stenosis rate.20 Second, few studies have investigated the impact of the number of infrapopliteal arteries treated on limb salvage in CLI patients and some studies found no significant improvement in wound healing and amputation rates when more than one vessel was re-vascularized.6,21 Fourth, although it is subjective, the degree of collateralization can be satisfactory to the operator. Fifth, aggressive infrapopliteal angioplasties could preclude future distal bypass procedure. Sixth, more aggressive treatment is not necessarily associated with better outcomes. Finally, treatment of both segments increases the operative times, amount of radiations, the risk of contrast induced nephropathy and cost of the procedure due to change to lower profile wires and balloons.
Gutierrez M. et al conducted a literature review of endovascular and surgical approaches for treatment of diabetic foot and CLI in PubMed from 2002 to 2018 and concluded that there are not enough data to recommend one method of revascularization over another and there is a real need to normalize demographic data, the severity of the disease, and the results of revascularization in diabetic patients with CLI.22 In order to evaluate the clinical outcomes for the two groups, we decided to study the major amputation rate, rate of secondary intervention and mortality excluding CLI with Rutherford category VI which represents a major tissue loss that necessitate major amputations. Previous studies have reported that successful endovascular interventions to the lower limbs associated with a decrease in the rate major amputation rates.23 However, few interventions have been shown to improve amputation-free survival or reduce major adverse limb events in CLI in DM population.17 This study demonstrated that diabetic patients with CLI who had concomitant femoropopliteal and infrapopliteal segments atherosclerotic lesions who underwent endovascular revascularization for both segments in the same procedure had a lower major amputation rate than those who underwent endovascular revascularization for the femoropopliteal segment alone. Restenosis after femoropopliteal interventions remains the Achilles’ heel of endovascular therapies and the potential benefit of secondary interventions should also be weighed against the patient’s functional status, comorbidities, and periprocedural risk.24 Our study showed that the rate of secondary interventions is similar in both groups. A recent meta-analysis reported diabetes to be associated with an increased risk of mortality in CLI.25 Other studies suggest patient rather than technical factors as the cause of the increased mortality after endovascular treatment.26 This study demonstrated that there were no differences in the outcomes regarding mortality in diabetic patients with CLI who had concomitant femoropopliteal and infrapopliteal segments atherosclerotic lesions who underwent endovascular revascularization for both segments in the same procedure.
This study has several limitations. First, it is a retrospective study. Second, due to small number of patients and different types of endovascular treatment (angioplasty, angioplasty with drug-coated balloons, angioplasty with regular stents, angioplasty with drug-coated stents and sub-intimal angioplasty of the SFA), we could not investigate the role of different treatment modalities on our clinical outcomes. Third, we used Rutherford classification system, however, it does not address whether or not there is an infection, as well as the extent, location, and depth of infection.22 Finally, Although the impact of planter arch disease on the success of proximal revascularization, whether open or endovascular, is likewise unknown, planter arch disease was not addressed in this study.27 Waiting for pending level 1 evidence from ongoing trials,27 further, prospective, multicenter, and randomized controlled studies are needed to establish treatment guidelines for revascularization strategies in this challenging and rapidly evolving field.
Conclusions
Endovascular infrapopliteal angioplasty in combination with femoropopliteal revascularization in diabetic type-II patients with CLI improves the clinical outcome regarding major amputation rate. However, there were no significant differences regarding the rate of secondary interventions and the mortality rate.
Author Contributions
All authors made a significant contribution to the work reported, whether that is in the conception, study design, execution, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation, or in all these areas; took part in drafting, revising or critically reviewing the article; gave final approval of the version to be published; have agreed on the journal to which the article has been submitted; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflict of interests in this work.
References
1. Mao CT, Tsai ML, Wang CY, et al. Outcomes and characteristics of patients undergoing percutaneous angioplasty followed by below-knee or above-knee amputation for peripheral artery disease. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e111130. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111130
2. Mustapha JA, Diaz-Sandoval LJ, Saab F. Tibial-pedal arterial access & retrograde interventions for advanced peripheral arterial disease & critical limb ischemia. Interv Cardiol. 2015;7(5). doi:10.2217/ica.15.33
3. Giannopoulos S, Armstrong EJ. Diabetes mellitus: an important risk factor for peripheral vascular disease. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2020;18(3):131–137. doi:10.1080/14779072.2020.1736562
4. Thiruvoipati T, Kielhorn CE, Armstrong EJ. Peripheral artery disease in patients with diabetes: epidemiology, mechanisms, and outcomes. World J Diabetes. 2015;6(7):961–969. doi:10.4239/wjd.v6.i7.961
5. Brooke BS, Kraiss LW, Stone DH. Improving outcomes for diabetic patients undergoing revascularization for critical limb ischemia: does the quality of outpatient diabetic care matter? Ann Vasc Surg. 2014;28(7):1719–1728. doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2014.05.009
6. Jongsma H, Bekken JA, Akkersdijk GP, et al. Angiosome-directed revascularization in patients with critical limb ischemia. J Vasc Surg. 2017;65(4):1208–1219. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2016.10.100
7. Aiello A, Anichini R, Brocco E. Treatment of peripheral arterial disease in diabetes: a consensus of the Italian Societies of Diabetes (SID, AMD), Radiology (SIRM) and Vascular Endovascular Surgery (SICVE). Nutri Metabol Cardiovas Dis. 2014;24:355–369. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2013.12.007
8. Darling JD, Bodewes TCF, Deery SE, et al. Outcomes after first-time lower extremity revascularization for chronic limb-threatening ischemia between patients with and without diabetes. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67:1159–1169. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2017.06.119
9. Faglia E, Paola LD, Clerici G, et al. Peripheral angioplasty as the first-choice revascularization procedure in diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia: prospective study of 993 consecutive patients hospitalized and followed between 1999 and 2003. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2005;29:620–627. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2005.02.035
10. Ozkan U, Oguzkurt L, Tercan F. Atherosclerotic risk factors and segmental distribution in symptomatic peripheral artery disease. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009;20:437–441. doi:10.1016/j.jvir.2009.01.010
11. Shaker M, Shehata M. Case series: role of balloon angioplasty in below the knee vessels treatment in diabetics. Open J Clin Med Case Rep. 2019;5(12):1572.
12. Motsumi MJ, Naidoo NG. Pattern and distribution of peripheral arterial disease in diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia (Rutherford clinical category 4-6). S Afr J Surg. 2017;55(3):49–58.
13. Lüscher TF, Creager MA, Beckman JA, Cosentino F. Diabetes and vascular disease pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: part II. Circulation. 2003;108:1655–1661. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000089189.70578.E2
14. Uccioli L, Meloni M, Izzo V, Giurato L, Merolla S, Gandini R. Critical limb ischemia: current challenges and future prospects. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2018;14:63–74. doi:10.2147/VHRM.S125065
15. Löfberg AM, Karacagil S, Ljungman C, et al. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty of the femoropopliteal arteries in limbs with chronic critical lower limb ischemia. J Vasc Surg. 2001;34:114–121. doi:10.1067/mva.2001.113486
16. Katsanos K, Tepe G, Tsetis D, Fanelli F. Standards of practice for superficial femoral and popliteal artery angioplasty and stenting. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2014;37:592–603. doi:10.1007/s00270-014-0876-3
17. Huizing E, Schreve MA, de Vries PM, JP, Ferraresi R, Kum S, Ünlü. Below-the-ankle angioplasty in patients with critical limb ischemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019;30:1361–1368.
18. Morris-Stiff G, Ogunbiyi S, Rees J, Davies CJ, Hicks E, Lewis MH. Variations in the anatomical distribution of peripheral vascular disease according to gender. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2011;93:306–309. doi:10.1308/003588411X571999
19. Biagioni RB, Biagioni LC, Nasser F. Infrapopliteal angioplasty of one or more than one artery for critical limb ischaemia: a randomised clinical trial. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2018;55(4):518–527. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2017.12.022
20. Gamal WM, Wagdy WM, Saluzzo C. Infrapopliteal angioplasty in diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Glob Surg. 2015;1(3):37–41. doi:10.15761/GOS.1000114
21. Soares RA, Matielo MF, Brochado Neto FC, Cury MVM, Marques RC, Sacilotto R. Number of infrapopliteal arteries undergoing endovascular treatment is not associated with the limb salvage rate in patients with critical limb ischemia. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64:1344–1350. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2016.04.020
22. Gutierrez M, Vicente S, Criado F, et al. Below-the-knee revascularization of critical limb ischemia in diabetic patients. Vasc Dis Manage. 2020;17(7):e150–154.
23. Kim J, Chun D, Kim S, et al. Trends in lower limb amputation in patients with diabetic foot based on vascular intervention of peripheral arterial disease in Korea: a population-based nationwide study. J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(26):e178. doi:10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e178
24. Sobieszczyk P, Eisenhauer A. Management of patients after endovascular interventions for peripheral artery disease. Circulation. 2013;128:749–757. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001560
25. Freisinger E, Malyar NM, Reinecke H, Lawall H. Impact of diabetes on outcome in critical limb ischemia with tissue loss: a large‑scaled routine data analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017;16:41. doi:10.1186/s12933-017-0524-8
26. Morris-Stiff G, Moawad M, Appleton N, et al. Long-term clinical outcome following lower limb arterial angioplasty. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2011;93:250–254. doi:10.1308/147870811X566394
27. Conte MS, Andrew Bradbury AW, Kolh P, et al. Global vascular guidelines on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia. J Vasc Surg. 2019;6(9):125–139.
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
