Back to Journals » Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management » Volume 12
Development and novel therapeutics in hepatocellular carcinoma: a review
Authors Ingle PV , Binti Samsudin SZ, Pei Qi C, Mei Kei N, Li Xuan H, Siu Ching Y, Chai Siaw Hui A, Wong San Ying A
Received 14 July 2015
Accepted for publication 22 October 2015
Published 16 March 2016 Volume 2016:12 Pages 445—455
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S92377
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Garry Walsh
Pravinkumar Vishwanath Ingle, Sarah Zakiah Samsudin, Pei Qi Chan, Mei Kei Ng, Li Xuan Heng, Siu Ching Yap, Amy Siaw Hui Chai, Audrey San Ying Wong
Department of Pharmacy Practice, School of Pharmacy, International Medical University, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Abstract: This review summarizes the epidemiological trend, risk factors, prevention strategies such as vaccination, staging, current novel therapeutics, including the drugs under clinical trials, and future therapeutic trends for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). As HCC is the third most common cause of cancer-related death worldwide, its overall incidence remains alarmingly high in the developing world and is steadily rising across most of the developed and developing world. Over the past 15 years, the incidence of HCC has more than doubled and it increases with advancing age. Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus is the leading cause of HCC, closely followed by infection with hepatitis C virus. Other factors contributing to the development of HCC include alcohol abuse, tobacco smoking, and metabolic syndrome (including obesity, diabetes, and fatty liver disease). Treatment options have improved in the past few years, particularly with the approval of several molecular-targeted therapies. The researchers are actively pursuing novel therapeutic targets as well as predictive biomarker for treatment of HCC. Advances are being made in understanding the mechanisms underlying HCC, which in turn could lead to novel therapeutics. Nevertheless, there are many emerging agents still under clinical trials and yet to show promising results. Hence, future therapeutic options may include different combination of novel therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC, novel therapeutics, treatment, management, molecular targeted therapies, clinical drug trial
Introduction
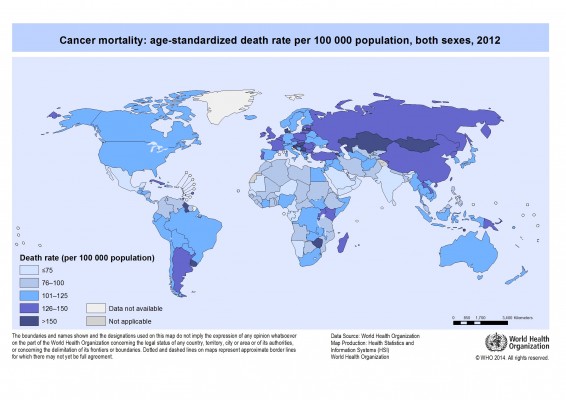
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is defined as the carcinoma emanating from the liver and also includes various underlying diseases.1,2 Globally, the cancer prevalence was reported to be 10.9 million per annum, and liver cancer came up as the sixth most common cancer with 749,000 cases1,2 and was ranked the third highest cause of cancer-related death with 692,000 mortalities per year.1 However, its geographical distribution is not uniform1–3 as shown in Figure 1.4 The highest HCC incidence occurs in resource-poor or developing countries such as sub-Saharan African, East Asia, and Melanesia, which covers 85% of reported global cases.2,3,5 Contrarily, incidence in developed countries is much lower, except in Southern Europe.2,3 To date, the mortality rate in the USA increased by 40% between the years of 1990 and 2004 as a result of hepatitis C virus (HCV) events.2
  | Figure 1 Cancer mortality: age-standardized death rate per 100,000 population, both sexes, 2008. |
Furthermore, HCC incidences increase with advancing age.1,3,6 The peak age for HCC incidence is at 70 years.2,3,7 However, peak age of incidence is less than 70 years in Chinese and black Africans.2,5,7 With regard to sex, it strikes males more than females, with a ratio of 2.4.3,6,7 Last decade, HCC mortality rose, particularly for male population in Austria, Denmark, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Portugal, Norway, Spain, Switzerland, and UK.2,3 This paper aims first at describing the current and future therapeutic trends in HCC management, second at identifying the preventative measures in lowering the incidence of HCC, and finally at reviewing the progress in novel therapeutics in developing and developed regions.
Risk factors
These variations of risk factors link to etiology, complexity, and geographical distribution, particularly between developing and developed regions (Table 1).1
Risk of HCC according to HBV genotype
Individuals with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection are at increased risk of developing end-stage liver disease (including cirrhosis, hepatic failure, and HCC), with a cumulative lifetime incidence of 15%–40%.11–13 Other important risk factors for HCC include the presence of HBV e-antigen – a surrogate marker of active viral replication – and the amount of HBV (ie, viral load) in serum.14,15
Several reports16–19 have also suggested that the genetic characteristics of HBV, including HBV genotype and specific genetic mutations, are associated with the development of HCC. Most of the recent studies suggest that the genetic characteristics of HBV, including HBV genotype and specific genetic mutations, are associated with the development of HCC.20–22
To date, HBV has been classified in to eight genotypes (A–H), according to intergroup divergence of 8% or more in the complete nucleotide sequence.23 Recent focus is on the clinically important differences in outcomes that are associated with the different HBV genotypes.24 The HBV genotypes have distinct geographical distributions25 and have been reported to have clinical relevance.26 For example, patients with genotypes C and D have a higher risk of disease progression and a poorer clinical outcome compared to the patients with genotypes A and B. Patients with genotypes A and B have a better response to IFN-based therapy than those with genotypes C and D.27 However, the association of genotypes B and C with HCC development remains controversial; some studies have shown that genotype C HBV infection is a risk factor for HCC,28,29 while others did not obtain the same results.30,31 The reason for these inconsistencies between the results, especially those derived from the same region,28,32 is unclear.
Staging
Introduction of various staging systems by different guidelines helps select the suitable interventions according to HCC classifications1,3,5,6,33 (Tables 2 and 3).
  | Table 2 Child–Pugh classification of severity of liver disease |
Management
Treatment
Resection
Resection is the first-line therapy for localized HCC without cirrhosis.3,5,6,34–37 Resection is not recommended in cirrhotic patients due to increased risk of perioperative decompensation.6,37,38 Nevertheless, resection is possible in cirrhotic patients whose liver transplantation (LT) is deemed to be unsuitable, provided that their hepatic function is well preserved.1,34
Portal vein hypertension is regarded as an absolute contraindication to resection in EASL–EORTC Clinical Practice Guidelines.3,35 Studies demonstrated that the 5-year survival rate is only 30% regardless of the Child–Pugh score in the presence of portal vein hypertension and elevated bilirubin level, compared to 70% 5-year survival in patients with normal bilirubin level without portal vein hypertension.34,37 However, in other studies, it was also demonstrated that the presence of significant portal vein hypertension does not influence the outcomes of resection, even in cirrhotic patients.38,39
Larger tumor is associated with higher risk of vascular invasion and dissemination.34 A cutoff of <2 cm was demonstrated as an independent predictor of survival rates in Japan, and the outcomes of each groups were 66% 5-year survival in <2 cm tumor group, 52% in 2–5 cm tumor group, and 37% in >5 cm tumor group after resection procedure.3
Recurrence rate occurs up to 70% after 5 years is the main problem with resection.1,34,37 However, the evidence to demonstrate the effectiveness of initiating adjunct therapy after resection in preventing recurrence is not conclusive.5,34
Liver transplantation
LT is the best curative therapy for candidates unsuitable to undergo liver resection as well as for patients with underlying cirrhosis. However, dismal results as in high recurrence rate and 5-years survival rates below 50% have been recorded due to poor patient selection.6,37
Generally, LT can only be performed in patients in early stage of HCC.34,38 Milan criteria defined patients with single nodule <5 cm, or up to three separate nodules <3 cm, with no evidence of gross vascular invasion and no regional nodal or distant metastases.5,40,41 Using Milan criteria of patient selection, posttransplantation outcome with 5-year survival rates exceeds 70% (as shown in several studies).34,35
Nevertheless, shortage of donor livers has caused an unbearably long transplant waiting time,34,35 resulting in waiting list exclusion when patients’ HCC progression extends beyond the transplantable criteria.42 The rate of waiting list exclusion may be as high as 25% if the waiting list is longer than 12 months.34,35 Model for End-stage Liver Disease score was therefore utilized to allocate the organ fairly according to priority.34,35,41
Neoadjuvant therapy, such as chemoembolization and percutaneous ablation, can be employed to maintain the tumor burden within the ranges of the Milan criteria and prevent dropout from the waiting list, especially if transplant waiting time exceeds 6 months and patient’s condition worsens.6,34,35 However, the long-term benefit of the therapy is still uncertain as there are several studies showing no survival benefit in employing these interventions.37,41
Percutaneous ablation
Percutaneous ablation is the best treatment option for patients with early-stage HCC (BCLC 0-A tumors) who are not suitable for resection or LT.34,35 The most common techniques are percutaneous ethanol injection (PEI) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA).36 Currently, RFA has progressively replaced PEI35,37,38 because RFA requires lesser treatment sessions and results in higher complete necrosis rate and long-term survival rates than PEI, as demonstrated in many studies.43–46
When comparing therapeutic outcomes of RFA with surgical resection, resection is more effective than RFA for larger tumors (>3, <5 cm) in terms of disease-free survival and overall survival, while RFA is more cost-effective than surgical resection for smaller early HCCs (<2 cm).47,48
Chemoembolization
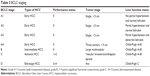
Chemoembolization is used as a palliative treatment for patients with inoperable HCC.49 It is the recommended first-line therapy for patients with intermediate-stage (BCLC stage B) disease having well-preserved liver function and asymptomatic multinodular tumors without vascular invasion or extrahepatic spread (Table 4).3
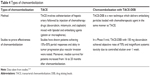  | Table 4 Types of chemoembolization |
Another technique called radioembolization, involving infusion of Iodine-131 or Yttrium-90 into hepatic artery, has been shown to exhibit antitumor results, but it is not recommended as a standard therapy as further research trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy.3
Systemic therapies
Perspectives on drug therapies
HCC is among the most chemoresistant tumors, and until 2007, no systemic chemotherapy was recommended for patients with advanced tumors (Tables 5 and 6).51–53 Systemic chemotherapy with cytotoxic agents, such as doxorubicin, gemcitabine, cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, or combined regimens for palliative care, was associated with low response rates (<10%) with only marginal improvements in survival. Moreover, these drugs are poorly tolerated in patients with underlying liver cirrhosis. Interferon (IFN) therapy, antiandrogens, or tamoxifen used in the treatment of advanced HCC show contradictory results without obvious benefit. A meta-analysis of seven RCTs, including 898 patients, evaluated tamoxifen versus conservative management and showed neither antitumor effects nor survival benefits for tamoxifen. Subsequent large RCTs reported negative results in terms of survival. Cisplatin, IFN, doxorubicin, and fluorouracil (PIAF) used in combination showed promising activity in a Phase II study. A randomized Phase III study including 188 patients with HCC was conducted to investigate the effect of PIAF combination compared to doxorubicin alone. The median survival rate of the PIAF group did not significantly differ from the doxorubicin group (8.67 versus 6.83 months), and patients treated with the PIAF regimen experienced a significantly higher rate of myelotoxicity.50–53
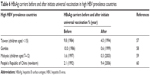  | Table 6 HBsAg carriers before and after initiate universal vaccination in high HBV prevalence countries |
Prevention
Understanding risk factors of HCC supports the rationale for designing of prevention strategies, which aids in avoiding infection, chronic liver damage, and carcinogenesis process as well as early diagnosis of the disease and reduces the risk of recurrence.54,55
Vaccination
HBV is attributable to more than 50% of the cases of HCC globally, it accounts for 15% of HCC in developed countries and 80%–90% of HCC in developing countries such as Asia and Africa.54,55 World Health Organization (WHO) introduced universal vaccination to all newborns and high-risk groups as routine immunization.54,56 Most of the studies showed that hepatitis B core antibody, hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) carriers, HCC incidence, and HCC-related mortality were decreased following initiation of universal vaccination (Table 6).57–61 Therapies stratified according to stage along with the treatment strategies and rational of HCC were summarized (Table 7).62–65
  | Table 7 Therapies stratified according to stage |
Antiviral treatment
Studies have shown that antiviral treatment of chronic HBV and HCV infections may reduce the risk of HCC.3,37,66 Chen et al14 demonstrated that incidence of HCC is associated with serum HBV DNA, which further supports the analysis showing that low viremia levels decreases the risk of HCC development. Therefore, antiviral therapy is used for HCC risk reduction, while viral suppression also reverses cirrhosis, another risk factor of HCC development.66,67
Oral nucleoside analogs (NAs) have been used to treat chronic hepatitis B.67 The use of first-generation NA is limited due to the development of resistance and virological relapse after treatment cessation.61 Newer generation NA with high antiviral and low drug-resistant potency, such as entecavir and tenofovir, are available.66,68 At the same time, combination therapy of pegylated IFN with ribavirin works well in preventing HCC development associated with HCV infection.68,69
Surveillance
Surveillance is a diagnostic test applied periodically to patients at risk of developing a disease, aiming to reduce disease-related mortality through early diagnosis (Table 8).3,35
  | Table 8 Categories of patients suitable for surveillance |
Serological and imaging tests are used in HCC surveillance, ultrasonography is the most widely used.3 Surveillance is mainly based on ultrasound examination as measuring alpha-fetoprotein levels, which is an example of serological test, has demonstrated inadequate sensitivity and specificity in recent studies.35
Other preventive measures
WHO recommends implementation of an integrated and comprehensive strategy based on five key elements as listed in Table 8, aiming at preventing transfusion-transmitted HBV and HCV infection, especially in sub-Saharan African countries where there is relatively high risk of such mode of transmission. On the other hand, risky behaviors such as tattooing, body piercing, and unprotected sexual intercourse should be avoided to prevent transmission of HCV and HBV, along with implementation of related health policies by governmental health agencies (Table 9).3,55,70
  | Table 9 Strategy to prevent transfusion-transmitted HBV and HCV infection by WHO |
Discussion
Current novel therapeutics
Surgical intervention that includes liver resection and LT is the mainstay of treatment of HCC, but the selection criteria for both differ in different published clinical guidelines, resulting in difficulty in selecting the most appropriate therapy in treating HCC.74–79 Certain groups of patients who are defined to have well-preserved liver function and are deemed to be fit to undergo resection (Child–Pugh A score) may be regarded as not suitable for resection due to other circumstances such as the presence of portal vein hypertension.
Meanwhile, the gold standard in selecting patients for LT, Milan criteria, possesses some limitations that may exclude some of the potential patients.18 University of California at San Francisco criteria have been proposed, in which selection is based on having a single tumor nodule up to 6.5 cm or three or fewer tumors, the largest of which is <4.5 cm with the sum of the tumor diameters <8 cm.80 Its outcome is comparable to patients who are selected by using Milan criteria.40 Nevertheless, more studies should be conducted to confirm the validity of this extended criteria. However, it is still preferable to establish a standardized universal classification system in evaluating the liver status in patients with HCC to ensure the most appropriate option is selected for the patients, for both resection and LT procedure.
To date, sorafenib is the first and only available systemic therapy approved by FDA for treatment of HCC.3 Nevertheless, many emerging agents are still under clinical trials and yet to show promising results.51,81
Future therapeutic trends
Living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) is proposed as it provides advantages to reduce the waiting time and increase the number of patients benefit from LT due to severe shortage of deceased donor livers. By comparing LDLT with deceased donor liver transplantation (DDLT), the waiting time is significantly shorter and dropout rate has reduced from 18% to 0%.40 However, it is still uncertain whether the outcome of LDLT is equivalent or more favorable to that of DDLT.82
For tumors with size <2 cm and with the BCLC stage A, both PEI and RFA achieve complete responses in more than 90% of cases with good long-term outcome, which may substitute the roles of surgical intervention in early HCC in the future. In future, technical developments may achieve ablation areas of 5 cm or more in diameter, which will make percutaneous ablation an effective alternative to surgery even for tumors measuring 3 cm or more.38
Future therapeutic options may include different combination of novel therapeutic interventions. Combination of TACE-DEB has lesser complications than TACE due to slow release of chemotherapeutic drug.83 TACE-DEB was also better tolerated and significantly decreased liver toxicity and adverse events and showed improved antitumoral effect.3,84
There are also studies revealing the possibility of combination therapy of sorafenib with either TACE or radioembolization as both these combinations had demonstrated better therapeutic outcomes with improved overall survival and time to progression.3,39,83,84 More studies need to be conducted to examine this possibility as well as to solve the uncertainties regarding dose, frequency, and duration of sorafenib in combination therapy.
Universal vaccination is also one of the therapeutics interventions for HCC, especially in developing countries. A cost-effectiveness analysis by Hung and Chen84 demonstrated that universal vaccination shows high cost-effectiveness in reducing long-term sequelae of acute hepatitis B infection, HCC death, and chronic illnesses,56,85 which is further supported by another cost-effectiveness analysis by Hong et al85 in Vietnam.80
However, an effective prophylaxis vaccine for HCV is not yet available. Thus, preventing HCC is completely dependent on antiviral therapy for patients, until an effective vaccine is developed.68 Antiviral therapy with nucleotide analogs may be preferable than IFN treatment due to less adverse side effects and can be considered as a cost-effective adjuvant therapy for HCC after curative treatment.80 However, the exact role of antiviral treatment in preventing HBV-related HCC has been difficult to establish, due to the slow biological evolution of HBV.66
Future technical aspect or extended indications for liver resection for HCC
Recent improvement in surgical techniques and perioperative care has increased the safety and expanded the indication of hepatic resection for HCC to include large tumors that require extended hepatectomy in cirrhotic patients. Selection of appropriate candidates for hepatectomy depends on careful assessment of the tumor status and liver function reserve. Evaluation of the general fitness of patients is also critical because comorbid illness is an important cause of postoperative mortality, even if the patients have good liver function reserve. With careful patient selection and surgical expertise, the current operative mortality of hepatectomy for HCC is approximately 5% or less in major centers. Improved long-term survival results after resection of HCC have also been reported recently, with an overall 5-year survival rate of approximately 50%. The improved perioperative and long-term survival results have strengthened the role of hepatectomy as the mainstay of treatment for HCC despite the availability of a number of other treatment options for localized HCC.86
The main clinical advantage of laparoscopy for cirrhotic patients is probably the significantly lower rate of postoperative ascitic decompensation, which was reported in four comparative studies and three meta-analysis. This finding could be explained by the preservation of portosystemic venous collateral circulation around the liver and parietal abdominal wall, limited mobilization and manipulation of the liver, restricted fluid requirements, and decreased blood loss. Gaillard et al87 advocated that the positive pressure of the pneumoperitoneum might exert a tamponade effect on bleeding from intra-abdominal varices, which are a low-pressure system, thus decreasing blood loss. Lower blood transfusion requirement is also an advantage of the laparoscopic approach in this very risky group of patients.87
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interests in this work.
References
Raoul J. Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma and current treatment options. Semin Nucl Med. 2008;38(2):S13–S18. | ||
Kew M. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and risk factors. J Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 2014;115–125. | ||
EASL–EORTC Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48(5):599–641. | ||
World Health Organization. [Internet]. WHO: cancer mortality and morbidity. Available from: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/mortality_morbidity/cancer/en/. Accessed December 23, 2014. | ||
Jelic S, Sotiropoulos G. Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2010;21(Suppl 5):v59–v64. | ||
Ryder S. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in adults. Gut. 2003;52(Suppl 3):1iii–8. | ||
Ha N, Ha N, Ahmed A, et al. Risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease: a case–control study. Cancer Causes Control. 2012;23(3):455–462. | ||
Kitya D, Bbosa G, Mulogo E. Aflatoxin levels in common foods of South Western Uganda: a risk factor to hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Cancer Care. 2009;19(4):516–521. | ||
Igboh NM, Nnamah NK, Onwubiko D, et al. Hepatic dysfunction in patients infected with human immune deficiency virus. Int J Pharma Res Rev. 2013;2(4):9–12. | ||
Trichopoulos D, Bamia C, Lagiou P, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma risk factors and disease burden in a European cohort: a nested case-control study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103(22):1686–1695. | ||
Yang H, Yeh SH, Chen PJ, et al. Associations between hepatitis b virus genotype and mutants and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100(16):1134–1143. | ||
Beasley RP. Hepatitis B virus. The major etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1988;61(10):1942–1956. | ||
McMahon BJ. Hepatocellular carcinoma and viral hepatitis. In: Wilson RA, editor. Viral Hepatitis: Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker; 1997:31530. | ||
Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA. 2006;295(1):6573. | ||
Yang HI, Lu SN, Liaw YF, et al. Hepatitis B e antigen and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(3):16874. | ||
Baptista M, Kramvis A, Kew MC. High prevalence of 1762(T) 1764(A) mutations in the basic core promoter of hepatitis B virus isolated from black Africans with hepatocellular carcinoma compared with asymptomatic carriers. Hepatology. 1999;29(3):94653. | ||
Kao JH, Chen PJ, Lai MY, Chen DS. Hepatitis B genotypes correlate with clinical outcomes in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2000;118(3):5549. | ||
Kao JH, Chen PJ, Lai MY, Chen DS. Basal core promoter mutations of hepatitis B virus increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B carriers. Gastroenterology. 2003;124(2):32734. | ||
Yu MW, Yeh SH, Chen PJ, et al. Hepatitis B virus genotype and DNA level and hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective study in men. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(4):26572. | ||
Mishra SK. Hepatitis B virus genotypes, mutations and the risks for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterol Hepatol Open Access. 2014;1(1):00002. doi:10.15406/ghoa.2014.01.00002. | ||
Kao JH, Chen PJ, Lai MY, Chen DS. Hepatitis B genotypes correlate with clinical outcomes in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2000;118(3):554–559. | ||
Yu MW, Yeh SH, Chen PJ, et al. Hepatitis B virus genotype and DNA level and hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective study in men. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(4):265–272. | ||
Chan HL-Y, Hui AY, Wong ML, et al. Genotype C hepatitis B virus infection is associated with an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2004;53:1494–1498. doi:10.1136/gut.2003. 033324. | ||
Orito E, Ichida T, Sakugawa H, et al. Geographic distribution of hepatitis B virus (HBV) genotype in patients with chronic HBV infection in Japan. Hepatology. 2001;34(3):590–594. | ||
Huy TT, Sall AA, Reynes JM, Abe K. Complete genomic sequence and phylogenetic relatedness of hepatitis B virus isolates in Cambodia. Virus Genes. 2008;36(2):299–305. | ||
Kao JH. Hepatitis B viral genotypes: clinical relevance and molecular characteristics. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17(6):643–650. | ||
Lin CL, Kao JH. The clinical implications of hepatitis B virus genotype: recent advances. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26 (Suppl 1):123–130. | ||
Chan HL, Hui AY, Wong ML, et al. Genotype C hepatitis B virus infection is associated with an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2004;53(10):1494–1498. | ||
Yu MW, Yeh SH, Chen PJ, et al. Hepatitis B virus genotype and DNA level and hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective study in men. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(4):265–272. | ||
Sumi H, Yokosuka O, Seki N, et al. Influence of hepatitis B virus genotypes on the progression of chronic type B liver disease. Hepatology. 2003;37(1):19–26. | ||
Yuen MF, Tanaka Y, Shinkai N, et al. Risk for hepatocellular carcinoma with respect to hepatitis B virus genotypes B/C, specific mutations of enhancer II/core promoter/precore regions and HBV DNA levels. Gut. 2008;57(1):98–102. | ||
Yuen MF, Sablon E, Yuan HJ, et al. Significance of hepatitis B genotype in acute exacerbation, HBeAg seroconversion, cirrhosis-related complications, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2003;37(3):562–567. | ||
Robert L, Oken M, Creech R, et al. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol. 1982;5(6):649–655. | ||
Bruix J, Sherman M; Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005;42(5):1208–1236. | ||
Bruix J, Sherman M; Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011;53(3):1020–1022. | ||
Liovet JM, Bruix J. Novel advancements in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma in 2008. J Hepatol. 2008;48:S20–S37. | ||
Dhanasekaran R, Limaye A, Cabrera R. Hepatocellular carcinoma: current trends in worldwide epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis, and therapeutics. Hepat Med. 2012;4:19–37. | ||
Raza A, Sood GK. Hepatocellular carcinoma review: current treatment, and evidence-based medicine. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(15):4115–4127. | ||
Santambrogio R, Kluger MD, Costa M, et al. Hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with Child-Pugh’s A cirrhosis: is clinical evidence of portal hypertension a contraindication. HPB (Oxford). 2012;15:78–84. | ||
Tsoulfas G, Curley SA, Abdalla EK, Barnett CC, Hertl M. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. UpToDate. 2013. | ||
EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56:908–943. | ||
de Villa V, Lo CM. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia. Oncologist. 2012;12(11):1321–1331. | ||
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Solbiati L, Gazelle GS. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment with radio-frequency ablation versus ethanol injection. Radiology. 1999;210(3):655–661. | ||
Lencioni RA, Allgaier HP, Cioni D, et al. Small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: randomized comparison of radio frequency thermal ablation versus percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology. 2003;228:235–240. | ||
Ansari D, Andersson R. Radiofrequency ablation or percutaneous ethanol injection for the treatment of liver tumors. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(10):1003–1008. | ||
Cha DI, Lee MW, Rhim H, Choi D, Kim YS, Lim HK. Therapeutic efficacy and safety of percutaneous ethanol injection with or without combined radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinomas in high risk locations. Korean J Radiol. 2013;14(2):240–247. | ||
Colecchia A, Schiumerini R, Cucchetti A, et al. Prognostic factors for hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(20):5935–5950. | ||
(a) Cucchetti A, Piscaglia F, Cescon M, et al. Cost-effectiveness of hepatic resection versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2013;59:300–307. (b) Kang B, Kim H-C, Chung JW, et al. Safety of chemotherapeutic infusion or chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma supplied exclusively by the cystic artery. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013;36(5):1313–1319. | ||
Llover JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–390. | ||
Cheng A-L, Kang Y-K, Lin D-Y. Sunitinib versus sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular cancer: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(32):4067–4075. | ||
illanueva A, Llovet JM. Targeted therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1410–1426. | ||
Llovet JM, Bruix J. Testing molecular therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma: the need for randomised phase II trials. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(6):833–835. | ||
Perz JF, Armstrong GL, Farrington LA, Hutin YJ, Bell BP. The contributions of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer worldwide. J Hepatol. 2006;45:529–538. | ||
Anna G, Nora C, Adriana S, Veronica V, Fabio F. Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2011;20:381–388. | ||
World Health Organization. Hepatitis B vaccine. 2005. Available from: http://www.who.int/vaccines/en/hepatitisb.shtml/shtml#strategies. Accessed October 23, 2015. | ||
Chan CY, Lee SD, Lo KJ. Legend of hepatitis B vaccination: the Taiwan experience. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;19(2):121–126. | ||
Viviani S, Jack A, Hall AJ, et al. Hepatitis B vaccination in infancy in The Gambia: protection against carriage at 9 years of age. Vaccine. 1999;17:2946–2950. | ||
Ng KP, Saw TL, Baki A, et al. Impact of expanded program of immunization against hepatitis B infection in school children in Malaysia. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2005;194:163–168. | ||
Sharma N, Kandpal J, Nautiyal SC, et al. Real time PCR usage in the quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA – clinical applications in disease management. Int J Pharma Res Rev. 2013;2(6):45–51. | ||
Liang X, Bi S, Yang W, et al. Epidemiological Serosurvey of hepatitis B in China – declining HBV prevalence due to hepatitis B vaccination. Vaccine. 2009;27:6550–6557. | ||
Fernandez-Rodriguez CM, Gutiérrez-García ML. Prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroinstest Pharmacol Ther. 2014;5(3):175–182. | ||
Bruix J, Hessheimer AJ, Forner A, Boix L, Vilana R, Llovet JM. New aspects of diagnosis and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2006;25:3848–3856. | ||
Dufour JF, Bargellini I, De Maria N, De Simone P, Goulis I, Marinho RT. Intermediate hepatocellular carcinoma: current treatments and future perspectives. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(Suppl 2):ii24–ii29. | ||
Lin S, Hoffmann K, Schemmer P. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Liver Cancer. 2012;1(3–4):144–158. | ||
Gomaa AI, Waked I. Recent advances in multidisciplinary management of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 2015;7(4):673–687. | ||
Chan HL, Wong GL, Tse CH, Chan HY, Wong VW. Viral determinants of hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in hepatitis B antigen negative chronic hepatitis B patients. J Infect Dis. 2011;204(3):408–414. | ||
The 5th Asia-Pasific Primary Liver Cancer Expert Meeting (APPLE 2014). In: Cheng AL, Hsu CH, Hsu C, editors. A Bridge to a Consensus on HCC Management. Taipei, Taiwan. 2014;3:285–397. | ||
Ueno Y, Sollano JD, Farrell GC. Prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma complicating chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:531–536. | ||
Mariano A, Mele A, Tosti ME, et al. Role of beauty treatment in the spread of parenterally transmitted hepatitis viruses in Italy. J Med Virol. 2004;74:216–220. | ||
CDC. Progress toward prevention of transfusion-transmitted hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection – Sub-Saharan Africa, 2000–2011. MMWR. 2014;63(29):613–619. | ||
CDC. Progress toward strengthening national blood transfusion services – 14 countries, 2008–2010. MMWR. 2011;60:1578–1582. | ||
World Health Organization. Blood safety and availability. 2013. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs279/en/index.html. Accessed October 23, 2015. | ||
Kanda T, Nakamoto S, Wu S, Yokosuka O. New treatments for genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C – focus on simeprevir. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014;10:387–394. | ||
Gentile I, Buonomo AR, Zappulo EM, et al. Asunaprevir, a protease inhibitor for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014;10:493–504. | ||
Valadez JA, Juárez IGG, Pedrero RR, Torre A. Management of chronic hepatitis C virus infection in patients with end-stage renal disease: a review. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015;11:329–338. | ||
Karnsakul W, Alford MK, Schwarz KB. Managing pediatric hepatitis C: current and emerging treatment options. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2009;5:651–660. | ||
Chae HB, Hann HW. Time for an active antiviral therapy for hepatitis B: an update on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2007;3(4):605–612. | ||
Dhillon R, Rossi S, Herrine SK. Pegylated interferon 2a and 2b in combination with ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C in HIV infected patients. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2008;4(4):789–796. | ||
Mazzaferro V, Chun YS, Poon RTP, et al. Liver transplantation for cellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15(4):1001–1007. | ||
Chong CCN, Wong GLH, Wong VWS, Lee KF, Lai PBS, Chan HLY. Role of anti-viral therapy on hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Liver Tumors – Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment. 2013. Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/liver-tumors-epidemiology-diagnosis-prevention-and-treatment/role-of-anti-viral-therapy-on-hepatitis-b-virus-hbv-related-hepatocellular-carcinoma-hc. Accessed October 23, 2015. | ||
Liapi E, Geschwind JFH. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for liver cancer: is it time to distinguish conventional from drug-eluting chemoembolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010:34(1):37–49. | ||
Llovet JM, Decaens T, Raoul J-L, Boucher E. Brivanib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma who were intolerant to sorafenib or for whom sorafenib failed: results from the randomized phase III BRISK-PS study. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(28):3509–3516. | ||
Lewis AL, Dreher MR. Locoregional drug delivery using image-guided intra-arterial drug eluting bead therapy. J Control Release. 2012;161(2):338–350. | ||
Hung HF, Chen TH. Probabilistic cost-effectiveness analysis of the long term effect of universal hepatitis B vaccination: an experience from Taiwan with high hepatitis B virus infection and Hepatitis B e antigen positive prevalence. Vaccine. 2009;27:6770–6776. | ||
Hong A, Robin D, Herman J, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of hepatitis B immunization in Vietnam: application of cost-effectiveness affordability curves in health care decision making. Value Health Regional. 2012;1:7–14. | ||
Poon RT-P, Fan S-T. Hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: patient selection and postoperative outcome. Liver Transpl. 2004;10(2 Suppl 1):S39–S45. | ||
Gaillard M, Tranchart H, Dagher I. Laparoscopic liver resections for hepatocellular carcinoma: current role and limitations. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(17):4892–4899. |
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.