Back to Journals » Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management » Volume 13
Comparison of prophylactic effect of UGIB and effects on platelet function between PPIs and H2RAs combined with DAPT: systematic review and meta-analysis
Authors Yi Z , Qiu T, Zhang Y , Liu Z, Zhai S
Received 10 November 2016
Accepted for publication 3 March 2017
Published 24 March 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 367—377
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S127292
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Deyun Wang
Zhan-Miao Yi,1 Ting-Ting Qiu,1,2 Yuan Zhang,3 Zhi-Yan Liu,1 Suo-Di Zhai1
1Department of Pharmacy, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, 2Department of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, People’s Republic of China; 3Department of Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Objective: We compared prophylactic effects of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs) on upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) associated with dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) and explored this influence on platelet function.
Methods: Randomized controlled trials and cohort studies comparing PPIs with H2RAs in adults receiving DAPT were collected from PubMed, EMBASE and Cochrane databases. Dichotomous data were pooled to obtain risk ratios (RRs) for UGIB, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), poor responders to clopidogrel and rehospitalization, and continuous data were pooled to obtain mean differences (MDs) for P2Y12 reaction units (PRUs), with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: Twelve clinical trials (n=3,301) met the inclusion criteria. Compared to H2RAs, PPIs lessened UGIB (RR =0.16, 95% CI: 0.03–0.70), and there was no significant difference in the incidence of PRUs (MD =18.21 PRUs, 95% CI: -4.11–40.54), poor responders to clopidogrel (RR =1.21, 95% CI: 0.92–1.61), incidence of MACEs (RR =0.89, 95% CI: 0.45–1.75) or rehospitalization (RR =1.76, 95% CI: 0.79–3.92). Subgroup analysis confirmed fewer PRUs in the H2RAs group compared to the omeprazole group (2 studies, n=189, MD =31.80 PRUs, 95% CI: 11.65–51.96). However, poor responder data for clopidogrel and MACEs might be unreliable because few studies of this kind were included.
Conclusion: Limited evidence indicates that PPIs were better than H2RAs for prophylaxis of UGIB associated with DAPT and had no effect on platelet function. Further study is needed to confirm these observations.
Keywords: proton pump inhibitors, histamine-2 receptor antagonists, dual-antiplatelet therapy, upper gastrointestinal bleeding, platelet function, meta-analysis
Introduction
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT; clopidogrel and aspirin) is commonly used for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular (CV) and cerebrovascular diseases. DAPT can reduce the risk of subsequent stroke for a year after the first event.1 In a randomized controlled trial (RCT), DAPT was confirmed to reduce the risk of stroke by 32% compared to aspirin alone in patients with minor stroke or transient ischemic attacks.2
As DAPT use increases, the incidence of DAPT-associated upper gastrointestinal (GI) injuries, including gastric mucosal erosions, peptic ulcers and bleeding, also rises. Morneau et al reported that DAPT therapy could increase twofold the risk of GI bleeding (GIB), especially in patients with multiple risk factors.3 Thus, GIB prophylaxis was suggested for patients receiving DAPT therapy.
In 2007, the American College of Cardiology recommended antiulcer drugs for patients with a history of GIB, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) effectively lowered the adjusted risk of aspirin-induced GIB by 28%.4 Meanwhile, histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs) therapy can prevent ulcers for patients receiving low-dose aspirin.5
Studies suggest that combination treatment with PPIs plus clopidogrel is associated with high platelet reactivity and more adverse events during long-term follow-up.6,7 PPIs were also shown to reduce responsiveness to standard clopidogrel doses and increased CV events for patients with the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C19 loss-of-function allele.8 Moreover, H2RAs may be as effective as PPIs plus DAPT for patients with no prior history of upper GI bleeding (UGIB).9 Therefore, H2RAs might be a reasonable alternative to PPIs, as they do not affect CYP 2C19 genotypes. Therefore, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare the efficacy and safety of PPIs compared with H2RAs for preventing UGIB associated with DAPT, and offered a foundation of evidence for clinical decision-making.
Materials and methods
Search strategy and inclusion criteria
We searched PubMed (January 1966 to August 2016), EMBASE (January 1974 to August 2016) and the Cochrane Collaboration’s Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (2016 Issue 8) to identify clinical trials comparing the efficacy of PPIs to H2RAs for patients treated with DAPT consisting of aspirin and clopidogrel. The following search terms were used: aspirin, acetylsalicylic, clopidogrel, proton pump inhibitors, PPIs, esomeprazole, pantoprazole, omeprazole, rabeprazole, lansoprazole, histamine receptor blocker, H2 receptor antagonists, H2 blocker, H2RA, cimetidine, ranitidine, famotidine, roxatidine, nizatidine and lafutidine. Reference lists of original articles and reviews were manually searched for additional relevant studies. Experts in this field of study were consulted.
For this review, inclusion criteria included 1) RCTs (parallel or crossover design) and cohort studies; 2) patients treated with aspirin and clopidogrel; 3) PPIs versus H2RAs; 4) primary outcome of UGIB; secondary outcomes were P2Y12 reaction units (PRUs), number of poor responders to clopidogrel, major adverse CV events (MACEs) and rehospitalization frequency. All manuscripts were in English. UGIB referred to hematemesis, melena or a hemoglobin decrease of >2 g/dL, with or without endoscopy. Poor clopidogrel responder was defined by a PRU value >240 or a PRU% <20% or a platelet reactivity index >50%. MACEs referred to death from CV causes, spontaneous myocardial infarction, unstable angina, stent thrombosis, target vessel revascularization, nontarget vessel revascularization and ischemic stroke. The systematic review with meta-analysis was registered on PROSPERO (No CRD42015030158).
Study selection and quality assessment
Two authors (ZMY and TTQ) independently selected potentially eligible studies from the literature according to title and abstracts. Then, full-text versions were screened for potentially eligible studies to determine eligibility based on inclusion criteria.
Two authors (ZMY and TTQ) independently assessed the risk of bias in included studies. The methodological quality of eligible RCTs was evaluated with the Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool,10 in which critical quality assessments are made separately for different domains including method of randomization, concealment of allocation, blinding, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting and other biases. Considering that the observational studies were more vulnerable to the potential selection bias than RCTs, the methodological quality of eligible cohort studies was evaluated with the Newcastle–Ottawa scale.11 Three domains including selection, comparability and outcome were assessed. All disagreements about study selection and quality assessment were resolved through discussion.
Data extraction and synthesis
Data extraction was performed by each author (ZMY and TTQ) according to a predesigned review form, and study characteristics (author, publication year and type of study), participant characteristics (inclusion criteria, sample size, age and sex), intervention information (dosage, administration route and duration) and outcome measures (primary and secondary outcomes) were collected. All disagreements were resolved through discussion.
Meta-analyses were performed with RevMan 5.3. Dichotomous and continuous outcomes were expressed with random effect model as the risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) and mean difference (MD) with 95% CI, respectively. Statistical heterogeneity was assessed with the Mantel–Haenszel chi-square test and quantified using an I2 test (P-value of heterogeneity was 0.10). Subgroup analyses among different PPIs were conducted to explore sources of clinical heterogeneity in data regarding PRUs. According to the guidance in Chapter 16 of Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, when carryover or period effects were not serious for crossover studies, all measurements were analyzed as if the trials were parallel-group trials.12 Sensitivity analysis was conducted by changing the random-effects methods to fixed-effects methods to pool the trials.
Results
Search results and study characteristics
Studies identified are depicted in Figure 1 along with strategies for including relevant papers. Among studies that retrieved full text for inspection, 20 studies were excluded, and the details were as following: 4 had no comparisons between PPIs and H2RAs, 4 were duplications, patients did not meet inclusion criteria in 3 studies, 2 were case series, 1 presented no separate data on the PPIs and H2RAs, 1 studied prescription rates of PPIs and H2RAs, 1 was a review, 1 was a commentary, 1 was an animal experiment, 1 was a case–control study and 1 was a Chinese article with English abstract (Figure 1).
  | Figure 1 Flow diagram for study selection. |
Table 1 depicts study characteristics, and bias risk data are shown in Tables 2 and 3. A total of 12 studies containing 3,301 patients (2,068 in the PPIs group, 1,233 in H2RAs group) were included in the analysis.13–24 The risk of bias for all included RCTs is high except the low risk of bias for Furtado et al14 and moderate risk of bias for Ng et al.16 For cohort studies, the risk of bias for Cappelletti Galante et al,21 Ng et al23 and Yew et al24 is moderate and the risk of bias for Macaione et al22 is high.
Incidence of UGIB
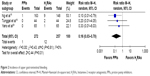
Three RCTs16,18,20 reported the incidence of UGIB, and Figure 2 depicts the lack of heterogeneity between included trials and the pooled RR, confirming that PPIs decreased UGIB compared to H2RAs. Ng et al conducted a cohort study to measure UGIB events and treatment effect of PPIs and H2RAs, and the risk of UGIB was marginally reduced by H2RAs (odds ratio [OR] =0.43, 95% CI: 0.18–0.91), but significantly reduced by PPIs (OR =0.04, 95% CI: 0.002–0.21) compared to controls.23
Antiplatelet effects
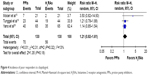
For antiplatelet effects, three outcomes were studied: PRUs, poor responders to clopidogrel (75 mg) and ADP-induced maximal amplitude (ADP-MA). Three RCTs reported the results of PRUs.13,14,18 The washout period for the study by Arbel et al13 was 2 weeks; blood samples were collected and results were analyzed in the manner of a parallel-group trial. Arbel et al’s13 study data were divided into two groups of similar subject size; Arbel et al 2013a compared omeprazole and H2RAs and Arbel et al 2013b compared pantoprazole and H2RAs. Heterogeneity of included trials was significant, and there were no statistically significant differences among PRUs between the PPIs and H2RAs groups (Figure 3). Subgroup analysis of the omeprazole group (n=163, 2 studies) indicated no significant heterogeneity between trials (P=0.16, I2=50%). At endpoint, the pooled MD of the subgroup was 31.82 PRUs (95% CI: 11.70–51.94), indicating that PRUs were fewer in the H2RAs group compared to the omeprazole group. The pantoprazole subgroup (1 study) had more PRUs compared to the H2RAs group (MD =8.00 PRUs, 95% CI: 2.66–13.34).
Moceri et al reported a decreased mean PRU% for those treated with esomeprazole compared to those treated with no drug (P<0.0001), but no statistical difference was found in the ranitidine group (P=0.97).15
Three RCTs15,18,20 reported of poor responders to clopidogrel (75 mg). The washout period in the study by Moceri et al15 was 48 h, and blood samples were collected at the end of each phase. This washout period was sufficient to eliminate the effect of clopidogrel for poor responders and data were assessed as if this was a parallel-group trial. Heterogeneity of included trials was insignificant (see Figure 4 for data), and there were no statistically significant differences among numbers of poor responders to clopidogrel between the PPIs and H2RAs groups (Figure 4).
Parri et al reported that pantoprazole plus DAPT significantly increased ADP-MA compared with ranitidine at 5 and 30 days’ follow-ups (P=0.01 and P=0.03, respectively), indicating that pantoprazole interfered with antiplatelet effects of clopidogrel.17 Uotani et al conducted a three-way randomized crossover study including 20 Japanese subjects and reported that rabeprazole plus DAPT did not attenuate antiplatelet function compared with famotidine combined with DAPT.19
Cardiovascular events
Two RCTs reported the incidence of MACEs16,20 and there was no heterogeneity between the trials (P=0.44, I2=0%) as well as no difference in the incidence of MACEs between PPIs and H2RAs therapy (RR =0.89, 95% CI 0.45–1.75). Yew et al published a retrospective cohort study in Singapore that included post-PCI patients who received either omeprazole or a H2RAs and DAPT and they confirmed that significantly more CV complications occurred in the omeprazole group (P=0.042).24
Rehospitalization
Two cohort studies reported the incidence of rehospitalization.21,22 Macaione et al’s study was divided into four groups (Figure 5) and each subgroup consisted of one-fourth of all patients. Macaione et al22 2012a depicted omeprazole versus H2RAs; Macaione et al 2012b reported esomeprazole versus H2RAs; Macaione et al 2012c included results of lansoprazole versus H2RAs; and Macaione et al 2012d included results of pantoprazole versus H2RAs.22 Heterogeneity of included trials was substantial and there were no statistically significant differences among incidence of rehospitalization between the PPIs and H2RAs groups (Figure 5).
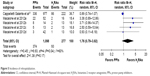  | Figure 5 Incidence of rehospitalization. |
Sensitivity analysis and publication bias
All pooled results were not affected by the different methods used. Due to a limited number of included studies for each outcome, we could not assess the risk of publication bias.
Discussion
This review compared the effectiveness and safety of PPIs to H2RAs for patients receiving DAPT, as assessed in RCTs and cohort studies. Limited evidence suggested that compared to H2RAs, PPIs decreased UGIB, and no differences were found in PRUs, poor responders to clopidogrel, or incidences of MACEs and rehospitalization. Among the PPIs, subgroup analyses suggested that omeprazole may increase PRUs.
A meta-analysis including ten RCTs by Mo et al showed that PPIs reduced LDA-associated UGIB.25 Another meta-analysis of 39 studies by Cardoso et al indicated that PPIs decreased the risk of UGIB for patients taking clopidogrel and these data agreed with our results.26 Only two trials were included in comparisons between PPIs and H2RAs by Mo et al,25 and no comparisons of this nature were made by Cardoso et al.26 Regarding CV events, Yasuda et al reported significantly more coronary stenotic lesions after treatment with PPIs compared with H2RAs,27 whereas the CALIBER study confirmed that both PPIs and ranitidine were associated with higher incidence of death or myocardial infarctions.28 A meta-analysis of RCTs and observational studies by Melloni et al had conflicting results regarding PPIs29 and CV outcomes, and a systematic review by Focks et al challenged the validity of conclusions about PPI–clopidogrel interactions on platelet function and MACEs based on quantitative analyses of predominantly nonrandomized data.30 A recent published RCT by Gargiulo et al also indicated that DAPT concomitant with PPIs did not increase death for myocardial infarction or cerebrovascular accident.31 We found no difference in the incidence of MACEs and between PPIs and H2RAs. This suggested that the safety profile of PPIs were comparable with H2RAs. However, the small number of included studies might compromise the validity of this conclusion.
Patients with increased upper GI risk are more likely to receive PPIs and patients with increased CV risk are more likely to receive DAPT instead of aspirin or clopidogrel alone, and DAPT treatment is more likely to be paired with PPIs due to increased UGIB risk compared to aspirin or clopidogrel alone. Therefore, in cohort studies, imbalances in baseline characteristics and prescription bias may affect observed outcomes; patient prognostic factors at the RCT baseline may differ from a cohort study. Here, we noted conflicting results between RCTs and cohort studies for ADP-MA and MACEs and these results may be biased due to inherent difference in study characteristics (study designs, study population and different treatment durations from 7 days to 35 months). DAPT length may influence the bleeding risk; the PRODIGY study suggested an increase in bleeding risk without benefit from ischemic adverse events,32 while benefit overcame the risk for some subgrousps at higher risk.33 Thus, more studies are needed to draw firm conclusions.
Our report is the first of its kind to directly compare PPIs with H2RAs for prophylaxis and safety when used with DAPT and we included RCTs and cohort studies. A recent meta-analysis to compare the effects of concomitant use of PPIs and DAPT concluded that observational studies and RCTs have conflicting outcomes regarding PPIs on CV outcomes when coadministered with DAPT.27 Thus, the results of both RCTs and cohort studies can decrease potential reporting bias. Subgroup analyses of four different types of PPIs to explore the potential effect differences indicate that omeprazole modified CYP 2C19 metabolism and reduced antiplatelet effects,34 and this was consistent with our results. Since 2009, the US FDA recommended against concomitant use of clopidogrel and omeprazole and suggested, instead, the use of a weak CYP 2C19 inhibitor, pantoprazole.35 However, in our study, two reports (one RCT and one cohort study) indicate that pantoprazole may have antiplatelet effects; so, we compared “poor responders to clopidogrel”, which was a more direct indicator of antiplatelet activity compared to PRUs.
Our study has some limitations. First, our topic has few reports in the literature and so clinical guidelines are similarly scarce36 or unjustified based on current evidence.37,38 Thus, high-quality research is required to assess clinical practices and support guideline recommendations. Second, in this systematic review, we could not combine RCTs with observational studies due to lack of matching propensity scores or reporting adjusted RRs. Although 12 studies were included in the review, only 8 RCTs were included in our meta-analysis. Additionally, aggregate sample sizes of all included studies were small and this decreased precision of estimates. Subgroup analysis based on individual CYP 2C19 genotypes and Heliobacter pylori status could not be performed because few studies reported these data. Furthermore, only English-language studies were included and conference abstracts were not manually searched, although important conference abstracts were included in databases searched and included in our review.
Conclusion
The available evidence suggests that PPIs outperformed H2RAs for prophylaxis of UGIB associated with DAPT, and no differences in platelet function were observed. Likely, differences in antiplatelet activity are caused by omeprazole, but larger randomized controlled studies are required to compare PPIs with H2RAs for preventing UGIB during DAPT treatment.
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by Award Number 2016B-YX007 from the Chinese Medical Association. We extend our special thanks to Hua Zhang from the Research Center of Clinical Epidemiology, Peking University Third Hospital for clarifying types of included studies. We thank Prof Shu-Sen Sun from the College of Pharmacy, Western New England University for editing assistance.
Author contributions
All authors contributed toward data analysis, drafting and revising the paper and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Wang Y, Pan Y, Zhao X, et al; CHANCE Investigators. Clopidogrel with aspirin in acute minor stroke or transient ischemic attack (CHANCE) trial: one-year outcomes. Circulation. 2015;132(1):40–46. | ||
Wang X, Zhao X, Johnston SC, et al; CHANCE investigators. Effect of clopidogrel with aspirin on functional outcome in TIA or minor stroke: CHANCE substudy. Neurology. 2015;85(7):573–579. | ||
Morneau KM, Reaves AB, Martin JB, Oliphant CS. Analysis of gastrointestinal prophylaxis in patients receiving dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel. J Manag Care Pharm. 2014;20(2): 187–193. | ||
Schjerning Olsen AM, Lindhardsen J, Gislason GH, et al. Impact of proton pump inhibitor treatment on gastrointestinal bleeding associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use among post-myocardial infarction patients taking antithrombotics: nationwide study. BMJ. 2015;351:h5096. | ||
He Y, Chan EW, Man KK, et al. Dosage effects of histamine-2 receptor antagonist on the primary prophylaxis of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-associated peptic ulcers: a retrospective cohort study. Drug Saf. 2014;37(9):711–721. | ||
Weisz G, Smilowitz NR, Kirtane AJ, et al. Proton pump inhibitors, platelet reactivity, and cardiovascular outcomes after drug-eluting stents in clopidogrel-treated patients: the ADAPT-DES study. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8(10):e001952. | ||
Yamane K, Kato Y, Tazaki J, et al. Effects of PPIs and an H2 blocker on the antiplatelet function of clopidogrel in Japanese patients under dual antiplatelet therapy. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2012;19(6):559–569. | ||
Simon N, Finzi J, Cayla G, Montalescot G, Collet JP, Hulot JS. Omeprazole, pantoprazole, and CYP2C19 effects on clopidogrel pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships in stable coronary artery disease patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;71(9):1059–1066. | ||
Yasu T, Sato N, Kurokawa Y, Saito S, Shoji M. Efficacy of H2 receptor antagonists for prevention of upper gastrointestinal bleeding during dual-antiplatelet therapy. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013;51(11):854–860. | ||
Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from: www.handbook.cochrane.org. Accessed November 10, 2016. | ||
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Available from: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Accessed November 10, 2016. | ||
Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from: http://www.cochrane-handbook.org | ||
Arbel Y, Birati EY, Finkelstein A, et al. Platelet inhibitory effect of clopidogrel in patients treated with omeprazole, pantoprazole, and famotidine: a prospective, randomized, crossover study. Clin Cardiol. 2013;36(6):342–346. | ||
Furtado RH, Giugliano RP, Strunz CM, et al. Drug interaction between clopidogrel and ranitidine or omeprazole in stable coronary artery disease: a double-blind, double dummy, randomized study. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2016;16(4):275–284. | ||
Moceri P, Doyen D, Cerboni P, Ferrari E. Doubling the dose of clopidogrel restores the loss of antiplatelet effect induced by esomeprazole. Thromb Res. 2011;128(5):458–462. | ||
Ng FH, Tunggal P, Chu WM, et al. Esomeprazole compared with famotidine in the prevention of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with acute coronary syndrome or myocardial infarction. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(3):389–396. | ||
Parri MS, Gianetti J, Dushpanova A, et al. Pantoprazole significantly interferes with antiplatelet effect of clopidogrel: results of a pilot randomized trial. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(5):2177–2181. | ||
Tunggal P, Ng FH, Lam KF, Chan FK, Lau YK. Effect of esomeprazole versus famotidine on platelet inhibition by clopidogrel: a double-blind, randomized trial. Am Heart J. 2011;162(5):870–874. | ||
Uotani T, Sugimoto M, Ichikawa H, et al. Comparison of preventive effects of rabeprazole and famotidine on gastric mucosal injury induced by dual therapy with low-dose aspirin and clopidogrel in relation to CYP2C19 genotypes and H. Pylori infection. Gastroenterology. 2013;144(5 Suppl 1):S478–S479. | ||
Yano H, Tsukahara K, Morita S, et al. Influence of omeprazole and famotidine on the antiplatelet effects of clopidogrel in addition to aspirin in patients with acute coronary syndromes: a prospective, randomized, multicenter study. Circ J. 2012;76(11):2673–2680. | ||
Cappelletti Galante M, Garcia Santos V, Bezerra da Cunha GW. Assessment of the use of clopidogrel associated with gastroprotective medications in outpatients. Farm Hosp. 2012;36(4):216–219. | ||
Macaione F, Montaina C, Evola S, Novo G, Novo S. Impact of dual antiplatelet therapy with proton pump inhibitors on the outcome of patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing drug-eluting stent implantation. ISRN Cardiol. 2012;2012:692761. | ||
Ng FH, Lam KF, Wong SY, et al. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with aspirin and clopidogrel co-therapy. Digestion. 2008;77(3–4):173–177. | ||
Yew MS, Yeo PSD, Ong JLP, et al. Omeprazole use is associated with increased cardiovascular complications in Asian patients on aspirin and clopidogrel after percutaneous coronary intervention. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7(2):S17–S18. | ||
Mo C, Sun G, Lu ML, et al. Proton pump inhibitors in prevention of low-dose aspirin-associated upper gastrointestinal injuries. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(17):5382–5392. | ||
Cardoso RN, Benjo AM, DiNicolantonio JJ, et al. Incidence of cardiovascular events and gastrointestinal bleeding in patients receiving clopidogrel with and without proton pump inhibitors: an updated meta-analysis. Open Heart. 2015;2(1):e000248. | ||
Yasuda H, Yamada M, Sawada S, et al. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding in patients receiving dual antiplatelet therapy after coronary stenting. Intern Med. 2009;48(19):1725–1730. | ||
Douglas IJ, Evans SJ, Hingorani AD, et al. Clopidogrel and interaction with proton pump inhibitors: comparison between cohort and within person study designs. BMJ. 2012;345:e4388. | ||
Melloni C, Washam JB, Jones WS, et al. Conflicting results between randomized trials and observational studies on the impact of proton pump inhibitors on cardiovascular events when coadministered with dual antiplatelet therapy: systematic review. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2015;8(1):47–55. | ||
Focks JJ, Brouwer MA, van Oijen MG, Lanas A, Bhatt DL, Verheugt FW. Concomitant use of clopidogrel and proton pump inhibitors: impact on platelet function and clinical outcome- a systematic review. Heart. 2013;99(8):520–527. | ||
Gargiulo G, Costa F, Ariotti S, et al. Impact of proton pump inhibitors on clinical outcomes in patients treated with a 6- or 24-month dual-antiplatelet therapy duration: Insights from the PROlonging Dual-antiplatelet treatment after Grading stent-induced Intimal hyperplasia studY trial. Am Heart J. 2016;174:95–102. | ||
Valgimigli M, Campo G, Monti M, et al; Prolonging Dual Antiplatelet Treatment After Grading Stent-Induced Intimal Hyperplasia Study (PRODIGY) Investigators. Short- versus long-term duration of dual-antiplatelet therapy after coronary stenting: a randomized multicenter trial. Circulation. 2012;125(16):2015–2026. | ||
Campo G, Tebaldi M, Vranckx P, et al. Short- versus long-term duration of dual antiplatelet therapy in patients treated for in-stent restenosis: a PRODIGY trial substudy (Prolonging Dual Antiplatelet Treatment After Grading Stent-Induced Intimal Hyperplasia). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(6):506–512. | ||
Norgard NB, Mathews KD, Wall GC. Drug-drug interaction between clopidogrel and proton pump inhibitors. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;43(7):1266–1274. | ||
US Food and Drug Administration. FDA reminder to avoid concomitant use of Plavix (clopidogrel) and omeprazole. Available from: www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm231161.htm. Accessed November 10, 2016. | ||
Bhatt DL, Scheiman J, Abraham NS, et al; American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus Documents. ACCF/ACG/AHA 2008 expert consensus document on reducing the gastrointestinal risks of antiplatelet therapy and NSAID use: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus Documents. Circulation. 2008;118(18):1894–1909. | ||
Abraham NS, Hlatky MA, Antman EM, et al; ACCF/ACG/AHA. ACCF/ACG/AHA 2010 expert consensus document on the concomitant use of proton pump inhibitors and thienopyridines: a focused update of the ACCF/ACG/AHA 2008 expert consensus document on reducing the gastrointestinal risks of antiplatelet therapy and NSAID use. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105(12):2533–2549. | ||
Tan HJ, Mahadeva S, Menon J, et al. Statements of the Malaysian Society of Gastroenterology & Hepatology and the National Heart Association of Malaysia task force 2012 working party on the use of antiplatelet therapy and proton pump inhibitors in the prevention of gastrointestinal bleeding. J Dig Dis. 2013;14(1):1–10. |
 © 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.