Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 10 » Issue 1
Cationic polyelectrolyte-mediated delivery of antisense morpholino oligonucleotides for exon-skipping in vitro and in mdx mice
Authors Wang M , Wu B, Tucker JD , Lu P, Lu Q
Received 5 June 2015
Accepted for publication 8 July 2015
Published 3 September 2015 Volume 2015:10(1) Pages 5635—5646
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S89910
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Mingxing Wang, Bo Wu, Jason D Tucker, Peijuan Lu, Qilong Lu
Department of Neurology, McColl-Lockwood Laboratory for Muscular Dystrophy Research, Cannon Research Center, Carolinas Medical Center, Charlotte, NC, USA
Abstract: In this study, we investigated a series of cationic polyelectrolytes (PEs) with different size and composition for their potential to improve delivery of an antisense phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) both in vitro and in vivo. The results showed that the poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDDAC) polymer series, especially PE-3 and PE-4, improves the delivery efficiency of PMO, comparable with Endoporter-mediated PMO delivery in vitro. The enhanced PMO delivery and targeting to dystrophin exon 23 was further observed in mdx mice, up to fourfold with the PE-4, compared with PMO alone. The cytotoxicity of the PEs was lower than that of Endoporter and polyethylenimine 25,000 Da in vitro, and was not clearly detected in muscle in vivo under the tested concentrations. Together, these results demonstrate that optimization of PE molecular size, composition, and distribution of cationic charge are key factors to achieve enhanced PMO exon-skipping efficiency. The increased efficiency and lower toxicity show this PDDAC series to be capable gene/antisense oligonucleotide delivery-enhancing agents for treating muscular dystrophy and other diseases.
Keywords: cationic polyelectrolytes, antisense delivery, exon-skipping, PMO, muscular dystrophy
Introduction
Antisense therapy has grown as a powerful strategy for the treatment of genetic disorders and infections. Antisense oligonucleotide-mediated exon-skipping has been demonstrated as a promising therapy to treat Duchenne muscular dystrophy by skipping specific dystrophin gene exon(s) to restore the reading frame of the mutation-containing transcripts.1–12 Antisense oligonucleotides are short, typically 15–30 base pairs of single-stranded sequences of synthetic nucleic acids, or chemically modified analogs, which have the ability to hybridize to specific targets by the base-pairing rules. Of the synthetic oligonucleotide chemistries, phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) is most widely used for exon-skipping in the dystrophin gene currently being applied in clinical trials.11–15 PMO, as a synthetic mimic of nucleic acid, has deoxyribose rings replaced with morpholino rings and linked through phosphorodiamidate inter-subunits, making it neutral under physiological conditions. It has exhibited excellent stability, and lower toxicity compared with its counterparts, such as 2′-O-methyl-phosphorothioate RNA and peptide nucleic acid.16,17 However, the relatively charge-neutral nature of PMO is associated with poor cellular uptake and rapid clearance from the bloodstream, which constitutes a major obstacle for effective delivery when treating neurogenetic disorders. Studies in a number of animal models have demonstrated that a significant therapeutic effect can be achieved with high doses of PMOs, which could be cost-inhibitive and have an increased risk of toxicity, especially for long-term systemic administration.5 To improve delivery efficiency, PMOs chemically modified with cell-penetrating peptides or dendrimeric octaguanidines have been devised, and are reported to show significant improvement in targeting dystrophin exons, leading to near normal levels of dystrophin expression in body-wide muscles by systemic delivery.3,4,6,9,10 However, the cationic modification is associated with higher toxicity, with LD50 near 100 mg/kg, making it unsuitable for use in clinical applications.3,6 Furthermore, the complicated synthesis and purification in modification increases the costs significantly, and potential immune responses to the targeting peptide could prevent repeated administration. The non-virus-mediated delivery strategy remains attractive because of the vector’s structural flexibility chosen from synthetic or natural compounds, capacity for delivery of larger therapeutic agents, ease of handling, greater safety, and less expense than viral vectors,18–20 especially for those commercial available compounds that have been widely applied in the field of environmental biology and biotechnology.
Polyelectrolytes (PEs) are polymers with ionizable groups that dissociate, leaving ions on the polymer chain and counter ions in polar solution. PEs have been investigated for numerous biochemical and medical applications.21,22 The permanent cationic characteristics, such as valence, charge density, and structure, would be expected to have an important impact on the compaction of oligonucleotides and subsequent transfection. In this study, we investigated several commonly used PEs as carriers for delivery of antisense PMO in vitro and in vivo. These include cationic PEs, poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDDAC), which is widely used as a flocculant agent and biosensor composite;23–25 poly(acrylamide-co-diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PADAC), and poly[bis(2-chloroethyl)ether-alt-1,3-bis[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]urea] quaternized (PBEBP), which are used in waste treatment for laundry, emulsion breaking, sludge dewatering and drainage; and protamine sulfate containing cell-penetrate peptide, which has been studied in gene therapy for increasing transduction by both viral and non-viral mediated delivery mechanisms.26,27
Materials and methods
Materials
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM), penicillin-streptomycin, fetal bovine serum, l-glutamine, and HEPES [4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid] buffer solution (1 M) were purchased from Gibco, Invitrogen Corp (Carlsbad, CA, USA). Phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer PMOE50 (5′-AACTTCCTCTTTAACAGAAAAGCATAC-3′), PMOE23 (5′-GGCCAAACCTCGGCTTACCTGAAAT-3′), and Endoporter were purchased from GeneTools (Philomath, OR, USA). PEs, protamine, and all other chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA), unless otherwise stated.
Cell viability assay
Cytotoxicity was evaluated in a C2C12E50 cell line using the MTS [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium]-based assay. Cells were seeded in a 96-well tissue culture plate at 1×104 cell per well in 200 μL of 10% fetal bovine serum-DMEM. Cells achieving 70%–80% confluence were exposed to polymer at different doses for 24 hours followed by addition of 20 μL of Cell Titer 96® Aqueous One Solution (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA). After further incubation for 4 hours, the absorbance was measured at 490 nm using a Tecan Infinite 500 plate reader (Tecan Systems Inc, San Jose, CA, USA) to obtain the metabolic activity of the cell. Untreated cells were taken as controls with 100% viability and wells without cells as blanks. The relative cell viability was calculated by:
(Atreated − Abackground) ×100/(Acontrol − Abackground) |
All viability assays were carried out in triplicate.
In vitro transfection
C2C12E50 and C2C12E23 myoblast cell lines expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) were used for in vitro experimentation. Expression of GFP was controlled by effective skipping of the inserted human dystrophin exon 50 sequence (hDysE50) or mouse dystrophin exon 23 sequence (mDysE23).18 The C2C12E50 cell line was maintained in 10% fetal bovine serum-DMEM in a humidified 10% CO2 incubator at 37°C. Approximately 5×104 C2C12E50 cells per well in 500 μL of 10% fetal bovine serum-DMEM medium were seeded and allowed to grow until confluence of 70%. The cell culture medium was replaced before addition of a polymer/PMOE50 (fixed at 5 μg) formulation with varying ratios. Polyethylenimine (PEI) 25,000 and Endoporter were used as a comparison. Transfection efficiencies indicated by GFP production were recorded after 48 hours of incubation with an Olympus IX71 fluorescent microscope (Olympus America Inc, Melville, NY, USA) and digital images taken with the DP Controller and DP Manager software (Olympus America Inc). Transfection efficiency was also examined quantitatively using flow cytometry. Cells were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; 1×, pH 7.4). After removal of PBS, 0.2 mL of 0.05% trypsin-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid was added, and the cells were incubated for 3 minutes at 37°C. Next, 1 mL of the growth medium was added, and cells were collected by centrifugation and resuspended in 0.5 mL of ice-cold PBS (1×, pH 7.4). Samples were run on a FACS Calibur flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). At least 1×104 cells were counted and analyzed with CellQuest Pro software package (BD Biosciences).
RT-PCR analysis for cell culture
Collected cells were initially washed twice with PBS, and RNA was extracted with TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen Corp) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA was stored at −80°C for later use. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed using RT-PCR Master Mix (2X) (USB Corp, Cleveland, OH, USA) to amplify the sequence of interest. Next, 100 ng of template RNA was used for each 25 μL RT-PCR reaction. The primer sequences for the RT-PCR were eGFP5′, 5′-CAGAATTCTGCCAATTGCTGAG-3′ and eGFP3′, 5′-TTCTTCAGCTTGTGTCATCC-3′. The cycle conditions for reverse transcription were 43°C for 15 minutes and 94°C for 2 minutes. The reaction was then cycled 30 times at 94°C for 30 seconds, 65°C for 30 seconds, and 68°C for 1 minute. The products were examined by electrophoresis on 1.5% agarose gel.
Cellular uptake and intracellular localization
To study cellular uptake and intracellular localization, fluorescein-labeled PMO (GeneTools) was combined with polymers at predetermined ratios, followed by imaging under confocal microscopy. C2C12 cells were seeded onto eight-well glass Nunc Lab-Tek II chamber slides (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at 5×103 cells/well, and cultured to 70% confluence before addition of polymer/PMO formulation for testing. Approximately 24 hours after addition of the samples, the cells were washed with warm PBS (1×, pH 7.4) to remove any residual polymer/PMO polyplex from cells and incubated with medium. Cells were also counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA) to label cellular nuclei. Cellular uptake was examined on a Zeiss LSM-710 inverted confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss Microscopy LLC, Thornwood, NY, USA), and the resulting images were analyzed for uptake and localization by single-channel images. Co-localization of polymer/PMO to the lysosome was visualized by merged channel images to assess the signal intensities of the labeled PMO and lysosomes relative to counterstained nuclei.
Transmission electron microscopy
The polymer/PMO polyplex solution containing 5 μg of PMO was prepared at a weight ratio of 5/5 (PE/PMO) in 200 μL of medium and analyzed using a Philips CM-10 transmission electron microscope (Philips Electronic North America Corp, Andover, MA, USA). The corresponding polymer and PMO only were used as comparison. The samples were prepared using negative staining with 1% phosphotungstic acid. Briefly, one drop of sample solution was placed on a formvar and carbon-coated carbon grid (Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA, USA) for 1 hour, and blotted dry, followed by staining for 3 minutes. Samples were analyzed at 60 kV. Digital images were captured with a digital camera system from 4 pi Analysis (Durham, NC, USA).
In vivo delivery and RT-PCR
This study was carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations in the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Carolinas Medical Center (breeding protocol 10-13-07A; experimental protocol 10-13-08A). All injections were performed under isoflurane anesthesia, and all efforts were made to minimize suffering.3,5,6,18
Animals and intramuscular injections
Dystrophic mdx mice aged 4–5 weeks were used for in vivo testing (five mice each in the test and control groups) unless otherwise stated. The PMOE23 (5′-GGCCAAACCTCGGCTTACCTGAAAT-3′) targeting the boundary sequences of exon and intron 23 of the mouse dystrophin gene (GeneTools) was used. For intramuscular injections, 2 μg of PMOE23 with or without polymer was used in 40 μL of saline for each tibialis anterior muscle. The muscles were examined 2 weeks later, then snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen-cooled isopentane and stored at −80°C.
RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from the muscle after dissection, and 100 ng of RNA template was used for a 50 μL RT-PCR with the RT-PCR Master Mix (2X) system (USB Corp, Cleveland, Ohio, USA). The primer sequences for the RT-PCR were Ex20Fo 5′-CAGAATTCTGCCAATTGCTGAG-3′ and Ex26Ro 5′-TTCTTCAGCTTGTGTCATCC-3′ for amplification of mRNA from exons 20 to 26. The conditions were 43°C for 15 minutes, 94°C for 2 minutes, then cycling 30 times at 94°C for 30 seconds, 56°C for 30 seconds, and 68°C for 1 minute. The products were examined by electrophoresis on 2% agarose gel. Bands with the expected size for the transcript with exon 23 deleted were extracted and sequenced. The intensity of the bands of the PCR-amplified products obtained from the treated mdx mouse muscles was measured using National Institutes of Health ImageJ software 1.42 and the percentage of exon-skipping was calculated with the intensity of the two bands representing both unskipped and skipped exons as 100%.
Antibodies, immunohistochemistry, and Western blots
Sections of 6 μm were cut from the muscles and stained with rabbit polyclonal antibody P7 for the dystrophin protein and detected by goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulins Alexa 594 (Invitrogen Corp). The maximum number of dystrophin-positive fibers in one section was counted using a BX51 fluorescent microscope (Olympus America Inc). Digital images were taken with the Olympus DP Controller and DP Manager software (Olympus America Inc) and the muscle fibers were defined as dystrophin-positive when more than two-thirds of the membrane of a single fiber showed continuous staining. Protein extraction and Western blot were performed as described previously.3,10,18 Briefly, the membrane was probed with NCL-DYS1 monoclonal antibody against dystrophin rod domain (1:200 dilution, Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA) followed by horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin (1:3,000 dilution, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) and the ECL™ Western blotting analysis system (Perkin-Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA). The intensity of the bands with appropriate size was measured and compared with that from normal muscles of C57BL mice using ImageJ software. Loading control of α-actin was detected by rabbit anti-actin antibody (Sigma Aldrich).
Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed for statistical significance using both one-way analysis of variance and the Student’s t-test, with a value of P≤0.05 being considered statistically significant. All data are reported as the mean ± standard deviation.
Results and discussion
The PEs applied in this study are commercially available and have been widely applied in the field of environment and biotechnology. Their structures and code names were shown in Figure 1.
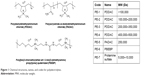  | Figure 1 Chemical structures, names, and codes for polyelectrolytes. |
PMO delivery in C2C12 myoblast cell lines expressing GFP/hDysE50
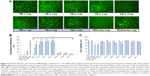
The C2C12E50 cell line was used to evaluate the efficacy of PEs for the delivery of PMO.18,28 This cell line expresses a GFP reporter, but its expression is disrupted by the insertion of the hDysE50. The expression of GFP in the reporter cells relies on the targeted removal of exon 50 by antisense oligonucleotides. First, we examined the cytotoxicity of the PEs using an MTS-based assay as shown in Figure 2. The toxicity of the PDDAC series including PE-1, PE-2, PE-3, and PE-4 was clearly size-dependent, being higher with increasing molecular weight of PDDAC. PE-5 (PADAC) and PE-6 (PBEBP) are structurally different from PDDAC. PE-5 contains insertion of around 55% polyacrylamide in composition; while PE-6 has a dispersed charged distribution due to the propyl urea spacer as compared with the PDDAC series. Protamine sulfate (PE-7) is a biocompatible and arginine-rich cell-penetrating polypeptide composed of only 50–110 amino acids, thus has a lower molecular weight and less toxicity than the PDDAC series.29–31
However, all PEs showed much lower cytotoxicity against PEI 25,000 at the same dose used. Viability dropped to less than 25%, 38%, and 62% for the cells treated with PEI 25,000 at a concentration of 20, 10, and 4 μg/mL, respectively. In contrast, all PEs except PE-4 at a dose of 20 μg/mL showed cell viability over 75%. PE-4 had the highest toxicity; however, over 67% of cells remained alive after treatment at a dose of 20 μg/mL. The relatively higher toxicity of PE-4 is probably related to its higher molecular weight and higher positive charges when compared with other PEs.
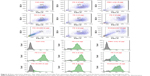
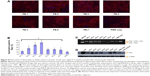
We next examined the effect of the PE polymers on exon-skipping of PMO. The PMO sequence, PMOE50 (5′-AACTTCCTCTTTAACAGAAAAG CATAC-3′) with previously confirmed efficacy for targeted removal of human dystrophin exon 50 was used.18–20 C2C12E50 GFP reporter cells were treated with a fixed amount (5 μg) of PMOE50 in 500 μL of 10% fetal bovine serum-DMEM medium formulated with each polymer at four different doses (1, 2, 5, and 10 μg). Transfection efficiency was examined by fluorescence microscopy. The results showed that almost all PE polymers, even at 1 μg, improved GFP expression compared with the PMOE50 alone. The highest levels of GFP expression were achieved at a dose of 2–5 μg with most PEs, especially with the PDDAC series, reaching up to 90% with PE-2/3/4 at the dose of 2 μg and comparable to or higher than Endoporter-mediated delivery (5 μg, effective dose in vitro, commercial reagent produced by GeneTools). A dose-dependent GFP expression is also illustrated by PE-3 at the doses of 1, 2, 5 μg (Figure 3). In contrast, less than 5% of the cells were GFP-positive when treated with PMOE50 alone. The exon-skipping efficiency remained higher at the 10 μg dose of PEs, but some toxicity was observed with PE-3/4. The transfection efficiency and cell viability of the PE/PMO formulation at the PE doses (1, 2, 5 μg) mixed with PMO (5 μg) in 500 μL of medium were also quantified by flow cytometry with Endoporter (5 μg) and PEI 25,000 (2 μg) as controls (Figures 3 and 4). GFP expression resulting from PDDAC-mediated PMO delivery was noted to be up to 20-fold higher when compared with PMO alone. The PDDAC series (PE-1/2/3/4) has more positive charges compared with PE-5 or PE-6 at the same weight dose. PE-5 has around 55% polyacrylamide in the main chain compared with the PDDAC series, thus certainly contains a reduced surface charge when forming a PE/PMO polyplex; PE-6 has a dispersed charged distribution as compared with the PDDAC series. The low transfection efficiency with protamine sulfate is likely due to a much lower molecular size, thus limited charge groups within the polyplex.
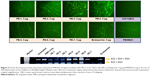
In order to assess the delivery potential of the PEs for PMO exon-skipping in muscle fibers, rather than in myoblasts, the PEs were also tested in the mouse dystrophin exon 23 reporter C2C12 myoblast cell (C2C12E23). GFP reporter expression is driven by a muscle creatine kinase promoter, therefore allowed us to test the potential for PMO delivery in differentiating or differentiated myotubes.18 Cells reaching around 70% confluence were incubated in the differentiation medium for 2 days and then treated with PE-formulated PMOE23. The results showed a similar trend as that obtained in C2C12E50 cells, with PE-2, PE-3, and PE-4 achieving higher GFP expression than other PEs, as illustrated in Figure 5 by fluorescence images and RT-PCR detection of exon 23 skipping. The levels of exon 23 skipping were 56.4%, 64.1%, 59.0%, 32.6%, 24.7%, 38.5%, 1.8%, 23.7%, and 10.1% for PE-1, PE-2, PE-3, PE-4, PE-5, PE-6, PE-7, Endoporter-formulated PMO, and PMO only, respectively. The results indicate the importance of molecular size, chemical structure, and positive charge distribution in the vector microstructure for both delivery efficiency and toxicity.
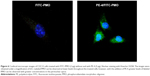
To examine whether PEs improve the cell uptake of PMO, we examined the intracellular localization of the PE/PMO polyplex. PE was complexed with 3′-carboxyfluorescein-labeled PMO at a weight ratio of 5/2. The presence of PE appeared to affect the pathway of PMO uptake, as demonstrated by confocal microscopy analysis. PMO alone distributed evenly within the cytoplasm of the cells, in agreement with a reported passive diffusion model.16 Signals for PMO were considerably stronger in cells treated with PE-4 and visualized as punctuates within the cytosol and especially around the nucleus (Figure 6). These results suggest that the presence of PEs alters the route of PMO internalization, probably eliciting endocytosis through formation of a complex.
Interaction between PE and PMO
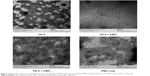
The affinity between a polymer and an oligonucleotide is an important parameter for their efficient delivery into cells. Here, we chose the most effective PE-4 from the PDDAC series and PE-5 for PE/PMO polyplex examination under transmission electron microscopy. As shown in Figure 7, the PE-4 polymer alone formed particles of different sizes, likely because of aggregation, whereas the PMO oligonucleotides alone formed particles with a size below 50 nm, likely resulting from hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen-bond among the PMO molecules. At a weight ratio of 5/5, the PE-4/PMO polyplex formed spherical particles with an average diameter around 20–40 nm. The PE-5/PMO polyplex formed larger particles than did the PE-4/PMO polyplex. This is probably the result of aggregation related to the uncharged hydrophobic polyacrylamide fragments within PE-5. The mechanisms of interaction between PMO and the PE molecules are not clear, but the chemical nature of PMO likely creates a hydrophobic interaction with the PEs, and a possible hydrogen-bond interaction between them. The positively charged groups within the PEs are unlikely to play a key role in the interaction with PMO; nonetheless, the surface charges of the polyplex may stabilize it in a biological environment for a longer period than PMO alone.
Delivery of PMO with PEs in vivo
We next evaluated the effect of the PE polymers on PMO delivery in vivo by intramuscular injection. PMOE23 targeting mouse dystrophin exon 23 was injected into each tibialis anterior muscle of mdx mice aged 4–5 weeks. The mouse contains a nonsense mutation in exon 23, preventing production of the functional dystrophin protein. Targeted removal of the mutated exon 23 is able to restore the reading frame of dystrophin transcripts, and thus the expression of the dystrophin protein. Based on the delivery performance of PEs in vitro, we chose 2 μg as an effective and safe dose, premixed with 2 μg of PMOE23 in 40 μL of saline. The treated tibialis anterior muscles were harvested 2 weeks later.
Immunohistochemistry showed that the PMOE23 alone induced up to 12% maximum dystrophin-positive fibers in one cross-section of the tibialis anterior muscle. The number of dystrophin-positive fibers increased dramatically in the muscles treated with PMOE23 mediated by PEs. The PDDAC series enhanced PMO-mediated exon-skipping with increasing molecular size. PE-3 and PE-4 achieved over 40% and 50% positive fibers respectively, ie, over fourfold as compared with PMO alone at the tested dose. Meanwhile, PE-5, PE-6, and PE-7 did not dramatically change the number of dystrophin-positive fibers (Figure 8). These results correlate well with the data in muscle cell lines in vitro, suggesting that the smaller PE molecule was less able to form an optimal complex with PMO, resulting in low transfection efficiency.32,33 PE-3 or PE-4 with higher transfection efficiency is probably due to larger molecular size, thus creating higher affinity binding sites with PMO. The positively charged PE-PMO complex is likely to be more stable in biological systems as the complex is expected to interact with various cells and biomacromolecules in the tissue and circulation, maintaining a longer circulation time.34,35 The levels of exon-skipping and corresponding dystrophin expression were also quantitatively determined by RT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. PMO formulated with PE-1, PE-2, PE-3, PE-4, PE-5, PE-6, PE-7 and PMO only achieved levels of exon-skipping at 4.1%, 30.5%, 22.9%, 25.5%, 0.2%, 20.8%, 0.8%, and 2.7%, respectively. Dystrophin protein expression levels were found to be 3.5%, 23.7%, 6.2%, 51.2%, 9.5%, and 3.7% of normal levels (taking muscles from C57 mouse as 100%) for PMO formulated with PE-1, PE-2, PE-3, PE-4, PE-6 and PMO only, respectively. Both quantitative and qualitative data therefore demonstrated the best performance with the PDDAC series, especially with PE-4. The results indicate the importance of molecular size and composition for the efficacy of delivery of uncharged PMO. However, more effective PEs are associated with higher toxicity, further highlighting the difficulty and complexity of developing non-viral oligonucleotide delivery agents for clinical use.
Conclusion
In summary, the cationic PEs have been evaluated for the first time as vectors for antisense PMO delivery in vitro and in dystrophic mdx mice. The results show that the PDDAC series, especially PE-3 and PE-4, improves the delivery efficiency of PMO, that is comparable to Endoporter-mediated PMO delivery in vitro. Significant enhancement of PMO delivery was also demonstrated in vivo, and up to fourfold with PE-4, when compared with PMO alone. No obvious local toxicity was observed at the test dose of PE-4. These data suggest that optimization of the molecular size, components, and density of the positive charge of PEs can achieve enhanced exon-skipping with PMO. PEs are therefore potential vehicles for antisense oligonucleotide delivery to achieve a therapeutic effect in diseases such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Drs David M Foureau and Fei Guo for their technical assistance with the flow cytometry and analysis, and Mrs Daisy M Ridings and Ben Wagner from the Electron Microscopy Core Laboratory for the negative staining and transmission electron micrographs. The authors also gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Carolinas Muscular Dystrophy Research Endowment at the Carolinas HealthCare Foundation and Carolinas Medical Center, Charlotte, NC, USA.
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Hoffman EP, Brown RH Jr, Kunkel LM. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 1987;51:919–928. | ||
Koenig M, Beggs AH, Moyer M, et al. The molecular basis for Duchenne versus Becker muscular dystrophy: correlation of severity with type of deletion. Am J Hum Genet. 1989;45:498–506. | ||
Wu B, Moulton HM, Iversen PL, et al. Effective rescue of dystrophin improves cardiac function in dystrophin-deficient mice by a modified morpholino oligomer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:14814–14819. | ||
Yin H, Moulton HM, Seow Y, et al. Cell-penetrating peptide-conjugated antisense oligonucleotides restore systemic muscle and cardiac dystrophin expression and function. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:3909–3918. | ||
Wu B, Lu P, Benrashid E, et al. Dose-dependent restoration of dystrophin expression in cardiac muscle of dystrophic mice by systemically delivered morpholino. Gene Ther. 2010;17:132–140. | ||
Wu B, Cloer C, Shaban M, Moulton H, Lu PJ, Lu QL. Long-term rescue of dystrophin expression and improvement in muscle pathology and function in dystrophic mdx mice by peptide-conjugated morpholino. Am J Pathol. 2012;181:392–400. | ||
van Deutekom JC, Janson AA, Ginjaar IB, et al. Local dystrophin restoration with antisense oligonucleotide PRO051. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2677–2686. | ||
Kinali M, Arechavala-Gomeza V, Feng L, et al. Local restoration of dystrophin expression with the morpholino oligomer AVI-4658 in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a single-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation, proof-of-concept study. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:918–928. | ||
Amantana A, Moulton HM, Cate ML, et al. Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, stability and toxicity of a cell-penetrating peptide-morpholino oligomer conjugate. Bioconjug Chem. 2007;18:1325–1331. | ||
Wu B, Li Y, Morcos PA, Doran TJ, Lu P, Lu QL. Octa-guanidine morpholino restores dystrophin expression in cardiac and skeletal muscles and ameliorates pathology in dystrophic mdx mice. Mol Ther. 2009;17:864–871. | ||
Goemans NM, Tulinius M, van den Akker JT, et al. Systemic administration of PRO051 in Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1513–1522. | ||
Mendell JR, Rodino-Klapac LR, Sahenk Z, et al. Eteplirsen for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann Neurol. 2013;74:637–647. | ||
Cirak S, Arechavala-Gomeza V, Guglieri M, et al. Exon skipping and dystrophin restoration in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy after systemic phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer treatment: an open-label, phase 2, dose-escalation study. Lancet. 2011;378:595–605. | ||
Fletcher S, Honeyman K, Fall AM, Harding PL, Johnsen RD, Wilton SD. Dystrophin expression in the mdx mouse after localised and systemic administration of a morpholino antisense oligonucleotide. J Gene Med. 2006;8:207–216. | ||
Malerba A, Sharp PS, Graham IR, et al. Chronic systemic therapy with low-dose morpholino oligomers ameliorates the pathology and normalizes locomotor behavior in mdx mice. Mol Ther. 2011;19:345–354. | ||
Summerton J, Weller D. Morpholino antisense oligomers design, preparation, and properties. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1997;7:187–195. | ||
Yano J, Smyth GE. New antisense strategies: chemical synthesis of RNA oligomers. Adv Polym Sci. 2012;249:1–48. | ||
Hu Y, Wu B, Zillmer A, et al. Guanine analogues enhance antisense oligonucleotide-induced exon skipping in dystrophin gene in vitro and in vivo. Mol Ther. 2010;18:812–818. | ||
Wang MX, Wu B, Tucker JD, Lu P, Cloer C, Lu QL. Evaluation of Tris[2-(acryloyloxy)ethyl]isocyanurate cross-linked polyethylenimine as antisense morpholino oligomer delivery vehicle in cell culture and dystrophic mdx Mice. Hum Gene Ther. 2014;25:419–427. | ||
Wang MX, Wu B, Lu P, Cloer C, Tucker JD, Lu QL. Polyethylenimine modified pluronics (PCMs) improve morpholino oligomer delivery in cell culture and dystrophic mdx mice. Mol Ther. 2013;21:210–216. | ||
Liverpool TB, Stapper M. The scaling behaviour of screened polyelectrolytes. Europhys Lett. 1997;40:485–490. | ||
Dobrynin AV, Colby RH, Rubinstein M. Scaling theory of polyelectrolyte solutions. Macromolecules. 1995;28:1859–1871. | ||
Jaeger W, Hahn M, Lieske A, Zimmermann A, Brand F. Polymerization of water soluble cationic vinyl monomers. Macromol Symp. 1996;111:95–106. | ||
Dautzenberg H, Gornitz E, Jaeger W. Synthesis and characterization of poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) in a broad range of molecular weight. Macromol Chem Phys. 1998;199:1561–1571. | ||
Dautzenberg H. Polyelectrolyte complex formation: Role of a double hydrophilic polymer. Macromol Chem Phys. 2000;201:1765–1773. | ||
Cornetta K, Anderson WF. Protamine sulfate as an effective alternative to polybrene in retroviral-mediated gene-transfer: implications for human gene therapy. J Virol Methods. 1989;23:187–194. | ||
Sorgi FL, Bhattacharya S, Huang L. Protamine sulfate enhances lipid-mediated gene transfer. Gene Ther. 1997;4:961–968. | ||
Sazani P, Kang SH, Maier MA, et al. Nuclear antisense effects of neutral, anionic and cationic oligonucleotide analogs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:3965–3974. | ||
Balhorn R. The protamine family of sperm nuclear proteins. Genome Biol. 2007;8:227. | ||
Laufer SD, Restle T. Peptide-mediated cellular delivery of oligonucleotide-based therapeutics in vitro: quantitative evaluation of overall efficacy employing easy to handle reporter systems. Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14:3637–3655. | ||
Maitani Y, Hattori Y. Oligoarginine-PEG-lipid particles for gene delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009;6:1065–1077. | ||
Barron LG, Kathleen B, Meyer B, Francis C, Szoka FC Jr. Effects of complement depletion on the pharmacokinetics and gene delivery mediated by cationic lipid-DNA complexes. Hum Gene Ther. 1998;9:315–323. | ||
Sakurai F, Nishioka T, Saito H, et al. Interaction between DNA-cationic liposome complexes and erythrocytes is an important factor in systemic gene transfer via the intravenous route in mice: the role of the natural helper lipid. Gene Ther. 2001;8:677–686. | ||
Hoshino Y, Nakamoto M, Miura Y. Control of protein-binding kinetics on synthetic polymer nanoparticles by tuning flexibility and inducing conformation changes of polymer chains. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:15209–15212. | ||
Nakamoto M, Hoshino Y, Miura Y. Effect of physical properties of nanogel particles on the kinetic constants of multipoint protein recognition process. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15:541–547. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.