Back to Archived Journals » Current Biomarker Findings » Volume 4
Biomarkers in sarcoidosis: a review
Authors Ahmadzai H, Loke WSJ, Huang S, Herbert C, Wakefield D, Thomas P
Received 23 January 2014
Accepted for publication 14 May 2014
Published 14 August 2014 Volume 2014:4 Pages 93—106
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CBF.S46196
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Hasib Ahmadzai,1,2 Wei Sheng Joshua Loke,1 Shuying Huang,1 Cristan Herbert,1 Denis Wakefield,3 Paul S Thomas2
1Inflammation and Infection Research Centre (IIRC), Faculty of Medicine, University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW, Australia; 2Department of Respiratory Medicine, Prince of Wales Hospital, Randwick, Sydney, NSW, Australia; 3Immunology of the Eye Clinic, St Vincent's Clinic, Darlinghurst, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Abstract: Sarcoidosis is a systemic granulomatous disease of undetermined etiology invariably affecting the lungs and thoracic lymph nodes. It has been termed an “immune paradox”, as there is peripheral anergy despite exaggerated inflammation at disease sites. The disease is usually self-limiting, although some individuals experience unremitting inflammation that may progress into pulmonary fibrosis and death. The inflammatory process is largely a T helper-1-driven immune response. Given its heterogeneous clinical manifestations, diagnosis is usually a clinical conundrum. Clinical and radiological findings alone are often inadequate to confirm the diagnosis. At present, sarcoidosis is usually a diagnosis of exclusion, confirmed by histological evidence of noncaseating granulomas in the absence of known granulomagenic agents. This has compelled researchers to look for disease-specific biomarkers that can help diagnose sarcoidosis and delineate its disease course, severity, and prognosis. In this review we highlight various investigations used to diagnose sarcoidosis, outline proposed biomarkers, and discuss novel methods of sampling biomarkers.
Keywords: sarcoidosis, biomarkers, inflammatory markers, exhaled breath condensate, proteomics, granuloma
Introduction
Sarcoidosis is a systemic granulomatous disease of unidentified etiology, with a heterogeneous clinical presentation and disease course. The majority of patients have lung and intrathoracic lymph node involvement. In most cases sarcoidosis is subacute and self-limiting; however, significant morbidity and death may result from pulmonary fibrosis or cardiac or neurological involvement. Sarcoidosis is usually confirmed by clinical and radiological findings and histopathology revealing noncaseating granulomas in the absence of known granulomagenic agents. Laboratory investigations are helpful in determining a diagnosis and characterizing disease severity.
In this review we discuss laboratory and immunological testing in sarcoidosis, including proposed biomarkers and novel sampling techniques. Immunological testing and measurement of a range of biomarkers in body tissues have helped improve knowledge of the pathophysiology of sarcoidosis. However, most available tests are limited due to a lack of reproducibility, specificity, and sensitivity. Nevertheless, novel laboratory investigations may improve future clinical testing, improving diagnostic sensitivity and identifying potential therapeutic targets.1
Serum chemistry and other initial investigations
Routine clinical and laboratory investigations
The recommended initial clinical tests for a patient with suspected sarcoidosis are outlined in Table 1. Routine blood tests may be helpful in screening for significant specific organ involvement. Peripheral blood lymphocytopenia is common2 as activated T-cells accumulate at disease sites, in addition to the effect of the increased serum anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-10 and increased circulating numbers of regulatory T-cells.1,3 This may contribute to the peripheral anergy seen in patients with sarcoidosis.4–6 Around 10%–20% of patients have elevated serum aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase levels on liver function tests,7,8 although hepatic involvement is clinically silent in the majority of patients.9 A recent study identified that progressive increases in red cell diffusion width may be used as a marker that predicts clinical deterioration in patients with sarcoidosis, with increased red cell diffusion width correlating with worsening radiographic stages of the disease.10
  | Table 1 Recommended initial clinical and laboratory investigations of patients with suspected sarcoidosis |
Renal disease is also infrequent; however, increased serum urea and creatinine concentrations generally reflect renal impairment related to longstanding hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, nephrolithiasis, nephrocalcinosis, or granulomatous interstitial nephritis.11
No clear organ-specific clinical biomarkers are available for suspected isolated ocular, cardiac, or neurosarcoidosis-manifestations associated with significant morbidity and mortality. In these cases, diagnosis usually depends on identifying sarcoid granulomas in other tissues with evidence of disease from radiological and other investigations. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biochemical analysis may be useful in supporting a diagnosis in suspected neurosarcoidosis, particularly with meningeal disease. International consensus criteria have been devised for a diagnosis of isolated ocular sarcoidosis with specific ophthalmological signs described by Herbort et al,12 in addition to ancillary clinical investigations listed in Table 1.
Given that no clear etiological agent has been identified to cause sarcoidosis, other factors, including racial and genetic features, are important and appear to be associated with disease features, including sites of involvement, disease presentation, and clinical course. African-Americans with sarcoidosis are more likely to suffer from more chronic and fatal disease types, as well as erythema nodosum and eye, liver, and bone marrow involvement, compared with Caucasians.8
With the lack of an adequately sensitive and specific diagnostic test, the diagnosis of sarcoidosis is based on important criteria, including compatible clinical and radiological findings, histological evidence of noncaseating granulomas on tissue biopsy, and exclusion of other possible diagnoses.7 Histological examination is an important step in the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Histological characteristics that may point toward sarcoidosis include noncaseating granulomas with a compact core of epithelioid and giant cells, fusion of giant cells to form multinucleated giant cells, and a zone of lymphocytes in the periphery of granulomas. It is important to note that histological evidence of granulomas is alone nondiagnostic, as other granulomatous disease needs to be excluded with other clinical, radiological, and laboratory findings.7 Biopsy samples should be investigated for alternative causes of granulomatous inflammation, including mycobacteria, fungi, parasites, and foreign particles such as beryllium.
Diagnosis of sarcoidosis is supplemented by characteristic radiological findings. The use of chest radiographs, with a radiographic classification of four “stages” has been utilized.7 In stage I there is bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy sometimes accompanied by paratracheal lymphadenopathy, stage II involves bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy with parenchymal infiltrates, stage III parenchymal infiltrates without hilar lymphadenopathy, and stage IV disease pulmonary fibrosis, often with honeycombing, hilar retraction, bullae, and cysts. It is important to note that despite this nomenclature, patients do not progress through these stages in any sequential order, and it is a classification of radiographic appearances. High-resolution computed tomography of the chest has higher sensitivity than chest radiography in diagnosis and evaluation of airways, airspace, and interstitial disease in sarcoidosis. Radiological signs such as the reversed halo sign, sarcoid galaxy sign, and headcheese sign are useful findings on high-resolution computed tomography, which may indicate diffuse interstitial lung disease suggestive of sarcoidosis, although these radiological signs have less usefulness for prognosis.
Other radiological investigations that are now becoming increasingly used in the diagnosis of sarcoidosis, especially cardiac disease, include magnetic resonance imaging and 18-F fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET). 18F-FDG PET scanning has also shown to be valuable in identifying occult sites for diagnostic biopsy in challenging cases where diagnosis is uncertain.14 PET scanning and magnetic resonance imaging have shown to be useful in the diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis, in which most patients have minimal or no symptoms but can present with sudden and life-threatening arrhythmias, and where no diagnostic gold standard exists. It has recently been shown that making the patient fast for a prolonged period prior to 18F-FDG PET is useful in evaluating active cardiac sarcoid lesions and inhibiting physiological myocardial 18F-FDG uptake. This modification in technique appeared to improve the specificity of the PET scan in diagnosing cardiac sarcoidosis.15
Tuberculin skin test and interferon-γ release assays
Despite having an exaggerated T helper-1 (TH1)-mediated immune response at sites of disease, patients with sarcoidosis usually have suppressed peripheral blood responses to common recall antigens,4,16 poor response to vaccinations,6,17 and depressed delayed type hypersensitivity reactions, including cutaneous anergy, to the tuberculin skin test,4 which is a diagnostic criterion for sarcoidosis.18 Tuberculin skin test anergy is less reliable in diagnosis of sarcoidosis compared with interferon (IFN)-γ release assays (IGRAs) in populations that have a significantly high incidence of tuberculosis infection.19,20 IGRAs utilize antigens specific for Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) complex, and thus they have higher sensitivity and specificity for detecting MTB complex infections than conventional tuberculin skin tests.21 The QuantiFERON®-TB Gold (Cellestis International, Melbourne, VIC, Australia) IGRA measures peripheral blood T-cell IFN-γ production, using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), from a patient previously exposed to specific MTB complex antigens, namely culture filtrate protein-10, early secretory antigenic target-6 (ESAT-6), and purified protein derivative (PPD).
A recent study measured IFN-γ release by bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) mononuclear cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) following ex vivo stimulation with whole PPD, ESAT-6, and culture filtrate protein-10. They identified that in patients with sarcoidosis, BAL and PBMC IFN-γ release was similar with controls and less compared with patients with tuberculosis.22
Other investigations have demonstrated, however, that other undegradable MTB antigens (not present in tuberculosis-specific IGRAs) may be pathogenic in sarcoidosis. Investigations using IFN-γ enzyme-linked immunospot and flow cytometry have shown higher PBMC and BAL TH1 responses to recombinant MTB catalase–peroxidase (mKatG)23 and mKatG peptides in patients with sarcoidosis compared with healthy controls, but no difference with PPD+ control subjects. These findings suggest that mKatG profiles a pathogenic antigen in some cases of sarcoidosis.16,24–26 In addition, greater peripheral blood TH1 responses have also been shown in patients with sarcoidosis compared with healthy PPD– controls following PBMC stimulation with mycobacterial heat shock proteins25,27 and MTB-related peptides from ESAT-6,16,25 mycolyl–transferase antigen 85A,25,28 and superoxide dismutase A.25
Calcium and vitamin D
Greater than 40% of patients with sarcoidosis develop hypercalciuria, and hypercalcemia occurs in 5%–10% of patients.29 Hypercalcemia in sarcoidosis is caused by increased serum 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (also known as calcitriol), which raises serum calcium concentrations by increasing intestinal absorption and osteoclastic bone resorption. In normal physiological states, the kidney hydroxylates vitamin D3 to its biologically active form (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3). Sarcoid macrophages also possess a 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1α-hydroxylase enzyme, which hydroxylates vitamin D3 to its active form and which is produced excessively in sarcoid granulomas.11,30 Sarcoid alveolar macrophages have been identified to be the source of excess calcitriol, through elevated 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1α-hydroxylase messenger ribonucleic acid (RNA) expression.31 Hypercalciuria is common in patients with sarcoidosis, due to increased calcium filtered at glomeruli, together with suppression of parathyroid hormone secretion by calcitriol, which reduces renal tubular calcium reabsorption.11 Serum calcium monitoring and 24-hour urinary calcium measurement are thus important in all patients with sarcoidosis.11
Recent evidence suggests also that vitamin D has important immunomodulating effects, including inhibition of antigen presentation by cells of the innate immune system, cytokine release, and proliferation of TH1 cells.32 Polymorphisms of the vitamin D receptor gene have been associated with increased risk of granulomatous disease, including sarcoidosis,33 and have also been shown to be related to bone mineral density and hyperparathyroidism. Although the vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism may affect the serum parathyroid hormone level, it is not itself a risk factor for hypercalcemia in sarcoidosis.34 Hyperparathyroidism and parathyroid adenomas are also sometimes the causative mechanism for hypercalcemia in patients with sarcoidosis.35
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and acute phase reactant C-reactive protein (CRP) have been used as nonspecific inflammatory biomarkers in many disorders. They are simple tests for assessing the degree of systemic inflammation. Very high levels of ESR and CRP have been measured in some patients with sarcoidosis who have active disease.36 ESR is more likely to be elevated in sarcoidosis-associated arthritis37 and erythema nodosum38 than other clinical presentations. High CRP is associated with severe fatigue in sarcoidosis,39 although CRP is generally lower compared with patients with tuberculosis.40
Genetic markers in sarcoidosis
Familial clustering of disease, increased concordance in monozygotic twins, and racial differences in disease incidence suggest that genetic factors play a role in the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis.1 Class I human leukocyte antigen (HLA) susceptibility alleles identified to be consistently associated with sarcoidosis risk include HLA-A*1, HLA-B*7, and HLA-B*8, which exist in most populations with acute sarcoidosis.1
The suspected immunopathogenesis of sarcoidosis is the presentation of insoluble antigen(s), expressed on HLA class II molecules on the surface of antigen-presenting cells, which activates CD4+ lymphocytes and triggers the sarcoid immune response. HLA class II genes are thus likely to play a significant role in sarcoidosis susceptibility.41 Table 2 summarizes important HLA and non-HLA gene associations identified in sarcoidosis.41 Chronic and severe pulmonary sarcoidosis has been consistently associated with the HLA-DRB1*1501/HLA-DQB1*0602 haplotype.1 There is also an increased association between sarcoidosis susceptibility and a BTNL2 gene single nucleotide polymorphism (rs2076530 G→A), independent of HLA class II alleles, which affects T-lymphocyte activation and regulation.42 The BTNL2 gene resides in the major histocompatibility complex class II region of chromosome 6p, a B7 family T-cell-negative costimulatory molecule related to the CD80 and CD86 costimulatory receptors.1,42 A nonfunctional BTNL2 molecule may lead to exaggerated lymphocyte activation, which is a factor in the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis.
  | Table 2 Summary of key human leukocyte antigen (HLA) and non-HLA gene associations identified in sarcoidosis |
T-cells from sites of sarcoid disease activity, including Kveim–Siltzbach skin reactions, show a restricted variable-α region (Vα) and variable-β region of the T-cell receptor (TCR), indicating TCR oligoclonal expansion in response to a limited group of antigens.1,43 BAL T-cells from HLA-DRB1*0301-positive patients with sarcoidosis predominantly express Vα2.3 (AV2S3+), which indicates that these T-cells are reacting to the unknown sarcoid antigen(s) when presented by the HLA-DRB1*0301 molecule.1,5
Recently, Bloom et al44 compared whole blood genome-wide transcriptional response profiles of pulmonary sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, and other similar pulmonary diseases, before and after treatment, and in purified leukocyte populations. They identified that tuberculosis and sarcoidosis had similar blood transcriptional profiles dominated by IFN-inducible transcripts, whereas other pulmonary diseases, such as pneumonia and lung cancer, showed distinct signatures dominated by inflammatory genes. In the future, it would be interesting to see how genetic factors and transcriptional signatures of sarcoidosis could be compared with other diseases, for rapid diagnosis and to determine appropriate patient treatment.
Lymphocyte markers: cytokines and chemokines
Immunopathogenesis of sarcoidosis and key cytokines and chemokines
The “immune paradox” associated with sarcoidosis may be explained by the proliferation of CD25brightFOXP3+ regulatory T-cells.5,45 Local sarcoid inflammation arises when a putative antigenic peptide is presented via major histocompatibility complex class II molecules to CD4+ TH1 lymphocytes. Clonal proliferation of these activated lymphocytes subsequently occurs, which produces increased amounts of IL-2 and IFN-γ.46 Also released are cytokines and chemokines produced by mononuclear phagocytes (including tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α], IL-6, IL-12, IL-18, and monocyte chemotactic protein-1).1,46 These initiate the formation of noncaseating granulomas, which, depending on TH1/TH2 predominance and the local cytokine network, results in either resolution or fibrosis, respectively.
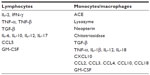
In general terms, TH1 cytokines inhibit fibrosis and promote granulomatous inflammation, whereas TH2 cytokines promote healing or progressive fibrosis.9 TH17 cells have been implicated in autoimmune and granulomatous disease and have recently been investigated in sarcoid immunopathogenesis. An increase in the number of BAL and peripheral blood IL-17A+ and IL-17A+ IFN-γ+ memory T-cells was recently identified in patients with sarcoidosis.47 Gene profiling studies in skin biopsies have also demonstrated increased TH1 and TH17 gene expression together with increased IL-23 and IL-23R expression in patients with sarcoidosis.48 Table 3 summarizes principal chemokines and cytokines involved in sarcoidosis.
Soluble IL-2 receptor
The soluble form of the IL-2 receptor (sIL-2R) is a T-cell IL-2 receptor used in monitoring graft rejection and can be elevated in certain infections and autoimmune diseases.49 Its concentrations are increased in the serum and BAL of patients with sarcoidosis,50,51 decreasing during remission and with therapy initiation.52 Levels are significantly higher in patients with active sarcoidosis, which indicates that sIL-2R may be a useful biomarker of disease activity.51,53 When sIL-2R was compared with serum amyloid A, CRP, and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), only sIL-2R predicted severity of sarcoidosis.37
β2-microglobulin
β2-microglobulin is a marker of lymphocyte activation and is elevated in the serum of ~25% of patients.54,55 Initial investigations in patients with sarcoidosis indicated that levels were elevated at the time of diagnosis, suppressed with corticosteroid therapy, and increased with relapse.56 One study identified that there were patients with acute sarcoidosis and erythema nodosum with elevated β2-microglobulin with normal ACE activity.55 A further study did not identify an association between β2-microglobulin and ACE,57 suggesting that lymphocyte and macrophage activation are not always present together. β2-microglobulin is thus limited, as it reflects only lymphocyte activation, compared with sIL-2R, which indicates both macrophage and lymphocyte activation. Serum β2-microglobulin has a low specificity and sensitivity, which has undermined its utility.
TNF-α
TNF-α plays a pivotal role in the formation and maintenance of sarcoid granulomas.58 It is produced by pulmonary epithelial cells, activated macrophages, and T-cells.59,60 TNF-α levels were also found to be higher in patients with sarcoidosis with active disease than in those with stable disease, suggesting its use as a prognostic marker.61 TNF-α release is strongly associated with the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis, with multiple studies indicating that TNF release is upregulated in BAL cells from patients with active sarcoidosis. However, TNF release appears to be compartmentalized, with increased release in BAL cells but almost no release by peripheral blood cells from the same patient.62 TNF polymorphisms may also play a role in sarcoid disease severity and in patients with erythema nodosum.63 In sarcoidosis there is increased expression of members of the TNF receptor superfamilies and related molecules, including the Fas (CD95)/Fas ligand (FasL) system, which regulate cell survival and death of T-cells. This indicates that dysregulation of T-cell apoptotic mechanisms may explain the absence of apoptosis in the sarcoid granuloma and persistence of inflammation.64 Programmed T-cell death is also inhibited by oncogene products, including the Bcl-2 family of genes, which, like Fas, is also highly expressed by T-lymphocytes surrounding granulomatous lesions in patients with sarcoidosis.64 Additionally, patients with progressive disease have overexpression of nuclear factor-κB (which is induced by TNF-α and IL-1β), as well as a downregulation of inhibitors of apoptosis. Whether apoptosis is dysregulated in chronic sarcoidosis or chronic disease as the result of antigen persistence with ongoing T-cell activation remains to be clarified.62
A recent clinical trial has shown an important immunoregulatory role of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) in sarcoidosis.65 Patients with active sarcoid alveolitis were treated with 4 weeks of nebulized VIP and were subsequently found to have significantly reduced production of TNF-α from BAL fluid mononuclear cells, as well as increased BAL numbers of immunoregulatory CD4+ CD127− CD25+ T-cells. In vitro experiments also showed that VIP was able to convert naive CD4+ CD25− T-cells into CD4+ CD25+ FOXP3+ regulatory T-cells, suggesting generation of peripheral regulatory T-cells by VIP treatment.65
Transforming growth factor-β
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cell signaling molecule that plays an important role in the attenuation of inflammation. It has been implicated in various fibrotic conditions.66 TGF-β induces fibroblast recruitment and transformation to the myofibroblast phenotype. Despite its role in fibrosis, earlier studies of TGF-β in sarcoidosis demonstrated an association between increased TGF-β levels and spontaneous clinical remission, suggesting that TGF-β has anti-inflammatory effects.67 One study showed that TGF-β2 and TGF-β3 genes were altered in sarcoidosis-associated pulmonary fibrosis, suggesting that intrinsic alterations in TGF-β may predispose to sarcoidosis-associated pulmonary fibrosis.68
CXCR3 ligands
CXCL9 is an IFN-γ-induced chemokine and is produced by monocytic cells. Signaling occurs through CXCR3, an inflammatory receptor present on CD4+ and CD8+ cells,69 and promotes T-cell recruitment to inflamed tissues.70 In sarcoidosis, elevated CXCL9 in BAL fluid, as well as transcripts and proteins of CXCL9 being upregulated in lung tissue and associated with disease progression, has been demonstrated.71,72
CXCL10- or IFN-γ-induced protein-10 (IP-10), a chemokine secreted in response to IFN-γ, has been found to be associated with active sarcoidosis. IP-10 levels were inversely correlated with pulmonary function and disease prognosis. The study also indicated that its predictive characteristics were superior to those of ACE.73 Therefore, IP-10 may be a diagnostic marker that could differentiate active from inactive sarcoidosis, but this needs confirmation.
CXCL11 is another chemokine mediated through CXCR3. It is an IFN-inducible T-cell α-chemoattractant. The gene expression and protein levels of CXCL11 were found to be elevated in the serum and BAL fluid of patients with sarcoidosis at radiological stage II,71 suggesting its potential use as a disease marker.
Other chemokines
The aforementioned chemokines mediated by CXCR3 have been associated only with early stages of pulmonary sarcoidosis.74 It is therefore possible that other chemokines may be involved in the transition from early inflammatory to late profibrotic stages. CCL2 and CCL5 have been shown to bestride the transition from type 1 to type 2 immune responses.75
The literature presents conflicting data regarding the association between chemokines and pulmonary sarcoidosis.76–78 Nonetheless, in the largest observational study to date, CCL2 and CCL5 protein levels were elevated in BAL fluid of pulmonary sarcoidosis compared with healthy controls, suggesting their utility as biomarkers. Explorative subgroup analysis demonstrated that CCL2 and CCL5 were elevated in all stages of pulmonary sarcoidosis, demonstrating the continuum of early inflammatory to late fibrotic sarcoidosis.79
CCL15 is a member of the macrophage inflammatory protein-1 family of chemokines.80 CCL15 was elevated in the BAL fluid of patients with sarcoidosis at radiological stage III and was shown in the same study to be associated with 2 year disease outcome,81 suggesting that CCL15 may be a marker of progressive sarcoidosis.
CCL16 is a chemoattractant for lymphocytes and monocytes. Macrophages, in response to CCL16, increase their production of IL-12, IL-1β, CCL2, and TNF-α.82 CCL16 protein expression levels were found to be elevated in patients with sarcoidosis, regardless of clinical phenotype, therefore suggesting its role in amplifying the inflammatory process.81
CCL18 upregulates collagen production by pulmonary fibroblasts, which, in turn, increases macrophage secretion of CCL18, perpetuating a positive feedback loop leading to pulmonary fibrosis.9 Levels of CCL18 have been investigated in the plasma of patients with sarcoidosis and were shown to be secreted in high quantities by sarcoid macrophages.83
Macrophage stimulating protein initiates and regulates immune responses.84 It has been found to be differentially expressed between acute and chronic sarcoidosis81 and has been shown to induce IL-1β and TNF-α production in alveolar macrophages of patients with sarcoidosis.85 The association is particularly pronounced in patients in radiological stage III,81 suggesting that macrophage stimulating protein may propagate the inflammatory process in sarcoidosis.
Immunological markers of sarcoid alveolitis in BAL and induced sputum
Pulmonary sarcoid alveolitis can be diagnosed by BAL fluid analysis with an elevated CD4+/CD8+ cell ratio >3.5:1, in the absence of known causes.1 However, the wide spectrum of this ratio among patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis and the possibility of developing CD8+ alveolitis among patients with sarcoidosis with human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) infections render this ratio less useful as an absolute diagnostic criterion.86 One investigation examined apoptosis in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with sarcoidosis in stimulated and nonstimulated conditions. Stimulation with MTB heat shock proteins induced CD4+ T-cell apoptosis in the peripheral blood of patients with sarcoidosis.87 It was hypothesized that apoptosis was increased in T-lymphocytes from peripheral blood in comparison with BAL fluid lymphocytes.87
Flow cytometric studies using samples from patients with sarcoidosis demonstrated that under unstimulated conditions, BAL CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells were significantly activated compared with peripheral blood lymphocytes.88 Other cellular surface activation markers, such as CD26, CD54, and HLA-DR, are also expressed on BAL lymphocytes of patients with active sarcoidosis.89 As CD4+ HLA-DR+ T-cells release IL-2 spontaneously, some researchers have suggested measurement of the activation state of the IL-2-mediated immune system based on frequencies of CD4+ HLA-DR+ T-cells. These cells are expected to decrease in inactive sarcoidosis, and this information may help to define different phases of the disease.90 It has also been noted that patients with sarcoidosis with the HLA-DRB1*0301 genotype largely express the TCR Vα2.3 (AV2S3+). Increased numbers of AV2S3+ CD4+ BAL T-cells may represent an acute phase of sarcoidosis, indicating clonal proliferation in response to inciting antigen(s).91
Upon stimulation by nonspecific mitogens, there is a dominant TH1 cytokine profile in BAL T-cells from patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis.89 In comparison with peripheral blood CD4+ T-cells, significantly greater BAL CD4+ T-cells express TH1-related receptors such as CXCR3, CCR5, IL-12R, and IL-18R in sarcoidosis, with reduced TH2 chemokine receptors (CXCR4, CCR4).92 Another study also found increased serum levels of TH1 chemokine IP-10 and TH2 chemokine CCL17 in patients with sarcoidosis compared with controls. IP-10 levels were higher in BAL fluid samples of patients with active sarcoidosis compared with controls, but CCL17 levels were not significantly different.93 Elevated numbers of the antiproliferative CD4+CD25bright FOXP3+ Treg (regulatory T) cells have also been found in the BAL fluid and peripheral blood of patients with active sarcoidosis. Our research group has also demonstrated greater proportions of activated CD39+ Treg to CD39− Teff (effector T) cells in patients with sarcoidosis compared with healthy controls (unpublished data). Presumably, these cells do not completely suppress the production of proinflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ and TNF-α at the disease site, and therefore sarcoid granulomas can still develop.5
Dendritic cells have also been identified to have an important role in the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis. Based on their phenotypes, dendritic cells may be divided into plasmacytoid or myeloid cell subtypes. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells are part of the innate immune system, expressing a variety of Toll-like receptors, and have an important role in immunity, secreting large amounts of IFN-α following Toll-like receptor-mediated stimulation. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells do not appear to play a large role in sarcoid immunopathogenesis, with similar numbers in BAL fluid of patients compared with healthy control subjects.62 There is, however, reduced dendritic cell function in sarcoidosis peripheral blood compared with that in healthy control subjects, suggesting that blunted end organ cellular immunity may contribute to sarcoidosis. Phenotypically immature, anergic myeloid dendritic cells are increased in sarcoidosis BAL fluid and cutaneous lesions, whereas mature dendritic cells have been located in disease sites in lymph nodes, which have also been shown to polarize the TH1 T-cells to lymph nodes.94
The less invasive method of induced sputum has detected the presence of elevated numbers of CD4+ IFN-γ+ T-cells, with increased CD4+/CD8+ T-cell ratios, in patients with active pulmonary disease.95 T-cell subsets in induced sputum and BAL fluid were also strongly correlated in patients with sarcoidosis.96
Specific markers of granulomatous inflammation
ACE
ACE is a glycoprotein enzyme normally secreted by monocytes, macrophages, and pulmonary endothelial cells into the bloodstream, and is responsible for the physiological reaction of converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II, which is important for blood pressure control. Elevated serum levels of ACE were found to be increased in approximately 60% of patients.9 ACE is ectopically produced by epithelioid and giant cells in sarcoid granulomas.97 Serum ACE activity can be a serum biomarker of sarcoid granuloma formation, but it has limited sensitivity and specificity through the stages of the disease and in response to corticosteroid treatment.98 Serum ACE activity may also be increased in a variety of other granulomatous and nongranulomatous conditions, and may be affected by ACE inhibitor medications, which also limits its use in the diagnosis of sarcoidosis.1 Furthermore, insertion/deletion (I/D) polymorphisms of the ACE gene and angiotensin II receptor 1 (AT2R1) gene are confounding factors that can affect ACE activity.99 Therefore, evaluation of ACE activity may be improved by genotyping patients for ACE I/D polymorphisms.
Besides serum, ACE activity has also been assessed in BAL fluid, CSF, and urine of patients with sarcoidosis, with elevation in the former two biological fluids.100 According to one study, increased CSF ACE activity levels with values ≥8 nmol/mL/min may be a useful biomarker for patients with suspected neurosarcoidosis.101
Lysozyme
Lysozyme, an enzyme produced by macrophages and epithelioid giant cells in sarcoid granulomas, has been found to be elevated in the serum of patients with active sarcoidosis.102 Serum lysozyme was also positively correlated with serum ACE, but the clinical usage of lysozyme remains limited as it is relatively insensitive and nonspecific being elevated in other conditions.103,104
Neopterin
Neopterin is released by activated macrophages as a metabolite of guanosine triphosphate in response to IFN-γ.104 It has been detected at higher levels in serum and urine of patients with sarcoidosis105 and lower levels with disease resolution.106 Combined elevation of neopterin and sIL-2R is associated with increased likelihood of progressive disease that requires long-term corticosteroid treatment.53
Chitotriosidase
Chitotriosidase is an enzyme responsible for breaking down chitin, a component of fungal cell wall and exoskeleton of certain animals and arthropods.104 It is found to be produced by alveolar macrophages in BAL fluid of patients with sarcoidosis. However, its role in sarcoid pathogenesis remains unknown.107 BAL and serum levels of chitotriosidase in patients with sarcoidosis were significantly higher than those in controls, whereas chitotriosidase levels generally rise with disease progression and decrease with treatment. There is also a correlation between BAL chitotriosidase levels and sarcoidosis radiological stages, serum ACE levels, and pulmonary fibrosis. Thus, it may be a useful biomarker of disease severity and prognostic factor for chronic fibrotic disease.108
Other markers
Serum amyloid A can also be considered as a nonspecific inflammatory marker of sarcoidosis, as it regulates granulomatous inflammation through Toll-like receptor-2.109 It also functions as an acute phase reactant, released together with CRP under systemic stimulation by IL-1 and IL-6.36
Raised endothelin-1 levels have been associated with the degree of lymphocytic alveolitis and number of macrophages in BAL fluid of patients with sarcoidosis.110 This vasoactive, bronchoconstrictive peptide, which has been identified in pulmonary fibroproliferative processes, has also been investigated in other biological fluids such as serum, urine, and lung tissues.111,112
Other potential markers of sarcoidosis include neutrophil-derived collagenase and elastase. The serum of some patients with sarcoidosis has demonstrated higher levels of collagenase, and the combination of raised BAL levels of collagenase and fibronectin has been associated with more severe fibrotic disease.113 Although elevated elastase is found in chronic stage III radiological disease, its role as a disease marker remains limited.114
The Kveim–Siltzbach test and putative antigens
The Kveim–Siltzbach test was used as the diagnostic test for sarcoidosis and was performed by intradermal injection of Kveim reagent, a validated suspension of allogeneic human sarcoid tissue, typically spleen or lymph nodes, homogenized in phosphate-buffered saline.115 This would develop into a papule at the injection site, which was biopsied around 6 weeks later. Histopathological presence of noncaseating epithelioid granulomas indicated sarcoidosis.116 The test was very useful in distinguishing sarcoidosis from other granulomatous diseases.117 However, it is now rarely used, as no commercially available preparation of the reagent exists, and each new Kveim–Siltzbach preparation requires validation in vivo, as well as posing risks of transmitting infections.116 Attempts at developing in vitro Kveim reactions and isolating the antigenic agent in the Kveim reagent have been unsuccessful.118
Based on the hypothesis that pathogenic antigens in sarcoidosis have similar physicochemical properties as Kveim reagent,119 this resulted in an investigation utilizing a limited proteomics approach to identify antigens with these characteristics in sarcoidosis tissue samples.120 Using specialized mass spectroscopy and protein immunoblotting techniques, mycobacterial catalase–peroxidase (KatG) protein was identified in 55% of samples that were also a target of the humoral immune response in a large number of sarcoidosis subjects.120 These results implied that this undegradable mycobacterial protein is a target of the adaptive immune response, causing granulomatous inflammation in at least a subset of sarcoidosis tissues. Subsequent studies also indicated greater PBMC and BAL TH1 responses to MTB-related KatG peptides in sarcoidosis patients compared with healthy subjects.23 In contrast, there was no significant difference when compared with PBMCs from PPD+ control subjects, profiling a pathogenic antigen in some patients with sarcoidosis.24–26
In addition, other recent findings using ELISA have identified high levels of antimycobacterial heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) antibodies in the sera of patients with sarcoidosis.121 This antigen increases expression of costimulatory molecules, suggesting that mycobacterial hsp70 positivity could lead to a reduction in immune tolerance, which may induce autoimmune inflammatory responses.27,122 Other findings that support this have included detection of mycobacterial hsp16, hsp65, and hsp70 in lymph nodes, sera, and circulating immune complexes in the blood of patients with sarcoidosis, using immunostaining.123 The mycobacterial hsp16 has been identified as an important marker of the dormant stage of mycobacteria.124 It has also been identified that PBMCs from patients with sarcoidosis and tuberculosis were similarly activated by in vitro exposure to recombinant mycobacterial heat shock proteins compared with PBMCs from healthy control subjects.125
We also recently demonstrated that following stimulation with pooled peptides from MTB-related ESAT-6 and KatG, there was an induction of greater numbers of IFN-γ-producing T-cells, together with increased IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α, in subjects with sarcoidosis compared with PPD negative healthy controls.16 Given that these antigens do not induce immune responses in all patients, novel techniques are needed to determine other pathogenic antigens.
The use of proteomics for identification of protein biomarkers
Proteomics provides the opportunity to simultaneously investigate alterations in the expression of proteins and their corresponding pathways. A variety of different proteomic techniques have been used for identifying BAL fluid and serum protein patterns in sarcoidosis. Two-dimensional electrophoresis and mass spectrometry have identified 85 proteins in BAL fluid, with 38 newly identified and possibly relevant proteins in BAL from patients with sarcoidosis.126 Proteins that were found were locally secreted and plasma-derived proteins and proteolytic or cell damage products with proinflammatory, anti-inflammatory, and antiprotease activity.127 Another more recent study investigated the soluble proteome of alveolar macrophages. They identified 69 protein species that were significantly altered in patients with sarcoidosis compared with healthy controls. These were associated with the clathrin-mediated endocytosis pathway and Fcγ-mediated phagocytosis pathway, possibly providing insights into the role of macrophage phagocytosis in sarcoid immunopathogenesis.128 A recent investigation has also interestingly identified aberrant expression of receptors for the Fc fragment of immunoglobulin G (FcγR) and complement receptors (CRs) on peripheral blood monocytes from patients with sarcoidosis.129 This study identified increased expression of the receptors FcγRI (CD64), FcγRII (CD32), and FcγRIII (CD16), with decreased expression of CR1 (CD35) and CR4 (CD11c) on peripheral blood CD14+ monocytes in patients with sarcoidosis compared with controls. The authors concluded that this may be responsible for altered phagocytic activity in sarcoidosis, leading to high or persistent antigen load and increased circulating immune complexes in sarcoidosis.129
Another technique employing a narrow range of pH gradients found new groups of serum and BAL proteins, most of which have a role in oxidative stress and inflammatory responses.130,131 Gel electrophoresis proteomics was also incorporated in another similar study to analyze BAL from patients genetically predisposed to chronic sarcoidosis (with the HLA-DRB1*15 genotype).132 Silva et al found aberrant protein patterns in patients compared with healthy controls and those with chronic beryllium disease.132 Healthy controls and patients with sarcoidosis had increased hsp70, peroxiredoxin 5, annexin A2, complement C3, and transthyretin compared with controls.132 Surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry is a new technique that has identified different disease-related proteins and protein patterns in serum.133 In BAL fluid of patients with sarcoidosis, proteins that are related to clinical course, including protocadherin-2 precursor, α1-antitrypsin, and albumin, were identified.134 Proteomic analysis has provided useful data identifying potential protein biomarkers in sarcoidosis that differ from those with other interstitial lung diseases. Large scale studies are required to validate their clinical utility.
Exhaled breath analysis
Lymphocyte and macrophage biomarkers
Pulmonary disease is one of the most common organ manifestations in sarcoidosis. Biomarkers sampled from the respiratory tract can thus provide direct insights into disease immunopathogenesis.1 Initial studies found greater exhaled nitric oxide levels in patients with sarcoidosis compared with healthy controls, which significantly decreased following corticosteroid treatment.135 Exhaled nitric oxide may reflect disease activity and is associated with amplified TH1 immune responses, resulting from induced nitric oxide synthase upregulation by TNF-α and IFN-γ.135 A recent investigation also showed elevated concentrations of nitrite/nitrate in the serum of patients with sarcoidosis compared with healthy control subjects. Lower levels of serum nitric oxide were shown to induce production of bacterial hsp16, a marker of the dormant stage of bacteria (eg, in mycobacteria and propionibacteria).124 In contrast, a recent study investigating exhaled nitric oxide measurement in patients with sarcoidosis, healthy controls, and patients treated with corticosteroids found that exhaled nitric oxide was not a clinically useful test for monitoring disease progression.136 Another study found significantly elevated exhaled carbon monoxide (reflecting increased oxidative stress) in patients with sarcoidosis compared with healthy controls.137 The prognostic usefulness of this measurement, however, remains undetermined.
Exhaled breath condensate (EBC) collection is a noninvasive, simple technique for sampling airway lining fluids and investigating exhaled biomarkers in respiratory disease.138 Although total protein concentrations are greater in BAL than EBC,139 biomarkers have been found in the EBC of patients with sarcoidosis. Inflammatory markers such as insulin-like growth factor-1, TNF-α, sTNF-RII, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, M-CSF (macrophage colony stimulating factor), and RANTES have been demonstrated to be correlated in BAL and EBC samples of patients with sarcoidosis.140,141 TGF-β1, vascular endothelial growth factor, and IL-8 have also been found in the EBC of patients with sarcoidosis.142 Our group found the markers of granulomatous inflammation, TGF-β1, and neopterin at increased levels in the EBC of patients with sarcoidosis compared with healthy control subjects,143 which may serve as airway biomarkers of disease activity.
Other studies have found elevated levels of exhaled eicosanoids, including cysteinyl leukotrienes and 8-isoprostane, in the BAL fluid and EBC of patients with sarcoidosis.144 There was a correlation between the levels of leukotriene B4 and 8-isoprostane in BAL fluid and EBC of patients with sarcoidosis.145 Compared with healthy subjects, EBC 8-isoprostane concentrations are elevated in active sarcoidosis, which may indicate disease severity or activity.146 Other biomarkers of oxidative stress, such as increased hydrogen peroxide and end products of lipid peroxidation, have also been shown to be raised in EBC and BAL of patients with sarcoidosis.147 Further research is needed to verify the utility of reactive oxygen species, growth factors, and products of oxidative stress in EBC.
microRNA
DNA polymorphisms have been implicated in the immune reactions in sarcoidosis148 and have been associated with various disease phenotypes.149 However, it cannot entirely explain phenotypic variability. Hence, there is a burgeoning interest in the role of small, noncoding RNAs, also known as microRNA (miRNAs), which have been known to repress gene translation.150 One study has recently shown an association between aberrant miRNA expression and the fibrotic progression in sarcoidosis.151
Members of the miRNA-29 (miR-29) family have been known to regulate the infectivity of HIV-1 virus.152 The downregulation and inhibition of miR-29a facilitate IFN-γ expression in T-cells.153 Our research group has demonstrated lower miR-29a and higher IFN-γ levels in EBC of patients with sarcoidosis compared with EBC of healthy controls. Moreover, we found no significant differences in miR-29a and IFN-γ expression levels in the PBMCs of both groups. This has led us to suggest that miR-29a is lowered in the presence of inflammation. miR-29a may have a role in modulating the TH1 profile within PBMCs and may also serve as an EBC marker of sarcoidosis (unpublished data).
Conclusion
Recent investigations have improved our understanding of sarcoid immunopathogenesis and disease biomarkers. New immunological techniques of identifying peripheral blood T-cell activation could further identify sarcoid antigenic peptides. Initial proteomic findings from serum and BAL need to be verified with large-scale studies to differentiate between sarcoidosis clinical phenotypes and to identify patients at risk of complications from chronic disease and pulmonary fibrosis. EBC analysis similarly needs to be improved for it to be used in clinical practice. Novel biomarker studies may help to pave the way to further improve our understanding of this enigmatic disease, including use of gene expression and multiplex protein analysis technology. Despite many potential biomarkers being identified for monitoring and diagnosis, there is still a lack of adequately specific and sensitive disease markers for clinical usage, necessitating further research on these fronts.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Ahmadzai H, Wakefield D, Thomas PS. The potential of the immunological markers of sarcoidosis in exhaled breath and peripheral blood as future diagnostic and monitoring techniques. Inflammopharmacology. 2011;19(2):55–68. | |
Gerke AK, Hunninghake G. The immunology of sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med. 2008;29(3):379–390. | |
Hunninghake GW, Fulmer JD, Young RC Jr, Gadek JE, Crystal RG. Localization of the immune response in sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979;120(1):49–57. | |
Mathew S, Bauer KL, Fischoeder A, Bhardwaj N, Oliver SJ. The anergic state in sarcoidosis is associated with diminished dendritic cell function. J Immunol. 2008;181:746–755. | |
Grunewald J, Eklund A. Role of CD4+ T cells in sarcoidosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2007;4(5):461–464. | |
Mert A, Bilir M, Ozaras R, Tabak F, Karayel T, Senturk H. Results of hepatitis B vaccination in sarcoidosis. Respiration. 2000;67(5):543–545. | |
Statement on Sarcoidosis. Joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the World Association of Sarcoidosis and other Granulomatous Disorders (WASOG), adapted by the ATS Board of Directors and by the ERS Executive Committee. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160(2):736–755. | |
Baughman RP, Teirstein AS, Judson MA, et al. Clinical characteristics of patients in a case control study of sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164(10 Pt 1):1885–1889. | |
Iannuzzi MC, Rybicki BA, Teirstein AS. Sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(21):2153–2165. | |
Ozsu S, Ozcelik N, Oztuna F, Ozlu T. Prognostic value of red cell distribution width in patients with sarcoidosis. Clin Respir J. Epub January 9, 2014. | |
Berliner AR, Haas M, Choi MJ. Sarcoidosis: the nephrologist’s perspective. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;48(5):856–870. | |
Herbort CP, Rao NA, Mochizuki M; members of the Scientific Committee of First International Workshop on Ocular Sarcoidosis. International criteria for the diagnosis of ocular sarcoidosis: results of the first International Workshop on Ocular Sarcoidosis (IWOS). Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2009;17(3):160–169. | |
Hunninghake GW, Costabel U, Ando M, et al. ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society/World Association of Sarcoidosis and other Granulomatous Disorders. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1999;16(2):149–173. | |
Teirstein AS, Machac J, Almeida O, Lu P, Padilla ML, Iannuzzi MC. Results of 188 whole-body fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography scans in 137 patients with sarcoidosis. Chest. 2007;132(6):1949–1953. | |
Morooka M, Moroi M, Uno K, et al. Long fasting is effective in inhibiting physiological myocardial 18F-FDG uptake and for evaluating active lesions of cardiac sarcoidosis. EJNMMI Res. 2014;4(1):1. | |
Ahmadzai H, Cameron B, Chui JJ, Lloyd A, Wakefield D, Thomas PS. Peripheral blood responses to specific antigens and CD28 in sarcoidosis. Respir Med. 2012;106(5):701–709. | |
Seyhan EC, Günlüoglu G, Altin S, et al. Results of tetanus vaccination in sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2012;29(1):3–10. | |
Gupta D, Chetty M, Kumar N, Aggarwal AN, Jindal SK. Anergy to tuberculin in sarcoidosis is not influenced by high prevalence of tuberculin sensitivity in the population. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2003;20(1):40–45. | |
Amicosante M. IGRAs for tuberculosis in sarcoidosis patients: is the immune response to mycobacteria helpful in the differential diagnosis or still a confounding factor? Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2011;28(2):85–86. | |
Gupta D, Kumar S, Aggarwal AN, Verma I, Agarwal R. Interferon gamma release assay (QuantiFERON-TB Gold In Tube) in patients of sarcoidosis from a population with high prevalence of tuberculosis infection. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2011;28(2):95–101. | |
Luetkemeyer AF, Charlebois ED, Flores LL, et al. Comparison of an interferon-gamma release assay with tuberculin skin testing in HIV-infected individuals. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175(7):737–742. | |
Hörster R, Kirsten D, Gaede KI, et al. Antimycobacterial immune responses in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Clin Respir J. 2009;3(4):229–238. | |
Chen ES, Wahlström J, Song Z, et al. T cell responses to mycobacterial catalase-peroxidase profile a pathogenic antigen in systemic sarcoidosis. J Immunol. 2008;181(12):8784–8796. | |
Oswald-Richter K, Culver DA, Hawkins C, et al. Cellular responses to mycobacterial antigens are present in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid used in the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Infect Immun. 2009;77(9):3740–3748. | |
Oswald-Richter K, Beachboard DC, Zhan X, et al. Multiple mycobacterial antigens are targets of the adaptive immune response in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Respir Res. 2010;11:161. | |
Drake WP, Dhason MS, Nadaf M, et al. Cellular recognition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ESAT-6 and KatG peptides in systemic sarcoidosis. Infect Immun. 2007;75(1):527–530. | |
Dubaniewicz A. Mycobacterium tuberculosis heat shock proteins and autoimmunity in sarcoidosis. Autoimmun Rev. 2010;9(6):419–424. | |
Hajizadeh R, Sato H, Carlisle J, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 85A induces Th-1 immune responses in systemic sarcoidosis. J Clin Immunol. 2007;27(4):445–454. | |
Iannuzzi MC. Advances in the genetics of sarcoidosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2007;4:457–460. | |
Reichel H, Koeffler HP, Barbers R, Norman AW. Regulation of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 production by cultured alveolar macrophages from normal human donors and from patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987;65(6):1201–1209. | |
Inui N, Murayama A, Sasaki S, et al. Correlation between 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1 alpha-hydroxylase gene expression in alveolar macrophages and the activity of sarcoidosis. Am J Med. 2001;110(9):687–693. | |
Burke RR, Rybicki BA, Rao DS. Calcium and vitamin D in sarcoidosis: how to assess and manage. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;31(4):474–484. | |
Niimi T, Tomita H, Sato S, et al. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism in patients with sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160(4):1107–1109. | |
Niimi T, Tomita H, Sato S, et al. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism and calcium metabolism in sarcoidosis patients. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2000;17(3):266–269. | |
Baughman RP, Janovcik J, Ray M, Sweiss N, Lower EE. Calcium and vitamin D metabolism in sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2013;30(2):113–120. | |
Rothkrantz-Kos S, van Dieijen-Visser MP, Mulder PG, Drent M. Potential usefulness of inflammatory markers to monitor respiratory functional impairment in sarcoidosis. Clin Chem. 2003;49(9):1510–1517. | |
Shorr AF, Murphy FT, Gilliland WR, Hnatiuk W. Osseous disease in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis and musculoskeletal symptoms. Respir Med. 2000;94(3):228–232. | |
Greenberg G, James DG, Feizi T, Bird R. Serum-proteins in sarcoidosis. Lancet. 1964;2(7373):1313–1315. | |
Drent M, Wirnsberger RM, de Vries J, van Dieijen-Visser MP, Wouters EF, Schols AM. Association of fatigue with an acute phase response in sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 1999;13(4):718–722. | |
Hind CR, Flint KC, Hudspith BN, Felmingham D, Brostoff J, Johnson NM. Serum C-reactive protein concentrations in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Thorax. 1987;42(5):332–335. | |
Spagnolo P, Grunewald J. Recent advances in the genetics of sarcoidosis. J Med Genet. 2013;50(5):290–297. | |
Rybicki BA, Walewski JL, Maliarik MJ, Kian H, Iannuzzi MC. The BTNL2 gene and sarcoidosis susceptibility in African Americans and whites. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;77(3):491–499. | |
Klein JT, Horn TD, Forman JD, Silver RF, Teirstein AS, Moller DR. Selection of oligoclonal Vβ-specific T cells in the intradermal response to Kveim-Siltzbach reagent in individuals with sarcoidosis. J Immunol. 1995;154:1450–1460. | |
Bloom CI, Graham CM, Berry MP, et al. Transcriptional blood signatures distinguish pulmonary tuberculosis, pulmonary sarcoidosis, pneumonias and lung cancers. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e70630. | |
Miyara M, Amoura Z, Parizot C, et al. The immune paradox of sarcoidosis and regulatory T cells. J Exp Med. 2006;203(2):359–370. | |
Ziegenhagen MW, Muller-Quernheim J. The cytokine network in sarcoidosis and its clinical relevance. J Intern Med. 2003;253:18–30. | |
Ten Berge B, Paats MS, Bergen IM, et al. Increased IL-17A expression in granulomas and in circulating memory T cells in sarcoidosis. Rheumatology. 2012;51(1):37–46. | |
Judson MA, Marchell RM, Mascelli M, et al. Molecular profiling and gene expression analysis in cutaneous sarcoidosis: the role of interleukin-12, interleukin-23, and the T-helper 17 pathway. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66(6):901–910. | |
Olejniczak K, Kasprzak A. Biological properties of interleukin 2 and its role in pathogenesis of selected diseases: a review. Med Sci Monit. 2008;14(10):RA179–RA189. | |
Ziegenhagen MW, Rothe ME, Schlaak M, Müller-Quernheim J. Bronchoalveolar and serological parameters reflecting the severity of sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 2003;21(3):407–413. | |
Grutters JC, Fellrath JM, Mulder L, Janssen R, van den Bosch JM, van Velzen-Blad H. Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor measurement in patients with sarcoidosis: a clinical evaluation. Chest. 2003;124(1):186–195. | |
Keicho N, Kitamura K, Takaku F, Yotsumoto H. Serum concentration of soluble interleukin-2 receptor as a sensitive parameter of disease activity in sarcoidosis. Chest. 1990;98(5):1125–1129. | |
Prasse A, Katic C, Germann M, Buchwald A, Zissel G, Müller-Quernheim J. Phenotyping sarcoidosis from a pulmonary perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177(3):330–336. | |
Bargagli E, Mazzi A, Rottoli P. Markers of inflammation in sarcoidosis: blood, urine, BAL, sputum, and exhaled gas. Clin Chest Med. 2008;29(3):445–458. | |
Selroos O, Klockars M. Relation between clinical stage of sarcoidosis and serum values of angiotensin converting enzyme and beta2- microglobulin. Sarcoidosis. 1987;4(1):13–17. | |
Mornex JF, Revillard JP, Vincent C, Deteix P, Brune J. Elevated serum beta 2-microglobulin levels and C1q-binding immune complexes in sarcoidosis. Biomedicine. 1979;31(7):210–213. | |
Parrish RW, Williams JD, Davies BH. Serum beta-2-microglobulin and angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in sarcoidosis. Thorax. 1982;37(12):936–940. | |
Baughman RP, Lower, EE. Fungal infections as a complication of therapy for sarcoidosis. QJM. 2005;98(6):451–456. | |
Fehrenbach H, Zissel G, Goldmann T, et al. Alveolar macrophages are the main source for tumour necrosis factor-α in patients with sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 2003;21(3):421–428. | |
Müller-Quernheim J. Sarcoidosis: Immunopathogenetic concepts and their clinical application. Eur Respir J. 1998;12(3):716–738. | |
Ziegenhagen MW, Benner UK, Zissel G, Zabel P, Schlaak M, Müller-Quernheim J. Sarcoidosis: TNF-alpha release from alveolar macrophages and serum level of sIL-2R are prognostic markers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156(5):1586–1592. | |
Zissel G, Prasse A, Müller-Quernheim J. Immunologic response of sarcoidosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;31(4):390–403. | |
Medica I, Kastrin A, Maver A, Peterlin B. Role of genetic polymorphisms in ACE and TNF-α gene in sarcoidosis: a meta analysis. J Hum Genet. 2007;52(10):836–847. | |
Semenzato G, Bortoli M, Brunetta E, Agostini C. Chapter 4. Immunology and pathophysiology. Eur Respir Mon. 2005;32:49–63. | |
Prasse A, Zissel G, Lützen N, et al. Inhaled vasoactive intestinal peptide exerts immunoregulatory effects in sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182(4):540–548. | |
Goodwin A, Jenkins, G. Role of integrin-mediated TGFβ activation in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009;37(4):849–854. | |
Zissel G, Homolka J, Schlaak J, Schlaak M, Müller-Quernheim J. Anti-inflammatory cytokine release by alveolar macrophages in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;154(3 Pt 1):713–719. | |
Kruit A, Grutters JC, Ruven HJ, et al. Transforming growth factor-β gene polymorphisms in sarcoidosis patients with and without fibrosis. Chest. 2006;129(6):1584–1591. | |
Groom JR, Luster AD. CXCR3 ligands: redundant, collaborative and antagonistic functions. Immunol Cell Biol. 2011;89(2):207–215. | |
Loetscher M, Loetscher P, Brass N, Meese E, Moser B. Lymphocyte-specific chemokine receptor CXCR3: regulation, chemokine binding and gene localization. Eur J Immunol. 1998;28(11):3696–3705. | |
Nishioka Y, Manabe K, Kishi J, et al. CXCL9 and 11 in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis: a role of alveolar macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;149(2):317–326. | |
Su R, Nguyen ML, Agarwal MR, et al. Interferon-inducible chemokines reflect severity and progression in sarcoidosis. Respir Res. 2013;14(1):121. | |
Geyer AI, Kraus T, Roberts M, et al. Plasma level of interferon γ induced protein 10 is a marker of sarcoidosis disease activity. Cytokine. 2013;64(1):152–157. | |
Busuttil A, Weigt SS, Keane MP, et al. CXCR3 ligands are augmented during the pathogenesis of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 2009;34(3):676–686. | |
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Vecchi A, Locati M. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004;25(12):677–686. | |
Iida K, Kadota J, Kawakami K, Matsubara Y, Shirai R, Kohno S. Analysis of T cell subsets and β chemokines in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Thorax. 1997;52(5):431–437. | |
Oshima M, Maeda A, Ishioka S, Hiyama K, Yamakido M. Expression of C-C chemokines in bronchoalveolar lavage cells from patients with granulomatous lung diseases. Lung. 1999;177(4):229–240. | |
Petrek M, Kolek V, Szotkowská J, du Bois RM. CC and C chemokine expression in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 2002;20(5):1206–1212. | |
Palchevskiy V, Hashemi N, Weigt SS, et al. Immune response CC chemokines CCL2 and CCL5 are associated with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2011;4:10. | |
Pardigol A, Forssmann U, Zucht HD, et al. HCC–2, a human chemokine: gene structure, expression pattern, and biological activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(11):6308–6313. | |
Arakelyan A, Kriegova E, Kubistova Z, et al. Protein levels of CC chemokine ligand (CCL)15, CCL16 and macrophage stimulating protein in patients with sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009;155(3):457–465. | |
Cappello P, Caorsi C, Bosticardo M, et al. CCL16/LEC powerfully triggers effector and antigen-presenting functions of macrophages and enhances T cell cytotoxicity. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;75(1):135–142. | |
Boot RG, Hollak CE, Verhoek M, Alberts C, Jonkers RE, Aerts JM. Plasma chitotriosidase and CCL18 as surrogate markers for granulomatous macrophages in sarcoidosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2010;411(1–2):31–36. | |
Wang MH, Zhou YQ, Chen YQ. Macrophage-stimulating protein and RON receptor tyrosine kinase: potential regulators of macrophage inflammatory activities. Scand J Immunol. 2002;56(6):545–553. | |
Gunella G, Bardelli C, Amoruso A, Viano I, Balbo P, Brunelleschi S. Macrophage-stimulating protein differently affects human alveolar macrophages from smoker and non-smoker patients: evaluation of respiratory burst, cytokine release and NF-κB pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;148(4):478–489. | |
Agostini C, Trentin L, Zambello R, et al. CD8 alveolitis in sarcoidosis: incidence, phenotypic characteristics, and clinical features. Am J Med. 1993;95(5):466–472. | |
Dubaniewicz A, Trzonkowski P, Dubaniewicz-Wybieralska M, Dubaniewicz A, Singh M, Mysliwski A. Comparative analysis of mycobacterial heat shock proteins-induced apoptosis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in sarcoidosis and tuberculosis. J Clin Immunol. 2006;26(3):243–250. | |
Wahlström J, Berlin M, Sköld CM, Wigzell H, Eklund A, Grunewald J. Phenotypic analysis of lymphocytes and monocytes/macrophages in peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Thorax. 1999;54:339–346. | |
Hill TA, Lightman S, Pantelidis P, Abdallah A, Spagnolo P, du Bois RM. Intracellular cytokine profiles and T cell activation in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Cytokine. 2008;42:289–292. | |
Saltini C, Spurzem JR, Lee JJ, Pinkston P, Crystal RG. Spontaneous release of interleukin 2 by lung T lymphocytes in active pulmonary sarcoidosis is primarily from the Leu3+DR+ T cell subset. J Clin Invest. 1986;77(6):1962–1970. | |
Wahlström J, Dengjel J, Persson B, et al. Identification of HLA- DR-bound peptides presented by human bronchoalveolar lavage cells in sarcoidosis. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(11):3576–3582. | |
Katchar K, Eklund A, Grunewald J. Expression of Th1 markers by lung accumulated T cells in pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Intern Med. 2003;254:564–571. | |
Nureki S, Miyazaki E, Ando M, et al. Circulating levels of both Th1 and Th2 chemokines are elevated in patients with sarcoidosis. Respir Med. 2008;102:239–247. | |
Zaba LC, Smith GP, Sanchez M, Prystowsky SD, Dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2010;42(1):32–39. | |
Tsiligianni I, Antoniou KM, Kyriakou D, et al. Th1/Th2 cytokine pattern in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and induced sputum in pulmonary sarcoidosis. BMC Pulm Med. 2005;5:8–13. | |
Sobiecka M, Kus J, Demkow U, et al. Induced sputum in patients with interstitial lung disease: a non-invasive surrogate for certain parameters in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008; 59(Suppl 6):645–657. | |
Pertschuk LP, Silverstein E, Friedland J. Immunohistologic diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Detection of angiotensin-converting enzyme in sarcoid granulomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981;75(3):350–354. | |
Brice EA, Friedlander W, Bateman ED, Kirsch RE. Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity, concentration, and specific activity in granulomatous interstitial lung disease, tuberculosis, and COPD. Chest. 1995;107(3):706–710. | |
Biller H, Ruprecht B, Gaede KI, Müller-Quernheim J, Zissel G. Gene polymorphisms of ACE and the angiotensin receptor AT2R1 influence serum ACE levels in sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2009;26(2):139–146. | |
Allen RK, Pierce RJ, Barter CE. Angiotensin-converting enzyme in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis. 1992;9(1):54–59. | |
Tahmoush AJ, Amir MS, Connor WW, et al. CSF-ACE activity in probable CNS neurosarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2002;19(3):191–197. | |
Miyoshi S, Hamada H, Kadowaki T, et al. Comparative evaluation of serum markers in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest. 2010;137(6):1391–1397. | |
Prior C, Barbee RA, Evans PM, et al. Lavage versus serum measurements of lysozyme, angiotensin converting enzyme and other inflammatory markers in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 1990;3(10):1146–1154. | |
Bargagli E, Maggiorelli C, Rottoli P. Human chitotriosidase: a potential new marker of sarcoidosis severity. Respiration. 2008;76(2):234–238. | |
Eklund A, Blaschke E. Elevated serum neopterin levels in sarcoidosis. Lung. 1986;164(6):325–332. | |
Planck A, Eklund A, Grunewald J. Markers of activity in clinically recovered human leukocyte antigen-DR17-positive sarcoidosis patients. Eur Respir J. 2003;21(1):52–57. | |
Boot RG, Hollak CE, Verhoek M, Alberts C, Jonkers RE, Aerts JM. Plasma chitotriosidase and CCL18 as surrogate markers for granulomatous macrophages in sarcoidosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2010;411(1–2):31–36. | |
Bargagli E, Margollicci M, Perrone A, et al. Chitotriosidase analysis in bronchoalveolar lavage of patients with sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2007;24(1):59–64. | |
Chen ES, Song Z, Willett MH, et al. Serum amyloid A regulates granulomatous inflammation in sarcoidosis through Toll-like receptor-2. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181:360–373. | |
Terashita K, Kato S, Sata M, Inoue S, Nakamura H, Tomoike H. Increased endothelin-1 levels of BAL fluid in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Respirology. 2006;11(2):145–151. | |
Sofia M, Mormile M, Faraone S, Alifano M, Carratù P, Carratù L. Endothelin-1 excretion in urine in active pulmonary sarcoidosis and in other interstitial lung diseases. Sarcoidosis. 1995;12(2):118–123. | |
Letizia C, Danese A, Reale MG, et al. Plasma levels of endothelin-1 increase in patients with sarcoidosis and fall after disease remission. Panminerva Med. 2001;43(4):257–261. | |
O’Connor C, Odlum C, Van Breda A, Power C, Fitzgerald MX. Collagenase and fibronectin in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in patients with sarcoidosis. Thorax. 1988;43(5):393–400. | |
Peros-Golubicic T, Ivicevic A, Bekic A, Alilovic M, Tekavec-Trkanjec J, Smojver-Jezek S. Lung lavage neutrophils, neutrophil elastase and albumin in the prognosis of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Coll Antropol. 2001;25(1):349–355. | |
Teirstein AS. The Kveim-Siltzbach test. Clin Dermatol. 1986;4(4):154–164. | |
Parrish S, Turner JF. Diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Dis Mon. 2009;55(11):693–703. | |
Mishra BB, Poulter LW, Janossy G, Sherlock S, James DG. The Kveim-Siltzbach granuloma. A model for sarcoid granuloma formation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;465:164–175. | |
Ahmadzai H, Thomas PS, Wakefield D. Chapter 9. Laboratory investigations and immunological testing in sarcoidosis. In: Eishi Y, editor. Sarcoidosis. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech Open Access Publishing; 2013:201–237. | |
Lyons DJ, Donald S, Mitchell DN, Asherson GL. Chemical inactivation of the Kveim reagent. Respiration. 1992;59:22–26. | |
Song Z, Marzilli L, Greenlee BM, et al. Mycobacterial catalase–peroxidase is a tissue antigen and target of the adaptive immune response in systemic sarcoidosis. J Exp Med. 2005;201(5):755–767. | |
Dubaniewicz A, Kämpfer S, Singh M. Serum anti-mycobacterial heat shock proteins antibodies in sarcoidosis and tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2006;86(1):60–67. | |
Detanico T, Rodrigues L, Sabritto AC. Mycobacterial heat shock protein 70 induces interleukin-10 production: immunomodulation of synovial cell cytokine profile and dendritic cell maturation. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004;135(2):336–342. | |
Dubaniewicz A, Dubaniewicz-Wybieralska M, Sternau A. Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and mycobacterial heat shock proteins in lymph node tissue from patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44(9):3448–3451. | |
Dubaniewicz A, Holownia A, Kalinowski L, Wybieralska M, Dobrucki IT, Singh M. Is mycobacterial heat shock protein 16 kDa, a marker of the dormant stage of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a sarcoid antigen? Hum Immunol. 2013;74(1):45–51. | |
Dubaniewicz A, Trzonkowski P, Dubaniewicz-Wybieralska M, Dubaniewicz A, Singh M, Mysliwski A. Mycobacterial heat shock protein-induced blood T lymphocytes subsets and cytokine pattern: comparison of sarcoidosis with tuberculosis and healthy controls. Respirology. 2007;12(3):346–354. | |
Magi B, Bini L, Perari MG, et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid protein composition in patients with sarcoidosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a two-dimensional electrophoretic study. Electrophoresis. 2002;23(19):3434–3444. | |
Rottoli P, Magi B, Perari MG, et al. Cytokine profile and proteome analysis in bronchoalveolar lavage of patients with sarcoidosis, pulmonary fibrosis associated with systemic sclerosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proteomics. 2005;5:1423–1430. | |
Silva E, Souchelnytskyi S, Kasuga K, Eklund A, Grunewald J, Wheelock ÅM. Quantitative intact proteomics investigations of alveolar macrophages in sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(6):1331–1339. | |
Dubaniewicz A, Typiak M, Wybieralska M, et al. Changed phagocytic activity and pattern of Fcγ and complement receptors on blood monocytes in sarcoidosis. Hum Immunol. 2012;73(8):788–794. | |
Sabounchi-Schütt F, Aström J, Hellman U, Eklund A, Grunewald J. Changes in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid proteins in sarcoidosis: a proteomics approach. Eur Respir J. 2003;21(3):414–420. | |
Sabounchi-Schütt F, Mikko M, Eklund A, Grunewald J, Aström J. Serum protein pattern in sarcoidosis analysed by a proteomics approach. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2004;21(3):182–190. | |
Silva E, Bourin S, Sabounchi-Schütt F, et al. A quantitative proteomic analysis of soluble bronchoalveolar fluid proteins from patients with sarcoidosis and chronic beryllium disease. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2007;24(1):24–32. | |
Bons JA, Drent M, Bouwman FG, Mariman EC, van Dieijen-Visser MP, Wodzig WK. Potential biomarkers for diagnosis of sarcoidosis using proteomics in serum. Respir Med. 2007;101(8):1687–1695. | |
Kriegova E, Melle C, Kolek V, et al. Protein profiles of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173(10):1145–1154. | |
Moodley YP, Chetty R, Lalloo UG. Nitric oxide levels in exhaled air and inducible nitric oxide synthase immunolocalization in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 1999;14(4):822–827. | |
Choi J, Hoffman LA, Sethi JM, Zullo TG, Gibson KF. Multiple flow rates measurement of exhaled nitric oxide in patients with sarcoidosis: a pilot feasibility study. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2009;26(2):98–109. | |
Ciarleglio G, Refini RM, Pieroni MG, et al. Exhaled carbon monoxide in sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2008;25(1):46–50. | |
Ahmadzai H, Huang S, Hettiarachchi R, Lin JL, Thomas PS, Zhang Q. Exhaled breath condensate: a comprehensive update. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013;51(7):1343–1361. | |
Jackson AS, Sandrini A, Campbell C, Chow S, Thomas PS, Yates DH. Comparison of biomarkers in exhaled breath condensate and bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:222–227. | |
Rozyi A, Czerniawska J, Stepniewska A, et al. Inflammatory markers in the exhaled breath condensate of patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006;57(Suppl 4):335–340. | |
Nakamura K, Mikuniya M, Takanashi S, et al. Is analysis of exhaled breath condensate an equivalent to bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in sarcoidosis patients? Hirosaki Med J. 2012;63(1):12–20. | |
Kowalska A, Puscinska E, Czerniawska J, et al. [Markers of fibrosis and inflammation in exhaled breathcondensate (EBC) and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis: a pilot study]. Pneumonol Alergol Pol. 2010;78(5):356–362. Polish. | |
Ahmadzai H, Cameron B, Chui J, Lloyd A, Wakefield D, Thomas PS. Measurement of neopterin, TGF-β1 and ACE in the exhaled breath condensate of patients with sarcoidosis. J Breath Res. 2013;7(4):046003. | |
Psathakis K, Papatheodorou G, Plataki M, et al. 8-Isoprostane, a marker of oxidative stress, is increased in the expired breath condensate of patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest. 2004;125:1005–1011. | |
Antczak A, Piotrowski W, Marczak J, Ciebiada M, Gorski P, Barnes PJ. Correlation between eicosanoids in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and in exhaled breath condensate. Dis Markers. 2011; 30(5):213–220. | |
Piotrowski WJ, Kurmanowska Z, Antczak A, Marczak J, Górski P. Exhaled 8-isoprostane as a prognostic marker in sarcoidois. A short term follow up. BMC Pulm Med. 2010;10:23–29. | |
Kwiatkowska S, Luczynska M, Grzelewska-Rzymowska I, Nowak D, Zieba M. [Comparison of oxidative stress markers in exhaled breath condensate and in serum of patients with tuberculosis and sarcoidosis]. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2005;19(109):37–40. Polish. | |
Culver DA. Sarcoidosis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2012;32(4):487–511. | |
Grunewald J. Review: role of genetics in susceptibility and outcome of sarcoidosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;31(4):380–389. | |
Jung M, Schaefer A, Steiner I, et al. Robust microRNA stability in degraded RNA preparations from human tissue and cell samples. Clin Chem. 2010;56(6):998–1006. | |
Crouser ED, Julian MW, Crawford M, et al. Differential expression of microRNA and predicted targets in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;417(2):886–891. | |
Nathans R, Chu CY, Serquina AK, Lu CC, Cao H, Rana TM. Cellular microRNA and P bodies modulate host-HIV-1 interactions. Mol Cell. 2009;34(6):696–709. | |
Ma F, Xu S, Liu X, et al. The microRNA miR-29 controls innate and adaptive immune responses to intracellular bacterial infection by targeting interferon-γ. Nat Immunol. 2011;12(9):861–869. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.