Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 8
Axial length estimation error caused by hidden double-peak on partial coherence interferometry in an eye with epiretinal membrane: a case report
Authors Kitaguchi Y, Yano S, Gomi F
Received 17 December 2013
Accepted for publication 13 January 2014
Published 13 March 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 555—559
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S59309
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 8
Yoshiyuki Kitaguchi, Shinsaku Yano, Fumi Gomi
Department of Ophthalmology, Sumitomo Hospital, Osaka, Japan
Abstract: Here we report a patient in whom there was a myopic shift after combined cataract surgery and pars plana vitrectomy against the epiretinal membrane, related to axial measurement estimation error caused by a hidden double-peak appearance on partial coherence interferometry measurement. A 52-year-old female presented with epiretinal membrane and underwent combined cataract surgery and pars plana vitrectomy. Axial length was measured with partial coherence interferometry. Although the signal curve in the summary display showed a single peak, a 1.6 diopter myopic shift occurred. Viewed retrospectively, six of 20 individual signal curves showed a double peak. Most of them showed a higher anterior peak, with only one having a higher posterior peak. The other 14 curves showed a single peak at a similar distance to an anterior peak. The anterior peak appeared to be derived from the epiretinal membrane. The possibility of a double peak should always be considered in patients with epiretinal membrane even if the summary display of the partial coherence interferometry measurement shows a single peak. Checking all signal curves would reduce the risk of missing a hidden double peak.
Keywords: intraocular lens, master, double peak, epiretinal membrane
Introduction
Accurate measurement of axial length has become essential for postoperative quality of vision after combined cataract surgery with pars plana vitrectomy, owing to the availability of minimally invasive cataract surgery and the vitrectomy technique.1,2
Partial coherence interferometry (PCI) is one of the best devices for accurate measurement of axial length.3–5 The advantage of PCI over ultrasound biometry is the use of infrared light.3,4 Optical measurement systems with PCI enable noncontact measurement, which eliminates variations due to compression of the cornea.3,4 Moreover, PCI measures the distance from the corneal vertex to the retinal pigment epithelium as axial length, whereas ultrasound measures up to the internal limiting membrane.6 This means the measured value of axial length obtained using PCI is not affected by retinal thickening associated with macular disease, ie, macular edema and epiretinal membrane (ERM).7
In some cases with macular disease, a double peak is actually observed in the data for axial length measurements using PCI. Kojima et al reported that the anterior peak corresponds to the surface of the retina and use of the anterior peak for intraocular lens power calculation causes a -1.2 D myopic spherical error.8 These investigators concluded that application of a posterior peak will achieve a predictable refractive outcome when a double peak is observed in PCI measurements. However, we report here a case with a single peak resulting in myopic shift, which postoperatively turned out to be a case of “hidden double peak.”
Case report
A 52-year-old female presented with ERM in her left eye (Figure 1A). Her visual acuity at the first visit was 20/25, with mild cataract on slit-lamp examination. The spherical equivalent was -1.5 D. ERM was identified on fundus examination and spectral domain optical coherence tomography (Spectralis®; Heidelberg Engineering, Dossenheim, Germany); this clearly showed a strained line with high intensity above the retina corresponding to the ERM. After 6 months, her retinal thickening became severe due to proliferating ERM, and her visual acuity dropped to 20/100 (Figure 1B). Combined cataract surgery with pars plana vitrectomy was planned.
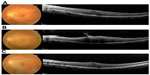  | Figure 1 Spectral domain optical coherence tomography B-scan images at the initial visit (A), before surgery (B), and after surgery (C). |
On preoperative examination, the IOLMaster® (version 5.4; Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany) was used for measurement of axial length by PCI. The measurement was repeated 20 times, and a signal curve synthesized from individual curves using an algorithm built into the IOLMaster was displayed as a summary.
The highest peak in the summary display was used for measurement of axial length because the signal curve appeared to be, at a glance, a single peak (Figure 2A). Keratometry readings were obtained by the automated keratometer incorporated in the IOLMaster. The SRK/T formula was used for intraocular lens power calculation.9
After giving informed consent, the patient underwent combined cataract surgery with pars plana vitrectomy. Phacoemulsification was performed with a 2.2 mm superior self-sealing clear corneal incision, and a foldable acrylic intraocular lens (AcrySof® IQ Model SN60WF; Alcon, Fort Worth, TX, USA) was injected in the capsular bag with full covered continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis. Transconjunctival pars plana vitrectomy was performed using the Alcon 25 gauge vitrectomy system (Alcon). The internal limiting membrane was peeled using indocyanine green staining after removing the ERM.
One month postoperatively, her best-corrected visual acuity was improved to 20/20 (Figure 1C). The spherical equivalent was -2.62 D despite aiming for -1.04 D, ie, the postoperative refractive error was -1.58 D.
Retrospectively viewing all the individual signal curves in the IOLMaster, eight of 20 curves showed more than two peaks. When the amplitude of the second highest peak was higher than 30% of the highest peak and the amplitude of the third highest peak was lower than 50% of the second highest peak, the curve was defined as a double peak, and when the third highest peak was higher than 50% of the second highest peak, the curve was defined as a multi-peak. According to this rule, six eyes showed a double peak and two eyes showed a multi-peak. In cases with a double peak, five curves had a higher anterior peak, whereas one curve had a higher posterior peak. The distance from the anterior peak to the posterior peak of these curves was approximately 0.6 mm. If the posterior peak of the double peak is applied to obtain the axial measurement, the postoperative refractive error is reduced to -0.37 D.
The other 14 curves showing single peaks might correspond to the retinal surface because the distance was almost equal to that of the anterior peak of the double peak (Figure 2B).
Discussion
A double peak in PCI measurements is one of the important causes for misjudgment of axial length.3,8 The origin of “pseudo” peaks in PCI is considered to be the retinal surface (ie, ERM) and choroid.3 Actually, a double peak is more frequently observed in patients with ERM (approximately 35.0%) than in those with other macular diseases,8 because of an increased signal from the retinal surface.
In this ERM case, PCI measurements showed a single peak instead of a double peak, probably because an increased signal from the ERM caused attenuation of the signal from the retinal pigment epithelium. An attenuated retinal pigment epithelium signal also appeared in spectral domain optical coherence tomography images, especially in the last preoperative images (Figure 1B). Although optical coherence tomography uses a broader bandwidth,10 both use an infrared light source and are based on an interferometric technique. Thus, the strength of the signals would correlate with each other.3
The averaging algorithm incorporated in the IOLMaster to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio may also cause the “hidden” posterior peak in the summary display. In this algorithm, an outlier is excluded at first. Secondly, the remaining measurement curves are averaged. Finally, the averaged curve is output in a summary display and the highest peak is used to calculate axial length. In this case, the highest peak originated from the signal of ERM in the majority of the measurement curves. The curves with a posterior peak corresponding to retinal pigment epithelium were then excluded from averaging. This resulted, on average, in a “hidden double peak.”
Our result suggests that all measurement curves on PCI should be carefully checked in eyes with macular disease even if the curve in the summary display appears as a single peak. When there is a double peak curve in any of the measurement displays, the possibility of a “hidden” posterior peak should be considered. Performing pars plana vitrectomy prior to cataract surgery might be another strategy to avoid a myopic shift with incorrect axial length evaluation.
With thicker ERM, it is possible that the posterior peak is attenuated and only the anterior peak appears in the individual signal curves. In such cases, a predictable refractive outcome would be achieved by adding the macular thickness measured by spectral domain optical coherence tomography to axial length,8 if it is certain that the only peak corresponds with ERM. Similar to this case, there might be a concern about a “hidden” posterior peak in other diseases in which high refractive matter exists on the retina or in the retina (ie, vitelliform macular dystrophy). The risk factor of double peak (for example, appearance on optical coherence tomography) should be established in a future study.
The limitation of this study is that the definition of double peak is not yet established. To avoid an arbitrary determination, we classified it according to our own original rule as described above. Using a broadband light source, peak splitting of PCI measurement is inevitable because of dispersion.10 Therefore we should be careful to distinguish a real peak from split peaks when the peak is as low as other split peaks. We believe our classification rule is reasonable for distinguishing signals of retinal structure from noises. In this study, myopic shift caused by vitrectomy itself is not discussed. It is reported that pars plana vitrectomy alone also raises myopic shift by 0.2 D.11,12 Although this case may also be affected, the main reason for the refractive error is likely to be axial length estimation error. Because this is a case study, the possibility of a simple prediction error with correct axial length cannot be ruled out. More cases would be needed to assure the existence of a hidden posterior peak in a summary display.
In conclusion, the possibility of a double peak should be considered in patients with ERM even if the summary display of the PCI measurement shows a single peak. Checking all signal curves may reduce the risk of myopic shift after combined cataract surgery with pars plana vitrectomy caused by overlooking a “hidden double peak”.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Chung TY, Chung GH, Lee JH, et al. Combined surgery and sequential surgery comprising phacoemulsification, pars plana vitrectomy, and intraocular lens implantation: comparison of clinical outcomes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002;28(11):2001–2005. | |
Demetriades AM, Gottsch JD, Thomsen R, et al. Combined phacoemulsification, intraocular lens implantation, and vitrectomy for eyes with coexisting cataract and vitreoretinal pathology. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003;135(3):291–296. | |
Drexler W, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Partial coherence interferometry: a novel approach to biometry in cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998;126(4):524–534. | |
Haigis W, Lege B, Miller N, et al. Comparison of immersion ultrasound biometry and partial coherence interferometry for intraocular lens calculation according to Haigis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2000;238(9):765–773. | |
Vogel A, Dick HB, Krummenauer F. Reproducibility of optical biometry using partial coherence interferometry: intraobserver and interobserver reliability. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001;27(12):1961–1968. | |
Attas-Fox L, Zadok D, Gerber Y, et al. Axial length measurement in eyes with diabetic macular edema: A-scan ultrasound versus IOL-Master. Ophthalmology. 2007;114(8):1499–1504. | |
Drexler W, Hitzenberger CK, Sattmann H, et al. Measurement of the thickness of fundus layers by partial coherence tomography. Opt Eng. 2005;34(3):701–710. | |
Kojima T, Tamaoki A, Yoshida N, et al. Evaluation of axial length measurement of the eye using partial coherence interferometry and ultrasound in cases of macular disease. Ophthalmology. 2010;117(9):1750–1754. | |
Retzlaff JA, Sanders DR, Kraff MC. et al. Development of the SRK/T intraocular lens implant power calculation formula. J Cataract Refract Surg.1990;16(3):333–340. | |
Hitzenberger CK, Baumgartner A, Fercher AF. Dispersion induced multiple signal peak splitting in partial coherence interferometry. Opt Commun. 1998;154(4):179–185. | |
Hamoudi H, Kofod M, La Cour M. Refractive change after vitrectomy for epiretinal membrane in pseudophakic eyes. Acta Ophthalmol. 2013;91(5):434–436. | |
Byrne S, Ng J, Hildreth A, Danjoux JP. Refractive change following pseudophakic vitrectomy. BMC Ophthalmol. 2008;8:19. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.

