Back to Journals » International Medical Case Reports Journal » Volume 7
Another cause of chest pain: Staphylococcus aureus sternal osteomyelitis in an otherwise healthy adult
Authors Vacek T, Rehman S, Yu S, Moza A, Assaly R
Received 4 May 2014
Accepted for publication 28 May 2014
Published 12 September 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 133—137
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IMCRJ.S67203
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Thomas P Vacek, Shahnaz Rehman, Shipeng Yu, Ankush Moza, Ragheb Assaly
Department of Internal Medicine, The University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo OH, USA
Abstract: Chest pain requires a detailed differential diagnosis with good history-taking skills to differentiate between cardiogenic and noncardiogenic causes. Moreover, when other symptoms such as fever and elevated white blood cell count are involved, it may be necessary to consider causes that include infectious sources. A 53-year-old female with no significant past medical history returned to the hospital with recurrent complaints of chest pain that was constant, substernal, reproducible, and exacerbated with inspiration and expiration. The chest pain was thought to be noncardiogenic, as electrocardiography did not demonstrate changes, and cardiac enzymes were found to be negative for signs of ischemia. The patient's blood cultures were analyzed from a previous admission and were shown to be positive for Staphylococcus aureus. The patient was started empirically on vancomycin, which was later switched to ceftriaxone as the bacteria were more sensitive to this antibiotic. A transthoracic echocardiogram did not demonstrate any vegetation or signs of endocarditis. There was a small right pleural effusion discovered on X-ray. Therefore, computed tomography as well as magnetic resonance imaging of the chest were performed, and showed osteomyelitis of the chest. The patient was continued on intravenous ceftriaxone for a total of 6 weeks. Tests for HIV, hepatitis A, B, and C were all found to be negative. The patient had no history of childhood illness, recurrent infections, or previous trauma to the chest, and had had no recent respiratory infections, pneumonia, or any underlying lung condition. Hence, her condition was thought to be a case of primary sternal osteomyelitis without known cause.
Keywords: substernal, pleuritic, myocardial infarction, differential
Introduction
There is a large differential for cardiogenic sources of chest pain: pericarditis, myocardial infarction (MI), aortic aneurysm rupture, heart failure, aortic stenosis, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Pericarditis is generally sharp pain relieved with leaning forward. MI and ischemia are long-lasting (>30 minutes), exertional, and can radiate to the arms and jaw. Ruptured aortic aneurysm is characterized by a severe and ripping sharp pain that can extend down the back and can be accompanied by blood pressure differential in the upper extremities. Valvular abnormalities and cardiomyopathy can also cause chest pain and may be detected on auscultation and echocardiogram, associated with syncope, fatigue, shortness of breath, jugular venous distension, orthopnea, etc.
Noncardiogenic causes are also important. Gastrointestinal sources include gastritis, esophagitis, peptic ulcer disease, esophageal spasm, and Boerhaave’s syndrome. Gastritis, esophagitis, and dyspepsia are generally correlated to acidic food intake or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use. Drinking cold water, or anxiety, can provoke esophageal spasm. Boerhaave’s syndrome is generally found in the alcoholic who retches profoundly with hematemesis. Musculoskeletal (costochondritis, Tietze syndrome, inflammation, fibromyalgia) sources of chest pain are generally reproducible in nature with palpation or by performing motions contracting chest wall muscles. Respiratory causes of chest pain (pulmonary embolism, pleurisy) can also be accompanied by cardiac arrest, desaturation, shortness of breath, and sharp pain with inspiration and expiration. Psychogenic or neurologic sources of chest pain include panic attack with periodic episodes of nervousness and sweating, or systemic conditions of neurotransmitter imbalance such as fibromyalgia.
This brings us to what we generally would place in the lower part of our differential as noncardiogenic. Infectious causes of chest pain can sometimes include shingles and is usually accompanied by a rash. In this case report, our patient was found to have osteomyelitis in her sternum, which is exceedingly rare in the immunocompetent patient.
Case presentation
The patient was a 53-year-old female with no significant past medical history who presented back to the hospital with similar complaints of chest pain. The family and social history were noncontributory. Electrocardiography (EKG) showed normal sinus rhythm with no ischemic changes (Figure 1). On previous admission, the patient had presented with new-onset chest pain that was sudden, constant, and severe, with fever and leukocytosis. The patient was deemed at that time to have a viral illness in addition to costochondritis and was discharged on cyclobenzaprine as well as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (ibuprofen).
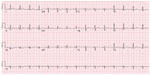  | Figure 1 Electrocardiogram. |
The patient’s chest pain did not improve, and she returned after the initial admission to the hospital. The blood cultures from the previous admission came back positive for Staphylococcus aureus. The patient had, at the previous admission, originally presented with leukocytosis at 19,000 white blood cells per mL and with fever as high as 102°F (39°C) that had both immediately trended down. Low-grade fever was also present on this admission without leukocytosis. The patient did have some days on which her heart rate was above 90 beats per minute and respirations were occasionally over 20, thus septic by criteria.
The Infectious Disease service was contacted for management of infection and recommended to repeat blood cultures to confirm no further growth of the organism after administration of antibiotics for 48 hours. The patient was also switched to intravenous (IV) ceftriaxone 2 g daily from IV vancomycin 1,250 mg twice daily, as the Staphylococcus bacteria were sensitive to ceftriaxone and resistant to penicillins. With the presentation of chest pain in addition to mild murmur, fever, and bacteremia, it was thought the patient may have some suggestion of endocarditis, and a transthoracic echocardiogram was performed. The patient had normal ejection fraction and only trivial regurgitation of valves, except for the mitral valve, which showed mild regurgitation.
A transesophageal echocardiogram was not performed because the treatment for the osteomyelitis and any possible endocarditis would have been the same; moreover, there were no gross abnormalities on the echocardiogram that would warrant surgical correction as would be the case with endocarditis. Urine cultures and urinalysis were shown to have no growth of bacteria. These were collected in the emergency department prior to antibiotics, indicating the urine was not a source of infection. The patient was not producing any sputum and had no cough. The patient also had good dentition. Colonoscopy was recommended, as the patient was 53 years and had not yet had one; however, the patient had not had any melena or hematochezia.
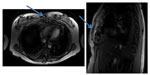
The patient also had a chest X-ray performed on this admission to search for a pulmonary cause of her infection. The patient did have evidence of a new, small, right pleural effusion that was best visualized on lateral projection and which was not present on the first chest X-ray from the prior recent admission. The second admission’s X-rays are shown in Figure 2. For this reason, computed tomography (CT) of the chest without contrast was performed to further investigate the cause of the effusion. CT of the chest did suggest a possible non-displaced fracture of the sternum versus osteomyelitis of the sternum. After CT of the chest indicated osteomyelitis, magnetic resonance imaging of the chest with and without contrast was performed to confirm this presence; Figure 3 shows the magnetic resonance imaging findings. Osteomyelitis involving the manubrium and upper part of the sternum body was suggested. This was consistent with clinical findings, as the patient was extremely tender to palpation in these areas without overlying erythema. The patient’s chest pain did improve during her hospital course with administration of IV antibiotics. She underwent 6 weeks of treatment with IV antibiotics (IV ceftriaxone 2 g once daily).
  | Figure 2 Chest X-rays. |
The patient received a total of four complete blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and basic metabolic panel tests while on her course of antibiotics. The patient was provided with ibuprofen as well as oxycodone/acetaminophen. Her erythrocyte sedimentation rate went from 38 mm/hr to 18 mm/hr, then 15 mm/hr, and then 20 mm/hr (0–20 is normal). C-reactive protein was 9.9 mg/L and trended downward to 0.3, then 0.1, and then 2.2 mg/L (0–7.0 mg/L is normal). The patient had no recurrence of infection, although her chest pain persisted in subsequent months. Interestingly, the patient was found to have an antinuclear antibody of 1:320 centromere pattern on subsequent laboratory testing in follow-up, after 5 months; this can indicate a rheumatologic disorder, which may have made her prone to joint destruction and subsequent infection.
Given that the patient was not immunocompromised to our or her knowledge, she had an HIV test performed and a hepatitis panel drawn. Prior to discharge, the hepatitis panel revealed negative hepatitis A, B core antibody, B surface antigen, and C antibody. She had negative urinalysis and a negative HIV test. The patient was found to have elevated liver function. On April 5, 2013, testing showed aspartate aminotransferase of 103 U/L, alanine aminotransferase of 180 U/L, and alkaline phosphatase at 135 U/L. The patient’s liver function tests trended downward to 76 U/L of aspartate aminotransferase and 144 U/L of alanine aminotransferase. Alkaline phosphatase level, however, trended slightly upward from 135 U/L to 150 U/L a couple of days later. The exact etiology of the elevated liver function tests is unclear, but may have been a complication of systemic inflammatory response syndrome/sepsis rather than induced by medication. The patient did not have a positive hepatitis panel or demonstrate any abdominal pain.
Discussion
Approximately 1% of primary care visits are related to chest pain, and 1.5% of these individuals will have unstable angina or acute MI. A quick and cost-effective means of ruling out cardiac causes is a 12-lead EKG to evaluate for such instances as the following: ST segment depressions or elevations; new onset of left bundle branch block; suggestions of old infarct such as Q waves; or new onset of T wave inversions.1 Chest pain or symptoms thought to be related to myocardial ischemia or infarction account for 8%–10% of the 119 million emergency department visits that occur yearly in the United States.2
There are very few cases of idiopathic causes of osteomyelitis of the sternum. Most of these cases involve cardiac surgery and the complications from sternal incision post-surgery.3,4 Infection post-cardiac surgery for procedures such as coronary artery bypass grafting and valve replacement is so common that one study even developed a model using mice to help deal with these infections; the study was used to determine the appropriate amount of antibiotic to administer.5 Other cases of sternal osteomyelitis involve an immunodeficiency with some kind of entrance point.6 Abscess appears to be common, as it featured in multiple cases of sternal osteomyelitis.7 Other cases of sternal osteomyelitis after incidental trauma have been reported, even after cardiopulmonary resuscitation involving compressions.8,9 Another source of infection of community-acquired methicillin-resistant S. aureus sternal osteomyelitis is IV drug use.10–12 Apparently, with repeated introduction of bacteria intravenously, there is greater risk of seeding the sternum. Interestingly, there have been several pediatric cases reported with no apparent risk factors.10
Treatment suggestions for sternal osteomyelitis vary throughout the literature, and the osteomyelitis has even been proposed to include surgery in earlier times as in an article from the 1970s, which states that the condition “warrants prompt recognition and surgical treatment”.13 Moreover, it is known that the offending agent is generally S. aureus or Pseudomonas; however, there have been multiple reports of tuberculosis causing these infections.13–15 Other rare bacteria have been implicated, including Apophysomyces elegans in a case involving minor trauma, for which treatment featured amphotericin B as well as extensive surgical debridement.16
Treatment of sternal osteomyelitis in recent literature includes debridement, if the osteomyelitis is extensive, as well as antibiotic use.16,17 Hyperbaric oxygen chamber therapy may also result in positive outcomes. Hyperbaric chamber use has also been shown to reduce the number of days spent in the intensive care unit, with mortality found to be lower than when the hyperbaric chamber is not used.17 Fortunately, our patient did not have such an extensive infection that an abscess was found, and the infection resolved with 6 weeks of IV ceftriaxone antibiotic treatment.
Conclusion
This report describes a patient who developed primary osteomyelitis of the sternum and manubrium without any history of IV drug abuse or any other obvious reason for bacterial introduction. The patient had no recent central lines placed or infections that could have accounted for this. Moreover, the patient was not known to be immunocompromised. Hence, this case stands as a rare event in medicine, wherein an individual developed primary osteomyelitis without a clear underlying cause. The positive ANA in follow-up with 1:320 titers, however, made her suspect for a possible rheumatologic disorder, which may have made her more prone to joint destruction and infection.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
McConaghy JR, Oza RS. Outpatient diagnosis of acute chest pain in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2013;87(3):177–182. | |
Gerber TC, Kontos MC, Kantor B. Emergency department assessment of acute-onset chest pain: contemporary approaches and their consequences. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85(4):309–313. | |
Asare KA, Jahng M, Pincus JL, Massie L, Lee SA. Sternal osteomyelitis caused by Aspergillus fumigatus following cardiac surgery: case and review. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2012;2:4–6. | |
Urbanski PP, Lindemann Y, Babin-Ebell J, Fröhner S, Diegeler A. Simultaneous surgery of the aortic valve and sternal osteomyelitis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88(3):987–989. | |
Barnea Y, Carmeli Y, Kuzmenko B, Navon-Venezia S. Staphylococcus aureus mediastinitis and sternal osteomyelitis following median sternotomy in a rat model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008;62(6):1339–1343. | |
Tordecilla Echenique Y, Salamanca Bautista MP, Arias Jiménez JL, Guisado Espartero E, Ortega Calvo M, Pérez Cano R. [Hematogenous sternal osteomyelitis and community acquired pneumonia in a methicillin-susceptible Staphilococcus aureus sepsis]. An Med Interna. 2005;22(4):191–193. Spanish. | |
Platt MA, Ziegler K. Primary sternal osteomyelitis with bacteremia and distal seeding. J Emerg Med. 2012;43(2):e93–e95. | |
Edelman DA, Losanoff JE, Richman BW, Jones JW. Sternal osteomyelitis after minor trauma. South Med J. 2009;102(9):982–984. | |
Mallinson RH, Tremlett CH, Payne BV, Richards JE. Sternal osteomyelitis after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. J R Soc Med. 1999; 92(2):87. | |
Kara A, Tezer H, Devrim I, et al. Primary sternal osteomyelitis in a healthy child due to community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and literature review. Scand J Infect Dis. 2007;39(5):469–472. | |
Martín J, Altés J, Reina J, Aguiló R, Riera M. [Primary sternal osteomyelitis caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in intravenous drug addicts]. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 1992;10(3):179–180. Spanish. | |
Randell PA, Somers L. Case of the month: “bugs are eating my soul” – sternal abscess, osteomyelitis, and mediastinitis complicating a closed sternal fracture. Emerg Med J. 2006;23(9):736–737. | |
Mittapalli MR. Value of bone scan in primary sternal osteomyelitis. South Med J. 1979;72(12):1603–1604. | |
Vasa M, Ohikhuare C, Brickner L. Primary sternal tuberculosis osteomyelitis: a case report and discussion. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2009;20(4):e181–e184. | |
Khan SA, Varshney MK, Hasan AS, Kumar A, Trikha V. Tuberculosis of the sternum: a clinical study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89(6):817–820. | |
Eaton ME, Padhye AA, Schwartz DA, Steinberg JP. Osteomyelitis of the sternum caused by Apophysomyces elegans. J Clin Microbiol. 1994;32(11):2827–2828. | |
Yu WK, Chen YW, Shie HG, Lien TC, Kao HK, Wang JH. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as an adjunctive treatment for sternal infection and osteomyelitis after sternotomy and cardiothoracic surgery. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;6:141. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.