Back to Journals » Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology » Volume 16
A Case of Giant Perianal Condylomata Acuminata with IgA Nephropathy Treated Successfully by a Topical Chinese Medicine Preparation Paiteling
Authors Wu YT , Ye DQ, Lian CH
Received 17 December 2022
Accepted for publication 7 March 2023
Published 20 March 2023 Volume 2023:16 Pages 693—696
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S400677
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jeffrey Weinberg
Yu-Tong Wu,1,* Dong-Qing Ye,2,* Cui-Hong Lian1
1Department of Dermatology, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, Shenzhen, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Dermatology, The Third People’s Hospital of Longgang District, Shenzhen, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Correspondence: Cui-Hong Lian, Department of Dermatology, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, 3002 Sungang West Road, Futian District, Shenzhen, People’s Republic of China, Tel +8615814692161, Fax +86 755-83366388, Email [email protected]
Abstract: Giant condylomata acuminata (a sexually transmitted disease caused by HPV infection) currently is treated in many methods. Surgery, the mainstay treatment of giant condylomata acuminata, may cause a high cost or scar formation. It is important to explore effective and safe treatment options. Although the external treatment of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of condyloma acuminatum has not been widely used, in our case, the use of traditional Chinese medicine successfully treated a perianal giant condyloma acuminatum patient who also suffered from mixed hemorrhoid and IgA nephropathy meanwhile. The treatment process was simple and the effect obvious. There was no recurrence more than 10 months after treatment finished, and the patients felt safe, comfortable and highly coordinated. The outcome of this case suggests that the traditional Chinese medicine might be considered as a mild and effective option for the treatment of giant condyloma acuminatum.
Keywords: giant condylomata acuminata, IgA nephropathy, Chinese medicine, HPV infection
Introduction
Condylomata acuminata (CA) is the most common sexually transmitted disease associated with human papilloma virus (HPV) infection. Giant condyloma acuminatum, also known as The Buschke-Löwenstein tumor, lesions are mega versions of CA. The incidence of Giant CA is rare but increasing. Human is the unique host of papillomavirus, currently human papillomavirus has been found more than 100 subtypes, HPV-6, 11, 16, 18 are major pathogens of CA. Usually, CA is easy to cure, but recurrences frequently happen, and there is even a risk of cancerization. The reasons for recurrences are related to several factors, such as subclinical infection, latent infection of local HPV, different subtypes of HPV, the long latent period of HPV, self-vaccination and abnormal cellular immune function of patients.1 Due to Giant CA’s rarity and lack of controlled studies, the most effective one is not clear.2 Surgery, the mainstay treatment, may cause a high cost or scar formation.3 External treatment is developing rapidly at home and abroad in recent years. Chinese medicine external treatment mainly includes Chinese medicine fumigation, rubbing, soaking, acupuncture, moxibustion, etc.4 At present, there are only a few cases of treating Giant CA with topical treatment of traditional Chinese medicine. Shu et al reported a case where a mass obstructing the urethral orifice was successfully treated with the Chinese medicine – Paiteling.5 Akhavizadegan H used a combination of electrocautery and a surgical scalpel to resect a huge genital wart, followed by long-term local treatment with podophyllin. The patient was cured, and consequently sexual function was preserved completely.6 Wang et al used paiteling treated 22 Giant CA patients with a cure rate of 86.36%. The adverse reactions mainly included pain and swelling, no serious adverse reactions occurred such as obvious scarring and obvious toxic side effects.7 At present, plenty of therapeutic methods are available in management of CA warts, including physical therapy (freezing, laser, microwave, photodynamic therapy), drug therapy (podophyllotoxin, imiquimod, interferon, thymic pentapeptide, mannan peptide, etc.), surgery and Chinese medicine therapy. It has been reported that topical use of traditional Chinese medicine preparation paiteling helps treat CA with satisfactory outcomes.8
We report herein a case of an adult with giant CA around the anus and multiple condylomatous lesions on the penis, who also suffered from mixed hemorrhoid and IgA nephropathy meanwhile, successfully cured with external application of Chinese medicine preparation paiteling.
Case Report
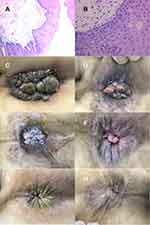
A 53-year-old man was admitted to our hospital in April 2020 for a perianal mass noticed over the last 2 months. Physical examination of the perianal region revealed massive verrucous lesions surrounding the anus, hyperkeratotic and giving an aspect of a cauliflower, and contact bleeding test seemed positive (Figure 1C). Three small warts were observed on the penis. He denied any anal or homosexual intercourse. No evidence of syphilis or HIV was shown in laboratory tests. A biopsy from fresh warts presented Koilocyte cells (Figure 1A and B). Owing to IgA nephropathy, he visited the Department of Nephrology for a long time and was treated with immunosuppressants, glucocorticoids, and then intermittent hemodialysis therapy. He refused recommendation for laser therapy or photodynamic therapy. Considering the possibility of a high risk of recurrence of traditional physical therapy, a high cost and a scarring formation tendency of surgery,2 he was treated with paiteling alone.
The treatment program was divided into three stages as follows: removing the warts, clearing latent infection and relapse prevention. Observation and vision inspection with acetic acid (VIA) test were conducted three months after the last treatment. The patient tolerated the treatment well. He developed mild pain and burning sensation intermittently. After several sessions of sclerosing agent injection treatment in other hospitals, his mixed hemorrhoids were well controlled. And during paiteling therapy, regular hemodialysis was performed to treat IgA kidney disease. The therapeutic effect was satisfactory and achieved clinical recovery with no recurrence occurring thus far (Figure 1D–H).
Discussion
Giant CA is a relatively rare venereal disease currently, with a mega size that increases the difficulty of treatment. This case is more complicated to treat as a result of the co-occurrence of other systemic diseases. Few treatment research studies are reported for giant CA patients with history of chronic kidney disease. For IgA nephropathy patients, long-term application of immunosuppressants inhibits immune function.9 It may cause a high rate of giant CA relapse. For this patient, pathogen examination showed that HPV infected his perianal area, penis, and anal canal. We consider that immune system is significantly inhibited, which increases the possibility of HPV infection and decreasing the body’s clearance effect on HPV as a result of suffering from chronic IGA nephropathy and long-term use of hormones and immunosuppressants.10 Hemorrhoids are caused by physiological structural changes around the anus and congestion in the subcutaneous vessels. Multiple methods can be used in the management of warts. Traditional treatment methods aimed at removing the perianal warts may leave new wounds with a secondary infection tendency. Defecation may even cause wound dehiscence and hemorrhage. Therefore, as a mild and effective choice, external application of traditional Chinese medicine was considered for this patient. In China, many experts have reported that paiteling is effective in eradicating CA lesions and improving quality of life. Hu et al reported that in their research, 100 CA patients received paiteling treatment, 92 of the patients were clinically cured and exhibited no recurrence. Results showed that paiteling could cure different subtypes of HPV infection.1 Zhang et al treated 68 CA patients with paiteling combined with photodynamic therapy compared with photodynamic therapy alone. The total effective rate was 94.12% (32/34) in combined therapy group, which was higher than that in photodynamic therapy alone group (76.47%, 26/34).11 Mao et al treated 55 CA patients with paiteling alone. The results showed that 53 cases were curative, the clearance rate is 96.36%, the recurrence rate is 3.64%.12 Dr. Zheng treated 392 CA patients with paiteling during 2002–2006, all patients were cured without relapse.13 As for non-sexual HPV infection, pateling is also effective. Qi et al reported that a patient with a 10-year history of subungual warts was cured after using paiteling.14
Paiteling is a pure Chinese medicine developed by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences research. It is composed of many ingredients, including Java brucea fruit oil, folium isatidis, spreading hedyotis herb, sophora flavescens and cnidium fruit.8 Folium isatidis has a broad-spectrum antibacterial and antiviral effect. Java brucea has high selectivity for infected cells and can destroy infected cells' cytoplasmic and mitochondrial membrane system, leading to degeneration and necrosis of wart cells. Sophora flavescens is beneficial to improve the body’s immunity function and can effectively restrain HPV DNA synthesis. These ingredients work synergetically to destroy the environment in which HPV grows, removing the HPV exiting in epidermal cells in time along with the exfoliation of necrotic cells, showing a protective effect on immune cells, preventing HPV from recurrence.15,16 The effects of cell inhibition and mild exfoliation are the basis of pharmacology. Meanwhile, paiteling liquid acts only on superficial skin without entering the dermis. That means the damage to deep skin tissues might be avoided, showing the safety of paiteling.
To conclude, the case shows that paiteling may be an effective therapy for giant CA. Further clinical trials are needed to assess the efficacy and safety of paiteling.
Consent Statement
Written informed consent was provided by the patient to have the case details and any accompanying images published. Publication of the case details was approved by Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital.
Funding
This study was supported by Foundation of Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital Clinical Research Programme (No. 20173357201827).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Hu Y, Lu Y, Qi X, et al. Clinical efficacy of paiteling in the treatment of condyloma acuminatum infected with different subtypes of HPV. Dermatol Ther. 2019;32(5):e13065. doi:10.1111/dth.13065
2. Salah E. Impact of multiple extragenital warts on quality of life in immune-competent Egyptian adults: a comparative cross-sectional study. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2018;11:289–295. doi:10.2147/CCID.S165908
3. Costa Almeida CE, Azevedo J, Botelho I, Vilaça J. Buschke-Löwenstein tumour: a rare and challenging entity. BMJ Case Rep. 2021;14(9):e244192. doi:10.1136/bcr-2021-244192
4. Xiao ZS, Xu CC, Cui BN. Research progress in the treatment of genital warts by external treatment of traditional Chinese medicine. Shandong J Trad Chin Med. 2018;37(9):4.
5. Shu HL, Yu B, Li CQ. Treatment of giant condyloma acuminatum with paiteling: a case report. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33(6):e13936. doi:10.1111/dth.13936
6. Akhavizadegan H. Electrocautery resection, shaving with a scalpel, and podophyllin: a combination therapy for giant condyloma acuminatum. World J Mens Health. 2015;33(1):39–41. doi:10.5534/wjmh.2015.33.1.39
7. Wang SL, Li J, Wang W, Bao TY. Observation of the clinical effects of Paiteling for 22 patients with giant condyloma acuminatum. Chin J Human Sex. 2019;28(6):145–147.
8. Wang MF, Lin L, Li LF. Efficacy and safety of giant condyloma acuminatum with monotherapy of topical traditional Chinese medicine: report of eight cases. Infect Drug Resist. 2021;14:1375–1379. doi:10.2147/IDR.S302195
9. Floege J, Rauen T, Tang S. Current treatment of IgA nephropathy. Semin Immunopathol. 2021;43:717–728. doi:10.1007/s00281-021-00888-3
10. Wu YX, Zhou Y, Jin ZJ. Effect of immunosuppressive therapy on HPV infection and the incidence of cervical cancer after renal transplantation. Int Obstet Gynecol. 2017;44(1):52–54.
11. Zhang C, Wu ZW, Shi WM. Effect of paiteling combined with photodynamic therapy on penile condyloma acuminatum and local HPV load level. Chin J Human Sex. 2017;26(11):68–72.
12. Mao LY, Xiong ML, Duan XQ, Zhou WM. Clinical observation on 55 cases of condyloma acuminatum treated with PAITELING. J Dermatol Venereol. 2019;41(5):647–649.
13. Zheng XH. Therapeutic effect of Traditional Chinese medicine “Pai Te Ling” on 392 cases with condyloma acuminatum. Chin J Human Sex. 2006;15(06):28.
14. Qi X, Yao W. Successful treatment of a patient with subungual warts using paiteling: a case report. Explore. 2022. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2022.10.006
15. Tao P, Zheng W, Meng X, et al. Effect of paiteling on human papillomavirus infection of the cervix. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017;7(6):957–964. doi:10.3892/mco.2017.1454
16. Wu T, Zhang B, Rao J, Tai YH. Efficacy observation of integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine on perianal condyloma acuminatum. Shanxi J Trad Chin Med. 2022;38(3):29–31.
 © 2023 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2023 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.