Back to Journals » Infection and Drug Resistance » Volume 14
The Effect of Talaromyces marneffei Infection on CD86 Expression in THP-1 Cells
Authors Yang D , Shen L, Chen R , Fu Y, Xu H, Zhang L, Liu D
Received 21 December 2020
Accepted for publication 31 January 2021
Published 19 February 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 651—660
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S297160
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Di Yang,1,* Lin-xia Shen,1,2,* Ri-feng Chen,1,* Yu Fu,1 Hong-yan Xu,1 Li-na Zhang,1 Dong-hua Liu1,3
1Department of Dermatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, 530021, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200040, People’s Republic of China; 3Guangxi Key Laboratory of AIDS Prevention and Treatment, School of Public Health, Nanning, 530021, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Correspondence: Dong-hua Liu
Department of Dermatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, No.6, Shuangyong Road, Qingxiu District, Nanning, Guangxi Province, 530021, People’s Republic of China
Email [email protected]
Background: Talaromyces marneffei (T. marneffei) is a destructive opportunistic dimorphic fungal which can cause lethiferous Talaromycosis, but the clearance of T. marneffei mainly depends on the innate immune response.
Objective: To investigate whether T. marneffei can inhibit the expression of CD86 in THP-1 cells after infection and discuss the potential mechanisms.
Methods: Western blot and immunoelectron microscopy were used to detect the CD86 expression on T. marneffei cultured on BHI medium at 37°C. Western blot, enzyme-linked immunoassay and immunofluorescence were used to detect the change of CD86 expression on macrophages incubating with T. marneffei. Enzyme-linked immunoassay was used to detect the content of CD86 in supernatant in the co-culture system. Immunohistochemistry and immunoelectron microscopy were used to detect the expression of CD86 on T. marneffei incubating with macrophages.
Results: T. marneffei did not express CD86 when cultured separately at 37°C detected by Western blot and immunoelectron microscopy, but it did express CD86 when incubated with macrophages detected by immunohistochemistry and immunoelectron microscopy. The CD86 expression of macrophages significantly decreased at 72 hours when infected with T. marneffei while the content of CD86 in supernatant significantly increased at 72 hours compared with the control group which were detected by Western blot, enzyme-linked immunoassay and immunofluorescence.
Conclusion: 1) After T. marneffei infection, CD86 expression on THP-1 decreased, and with the progression of infection, insufficient polarization of M1 macrophages gradually appeared; 2) T. marneffei may adsorb or uptake CD86 in supernatant produced by macrophages during the contact with THP-1 cells, thus leading to the consumption of CD86 in macrophages.
Keywords: Talaromyces marneffei, T. marneffei, macrophages, CD86, THP-1, immunoelectron microscopy
Introduction
Talaromyces marneffei is a destructive opportunistic and dimorphic fungal which can cause lethiferous Talaromycosis. It is a facultative intracellular pathogen, inhalation of aerosolized conidia from the environment is the main route of infection, the conidia convert to fission yeast in the respiratory tract which is called pathogenic phase. The number of T. marneffei in HIV-negative patients is increasing year by year from the extensive application of organ transplantation, chemotherapy, immunosuppressive agents, tumor targeting and other therapies.1 Host macrophages respond to microbial insults and prevent the spread of infection, as they do in T. marneffei infection. T. marneffei grows as a fission yeast inside the macrophages while appearing extra cellularity as elongated arthroconidia-like yeast cells. It changes into pathogenic state at body temperature (37°C) which activates mononuclear macrophages, then get killed and cleared by heat, oxidative substances and acid released by macrophages. Reproduction in host immune cell phagocytes is an excellent survival strategy for this facultative intracellular pathogen to evade the adaptive immune response. T. marneffei has a series of self protection mechanism against the lethal effect on macrophage, such as MAPK signal cascade, melanin molecule, heat shock protein, binary conversion, laccase, cytochrome P450, modification of gene expression and so on, which causes macrophages fragmentation, and the spread of infection.2–4 With the progress of T. marneffei infection, macrophage pattern recognition receptors and risk-related molecular pattern receptors are activated, secret a variety of anti-inflammatory factors, and up-regulating CD86 on macrophages which is beneficial for host elimination of T. marneffei. At the same time macrophages can also secrete high level co-stimulating molecule CD80/CD86 as antigen-presenting cells (APCs), binding with corresponding ligands on the surface of Th cells, promoting cytotoxic T cell activation and thus eliminate T. marneffei.5
CD86, also known as B7-2, Freeman first cloned the cDNA sequence and named it in 1989, then he discovered its important co-stimulatory effect.6 CD86 is mainly expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as dendritic cells (DCs), mononuclear macrophages, endothelial cells, memory T lymphocytes and activated B lymphocytes, which is consistent with the role as a critical costimulatory molecule in the initial steps of T cell activation. CD86 is also a surface marker of M1 macrophage polarization at the same time. When phagocytized by macrophages, LPS and IFN-γ derived from pathogens would polarize macrophages into inflammatory phenotypes, surface marker for M1 increased, and the anti-inflammatory ability of macrophages highly enhanced.
In our previous experiment, we accidentally found that the conidia of T. marneffei were CD86 positive detected by immunohistochemistry in the lesions of HIV-positive patients. Repeated immunohistochemical staining of CD86, CD163 and CD1a confirmed that the expression of CD86 on conidia was common rather than incidental in both HIV-negative and HIV-positive patients. Therefore, we considered that T. marneffei conidia in skin lesions of infected patients can express glycoproteins which are similar to human CD86. We were curious about where was CD86 on conidia came from, so we proposed two inferences. The first was that T. marneffei expressed CD86 itself, and the other was that T. marneffei can adsorb or uptake CD86 from macrophages.
Materials and Methods
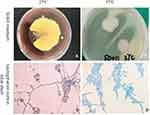
T. marneffei strain used in our study was isolated from skin lesion of patient with Talaromycosis through the routine hospital laboratory procedure, which was approved by the Ethics Committee of the first Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University (Nanning, China). The strain was cultured at 25°C and 37°C for 7 days for morphological identification (Figure 1). The DNA was extracted for PCR amplification and agarose gel electrophoresis, the ITS1 primer sequence was forward 5ʹ- TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3ʹ and ITS4- primer sequence was forward 5ʹ-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3ʹ. The amplified products were identified by deoxyribonucleic acid sequencing of the fungal internal transcribed spacer region.
A model of vitro T. marneffei infection with M1 macrophages was constructed in our research (Figure 2). THP-1 cells are human monocytes, which can differentiate into macrophages under the induction of PMA. The THP-1 cell line used in this study was purchased from Cell Bank, Chinese Academy of Sciences. THP-1 cells were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium (RPMI 1640, Gibco, Thermo Fisher, USA) for subculture containing 10% of heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (Gibco, Thermo Fisher, USA) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin solution (100U/mL penicillin G, 0.1mg/mL streptomycin sulfate, Solarbio, China). THP-1 cells were differentiated into macrophages by incubating with 50ng/μL PMA (Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, Meilunbio, China) for 48 hrs in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM, Gibco, Thermo Fisher, USA) which contained 10% of heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin-streptomycin solution. Macrophages polarized to M1 macrophages under the stimulation of 100 ng/μL LPS (Meilunbio, China) and 20ng/μL IFN-γ (Novoprotein, China) for 24 hrs. At this time, T. marneffei infected M1 macrophages at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 5 at 37°C for 24, 48 and 72 hrs respectively, the cells and supernatant were collected for subsequent experiments. M1 macrophages in DMEM without T. marneffei were used as control group.
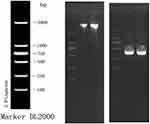 |
Figure 2 The DNA electrophoresis results (left) and the electrophoresis result of PCR amplification products (right). |
To verify the first inference, the expression of CD86 on T. marneffei conidia without incubation with M1 macrophages were detected by Western blot and immune-electron microscopy (IEM). T. marneffei conidia cultured on BHI medium at 37°C for 7 days were used separately to IEM and Western blot. T. marneffei conidia were grinded in liquid nitrogen, and the proteins were released in the cleavage of yeast buster proteins extraction reagent (Merck, Germany) for Western blot. T. marneffei conidia were fixed, embedded and marked for IEM.
To verify the other inference, the expression of CD86 on conidia was detected by IEM and IHC after incubating with M1 macrophage. The changes of CD86 expression of co-culture system were detected by WB, IF and ELISA.
Western Blotting (WB)
Cellular proteins were lysed by RIPA (Cell Signaling, USA) on ice and boiled for 5 mins before adding sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) buffers. Proteins were isolated on SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to PVDF membrane for non-specific antibody sealing with 5% skim milk. Antibody labeling was performed in PVDF membrane in turn. Primary antibody (Rabbit anti-CD86 antibody from Abcam, UK), β-actin antibody (Rabbit polyclonal to beta-actin from Abcam, USA), second antibody (Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H+L (HRP) from Engibody, USA). Finally, the protein bands were photographed by chemiluminescence and calculated quantitatively by Image J.
Immunofluorescence (IF)
Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 mins at room temperature. Blocking non-specific antibody with PBS which contained 0.1% Triton-X 100 and 1% FBS at room temperature for 20 mins. For labeling, cells were incubated overnight at 4°C with the primary antibody (Rabbit anti-CD86 antibody from Abcam, UK). The negative control group was incubated with PBS instead of primary antibody. After three times washing with PBS, cells were incubated for 1 hr avoiding light at room temperature with second antibody (Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L), Alexa Fluor 488 AffiniPure from YASEN, China). The images were then observed and collected under the confocal microscope, the fluorescence intensities were calculated quantitatively by Image J.
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
The content determination of CD86 in macrophages and supernatant was assayed by using a double-antibody sandwich ELISA kit (Bioss, China).
Immune Electron Microscopy (IEM)
Cells were fixed overnight with a phosphate buffer (PH=7.2) of 4% paraformaldehyde and 1% glutaraldehyde, and dehydrated with a gradually high concentration of ethanol. Cells were embedded with Lowicrys K4M resin and polymerized under UVA at −20°C. The cells were ultra-thin sectioned to a thickness of 50–70nm, incubated with the primary antibody (Mouse anti-CD86/B7-2 from NOVUS, USA) and second antibody (6nm Colloidal Gold AffiniPure Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) from Jackson Immuno Research, USA) on a nickel net. The images were observed and collected under a transmission electron microscope after conventional staining.
Immunohistochemical (IHC)
Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 mins at room temperature. Blocking non-specific antibody with PBS which contained 0.1% Triton-X 100 and 1% FBS at room temperature for 20 mins. For labeling, cells were incubated overnight at 4°C with the primary antibody (Rabbit anti-CD86 antibody from Abcam, UK) and for 1 hr at room temperature with the second antibody (Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG HRP from Abcam, UK). Finally, the target protein appears brown under the reaction against 3,3ʹ-diaminobenzidine (DAB). The negative control group was incubated with PBS instead of primary antibody. The images were then observed and collected under the light microscope.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical software SPSS 22.0 was used for analysis. The counting data were represented by chi-square test, and measurement data were represented by mean± standard deviation (X±SD). Comparison between groups was performed by independent sample T test, and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Ethics Statement
The authors confirm that the ethical policies of the journal, as noted on the journal’s author guidelines page, have been adhered to.
Results
Morphological Changes of T. marneffei and M1 Macrophages
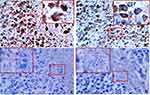
The morphological characteristics of the isolates were consistent with T. marneffei (Figure 1). The sequence alignment of PCR amplified products (Figure 2) showed that the similarity of DNA between the isolates and T. marneffei was 99%. The morphological changes of M1 macrophages during T. marneffei infection were observed under an optical microscope (Figure 3). M1 macrophages phagocytized T. marneffei after infection. With the prolongation of the infection process, the gemmation of conidia and mycelia increased (Figure 3B), nutrient consumption in supernatant increased, the macrophages deformation, disintegration and death increased (Figure 3B, D and F) compared with the control group (Figure 3A, C and E).
Detection of CD86 Expression of T. marneffei Separately Cultured at 37°C
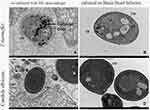
The proteins of T. marneffei were extracted for Western blotting, and M1 macrophages were used as the control group, but there was no positive band of 80kd (Figure 4). Immunoelectron microscopy was used to detect the expression of CD86 of T. marneffei and the control group (candida albicans), no colloidal gold particles were found either on T. marneffei or candida albicans growing at 37°C BHI. The same was true when candida albicans co-cultured with macrophages (Figure 5B, C and D). These results disproved the first inference that T. marneffei itself express CD86.
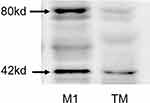 |
Figure 4 CD86 expression of T. marneffei protein was detected by Western blot. There was no positive band of 80kd compared with the protein from M1 macrophage. |
Changes of CD86 Expression of the Co-Culture Model
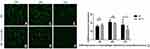
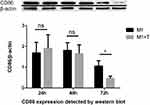
The immunofluorescence, Western blot and Elisa both showed that there was no significant difference of macrophages CD86 expression between the infection group and the control group at 24 and 48 hrs (nsp >0.05). But the expression of CD86 on macrophages was significantly decreased when infected with T. marneffei at 72 hours compared with the control group (*p < 0.05) (Figures 6A–G, 7 and 8A, B). The Elisa showed that there was no significant difference in the content of CD86 in supernatant between the infection group and the control group at 24 and 48 hrs (nsp >0.05). But it was significantly increased when infected with T. marneffei at 72 hours compared with the control group (*p < 0.05) (Figure 8A and B). With the progression of infection, the surface marker for M1 macrophages decreased indicated that insufficient polarization of M1 macrophages gradually appeared.
Detection of CD86 Expression on T. marneffei Incubated with Macrophages
Colloidal gold particles were specifically adsorbed on T. marneffei after co-culturing with M1 macrophages for 24 hours detected by IEM (Figure 5A). Macrophages and T. marneffei were CD86 positive (Figure 9A and B) but CD163 (Figure 9C) and CD1a (Figure 9D) negative detected by immunohistochemistry. These results suggested that T. marneffei expressed CD86 when incubating with M1 macrophages.
Discussion
The skin and mucous membranes are the first defense of the host against microbial infection, once the physical barrier is broken, neutrophils and macrophages provide the first cellular line of defense against pathogens. Polarization is one of the ways for macrophages to fight pathogen invasion. The pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) of macrophages are activated after microbial exposure.7,8 Macrophage polarization has been classically clustered into two major types, classically activated macrophages (M1) and alternatively activated macrophages (M2). The strictly clear-cut dichotomy between M1 and M2 does not always exist because of the complex pathogenic mechanism of bacteria, fungi, viruses, parasites,9 which means M1/M2 interconversion occurs continuously with the local concentration of cytokines in the host or with the depletion of a certain type of macrophages. At the early stage of T. marneffei infection, it has a similar effect to bacterial lipopolysaccharide and can induce M0 macrophages to differentiate into M1 macrophages. However, with the progression of infection, macrophages initiated the anti-inflammatory mechanism, and the surface markers of M2 macrophages (Arg-1, CD206) gradually increased while M1 markers (TNF-α, CD86) decreased.10,11 We considered that T. marneffei may absorb or uptake soluble CD86 that secreted into the supernatant by M1 macrophages through some unknown mechanism during M1/M2 cell conversion.
T cells mainly undertake cellular immune function and CD4+T cells are stimulated to differentiate into Th1 cells or Th2 cells. The reduction of CD4+T cells is a common phenomenon in HIV or non-HIV patients with T. marneffei infection.12 The binding of B7 molecules to different ligands results in the difference of Ca2+ influx, thus affecting the activation state of T cells. The interaction between CD86 and CD28 provides the signals needed to trigger the activation, expansion and differentiation of T cells, which increased Th1 cells differentiation. The decrease of CD86 costimulatory molecular signal may lead to the inactivation and lack of proliferation of cytotoxic T cells in the host. The CD80/CD86 co-stimulation pathway plays an important role in regulating Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation, mouse models have shown that knocking out CD86 and CD80 results in the decrease of IFN-γ and increase of IL-4.13 We considered that the adsorption or uptake of CD86 by T. marneffei may be related to the antigen presentation of APC. CTLA-4 and CD28 on T cells share two ligands (CD86 and CD80), Qureshi and his colleagues had discovered that CTLA-4 can capture CD86 from antigen-presenting cells by a process of trans-endocytosis.14 We speculated that T. marneffei, like CTLA-4, may also intend to deplete extracellular CD86, which will reduce the binding of CD28 to CD86 and inhibit Th1 cell activation, escape the killing of immune cells eventually.
Homologous proteins expression of microorganisms is rare except for leishmania. After studying 33 cases of leishmaniasis, including L.tropica and L.large Leishmaniasis, Jabbour et al15,16 found that cultured promastigotes were CD1a negative, but amastigotes in papillary dermal were CD1a strong and diffuse positive. They believed that leishmania amastigotes acquired CD1a from dendritic cells during the interaction with an inflammatory response. We speculated that T. marneffei, like amastigotes absorbed CD86 from macrophages when phagocytosed by first contact macrophages. Once the antigen clearance was insufficient, CD86+T. marneffei would spread to nearby organs along with macrophages, and produce more CD86+ T. marneffei.
In the immunoelectron microscope experiment, the cell wall of the co-cultured T. marneffei was thinner, the structure was looser, the cytoplasm was more dispersed, and the organelle structure was fuzzier compared with that of the single-cultured T. marneffei (Figure 5A and B), which indicated that the immune clearance of macrophages had a significant killing effect on T. marneffei. The ideal comparison of T. marneffei is histoplasma capsulatum, followed by cryptococcus, leishmania, and candida albicans, which are difficult to distinguish under light microscopy because of their similar size and shape. But why we chose candida albicans as the control in IEM? Previous research had found that histoplasma capsulatum has an inhibitory effect on the innate immune system, cryptococcus and leishmania will induce macrophages to M2 differentiation.17,18 Candida albicans and T. marneffei both promote macrophages to M1 differentiation, causing CD86 and immunoactive substance increase,10,19 so candida albicans was selected as the control of T. marneffei in immunoelectron microscopy after overall consideration. Colloidal gold particles were neither on Candida albicans cultured separately at 37°C nor co-cultured with macrophage detected by IEM (Figure 5C and D).
Finally, our research is just a pilot study for the CD86 positive expression of T. marneffei after infecting with macrophage, further experiments will be needed to explore the specific mechanism.
Conclusion
1) After T. marneffei infection, CD86 expression of THP-1 decreased, and with the progression of infection, insufficient polarization of M1 macrophages gradually appeared; 2) T. marneffei may adsorb or uptake CD86 in supernatant produced by macrophages during contact with THP-1 cells, thus leading to the consumption of CD86 in macrophages.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank all the researchers for your hard work and dedication to the research. I would like to thank Raqib Khan for revising the grammar of this article.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81760564).
Disclosure
The authors report conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Lee PP, Lau YL. Cellular and molecular defects underlying invasive fungal infections-revelations from endemic mycoses. Front Immunol. 2017;8:735. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.00735
2. Pongpom M, Vanittanakom P, Nimmanee P, Cooper CR
3. Payne M, Weerasinghe H, Tedja I, Andrianopoulos A. A unique aspartyl protease gene expansion in Talaromyces marneffei plays a role in growth inside host phagocytes. Virulence. 2019;10(1):277–291. doi:10.1080/21505594.2019.1593776
4. Chen R, Ji G, Xi L, et al. Role of autophagy in regulating the immune response of dendritic cells to Talaromyces marneffei infection. Microb Pathog. 2018;123:120–125. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2018.06.044
5. Tang Y, Zhang H, Xu H, et al. Dendritic cells promote treg expansion but Not Th17 generation in response to talaromyces marneffei yeast cells. Infect Drug Resist. 2020;13:805–813. doi:10.2147/IDR.S239906
6. Freeman GJ, Gribben JG, Boussiotis VA, et al. Cloning of B7-2: a CTLA-4 counter-receptor that costimulates human T cell proliferation. Science. 1993;262(5135):909–911. doi:10.1126/science.7694363
7. Li Z, Scott MJ, Fan EK, et al. Tissue damage negatively regulates LPS-induced macrophage necroptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23(9):1428–1447. doi:10.1038/cdd.2016.21
8. Zhang Y, Liang C. Innate recognition of microbial-derived signals in immunity and inflammation. Sci China Life Sci. 2016;59(12):1210–1217. doi:10.1007/s11427-016-0325-6
9. Atri C, Guerfali FZ, Laouini D. Role of human macrophage polarization in inflammation during infectious diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(6):1801. doi:10.3390/ijms19061801
10. Lu S, Li D, Xi L, Calderone R. Interplay of interferon-gamma and macrophage polarization during Talaromyces marneffei infection. Microb Pathog. 2019;134:103594. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103594
11. Smith TD, Tse MJ, Read EL, Liu WF. Regulation of macrophage polarization and plasticity by complex activation signals. Integr Biol. 2016;8(9):946–955. doi:10.1039/c6ib00105j
12. Li YY, Dong RJ, Shrestha S, et al. AIDS-associated Talaromyces marneffei central nervous system infection in patients of southwestern China. AIDS Res Ther. 2020;17(1):26. doi:10.1186/s12981-020-00281-4
13. Li JG, Du YM, Yan ZD, et al. CD80 and CD86 knockdown in dendritic cells regulates Th1/Th2 cytokine production in asthmatic mice. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(3):878–884. doi:10.3892/etm.2016.2989
14. Qureshi OS, Zheng Y, Nakamura K, et al. Trans-endocytosis of CD80 and CD86: a molecular basis for the cell-extrinsic function of CTLA-4. Science. 2011;332(6029):600–603. doi:10.1126/science.1202947
15. Jabbour MN, Issa G, Charafeddine K, et al. The immune microenvironment in cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29(6):1170–1179. doi:10.1111/jdv.12781
16. Sundharkrishnan L, North JP. Histopathologic features of cutaneous leishmaniasis and use of CD1a staining for amastigotes in old world and new world leishmaniasis. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44(12):1005–1011. doi:10.1111/cup.13032
17. Ray SC, Rappleye CA. Flying under the radar: histoplasma capsulatum avoidance of innate immune recognition. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019;89:91–98. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.03.009
18. Eastman AJ, He X, Qiu Y, et al. Cryptococcal heat shock protein 70 homolog Ssa1 contributes to pulmonary expansion of Cryptococcus neoformans during the afferent phase of the immune response by promoting macrophage M2 polarization. J Immunol. 2015;194(12):5999–6010. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1402719
19. Guan X-H, Hong Y-X, Qi R-Q, Gao X-H. Keratinocytes contribute to the recruitment and M1 polarisation of macrophages during C. albicans colonisation. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-Grand). 2018;64(12):15–21. doi:10.14715/cmb/2018.64.12.4
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.