Back to Journals » Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment » Volume 14
Safety and effectiveness of rapid-acting intramuscular olanzapine for agitation associated with schizophrenia – Japan postmarketing surveillance study
Authors Katagiri H, Taketsuna M, Kondo S, Kajimoto K, Aoi E, Tanji Y
Received 24 July 2017
Accepted for publication 11 October 2017
Published 12 January 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 265—272
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S147124
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Taro Kishi
Video presented by Hideaki Katagiri
Views: 2821
Hideaki Katagiri,1 Masanori Taketsuna,2 Shinpei Kondo,3 Kenta Kajimoto,4 Etsuko Aoi,5 Yuka Tanji1
1Bio Medicine, 2Statistical Sciences, 3Post Marketing Study Management, 4Scientific Communications, Medicines Development Unit Japan, 5Global Patient Safety Japan, Quality and Patient Safety, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Kobe, Japan
Objective: The objective of this study was to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of rapid-acting intramuscular (IM) olanzapine in the treatment of acute agitation associated with schizophrenia in real-world clinical settings in Japan.
Methods: In this multicenter, postmarketing surveillance (PMS) study, patients with acute agitation associated with schizophrenia were treated with IM olanzapine daily in a daily clinical setting. The observational period ranged from 1 to 7 days, including the day of initial administration. Safety was assessed by reporting treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and adverse drug reactions (ADRs). The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale – Excited Component (PANSS-EC) score was used to evaluate effectiveness at baseline and at 2 hours (after each administration), 2 days, and 3 days (end of the observational period) from the last administration of the IM olanzapine injection.
Results: The safety analysis set included 999 patients, and the initial dose of 10 mg was administered to 955 patients. TEAEs were reported in 28 patients (36 events), the most common of which were dyslalia (5 patients), akathisia and somnolence (4 patients each), hepatic function abnormal (3 patients), and constipation and dehydration (2 patients each). One serious adverse event of akathisia occurred during the observation period. The PANSS-EC score (mean ± standard deviation) was 23.3±6.4 (n=625) at baseline, 16.9±7.0 (n=522) at 2 hours after initial injection, and 14.9±6.5 (n=650) at the last observation carried forward.
Conclusion: The results of this Japanese PMS study demonstrated that IM olanzapine is safe and has a favorable effectiveness profile in the treatment of schizophrenia patients with acute agitation.
Keywords: agitation, Japanese, postmarketing surveillance study, rapid-acting intramuscular olanzapine, schizophrenia, PANSS-EC
Introduction
Schizophrenia is a chronic, remitting, and relapsing psychiatric disorder that is associated with significant dysfunction and increased mortality.1–3 Agitation is commonly reported during an acute psychotic episode, and severe agitation may be accompanied by verbal and physical aggression. Patients may engage in forms of violence that can pose a danger to themselves or to others.4,5 Therefore, it is important to rapidly treat agitated patients in order to facilitate rapid alleviation of symptoms.
In order to secure the safety of patients and caregivers, intramuscular (IM) olanzapine was developed for the rapid tranquilization of patients with acute agitation associated with schizophrenia, and it was approved first as a rapid-acting, atypical, antipsychotic parenteral drug in Japan in 2012. Oral administration of medications is often preferable to parenteral administration,6 and orally disintegrating tablets and liquid medication were frequently used in the treatment of acute schizophrenia. However, oral administration may be difficult in patients with acute agitation. In these cases, patients may sometimes refuse treatment or treatment may need to be managed with the help of other people or by physically controlling the patient.7 Parenteral (IM or intravenous) administration of treatment can enable more rapid onset of drug action, thereby leading to a faster improvement in symptoms7–9 to calm agitated patients refusing oral medications.
IM olanzapine is one of the first chosen drugs among parenteral formulations used for the treatment of acute-phase schizophrenia.10,11 From the expert consensus survey from physicians who joined the Japanese Association for Emergency Psychiatry, olanzapine (45%), haloperidol (22%), and haloperidol + biperiden (17%) were selected as the first choice of IM injection for the treatment of psychotic acute agitation.9 In addition, meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials reported that IM olanzapine is preferred over IM haloperidol because of the lower risk of extrapyramidal syndromes (EPS).12 Although IM olanzapine is one of the first-line agents for the treatment of acute agitation associated with schizophrenia in Japan, evidence from daily clinical setting of its safety and effectiveness is limited.13 Clinical trials are conducted under strict conditions with many inclusion and exclusion criteria that may not be directly applicable to daily clinical practice, where drugs are administered to patients with varied clinical histories and circumstances.14 Thus, observational studies are useful for assessing the safety and effectiveness of interventions in real-world clinical settings. Here, we provide an evaluation of the clinical utility of rapid-acting IM olanzapine from the results of a postmarketing surveillance (PMS) study in the treatment of patients with acute agitation associated with schizophrenia.
Methods
Study design
This was a multicenter PMS study with a 3-day observation period that included the initial day of administration. When patients were administered additional IM olanzapine during the observation period, this observational period was extended by another 3 days. The maximum observational period was 7 days, including the initial day of administration. A total of 1,016 case report forms were collected from patients at 192 sites across Japan. This PMS study was conducted between May 1, 2013, and April 30, 2016, using a continuous registration method. The study was mandated by the Japan Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and was conducted in accordance with the Good Postmarketing Study Practice of the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law of Japan. The Japanese regulatory authority does not require informed consent to be obtained from patients in postmarketing observational studies; hence, informed consent was not obtained from these patients.
Study population
The participants were patients with schizophrenia who had psychomotor agitation and had received the rapid-acting IM injection formulation of olanzapine. The dose of administration of IM olanzapine was decided at the physician’s discretion and in consideration of the approved prescribing information in Japan, where the recommended dose of 10 mg is administered as a single IM injection. When the effect was insufficient, up to 10 mg of a single IM injection could be administered in addition at an interval of ≥2 hours after the previous administration up to 2 times daily, including additional administration. Dosage reduction had to be considered according to age and symptoms.15
Patients were excluded from the study if they had contraindications to IM olanzapine as listed in the package insert,15 specifically comatose state; if they were under the effect of central nervous system depressants, such as barbiturate derivatives; if they had a medical history of hypersensitivity to any ingredients of IM olanzapine; and if they currently used adrenaline. Considering the safety and effectiveness, the evaluable population included patients who had received at least one dose of IM olanzapine. For the effectiveness of population, patients who were administered olanzapine for off-label use were excluded from the analyses.
Safety evaluation
Safety was assessed by the reporting of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and adverse drug reactions (ADRs), defined as among TEAEs for which causal relation to olanzapine could not be excluded. All TEAEs and ADRs were reported by treating physicians. Recorded TEAEs and ADRs were classified using preferred terms and system organ classes according to the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA; version 19.1, MedDRA MSSO, McLean, VA, USA).31
Effectiveness evaluation
The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale – Excited Component (PANSS-EC)16 score was measured at baseline and at 2 hours (after each administration). Additionally, the PANSS-EC score was measured at 2 days and 3 days (end of the observational period) from the last administration of the rapid-acting IM olanzapine injection.
Statistical analysis
Patient characteristics were summarized by frequency tables with summary statistics. In the analysis, continuous variables were evaluated with summary statistics using mean and standard deviation (SD) values. Categorical variables, including binary variables, were evaluated using frequencies and proportions. For the safety analyses, the incidence of ADRs was listed. For the efficacy analyses, PANSS-EC was measured at baseline and each follow-up period, and this was summarized using mean and SD values. Changes from baseline to each follow-up period were assessed using the 2-sided 95% confidence intervals (CIs). All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS Version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
Results
Baseline patient characteristics
A total of 1,016 case report forms were collected from patients, and the safety analysis set included 999 patients, of whom 998 were included in the effectiveness analysis set (Figure 1). For the effectiveness analysis set, one patient was excluded due to off-label use: patients with psychiatric disorders caused by stimulants. The major patient baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1. In the safety analysis set, the mean age ± SD was 46.1±15.3 years. A total of 860 (86.1%) patients were <65 years, 103 (10.3%) patients were ≥65 to <75 years, and 36 (3.6%) patients were ≥75 years of age. A total of 514 (51.5%) patients were women and 485 (48.5%) were men. The mean ± SD duration of schizophrenia was 17.5±13.5 years. In all, 20 (2.0%) patients reported having a family member with a history of diabetes, and 65 (6.5%) patients had diabetes-related complications (DRDC). A total of 914 (91.5%) patients reported taking a concomitant medication, with the most common concomitant medications being psychotropic drugs (90.9%; antipsychotics [88.9%], benzodiazepine [38.1%]; Table 1). Concomitant medication was defined as medication that was administered during the observation period and a day before the observation period. Oral olanzapine was also defined as concomitant medication, because the target medication for this study was rapid-acting IM olanzapine.
  | Figure 1 Disposition of patients. |
At the initial dose of IM olanzapine, 848 (84.9%) patients were hospitalized (Table 1). The initial dose of IM olanzapine was 2.5 mg in 1 (0.1%) patient, 5.0 mg in 39 (3.9%) patients, 7.5 mg in 1 (0.1%) patient, and 10 mg in 955 (95.6%) patients (Table 2). IM olanzapine was administered more than once within 24 hours of each injection in 110 (11.0%) patients. The most prevalent injection site was the gluteal region in 526 (52.7%) patients, followed by the shoulder in 335 (33.5%) patients throughout the study period (Table 2).
Safety evaluation
TEAEs were reported in 28 patients (36 events) among 999 patients in the safety analysis set. Reported TEAEs (≥2 patients) were dyslalia (5 patients), akathisia and somnolence (4 patients each), hepatic function abnormal (3 patients), and constipation and dehydration (2 patients each; Table 3). ADRs were reported in 19 patients (26 events). Specifically, reported ADRs (≥2 patients) were dyslalia (5 patients), somnolence (4 patients), akathisia and hepatic function abnormal (3 patients each), and constipation (2 patients; Table 3). One serious adverse event (0.1%) of akathisia occurred during the observation period. This patient (outpatient) remitted after administration of IM olanzapine and returned home. However, the patient returned to the hospital because of itching, which was judged as akathisia. The patient fell asleep and was hospitalized at the discretion of the physician. The next day, the patient did not experience the event.
  | Table 3 Occurrence of ADRs and TEAEs |
For diabetic-related complications, of the 999 patients, 65 had DRDCs, including high HbA1c and high blood glucose during this study. The number of patients with DRDCs who reported TEAEs was 5 (7.7%), and those who reported ADRs was 4 (6.2%). Among them, abnormal blood glucose was reported as a diabetes-related TEAE, not ADR.
Table 4 shows the details of the use of IM olanzapine on each day (Days 1–7) of the observation period. A total of 28 (2.8%) patients reported TEAEs, and of these, 22 (2.8%) patients who had any TEAE were administered one dose of IM olanzapine. In addition, 6 (2.9%) patients who reported TEAEs were administered ≥2 doses of IM olanzapine (Table 4).
  | Table 4 Safety summary by injection pattern |
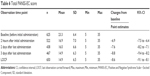
Parenteral (ie, intravenous or IM) benzodiazepine and antipsychotic drug were used in 12 and 60 patients, respectively. One (8.3%) patient who used parenteral benzodiazepine experienced 1 TEAE (pneumonia aspiration), and 4 (6.7%) patients who used a parenteral antipsychotic drug experienced 4 TEAEs (dehydration, dystonia, somnolence, and blood creatine phosphokinase increased); no serious event was reported. In addition, oral benzodiazepine, oral antipsychotic drug, and oral olanzapine were used in 375, 529, and 547 patients, respectively (Table 5). In all, 16 (4.3%) patients who took oral benzodiazepine, 14 (2.6%) patients who took oral antipsychotic drug, and 17 (3.1%) patients who took oral olanzapine experienced 23, 16, and 25 TEAEs, respectively; no serious event was reported (Table 5).
  | Table 5 TEAEs by concomitant use of benzodiazepine and antipsychotic drugs |
Effectiveness evaluation
The mean ± SD total PANSS-EC score was 23.3±6.4 (n=625) at baseline (before initial administration), 16.9±7.0 (n=522) 2 hours after initial administration, and 14.9±6.5 (n=650) at the final observation (with the last observation carried forward [LOCF] approach). A significant improvement in the total PANSS-EC score was observed 2 hours after administration of the initial dose, and the score was maintained through the end of the observational period (Table 6). In addition, the PANSS-EC subscores of excitement, hostility, tension, uncooperativeness, and poor impulse control were improved 2 hours after administration (Figure 2).
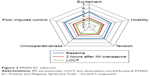  | Figure 2 PANSS-EC subscore. |
Discussion
This postmarketing study confirms the safety and effectiveness of rapid-acting IM olanzapine in treating schizophrenia patients with agitation in real-world clinical settings. The mean PANSS-EC score before the start of treatment was 23.3, indicating that our patients treated with IM olanzapine daily had a similar degree of agitation if compared with participants in other clinical trials (PANSS-EC: 23.5 and 21.1)17,18 and naturalistic studies (PANSS-EC: 26.5 and 28.0).19,20
The analyses of this PMS study revealed that IM olanzapine was mainly administered to patients hospitalized (84.9%) and in most clinical trials that investigated antipsychotic treatment among inpatients with agitation.21,22 The recommended starting dose of olanzapine as a single IM injection is 10 mg in patients with agitation associated with schizophrenia.15 In this PMS study, the initial dose was primarily 10 mg, and treatment was completed with a single dose in ~80% of patients, thus indicating overall proper usage of IM olanzapine in our clinical settings. The remaining ~20% of patients had consecutive administration; however, no serious adverse events were reported.
There was a low incidence of TEAEs (2.8%, 28/999 patients). The most common adverse events were dyslalia (0.5%), akathisia (0.4%), and somnolence (0.4%). Although somnolence is one of the most common adverse events reported17,23 in the rapid-acting IM olanzapine treatment, a previous study has shown that there were no significant differences in the somnolence rates between patients treated with olanzapine versus placebo.17 A previous study showed no incidence of treatment-emergent akathisia in Japanese patients treated with IM olanzapine for schizophrenia-related acute agitation,17 and another observational study reported that the adverse event of akathisia is very rare in patients receiving parenteral olanzapine in the emergency department.24 In addition, this study showed no particular concern about safety in patients administered daily with rapid-acting IM olanzapine or with concomitant medications.
This PMS study included 20 (2.0%) patients with a history of diabetes in a family member and 65 (6.5%) patients with complications related to diabetes. Previous studies have reported an increased risk of developing diabetes during treatment with antipsychotics such as olanzapine.25–27 However, this PMS study showed that only one patient reported a diabetes-related ADR who had diabetic complications at baseline. Even though the population with diabetic complications at baseline was small in this study, we did not highlight that treatment with rapid-acting IM olanzapine potentially increased the risk of diabetes-related adverse events. As previously recommended, it can be useful to monitor patients who are at a higher risk of developing diabetes during treatment with antipsychotics such as olanzapine.26,27
Previous studies have shown that IM olanzapine is effective without the addition of benzodiazepines22 and that coadministration of IM olanzapine with benzodiazepine may increase the risk of somnolence.28 It is reported that a Lilly-maintained safety database (estimated worldwide patient exposure to IM olanzapine, N=539,000) was searched for all spontaneous adverse events reported in temporal association with olanzapine IM treatment.29 The report found 83 cases that were considered as serious, including 29 fatalities, and in these fatalities, concomitant benzodiazepines were reported in 66% of cases and indicated that clinicians should use caution when using IM olanzapine and parenteral benzodiazepines simultaneously. Although there were no remarkable serious cases in this PMS, it is important to use much caution when treating agitated patients concomitantly with parental benzodiazepines.
Previous clinical trials reported a significant improvement from baseline in PANSS-EC scores 2 hours after IM olanzapine.17,28,30 Similar results were seen in this PMS study, where there was an improvement in the PANSS-EC total score and in all 5 subitems when comparing changes from baseline to 2 hours after the IM olanzapine injection.
There are various limitations in the interpretation of results from this PMS study. Owing to the noninterventional observational nature of this study, baseline characteristics varied among participants, and it is possible that many unrecognized confounding factors, such as concomitant medications, may have affected the results of the analyses, thus making it challenging to determine a potential increase in risk following treatment with the study drug. In addition, it is common to have missing values in an observational study. Another major limitation is the lack of a control group and the presence of only one cohort in which patients were not randomized.
Conclusion
This study confirms the safety and effectiveness of rapid-acting IM olanzapine, administered daily, in the treatment of schizophrenia patients with agitation, providing valuable information from real-world clinical settings.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all patients, physicians, and paramedics who participated in this study. Medical writing assistance was provided by Deborah D’Souza, PhD, inVentiv Health Clinical, LLC, who was funded by Eli Lilly Japan K.K. This study was sponsored by Eli Lilly Japan K.K.
Disclosure
All the authors are employees of Eli Lilly Japan K.K. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Bushe CJ, Taylor M, Haukka J. Mortality in schizophrenia: a measurable clinical endpoint. J Psychopharmacol. 2010;24(4 suppl):17–25. | ||
Tandon R, Keshavan MS, Basrallah HA. Schizophrenia, “Just the Facts”: what we know in 2008 part 1: overview. Schizophr Res. 2008;100(1–3):4–19. | ||
Fagiolini A, Goracci A. The effects of undertreated chronic medical illnesses in patients with severe mental disorders. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70(suppl 3):22–29. | ||
Lehman AF, Lieberman JA, Dixon LB, et al. American Psychiatric Association: Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Schizophrenia. 2nd ed. Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing Inc; 2010. | ||
Marco CA, Vaughan J. Emergency management of agitation in schizophrenia. Am J Emerg Med. 2005;23(6):767–776. | ||
Hasan A, Falkai P, Wobrock T, et al. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) Guidelines for Biological Treatment of Schizophrenia, part 1: update 2012 on the acute treatment of schizophrenia and the management of treatment resistance. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2012;13(5):318–378. | ||
Mohr P, Pecenák J, Svestka J, Swingler D, Treuer T. Treatment of acute agitation in psychotic disorders. Neuro Endocinol Lett. 2005;26(4):327–335. | ||
Dahl SG. Pharmacokinetics of antipsychotic drugs in man. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1990;358:37–40. | ||
Toyoaki Hirata T, Sugiyama N. The Japanese Association for Emergency Psychiatry. Guideline, 2015. Chiba: The Japanese Association for Emergency Psychiatry; 2015. Available from: http://www.jaep.jp/gl/2015_all.pdf. Accessed June 12, 2017. | ||
American Psychiatric Association. Practice guidelines for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia. 2nd ed. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association; 2004. | ||
Allen MH, Currier GW, Carpenter D, Ross RW, Docherty JP. Expert Consensus Panel for Behavioral Emergencies 2005. The expert consensus guideline series. Treatment of behavioral emergencies 2005. J Psychiatr Pract. 2005;11(suppl 1):5–108. | ||
Kishi T, Matsunaga S, Iwata N. Intramuscular olanzapine for agitated patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;68:198–209. | ||
Suzuki H, Gen K. A naturalistic comparison of the efficacy and safety of intramuscular olanzapine and intramuscular levomepromazine in agitated elderly patients with schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2013;9:1281–1287. | ||
Rogers AS. Adverse drug events: identification and attribution. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1987;21(11):915–920. | ||
Zyprexa [prescribing information] [webpage on the Internet]. Kobe: Eli Lilly Japan K.K; 2017. Available from: http://www.info.pmda.go.jp/go/pack/1179408E1020_1_06/. Accessed June 12, 2017. | ||
Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A, Ramirez PM, Opler M, White L. Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) Technical Manual. North Tonawanda: Multi-Health System Inc.; 2006. | ||
Katagiri H, Fujikoshi S, Suzuki T, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of rapid-acting intramuscular olanzapine in Japanese patients for schizophrenia with acute agitation. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13:20. | ||
Huang CL, Hwang T, Chen Y, et al. Intramuscular olanzapine versus intramuscular haloperidol plus lorazepam for the treatment of acute schizophrenia with agitation: an open-label, randomized controlled trial. J Formos Med Assoc. 2015;114(5):438–445. | ||
San L, Arranz B, Querejeta I, Barrio S, De La Gándara J, Pérez V. A naturalistic multicenter study of intramuscular olanzapine in the treatment of acutely agitated manic or schizophrenic patients. Eur Psychiatry. 2006;21(8):539–543. | ||
Walther S, Moggi F, Horn H, et al. Rapid tranquilization of severely agitated patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders a naturalistic, rater-blinded, randomized, controlled study with oral haloperidol, risperidone, and olanzapine. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014;34(1):124–128. | ||
Wilson MP, Pepper D, Currier GW, Holloman GH Jr, Feifel D. The psychopharmacology of agitation: consensus statement of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry Project BETA Psychopharmacology Workgroup. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(1):26–34. | ||
Breier A, Meehan K, Birkett M, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled dose-response comparison of intramuscular olanzapine and haloperidol in the treatment of acute agitation in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2002;59(5):441–448. | ||
Kinon BJ, Ahl J, Rotelli MD, McMullen E. Efficacy of accelerated dose titration of olanzapine with adjunctive lorazepam to treat acute agitation in schizophrenia. Am J Emerg Med. 2004;22(3):181–186. | ||
Cole JB, Moore JC, Dolan BJ, et al. A prospective observational study of patients receiving intravenous and intramuscular olanzapine in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 2017;69(3):327.e2–336.e2. | ||
Carlson C, Hornbuckle K, DeLisle F, Kryzhanovskaya L, Breier A, Cavazzoni P. Diabetes mellitus and antipsychotic treatment in the United Kingdom. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2006;16(5):366–375. | ||
Kessing LV, Thomsen AF, Mogensen UB, Andersen PK. Treatment with antipsychotics and the risk of diabetes in clinical practice. Br J Psychiatry. 2010;197(4):266–271. | ||
Lambert BL, Cunningham FE, Miller DR, Dalack GW, Hur K. Diabetes risk associated with use of olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone in veterans health administration patients with schizophrenia. Am J Epidemiol. 2006;164(7):672–681. | ||
Kittipeerachon M, Chaichan W. Intramuscular olanzapine versus intramuscular aripiprazole for the treatment of agitation in patients with schizophrenia: a pragmatic double-blind randomized trial. Schizophr Res. 2016;176(2–3):231–238. | ||
Marder SR, Sorsaburu S, Dunayevich E, et al. Case reports of postmarketing adverse event experiences with olanzapine intramuscular treatment in patients with agitation. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;71(4):433–441. | ||
Suzuki H, Gen K, Takahashi Y. A naturalistic comparison of the efficacy and safety of intramuscular olanzapine and intramuscular haloperidol in agitated elderly patients with schizophrenia. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2013;3(6):314–321. | ||
ICH. Introductory guide MedDRA version 19.1. McLean, VA: MedDRA; 2016. Available from: https://www.meddra.org/sites/default/files/guidance/file/intguide_19_1_english.pdf. Accessed November 27, 2017. |
 © 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.