Back to Journals » Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management » Volume 16
Machine Learning to Predict the 1-Year Mortality Rate After Acute Anterior Myocardial Infarction in Chinese Patients
Authors Li Y , Jiang L, He J, Jia K, Peng Y , Chen M
Received 29 October 2019
Accepted for publication 20 December 2019
Published 9 January 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 1—6
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S236498
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Deyun Wang
Yi-ming Li, 1,* Li-cheng Jiang, 2,* Jing-jing He, 1 Kai-yu Jia, 1 Yong Peng, 1 Mao Chen 1
1Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Cardiology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Chengdu Medical College, Chengdu, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Correspondence: Yong Peng; Mao Chen
Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, 37 Guoxue Street, Chengdu 610041, People’s Republic of China
Email [email protected]; [email protected]
Abstract: A formal risk assessment for identifying high-risk patients is essential in clinical practice and promoted in guidelines for the management of anterior acute myocardial infarction. In this study, we sought to evaluate the performance of different machine learning models in predicting the 1-year mortality rate of anterior ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients and to compare the utility of these models to the conventional Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) risk scores. We enrolled all of the patients aged > 18 years with discharge diagnoses of anterior STEMI in the Western China Hospital, Sichuan University, from January 2011 to January 2017. A total of 1244 patients were included in this study. The mean patient age was 63.8± 12.9 years, and the proportion of males was 78.4%. The majority (75.18%) received revascularization therapy. In the prediction of the 1-year mortality rate, the areas under the curve (AUCs) of the receiver operating characteristic curves (ROCs) of the six models ranged from 0.709 to 0.942. Among all models, XGBoost achieved the highest accuracy (92%), specificity (99%) and f1 score (0.72) for predictions with the full variable model. After feature selection, XGBoost still obtained the highest accuracy (93%), specificity (99%) and f1 score (0.73). In conclusion, machine learning algorithms can accurately predict the rate of death after a 1-year follow-up of anterior STEMI, especially the XGBoost model.
Keywords: machine learning, prediction model, acute anterior myocardial infarction
Corrigendum for this paper has been published
Introduction
As a well-known dangerous disease, acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is associated with a high incidence of mortality and morbidity.1 Compared with patients with other sites of AMI, patients with anterior wall infarctions suffer from a greater risk of death and cardiovascular events. From previous reports, the 1-year mortality rate after anterior AMI ranges from 6–10%.2 A formal risk assessment for identifying high-risk patients is essential in clinical practice and promoted in guidelines for the management of AMI. Traditionally, the most commonly used risk assessment tools are derived from the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI)3 and Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE).4 These risk scores were developed from conventional statistical methods and are accompanied by some inherent limitations from missing value imputation, feature selection, model development and validation.
Machine learning is a method that combines data science and statistical techniques to give computers the ability to learn from training set and solve the task without being explicitly programmed. The path of machine learning avoids priori assumptions of the model, which may offer additional knowledge and information. This method has been gradually applied in clinical practice and in the field of cardiology. Each algorithm has its own strength in different fields. In this study, we sought to evaluate the performance of different machine learning models (including naïve Bayes (NB), logistic regression, k nearest neighbours (KNN), decision tree, random forest and XGBoost) in predicting the 1-year mortality rate of anterior ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients and to compare the utility of these models to the conventional GRACE risk score risk scores.
Method
This study was conducted with a hospital-based dataset. We consecutively enrolled aged >18 years patients with discharge diagnoses of acute anterior wall myocardial infarctions in the Western China Hospital, Sichuan University, from January 2011 to January 2017. The patients with anterior STEMI were eligible for inclusion if they were restricted to participants with 1) ischemic chest discomfort that increased or occurred at rest; 2) ST segment elevation ≥ 0.1 mV in ≥2 contiguous anterior leads; 3) elevated cardiac troponin I levels (≥0.03 μg/L) or elevated cardiac troponin T levels (≥42 ng/L).5 The collection of patient data included the demographic information, baseline characteristics at admission, diagnosis and treatment during hospitalization, discharge diagnoses and medication, and approximately 59 features. The follow-up period ended in January 2018. The follow-up information was collected through contact with the patients’ physicians and patients or their families. These inclusion and exclusion criteria were met by 1305 anterior STEMI patients enrolled from the database. After excluding patients who were lost to follow-up (n = 61), 1244 patients were included in the data analysis. The baseline demographics and clinical characteristics were compared between the non-surviving patients and survivors after a 1-year follow-up. Continuous variables are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD), and categorical variables are reported as counts and percentages. T-tests and chi-squared tests were used to evaluate the differences in continuous and categorical variables between groups, respectively. The GRACE risk score used to analyse mortality has been described previously, and the calculation was performed following the published formula.
Six machine learning classifiers (GaussianNB, logistic regression, KNN, decision tree, random forest and XGBoost) were both supervised methods and applied to predict the survival status after a 1-year follow-up. The supervised learning aims to build the concise models of the distribution of class outcomes (in machine learning, called labels) in terms of predictor parameters.6 All models were validated with 10-fold cross-validation. In feature engineering, all the categorical features were transformed by one-hot encoding, and the missing value was imputed by the missForest method,7 which had a noticeable improvement in performance compared to traditional methods such as multiple imputation with chained equations. For feature importance ranking, we use two tree-based methods, random forest and XGBoost. The performance of the model was defined by the following metrics: area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC), sensitivity, specificity and f1 score.
Data analyses were performed using Python (version 3.7) with the scientific libraries “scikit-learn”, “XGBoost” and Stata (Release 15. College Station, TX: StataCorp LLC).
Results
From January 2011 to January 2017, a total of 1244 patients were included in this study. The mean patient age was 63.8±12.9 years, and the proportion of males was 78.4%. The majority (985, 75.18%) received reperfusion therapy. The average follow-up period was 36.7 months. There were 185 patients who died within 1 year after admission (mortality rate was 14.87%). The baseline characteristics of this study population were stratified according to patients who survived until the 1-year period and those who died. The differences in demographic information, baseline characteristics of admission, and treatment during hospitalization between the two groups are summarized in Table 1. The details of all 59 features are listed in are list in supplement 1.
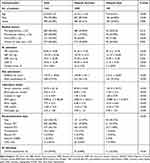 |
Table 1 Clinical Characteristics of the Study Population |
Six machine learning algorithms (GaussianNB, logistic regression, KNN, decision tree, random forest and XGBoost) were developed to predict the overall 1-year mortality rate post STEMI with all available features. All the hyperparameters of the models were set carefully following the tutorials or preliminary experiment. The XGBoost classifier (AUC=0.942) outperformed the other models in terms of the ROC cross validation results (logistic regression (AUC=0.931), Gaussian naïve Bayes (AUC=0.924), KNN (AUC=0.709), decision tree (AUC=0.772), random forest (AUC=0.932)) (Figure 1). The other metrics of each model are summarized in Table 2. XGBoost also achieved the highest accuracy (92%), specificity (99%) and F1 score (0.74). Regarding sensitivity, the Gaussian naïve Bayes (77%) and random forest (75%) algorithms performed better than the other models. The AUC of the GRACE risk score was 0.794, and the metrics are summarized in Table 2.
 |
Figure 1 ROC analysis result of six classifiers for the prediction of 1-year mortality with all available features. Abbreviation: ROC, receiver operating characteristic curve. |
 |
Table 2 Comparison of Validation Results of Six Machine Learning Models |
Moreover, we selected the repeat features with top-20 feature-ranking with the random forest and XGBoost methods, including the following 15 variables: New York Heart Association (NYHA) Classification at discharge, heart failure at admission, heart rate, age, left ventricular ejection fraction, serum cystatin, initial BNP, Platelet, Fibrinogen, Blood creatinine, blood glucose, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, total bilirubin, blood urea nitrogen, and revascularization type. The ROC analysis results of each model are presented in Figure 2, in which the random forest method showed the highest AUC (0.943). However, the XGBoost still showed the highest accuracy (92%), specificity (99%) and f1 score (0.73) (Table 2).
 |
Figure 2 ROC analysis result of six classifiers for the prediction of 1-year mortality with 20 top features. Abbreviation: ROC, receiver operating characteristic curve. |
Discussion
Although STEMI is associated with a poor prognosis and a high incidence of death and cardiovascular events, especially those located in the anterior wall, it is still difficult to predict the long-term outcomes of these patients. Usually, the GRACE risk score is used to estimate the follow-up outcomes after acute coronary syndrome, and the 2.0 version expanded upon the original version for long-term prediction. However, these traditional assessment tools were derived from statistical methods. In these Cox proportional hazards regression models, the researcher carried pre-assumptions and performed subjective feature selection before model fitting, which thus may lead to a loss of potential knowledge.
The idea of machine learning has been gradually applied for medical data analysis or image recognition. In the current study, we compared six popular supervised algorithms and investigated the utility of machine learning for predicting the 1-year mortality rate of a Chinese myocardial infarction population. In two previous articles, the random forest method demonstrated better prediction ability for short-term mortality after STEMI than the other machine learning classifiers (without XGBoost).8,9 However, we found a noticeable improvement in the prediction ability of the XGBoost algorithm in both the full variable model and after feature ranking selection compared with other machine classifiers and conventional risk scores. Although both algorithms are based on decision trees as random forests, XGBoost is derived from boosting rather than bagging. This method powerfully reduces variance and reduces bias.10 As a novel algorithm published in 2016, XGBoost has gained wide popularity in the data science community. Recently, numerous reports have demonstrated that this method can be generalized and has robustness in clinical practice.11,12 Moreover, the high accuracy of this model from our work also confirmed this opinion.
Our work has several limitations due to the retrospective design of the study. The patient enrolment and data collection processes may be accompanied by selection or measurement bias, and we could not evaluate the effect of the model on direct interventions. Furthermore, this is a single-centre study that included only Chinese patients. Nonetheless, the results of the cross-validation analysis of the machine learning model still provides an effective and robust method for predicting the 1-year mortality rate of patients after anterior STEMI.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study was conducted after the acquisition of written informed consent from the participating patients and upon the approval by the ethics committee of West China Hospital, Sichuan University. The study protocol was approved by the local institutional review boards in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Acknowledgment
We thank Dr. Zhuo-lun Li from Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Tandon School of Engineering, New York University, New York, US, for providing the assistance of statistics and debugging in Python work.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Rasoul S, Ottervanger JP, de Boer MJ, et al. Predictors of 30-day and 1-year mortality after primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Coron Artery Dis. 2009;20(6):415–421. doi:10.1097/MCA.0b013e32832e5c4c
2. Kennedy HL, Goldberg RJ, Szklo M, Tonascia JA. The prognosis of anterior myocardial infarction revisited: a community-wide study. Clin Cardiol. 1979;2(6):455–460. doi:10.1002/clc.v2:6
3. Morrow DA, Antman EM, Charlesworth A, et al. TIMI risk score for ST-elevation myocardial infarction: A convenient, bedside, clinical score for risk assessment at presentation: an intravenous nPA for treatment of infarcting myocardium early II trial substudy. Circulation. 2000;102(17):2031–2037. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.102.17.2031
4. Fox KA, Dabbous OH, Goldberg RJ, et al. Prediction of risk of death and myocardial infarction in the six months after presentation with acute coronary syndrome: prospective multinational observational study (GRACE). BMJ. 2006;333(7578):1091. doi:10.1136/bmj.38985.646481.55
5. Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: the Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2017;39(2):119–177.
6. Kotsiantis SB. Supervised machine learning: a review of classification techniques.
7. Stekhoven DJ, Bühlmann P. MissForest—non-parametric missing value imputation for mixed-type data. Bioinformatics. 2011;28(1):112–118. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr597
8. Shouval R, Hadanny A, Shlomo N, et al. Machine learning for prediction of 30-day mortality after ST elevation myocardial infraction: an Acute Coronary Syndrome Israeli Survey data mining study. Int J Cardiol. 2017;246:7–13. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.05.067
9. Li X, Liu H, Yang J, Xie G, Xu M, Yang Y. Using machine learning models to predict in-hospital mortality for ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2017;245:476–480.
10. Chen T, Guestrin C. XGBoost.
11. Polano M, Chierici M, Dal BM, et al. A pan-cancer approach to predict responsiveness to immune checkpoint inhibitors by machine learning. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(10). doi:10.3390/cancers11101562
12. Chen T, Li X, Li Y, et al. Prediction and risk stratification of kidney outcomes in IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019;74(3):300–309. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.02.016
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
