Back to Journals » Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment » Volume 13
Effects of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation on emotional working memory capacity and mood in patients with Parkinson's disease
Authors Merkl A, Röck E, Schmitz-Hübsch T, Schneider G, Kühn AA
Received 2 November 2016
Accepted for publication 31 January 2017
Published 19 June 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 1603—1611
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S126397
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Roger Pinder
Angela Merkl,1,2 Eva Röck,1 Tanja Schmitz-Hübsch,1,3 Gerd-Helge Schneider,4 Andrea A Kühn1,3,5
1Department of Neurology, Charité – University Medicine Berlin, Campus Virchow Klinikum, 2Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Charité – University Medicine Berlin, Campus Benjamin Franklin, 3NeuroCure, Charité – University Medicine Berlin, 4Department of Neurosurgery, Charité – University Medicine Berlin, Campus Virchow Klinikum, 5Berlin School of Mind and Brain, Charité – University Medicine Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Background: In Parkinson’s disease (PD), cognitive symptoms and mood changes may be even more distressing for the patient than motor symptoms.
Objective: Our aim was to determine the effects of bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation (STN-DBS) on working memory (WM) and mood.
Methods: Sixteen patients with PD were assessed with STN-DBS switched on (DBS-ON) and with dopaminergic treatment (Med-ON) compared to switched off (DBS-OFF) and without dopaminergic treatment (Med-OFF). The primary outcome measures were a Visual Analog Mood Scale (VAMS) and an emotional 2-back WM task at 12 months after DBS in the optimal DBS-ON/Med-ON setting compared to DBS-OFF/Med-OFF.
Results: Comparison of DBS-OFF/Med-OFF to DBS-ON/Med-ON revealed a significant increase in alertness (meanoff/off =51.59±24.54; meanon/on =72.75; P=0.016) and contentedness (meanoff/off =38.73±24.41; meanon/on =79.01±17.66; P=0.001, n=16), and a trend for reduction in sedation (P=0.060), which was related to stimulation as shown in a subgroup of seven patients. The N-back task revealed a significant increase in accuracy with DBS-ON/Med-ON compared to DBS-OFF/Med-OFF (82.0% vs 76.0%, respectively) (P=0.044), regardless of stimulus valence.
Conclusion: In line with previous studies, we found that patients rated themselves subjectively as more alert, content, and less sedated during short-term DBS-ON. Accuracy in the WM task increased with the combination of DBS and medication, possibly related to higher alertness of the patients. Our results add to the currently mixed results described for DBS on WM and suggest that there are no deleterious DBS effects on this specific cognitive domain.
Keywords: deep brain stimulation, Parkinson’s disease, working memory, neuropsychiatric
Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a disorder of basal ganglia (BG) circuit function. Cognitive impairments, including working memory (WM) deficits in PD, are thought to result from loss of ascending dopaminergic projections to prefrontal cortex (pfC) terminal fields, particularly those in lateral pfC.1 In PD, cognitive symptoms and mood changes may be even more distressing for the patient than motor symptoms.2 Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation (STN-DBS) is an established treatment for motor complications in advanced PD, which alleviates dyskinesia and improves quality of life.3 Studies on neuropsychiatric changes after STN-DBS are still heterogeneous. There is evidence that, in addition to the motor loop, other cortico-BG-thalamocortical loops that are associated with cognitive (dorsolateral and lateral orbitofrontal loops) and emotional function (anterior cingular loop) may be affected by DBS by current spread, leading to changes in cognition and emotion.1 The subthalamic nucleus is part of the hyperdirect pathway, which connects regions of the frontal cortex to the BG and may be critical in supporting integrative functions of BG-thalamo-cortical circuits through rapid inhibition of thalamo-cortical pathways.4 Evaluation of cognition and mood in STN-DBS has yielded several results. STN-DBS itself has been associated with decrements in focal neuropsychological domains, including reductions in WM, lexical fluency, and learning and recall efficiency.5 However, this is not consistently reported as other studies report unchanged,6,7 improved or reduced memory, attention, and executive functions after STN-DBS8 in PD. In particular, reports on WM are mixed. Whereas some investigators have reported WM improvements9 together with increased psychomotor speed,10 others have shown either no change or worsening of WM.11
Two possible hypotheses currently exist. Changes in mood and cognition might be due to spread of current to adjacent pathways and regions within the STN mediating non-motor function,12 or they may be due to lesions along the trajectory for STN-DBS with the lead location near the head of the caudate nucleus.13 The STN-DBS lead trajectory passes through the pfC, the subcortical white matter, the anterior limb of the internal capsule, and the BG; it was recently shown13 that passage of the chronic lead through the head of the caudate increases the risk of global cognitive decline. These structures are all involved in cognitive or emotional functions, and the STN itself subdivides into a motor but also a limbic and an associative part.2 Moreover, patients with PD can have non-motor mood symptoms related to: dopaminergic deficit (ie, due to reduction in dopaminergic medication after the DBS and to the progression of the disease and continued loss of dopaminergic projections) affecting the mesolimbic system (such as apathy, anxiety, depression, pain – hypodopaminergic syndrome) and dopaminergic overdose (impulse control disorders, punding – hyperdopaminergic syndrome).2 Deficits in verbal fluency and WM appear early in the disease course of PD, and are present in mildly depressed PD patients as well as those with moderate to severe depression. Previous studies suggest that decline in these cognitive functions varies in relationship to the severity of depression.14 Costa et al14 showed that patients with PD and major depression performed significantly worse than those without depression on measures of episodic and WM, abstract reasoning, and visuospatial abilities. PD patients with minor depression showed some impairment in these tasks, but they did not reach statistical significance. Moreover, neuropsychological dysfunction increases with increasing severity of depression in PD patients and is primarily linked to dysexecutive function. Furthermore, it is likely that a common neuropathological process involving the BG, limbic system, thalamus and their connections with the dorsolateral pfC, orbitofrontal cortex, and the anterior cingulate underlies both depression and executive dysfunction in PD.15 So far, there are several studies evaluating the effects of STN-DBS on mood. First, studies that investigated mood effects during STN-DBS switched on (DBS-ON) or switched off (DBS-OFF) in PD and studies examining mood before and after STN-DBS surgery, respectively. DBS-ON correlated with prefrontal oxygenated hemoglobin changes relative to DBS-OFF in a mood-eliciting near-infrared spectroscopy study in response to both positive and negative videos.16 These changes were specific to emotional stimuli and were not seen during neutral stimuli, and results may suggest that STN stimulation influences the prefrontal cortical representation of positive and negative emotions.16 In a study by Eisenstein et al,17 PD participants with STN-DBS, who had been diagnosed with current mood disorders, experienced greater STN-DBS-induced improvement in mood. However, Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) and anxiety scores did not modulate this mood response to STN-DBS, rather the categorical diagnosis of mood disorders. Some studies have found reduced depression, apathy and psychiatric symptoms with DBS-ON relative to DBS-OFF. Case studies demonstrate that some patients experience adverse changes in mood-related behavior with STN-DBS, including fits of laughter, hypomania, and severe transient depression.17 A review on STN-DBS-induced changes in non-motor symptoms (NMS) in PD showed that the number and the severity of most NMS decrease after STN-DBS, which can have a major impact on patients’ quality of life.18
Our aim was to determine STN-DBS-induced short-term changes (DBS-ON vs DBS-OFF) in emotional WM and mood after bilateral STN-DBS. We chose an emotional WM task to investigate the effect of salient stimuli on WM performance. We correlated symptom severity, ie, the BDI-II, with performance in WM.
Material and methods
Subjects
We assessed 16 non-demented patients (seven women; mean age 61.50±7.31 [range 49–72] years; mean disease duration 10.88±4.48 [range 3–19] years) with PD who had undergone STN-DBS for severe PD motor fluctuations and were treated with chronic DBS for at least 12 months. Demographic and clinical data are shown in Table 1. Surgical implantation of the leads (bilaterally in the STN) and the neurostimulation was performed as previously described.19 The DBS electrode used was model 3,389 (Medtronic Neurological Division) with four platinum-iridium cylindrical surfaces (1.27 mm diameter and 1.5 mm length) and a contact-to-contact separation of 0.5 mm. Contact 0 was the most caudal and contact 3 was the most rostral. Electrode implantation was performed according to the standard procedures of the surgical center. The intended coordinates for the STN were 12 mm lateral from the midline, 3 mm behind the mid-commissural point, and 4 mm below the anterior commissure–posterior commissure line. Adjustments to the intended surgical coordinates were made according to direct visualization of the STN on individual pre-operative (pre-op) stereotactic T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Post-operative (post-op) MRI was performed in all patients to confirm targeting and suggested that at least one contact was within the STN. After surgery, dopamine agonists were withdrawn and levodopa (L-dopa) was reduced according to the improvement in motor state with DBS (Table 1). Written informed consent was obtained from the patients, and the ethics committee of the Charité University-Medicine in Berlin approved the study. In terms of psychotropic medications, one patient was taking clonazepam, one patient was taking citalopram (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor), and one patient was taking antipsychotic medication (quetiapine) at the time of the study. No other psychotropic medications were reported. Other medications are shown in Table 1.
Questionnaires
Subjects were assessed on the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) part III motor scale, the revised edition BDI-II,20 and the Mattis Dementia Rating Scale (MDRS)21 pre-op and 12 months post-op. Depressive symptom burden was defined as a BDI-II score above 17 points. The threshold for detecting depression can vary according to the type of patients.22 We set the threshold above 14 up to 17 to detect mild clinical depression in PD patients. To our knowledge, a cutoff of 17 for the BDI-II has good sensitivity and specificity to detect clinical depression. Using the MDRS,21 cognitive decline was defined as an MDRS score <130 (Table 1).
VAMS
The Visual Analog Mood Scale (VAMS)23 was applied to define short-term mood changes during each condition and was developed to evaluate current subjective mood state. We used a 16-item VAMS developed by Bond and Lader,23 which has been used in PD patients with STN-DBS24 and to examine the short-term effects on mood of STN-DBS-ON vs DBS-OFF.25 This scale was chosen because it was easy for participants to understand and complete and is repeatable over several sessions. The VAMS covers a wide range of moods, including most of the basic moods, and has been shown to be sensitive to changes in mood state in response to a range of drugs that are known to affect motor performance. It also includes somatic and alertness items, which may be relevant to STN-DBS. The 16 items are loaded onto three psychometrically-validated factors: “Alert-Sedated” (alert, strong, clear-headed, well-coordinated, energetic, quick-witted, attentive, proficient, interested), “Contented-Discontented” (contented, tranquil, happy, amicable, gregarious) and “Calm-Sedated” (calm, sedated). Each of the items involves a 100 mm horizontal line with word pairs on both sides (eg, Alert-Sedated). Patients indicate the point along the horizontal line that best describes how they are currently feeling. The score for each mood ranges from 0 to 100, with 100 presenting a maximal level of that mood and zero representing a minimal level (or absence) of that mood.
WM task
Participants were presented an adapted version of an emotional N-back paradigm (EMOBACK)26 that requires participants to decide whether the current stimulus word matches the one presented here and two trials earlier (2-back). This paradigm involves a number of key processes within WM and reliably engages different dorsolateral prefrontal brain regions within a fronto-striatal network.26 The stimuli of the emotional N-back task consist of emotional words related to the distinct emotions, like sadness and joy, and neutral words and were drawn from the Berlin Affective Word List.27 So far, the EMOBACK task has not been used in patient populations with movement disorders. It has been validated in two studies. Weigand et al28 described lateralized effects of prefrontal repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on emotional WM in healthy participants. In a second study by Scheidegger et al,29 the authors investigated ketamine in healthy subjects and showed that ketamine modulates cognition-emotion interaction in the brain by inducing lateralized and valence-specific effects in emotion-related cortical midline regions, WM-related lateral prefrontal regions and insula. The EMOBACK task provides a novel means of studying the interface between WM and emotion. Participants performed four parallel versions (respective to the four stimulation/medication conditions) of the EMOBACK task 12 months after STN-DBS to exclude repetition and memory effects. Participants were trained prior to the start of the task. They were given up to three practice blocks (25 trials each) per condition, with feedback on their performance, until they demonstrated that they fully understood the task and their performance stabilized to a cut-off of over 50% probability in the N-back task. Reaction times (RTs) and accuracy measures were obtained for each trial. The task was programmed using Presentation software (Version 16.2, Neurobehavioral Systems Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA). The order of the DBS status was randomized and patients were assessed for each condition with the parallel sets of the EMOBACK task on different consecutive days and during the morning. Patients were pseudo-randomly assigned to one of four groups, to test the effects of DBS-ON or DBS-OFF and “with dopaminergic treatment” (Med-ON) or “without dopaminergic treatment” (Med-OFF) on VAMS and emotional WM. Half of the patients started with ON conditions.
Experimental set-up
All subjects were assessed on the UPDRS-III motor scale. On the morning of the DBS-OFF/Med-OFF testing, the neuropsychological evaluation started 30 minutes after the DBS device was switched off when a stable clinical status was achieved. It has been shown that about 75% of motor change occurs within 20 minutes after change of condition.30 Longer periods were not acceptable due to study constraints. Last dopaminergic drug intake was at least 12 hours before. On the day of DBS-ON/Med-ON testing, the neuropsychological evaluation started with a delay of 30 minutes after the last L-dopa intake and the initial motor score testing. The EMOBACK task was done in front of a computer. Participants were seated in a comfortable chair in a silent room, and the monitor was placed at eye level 90 cm from the patients. They were instructed to press, as quickly as possible, a button on the left of the computer’s keyboard if a target word was presented, and a button on the right side if a non-target word was presented. The duration of stimulus presentation was 1,000 ms, the interstimulus interval was 2,000 ms, and a total of 15 words, negatively valenced, neutral, or positively valenced were presented per run. In total, ten runs were presented. The words were presented as white uppercase letters in the center of a black screen. The VAMS was given to the patients after the N-back task was undertaken, using paper and a pen. Data on RTs of the EMOBACK task of three patients had to be discarded from the analyses in order to reduce the influence of outliers. Four patients had not properly filled out the VAMS and these questionnaires were discarded from analysis.
Statistical analysis
Questionnaires
All but the MDRS questionnaires were normally distributed (Shapiro-Wilk). As the number of pairs was small, we always compared the two most important randomized conditions, first the comparison DBS-ON/Med-ON vs DBS-OFF/Med-OFF and calculated the stimulation effect (DBS-ON/Med-OFF vs DBS-OFF/Med-OFF) if patients had participated in all four settings. 2×5 repeated measures (rm) ANOVA with two conditions (DBS-ON/Med-ON vs DBS-OFF/Med-OFF) and five VAMS variables (contentedness, discontent, calmness, alertness, sedation) with Bonferroni corrections for alpha error accumulation due to multiple testing were applied. Student’s t-test and, if normalization was not given, non-parametric tests (Mann–Whitney U test, exact Wilcoxon sign rank test) were applied. Emotional 2-back WM task: differences in accuracy and RTs between DBS-OFF and DBS-ON were analyzed by means of 2×3 rmANOVAs (two factors: 1. “stimulation condition”: DBS-ON/Med-ON vs DBS-OFF/Med-OFF; 2. “valence” with three conditions, negative × neutral × positive) and post hoc Bonferroni correction. Means and standard deviations are shown in results. Pearson’s bivariate correlations and Spearman-Rho correlations between mood, cognition, and motor scores were calculated.
Results
At 12 months post-op, patients showed significant improvement in motor symptoms with STN-DBS, with a significant mean reduction in UPDRS III of 50% (DBS-OFF meanpre-op =32.80±8.21; DBS-ON/Med-OFF meanpost-op =16.82±9.64; Student’s t-test, T=3.884; P=0.004). Group mean BDI was also significantly reduced with STN-DBS (DBS-OFF meanpre-op =11.55±5.12; DBS-ON/Med-OFF meanpost-op =8.0±5.17; T=2.512; P=0.036; 30% reduction). Post-op MDRS was available in 10/16 patients, with values that were similar to pre-op values (DBS-OFF meanpre-op =141.3±3.52; DBS-ON/Med-OFF meanpost-op =140.1±4.22; P=0.51). None of the patients reported cognitive decline with DBS (Table 1).
VAMS analysis DBS-ON/Med-ON vs DBS-OFF/Med-OFF
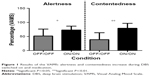
We found a significant main effect for stimulation condition (F(1,11) =7.693; P=0.018) and VAMS variables (F(4,8) =9.775; P=0.004) and a significant interaction effect between stimulation condition and VAMS variables (F(4,8) =5.868; P=0.017) (Figure 1). Post hoc analyses revealed a significant increase in contentedness (%) with DBS-ON/Med-ON compared to DBS-OFF/Med-OFF (meanoff/off =38.73±24.41; meanon/on =79.01±17.66; P=0.001, Bonferroni corrections; n=12) and a reduction of discontentedness (meanoff/off =44.11±17.37; meanon/on =26.04±20.43; F(df)1 =5.445; P=0.029). Furthermore, we revealed a significant increase in alertness (meanoff/off =51.59±24.54; meanon/on =72.75; F(df)1 =6.758; P=0.016) and a tendency for a significant reduction of sedation (meanoff/off =47.34±27.10; meanon/on =29.73±14.57; F(df)1 =3.92; P=0.060) for DBS-ON/Med-ON vs DBS-OFF/Med-OFF. The factor calmness was not significantly different between conditions (meanoff/off =59.07±12.29; meanon/on =61.03±8.23; F(df)1 =0.211; P=0.650).
Subpopulation analysis
In a subgroup of seven patients, a further analysis was done on DBS-ON/Med-OFF to disentangle the short-term effects of DBS and medication on mood. A significant stimulation effect was found for contentedness with DBS-OFF/Med-OFF vs DBS-ON/Med-OFF (meanoff/off =38.73±24.41; meanon/off =79.08±15.05; P=0.001, Bonferroni corrections; n=7), as well as an improvement in alertness (meanoff/off =49.88±21.04; meanon/off =64.85±24.25; Z=−2.366; P=0.018, n=7) and a reduction in sedation (meanoff/off =50.71±23.39; meanon/off =35.83±27.01; Z=−2.366; P=0.018, non-parametric, n=7).
Emotional N-back task
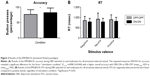
Table 2 and Figure 2 show accuracy and RT for both condition and emotional valence.
Emotional N-back task: accuracy
The rmANOVA for accuracy revealed a significant difference for the factor “stimulation condition” (F(1,14) =4.898; P=0.044), with a higher overall accuracy with DBS-ON vs DBS-OFF (meanon/on: 82% vs meanoff/off: 76%), but no significant difference between emotional valences (F(2,13) =0.319; P=0.732) and no significant interaction between condition and valence (F(2,13) =1.396; P=0.282).
Emotional N-back task: RTs
Overall, response times for negatively valenced words were faster (meanneg: 813.74±48.65 ms) compared to positive stimuli (meanpos: 851.85±56.15 ms; P=0.025; 95% confidence interval: −70.449, −5.769), regardless of stimulation condition.
Emotional N-back task: RT for correct responses
Similarly, the rmANOVA for RT of correct responses revealed no main effect for the factor stimulation condition (DBS-ON/Med-ON vs DBS-OFF/Med-OFF) (P=0.641) (Table 2). A significant main effect was observed for the factor emotional valence (P=0.026), but no significant interaction effect between stimulation condition and valence occurred (P=0.128). Patients showed faster response times for negative stimuli (meanneg: 808.58±49.51 ms) than for positive stimuli, regardless of stimulus condition (meanpos: 904.42±68.04 ms).
RT for incorrect responses
The rmANOVA for RT of incorrect responses revealed no main effect for stimulation condition (DBS-ON/Med-ON vs DBS-OFF/Med-OFF) (P=0.134) and no significant valence effect (P=0.520) or interaction (valence × condition) effect (P=0.723).
Comparison between correct and false responses revealed a significant effect (F(1,14) =29.122; P=0.000) with faster response times for correct responses (mean: 811.84±59.53 ms) compared to incorrect responses (mean: 1013.62±59.53 ms). There was no interaction effect between stimulation condition and correct/incorrect responses (F(1,14) =0.283; P=0.603).
To evaluate whether improved accuracy with DBS-ON for the WM task was directly related to increased alertness, we correlated the individual change in accuracy with change in the VAMS alertness, contentedness, and sedation score. However, we failed to show a direct relationship. There was no significant correlation between the improvement in accuracy in the WM task and the change in alertness (Spearman-rho =−0.185; P=0.586) after 12 months follow-up of DBS treatment. No significant correlations were found between the change in the self-rating questionnaire BDI-II and improvement in accuracy in the WM task (Spearman-rho =0.156; P=0.646), and no correlation between the change in MDRS and the improvement in accuracy (Spearman-rho =−0.289; P=0.339). The decrease in L-dopa-equivalent medication did not correlate with improvement in accuracy in the WM task (Spearman-rho =0.364; P=0.166). Moreover, changes in accuracy did not significantly correlate with age or disease duration.
Discussion
Our main results are that WM task performance improved with short-term STN-DBS. Patients with DBS-ON performed the task with a higher overall accuracy, regardless of the emotional valence of the stimuli. Response times were faster for negative than positive stimuli, regardless of stimulation condition. Furthermore, PD patients who were DBS-ON/Med-ON rated themselves subjectively as more alert and content compared to DBS-OFF/Med-OFF. Importantly, in a subgroup of patients this effect was induced by short-term STN-DBS alone.
It is noteworthy that PD patients without DBS treatment often suffer from impairments in executive functions, such as WM deficits, and the well-known dopamine depletion in the striatum probably contributes to these impairments through decreased connectivity between task-related brain networks.31 On the contrary, PD patients compared to controls have shown a compensatory increased activation in WM-related brain areas (ie, pfC) to maintain behavioral performance in the presence of network deficits.32 Our results demonstrate that task performance in the WM task may be modulated through DBS. Importantly, and in line with previous investigations, the cognitive effects observed in patients with PD following STN-DBS reflect the intrinsic role of the STN in non-motor domains. Previous research comparing two different targets, involving counterbalanced “ON” vs “OFF” stimulation following DBS for PD suggests that neurocognitive performance is slightly lower with DBS-OFF.10 Further large controlled studies and numerous cohort studies have demonstrated conflicting results on global cognitive abilities, attention, and memory and executive functions after STN-DBS.7,31,33 For example, a randomized, controlled trial of bilateral STN and globus pallidus internus (GPi)-DBS vs best medical treatment found that DBS patients experienced small decrements on measures of WM, processing speed and visual delayed recall.33 Selzler et al34 examined the effects of STN-DBS on motor disability and visual WM, with participants in the Med-OFF condition and DBS-ON or DBS-OFF, and concluded that DBS improved clinical motor function but had little effect on WM performance. Whereas some STN-DBS and GPi-DBS studies have reported WM improvements after treatment,9,10 others have shown either no change35 or worsening of WM.11,36 Electrode placement is critical with respect to non-motor function during STN-DBS. Preventing stimulation of the limbic and associative parts of the STN might help to reduce stimulation-induced behavioral side effects. Moreover, the passage of the chronic lead through the head of the caudate nucleus can increase the risk of global cognitive decline.13 In our study, we demonstrated improvement in accuracy and no changes in response times for WM during short-term DBS. On one hand, this might contradict an improvement in WM in PD patients due to DBS; on the other, it might exclude increased impulsivity due to DBS. Interestingly, our patients also showed higher alertness and contentedness during short-term DBS-ON, which could itself improve WM function. However, a direct relation of DBS-induced changes could not be shown. Following STN-DBS positron emission tomography studies have demonstrated increased blood flow to dorsolateral and motor regions of pfC in addition to the anterior cingulate,37 which may account for the motor benefits but might also account for WM improvement following DBS.
The impact of emotional content on WM has been examined in only a small number of studies, providing conflicting results. At the behavioral level in healthy subjects, negative stimuli were shown to have both impairing and facilitating38 effects on WM, while an improved performance was demonstrated for positive stimuli.39 Grimm et al26 showed that emotional stimuli in the context of a WM task yielded increased activation in WM-related lateral prefrontal regions, whereas cognitive effort enhanced deactivation in emotion-related cortical midline regions. Our results did not show a significant difference between the various emotional stimulus categories for PD patients after STN-DBS. The absence of difference between the emotional stimuli categories may be explained by the small sample size, ie, the lack of power of the statistical test.
Alertness and contentedness increased after STN-DBS. Subjectively perceived mood changes associated with STN-DBS are reported in both positive and negative directions.40 The direct effect of DBS on limbic-associative STN is thought to influence emotional modifications,41 ie, improvement in apathy with acute stimulation, acute well-being such as euphoria and a decrease in sedation, mania, and impulsive behavior in high conflict situations or aggressive behavior.41 The higher alertness and contentedness in our patients are in line with the general notion of STN stimulation-related increase in appetitive functioning, whereas long-term effects of chronic worsening of apathy have been related to reduction in dopamine replacement therapy.41
In contrast to a previous study,42 we did not find a correlation between age or disease duration with task performance, possibly due to small and rather homogenous sample size.
Several limitations of this study have to be addressed. A limitation is that we had no age-matched healthy control group. Although accuracy improved significantly during DBS-ON compared to DBS-OFF, the study could not make any conclusions about the improvement resulting from a genuine impairment in drug and DBS naïve patients. However, we compared the group against DBS-OFF/Med-OFF. In the same vein, due to this experimental set-up we could not draw conclusions upon differences between PD patients and controls for contentedness, discontentedness or alertness. Another important limitation is the fact that patients did not perform the emotion WM task with DBS-ON/Med-OFF. Therefore, we cannot show if the effect observed in this task was caused by the medication or electrical stimulation. A possible effect of the medication on this task could be a reduced speed due to sedation. However, we did not find any RT changes. A further limitation was that to improve precision, it would have been necessary to register electromyography on the finger muscle, which has been done in previous studies.43 Another limitation is the lack of a task evaluating only the finger motor speed, as control task was not applied. In addition, the use of self-report questionnaires, utilization of VAMS, and the small sample size make this study less representative.
In conclusion, we showed that STN-DBS can improve neurocognitive activity in fronto-striatal circuits, rather than detrimental effects. The differences in our study in neuropsychological outcomes of STN-DBS between conditions are small and they must be interpreted with caution given the small size of our sample. Future studies should investigate effects in patients under STN-DBS across different WM loads. However, the results of the current study are consistent with results from previous studies12,17,24,42 in identifying cognitive and mood changes after short-term STN-DBS. The present work adds further evidence for improvement in NMS of PD patients with STN-DBS.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG, grants KFO 247 and KU 2261/6-1) and “Rahel Hirsch Grant” to AM (Senat für Gesundheit und Soziales Berlin). We thank Julian Neumann for stimulus programming assistance and Axel Lipp for support with patient management.
Disclosure
AAK has received speakers honoraria from Medtronic, St Jude Medical, Boston Scientific. AAK is a consultant for Boston Scientific. GHS has received speakers honoraria from Medtronic, St Jude Medical. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Alexander GE, Crutcher MD. Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci. 1990;13(7):266–271. | ||
Castrioto A, Lhommee E, Moro E, Krack P. Mood and behavioural effects of subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(3):287–305. | ||
Limousin P, Krack P, Pollak P, et al. Electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in advanced Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(16):1105–1111. | ||
Mink JW. The basal ganglia: focused selection and inhibition of competing motor programs. Prog Neurobiol. 1996;50(4):381–425. | ||
Temel Y, Kessels A, Tan S, Topdag A, Boon P, Visser-Vandewalle V. Behavioural changes after bilateral subthalamic stimulation in advanced Parkinson disease: a systematic review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2006;12(5):265–272. | ||
Zangaglia R, Pasotti C, Mancini F, Servello D, Sinforiani E, Pacchetti C. Deep brain stimulation and cognition in Parkinson’s disease: an eight-year follow-up study. Mov Disord. 2012;27(9):1192–1194. | ||
Witt K, Daniels C, Reiff J, et al. Neuropsychological and psychiatric changes after deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: a randomised, multicentre study. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(7):605–614. | ||
Smeding HM, Speelman JD, Huizenga HM, Schuurman PR, Schmand B. Predictors of cognitive and psychosocial outcome after STN DBS in Parkinson’s Disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011;82(7):754–760. | ||
Mollion H, Dominey PF, Broussolle E, Ventre-Dominey J. Subthalamic nucleus stimulation selectively improves motor and visual memory performance in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2011;26(11):2019–2025. | ||
Pillon B, Ardouin C, Damier P, et al. Neuropsychological changes between “off” and “on” STN or GPi stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology. 2000;55(3):411–418. | ||
Saint-Cyr JA, Trepanier LL, Kumar R, Lozano AM, Lang AE. Neuropsychological consequences of chronic bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2000;123(Pt 10):2091–2108. | ||
Okun MS, Fernandez HH, Wu SS, et al. Cognition and mood in Parkinson’s disease in subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus interna deep brain stimulation: the COMPARE trial. Ann Neurol. 2009;65(5):586–595. | ||
Witt K, Granert O, Daniels C, et al, Relation of lead trajectory and electrode position to neuropsychological outcomes of subthalamic neurostimulation in Parkinson’s disease: results from a randomized trial. Brain. 2013;136(Pt 7):2109–2119. | ||
Costa A, Peppe A, Carlesimo GA, Pasqualetti P, Caltagirone C. Major and minor depression in Parkinson’s disease: a neuropsychological investigation. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13(9):972–980. | ||
Blonder LX, Slevin JT. Emotional dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Behav Neurol. 2011;24(3):201–217. | ||
Bick SK, Folley BS, Mayer JS, et al. Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation alters prefrontal correlates of emotion induction. Neuromodulation. Epub 2016 Oct 12. | ||
Eisenstein SA, Dewispelaere WB, Campbell MC, et al. Acute changes in mood induced by subthalamic deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease are modulated by psychiatric diagnosis. Brain Stimul. 2014;7(5):701–708. | ||
Klingelhoefer L, Samuel M, Chaudhuri KR, Ashkan K. An update of the impact of deep brain stimulation on non motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2014;4(2):289–300. | ||
Brucke C, Huebl J, Schonecker T, et al. Scaling of movement is related to pallidal gamma oscillations in patients with dystonia. J Neurosci. 2012;32(3):1008–1019. | ||
Beck AT, Steer RA, Ball R, Ranieri W. Comparison of Beck Depression Inventories-IA and -II in psychiatric outpatients. J Pers Assess. 1996;67(3):588–597. | ||
Mattis A. Dementia Rating Scale Professional Manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources; 1988. | ||
Wang YP, Gorenstein C. Psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory-II: a comprehensive review. Rev Bras Psiquiatr. 2013;35(4):416–431. | ||
Bond A, Lader M. The use of analogue scales in rating subjective feelings. British Journal of Medical Psychology. 1974;47(3):211–218. | ||
McDonald LM, Page D, Wilkinson L, Jahanshahi M. Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus improves sense of well-being in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2012;27(3):372–378. | ||
Campbell MC, Black KJ, Weaver PM, et al. Mood response to deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2012;24(1):28–36. | ||
Grimm S, Weigand A, Kazzer P, Jacobs AM, Bajbouj M. Neural mechanisms underlying the integration of emotion and working memory. Neuroimage. 2012;61(4):1188–1194. | ||
Vo ML, Conrad M, Kuchinke L, Urton K, Hofmann MJ, Jacobs AM. The Berlin Affective Word List Reloaded (BAWL-R). Behav Res Methods. 2009;41(2):534–538. | ||
Weigand A, Grimm S, Astalosch A, et al. Lateralized effects of prefrontal repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on emotional working memory. Exp Brain Res. 2013;227(1):43–52. | ||
Scheidegger M, Henning A, Walter M, et al. Effects of ketamine on cognition-emotion interaction in the brain. Neuroimage. 2016;124(Pt A):8–15. | ||
Temperli P, Ghika J, Villemure JG, Burkhard PR, Bogousslavsky J, Vingerhoets FJ. How do parkinsonian signs return after discontinuation of subthalamic DBS? Neurology. 2003;60(1):78–81. | ||
Volkmann J, Daniels C, Witt K. Neuropsychiatric effects of subthalamic neurostimulation in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010;6(9):487–498. | ||
Trujillo JP, Gerrits NJ, Veltman DJ, Berendse HW, van der Werf YD, van den Heuvel OA. Reduced neural connectivity but increased task-related activity during working memory in de novo Parkinson patients. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015;36(4):1554–1566. | ||
Weaver FM, Follett K, Stern M, et al. Bilateral deep brain stimulation vs best medical therapy for patients with advanced Parkinson disease: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009;301(1):63–73. | ||
Selzler K, Burack M, Bender R, Mapstone M. Neurophysiological correlates of motor and working memory performance following subthalamic nucleus stimulation. J Cogn Neurosci. 2013;25(1):37–48. | ||
Ardouin C, Voon V, Worbe Y, et al. Pathological gambling in Parkinson’s disease improves on chronic subthalamic nucleus stimulation. Mov Disord. 2006;21(11):1941–1946. | ||
Hershey T, Revilla FJ, Wernle A, Gibson PS, Dowling JL, Perlmutter JS. Stimulation of STN impairs aspects of cognitive control in PD. Neurology. 2004;62(7):1110–1114. | ||
Sestini S, Scotto di Luzio A, Ammannati F, et al. Changes in regional cerebral blood flow caused by deep-brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. J Nucl Med. 2002;43(6):725–732. | ||
Lindstrom BR, Bohlin G. Threat-relevance impairs executive functions: negative impact on working memory and response inhibition. Emotion. 2012;12(2):384–393. | ||
Perlstein WM, Elbert T, Stenger VA. Dissociation in human prefrontal cortex of affective influences on working memory-related activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(3):1736–1741. | ||
Lewis CJ, Maier F, Horstkotter N, et al. Subjectively perceived personality and mood changes associated with subthalamic stimulation in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Psychol Med. 2015;45(1):73–85. | ||
Lhommee E, Klinger H, Thobois S, et al. Subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: restoring the balance of motivated behaviours. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 5):1463–1477. | ||
Daniels C, Krack P, Volkmann J, et al. Risk factors for executive dysfunction after subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2010;25(11):1583–1589. | ||
Heekeren HR, Marrett S, Ungerleider LG. The neural systems that mediate human perceptual decision making. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9(6):467–479. |
 © 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.