Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 18
Repeated Intravenous Administration of Silica Nanoparticles Induces Pulmonary Inflammation and Collagen Accumulation via JAK2/STAT3 and TGF-β/Smad3 Pathways in vivo [Corrigendum]
Yu Y, Zhu T, Li Y, et al. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:7237–7247.
The authors have advised due to an error at the time of figure assembly, Figure 1Ba on page 7240 is incorrect. The correct Figure 1 is as follows.
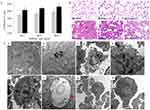 |
Figure 1 Lung injuries induced by SiNPs through intravenous injection in mice. (A) The coefficients of lungs increased significantly in the SiNP-treated group. Data are expressed as means±SD (n=5). *P<0.05 compared with control. Gray, control; black, admin. (B) Histopathologic changes in mice lungs induced by SiNPs. Black arrow: red blood cells in the area of alveoli; Red arrow: alveoli septum thicken and inflammatory cell infiltration. Scale bar: 20 μm. (C) Ultrastructural observation in mice lungs observed by TEM. (a, b) SiNPs (red arrows) deposited in lungs at 15th day. Scale bar: (a) 1 μm; (b) 200 nm. (c, d) Ultrastructural changes of alveolar macrophages in lungs of SiNP-treated mice at 30th day: extensive vacuolization (red star), mitochondrial fusion (red hollow triangle), mitochondrial cristae disappearance (red asterisk). Scale bar: (c) 0.5 μm; (d) 200 nm. (e, f) Vacuolization (red triangle) in the basophilic granulocyte in lungs of SiNP-treated mice at 30th day. Scale bar: (e) 1 μm; (f) 100 nm. (g, h) Cell cluster consisted of multinucleate cell (hollow star) and type I alveolar epithelial cell (hollow diamond) in lungs of SiNP-treated mice at 60th day. Scale bar: (e) 2 μm; (f) 1 μm.
|
The authors affirm that this error does not affect the results, discussion, and conclusions of the reported study and apologize for any inconvenience caused to the readers.
Read the original article
 © 2023 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2023 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
 © 2023 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2023 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.

