Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 10 » Issue 1
Biodegradable double nanocapsule as a novel multifunctional carrier for drug delivery and cell imaging
Authors Qian K, Wu J, Zhang E, Zhang Y, Fu A, Wu S
Received 1 March 2015
Accepted for publication 27 April 2015
Published 25 June 2015 Volume 2015:10(1) Pages 4149—4157
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S83731
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Lei Yang
Kun Qian,1,2 Jing Wu,1 Enqi Zhang,1 Yingge Zhang,3 Ailing Fu1
1School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Southwest University, 2College of Plant Protection, Southwest University, Chongqing, People’s Republic of China; 3Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Key Laboratory of Nanopharmacology and Nanotoxicology, Beijing Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, People’s Republic of China
Abstract: Highly-efficient delivery of macromolecules into cells for both imaging and therapy (theranostics) remains a challenge for the design of a delivery system. Here, we suggested a novel hybrid protein–lipid polymer nanocapsule as an effective and nontoxic drug delivery and imaging carrier. The biodegradable nanocapsules showed the typical double emulsion features, including fluorescently labeled bovine serum albumin shell, oil phase containing poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) and linoleic acid, and inner aqueous phase. The nanocapsules were spherical in shape, with an average size of about 180 nm. Proteins packed into the inner aqueous phase of the nanocapsules could be delivered into cells with high efficiency, and the fluorescence of the fluorescently labeled bovine serum albumin could be used for tracing the protein migration and cellular location. Further studies suggested that the co-delivery of transcription factor p53 and lipophilic drug paclitaxel with the nanocapsules acted synergistically to induce Hela cell apoptosis, and the fluorescence of apoptotic cells was clearly observed under a fluorescence microscope. Such multifunctional delivery system would have great potential applications in drug delivery and theranostic fields.
Keywords: emulsion, protein transport, fluorescence labeling, theranostics, cell apoptosis
Introduction
The intracellular delivery of proteins with high efficacy has been a key issue for protein therapy because of macromolecular properties and polarity of therapeutic proteins.1 Although nanoformulation provides an interesting approach to the direct delivery of proteins,2,3 the use of biodegradable nanocapsules still holds great promise because of their remarkable superiority in cell transduction efficiency and biocompatibility.4 Besides the delivery of proteins into cells, real-time and noninvasive assessment of delivery efficiency and therapeutic response is another important task, and the assessment requires concomitant delivery of imaging agents in one capsule, not only to trace the transduction process but also to measure cell response.5 Therefore, a multifunctional capsule should be developed that can be simultaneously used for intracellular protein delivery, imaging, and therapy (theranostics).
Among the available nanosized carriers, albumin has been widely used over the past 30 years to produce formulations; nanoparticles prepared with albumin are biocompatible, biodegradable, nonantigenic, and relatively easy to prepare.6–8 Additionally, albumin on the particle surface can selectively penetrate cancer cells by active or passive transport mechanism,9–11 evidenced by the first albumin-stabilized nanoformulation (ABI 007; Abraxane®, Celgene, New Jersey, USA)12–14 that was approved by the US Food and drug administration (FDA) in 2005. Nevertheless, the frequent form of protein-based nanocarriers we used for drug delivery is single emulsion,11,15 and there is almost no studies that utilize albumin to form a nanosized double emulsion capsule with the dual function of protein delivery and cancer cell imaging.
Here, we suggested a novel double nanocapsule consisting of protein and lipid produced by double emulsion technique.16,17 The hybrid protein–lipid polymer nanocapsule is composed of three layers (outer aqueous phase, oil phase, and inner aqueous phase) to form a compact capsule that offers separated microenvironment for cell imaging and drug delivery. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) in the outer aqueous phase is labeled by fluorescence agents for imaging, the separated oil phase can dissolve anticancer lipophilic molecules (5-fluorouracil, paclitaxel or doxorubicin) for therapeutic application, and the interested proteins are encapsulated to the inner aqueous phase to provide a potential way for protein delivery. Compared with the previously reported BSA capsules in nanosize or microsize,18–21 this novel fluorescent-labeled, biodegradable, and protein-lipid-polymer nanocapsule presented typical w/o/w features that could be used for the co-delivery of lipophilic and protein drugs for theranostics.
Material and methods
Materials
Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), tetramethylrhodamine (TRITC), BSA, pluronic F-68, and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, (St Louis, MO, USA). Lecithin and linoleic acid were from Acros Organics (Belgium, USA). Human cervical carcinoma (Hela) cells were stored in the laboratory of Southwest University (Chongqing, People’s Republic of China). All the reagents for cell culture were from HyClone (Logan, Utah, USA).
Preparation and purification of proteins
To obtain the FITC labeled BSA or TRITC labeled BSA, FITC/TRITC was dissolved in 0.5 mol/L carbonate buffered saline (CBS; pH 9.5), and BSA was dissolved in 0.5 mol/L carbonate buffered saline (CBS; pH 9.5) and mixed for 30 minutes at 4°C. Subsequently, the solutions of FITC/TRITC were added into the protein solutions at a slow speed and reacted for 5 hours in the dark at 4°C. After the reaction, uncombined fluoresceins were dialyzed by phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and the conjugates were purified with the quick Sephadex® G25 columns (Sigma-Aldrich). The final conjugates were lyophilized in a lyophilizer (Thermo Fisher Co., Waltham, MA, USA) and stored in the freezer.
The plasmids of pET28a/p53 and pET28a/nuclear location signal (NLS)–green fluorescence protein (GFP) containing NLS peptide (PKKKRKV)22 and GFP were constructed and stored in our laboratory.23,24 The NLS–GFP and p53 proteins were, respectively, expressed in Escherichia coli (E. coli) and BL21, and were purified with Ni-NTA resin column (Amersham Pharmacia Co., Shinjuku-Ku, Tokyo, Japan), according to previous reports.25 p53 was analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE). The protein concentrations were determined by the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) method according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Beyotime Biotechnology, Jiangsu, People’s Republic of China).
Preparation and characterization of the hybrid protein–lipid polymer nanocapsules
The nanocapsules were prepared by using the modified w/o/w double emulsion technique.26,27 Firstly, lecithin (0.2 g) as the surfactant was dissolved in the mixture solution of dichloromethane (1 mL) and ethanol (0.2 g) containing 0.5 g linoleic acid and 1% (w/v) PLGA, and then the protein solution was added into the oil and emulsified using a syringe pump in an ice bath to form the primary emulsion (w/o). This mixture was added dropwise and dispersed in the mixture of 2% fluorescently labeled BSA solution and 0.5% pluronic F-68 to prepare double emulsion (w/o/w). The solvent was evaporated for 6 hours under magnetic stirring. The nanocapsules were purified through four centrifugation/redispersion cycles (20,000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C), and then stored at 4°C for use.
Size and zeta potential of the nanocapsules were measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS) apparatus (Zetasizer Nano ZS; Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM; Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) was used to observe the structure of the nanocapsules.
Encapsulation efficiency
Encapsulation efficiency was determined by using 10% Triton X-100 for demulsification. The amount of fluorescently labeled BSA was analyzed using SpectraMax M5 Microplate Reader (Molecular Devices LLC, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). For FITC–BSA measurement, excitation and emission wavelengths were 490 and 525 nm, respectively; for TRITC–BSA, excitation and emission wavelengths were 550 and 620 nm, respectively. The encapsulation efficiency was defined as follows: encapsulation efficiency (%) = amount of encapsulated fluorescently labeled BSA/total amount of fluorescently labeled BSA added initially during preparation.
Cell culture and fluorescence imaging
Human cervical carcinoma (Hela) cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) containing 10% fetal calf serum (FCS), 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin. The cells were maintained in humidified 5% CO2, 37°C incubator (Thermo Fisher Co.).
Before being treated with nanocapsules, the cells were incubated in a 24-well plate at a density of 5×104 cells/well overnight, and then the cell morphology and confluence were observed under an optical microscope. When the cell confluence reached 80%, different concentrations of nanocapsules was added into the cell media (containing 10% FCS) for further incubation. Following incubation for a period of time, the cell media were washed and replaced with fresh DMEM. The cells were observed and photographed by using fluorescence microscope (Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) or confocal microscope (Zeiss LSM 510, Zeiss, Germany).
Cell viability assay
The Hela cells were cultured at a density of 5×103 cells/well in 96-well plates, incubated overnight, and supernatant was then discarded. Different concentrations of nanocapsules were diluted by DMEM containing 10% FCS, penicillin (100 U/mL), and streptomycin (100 μg/mL), and then added into the 96-well plates. The wells with no proteins acted as the positive control, and the wells with no cells were considered as the blank control. After incubation for 1 hour and 24 hours, the cell media were replaced by fresh DMEM, and the cell viabilities were measured using AlamarBlue cell viability assay reagent (Pierce, Nashville, TN, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The fluorescence intensities were recorded on a microplate reader (SpectraMax M5).
Results
Characterization of the double nanocapsules
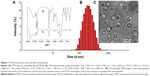
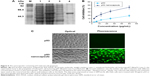
After identifying the structures of lecithin and PLGA by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (Figure 1A), the nanocapsules were prepared by double emulsion techniques, and then the size and shape were examined by DLS and TEM. DLS measurements of aqueous solutions of the protein–lipid polymer nanocapsules showed a mean diameter of ~180 nm (Figure 1B), and that of zeta potential was −36.47 mV. The nanocapsules displayed spherical shape with good dispersion (Figure 1C). Moreover, the structure showed obvious double emulsion features, including inner aqueous phase, oil phase, and outer aqueous phase, observed under TEM.
The nanocapsule delivery of fluorescently labeled BSA into cells with high efficiency
The capsules containing fluorescently labeled BSA (FITC–BSA as shell and TRITC–BSA as core) were prepared first to investigate the encapsulation efficiency and cell uptake process. As a result, the encapsulation yields of FITC–BSA and TRITC–BSA were 68.21%±5.19% and 84.32%±3.65%, respectively, indicating relatively high entrapment efficiency through the double emulsion technique.
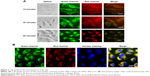
The results of cellular uptake showed that after addition of the nanocapsules into cell media for 15 minutes, green and red fluorescence were captured on the cell membranes, indicating that the nanocapsules attached to the cell membranes. Subsequently, the membrane fluorescence gradually decreased, and fluorescence spots were detected in the cytosol (Figure 2A), suggesting that the nanocapsules migrated from the membranes to the cytosol. Following 60 minutes of incubation, the images showed a homogeneous distribution of the fluorescence within the cytosol (Figure 2A and B).
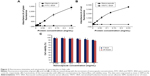
Cell transduction efficiency was determined by examining the relationship between concentration and fluorescence intensity. Cells transduced with the nanocapsules displayed strong fluorescence intensities that were closely dependent on the concentrations (Figure 3A and B). However, at the same protein concentrations, cells incubated with the controls of FITC–BSA and TRITC–BSA did not show any fluorescence.
The cytotoxicity of the nanocapsules was investigated in Hela cells following incubation for 1 and 24 hours. All of the cell viability values were higher than 85% when adding the nanocapsules with different concentrations (0.125–4 mg/mL) into the cell media (Figure 3C), suggesting that the nanocapsules had a good biocompatibility and could be used for drug delivery.
The nanocapsule delivery of NLS–GFP into cell nuclei
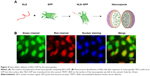
To identify the cell transduction ability of the delivery system, TRITC–BSA and NLS–GFP were assembled as shell and core of capsules, respectively, to observe the distribution of fluorescence. NLS was fused with GFP through genetic engineering technique to produce NLS–GFP fusion protein and further packed into the inner aqueous phase to form the double nanocapsules (Figure 4A). After 1 hour of incubation with the nanocapsules, the cytosol of Hela cells showed obvious red fluorescence, whereas strong green fluorescence appeared in the cell nuclei (Figure 4B), indicating successful intercellular delivery of NLS–GFP.
The nanocapsule delivery of wild-type p53 for inducing cell apoptosis
Wild-type p53 plays a crucial role in the regulation of cell apoptosis, induction of cell cycle arrest, recognition and repair of DNA damage, inhibition of cell malignant proliferation, and cell transformation in the cytoplasm and nucleus.28,29 Complement of wild-type p53 has become a potential strategy for protein therapy of cancer cells. However, the low cell permeability of p53 requires highly efficient carrier to improve its cell transduction.
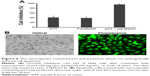
The nanocapsules containing wild-type p53 (Figure 5A) were prepared by encapsulating p53 into the inner aqueous phase, and FITC–BSA was used as shell. The results showed that the nanocapsule containing different concentrations of p53 (2.5–50 μg/mL) inhibited Hela cell growth in a concentration-dependent manner after 24 hours of incubation, which showed a significantly higher cell inhibition rate than the corresponding amount of p53 alone (Figure 5B). Additionally, the cells treated with p53 nanocapsules showed similar morphologic changes, including cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, and the presence of “apoptosis bodies” under the optical microscope, as well as displaying obvious fluorescence under the fluorescence microscope (Figure 5C).
Synergistic anticancer effect of nanocapsules containing p53 and paclitaxel
To examine whether the system could be used to deliver drugs into cells for theranostics, the nanocapsules containing p53 and paclitaxel30,31 were prepared; paclitaxel was dissolved in the oil phase (loading amount of 50 μg/mL) and the wild-type p53 (loading amount of 50 μg/mL) was packed into the inner aqueous phase. After 24 hours of incubation, Hela cells showed the features of cell apoptosis. Under the fluorescence microscope, green fluorescence was observed due to the fluorescence of FITC–BSA on the surface of the nanocapsule shell. Compared with the p53 or paclitaxel nanocapsule at each concentration, the synergistic anticancer effect was detected obviously by cell viability assay (Figure 6), suggesting that the system could simultaneously deliver lipophilic drugs and hydrophilic proteins into cells for theranostics.
Discussion
Here, we suggested a novel double nanocapsule with a mean size of about 180 nm for cell imaging and delivery of lipophilic drugs and hydrophilic proteins. Such capsules were composed of biodegradable and biocompatible materials, including BSA, pluronic F-68, PLGA, linoleic acid, and lecithin, wherein fluorescently labeled BSA was used as capsule shell, and a small amount of pluronic F-68, which is approved by the FDA for use in humans,32,33 was used to help reduce the surface free energy between oil and water.
During the preparation of the nanocapsules, combination of the biodegradable polymer PLGA and unsaturated fatty acid linoleic acid was chosen as the oil phase to enable proteins to assemble on the surface of the nanocarrier as well as to increase the content of lipophilic drugs in the oil phase. Although PLGA alone has been used to fabricate the nanoparticles with core–shell structures, significant loss of the surface ligand can occur, likely due to hydrolysis of the PLGA.34 Thus, fatty acids are attempted to form the oil phase when cooperation with PLGA. Additionally, previous studies have suggested that linoleic acid exhibits the highest protein (avidin) incorporation on the PLGA nanoparticle surface (~60% increase compared with palmitic acid).35 Therefore, combination of the biodegradable PLGA and linoleic acid as the oil phase might be an optimal choice to prepare nanocapsules.
Furthermore, the subcellular localization of proteins should be a matter of concern because functional proteins play their roles in specific organelles, which requires that the delivery system cannot interfere with intracellular protein distribution.36,37 Double nanocapsules designed to encapsulate proteins in their separated microsphere structures can protect the structural and functional integrities of proteins when they are transported into the cytosol and then redistributed within the cells.38–40 Besides the transport of BSA into the cytosol, the study showed that the nanocapsules delivered NLS–GFP into the nucleus, indicating that the structure of nanocapsules did not interfere with the migration of proteins.
The cell uptake process was traced using the nanocapsules, including FITC–BSA and TRITC–BSA. The fluorescence was detected on the cell membrane after 15 minutes of incubation, which then gradually appeared and was located in the cytosol, indicating that the nanocapsules moved from the membranes to the cytosol within 1 hour. The internalization pathway of the nanocapsules seemed to be endocytosis mechanism because fluorescence spots appeared in the cytosol after incubation for 30 minutes. Also, previous studies reported that cells uptake the albumin nanoparticles by receptor-mediated endocytosis, since there exists cancer-specific albumin-binding protein on the tumor cell lines, evidenced by competition studies of free albumin and co-precipitation results of albumin receptors.41,42 These studies implied that albumin nanocarriers might be used for specific tumor cell imaging in vitro and in vivo.
For the past decade, the development of a multifunctional theranostic formulation has made momentous progress in the drug delivery field.43,44 The nanocapsules containing fluorescently labeled albumin as shell seem to be a promising formulation for imaging, tracing, drug delivery, and other applications because they are composed of biocompatible and biodegradable blockers and show little toxicity on cells as they are incubated with the nanocapsules including fluorescently labeled BSAs. When the nanocapsules were used for therapy, therapeutic protein p53 and lipophilic drug paclitaxel could be, respectively, encapsulated in the inner aqueous phase and oil phase to compose a theranostic nanocapsule. The results also showed that the double nanocapsules could induce Hela cell apoptosis and the inhibition rate reached ~100%, while relatively low antiproliferative effect of paclitaxel or p53 nanocapsule indicated that paclitaxel and p53 in one capsule acted synergistically to induce the apoptosis. Also, the apoptotic cells could be observed under a fluorescence microscope due to the fluorescence of FITC–BSA on the nanocapsule shell. Such a multifunctional delivery system has a great potential for theranostics in which chemicals and proteins act synergistically.
Conclusion
In summary, we suggested a novel multifunctional drug delivery system based on biodegradable protein–lipid–polymer nanocapsules. The theranostic drug delivery system in the study has at least three advantages over the reported drug carriers: (1) the system is formed as a w/o/w double capsule structure in nanosize and fluorescently labeled BSA is used as shell, compared with the single emulsion of the other protein-based nanocarriers,11,15,45 (2) fluorescently labeled BSA of the shell can not only be used as an imaging agent, but also can selectively recognize cancer cells,9,10,46 when conjugated with specific ligands, which may provide the possibility of targeting anticancer treatment, and (3) the system can deliver intact proteins in the inner water phase and lipophilic drugs in the oil phase simultaneously for synergistic effect, compared with other systems for a single-drug delivery.47,48 Therefore, such a multifunctional capsule system could be considered a new theranostic methodology for targeting and treating cancer.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (81273416), the Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Scholars, Ministry of Education of China (2012-940), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2013A030), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2013 C030), and the New Century Excellent Talents Award in University, Ministry of Education of China.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Fu A, Tang R, Hardie J, et al. Promises and pitfalls of intracellular delivery of proteins. Bioconjug Chem. 2014;25:1602–1608. | ||
Kashiwada A, Tsuboi M, Matsuda K. Target-selective one-way membrane fusion system based on a pH-responsive coiled coil assembly at the interface of liposomal vesicles. Langmuir. 2011;27:1403–1408. | ||
Choi S, Lee KD. Enhanced gene delivery using disulfide-crosslinked low molecular weight polyethylenimine with listeriolysin o-polyethylenimine disulfide conjugate. J Control Release. 2008;131: 70–76. | ||
Rescignano N, Tarpani L, Tiribuzi R, et al. Protein encapsulation in biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles: morphology, fluorescence behaviour and stem cell uptake. Macromol Biosci. 2013;13: 1204–1212. | ||
Tang SY, Sivakumar M, Nashiru B. Impact of osmotic pressure and gelling in the generation of highly stable single core water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) nano multiple emulsions of aspirin assisted by two-stage ultrasonic cavitational emulsification. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;102:653–658. | ||
Tekade RK, Youngren-Ortiz SR, Yang HN, et al. Designing hybrid onconase nanocarriers for mesothelioma therapy: a Taguchi orthogonal array and multivariate component driven analysis. Mol Pharm. 2014; 11:3671–3683. | ||
Yan M, Du J, Gu Z, et al. A novel intracellular protein delivery platform based on single-protein nanocapsules. Nat Nanotechnol. 2010;5:48–53. | ||
Comes Franchini M, Baldi G, Bonacchi D, et al. Bovine serum albumin-based magnetic nanocarrier for MRI diagnosis and hyperthermic therapy: a potential theranostic approach against cancer. Small. 2010;6: 366–370. | ||
Huang Y, Luo Y, Zheng W, et al. Rational design of cancer-targeted BSA protein nanoparticles as radiosensitizer to overcome cancer radioresistance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6:19217–19228. | ||
Ding D, Tang X, Cao X, et al. Novel self-assembly endows human serum albumin nanoparticles with an enhanced antitumor efficacy. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2014;15:213–222. | ||
Lohcharoenkal W, Wang L, Chen YC, et al. Protein nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers for cancer therapy. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014: 180549. | ||
Di Costanzo F, Gasperoni S, Rotella V, et al. Targeted delivery of albumin bound paclitaxel in the treatment of advanced breast cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2009;2:179–188. | ||
Gupta N, Hatoum H, Dy GK. First line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer-specific focus on albumin bound paclitaxel. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:209–221. | ||
Miele E, Spinelli GP, Miele E, et al. Albumin-bound formulation of paclitaxel (Abraxane ABI-007) in the treatment of breast cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 2009;4:99–105. | ||
Pescina S, Sonvico F, Santi P, et al. Therapeutics and carriers: the dual role of proteins in nanoparticles for ocular delivery. Curr Top Med Chem.2015;15:369–385. | ||
Koga K, Takarada N, Takada K. Nano-sized water-in-oil-in-water emulsion enhances intestinal absorption of calcein, a high solubility and low permeability compound. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2010;74:223–232. | ||
Schwarz JC, Klang V, Karall S, et al. Optimisation of multiple W/O/W nanoemulsions for dermal delivery of acyclovir. Int J Pharm. 2012;435: 69–75. | ||
Jung B, Anvari B. Synthesis and characterization of bovine serum albumin-coated nanocapsules loaded with indocyanine green as potential multifunctional nanoconstructs. Biotechnol Prog. 2012;28:533–539. | ||
Hu CS, Chiang CH, Hong PD, et al. Influence of charge on FITC-BSA-loaded chondroitin sulfate-chitosan nanoparticles upon cell uptake in human Caco-2 cell monolayers. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7: 4861–4872. | ||
Chen X, Lv G, Zhang J, et al. Preparation and properties of BSA-loaded microspheres based on multi-(amino acid) copolymer for protein delivery. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:1957–1965. | ||
Kim BS, Oh JM, Kim KS, et al. BSA-FITC-loaded microcapsules for in vivo delivery. Biomaterials. 2009;30:902–909. | ||
Cogoi S, Codognotto A, Rapozzi V, et al. Antigene property of PNA conjugated to the nuclear localization signal peptide. Nucleos Nucleo Nucl. 2005;24:971–974. | ||
Zhao B, Sun M, Liu T, et al. Effects of RDP-p53 fusion protein on inflammatory cytokine of mice. Sci Techno Engin. 2014;14:1–3. | ||
Chen X, Fu A. Application and mechanism of membrane penetrating peptide. Chem Life. 2008;28:311–314. | ||
Fu A, Zhao Z, Gao F, et al. Cellular uptake mechanism and therapeutic utility of a novel peptide in targeted-delivery of proteins into neuronal cells. Pharm Res. 2013;30:2108–2117. | ||
Zhao XL, Cai YQ, Wang T, et al. Nuclear-targeted drug delivery of NLS peptide-conjugated monodisperse mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:5722–5725. | ||
Sneh-Edri H, Likhtenshtein D, Stepensky D. Intracellular targeting of PLGA nanoparticles encapsulating antigenic peptide to the endoplasmic reticulum of dendritic cells and its effect on antigen cross-presentation in vitro. Mol Pharm. 2011;8:1266–1275. | ||
Goh AM, Coffill CR, Lane DP. The role of mutant p53 in human cancer. J Pathol. 2011;223:116–126. | ||
Yoshida K, Miki Y. The cell death machinery governed by the p53 tumor suppressor in response to DNA damage. Cancer Sci. 2010;101: 831–835. | ||
Zhu LH, Li XP, Wang JL, et al. Effect of liposome encapsulated paclitaxel on cervical carcinoma cells in vitro. Chin J Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2008;19:363–366. | ||
Zheng XL, Wang TT, Fu M, et al. Inhibitory effect of recombinant human adenovirus-P53 combined with paclitaxel on human cervical cancer HeLa cells and its mechanism. Chin J Cancer Biother. 2013;20:192–196. | ||
Mei L, Zhang Y, Zheng Y, et al. A novel docetaxel-loaded poly (ε-caprolactone)/pluronic F68 nanoparticle overcoming multidrug resistance for breast cancer treatment. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2009;4: 1530–1539. | ||
Grover FL, Amundsen D, Warden JL, et al. The effect of pluronic F-68 on circulatory dynamics and renal and carotid artery flow during hemorrhagic shock. J Surg Res. 1974;17:30–35. | ||
Pirooznia N, Hasannia S, Lotfi AS, et al. Encapsulation of alpha-1 antitrypsin in PLGA nanoparticles: in vitro characterization as an effective aerosol formulation in pulmonary diseases. J Nanobiotechnology. 2012;10:20. | ||
Park J, Mattessich T, Jay SM, et al. Enhancement of surface ligand display on PLGA nanoparticles with amphiphilic ligand conjugates. J Control Release. 2011;156:109–115. | ||
Huang X, Li M, Green DC, et al. Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2239. | ||
She WC, Luo K, Zhang C, et al. The potential of self-assembled, pH-responsive nanoparticles of mPEGylated peptide dendron-doxorubicin conjugates for cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 2013;34:1613–1623. | ||
Cronican JJ, Thompson DB, Beier KT, et al. Potent delivery of functional proteins into mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo using a supercharged protein. ACS Chem Biol. 2010;5:747–752. | ||
Jun JY, Nguyen HH, Paik SYR, et al. Preparation of size-controlled bovine serum albumin (BSA) nanoparticles by a modified desolvation method. Food Chem. 2011;127:1892–1898. | ||
Garcia-Fuentes M, Torres D, Alonso MJ. Design of lipid nanoparticles for the oral delivery of hydrophilic macromolecules. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2003;27:159–168. | ||
Kim H, Robinson SB, Csaky KG. Investigating the movement of intravitreal human serum albumin nanoparticles in the vitreous and retina. Pharm Res. 2009;26:329–337. | ||
Liu ZY, Dong CH, Wang XM, et al. Self-assembled biodegradable protein-polymer vesicle as a tumor-targeted nanocarrier. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6:2393–2400. | ||
Nahire R, Haldar MK, Paul S, et al. Multifunctional polymersomes for cytosolic delivery of gemcitabine and doxorubicin to cancer cells. Biomaterials. 2014;35:6482–6497. | ||
Kumar R, Kulkarni A, Nagesha DK, et al. In vitro evaluation of theranostic polymeric micelles for imaging and drug delivery in cancer. Theranostics. 2012;2:714–722. | ||
Wang G and Uludag H. Recent developments in nanoparticle-based drug delivery and targeting systems with emphasis on protein-based nanoparticles. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2008;5:499–515. | ||
Zhanga L, Houb S, Maob S, Weic D, Songb X, Lub Y. Uptake of folate-conjugated albumin nanoparticles to the SKOV3 cells. Int J Pharm. 2004;287:155–162. | ||
Sun X, Liu Z, Welsher K, et al. Nano-graphene oxide for cellular imaging and drug delivery. Nano Res. 2008;1:203–212. | ||
Bianco A, Kostarelos K, Prato M. Applications of carbon nanotubes in drug delivery. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2005;9:674–679. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.