Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 12
The effects of repeated Ozurdex injections on ocular hypertension
Authors Bahadorani S, Krambeer C, Wannamaker K, Tie W, Jansen M, Espitia J, Sohn JH, Singer MA
Received 12 August 2017
Accepted for publication 30 November 2017
Published 3 April 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 639—642
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S148990
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Sepehr Bahadorani,1 Chelsey Krambeer,2 Kendall Wannamaker,1 Wayne Tie,1 Michael Jansen,1 Jason Espitia,2 Jeong-Hyeon Sohn,1 Michael A Singer2
1Department of Ophthalmology, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX, USA; 2Medical Center Ophthalmology Associates, San Antonio, TX, USA
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to correlate the degree of ocular hypertension with the number of Ozurdex injections.
Methods: Intraocular pressure (IOP) fluctuations for a total of 183 injections were studied over a period of at least 12 months. The main indications for treatment were uveitis, diabetic macular edema, and retinal vein occlusion.
Results: Results of the study demonstrate that repeated Ozurdex injections do not increase the frequency of IOP spikes beyond 30 mmHg. For lower IOPs, however, a positive correlation exists. Furthermore, patients with primary open angle glaucoma and uveitis had the highest IOP response to repeated injections. On average, patients with an IOP of ≥28.6 mmHg received pressure lowering medications, after which their IOP reached a stable level (16.7 mmHg) without the need for additional interventions.
Conclusion: The data support the conclusion that multiple Ozurdex injections does not increase the frequency of IOP spikes beyond 30 mmHg, but patients still must be closely monitored if they have a history of primary open angle glaucoma.
Keywords: Ozurdex, dexamethasone, glaucoma, intraocular pressure, ocular hypertension
Introduction
Dexamethasone intravitreal implant (0.7 or 0.35 mg) (Ozurdex, Allergan, Inc., Irvine, CA, USA), also known as Ozurdex®, consists of micronized dexamethasone in a biodegradable copolymer of polylactic-co-glycolic acid which slowly releases steroids into the vitreous over a period of about 6 months.1,2 Multiple studies show that dexamethasone intravitreal implant is an effective means of improving best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and reducing diabetic macular edema (DME) in patients that are resistant to anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) therapy.3 Likewise, the dexamethasone implant is an effective adjunct treatment for management of macular edema in patients with chronic non-infectious uveitis or retinal vein occlusions.4–6
Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is a major downside to dexamethasone implants and, yet, it is not clear how repeated injections affect the incidence of ocular hypertension. A number of studies, including the MEAD (macular edema: assessment of implantable dexamethasone in diabetes) study, have investigated the effects of Ozurdex injections on intraocular pressure. According to the MEAD study, IOPs were usually controlled with medication or no therapy, while 0.6% of patients in the 0.7 mg dexamethasone implant group and 0.3% in the 0.35 mg implant group required trabeculectomy.7 A recent study also demonstrated that ocular hypertension, which is defined as intraocular pressure of at least 25 mmHg or an increase of at least 10 mmHg from baseline, was recorded for 28.5% of injected eyes, and that IOP lowering medication was required for 31% of eyes. The study concluded that episodes of Ozurdex-mediated ocular hypertension are generally transient and can be successfully managed with topical treatment.8
It is now clear that ocular hypertension caused by Ozurdex injections can be managed with topical medications. However, it is not yet clear how repeated injections of Ozurdex affect the successful control of IOP with topical medications. The purpose of this study is to investigate the frequency and degree of ocular hypertension associated with sequential injections of dexamethasone intravitreal implants, and to determine whether topical medications are sufficient for controlling IOP in these patients.
Methods
This retrospective review was approved by Specialty Surgery Center IRB prior to the start of the study. The study was conducted on patients who received one or more dexamethasone implants, and all patients signed a consent form allowing their protected health information to be used. The primary outcome included highest mean IOP and frequency/degree of ocular hypertension that developed following treatments. The degree of ocular hypertension was defined as IOP measurements of ≥23 (mild), ≥25 (moderate), or ≥30 (severe) mmHg. These values were selected based on a review of other literatures as well as the definition of ocular hypertension by our glaucoma specialists (≥23 mmHg). The main indications for treatment were uveitis, diabetic macular edema (DME), and branch (BRVO) or central (CRVO) retinal vein occlusion. Statistical significance was determined using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Topical medications that were used for lowering intraocular pressure include combigan, brimonidine, cosopt, simbrinza, bimatoprost, travoprost, latanoprost, timolol, and dorzolamide. To avoid selection bias, patients who showed IOP spikes were not switched to Anti-VEGF, and repeated Ozurdex injections were not withheld.
Results
A total of 183 eyes were treated for 171 patients, where 139 eyes received a single injection, 25 eyes received two injections, and 19 eyes received three injections. As Figure 1 depicts, the frequency of ocular hypertension was: mild (31%, 26%, 53%), moderate (26%, 24%, 42%), and severe (12%, 12%, 11%) for single, two, or three injections, respectively. On average, patients with an IOP of ≥28.6 mmHg received pressure lowering medications, after which IOP reached a stable level (16.7 mmHg).
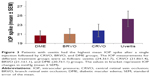
Following a single injection, patients with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) had a significantly higher IOP (25.1±1.7) compared to patients with no medical or family history of glaucoma (20.8±0.65) (P-value =0.004) (Figure 2). Among the treatment groups, patients with uveitis (24.3±1.7) had the highest IOP after single injection followed by CRVO (21.8±1.4), BRVO (21.1±1.1), and DME (20.7±1.1) groups (uveitis versus DME P-value =0.054) (Figure 3). The values in bracket represent IOP changes in mmHg (mean ± SEM).
Discussion
Cataract and ocular hypertension are the main long-term side effects of Ozurdex, but the degree of ocular hypertension is often mild-to-moderate, and patients rarely require surgical intervention.7,9,10 According to the HURON study, less than 10% of patients with Ozurdex injections presented with an IOP of ≥25 mmHg.11 Likewise, the GENEVA study showed that only 16% of patients who received Ozurdex had an IOP peak of 25 mmHg or higher.12 Nevertheless, it is not clear how repeated injections can affect the frequency and degree of ocular hypertension. The purpose of our study was to assess the effects of repeated Ozurdex injections on intraocular pressure of a cohort of patients from the everyday clinical practice who needed intervention for diabetic macular edema, uveitis, or retinal vein occlusion.
The results of our study demonstrate that the frequency of mild (≥23 mmHg) and moderate (≥25 mmHg) ocular hypertension increases with repeated injections of Ozurdex (Figure 1), and yet, the frequency of severe ocular hypertension (≥30 mmHg) remains comparable regardless of the frequency of injections. Therefore, if a patient did not have an IOP spike of above 30 mmHg after a single implant of Ozurdex, it is unlikely that subsequent implants cause such an IOP spike. The results of the study also support the fact that Ozurdex-mediated ocular hypertension could be well-controlled with topical medications, where an average IOP of ≥28.6 mmHg has been lowered to 16.7 mmHg.
Among patients who have received an Ozurdex implant, patients with prior history of primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) had a significantly higher IOP spike compared to the control group, indicating that POAG is a risk factor to Ozurdex-mediated IOP elevation (Figure 2). Patients with a positive family history of glaucoma also had an IOP spike higher than the control group, although not statistically significantly likely due to a relatively small sample size. These findings are consistent with previous risk factors that were identified for steroid-induced rises in IOP, including POAG and positive family history of glaucoma.13 Therefore, Ozurdex implants should be used with caution in patients with a prior history of POAG, and even possibly patients with a positive family history.
Finally, patients with uveitis had the highest IOP spike compared to the DME and retinal vein occlusion treatment groups (Figure 3). We speculate that this finding could be possibly attributed to prior steroid treatment in patients with uveitis, versus uveitis-mediated IOP elevation, or possibly a combination of both mechanisms.14 However, the benefits of Ozurdex injection for uveitis treatment will likely outweigh the potential temporary IOP spike seen in these patients.
Conclusion
Results of this study show that sequential dexamethasone implant injections increase the incidence of mild (≥23 mmHg) and moderate (≥25 mmHg) ocular hypertension, but not severe (≥30 mmHg) hypertension. Among treatment groups, patients with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) had a significantly higher IOP spike compared to the control group. Therefore, given their increased susceptibility for IOP elevations, dexamethasone implants should be used with caution in patients with POAG. Finally, patients with uveitis had the highest IOP spike, presumably due to the uveitis-mediated IOP spike, as well as previous treatments with steroids.
Disclosure
Dr Michael A Singer’s disclosures are as follows: Consultant for Allergan, Genentech, Regeneron, Santen, Clearside, Aerpio, Alimera. Research support from Allergan, Genentech, Regeneron, Ampio, Optos, Aerpio, Allegro, Diachii, Clearside. None of the other authors have relevant conflicts of interest.
References
Haghjou N, Soheilian M, Abdekhodaie MJ. Sustained release intraocular drug delivery devices for treatment of uveitis. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2011;6(4):317–329. | ||
Chang-Lin JE, Attar M, Acheampong AA, Robinson MR, Whitcup SM, Kuppermann BD, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a sustained-release dexamethasone intravitreal implant. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(1):80–86. | ||
Khan Z, Kuriakose RK, Khan M, Chin EK, Almeida DR. Efficacy of the intravitreal sustained-release dexamethasone implant for diabetic macular edema refractory to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy: meta-analysis and clinical implications. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2017;48(2):160–166. | ||
Whitcup SM, Robinson MR. Development of a dexamethasone intravitreal implant for the treatment of noninfectious posterior segment uveitis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1358:1–12. | ||
Garweg JG, Zandi S. Retinal vein occlusion and the use of a dexamethasone intravitreal implant (Ozurdex®) in its treatment. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016;254(7):1257–1265. | ||
Hahn P, Fekrat S. Best practices for treatment of retinal vein occlusion. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2012;23(3):175–181. | ||
Boyer DS, Yoon YH, Belfort R Jr, et al. Three-year, randomized, sham-controlled trial of dexamethasone intravitreal implant in patients with diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. 2014;121(10):1904–1914. | ||
Malclès A, Dot C, Voirin N, et al. Safety of intravitreal dexamethasone implant (OZURDEX): the SAFODEX study. Incidence and risk factors of ocular hypertension. Retina. 2017;37(7):1352–1359. | ||
Fassbender Adeniran JM, Jusufbegovic D, Schaal S. Common and rare ocular side-effects of the dexamethasone implant. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2017;25(6):834–840. | ||
Pacella F, Romano MR, Turchetti P, et al. An eighteen-month follow-up study on the effects of intravitreal dexamethasone implant in diabetic macular edema refractory to anti-VEGF therapy. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016;9(10):1427–1432. | ||
Lowder C1, Belfort R Jr, Lightman S, et al. Dexamethasone intravitreal implant for noninfectious intermediate or posterior uveitis. Arch Ophthalmol. 2011;129(5):545–553. | ||
Haller JA, Bandello F, Belfort R Jr, et al. Randomized, sham-controlled trial of dexamethasone intravitreal implant in patients with macular edema due to retinal vein occlusion. Ophthalmology. 2010;117(6):1134–1146. | ||
European Glaucoma Society. Terminology and Guidelines for Glaucoma. 4th ed. Savona: PubliComm; 2014. | ||
Taurone S, Ripandelli G, Pacella E, et al. Potential regulatory molecules in the human trabecular meshwork of patients with glaucoma: immunohistochemical profile of a number of inflammatory cytokines. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(2):1384–1390. |
 © 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.