Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 13
Recommendations for the management of elevated intraocular pressure due to bleb fibrosis after XEN gel stent implantation
Authors Vera V, Sheybani A, Lindfield D, Stalmans I, Ahmed IIK
Received 21 November 2018
Accepted for publication 11 February 2019
Published 18 April 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 685—694
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S195457
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Video 5 Bleb revision by Iqbal Ike K Ahmed.
Views: 765
Vanessa Vera,1 Arsham Sheybani,2 Dan Lindfield,3 Ingeborg Stalmans,4 Iqbal Ike K Ahmed5
1Department of Glaucoma, Unidad Oftalmologica de Caracas, Caracas, Venezuela; 2Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, MO, USA; 3Department of Ophthalmology, Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford, Surrey, UK; 4Glaucoma Unit, University Hospitals UZ Leuven, Leuven, Belgium; 5Glaucoma and Advanced Anterior Segment Surgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Abstract: Surgical management of glaucoma offers a means of effective disease control. A gel stent that facilitates drainage to the subconjunctival space offers intraocular pressure (IOP) reduction similar to traditional glaucoma filtering surgeries in a less invasive manner. However, like all subconjunctival filtering procedures that result in a bleb, fibrosis can present as a cause of elevated IOP. The following proposed techniques and recommendations for managing elevated IOP due to bleb fibrosis after gel stent implantation are based on the clinical experience of the authors. The goal of this paper is to improve outcomes following gel stent surgery by providing guidance on assessment of bleb function and strategies for bleb enhancement.
Keywords: glaucoma gel stent, bleb management, bleb fibrosis, glaucoma surgery, glaucoma filtering surgery, bleb needling
Introduction
The glaucoma treatment landscape has changed significantly in the last few years with the introduction of a variety of new surgical procedures. While the use of the subconjunctival space to drain aqueous humor from the anterior chamber has been a cornerstone of glaucoma surgery for more than a century,1 traditional bleb-forming procedures, such as trabeculectomy, are associated with significant risks. The XEN gel stent (Allergan PLC, Irvine, CA, USA) seeks to achieve outcomes similar to a trabeculectomy with higher predictability, faster recovery, less tissue manipulation, and fewer sight-threatening complications.2,3
The gel stent is a hydrophilic tube 6 mm long with an inner diameter of ~45 μm that drains aqueous from the anterior chamber to the subconjunctival space. The device is implanted ab interno to minimize tissue disruption and is designed to restrict the flow of aqueous in order to minimize the risk of hypotony.4 General recommendation for preoperative assessment, surgical technique, and postoperative follow-up has been published.5 However, very few guidelines on management options for bleb failure are available.
Wound healing
The natural wound healing process after filtration surgery may result in decreased aqueous outflow due to subconjunctival and episcleral fibrosis. Furthermore, the mere presence of fluid or a pressure head in the subconjunctival space stimulates a cellular reaction that reduces tissue porosity.6 The aqueous in glaucoma patients and others with elevated IOP contains higher levels of inflammatory cytokines PGE2 and TGFβ, substances that play a key role in inflammation and postoperative fibrosis.7,8 As inflammation and fibrosis have been primary causes of failure in filtering surgeries,9 understanding the wound healing process is advantageous to preventing filtration failure. The first stage of wound healing is the inflammatory phase, of which hemostasis is an integral part. Blood clotting results in the secretion of pro-inflammatory and proangiogenic cytokines, thereby impacting the diameter and permeability of the conjunctival and episcleral vessels. In addition, the trauma of the procedure induces the release of macrophage-recruiting chemotoxins that further stimulate the secretion of growth factors. Fibroblasts proliferate and subsequently deposit type 3 collagen. During the maturation phase, balanced production and degradation of the extracellular matrix accompanied by the production of type 1 collagen produce a tissue-strengthening effect.10 These collagen deposits can limit filtration.
In bleb development, the remodeling process is continuous, and subconjunctival fibrotic tissue can form early or late after surgery. Clinically, this tissue reaction can result in an encapsulated or a fibrotic bleb. If the bleb becomes encapsulated by tissue, it usually presents as a tense, elevated, smooth dome with a thick wall and an aqueous-filled cavity. In this situation, the surface area involved in filtration is limited which may lead to elevated IOP despite the presence of the bleb. Encapsulated blebs typically form between 2 and 6 weeks following traditional filtration surgery and occur in 8.3%–28% of eyes filtered.11
Subconjunctival fibrosis usually appears clinically as a flat bleb and is due to a more aggressive cicatrizing response. This can occur postoperatively at any time, although it typically happens in the first few months after surgery. The bleb created by a gel stent has some similarities to trabeculectomy blebs, although there are also significant differences. The authors of this paper present management strategies specific to gel stent blebs.
Bleb failure risk factors
Increased risk of bleb failure is associated with the following factors: young age, aphakia, active anterior segment neovascularization, conjunctival inflammation, uveitis, chronic medication use, previously failed glaucoma filtering surgery, and race, among others. The use of topical prostaglandins and beta blockers, the most common first-line treatments for glaucoma, has also been shown to increase the recruitment of inflammatory cells and intensify the wound healing cycle.12,13
Preoperative conjunctival optimization
During the preoperative period, it is beneficial to eliminate or reduce causes of conjunctival inflammation.14 This involves treating ocular surface and lid margin diseases as well as reducing toxicity to the conjunctiva from chronic glaucoma medication use. This is generally achieved by administering topical steroids, reducing or stopping topical IOP-lowering medications (replacing them with preservative-free [PF] alternatives and/or oral acetazolamide), and using PF lubricants, cyclosporine, or other interventions.5 Depending upon the severity of the case, any combination of the above can be implemented 1–4 weeks prior to surgery.
Intraoperative optimization
Intraoperative factors can also be optimized to reduce the risk of fibrosis.5 It is important to ensure that the distal tip of the implant is free and mobile (not caught within tenons tissue). This facilitates the formation of a diffuse, unrestricted bleb. The implant should be positioned ~1 mm in the anterior chamber, 2 mm in the scleral channel, and 3 mm in the subconjunctival space to ensure outflow occurs as posterior to the limbus as possible. This positioning will also help to prevent migration of the implant.5
Pharmacologic agents to modulate the wound healing response can also be used at the time of surgery. Differences in age, ethnicity, and prior surgical outcomes among patients dictate the need for tailoring of the antifibrotic strategy to suit the needs of the individual patient.
The use of antimetabolites intraoperatively and postoperatively in subconjunctival filtering surgeries has been reported.15,16 Antimetabolites such as mitomycin C (MMC) and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) have both been successfully used to reduce the scarring process.17,18 MMC is an alkylating agent that interferes with the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of fibroblasts.19 5-FU is an antimetabolite that specifically antagonizes various phases of protein synthesis.20 In traditional filtration surgery, MMC has been found to be more effective than 5-FU.21 However, oxidized MMC is inactive and requires chemical or enzymatic reductive activation to bind to DNA, after which it inhibits DNA replication, mitosis, and protein synthesis.22,23 For those cases where MMC does not appear to have any effect, this is possibly due to a lack of chemical or enzymatic activation. In these instances, the use of 5-FU is recommended.
It should be noted that in early studies of the first generation of the XEN gel stent, no MMC or other antifibrotic agent was used, and the failure rate was between 50% and 80%.24,25 Failure rates were reduced when MMC was utilized. There is growing evidence that injecting MMC at the time of XEN implantation and also during needling procedures is becoming the standard of care.25–27 As an alternative, the use of 5-FU during needling procedures has also been shown to be useful.28
Finally, better control of intraoperative bleeding can help reduce the secretion of proinflammatory and proangiogenic cytokines, improve visibility, and minimize the wound healing response. Using topical phenylephrine may help with vasoconstriction and avoiding subconjunctival and scleral vessels may help reduce subconjunctival hemorrhage.
Postoperative wound modulation
Corticosteroids have been traditionally used to stunt fibrosis by modifying the inflammatory response following glaucoma-filtering surgery, and their use appears to correlate with better IOP control.29–32 Although glaucoma patients are at heightened risk for a steroid response,33 steroid response is less common after filtering surgery.
Prophylactic injections of 0.1 mL of 5-FU (50 mg/mL) to the bleb area can be performed during the early postoperative period at the slit lamp and have been reported to reduce the possibility of more invasive interventions following trabeculectomy.34 Some authors recommend doing this routinely at week 2 or 3, without waiting for the bleb morphology to change or the IOP to rise. However, the authors suggest avoiding prophylactic use of 5-FU in cases where IOP is ≤8 mmHg or in presence of prominent blebs.
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays a role in physiological and pathological angiogenesis, and higher levels of VEGF are associated with failed glaucoma filtering surgeries.35 Therefore, injections of anti-VEGF agents bevacizumab and ranibizumab have also been used to modulate wound healing. In general, the use of anti-VEGF agents is associated with more diffuse blebs with reduced vascularity and reduced needling rates.36 However, the use of anti-VEGF does not appear to produce a lower IOP when compared to the use of MMC.37–39 Overall, anti-VEGF agents have some advantages and may be complementary to MMC,40 but have yet to establish better results over other antiscarring options currently available.
Enhancement after implant placement
The XEN stent is currently the only ab interno micro-invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS) capable of being enhanced by needling in the postoperative phase. This is in stark contrast to the majority of MIGS in which medications are the only option when IOPs are not at goal. Needling is a secondary procedure intended to free restrictions to aqueous outflow due to fibrosis, and it has been shown as an effective way to re-establish aqueous flow and lower IOP.41,42 The Preferred Practice Patterns published by the American Academy of Ophthalmology also include needling as an effective means of reviving filtering blebs.43
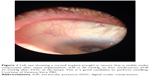
Bleb appearance and IOP should be factored in the decision-making process when considering needling a XEN bleb. A high bleb with a hyporeflective wall has been described as characteristic of a well-functioning trabeculectomy bleb.44 In contrast, a bleb following gel stent placement is rather low-lying and diffuse,45–47 and slit lamp assessment of improper outflow due to increasing tissue resistance can be initially challenging. Therefore, IOP is the best parameter to evaluate the need to release fibrosis during the surgeons’ learning curve, rather than the bleb appearance. The ideal IOP on postoperative day 1 is between 3 and 10 mmHg.5 If the IOP is in the high teens or above in the early postoperative period, this may represent an implant that is imbedded in tenons tissue and surgeons should consider needling (Figure 1).26
When the IOP is elevated, the surgeon should first perform gonioscopy to confirm the positioning of the stent, ensure that it is patent at both ends, verify that the internal ostium is not occluded, and rule out retained viscoelastic. It is also worthwhile to explore if the patient is manifesting an elevated IOP response to the postoperative steroid regimen. In rare cases, YAG laser and/or iridoplasty may be performed through a gonioscopy mirror to remove an internal ostium obstruction such as pigment, Descemet’s membrane, iris, blood, etc. Table 1 lists the factors to consider and their influence on the decision to needle the XEN bleb.
  | Table 1 Factors to consider in XEN bleb intervention |
Timing and technique of needling
The optimal time to perform a needling procedure after the XEN gel stent surgery is not well elucidated. In general, needling occurs in the first 2–3 months after surgery. However, if the IOP is not at goal and the bleb area is contracting, bleb needling should be considered when the stent can be visualized under the conjunctiva. If and when needling occurs, the authors describe three different types of needling:
- Type 1: dissection of fibrosis in the subconjunctival-intratenon space
- Type 2: clearance of a fibrotic cap at the external implant tip
- Type 3: needling of an encapsulated bleb if aqueous suppressant therapy proved unsuccessful (or if preferred, as first approach).
Many surgeons find it useful to use a bent needle/blade as the angle aids access to the desired site and facilitates rotating the cutting edge of the tool. A 27-gauge needle is useful for mechanically increasing the bleb area. A 30-gauge needle is preferred for fine needling when there is no scarring present and the surgeon wants to clear the implant tip. Many surgeons also find a 23/24-gauge microvitreoretinal blade particularly efficacious as the fine cutting edge can cut away denser scars and clear the delicate tip of the stent.
As this paper is a presentation of the authors’ considerable experience, they find it helpful to share their individual needling techniques.
Arsham Sheybani, MD
I perform needling at the slit lamp with tetracaine or lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel as a topical anesthesia. It is important to avoid subconjunctival hemorrhage, and therefore I place a drop of phenylephrine prior to the procedure to blanch the vessels. Pressing a tetracaine-soaked cotton tip over the area of needling also eliminates pain for the patient. Holding the eye open with a lid speculum is not required but may be used at the surgeon’s discretion. I generally use my third digit to elevate the lid while my index finger and thumb hold the needle. Insert a 27-gauge needle 2–3 clock hours away from the XEN gel stent site and once the needle reaches the implant, gently sweep it above and below the distal end of the stent to clear the fibrous attachments. I consider the procedure successful if the bleb has a very low elevation and the implant is mobile.
If there is no flow of aqueous visible, I may intentionally amputate the tip of the stent with my needle. The rational is that the implant tip is imbedded in tenons tissue and freeing it will allow aqueous to flow. I have also performed YAG laser to the internal portion of the XEN if the bleb is not raised after needling. If there is no ischemia in the conjunctiva after the original XEN implantation, follow needling with an injection of 20–40 μg of MMC around the bleb area and/or 0.1 mL of 5-FU for a total of 5 mg behind the bleb.
I direct the patient to stop use of any topical glaucoma medications and prescribe prednisolone acetate and an antibiotic for 1 week. I will usually try needling the bleb twice. If needling fails twice but I know there is flow through the implant, I will perform an open revision. If I cannot detect flow through the implant, I will proceed with a tube shunt. In a few instances, I have performed a second XEN implant.
Video 1 XEN needling by Arsham Sheybani.
Iqbal Ike K Ahmed, MD
Prior to needling, I first evaluate the conjunctiva to make sure it is healthy. If the conjunctiva is very inflammed, I delay needling, cease any agents that may be causing inflammation, prescribe a topical corticosteroid, and treat any blepharitis.
The day of the needling, I prepare the eye with tetracaine, iodopovidone, antibiotics, etc. In patients where 0.4 mg/mL × 0.1 mL of MMC (40 μg absolute dose) was used at the time of surgery, I begin the needling procedure by injecting 0.5 mg/mL × 0.15 mL of MMC (75 μg absolute dose) into the subconjunctiva making sure it covers the distal end of the stent. I do not mix it with lidocaine. I use 5-FU if the MMC does not seem to be having the desired effect. I may use an anti-VEGF agent if the eye is very red at the time of needling and repeat later as needed.
At the slit lamp, I use a 27-gauge slit knife (MANI, Inc., Tochigi, Japan) bent to make it short, and enter the conjunctiva in the adjacent quadrant. I find a lid speculum gets in my way, so I ask the patient to look down. I slide the knife under the distal end of the stent, swipe it toward the fornix, and then repeat the action above the stent. I repeat this motion as needed to release fibrosis and allow the XEN gel stent to be positioned more anteriorly and superficially. If necessary, I will amputate the distal end of the stent. I expect to see the stent free and mobile, the bleb raising, and the fibrotic tissue swept away. I will inject sodium hyaluronate once I have a bleb.
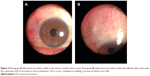
A surgeon could perform the procedure in the operating room initially if uncertain at the slit lamp. I recommend needling a bleb when IOP is elevated and the bleb starts contracting, but before the bleb is gone; do not miss the opportunity. It is important to know which cases should go straight to open revision (Figure 2). I will attempt needling twice before moving on to another therapeutic option.
Video 2 Xen needling by Iqbal Ike K Ahmed.
Ingeborg Stalmans, MD
If the conjunctiva is hypervascular, I use subconjunctival injections of bevacizumab, topical corticosteroids, and preservative-free glaucoma drops days or weeks prior to needling. I mostly perform needling in the operating room.
On needling day, I prepare the eye by alternating 3 drops of tetracaine, with 2 drops of apraclonidine as a vasoconstrictor, and then iodopovidone. My technique for clearing fibrosis depends on the type of blockage present. For a clearly visible stent without obvious scar, I use a 30-gauge needle. I first aim for the tip to see if pulling sub-Tenons away will resume aqueous outflow. If not, I very cautiously swipe over and under the stent, approaching the stent very closely to open up the “sock” around it. The stent can very easily be cut, so it is important to use caution.
If the stent tip is free and mobile and slow bleb formation is visible, I am satisfied with the needling. Often, I will digitally massage the eye to convincingly see the bleb formation. Sometimes, it is possible to see sub-Tenon’s capsule being displaced posteriorly.
Video 3 Needling fibrotic bleb after XEN + subconjunctival injection of anti-fibrotics.
If there is a scar around or behind the stent, I use a 27-gauge vitreoretinal blade to cut through the scar to create a new filtering space. For a thick-walled, encapsulated bleb that has not responded to topical aqueous suppressants, I use a 27-gauge vitreoretinal blade to gently cut the wall of the cyst open.
Video 4 Needling an encapsulated bleb after XEN gel stent.
After needling, I first inject 0.05 mL of bevacizumab at 25 mg/mL (total dose 1.25 mg) into the subconjunctiva just behind the tip of the stent, followed by 0.1 mL of MMC at 0.1 mg/mL (total dose 10 μg) posterior to that. My objective is to keep the MMC away from the limbus and have the complementary effect of the two antiscarring agents. I also inject a subconjunctival steroid depot inferiorly. Postoperatively, I have the patient use a topical antibiotic four times a day for a few weeks and a topical corticosteroid six times a day for 1 month and then slowly taper.
I recommend needling only when the stent is visible, and to use meticulous preparation to avoid bleeding. I will generally perform needling just once, and will perform it twice only in exceptional cases. I prefer bleb revision if there is thick scar, or inserting a second XEN gel stent if there is no visible scar. Lack of scarring indicates that the first implant was likely not well placed or not patent. Otherwise, I will move on to another filtering surgery.
Dan Lindfield, MD
I personally use two approaches to postoperative bleb management: pharmacological bleb modulation with 5-FU and/or physical bleb modulation with needling.
I perform pharmacological bleb modulation in all of my patients prophylactically. Three weeks after XEN implantation, I inject 0.1 mL of 50 mg/mL solution of 5-FU (5 mg) into the subconjunctiva above the XEN gel stent distal tip. I only withhold this step if IOP is ≤8 mmHg or over draining.
When pharmacological bleb modulation fails, I perform physical bleb modulation or needling in the operating room. I apply topical adrenaline (1 mg in 1.0 mL) on a cotton swab to blanch the area. In cases of primary needling, I use a 30-gauge long needle to inject 0.1 mL of 5-FU (50 mg/mL); in the rare cases that I perform needling a second time, I switch to 0.1 mL of 0.2 mg/mL MMC.
I enter the conjunctiva as far away from the stent tip as possible to minimize potential entry site leak. If the bleb deflates through the entry site, it is less likely to function. I then perform copious sweeping while trying to avoid hemorrhage. I expect to see a slow filling of the bleb area. I suggest new surgeons use topical adrenaline and perform needling in the operating theater as you will have more control and a better view of the implant. Avoid any conjunctival vessels in addition to taking care not to perforate the gel stent.
Vanessa Vera, MD
If I suspect I might need to perform needling, (IOP starts creeping up, bleb starts shrinking, conjunctival vascularity is excessive, etc), I start preparing the conjunctiva by increasing topical corticosteroids and/or injecting a subconjunctival anti-VEGF if vascularity is a concern. On the day of the needling, if the conjunctiva is vascular, I use 20–40 μg of MMC, injected 10 minutes prior to the needling procedure. If the conjunctiva is avascular, I prefer to inject 0.1 mL (50 mg/mL) of 5-FU (5 mg) into the bleb area after needling is performed.
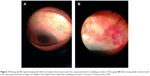
I perform needling at the slit lamp using a 27-gauge bent needle on an insulin syringe. I ask the patient to look down and enter the conjunctiva 2–3 clock hours away from the implant. I place my needle bevel halfway under the subconjunctival portion of the implant, not too close to scleral exit as it is easy to accidentally cut it, nor at the implant tip. I then sweep away from the implant. I go back again, this time placing the needle bevel halfway over the stent, and sweep away. If I do not see any bleb formation I repeat this, focusing on the area where most resistance was felt. I continue to sweep with the needle until the fibrotic tissue is mechanically broken and satisfactory outflow is seen. Ideally, at the end of the procedure I will see that the tip of the implant is free and mobile from the surrounding tissue and that there is low elevation of the conjunctiva. This low elevation can make the implant a bit more difficult to visualize compared to the pre-needling view (Figure 3). Following the procedure, I use the same antibiotic and steroid regimen as after the initial surgery.
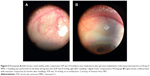
I avoid entering with the needle in an area that is avascular or too close to where the bleb will form. I also avoid subconjunctival hemorrhage, perforating the conjunctiva and/or inadvertently cutting the implant (Figure 4). I do amputate the distal end of the stent when there is no flow. To do this, I place the needle bevel angled over the implant and press down against the sclera. I will attempt needing twice, but if the bleb fails within a few days of first needling or if too much tissue resistance was felt during first needling, then I will not needle a second time.
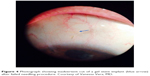  | Figure 4 Photograph showing inadvertent cut of a gel stent implant (blue arrow) after failed needling procedure. Courtesy of Vanessa Vera, MD. |
I recommend performing needling only when the stent is plainly visible under the conjunctiva, without the aid of a laser suture lysis lens or a gonio lens to locate it. If you cannot see the stent, then that is not the right patient to needle.
There is consensus among all authors that the goal is to have the XEN gel stent released from Tenon’s capsule, the distal end free and mobile, and a low, diffuse bleb. Needling should not be performed more than twice, and should not be attempted at all if the implant is not clearly visible. Achieving an IOP ≤10 mmHg right after needling (Figure 5) may be indicative of good long-term prognosis.5
Just as with the initial surgical procedure, the potential risks following needling of the XEN bleb are minimized compared to needling a trabeculectomy bleb.28 While profound hypotony, flat chamber, and hyphema are all possible complications after needling a trabeculectomy bleb, they are all very unlikely to happen following needling of a XEN bleb.
Alternative options to needling
While needling can be very effective, it is not always successful at achieving the desired IOP. When needling has been attempted and an acceptable IOP is not achieved and sustained, or in cases where the XEN gel stent cannot be visualized under the conjunctiva due to a dense and opaque layer of tissue, other options should be considered. These may include:
- Resume IOP-lowering medications. If needling was recently performed, consider starting with a preservative-free aqueous suppressant5 instead of a prostaglandin to avoid adding proinflammatory factors (Figure 6).
- Perform a bleb revision (open conjunctiva).
- Consider converting to a different surgical treatment.
Bleb revision with open conjunctiva
In cases when the implant cannot be visualized under the conjunctiva or with poorly functioning encapsulated bleb, a bleb revision may be the most appropriate next step. The conjunctiva is incised and opened at the limbus spanning 2–3 clock hours. The posterior conjunctiva is then dissected down to the scleral bed and all adhesions that have formed between the conjunctiva and the sclera are released. Gentle cautery is performed to maintain hemostasis. The dissection should be performed with caution when approaching the area of stent placement through the sclera. Once the implant is fully released from the fibrotic tissue, ensure the implant is patent and flowing by injecting balanced salt solution (BSS) into the anterior chamber (Video 5). Outflow through the implant is difficult to visualize as the flow rate may be very low; therefore, fluorescein strips may be used along with sponges to determine the absence or presence of flow.
Video 5 Bleb revision by Iqbal Ike K Ahmed.
After the stent is fully liberated and flow is confirmed, it may still be necessary to perform additional dissection to remove adhesions and create a potential space for filtration. In some cases, a tenectomy may be necessary to prevent future implant fibrosis. The conjunctiva may be closed with sutures to ensure a watertight seal. The authors recommend an injection of an antifibrotic agent during bleb revision surgery (MMC, 5FU, anti-VEGF, and/or corticosteroids).
Conclusion
The key to successful needling include identifying the right candidate for intervention and using the appropriate technique. Except in cases of encapsulation when aqueous suppressants have proven unsuccessful, needling should not be attempted in cases where the XEN gel stent is not visible under the conjunctiva. If the stent cannot be visualized, surgeons should consider a bleb revision or other interventions, such as restarting topical medications or another glaucoma procedure.
If the patient is an appropriate candidate for needling, reducing conjunctival inflammation or subconjunctival hemorrhage can help improve the chances for success. An inflamed conjunctiva should be treated pre-emptively. The use of antimetabolites and other antifibrotic agents are associated with greater needling success rates, and the authors encourage their use. Freeing the XEN implant from Tenon’s tissue and elevating a bleb is the goal of needling. After needling, there should be a reduction in IOP confirming improved outflow.
The suggested approaches to bleb management following implantation of the XEN gel stent are based on published best practices in ophthalmology and the collective, considerable experience of the authors. This information is meant to complement, not replace formal training with the XEN gel stent, and should always be applied to an individual patient at the surgeon’s discretion.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the input and assistance of Herbert Reitsamer, MD; Luis Abegão Pinto, MD, PhD; Nate Radcliffe, MD; Francisco Millan, MD; and Maria E. Reveron, MD, on the paper. Medical writing, editorial, and other assistance: editorial assistance in the preparation of this article was provided by Adrianne Resek, MA. Support for this editing assistance was funded by Allergan.
Author contributions
All authors contributed to development of content, drafting and revising the article, gave final approval of the version to be published, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
All authors are consultants for Allergan. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Lewis RA. Ab interno approach to the subconjunctival space using a collagen glaucoma stent. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014;40(8):1301–1306. | ||
Mansouri K, Guidotti J, Rao HL, et al. Prospective evaluation of standalone XEN gel implant and combined phacoemulsification-XEN gel implant surgery 1-year results. J Glaucoma. 2017;27:140–147. | ||
Schlenker MB, Gulamhusein H, Conrad-Hengerer I, et al. Efficacy, safety, and risk factors for failure of Standalone ab Interno gelatin Microstent implantation versus Standalone trabeculectomy. Ophthalmology. 2017;124(11):1579–1588. | ||
Sheybani A, Reitsamer H, Ahmed IIK. Fluid dynamics of a novel Micro-Fistula implant for the surgical treatment of glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56(8):4789–4795. | ||
Vera V, Ahmed IIK, Stalmans I, Reitsamer H. Gel stent implantation – recommendations for preoperative assessment, surgical technique, and postoperative management. US Ophthalmic Review. 2018;11(1):38–46. | ||
Pandav SS, Ross CM, Thattaruthody F, et al. Porosity of bleb capsule declines rapidly with fluid challenge. J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2016;10(3):91–96. | ||
Freedman J, Iserovich P. Pro-inflammatory cytokines in glaucomatous aqueous and encysted Molteno implant blebs and their relationship to pressure. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013;54(7):4851–4855. | ||
Freedman J, Goddard D. Elevated levels of transforming growth factor beta and prostaglandin E2 in aqueous humor from patients undergoing filtration surgery for glaucoma. Can J Ophthalmol. 2008;43(3):370. | ||
Skuta GL. Parrish RK 2nd. Wound healing in glaucoma filtering surgery. Surv Ophthalmol. 1987;32(3):149–170. | ||
Lockwood A, Brocchini S, Khaw PT. New developments in the pharmacological modulation of wound healing after glaucoma filtration surgery. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013;13(1):65–71. | ||
Ignjatović Z, Misailović K, Kuljaca Z. [Encapsulated filtering blebs – incidence and methods of treatment]. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2001;129(11–12):296–299. Serbian. | ||
Sherwood MB, Grierson I, Millar L, Hitchings RA. Long-term morphologic effects of antiglaucoma drugs on the conjunctiva and tenon’s capsule in glaucomatous patients. Ophthalmology. 1989;96(3):327–335. | ||
Baudouin C, Liang H, Hamard P, et al. The ocular surface of glaucoma patients treated over the long term expresses inflammatory markers related to both T-helper 1 and T-helper 2 pathways. Ophthalmology. 2008;115(1):109–115. | ||
Baudouin C. Ocular surface and external filtration surgery: mutual relationships. Dev Ophthalmol. 2012;50:64–78. | ||
The fluorouracil filtering surgery Study Group. Five-year follow-up of the fluorouracil filtering surgery study. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996;121:349–366. | ||
Palmer SS. Mitomycin as adjunct chemotherapy with trabeculectomy. Ophthalmology. 1991;98(3):317–321. | ||
Wilkins M, Indar A, Wormald R. Intra-operative mitomycin C for glaucoma surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;4:CD002897. | ||
Holló G. Wound healing and glaucoma surgery: modulating the scarring process with conventional antimetabolites and new molecules. Dev Ophthalmol. 2017;59:80–89. | ||
Seong GJ, Park C, Kim CY, et al. Mitomycin-C induces the apoptosis of human tenon’s capsule fibroblast by activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 and caspase-3 protease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46(10):3545–3552. | ||
Occleston NL, Alexander RA, Mazur A, Larkin G, Khaw PT. Effects of single exposures to antiproliferative agents on ocular fibroblast-mediated collagen contraction. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994;35(10):3681–3690. | ||
Cabourne E, Clarke JCK, Schlottmann PG, Evans JR. Mitomycin C versus 5-fluorouracil for wound healing in glaucoma surgery. Cochrane Database of Systemic Reviews. 2015;102(9):CD006259. | ||
Lama PJ, Fechtner RD. Antifibrotics and wound healing in glaucoma surgery. Surv Ophthalmol. 2003;48(3):314–346. | ||
Verweij J, Pinedo HM. Mitomycin C: mechanism of action, usefulness and limitations. Anticancer Drugs. 1990;1(1):5–13. | ||
Sheybani A, Dick HB, Ahmed IIK. Early clinical results of a novel ab Interno gel stent for the surgical treatment of open-angle glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2016;25(7):e691–e696. | ||
Morgan WH, Quill B, Cringle SJ, House PH, Yu D-Y, Dy Y. Long-term results using gelatin Microfistulae implantation without antimetabolite. Ophthalmology. 2018;125(11):1828–1829. | ||
Hengerer FH, Kohnen T, Mueller M, Conrad-Hengerer I. Ab Interno gel implant for the treatment of glaucoma patients with or without prior glaucoma surgery: 1-year results. J Glaucoma. 2017;26(12):1130–1136. | ||
Midha N, Rao HL, Mermoud A, Mansouri K. Identifying the predictors of needling after XEN gel implant. Eye (Lond). Epub 2018 Sep 11. | ||
Arnljots TS, Kasina R, Bykov VJN, Economou MA. Needling with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) after XEN gel stent implantation: 6-month outcomes. J Glaucoma. 2018;27(10):1–899. | ||
Seibold LK, Sherwood MB, Kahook MY. Wound modulation after filtration surgery. Surv Ophthalmol. 2012;57(6):530–550. | ||
Araujo SV, Spaeth GL, Roth SM, Starita RJ. A ten-year follow-up on a prospective, randomized trial of postoperative corticosteroids after trabeculectomy. Ophthalmology. 1995;102(12):1753–1759. | ||
Kahook MY, Camejo L, Noecker RJ. Trabeculectomy with intraoperative retrobulbar triamcinolone acetonide. Clin Ophthalmol. 2009;3:29–31. | ||
Tham CCY, Li FCH, Leung DYL, et al. Intrableb triamcinolone acetonide injection after bleb-forming filtration surgery (trabeculectomy, phacotrabeculectomy, and trabeculectomy revision by needling): a pilot study. Eye. 2006;20(12):1484–1486. | ||
Tripathi RC, Parapuram SK, Tripathi BJ, Zhong Y, Chalam KV. Corticosteroids and glaucoma risk. Drugs Aging. 1999;15(6):439–450. | ||
Reinthal EK, Denk PO, Grüb M, Besch D, Bartz-Schmidt KU. Dose, timing and frequency of subconjunctival 5-fluorouracil injections after glaucoma filtering surgery. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007;245(3):369–375. | ||
Lopilly Park H-Y, Kim JH, Ahn MD, Park CK. Level of vascular endothelial growth factor in tenon tissue and results of glaucoma surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 2012;130(6):685–689. | ||
Vandewalle E, Abegão Pinto L, van Bergen T, et al. Intracameral bevacizumab as an adjunct to trabeculectomy: a 1-year prospective, randomised study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2014;98(1):73–78. | ||
Kahook MY. Bleb morphology and vascularity after trabeculectomy with intravitreal ranibizumab: a pilot study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010;150(3):399–403. | ||
Li Z, van Bergen T, van de Veire S, et al. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor reduces scar formation after glaucoma filtration surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50(11):5217–5225. | ||
Franco L, Rassi B, Avila MP, Magacho L. Prospective study comparing mitomycin C or bevacizumab as adjuvant in trabeculectomy revision by needling. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2016;26(3):221–225. | ||
van Bergen T, Vandewalle E, Moons L, Stalmans I. Complementary effects of bevacizumab and MMC in the improvement of surgical outcome after glaucoma filtration surgery. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015;93(7):667–678. | ||
Nikita E, Murdoch I. Same-site surgical revision of failed trabeculectomy blebs with mitomycin C augmentation: long-term follow-up. Eye. 2018;32(2):352–358. | ||
Anand N, Khan A. Long-term outcomes of needle revision of trabeculectomy blebs with mitomycin C and 5-fluorouracil: a comparative safety and efficacy report. J Glaucoma. 2009;18(7):513–520. | ||
Be P Jr, Rosenberg LF, Gedde SJ, et al. Primary open-angle glaucoma preferred practice pattern guidelines. Ophthalmology.2016;126(1):41–111. | ||
Narita A, Morizane Y, Miyake T, et al. Characteristics of successful filtering blebs at 1 year after trabeculectomy using swept-source three-dimensional anterior segment optical coherence tomography. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2017;61(3):253–259. | ||
Lenzhofer M, Strohmaier C, Hohensinn M, et al. Longitudinal bleb morphology in anterior segment OCT after minimally invasive transscleral ab interno glaucoma gel microstent implantation. Acta Ophthalmol. Epub 2018 Aug 29. | ||
Olate-Pérez Á, Pérez-Torregrosa VT, Gargallo-Benedicto A, et al. Estudio prospective de las ampollas de filtracion poscirugia de implante XEN45 [Prospective study of filtration blebs following XEN45 implantation]. Archivos de la Sociedad Espanola de Oftalmologia. 2017;92(8):366–371. Spanish. | ||
Fea AM, Spinetta R, Cannizzo PML, et al. Evaluation of bleb morphology and reduction in IOP and glaucoma medication following implantation of a novel gel stent. Journal of Ophthalmology. 2017;2017(9):1–9. |
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.