Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 13
Intraductal meibomian gland probing: background, patient selection, procedure, and perspectives
Received 16 February 2019
Accepted for publication 26 March 2019
Published 10 July 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1203—1223
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S183174
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Video abstract presented by Steven L Maskin
Views: 5935
Steven L Maskin, Sreevardhan Alluri
Dry Eye and Cornea Treatment Center, Tampa, FL, USA
Abstract: Obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction is the most common cause of dry eye. Its conventional treatment has focused on using heat and pressure with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial therapies but has often been a frequent, frustrating experience for patient and physician. New evidence from Meibomian gland intraductal probing suggests fixed intraductal strictures and obstruction correlating to periductal fibrosis first described in 1997. The use of intraductal probing has been reported, by this author and in at least ten independent peer-reviewed academic papers from around the world, to consistently lead to statistically significant improvement in signs and symptoms of gland dysfunction including cases refractory to other extensive treatments. This review will focus on the background of meibomian gland intraductal probing as well as patient selection, procedure, and perspectives.
Keywords: meibomian gland dysfunction, meibomian gland probing, maskin probing, lipiflow,R IPL, dry eye
Erratum for this paper has been published
Background
Frequent questions from Patients answered in this paper:
- P1 Why do warm compresses increase my MGD symptoms and make my eyes uncomfortable? See the Concepts section.
- P2 Why does gland expression cause increased lid inflammation, soreness and swelling, yet I feel more lubrication in my tears? See the Concepts section.
- D1 Are glands that show expressible meibum healthy? See the Concepts section.
- D2 Is Meibomian Gland Probing painful? See the Performing a well tolerated probing procedure section and perspective #16.
- D3 Does Meibomian Gland Probing lead to gland damage? See the Performing a well tolerated probing procedure section and perspective #16.
Introduction
Paradigm shift
The term “paradigm shift”1 describes a fundamental change in underlying beliefs or theory. A fundamental change has occurred for me (SLM) during the last 12 years in how to best treat obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction (o-MGD), the most common cause of dry eye in the world.2 I (SLM) have managed MGD for over 30 years and its treatment, which was once a frustrating experience of frequent failure for patient and physician, has become a safe, positive, and gratifying experience that helps consistently restore comfort to patients’ eyes with greater than 75% reduction in severity of symptoms.3–23
This success in delivering comfort to patients’ eyes is attributed to the development of methods and apparatus to perform intraductal meibomian gland probing (MGP) as well as adjunctive intraductal microtube injection of medicaments.19 As an epidermal appendage embryologically derived from surface ectoderm,23 the Meibomian gland can be cannulated and treated from the inside safely. This finding expands the range of tissues and organs that are internally cannulated in routine medical practice at the beginning of the twenty-first century. These include exocrine salivary glands as well as pancreas and biliary tree, in addition to cerebral, coronary, and renal arteries, plus the urethra and esophagus for treatment of strictures. For urethral and esophageal lumen strictures, the internal approach to dilating the lumen is an effective, targeted treatment of fixed, internal mechanical obstruction. We have found the same to be true of treating duct lumen strictures of Meibomian glands with intraductal probing.
Concepts
A key finding during MGP is fixed mechanical resistance upon inserting the probe through the orifice, distal, and proximal duct lumen. We describe this finding as fixed, firm, focal, unyielding resistance (FFFUR). This discovery of fixed mechanical resistance was found in 70-74% of the upper and 55-60% of the lower lid meibomian gland MGs.21,24 This type of resistance is thought to represent periductal fibrosis contracting around the external duct wall leading to strictures and compromise of the ductal lumen with partial or complete obstruction to meibumflow.21,23–29 The concept of a duct lumen with compromised intraductal integrity from externally contracting fixed periductal fibrosis was not previously contemplated in the literature but has transformed our understanding and treatment of this disease. The awareness of FFFUR is essential to the understanding of obstructive MGD and explains the history of frustration and difficulty with the conventional treatments using heat and pressure as well as lid scrubs along with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory therapies which together do not relieve fixed obstructions. However, the appreciation of this type of resistance is only obtained through personally performing the probing procedure. This resistance is relieved with gland probing leading to equilibration of intraductal pressures. While traditional and even new approaches of treatment30–33 continue to use heat and pressure to deliver the non-fixed obstruction into the tear film, these same approaches may paradoxically exacerbate symptoms and signs of obstructive MGD if performed before intraductal integrity has been restored, analogous to squeezing a blemish (P1).32–37
Periductal fibrosis is thought to develop in the setting of local disease causing ocular surface or lid inflammation as well as regional or systemic disease with associated periglandular inflammation.3,21,23–27,33–37 This band-like fibrosis may exist at a single or multiple depths. Fixed obstruction raises intraductal pressure with subsequent gland atrophy proximal (or deep) to the obstruction. Figure 1 shows a proposed classification of glands with o-MGD and distal or proximal periductal fibrosis named Complete Distal (CDO) and Proximal (CPO) obstruction, respectively, in contrast with Partial Distal (PDO) obstruction. The fibrosis in CDO is thought to occur just inside the orifice such that there is no communication between the orifice and even a single acinus. This gland is not expressible. There is elevated intraductal pressure throughout the entire gland with lid tenderness (LT). If not relieved, this type of obstruction will lead to whole gland atrophy. In contrast, the fibrosis in CPO is thought to occur more proximally (deeper) such that there remains at least one acinus in communication with the orifice making this an expressible gland. To be clear, a seemingly healthy expressible gland is usually not healthy as it frequently demonstrates proximal (deep) obstruction (CPO) with FFFUR. Proximal obstruction with increased intraductal pressure may lead to gland atrophy behind the obstruction and a short or truncated gland (D1). A recent study24 showed expressible and nonexpressible glands have no significant difference in frequency of FFFUR, detected in 67% of all glands with a 1 mm probe and up to 94% with a 2 mm probe (perspective #14). PDO represents a gland without stricture or FFFUR which is expressible and lacks tenderness suggesting normal intraductal pressure. In extrapolating these concepts to describe a lid, if there are less than five expressible glands than the lid is considered either CDO if tender or complete distal obstruction-non functional (CDO-NF) if not tender (Figure 1). If there are five or more expressible glands, then the lid is described as either CPO if tender or PDO if not. As noted above, these types of strictures and obstructions are fixed and unyielding and require the intraductal passage of the probe for diagnosis and successful relief. Patient and physician hear the belt of scar tissue “pop”, releasing circumferential tension from the duct as intraductal pressures equilibrate and sequestered meibum is seen flowing out through the orifice along the wire probe (Figure 2). These concepts help explain the seemingly conflicting, confusing findings where patients treated with heat and pressure, for example with gland expression, sense increased lubrication released from in front of CPO, but also increased lid inflammation, soreness, and swelling from trapped meibum with increased intraductal pressure behind the CPO (P2). This is why probing should be performed as initial therapy to restore anatomic intraductal integrity by establishing and/or confirming a patent outflow tract. Probing provides unequivocal positive physical proof of a patent duct/orifice outflow tract. Probing relieves all obstruction, non-fixed and fixed. Post probing heat and manual expression may be used to accelerate a more complete delivery of the previously sequestered, but now liberated meibum while together promoting an improvement in de novo meibum synthesis.
 |
Figure 1 o-MGD classification diagram. The top row of images represents a fixed, firm, focal, unyielding resistance (FFFUR) with obstruction (indicated by the orange ring around the gland duct) of the meibomian gland (MG) distal to all acini. This type of obstruction will initially present with lid tenderness (LT), as meibum is being produced without an escape, leading to the build-up of pressure behind the obstruction (this obstruction is termed complete distal obstruction, or CDO, as depicted in the first image of the top row). Eventually, the build-up of pressure will result in a loss of function of the gland (termed complete distal obstruction non-functional, or CDO-NF, as depicted in the middle image of the top row), ultimately resulting in MG dropout as the entire gland atrophies (top row, right). No meibum will be expressed from this gland. The first two images in the bottom row represent a fixed proximal obstruction (indicated by the orange ring around the more proximal gland duct) of the MG, in which one or more acini are in communication with the central duct and orifice. LT will be present, as meibum is being produced without an escape, leading to the build-up of pressure behind the obstruction. However, this classification of MGs will have expressible meibum, as the acini located distally to the obstruction still remains in communication with the central duct and orifice (this obstruction is termed complete proximal obstruction, or CPO, as depicted in the first image of the bottom row). Eventually, the build-up of pressure will result in a loss of function of the gland proximal to the obstruction (CPO-NF). Without relief of obstruction, there would ultimately be significantly increased numbers of short, truncated MG (middle image, bottom row) showing proximal atrophy. The final classification of partial distal obstruction (or PDO, as depicted in the bottom row, right), is the result of a partial distally obstructed gland, such as orifice squamous metaplasia. This gland presents with no LT, as there is not a complete obstruction, and meibum is able to be expressed at the orifice. Reproduced with permission from Maskin SL. Intraductal meibomian gland probing: a paradigm shift for the successful treatment of obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. In: Tsubota K, ed. Diagnosis and treatment of meibomian gland dysfunction. Tokyo, Japan: Kanehara & Co., Ltd; 2016:149-167.7 |
 |
Figure 2 Release of occult trapped meibum along intraductal Meibomian gland probe and out through orifice after relief of a fixed, firm, focal unyielding resistance (FFFUR) type of obstruction. Reproduced with permission from Maskin SL. Intraductal meibomian gland probing relieves symptoms of obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2010;29(10):1145–1152 (https://journals.lww.com/corneajrnl/Abstract/2010/10000/Intraductal_Meibomian_Gland_Probing_Relieves.13.aspx).4 |
Clinical results of MGP
Our results
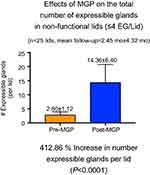
After probing we have seen a dramatic and immediate resolution (within 1 week) of LT in 86% of 144 lids, while 82% of 215 lids at 3–6 months, and 58% of 113 lids at one year, remained non-tender (Figure 3). There was a return of meibum secreting lid functionality (five or more expressible glands per lid from previous CDO or CDO-NF lids with four or less expressible glands per lid) in 94% of 64 lids at 1 week, 92% of 102 lids at 3–6 months, and 74% of 46 lids at one-year follow-up (Figure 4). There was also an increase in numbers of expressible glands by 412% (p<0.001) (Figure 5) in a series of 25 lids with pre-probing average number of expressible glands at 2.8 increasing to 14.4 at a mean follow-up of 2.4 months.3 Figure 6 shows an example of the clinical improvement in lid margin appearance 2 months after probing with the decreased vascular caliber and reduced orifice inflammation. We also reported at ARVO 2017 and published in British Journal of Ophthalmology 2018 that MGP was associated with an increase in meibomian gland tissue area and growth from atrophied meibomian glands as viewed on infrared meibography (Figure 7). We found 41.2% of the lids with follow up between 4.5 and 12 months showing signs of growth. Individual lids showed a significant increase in mean individual gland area (MIGA) up to 21.13% (p=0.0277). Collectively, for all 13 lids and 149 glands studied, we found a significant increase of 6.38% in total glandular area (p=0.0447) and a significant increase of 6.23% in MIGA (p=0.0003). These results suggest that under favorable conditions, including (1) MGP providing positive physical proof of a patent duct/orifice outflow tract and (2) treatment of suppressive co-morbid disease, that MGP may permit or perhaps promote MG growth. We have seen four types of growth including (1) a lengthening of shortened glands reversing proximal atrophy (Figure 7), (2) the partial restoration of faded glands with increased density and better definition, (3) appearance of a new gland, (4) restoration of a continuous gland from discontinuous segments of MG tissue. Successful MG growth is essential to restore full, functional, healthy, and resilient MG lid populations. Healthy whole glands are preferable to functional yet partially atrophic glands as healthy whole glands can experience subsequent partial atrophy and still retain functionality, while already partially atrophic glands with obstruction may lead to whole gland atrophy. There is clinical value to the resilience of a restored gland. This growth of MG tissue may be related to the removal of the suppressive effect of elevated intraductal pressure. Alternatively, probing may activate MG stem cells with a direct mechanical intraductal stimulus through debridement of cornified ductal epithelium which could initiate proliferative effects with stem cell-induced transient amplifying daughter cells, leading to differentiation of ductal and acinar epithelium.3
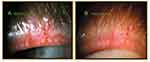 |
Figure 6 Clinical exam findings post probing: Pre-probing photo, (A) shows the appearance of left upper lid with lid margin vascular engorgement and gland plugging; (B) is 2 months after gland probing showing vessel regression with a marked reduction in vascular caliber and gland plugging. There was an associated marked reduction in lid tenderness visual analog scale (VAS) from the pre-probing score of 45 out of 100 to his latest score of 0 at 23 months post probing. The lid showed intact meibum secreting functionality with more than 10 glands showing expressible meibum. Reproduced with permission from Maskin SL. Intraductal meibomian gland probing: a paradigm shift for the successful treatment of obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. In: Tsubota K, ed. Diagnosis and treatment of meibomian gland dysfunction. Tokyo, Japan: Kanehara & Co., Ltd; 2016:149–167.7 |
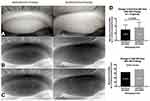 |
Figure 7 Post probing example of increased Meibomian gland tissue area on infrared meibography: The rectangles in (A–C) highlight the atrophic area in the TMF where growth has occurred. (A). Pre and post probing image capture from IR meibography video. (B) Pre and post probing image capture after being processed through Adobe Photoshop simply to desaturate and invert the color image. (C) Pre and post probing traces of the total measurement field (TMF), and each individual meibomian gland (MG). The pre-probing images show proximal atrophy with shortened gland length. Post probing shows an increased lengthening of these glands. (D) Statistical analysis revealed a significant increase in glandular tissue post probing (t=5.947, p=0.0001), representing a 19.93% growth in total MG tissue area. Reproduced from Growth of meibomian gland tissue after intraductal meibomian gland probing in patients with obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction, Maskin SL, Testa WR, 102, 59-68, Copyright © 2018, with permission from BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.3 |
Review of the literature
At the time of writing this manuscript, there are ten independent published papers in the peer- reviewed literature whose results are consistent with my findings (Table 1). The most recent was published in 2019 from India where Nirupama et al23 studied 30 patients prospectively over 6 months. These patients were refractory to medical therapy without improvement in signs or symptoms for 8 weeks prior to probing. By 1 month after probing, 73% of patients had an improvement in lid margin congestion, TBUT, and OSDI while by 6 months after probing, 93.3% of patients had improvement in TBUT from 5.33 to 9.87 seconds (p=0.0001) and OSDI from 26 to 13.5 ( p= 0.0001) and all patients showed improvement in lid margin congestion.
 |
Table 1 Review of literature for meibomian gland probing |
Incekalan and colleagues published their study in 2018 comparing probing to conventional treatment and found more rapid symptom relief post probing as measured by ocular surface disease index (OSDI), and improvements in Schirmer 1 test, tear film break up time, and meibum score (p<0.05).22 In 2017, a study from the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Institute showed the effects of probing on 70 lids of 41 patients resulting in over 91% of the cases experiencing symptomatic improvement typically within 1 week of probing with no complications during follow-up which averaged 3.5 months.5 Also in 2017 from Cuba, researchers found, in a prospective longitudinal study of probing in 50 eyes of 25 patients, an improvement in break up times, reduction in artificial tear usage and OSDI at 1 and 6 months (p<0.001).6 One of two 2016 papers on intraductal probing published in the June issue of CORNEA evaluated efficacy and safety of probing in 49 patients with obstructive MGD refractory to eyelid warming, massage, and artificial tears. Patients were randomized into two treatment groups including probing plus topical steroid vs steroid alone and followed up at 1 day, 1 week, and 1 month. Before applying any medications, 76% of the patients obtained immediate symptom relief 1 day after probing. The probing plus steroid group also had statistically significant improvements compared to the steroid only group in meibum grade (p<0.001), lid margin abnormalities (p<0.001) and tear break up time (TBUT) (p<0.029). 8 The second 2016 paper from the same issue, prospectively looked at 58 eyes of 30 obstructive MGD patients who were refractory to medical therapy for at least 6 months. TBUT increased from 5 s at baseline to 13 s at 3 months after probing (p<0.001). There were also statistically significant post probing decreases in conjunctival hyperemia (p<0.001) and eyelid margin vascularization (p=0.004) and the OSDI also showed a significant improvement at 3 months post probing.9 A 2015 study from Japan, looked at six lids of three patients with refractory obstructive MGD that underwent probing. At the 1-month post-operative visit, all cases showed improvement in meibum lipid level and meibum viscosity with two cases showing an improvement in tear break-up time. There were no morphological changes in the Meibomian glands noted in any case using infrared meibography analysis.10 Another study, published in 2015, showed in a prospective longitudinal study, a statistically significant improvement in the probed eye of 16 patients for clinical parameters including TBUT (p<0.001), visual acuity (p<0.001), level of pain (p=0.008), and photophobia (p<0.001) when compared to the non-probed eye.11 A study from China was published in 2014 in which investigators studied 111 age and sex-matched patients in a prospective, randomized design over 1 month.12 The study compared MGP with and without intraductal injection of an antibiotic/steroid combination to conventional treatment of eyes with MGD using lid hygiene plus topical antibiotic/steroid/artificial tear drops. The study reported statistically significant improvement for both MGP treatment groups in OSDI, break up times, corneal fluorescein staining, Schirmer 1 test, and lid margin scores compared to the conventional treatment group. Confocal microscopy was also performed which showed no post probing degenerative changes in morphology of MG acinar units, nor MG scars. The tenth study was also prospective. It was published in 2012 on 40 lids of 10 patients, and showed a statistically significant improvement in post probing OSDI scores at 1 and 6 months.13 There was no adverse sequella reported in any of these studies. An independent prospective, double blinded, randomized controlled trial comparing MGP with sham probing was presented at the 2016 American Academy of Ophthalmology showing statistical significance for improved symptoms when treatment included probing according to Symptom Assessment in Dry Eye (p<0.007 and p=0.009) and OSDI (p=0.02), as well as signs of reduced lid telangiectasia (p=0.04).14 An independent study of probing presented at the European Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgeons in 2014 showed a statistically significant rapid relief of symptoms using OSDI as well as clinical parameters as tear breakup time, Schirmer’s test, and meibum score compared to control eyes.22 Two studies presented at the 2014 American Academy of Optometry also showed significant improvement in outcome measures for probing when compared to conventional lid hygiene therapy15 and lipid-containing artificial tears.16 Based on my personal experience of probing approximately 4,000 lids and 100,000 glands and feedback received from numerous eye doctors and patients I have probed from around the globe, I am confident that this procedure will launch a new era in understanding MG function and dysfunction and furthermore to control MGD.
The aha moment
I (SLM) am often asked by colleagues and patients how I came to propose MGP. I have been thinking about meibomian glands for many years. My Cornea/External diseases research and clinical fellowships were from 1988 to 1991 at Bascom Palmer Eye Institute. My research included the culture of rabbit meibomian gland ductal and acinar epithelial clones in serum-free media looking at effects of growth factors on cellular proliferation and differentiation.39,40 Since entering private practice in Tampa, Florida in 1991, I have focused on non-refractive cornea and external disease cases. Dry eye was not a popular disease to manage in part because of the difficulty in treating MGD. Naturally, dry eye patients were sent to me to diagnose and manage. The demand was so great that I authored a lay book to educate patients with dry eye.41 There was little to offer patients over the conventional therapies of lid hygiene, oral and topical antibiotics and topical steroid. The underlying cause of MGD was felt to be distal duct keratinization and meibum thickening leading to obstruction which caused elevated intraductal pressure and secondary cystic changes in acini with squamous metaplasia, atrophy, and fibrosis.42 To me, these explanations seemed incomplete. Why do we see atrophy in certain parts of glands resulting in a short gland whereas other glands in the same lid we find a completely atrophic gland? Why would the lid get tender over a gland? Why would this tenderness be present at times, whether or not the gland showed expressible meibum? Not having a clear answer to these and other questions, I concluded that the key to unlocking this mystery was within the gland itself. I was determined to find a safe way to enter the gland. Seeing many patients with progressive atrophy of their MGs over time and some of them becoming miserable with intractable pain, incapacitation, depression, and even attempted suicide, the risk of doing nothing or persisting with the failed conventional therapy of the day for intractable cases was not acceptable.
The ideal patient presented one day. He was a middle aged moderately overweight man with severe obstructive MGD, crying out in frustration over his extremely tender lids. He had been to many ophthalmologists without relief having tried the usual treatments. After obtaining informed consent, I assembled a sterile prototype probe and entered five glands in the outer third of the lower lid. There were multiple foci of strictures with fixed resistance at various lengths within the ducts which I could penetrate, allowing sequestered meibum to emerge through the orifices. As the fixed resistance was relieved, the patient and I could hear an audible pop or gritty (multiple pops) sound. I was amazed as I had not anticipated this finding. It later became clear that the fixed resistance was from periductal fibrosis contracting around the external duct wall with a secondary compromise of the internal duct lumen. By the time I finished probing the lower lid, my patient was all smiles. After probing his four lids, he jumped out of the exam chair and gave me a big hug…his suffering was over.6
Patient selection
Based on current understandings, concepts and clinical results, we offer our patient selection approach.
Category of patients
Patients with MGD
Probing has become the initial therapy for MGD in my practice. Its purpose is to release the tight bands of periductal fibrosis contracting around the external duct wall with secondary stricture of the compromised duct lumen. Probing is able to unequivocably with positive physical proof, restore (or confirm) anatomic intraductal integrity by relief of FFFUR thereby eliminating intraductal resistance. Relief of resistance equilibrates intraductal pressures and restores meibum flow. Probing is also used for maintenance of ductal integrity by helping prevent recurrent obstruction with a subclinical progression of the disease and possible initial or progressive gland atrophy (as seen on meibography). An analogy may be dentistry with periodic prophylactic tooth scaling and cleaning in the absence of caries or gingival disease.
For patient selection, we (and others)3–22 have shown that all stages of symptomatic MGD would benefit from probing by safely reducing symptoms and improving signs without side effects. This includes symptomatic patients with:
- Lid tenderness and soreness which suggests elevated intraductal pressure behind an obstruction,
- Lipid tear deficiency,
- Non-expressible and expressible glands with slit lamp signs of MGD. Signs of MGD may include lid margin or tarsal hyperemia, lid margin telangiectasia, thickening or irregularity, orifice metaplasia, and anterior migration of line of Marx,
- Non-obvious MGD (NOMGD) with minimal to no slit lamp signs of MGD except reduced numbers of expressible glands,43
- Early hordeolum or chalazion with possible adjunctive intraductal microtube steroid injection,19,44
- “Neuropathic” eye pain as we have found occult fixed obstruction (FFFUR) in these patients (see Diagnostic evaluation of occult disease as well as therapeutic intervention),
- Lids showing signs of MG obstruction on infrared meibography or transillumination including dilated ducts and cystic acini as well as atrophic changes.
MGD is the most common cause of dry eye occurring in about 86% of the dry eye cases and is the indication for MGP.2 However, onset and progression of MGD are greatly impacted by numerous factors. These factors include environmental, behavioral (contact lenses, LASIK, quality of sleep) as well as local, regional and systemic co-morbidities. These factors may be episodic, seasonal or wax and wane. Thus, MGD often develops in a non-linear manner leading to delay in diagnosis while the disease progresses subclinically. Subclinical progression of MGD was noted in our 20104 report on MGP for MGD. In that paper, we reported that after successful treatment with MGP, patients frequently observed improvement in symptoms not previously appreciated.4 These improvements were in addition to the resolution of the presenting complaint. They had not realized the slow gradual deterioration of comfort or blurred vision until restored. This underscores the possibility that early detection of subclinical MGD may be achieved with diagnostic probing in patients with signs of MGD. Diagnostic probing, is in essence therapeutic as well which, could lead to prevention of structural changes in the glands. Thus, in addition to the seven indications above, we would consider probing subclinical asymptomatic patients with:
- Non-expressible and expressible glands plus slit lamp signs of MGD43
- NOMGD with minimal to no slit lamp signs of MGD except reduced numbers of expressible glands on repeat examinations.
- Changes of obstructed Meibomian glands on infrared meibography including cystic changes, dilated ducts and gland atrophy.
There are times when gland probing is useful to diagnose (and treat) occult FFFUR. As an example, I have diagnosed occult FFFUR in approximately two dozen patients diagnosed with neuropathic eye pain. These patients were without commensurate slit lamp signs of disease including tarsal and bulbar hyperemia and vital staining. Three recent cases within the past year had typical severe burning pain refractory to topical anesthetic. Mild proximal atrophy with cystic changes were noted on infrared meibography.45,46 These cases had no lid tenderness with significant numbers of expressible glands. Interestingly, gland probing of these lids with a 1 mm probe found greater than 92% of the glands with FFFUR. Probing helped reverse symptoms. Probing was able to detect and relieve occult intraductal obstruction and restore or confirm anatomic intraductal integrity and a patent duct/orifice outflow tract with positive physical proof of outflow patency.3,4 This experience suggests occult obstructive MGD with proximal fixed obstruction may present with symptoms suggestive of neuropathic eye pain.47,48 Furthermore, MGP is able to identify the presence of FFFUR in the absence of slit lamp findings of tarsal fibrosis and without access to confocal microscopy (which can demonstrate periductal fibrosis).3,21,23–27 In addition to identifying occult FFFUR, the location of FFFUR at the 1, 2, or 4 mm level may provide a diagnostic differential depth analysis potentially revealing the underlying source of pathology such as distal duct, orifice, lid margin, and tear film vs a more proximal conjunctival or periglandular/autoimmune source of inflammation.49,50 Identification of non-FFFUR obstruction described as non-fixed, non-focal, easily yielding (SFT) soft resistance may indicate altered duct/ductal contents.24 Thus, probing may provide a useful diagnostic assessment as well as therapeutic intervention.
Patients with MGD and other ocular surface diseases
We have observed that surface co-morbidities reduce Meibomian gland function and duration of benefit of probing. This includes patients with aqueous tear deficiency (ATD), allergy, and friction related diseases such as conjunctival chalasis and superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis. These co-morbidities should be diagnosed and treated. We also recommend following patients after glaucoma device placement and trabeculectomy as well as scleral and contact lens wear for friction induced MGD.51 Other surface diseases affecting MG health include anterior blepharitis, and lagophthalmos with incomplete or reduced blink and nocturnal lagophthalmos. In these settings, we anticipate MG obstruction and may provide initial or maintenance probing if symptomatic or subclinical and asymptomatic with signs of MGD. If glands are inflamed, we would consider adjunctive intraductal microtube steroid injection in addition to targeting co-morbid surface disease.19,44
Patients with MGD and pre-op for cataract or refractive surgery
It has been noted with increasing frequency that patients presenting for cataract and refractive surgery have MGD which is often exacerbated from surgery leading to unhappy postoperative patients complaining of poor vision and discomfort.52 In a recent study, over half of cataract surgery patients presenting for surgery were found to have MGD with half of these MGD cases asymptomatic. More than half of all patients (56%) had MGD atrophy on meibography. In this setting, we suggest gland probing if (1) symptomatic MGD is present or with (2) subclinical and asymptomatic MGD plus slit lamp findings of MGD or with (3) MG obstruction on infrared meibography in order to pre-empt postoperative exacerbation of disease. We would also consider possible preoperative and an increase of postoperative topical corticosteroid therapy.
Other
Patients who have glaucoma on topical antihypertensive meds may have secondary inflammation with exacerbation of MGD. Cosmetics including skin foundation, eyeliner, and mascara as well as LatisseR and other lash enhancers plus make-up removers may increase lid margin inflammation with an adverse effect on gland function. Delayed tear clearance53 leads to stagnation of tear with the accumulation of preservatives, irritants, allergens, toxins, microbes, and other noxious stimuli with secondary surface inflammation and exacerbation of MGD. Patients with keratinized surfaces such as with Vitamin A deficiency as well as tarsal inflammation seen with graft vs host disease, chemical, and thermal injury and other cicatrizing disease typically have accompanying obstructive MGD. Patients in these various clinical situations will nearly all have symptomatic or subclinical obstructive MGD and would benefit from probing for diagnosis and/or therapy to restore anatomic intraductal integrity.
Procedure
Performing a well tolerated probing procedure (see perspective #16)
To ensure a well-tolerated procedure (D2), I use my proprietary jojoba anesthetic ointment (JAO) containing 8% lidocaine and 25% jojoba wax available from O’Brien Pharmacy, Mission Kansas. JAO is kept in office lab refrigerator until use. The patient is reclined in the exam room chair. After placing one drop of topical anesthetic into the inferior fornix, I place a bandage contact lens on the eye and a generous amount of JAO on the lower lid margins. The eye is closed for 10–15 mins during which time both upper and lower lid margins are anesthetized. The eye is opened, and the second drop of topical anesthetic is placed in the inferior fornix. The patient chair is returned to the upright position and probing is begun after the patient is brought to the slit lamp. The head must be against the forehead rest and the chin against the chin rest. As probing is begun, if the patient’s lids are sensitive, a second round of JAO applied to the lid margin is typically successful in making the procedure well tolerated with a 1 mm probe (D2) (also check the expiration date of the jojoba anesthetic as it can lose potency within 2 months or near the expiration date. If not refrigerated, it can lose potency within 2 weeks.). Use of longer probes may require infiltrative anesthesia which is greatly eased with initial use of JAO.5
The stainless-steel probes are 76 microns in diameter with lengths of 1,2, 4, and 6 mm. I start with a 1 mm probe on all patients as this length is the stiffest and most likely to safely advance through orifice lumen strictures into the distal duct. (Katena Products Inc, Denville, NJ, USA). The probe follows the course of the duct similar to placing your arm through your shirt sleeve. The longer probes enable reaching into the deepest part of the glands if necessary, for example, to unblock an early hordeolum. The longer probes are also used for persistent deeper LT. The probes are non-sharp to minimize alteration of tissue and allow a better feel of resistance during the procedure rather than sharp blades which would slice their way through the tissue without yielding diagnostic information about the type and extent of resistance as well as possibly cut through the duct wall.
As the probe is inserted through the orifice and into the central duct, you typically encounter resistance within the lumen. This resistance may be relieved by advancing the probe using a short dart throwing or jab motion, generating the audible “pop” or multiple pops described as a “gritty” sensation. The patient also hears the “pops” and “gritty” sensations and can appreciate the instant relief of elevated intraductal pressure as the obstruction is relieved and intraductal pressures equilibrate with relief of tenderness. This is analogous to a lumen obstruction in the gastrointestinal tract. For example, with a bowel obstruction, there is elevated intraluminal pressure, with tenderness and secondary inflammation. With relief, there is equilibration of intraluminal pressures, as well as the resolution of abdominal tenderness and inflammation. As the Meibomian gland intraductal obstruction is relieved, you can often note sequestered meibum release along the wire probe to exit through the now patent outflow channel and orifice. Dot hemorrhages at the orifice frequently occur with probing likely from the relief of disorganized periductal fibrovascular scar tissue. These hemorrhages are self-limited and do not need pressure or other treatment. After probing, glands may receive adjunctive intraductal microtube injection of therapeutics such as dexamethasone (see perspective #3) if indicated. Topical corticosteroid use may also be used if significant inflammation is present. After probing is completed, the contact lens is removed and the ocular surface is copiously irrigated with sterile preservative-free saline such as Purilens (www.purilens.com). A cotton-tipped applicator is then used to remove any residual JAO from the lid margin. An alternative anesthesia approach uses a cotton pledget soaked in 4% lidocaine placed in the fornix, followed by injection of 2% lidocaine with epinephrine into the forniceal subconjunctival space with subsequent subcutaneous lidocaine injection just anterior to lid margin if necessary.5
There are some physicians who have expressed concern that probing may damage the gland in some way (D3). Independent studies have specifically evaluated this with confocal microscopy and meibography and found no adverse effects on the morphology of acinar units or scarring.10,12 The many peer-reviewed published papers and presentations on MGP all found no adverse effects.3–23 However, all studies did show significant benefit by using gland probing with relief of symptoms and signs of o-MGD (see perspective #1).3–23
Impact of probing on patients
It is generally accepted that aging and o-MGD are associated with dropout and atrophy of MGs as seen by infrared meibography.45,46 Untreated, symptoms develop from lipid tear deficiency as well as fixed and non-fixed obstruction, with elevated intraductal pressure leading to LT, inflammation and subsequent gland atrophy. In my practice (SLM), patients’ symptoms after probing and treatment of co-morbidities are dramatically and immediately resolved, analogous to symptom resolution after relief of a gastrointestinal obstruction with inflammation and abdominal tenderness. Inadequately treated, progressive o-MGD along with other surface diseases, such as ATD, may lead to severe unrelenting pain with debilitation and psychosocial problems as stress, anxiety, depression, and even suicidal ideation as surface nerves become highly sensitized and may lead to autonomous firing of peripheral and central afferent nerves described as neuropathic eye pain. This may lead to the use of systemic medications with potent addictive and other side effects. Over my career I have managed approximately two dozen patients from around the US and abroad diagnosed with neuropathic pain who have attempted suicide, were hospitalized for suicidal ideation or had detailed plans to end their life. No counseling was able to help their unrelenting eye pain which was simply too much to bear and all were planning on suicide to escape their pain. Invariably, all patients had occult ocular surface disease including MGD. Targeted treatment reduced and eliminated the pain and none carried out their suicide plans. Significantly, patients did well in part by identifying occult intraductal proximal MG obstruction in expressible glands and restoring integrity to the intraductal space and functionality to MGs. Probing has repeatedly demonstrated a significant beneficial and restorative effect on the meibomian gland in a variety of clinical settings.
Management strategy after probing
Due to its location, MGs will always be under assault from co-morbid local diseases such as allergy, microbial infection, and ATD as well as systemic diseases such as autoimmune disease, hormonal disease, neurological, sleep disorders, and others.3 These diseases can all lead to surface and periglandular inflammation with subsequent periductal fibrosis and obstruction and therefore must be diagnosed and treated.37 In this way, the Meibomian Gland is a barometer of the health of the entire body. This is why probing should be repeated, as in the dental analogy, at approximately yearly intervals to maintain ductal integrity and patency of outflow channel with positive physical proof of patency as well as reduce the risk of gland atrophy for a disease which may progress in a subclinical manner. Probing one time and then using heat and pressure techniques for long-term follow-up treatments will not prevent asymptomatic, subclinical recurrent disease which may begin to gradually return within a few months (unpublished data).
Patients with symptoms relieved from probing need to be monitored on every visit to detect early re-obstruction with a progression of the disease, even if the patient is symptom free. This can include checking for LT and expressible glands on every exam plus meibography every 4–6 months. Symptom relief from MGP should last about 1 year. If symptoms reappear earlier than 1-year post probing, or there is a decrease in the number of expressible glands or increase in LT, then there is an unrecognized, or inadequately treated local, regional or systemic co-morbid disease. Probing provides positive physical proof of patency, but once achieved the patent outflow channel must be defended against all co-morbid sources of inflammation which would re-obstruct the outflow tract.
Probing facilitates removal of sequestered and other retained intraductal contents by relief of intraductal resistance and establishment of a patent outflow tract, allowing natural meibum secretion and delivery to the tear film to resume. In summary, initial and maintenance probing: 1) relieves all sources of obstruction to restore or confirm ductal integrity, 2) maintains patency of outflow channel, and 3) appears to promote or enable meibomian gland tissue growth as seen on IR-meibography.
Case study of a 66-year-old woman
Figures 8, 9, and Table 2 show pre and post probing appearance of left upper and lower lid of a 66-year-old woman with obstructive MGD. For each lid, there was a post probing increase of the number of expressible glands with an improved status from a CDO with less than five expressible glands per lid plus LT, to a PDO with greater than 10 expressible glands per lid plus no LT. Subsequently, co-morbid disease consisting of anterior blepharitis and gastrointestinal flu with use of anticholinergic medications may have had an adverse impact on MG status with change in status from PDO to CPO characterized by LT and reduced expressible glands. In this case, restored gland status was achieved with the treatment of anterior blepharitis and resolution of flu plus discontinuation of oral pharmaceutical therapy. It was not necessary to re-probe.
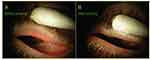 |
Figure 8 Case study of probing for a 66-year-old woman with obstructive MGD (upper lid): (A) before probing, the left upper lid had 0 expressible glands and VAS showed 44 out of 100 scale for tenderness for a diagnosis of complete distal obstruction (CDO), while 1 week after probing (LU After); (B) the same lid had more than 10 expressible glands and VAS showed 7 of 100 in tenderness for a diagnosis of partial distal obstruction (PDO). Reproduced with permission from Maskin SL. Intraductal meibomian gland probing: a paradigm shift for the successful treatment of obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. In: Tsubota K, ed. Diagnosis and treatment of meibomian gland dysfunction. Tokyo, Japan: Kanehara & Co., Ltd; 2016:149–167.7 |
 |
Figure 9 Case study of probing of lower lid for patient in Figure 8: (A) before probing, the left lower lid had 0 expressible glands and VAS of 47 of 100 tenderness for diagnosis of CDO, while 1 week after probing (LL After); (B) the same lid had more than 10 expressible glands and VAS showed 0 of 100 tenderness for a diagnosis of PDO. Reproduced with permission from Maskin SL. Intraductal meibomian gland probing: a paradigm shift for the successful treatment of obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. In: Tsubota K, ed. Diagnosis and treatment of meibomian gland dysfunction. Tokyo, Japan: Kanehara & Co., Ltd; 2016:149–167.7 |
 |
Table 2 Case study of meibomian gland probing |
Perspectives (plus selected fundamentals)
- Intraductal Probing Meibomian Glands is Safe10,12 and Analogous to Treating Other Tissues and Organs From the Inside:
Our ability to safely cannulate and treat the Meibomian gland from the inside broadens the range of tissues and organs that are internally cannulated in routine medical practice at the beginning of the twenty-first century. These include exocrine salivary glands as well as pancreas and biliary tree, in addition to cerebral, coronary, and renal arteries, plus the urethra and esophagus for treatment of strictures. The Meibomian gland is a skin appendage embryologically derived from surface ectoderm.23 In contrast to the Meibomian gland, the urethra and esophagus are embryologically derived from endoderm and have lumens in continuity with vital organs. For urethral and esophageal lumen strictures, the internal approach to dilating the lumen is an effective targeted treatment of mechanical blockage. We have found the same to be true of treating internal strictures of the Meibomian glands with intraductal probing.
It is important when probing the MG to do so effectively with minimal unnecessary disturbance of glandular tissue. As noted above, post probing confocal microscopy has shown no degenerative changes in morphology of MG acinar units, nor MG scars.10,12 The instruments I have developed are fine, non-sharp probes to penetrate the orifice, advancing through the duct to relieve obstruction by releasing tight bands of periductal fibrosis.
The 110-micron small bore tube may be used to inject medicaments after use of the 76-micron probe to open and dilate orifice. I have used this microtube extensively to inject intraductal dexamethasone and other therapeutics after probing. This enables treatment of inflamed glands with steroid and removal of stagnant secretions from the glands with a lavage effect. I use intraductal microtube steroid injection when a patient has severe co-morbid diseases, retreatments, inflamed glands, and chalazion. If the desire is to inject a small particle suspension, then the gland is dilated with the 150-micron dilator after the 76-micron probe, followed by use of the 152-micron large bore tube to inject the suspension.19,44
Probing provides intraductal findings which can reveal the status of the Meibomian gland intraductal space. This information includes whether there is fixed, firm mechanical resistance from single or multiple pops (“gritty”) indicating periductal fibrosis (FFFUR) or from non-fixed, non-focal, easily yielding soft resistance (SFT), possibly reflecting altered duct and/or ductal contents.24
There are glands that I probe which do not demonstrate resistance. These “no resistance” or “NR” glands occur in about 16% of all glands24 and may represent normal glands without periductal fibrosis. However, in some cases, there appears to be significant periglandular connective tissue weakness or abnormal duct in which the duct dilates without obstruction and the probe does not encounter resistance.
Some have asked me how to prevent a false passage when probing. When you penetrate the orifice and enter the gland, the effect is tantamount to passing your arm into a shirt sleeve. The probe simply follows the duct in the same fashion. Out of my approximately 100,000 glands probed, there have been less than a handful of glands early on, more than 10 years ago, that led to a false passage. This was before the 1 mm probe (the shortest and stiffest) was introduced. There were no sequela.
The purpose of probing is to reverse the compromised integrity of the intraductal space from the effect of lumen strictures and obstruction secondary to contracting periductal fibrosis around the external duct wall. Probing will restore the anatomic intraductal integrity by establishing unequivocally (or confirming) with positive physical proof that there is a patent outflow channel without obstruction. By relief of obstructions, probing equilibrates intraductal pressures and promotes removal of sequestered and other retained intraductal contents, helping to relieve symptoms of MGD. At times the introduction of intraductal lavage or pharmaceutical microtube injection will act to remove sludged material that was not removed with probing and subsequent expression alone.
In my view, the Meibomian gland is the center of an integrated dry eye system of local and systemic component sub-systems whose healthy functioning serves a vital, supportive role in the healthy functioning of Meibomian glands. When the Meibomian glands become dysfunctional or lose expressibility, these support sub-systems must be evaluated for the co-morbid disease. The overall clinical strategy which has been highly successful for my patients with MGD has been to probe glands to restore integrity to the intraductal space, then defend these glands from re-occluding by treatment of co-morbid diseases. The MGs will re-occlude in the presence of secondary inflammation from numerous co-morbid sources. This includes local diseases such as aqueous tear deficiency (ATD), conjunctivochalasis, anterior blepharitis, and allergy. Other local co-morbid conditions which may exert mechanical frictional trauma with inflammatory sequela to the glands include Salzmann’s nodular degeneration, glaucoma bleb or seton dome, elevated or protruding retinal encircling element as well as scleral and other contact lens wear. Systemic diseases with similar adverse impact include autoimmune diseases as Sjögren’s syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis, but also sleep deprivation, the common cold, and perhaps even dietary binges (see below). This places the Meibomian gland as a barometer of the health of the ocular surface and in some cases systemic health as well.
Our early studies suggested approximately 40% of the patients have post probing retreatment at an average of 18 months. More recent studies recommend annual maintenance probing. However, if the patient develops a co-morbid disease such as ATD and this is not treated adequately, the duration of benefit from MGP is shortened to 1–3 months. This finding is important to understand in order to avoid having to unnecessarily retreat patients. I have had patients come to me for second opinions as they have had great probing results lasting only 2 months and have been re-probed several times within a year. Each of these patients had an inadequately treated co-morbid disease. In one of these cases, a patient with ATD was treated with Restasis® with only partial improvement, leaving the patient aqueous deficient. Punctal occlusion was used to restore good tear volume, and the patient did not need further probing for at least another year. Alternatively, I have had patients doing well-post MGP develop anterior blepharitis and become blocked again. Treatment with antibiotic ophthalmic ointment eliminated the infection, but the glands remained blocked needing to be re-probed. However, other cases of treated anterior blepharitis have led to the restoration of functional glands with expressible meibum. In summary, each co-morbid condition is different. Some will show restoration of MG functionality spontaneously after reversing the co-morbid condition, others will need to be re-probed to restore functionality.
An interesting common theme has emerged in a few of my patients where they have had painful MGD for years and have suffered greatly until relieved with MGP. These patients became so happy they celebrated with bingeing on saturated fats and simple sugars, gaining significant weight over a short time, for example, 10 pounds in 1 week. Interestingly, follow-up exam has shown reduced functionality of glands as their MGD Classification changed from CDO (pre probing with LT and less than 5 expressible glands per lid) to PDO (post probing with no LT and 5 or greater expressible glands per lid) to CDO-NF (post binge with no expressible meibum and no LT) suggesting glands were dormant and not synthesizing meibum. In each case after returning to a normal diet, I have repeatedly seen the MG exam show a return to expressible glands without tenderness (PDO). These anecdotes suggest a binge diet may lead to a type of gland cellular latency with reduced cell proliferation and differentiation. I have also seen caffeine (coffee, tea, soda, chocolate) worsen MGD functionality. Although there are some papers54 showing increase tear with caffeine, I have seen an exacerbation of symptoms. This may be through a few different mechanisms. Caffeine is a diuretic, so can lead to dehydration. Caffeine is also a stimulant so may cause lid retraction with increased fissure width stretching the tear film to instability. Its stimulant effect may also increase blink rate making for poor quality of blink as well as increase pupil size leading to photophobia and secondary blepharospasm. There is an animal model of MGD using topical epinephrine leading to increased ductal keratinization and obstruction which may also occur in the setting of systemic caffeine use by increasing circulating and tear film epinephrine.55,56 Another systemic dietary consideration in the setting of MGD is an abnormal serum cholesterol level.57
Over the nearly 15 years I have provided MGP to my patients, I have noted a pattern of acute MGD symptoms when patients have been exposed to particulate matter in an occupational or recreational setting. Exposure to dust and other particulate matter can cause acute as well as chronic Meibomian gland obstruction with severe pain and LT. Interestingly, I have seen at least eight patients with a history of acute obstructive MGD develop after exposures to: volcano smoke in Guatemala, heavy outdoor dust at a Renaissance Festival, a large dust plume from emptying a vacuum cleaner bag, residual smoke from California wildfires, campfire and candle smoke, as well as agriculture industry dust such as straw dust on a dairy farm, and dust on a deer farm. Particulate dust matter may contain a variety of irritants. For example, agriculture industry dust contains organic products including mold, fungus, pesticides, herbicides, animal-derived particles, feed, and bedding particles and endotoxins.59 For these patients, symptom onset was acute and incapacitating while lasting for months or longer prior to presentation to my office. Interestingly, patients were able to track symptom onset back to the environmental exposure and had a clear recollection of the inciting event. MGP was able to consistently relieve gland obstruction and help provide relief of symptoms. Eye cosmetics that are particulate matter such as foundation, eyeliner, mascara, and shadow can also inflame the lid margins and lead to o-MGD.
Theoretically, only one acinus is necessary to restore a non-meibum expressing gland to one that does express. Therefore, I probe all orifices even if I can not visualize glandular elements on meibography. If there is acinar tissue or stem cells present, then improving the microenvironment by unblocking obstructions and treating co-morbid diseases gives those cells an environment to promote growth and differentiation. In summary, even if meibography shows extensive loss of MG tissue, I still probe as I have achieved good results.
TBUT reflects tear film stability and lipid tear status mostly impacted by Meibomian glands of the upper and lower lids. I have seen cases with extensive gland atrophy with normal TBUT from a few hypersecreting acini of a few residual glands. I do not give up on even the most advanced cases of atrophic MGD. I probe these glands to maximize functionality.
MGP may be helpful to diagnose occult FFFUR as well as help therapeutically in the setting of symptoms of ocular surface disease without definitive signs of MGD. It is an important initial treatment for MGD to restore normal anatomic intraductal integrity, with subsequent consideration of adjunctive heat and pressure treatments.
Our recent studies show expressible and non-expressible glands have no significant difference of the frequency of FFFUR, which was detected in 67% of all glands using a 1 mm probe while up to 94% with a 2 mm probe.24 This finding means that for lids with obstructive MGD, all glands should be probed.
This is a still unsettled area which attempts to explain the severe seemingly intractable pain that some patients develop in the setting of LASIK, and other eye surgery along with dry eye as well as other patients, for example, with small fiber neuropathy or fibromyalgia. These patients have been described as having centralized neuropathic pain indicated by severe pain without significant signs refractory to topical anesthetic and have been often treated with autologous serum drops, platelet-rich plasma drops, scleral lens, oral gabapentin, and prokeraR. These patients are at times sent to pain management doctors and may elect to undergo extreme measures such as CNS implanted pain pumps.60
In my own experience, during my career of nearly 30 years with the last 5 years limited to dry eye cases only, I have managed approximately two dozen patients with a diagnosis of neuropathic pain. These patients have come to Tampa for my evaluation after having attempted suicide or hospitalized for suicidal ideation or simply had detailed plans to end their lives. No counseling could help their unrelenting eye pain which was simply too much to bear leading all of these patients to plan on suicide to escape their pain. Furthermore, they had no hope as they could not find a doctor to help them. Invariably, all patients had an occult ocular surface disease. Targeted treatments reduced and eliminated the pain and none of them carried out their suicide plans. One of my patients’ case was published in BJO 20183 (case #1). Based on my experience, there are two possible conclusions. First, these patients had true centralized neuropathic pain, and the targeted treatment of occult, severe underlying nociceptive pain reduced and reversed central NP. Another more likely possibility is that pain refractory to topical anesthetic is not a reliable test to identify central NP. Perhaps these patients simply demonstrated peripheral neuropathic pain with heightened sensitivity to nociceptive pain rather than true central neuropathic pain and topical anesthetic was unable to fully anesthetize the highly sensitized ocular surface nerves (It is important to note when evaluating these patients that proparacaine, an ester type local anesthetic, has been shown to lose potency after two weeks at room temperature in an animal model61). To help clarify, the future evaluation of neuropathic pain with the proparacaine challenge test should employ fully potent anesthetic. This may be accomplished by keeping a dedicated bottle refrigerated for these cases.
Obtaining an adequately anesthetized lid and a relaxed patient will allow probing to be well tolerated and to achieve the best outcomes. First, we treat co-morbid anterior blepharitis prior to probing to reduce lid sensitivity. Possible anxiety for the procedure may be managed by reducing caffeine usage prior to probing or use of an anxiolytic. We have one patient who takes valium prior to probing. If patients are sensitive to probing, we give a second round of JAO to the lid margin (Make sure the JAO has not expired. Even refrigerated, the JAO will lose potency within 2 months. At room temperature, potency may be lost within two weeks). Patients with chronic longstanding MGD may have denser periductal fibrosis possibly requiring a single lid probing procedure to be done piecemeal over two visits. Probing during the follow-up visit will be easier as some of the fibrosis will have been released. This is analogous to treating advanced anterior blepharitis with heavy lash crusting and highly sensitive lid margins where patients avoid touching their lids. The sensitive lid margins rapidly improve with therapy using appropriate antibiotic ointment allowing for the subsequent marked reduction in lid sensitivity allowing for ease of ongoing lid hygiene. If a deeper level of anesthetic is still needed, then infiltrative anesthetic is an option. We have used this approach in less than 0.5% of cases.5
Summary
Fixed intraductal strictures and obstructions lead to elevated intraductal pressure and lid tenderness. If not relieved, Meibomian glands may atrophy causing additional clinical symptoms and even severe pain, with incapacitation and psychosocial sequelae. Furthermore, the goal of treating Meibomian gland dysfunction should not be limited to symptom relief and stabilizing age or disease associated gland atrophy, but rather to grow Meibomian glands and restore a full, functional, healthy, and resilient Meibomian gland lid population. Fortunately, we now have a safe, proven intraductal procedure that will restore intraductal integrity, providing positive physical proof of the relief of all fixed and non-fixed strictures and obstructions and appears to be associated with tissue growth on infrared meibography. That procedure is MGP.
Acknowledgment
Parts of this manuscript provide updates to material published in Maskin SL. Intraductal Meibomian gland probing: A paradigm shift for the successful treatment of obstructive Meibomian gland dysfunction. In: Kazuo Tsubota, ed. Diagnosis and Treatment of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction. Tokyo, Japan: Kanehara; 2016: 149–167.
Disclosure
Dr Steven L Maskin owns patents on devices and methods of intraductal meibomian gland diagnosis and treatments as well as jojoba based topical anesthesia and therapies for meibomian gland disease. Dr Steven L Maskin reports royalties and consultant fees from Katena, during the conduct of the study. In addition, Dr Steven L Maskin has a patent US 10,159,599 issued to MGD Innovations, a patent US 9,510,844 issued to MGD Innovations, a patent EU 2,222,355 issued to MGD Innovations, a patent US 8,906,427 issued to MELBJ Holdings, a patent US 8,455,016 issued to MELBJ Holdings. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Paradigm shift. Oxford Dictionary. Oxford University Press: New York, NY; 2019.
2. Lemp MA, Crews LA, Bron AJ, Foulks GN, Sullivan BD. Distribution of aqueous-deficient and evaporative dry eye in a clinic-based patient cohort: a retrospective study. Cornea. 2012;31:472–478. doi:10.1097/ICO.0b013e318225415a
3. Maskin SL, Testa WR. Growth of meibomian gland tissue after intraductal meibomian gland probing in patients with obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Br J Ophthalmol. 2018;102:59–68. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2016-310097
4. Maskin SL. Intraductal meibomian gland probing relieves symptoms of obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2010;29(10):1145–1152. doi:10.1097/ICO.0b013e3181d836f3
5. Syed ZA, Sutula FC. Dynamic intraductal meibomian probing: a modified approach to the treatment of obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;33:307–309. doi:10.1097/IOP.0000000000000876
6. Cardenas Diaz GA, Guerra Almaguer M, Hernandez Lopez I et al. Efficacy of intraductal probing in meibomian gland dysfunction. Rev Cubana De Oftalmol. 2017;30:1–12.
7. Maskin SL. A paradigm shift for the successful treatment of obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. In: Tsubota K, editor. Diagnosis and Treatment of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction. Kanehara & Co., LTD. Tokyo, Japan; 2016:149–167.
8. Ma X, Lu Y. Efficacy of intraductal meibomian gland probing on tear function in patients with obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2016;35:725–730. doi:10.1097/ICO.0000000000000777
9. Sik Sarman Z, Cucen B, Yuksel N, Cengiz A, Caglar Y. Effectiveness of intraductal meibomian gland probing for obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2016;35:721–724. doi:10.1097/ICO.0000000000000820
10. Nakayama N, Kawashima M, Kaido M, et al. Analysis of meibum before and after intraductal meibomian gland probing in eyes with obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2015;34:1206–1208.
11. Fermon S, Zaga IH, Alvarez Melloni D. Intraductal meibomian gland probing for the treatment of blepharitis. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2015;90:76–80. doi:10.1016/j.oftal.2014.04.014
12. Dongju Q, Hui L, Jianjiang X. Clinical research on intraductal meibomian gland probing in the treatment of patients with meibomian gland dysfunction. Chin J Optom Ophthalmol. 2014;16:615–621.
13. Wladis EJ. Intraductal meibomian gland probing in the management of ocular rosacea. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;28:416–418. doi:10.1097/IOP.0b013e3182627ebc
14. Hamrah P, Keirkhah A, Jamali A, et al. A Randomized Sham-Controlled Trial of Intraglandular Meibomian Gland Probing for Obstructive Meibomian Gland Dysfunction. Chicago: American Academy of Ophtalmology; 2016.
15. Narayanan S, Mickles C, Conner C, et al. Evaporative Dry Eye Treatment with Retaine MGD Artificial Tears OR Intraductal Meibomian Gland Probing. A Comparision. Orlando, Florida: American Academy of Optometry; 2014.
16. Mickles C, Connor C, Brinkley D, et al. Unplugged: A Comparision of Intraductal Meibomian Gland Probing and Conventional Meibomian Gland Dysfunction Treatment. Denver, Colorado: American Academy of Optometry; 2014.
17. Maskin SL. Intraductal meibomian gland probing relieves symptoms of obstructive MGD. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50:1.
18. Maskin SL. Intraductal Meibomian Gland Probing and Distinct Visual Analog Scale Response Profiles for Symptoms of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction. Chicago: American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO); 2010.
19. Maskin SL, Kantor K. Intraductal meibomian gland probing with adjunctive intraductal microtube steroid injection (MGPs) for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:1.
20. Maskin SL. Intraductal Meibomian Gland Probing to Restore Gland Functionality for Obstructive Meibomian Gland Dysfunction. Orlando, Florida: American Academy of Ophthalmology; 2011.
21. Maskin SL. Meibomian gland probing findings suggest fibrotic obstruction is a major cause of Obstructive Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (O-MGD). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53:1.
22. Incekalan TK, Harbiyeli II, Yagmur M, Erdem E. Effectiveness of intraductal meibomian gland probing in addition to the conventional treatment in patients with obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction AU - Incekalan, Tuğba Kurumoglu. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. Epub 2018 Sep 20.
23. Nirupama D, Hymavathi B, Prathima L,
24. Knop E, Knop N, Millar T, Obata H, Sullivan DA. The international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: report of the subcommittee on anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology of the meibomian gland. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:1938–1978. doi:10.1167/iovs.10-6997c
25. Maskin SL, Alluri S. Expressible meibomian glands have occult fixed obstructions: findings from meibomian gland probing to restore intraductal integrity. Cornea. 2019;38:880–887.
26. Cher I. Meibomian marginal dimples: clinical indicants of reactive pathogenic processes. In: Lass J, editor. Advances in Corneal Research: Selected Transections of the World Congress on the Cornea. Vol IV. New York: Plenum Press; 1997:27–35.
27. Foulks GN, Bron AJ. Meibomian gland dysfunction: a clinical scheme for description, diagnosis, classification, and grading. Ocul Surf. 2003;1:107–126.
28. Matsumoto Y, Sato EA, Ibrahim OMA, Dogru M, Tsubota K. The application of in vivo laser confocal microscopy to the diagnosis and evaluation of meibomian gland dysfunction. Mol Vis. 2008;14:1263–1271.
29. Maskin SL. When meds are not enough: surgical considerations fo rchronic dry eye. Ophthalmol Manage. 2009;45–50.
30. Maskin SL. Dry eye relief: peeling back layers to reveal root causes, select right tools and improve tear quality. Ophthalmol Manage. 2011;19–23.
31. Korb DR, Blackie CA. Restoration of meibomian gland functionality with novel thermodynamic treatment device-a case report. Cornea. 2010;29:930–933. doi:10.1097/ICO.0b013e3181ca36d6
32. Lane SS, DuBiner HB, Epstein RJ, et al. A new system, the LipiFlow, for the treatment of meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2012;31:396–404. doi:10.1097/ICO.0b013e318239aaea
33. Toyos R, McGill W, Briscoe D. Intense pulsed light treatment for dry eye disease due to meibomian gland dysfunction; a 3-year retrospective study. Photomed Laser Surg. 2015;33:41–46. doi:10.1089/pho.2014.3819
34. Vegunta S, Patel D, Shen JF. Combination therapy of Intense Pulsed Light Therapy and Meibomian Gland Expression (IPL/MGX) can improve dry eye symptoms and meibomian gland function in patients with refractory dry eye: a retrospective analysis. Cornea. 2016;35:318–322. doi:10.1097/ICO.0000000000000735
35. Qazi Y, Kheirkhah A, Blackie C, et al. In vivo detection of clinically non-apparent ocular surface inflammation in patients with meibomian gland dysfunction-associated refractory dry eye symptoms: a pilot study. Eye. 2015;29:1099. doi:10.1038/eye.2015.28
36. Matsumoto Y, Shigeno Y, Sato EA, et al. The evaluation of the treatment response in obstructive meibomian gland disease by in vivo laser confocal microscopy. Graefe‘S Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009;247:821–829. doi:10.1007/s00417-008-1017-y
37. Korb DR, Blackie CA. Meibomian gland therapeutic expression: quantifying the applied pressure and the limitation of resulting pain. Eye Contact Lens. 2011;37:298–301. doi:10.1097/ICL.0b013e31821bc7c5
38. Fermon S, Zaga IH, Alvarez Melloni D. [Intraductal meibomian gland probing for the treatment of blepharitis]. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2015;90(2):76–80. Spanish.
39. Maskin SL, Tseng SC. Culture of rabbit meibomian gland using collagen gel. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991;32:214–223.
40. Maskin SL, Tseng SC. Clonal growth and differentiation of rabbit meibomian gland epithelium in serum-free culture: differential modulation by EGF and FGF. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992;33:205–217.
41. Maskin SL. Reversing Dry Eye Syndrome: Practival Ways to Improve Your Comfort, Vision and Appearance. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press; 2007.
42. Obata H. Anatomy and histopathology of human meibomian gland. Cornea. 2002;21:S70–S74.
43. Blackie CA, Korb DR, Knop E, Bedi R, Knop N, Holland EJ. Nonobvious obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2010;29:1333–1345. doi:10.1097/ICO.0b013e3181d4f366
44. Flora MR. Intraductal drug delivery effective in meibomian gland dysfunction. Primary Care Optometry News. 2014;19:1–4.
45. Arita R, Itoh K, Inoue K, Amano S. Noncontact infrared meibography to document age-related changes of the meibomian glands in a normal population. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:911–915. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2007.06.031
46. Arita R, Itoh K, Inoue K, et al. Noncontact meibography detects changes in meibomian glands in the aging process in a normal population and patients with meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2009;28:S75–S79. doi:10.1097/ICO.0b013e3181ae6bec
47. Galor A, Zlotcavitch L, Walter SD, et al. Dry eye symptom severity and persistence are associated with symptoms of neuropathic pain. Br J Ophthalmol. 2015;99:665–668. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2014-306057
48. Rosenthal P, Borsook D. Ocular neuropathic pain. Br J Ophthalmol. 2016;100:128–134. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2014-306280
49. Kozak I, Bron AJ, Kucharova K, et al. Morphologic and volumetric studies of the meibomian glands in elderly human eyelids. Cornea. 2007;26:610–614. doi:10.1097/ICO.0b013e318041f0d2
50. Milz S, Neufang J, Higashiyama I, Putz R, Benjamin M. An immunohistochemical study of the extracellular matrix of the tarsal plate in the upper eyelid in human beings. J Anat. 2005;206:37–45. doi:10.1111/j.0021-8782.2005.00363.x
51. Vu CHV, Kawashima M, Yamada M, et al. Influence of meibomian gland dysfunction and friction-related disease on the severity of dry eye. Ophthalmology. 2018;125:1181–1188. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2018.01.025
52. Cochener B, Cassan A, Omiel L. Prevalence of meibomian gland dysfunction at the time of cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2018;44:144–148. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2017.10.050
53. Maskin SL. Effect of ocular surface reconstruction by using amniotic membrane transplant for symptomatic conjunctivochalasis on fluorescein clearance test results. Cornea. 2008;27:644–649. doi:10.1097/QAI.0b013e31815e723f
54. Osei KA, Ovenseri-Ogbomo G, Kyei S, Ntodie M. The effect of caffeine on tear secretion. Optom Vis Sci. 2014;91:171–177. doi:10.1097/OPX.0000000000000129
55. Jester JV, Nicolaides N, Kiss-Palvolgyi I, et al. Meibomian gland dysfunction. II. The role of keratinization in a rabbit model of MGD. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1989;30:936–945.
56. Trope GE, Rumley AG. Catecholamine concentrations in tears. Exp Eye Res. 1984;39:247–250.
57. Dao AH, Spindle JD, Harp BA, Jacob A, Chuang AZ, Yee RW. Association of dyslipidemia in moderate to severe meibomian gland dysfunction. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010;150:371–375.e371. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2010.04.016
58. Han JY, Kang B, Eom Y, Kim HM, Song JS. Comparing the effects of particulate matter on the ocular surfaces of normal eyes and a dry eye rat model. Cornea. 2017;36:605–610. doi:10.1097/ICO.0000000000001171
59. Hornick MK Evaluating exposures to inhalable dust among dairy parlor workers. MS (Master of Science) thesis, University of Iowa. 2013.
60. Dieckmann G, Goyal S, Hamrah P. Neuropathic corneal pain: approaches for management. Ophthalmology. 2017;124:S34–S47. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2017.08.004
61. Stiles J, Krohne S, Rankin A, Chang M. The efficacy of 0.5% proparacaine stored at room temperature. Vet Ophthalmol. 2001;4:205–207.
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.