Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 15
Exosomal lncRNA AK139128 Derived from Hypoxic Cardiomyocytes Promotes Apoptosis and Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Cardiac Fibroblasts
Received 1 December 2019
Accepted for publication 8 April 2020
Published 12 May 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 3363—3376
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S240660
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Lei Wang, Jun Zhang
Cardiovascular Department, Cangzhou Central Hospital, Cangzhou, Hebei Province 061001, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Jun Zhang Tel +86-13315777566
Email [email protected]
Introduction: Myocardial infarction (MI) is the leading cause of congestive heart failure and mortality. Hypoxia is an important trigger in the cardiac remodeling of the myocardium in the development and progression of cardiac diseases.
Objective: Thus, we aimed to investigate the effect of hypoxia-induced exosomes on cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) and its related mechanisms.
Materials and Methods: In this study, we successfully isolated and identified the exosomes from hypoxic cardiomyocytes (CMs). Exosomes derived from hypoxic CMs promoted apoptosis and inhibited proliferation, migration, and invasion in CFs. RNA-Seq assay suggested that long noncoding RNA AK139128 (lncRNA AK139128) was found to overexpress in both hypoxic CMs and CMs-secreting exosomes. After coculturing with CFs, hypoxic exosomes increased the expression of AK139128 in recipient CFs. Moreover, exosomal AK139128 derived from hypoxic CMs stimulated CFs apoptosis and inhibited proliferation, migration, and invasion. Furthermore, the effect of exosomal AK139128 derived from hypoxic CMs could also exacerbate MI in the rat model.
Conclusion: Taken together, hypoxia upregulated the level of AK139128 in CMs and exosomes and exosomal AK139128 derived from hypoxic CMs modulated cellular activities of CFs in vitro and in vivo. This study provides a new understanding of the mechanism underlying hypoxia-related cardiac diseases and insight into developing new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: myocardial infarction, hypoxia, cardiomyocytes, cardiac fibroblasts, exosome, LncRNA AK139128
Introduction
Myocardial infarction (MI) is the leading cause of congestive heart failure and subsequent mortality around the world.1 From a pathologic perspective, MI is characterized by myocardial cell death thanks to the prolonged ischemic insult, which is a consequence of the aberrant balance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand.2,3 Accordingly, the pathophysiologic conditions associated with this impaired balance between oxygen supply and demand may also play essential roles in the pathogenesis of MI.3 Furthermore, it has been reported that apoptosis is responsible for the clean removal of dead myocardial cells, while necrosis results in the secretion of inflammation-related signals.4,5 Growing evidence has reported that both apoptosis and necrosis may interact or take place at a continuum in pathologic processes.5 As such, it is indicated that apoptosis and necrosis are two primary mechanisms underlying myocardial cell death, although their contributions in MI remains to be elucidated.
In the past decades, numerous studies reported that hypoxia is the triggering factor for apoptosis in cardiac cells, which is associated with the cardiac remodeling of the myocardium in the development and progression of cardiac diseases.6 Also, myocardial hypoxia is the consequence of the acute decrease of coronary blood flow, contributing to various cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure and MI.7 Tanaka et al demonstrated that neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (CMs) and nonmyocytes cultured in 95% N2-5% CO2 condition lead to increased apoptosis.8 Kang et al reported that 24-hour reoxygenation after 6 hours of hypoxia causes significant increases in apoptosis in adult CMs.9 Also, hypoxia can activate transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) and its downstream signaling pathway, thereby regulating proliferation and apoptosis of cardiac fibroblasts (CFs).10,11 Thus, understanding hypoxia-induced apoptosis in cardiac cells is essential for the development of therapeutic strategies for heart diseases.
Exosomes, 40–100 nm in diameter, are nano-sized vesicles that are secreted from cells into the extracellular environment and are present in almost all biological fluids.12 It has been demonstrated that various functioning molecules, including lipids, proteins, mRNAs, and non-coding RNAs, are found in the exosomal lumen.13 Subsequently, these molecules can be taken up by neighboring or distant cells, thereby regulating the cell activities of recipient cells.14 Thus, exosome-mediated intercellular communication has brought increasing attention to its potential of molecule-transferring. A study conducted by Yang et al revealed that exosomal miRNA-30a derived from hypoxia-treated CMs can modulate autophagic activity.15 Moreover, exosomes secreted from hypoxia-treated H9c2 cells can alleviate hypoxia-induced apoptosis through mediating several miRNAs.16 Together, hypoxia-induced exosomes and their carrying molecules may play essential roles in apoptosis of hypoxia-associated infarcted CMs.
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a cluster of non-coding RNA molecules composed of more than 200 nucleotides in length.17 The lncRNAs are a highly heterogeneous group of transcripts that regulate gene expression through diverse mechanisms,18 thus exerting essential roles in a variety of biological processes. Recently, lncRNAs are increasingly recognized to participate in the regulation of hypoxia-associated apoptosis of cardiac cells. For example, lncRNA p21 is involved in p53-mediated apoptosis induction.19 In addition, Mimura et al reported that lncRNA DARS‐AS1 is modulated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) under hypoxic conditions and plays an essential role in the regulation of apoptosis in renal tubular cells.20 Recently, lncRNA AK139128 was found to promote cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy in hypoxia-reoxygenation injury.21 Given the emerging role of AK139128 in hypoxia-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes, this study aimed to investigate whether exosomal AK139128 derived from hypoxic CMs could modulate CFs growth, proliferation, and apoptosis, as well as the related mechanisms.
Materials and Methods
Animals
All experimental procedures involved in the care and use of animals in this study were approved by the Institutional Authority for Animal Care and Use Committee of Cangzhou Central Hospital and conformed to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.22
Cell Culture and Hypoxia Treatment
Adult rat CMs were isolated from the ventricles of male Sprague-Dawley rats (n=3; The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME, USA) based on the previously published protocol.23 To mimic the MI in vitro, CMs were administered low-glucose and anaerobic Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM; Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) that was pretreated with 95% N2 and 5% CO2 for at least 20 min. Next, CMs were incubated in a hypoxic condition with 1% O2 for 48–72 hours.24 Also, CFs were isolated from the rat heart as previously described (n=3).25 Meanwhile, CFs were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and gentamicin (10 μg/mL) and incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. The morphology of CMs and CFs were imaged by phase-contrast microscopy. The 2–3 passages of CFs were used for subsequent experiments.
Exosomes Isolation
Exosomes were isolated from normoxic and hypoxic CMs (1×106) according to the previously described protocol.26 Briefly, the supernatants of CMs were collected and then centrifuged at 10,000 g for 30 minutes to exclude cellular debris and cells. Next, the supernatants were transferred to a new tube, filtered via the membrane with a 0.22 μm pore size, and centrifuged at 120,000 g for 2 hours at 4 °C. The isolated exosome pellets were washed with sterile PBS once and resuspended in 500 μL of PBS. Exosomes (1 or 5 μg/mL) were quantified through the BCA protein assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) and used to coculture with CFs for 24 hours.27
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Exosomes were absorbed onto a 400-mesh copper grid and stained with 2% phosphotungstic acid solution for 10 min at room temperature. The morphology of exosomes was imaged by a transmission electron microscope (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan)
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
The diameter distribution of exosomes was measured through Nanosight NTA NS300 (Malvern Instruments Ltd., Malvern, UK). The parameter settings of capture and analysis were based on the manufacturer’s instructions.
RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Exosomes were treated with RNase A (10 μg/mL; Promega™ Corporation, Madison, WI, USA) for 10 minutes at room temperature followed by the treatment of RNase inhibitor (1 U/μL; Promega™ Corporation, Madison, WI, USA). Total RNAs were isolated from cells and exosomes using the RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The first-strand cDNAs were synthesized using the First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit for qRT-PCR (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mo, USA). The qRT-PCR reactions were performed using FastStart Essential DNA Green Master (Roche, Nutley, NJ, USA) on a Lightcycler platform (Roche, Mannheim, Germany). The primer information was as following: β-Actin: forward, 5ʹ-TCCCTGGAGAAGAGCTACGA-3ʹ, reverse, 5ʹ-AGCACTGTGTTGGCGTACAG-3ʹ and AK139128: forward, 5′-TCGCAAAGGCGGTTGCCTAT-3′, reverse, 5′-CAAGGTTGGGTAGCTTCAGA-3′. The data were analyzed using the ΔΔCT method,28 and β-actin was used as an internal control.
RNA-Seq
Total RNA isolation was the same as mentioned above. Adapter ligation, cDNA synthesis, PCR amplification, and construction of RNA libraries were performed by using TruSeq Stranded Total RNA Library Prep Kit (Illumina, US) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Then, RNA-Seq assay was performed on the Illumina Hi-seq 2500 platform. The reads with the percentage of unknown bases (> 10%) and the percentage of the low-quality base (quality value ≤ 5) were removed. The reads with high quality were matched to the hg19 genome sequence using the Bowtie software.29 The R package edgeR was applied to determine differentially expressed genes. The genes with more than 2-fold change in expression and adjusted p-value was less than 0.05 were identified as the significantly expressed genes.
Western Blotting
Total proteins of cells or exosomes were extracted using the lysis buffer (Bio-Rad, Des Plaines, IL, USA). The protein concentrations were determined using the Bradford relative protein quantification assay (Bio-Rad, Des Plaines, IL, USA). The protein extracts were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. Next, the membranes were incubated with CD63 (1:1000), Hsp70 (1:1000), Hsp90 (1:1000), TSG101 (1:500), Bax (1:1000), Bcl-2 (1:1000), Myosin Heavy Chain 6 (MYH6) (1:500), Myosin Heavy Chain 7 (MYH7) (1:1500), Troponin T type 2 (TNNT2) (1:1000), Troponin T (TropT) (1:1000), Vimentin (1:1000), Hyaluronan proteoglycan link protein 1 (Hapln1) (1:1000), Discoidin Domain Receptor 2 (DDR2) (1:1000), and GAPDH (1:2000) (Santa Cruz, Shanghai, China) at 4°C overnight. The protein expressions were determined using the chemiluminescent assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA), and the intensity of protein bands was quantified by ImageJ software.30
Exosome Fluorescence Assay
Exosomal RNAs were labeled with fluorescent dyes using Exo-GLOW™ Exosome Labeling Kits (System Biosciences, Palo Alto, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Images were taken by an Olympus BX51 Fluorescence Microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
Cell Transfection
The CMs were transfected with pRNAT-U6.1⁄control shRNA or pRNAT-U6.1⁄ AK139128 shRNA plasmid using the Lipofectamine™ 3000 Transfection Reagent (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
CCK-8 Assay
The CFs proliferation was determined by Cell Counting Kit-8 assays (Dojindo Molecular Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Absorbance was measured at 490 nm using an automatic multiwell spectrophotometer (Bio-Rad, Des Plaines, IL, USA)
Migration and Invasion Assays
The CFs (1 × 105) were subjected to Transwell (migration; BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and invasion assays (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and as previously described.31
Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
The determination of apoptotic levels of CFs was performed using the TUNEL Assay Kit (Abcam, Shanghai, China) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. The apoptotic levels were evaluated using an Olympus BX51 Fluorescence Microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
Rat Model of MI
Male specific-pathogen-free (SPF) Sprague-Dawley rats (8–12 weeks, body weight: 260–300 g; The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME, USA) were acclimated for one week before the experiments. Throughout the acclimation and experiment periods, rats were individually housed in polycarbonate cages in standard conditions, including 23 ± 2°C temperature, 55 ± 7% humidity, and 12-h light/dark cycle. Rats were fed standard rodent diet and water ad libitum. The rat model of MI was established, as previously described.32 Briefly, under tracheostomy surgery, anesthesia rats were incubated with an 18-gauge intravenous catheter with a tapered tip. Next, MI was introduced by ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery, 2 to 3 mm from the tip of the left auricle, with polypropylene suture in the fourth intercostal space. After surgery, coronary occlusion was evaluated by monitoring the development of a pale color in the distal myocardium. Next, purified siRNA AK139128-treated exosomes (10 μg), shRNA control-treated exosomes (10 μg), and PBS were injected into the infarct border zone at four different sites.33,34 Rats were sacrificed three weeks post-injection.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism Software (GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). Data were presented as mean ± SD. Statistical differences were determined with Student’s t-test and one-way analysis of variance. P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. At least three replicates were in each treatment.
Results
Isolation of CMs and CFs
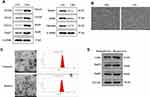
After isolation of CMs and CFs, we first performed Western blotting assay to determine several surface makers of CMs and CFs,35,36 respectively. As shown in Figure 1A, MYH6, MYH7, TNNT2, and TropT positively expressed in CMs, relative to CFs. Also, the fibroblast-specific markers Hapln1, DDR2, and Vimentin displayed higher expression in CFs. Meanwhile, the morphology of cultured cells was imaged under phase-contrast microscopy (Figure 1B). Collectively, the results showed the successful isolation of CMs and CFs in this study.
Identification of Exosomes Derived from Normoxic and Hypoxic CMs
Exosomes were isolated from normoxic and hypoxic CMs, respectively. The morphology of exosomes was evaluated by TEM (Figure 1C). Both normoxic and hypoxic exosomes displayed bilayer lipid membranes, and the diameter of exosomes was 100–200 nm, as shown in Figure 1A. Also, Western Blotting was performed to assess the exosome protein markers in normoxic and hypoxic exosomes, respectively. The results suggested that both normoxic and hypoxic exosomes positively expressed exosomal markers CD63, Hsp70, Hsp90, and TSG101 (Figure 1D). Together, these results suggest that exosomes isolated from normoxic and hypoxic CMs may exhibit classical exosome characteristics.
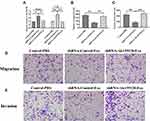
Exosomes Derived from Hypoxic CMs Promote CFs Apoptosis and Inhibit Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion
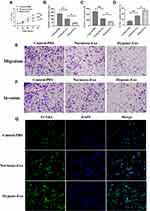
To investigate the roles of hypoxic exosomes in biological processes of CFs, we cocultured CFs with normoxic or hypoxic exosomes. The results from the CCK-8 assay revealed that CFs cocultured with hypoxic exosomes showed lower cell viability than those cocultured with normoxic exosomes or the PBS control (Figure 2A). Also, the hypoxic exosome-treated CFs displayed inhibited abilities of migration (Figure 2B and E) and invasion (Figure 2C and F) compared to CFs treated with normoxic exosomes or the PBS control. Furthermore, the TUNEL assay revealed that hypoxic exosomes promoted apoptosis in CFs compared to normoxic exosomes or the PBS control (Figure 2D and G).
Hypoxic Exosomes Affect Cell Activities of CFs Through Exosome-Mediated Transferring of AK139128
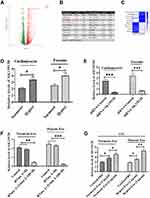
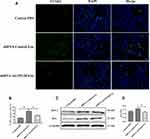
To investigate if exosome-carrying RNAs were internalized by CFs, exosomal RNAs derived from normoxic and hypoxic exosomes were labeled with green dyes and cocultured with CFs. The results revealed that the labeled exosomal RNAs were internalized by CFs (Figure 3), indicating that exosomal RNAs may be associated with the effect of hypoxic exosomes on CFs. Next, we conducted the RNA-Seq assay to further determine the functional lncRNAs in exosomes. The results demonstrated that a list of lncRNAs differentially expressed between normoxic and hypoxic exosomes (Figure 4A and B), of which AK139128 was one of lncRNA with the highest upward trend. By performing the qRT-PCR assay, we found that the expressions of these lncRNAs were consistent with the results obtained from RNA-Seq assay (Figure 4C). Thus, we selected AK139128 as a potential essential candidate and focused its effect on the hypoxic exosomes-mediated role in CFs. As shown in Figure 4D, hypoxia treatment led to higher expression of AK139128 in both CMs and CMs-derived exosomes. To further investigate the presence of AK139128 within exosomes, we applied RNase to both normoxic and hypoxic exosomes since the bilayer membrane of exosomes can prevent RNAs from degradation by RNase. The results showed that the administration of RNase did not affect the abundance of AK139128 in both normoxic and hypoxic exosomes whereas the combination of RNase and Triton X-100, which is commonly used to lyse cells or to permeabilize the cell membranes, could significantly inhibit the expression of AK139128 (Figure 4F). Furthermore, the expression of AK139128 in CFs was assessed after treating with normoxic and hypoxic exosomes, which revealed that the expression of AK139128 was increased in CFs in a concentration-dependent pattern compared to the PBS control (Figure 4G). Together, these results demonstrated that AK139128 may be involved in hypoxia-coping mechanisms of CMs and may participate in the effect of hypoxic exosomes on CFs.
 |
Figure 3 Internalization of exosomal RNAs derived from normoxic and hypoxic CMs. Green fluorescent dye-labeled normoxic and hypoxic exosomal RNAs were uptake by normal CMs. |
Exosomal AK139128 Derived from Hypoxic CMs Promotes CFs Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion
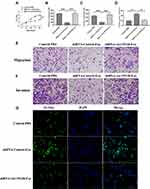
To further determine the function of AK139128 on the effect of hypoxic exosomes on CFs, we tested the siRNA AK139128 efficacy in hypoxic CMs, and the result revealed that siRNA AK139128 significantly inhibited the expression of AK139128 in both CMs and exosomes compared to the siRNA control (Figure 4E). Moreover, exosomes derived from siRNA control-treated hypoxic CMs significantly inhibited CFs proliferation relative to those of siRNA AK139128 or the PBS control-treated groups (Figure 5A). Moreover, hypoxic exosomes secreted from shRNA control-treated hypoxic CMs suppressed the abilities of migration (Figure 5B and E) and invasion (Figure 5C and F) as well as enhanced apoptotic activities (Figure 5D and G) of CFs. Collectively, these results demonstrated that the effect of hypoxic exosomes on CFs might be mediated, at least in part, by exosomal AK139128.
Exosomal AK139128 Derived from Hypoxic CMs Exacerbates Myocardial Infarction in the Rat Model of MI
In MI rat model, siRNA AK139128-treated and shRNA control-treated exosomes were administrated into the infarct border zone. QRT-PCR experiments revealed that AK139128-carrying exosomes derived from hypoxic CMs could increase the level of AK139128 in CFs and heart tissues while siRNA AK139128-treated exosomes did not affect the expression of AK139128 (Figure 6A). At the cellular level, exosomal AK139128 inhibited the abilities of migration (Figure 6B and D) and invasion (Figure 6C and E) in CFs compared with those treated with siRNA AK139128-treated exosomes or PBS control. Also, CFs treated with shRNA control-treated exosomes displayed higher apoptotic levels (Figure 7A and B), along with increased level of Bcl-2 while decreased expression of Bax, as determined by Western Blotting assay (Figure 7C and D). Together, these resulted suggested that exosomal AK139128 enhances apoptosis and inhibits cell migration ability in the rat model of MI.
Discussion
In the cardiovascular system, accumulating studies on both humans and animals demonstrated that apoptosis plays an essential role in the development and pathology of various cardiovascular diseases.37 In particular, the roles of hypoxia and reoxygenation can lead to alterations in the reduction-oxidation reaction, which is regarded as the leading cause of oxidative stress and the impairment of cardiac tissues in MI.38,39 During hypoxia, the generations of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and ATP, which are essential for high levels of metabolic needs of CMs are interrupted.38,39 In addition to these hypoxic responses, increased exosome secretion is also reported in hypoxic CMs that are enriched with various angiogenic and apoptosis-regulating factors.40 In the present study, we successfully isolated and identified the exosomes from hypoxic CMs and found the overexpression of AK139128 in hypoxic exosomes. Also, the high expression of AK139128 could be transferred through exosome-mediated pathways to promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in recipient CFs. Furthermore, the effect of exosomal AK139128 was also verified through in vivo studies.
Hypoxia is a potent factor that promotes the secretion of exosomes in CMs. Gupta et al first reported that moderate hypoxia administration for 2 hours significantly elevates the release of exosomes by two-times.41 Exosomes derived from primary cultured hypoxic CMs are enriched with high levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, a pro-inflammatory cytokine.24 Also, exosomes secreted from hypoxic cardiac progenitor cells contain more angiogenic factors compared with those derived from normoxic cells.42 Recently, the opposite roles, such as pro-apoptosis or anti-apoptosis, of exosomes derived from hypoxia cardiac cells have been reported.40 The precise mechanism underlying this discrepancy is still not fully understood, but different durations and intensities of hypoxic exposure may be associated with such opposite effects. In this study, we observed that CFs cocultured with hypoxic exosomes could lead to increased apoptosis while suppressing cell proliferation, invasion, and migration abilities. In previous studies, exosomal heat shock protein (HSP)-60 can promote inflammation and apoptosis in CMs through the toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway.41,43 Thus, it is suggested that hypoxic exosomes and their carrying factors secreted from cardiac cells may play essential roles in the modulation of cell activities in the pathogenesis of various cardiovascular diseases.
Exosomes are secreted from multiple cardiac cell types, such as CMs, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts. A growing body of studies demonstrated that cardiac exosomes play a crucial role in intercellular communication of physiological and pathological processes in the heart.44,45 Among cardiac cell-communicating networks, cardiomyocyte-fibroblasts cross-talk has been reported in several previous studies. For example, CFs treated with exosomes derived from CMs exhibit significant alterations in gene expression profiles, where 175 genes are upregulated while 158 genes are downregulated.46 Exosomes derived from CMs result in excess collagen synthesis in CFs through the STAT-3 pathway in cardiac hypertrophy.47 Moreover, CFs can modulate cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through exosomal miRNA-21.48 Meanwhile, the cross-talk between cardiomyocytes and CFs exerts critical roles in adaptive responses of the heart in response to the elevated workload induced by MI or hypertension.49 Thus, exploring the precise mechanism underlying this essential interplay between cardiomyocytes and CFs could contribute to understanding the progression of various cardiovascular diseases and the development of novel therapies.
The CFs participate in the regulation of myocardial function in a paracrine pattern.50 An essential factor mediating intercellular communication between cardiomyocytes and CFs is the TGF-β signaling pathway.51 In this study, we found another factor, AK139128, was significantly upregulated in both hypoxic CMs and their exosomes in response to hypoxia treatment and the knockdown of AK139128 in exosomes could reverse the effect of hypoxic exosomes on CFs, indicating the potential roles of AK139128 in hypoxia-coping mechanisms of CFs. In a recent study, AK139128 is reported to play positive roles in apoptosis and autophagy in myocardial hypoxia-reoxygenation injury,21 thereby drawing our interest in the effect of exosomal AK139128 in CMs. To date, the majority of studies reporting the exosomal communicators between cardiomyocytes and CFs have been the focus of miRNAs, such as miRNA-21,48 miRNA-27a, miRNA-28a, and miRNA-34a.52 Thus, the effect of exosomal AK139128 derived from hypoxic cardiomyocytes on CFs demonstrates an essential role of lncRNAs in hypoxia-associated responses of cardiac cells, providing novel insights into the cardiac cells cross-talk.
In conclusion, the results suggest that hypoxia exposure upregulates the expression of AK139128 in both CMs and exosomes and that exosomal AK139128 derived from hypoxic CMs promotes apoptosis and inhibits cell proliferation in CFs in vitro and in vivo. These findings contribute to understanding the mechanisms underlying hypoxia-related cardiac diseases and help in developing novel therapeutic strategies.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Martin-Rendon E, Brunskill SJ, Hyde CJ, Stanworth SJ, Mathur A, Watt SM. Autologous bone marrow stem cells to treat acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review. Eur Heart J. 2008;29(15):1807–1818. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehn220
2. Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD. Universal definition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50(22):2173–2195. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.09.011
3. Frangogiannis NG. Pathophysiology of myocardial infarction. Compr Physiol. 2011;5:1841–1875.
4. Konstantinidis K, Whelan RS, Kitsis RN. Mechanisms of cell death in heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32(7):1552–1562. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.224915
5. Nicotera P, Melino G. Regulation of the apoptosis–necrosis switch. Oncogene. 2004;23(16):2757. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207559
6. Bonavita F, Stefanelli C, Giordano E, et al. H9c2 cardiac myoblasts undergo apoptosis in a model of ischemia consisting of serum deprivation and hypoxia: inhibition by PMA. FEBS Lett. 2003;536(1–3):85–91. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00029-2
7. Cassavaugh J, Lounsbury KM. Hypoxia‐mediated biological control. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(3):735–744. doi:10.1002/jcb.22956
8. Tanaka M, Ito H, Adachi S, et al. Hypoxia induces apoptosis with enhanced expression of fas antigen messenger RNA in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 1994;75(3):426–433. doi:10.1161/01.RES.75.3.426
9. Kang PM, Haunstetter A, Aoki H, Usheva A, Izumo S. Morphological and molecular characterization of adult cardiomyocyte apoptosis during hypoxia and reoxygenation. Circ Res. 2000;87(2):118–125. doi:10.1161/01.RES.87.2.118
10. Chu W, Li X, Li C, et al. TGFBR3, a potential negative regulator of TGF‐β signaling, protects cardiac fibroblasts from hypoxia‐induced apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226(10):2586–2594. doi:10.1002/jcp.22604
11. Clancy RM, Zheng P, O’Mahony M, et al. Role of hypoxia and cAMP in the transdifferentiation of human fetal cardiac fibroblasts: implications for progression to scarring in autoimmune‐associated congenital heart block. Arthritis Rheum off J Am Coll Rheumatol. 2007;56(12):4120–4131. doi:10.1002/art.23061
12. Simons M, Raposo G. Exosomes–vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21(4):575–581. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007
13. Sato-Kuwabara Y, Melo SA, Soares FA, Calin GA. The fusion of two worlds: non-coding RNAs and extracellular vesicles-diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Int J Oncol. 2015;46(1):17–27. doi:10.3892/ijo.2014.2712
14. Zhang J, Li S, Li L, et al. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: trafficking, sorting, and function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015;13(1):17–24. doi:10.1016/j.gpb.2015.02.001
15. Yang Y, Li Y, Chen X, Cheng X, Liao Y, Yu X. Exosomal transfer of miR-30a between cardiomyocytes regulates autophagy after hypoxia. J Mol Med. 2016;94(6):711–724. doi:10.1007/s00109-016-1387-2
16. Zhang J, Ma J, Long K, et al. Overexpression of exosomal cardioprotective miRNAs mitigates hypoxia-induced H9c2 cells apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4):711. doi:10.3390/ijms18040711
17. Yao Y, Li J, Wang L. Large intervening non-coding RNA HOTAIR is an indicator of poor prognosis and a therapeutic target in human cancers. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(10):18985–18999. doi:10.3390/ijms151018985
18. Huarte M. The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer. Nat Med. 2015;21(11):1253. doi:10.1038/nm.3981
19. Huarte M, Guttman M, Feldser D, et al. A large intergenic noncoding RNA induced by p53 mediates global gene repression in the p53 response. Cell. 2010;142(3):409–419. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.040
20. Mimura I, Hirakawa Y, Kanki Y, et al. Novel lnc RNA regulated by HIF‐1 inhibits apoptotic cell death in the renal tubular epithelial cells under hypoxia. Physiol Rep. 2017;5(8):e13203. doi:10.14814/phy2.13203
21. Zhu Z, Zhao C. LncRNA AK139128 promotes cardiomyocyte autophagy and apoptosis in myocardial hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. Life Sci. 2019;116705. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116705
22. Council NR. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press; 2010.
23. Simpson P, Savion S. Differentiation of rat myocytes in single cell cultures with and without proliferating nonmyocardial cells. Cross-striations, ultrastructure, and chronotropic response to isoproterenol. Circ Res. 1982;50(1):101–116. doi:10.1161/01.RES.50.1.101
24. Yu X, Deng L, Wang D, et al. Mechanism of TNF-α autocrine effects in hypoxic cardiomyocytes: initiated by hypoxia inducible factor 1α, presented by exosomes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012;53(6):848–857. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.10.002
25. Long CS, Henrich CJ, Simpson P. A growth factor for cardiac myocytes is produced by cardiac nonmyocytes. Cell Regul. 1991;2(12):1081–1095. doi:10.1091/mbc.2.12.1081
26. Wang Y, Zhang L, Li Y, et al. Exosomes/microvesicles from induced pluripotent stem cells deliver cardioprotective miRNAs and prevent cardiomyocyte apoptosis in the ischemic myocardium. Int J Cardiol. 2015;192:61–69. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.05.020
27. Chen L, Wang Y, Pan Y, et al. Cardiac progenitor-derived exosomes protect ischemic myocardium from acute ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;431(3):566–571. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.015
28. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
29. Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 2012;9(4):357–359. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1923
30. Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW. NIH image to imageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods. 2012;9(7):671. doi:10.1038/nmeth.2089
31. Jun J, Cho J-E, Shim YH, Shim J, Kwak Y. Effects of propofol on the expression of matric metalloproteinases in rat cardiac fibroblasts after hypoxia and reoxygenation. Br J Anaesth. 2011;106(5):650–658. doi:10.1093/bja/aer006
32. Tang YL, Zhao Q, Qin X, et al. Paracrine action enhances the effects of autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on vascular regeneration in rat model of myocardial infarction. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;80(1):229–237. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.02.072
33. Teng X, Chen L, Chen W, Yang J, Yang Z, Shen Z. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes improve the microenvironment of infarcted myocardium contributing to angiogenesis and anti-inflammation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(6):2415–2424. doi:10.1159/000438594
34. Li T-S, Cheng K, Malliaras K, et al. Direct comparison of different stem cell types and subpopulations reveals superior paracrine potency and myocardial repair efficacy with cardiosphere-derived cells. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59(10):942–953. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.11.029
35. Furtado MB, Costa MW, Pranoto EA, et al. Cardiogenic genes expressed in cardiac fibroblasts contribute to heart development and repair. Circ Res. 2014;114(9):1422–1434. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302530
36. Ieda M, Tsuchihashi T, Ivey KN, et al. Cardiac fibroblasts regulate myocardial proliferation through β1 integrin signaling. Dev Cell. 2009;16(2):233–244. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.12.007
37. Haunstetter A, Izumo S. Apoptosis: basic mechanisms and implications for cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 1998;82:1111–1129.
38. Jeroudi MO, Hartley CJ, Bolli R. Myocardial reperfusion injury: role of oxygen radicals and potential therapy with antioxidants. Am J Cardiol. 1994;73(6):B2–B7. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(94)90257-7
39. Zweier J. Measurement of superoxide-derived free radicals in the reperfused heart. Evidence for a free radical mechanism of reperfusion injury. J Biol Chem. 1988;263(3):1353–1357.
40. Chistiakov DA, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV. Cardiac extracellular vesicles in normal and infarcted heart. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(1):63. doi:10.3390/ijms17010063
41. Gupta S, Knowlton AA. HSP60 trafficking in adult cardiac myocytes: role of the exosomal pathway. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292(6):H3052–6. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01355.2006
42. Gray WD, French KM, Ghosh-Choudhary S, et al. Identification of therapeutic covariant microRNA clusters in hypoxia-treated cardiac progenitor cell exosomes using systems biology. Circ Res. 2015;116(2):255–263. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.304360
43. Tian J, Guo X, Liu X-M, et al. Extracellular HSP60 induces inflammation through activating and up-regulating TLRs in cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 2013;98(3):391–401. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvt047
44. Sahoo S, Losordo DW. Exosomes and cardiac repair after myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 2014;114(2):333–344. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.300639
45. Sluijter JP, Verhage V, Deddens JC, van den Akker F, Doevendans PA. Microvesicles and exosomes for intracardiac communication. Cardiovasc Res. 2014;102(2):302–311. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvu022
46. Waldenström A, Gennebäck N, Hellman U, Ronquist G, Qin G. Cardiomyocyte microvesicles contain DNA/RNA and convey biological messages to target cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34653. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034653
47. Datta R, Bansal T, Rana S, et al. Myocyte-derived Hsp90 modulates collagen upregulation via biphasic activation of STAT-3 in fibroblasts during cardiac hypertrophy. Mol Cell Biol. 2017;37(6):e00611–16. doi:10.1128/MCB.00611-16
48. Bang C, Batkai S, Dangwal S, et al. Cardiac fibroblast–derived microRNA passenger strand-enriched exosomes mediate cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(5):2136–2146. doi:10.1172/JCI70577
49. Kakkar R, Lee RT. Intramyocardial fibroblast myocyte communication. Circ Res. 2010;106(1):47–57. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.207456
50. Pedrotty DM, Klinger RY, Kirkton RD, Bursac N. Cardiac fibroblast paracrine factors alter impulse conduction and ion channel expression of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 2009;83(4):688–697. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvp164
51. Cartledge JE, Kane C, Dias P, et al. Functional crosstalk between cardiac fibroblasts and adult cardiomyocytes by soluble mediators. Cardiovasc Res. 2015;105(3):260–270. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvu264
52. Tian C, Gao L, Zimmerman MC, Zucker IH. Myocardial infarction-induced microRNA-enriched exosomes contribute to cardiac Nrf2 dysregulation in chronic heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018;314(5):H928–H39. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00602.2017
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.