Back to Journals » Research and Reports in Urology » Volume 8
Evaluation and management of overactive bladder: strategies for optimizing care
Authors Willis-Gray M, Dieter A, Geller E
Received 17 March 2016
Accepted for publication 30 May 2016
Published 27 July 2016 Volume 2016:8 Pages 113—122
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/RRU.S93636
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jan Colli
Marcella G Willis-Gray, Alexis A Dieter, Elizabeth J Geller
Division of Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Abstract: Overactive bladder (OAB) is a common condition affecting millions of men and women worldwide. It is an embarrassing condition with far-reaching consequences. Although many treatment options exist, no single treatment has been proven to be most effective. Often a combination of therapy is required to successfully manage OAB symptoms. In this review, we provide an overview of OAB, including risk factors for development of OAB; keys to diagnosis; therapeutic options including conservative and medical management, as well as treatments for refractory OAB; when to consider referral to a specialist; and resources for clinicians and patients. The aim of this review is to inform clinicians regarding OAB management in order to improve patient counseling and care.
Keywords: overactive bladder, urge incontinence, urinary incontinence, bladder training, lifestyle modifications
Introduction
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a common condition1 that is defined as “urinary urgency, usually accompanied by frequency and nocturia, with or without urge urinary incontinence” by the International Continence Society.2 OAB affects >38 million Americans and one in every three elderly adults.1 One study on OAB prevalence found that 36% of men and 43% of women aged 40 years and older reported OAB symptoms.3
OAB has far-reaching consequences for both physical and mental health, with symptoms such as skin breakdown due to leakage, sleep disturbance, fall-related injuries, depression, prolonged hospital stays, admission to a nursing home, and lower quality of life.1,4–6 OAB is also associated with an increased risk of other adverse health conditions.7,8 Patients with OAB have an average of 84% more yearly visits to a physician and 21% more urinary tract infections (UTIs), which increases the cost and health care visits and even predisposes them to other health problems such as skin breakdown due to increased leakage. People with OAB also have a higher risk of fall-related injuries and fractures, as well as prolonged hospital stays and admission to a nursing home.
OAB is an embarrassing condition that interferes with not only social functioning but also a wide range of activities of daily living. People with OAB are more likely to limit social outings, physical activity, and participation in social events.6 There are also consequences with job performance, including decreased productivity at work due to frequent bathroom trips, lost time at work due to related illnesses, physician visits and hospitalization, and even loss of employment due to the detrimental effect on job performance.
The annual direct costs of OAB in the US – including diagnostic tests, physician visits, medications, treatment procedures, and supplies such as pads, diapers, and home care – total over $12 billion.7 This estimated cost is comparable to the annual costs of breast cancer ($12.7 billion) and osteoporosis ($13.8 billion). Consequent costs are those resulting from the diagnosis and treatment of related illnesses, including the physical illnesses described earlier, such as UTIs, fall-related injuries, and hospital and nursing home admissions. In addition, there are indirect costs of OAB, including loss of work productivity, time off from work for treatment, and inability to maintain employment.8,9 These indirect costs have been estimated at $841 million annually. Each of these consequences of OAB has an inherent cost to both the individual and the insurance company and increases national health care cost. As health care providers, we can decrease the significant health care and economic burdens associated with OAB by investing more health care resources to find effective and safe OAB treatments.
The objective of this review article is to describe the etiology and risk factors for OAB, diagnosis and management options, and when to refer for specialized management and to provide patient and clinician resources.
Risk factors
OAB is a highly prevalent disease. Age is probably the best-known risk factor for developing OAB. Prevalence increases with age, rising to 30.9% in those older than 65 years.10,11 In women, postmenopausal status has also been associated with an increase in OAB symptoms. This association is thought to be related to lower estrogen levels after menopause, as estrogen has an important role in the modulation of lower urinary tract function. Estrogen receptors have been discovered in the vagina, urethra, bladder, and pelvic floor musculature, and there is a potential role for vaginal estrogen in the treatment of OAB symptoms.11,12
Another risk factor for OAB is race. Coyne et al showed that African American and Hispanic men and women were more likely to have OAB.13 The epidemiology of lower urinary tract symptoms study found African American and Hispanic race as predictors of OAB in men but did not find a higher risk of OAB in African American and Hispanic women.14 Prolapse has been considered as a risk factor for OAB. Although women with pelvic organ prolapse have a greater prevalence of OAB symptoms, there is no consistent evidence demonstrating a relationship between the compartment or stage of prolapse and the presence of OAB symptoms. Studies have shown that treatment of prolapse (whether with pessary or surgery) results in improvement of OAB symptoms.15 It is unclear if this relationship is causal. Incontinence surgery may also be a risk factor for OAB. The development of OAB is a known risk after midurethral sling surgery with de novo OAB occurring in between 15% and 29% of patients within 1–3 months postoperatively.16,17 Finally, neurologic disease is known to affect lower urinary tract function.18
For men, comorbidities, including arthritis, depression, heart disease, hypertension, mobility limitations, neurological conditions, recurrent UTI, benign prostatic hypertrophy, and prostatitis, are predictors of OAB.6 For women, comorbidities including arthritis, depression, irritable bowel syndrome, neurological conditions, recurrent UTI, and sleep apnea are more likely to be associated with OAB.13
Lifestyle and behavioral factors play a role in OAB as well. A body mass index (BMI) of >30 kg/m2 is another risk factor for OAB symptoms.12 Studies have found smoking to be a risk factor for increased urgency, but this has not been consistent with other studies.12,19 High caffeine intake (>400 mg/d) has also been associated with OAB.20 There are also behaviors that can increase the likelihood of OAB. These include both inadequate and excessive fluid intake, caffeine, carbonated beverages, spicy food, artificial sweeteners, and alcohol.22,23 Identifying modifiable risk factors earlier on can aid in the treatment of OAB.
Diagnosis
OAB is defined as “urinary urgency, usually accompanied by frequency and nocturia, with or without urge urinary incontinence” by the International Continence Society.2 Thus, the diagnosis of OAB requires an assessment of the patients’ signs and symptoms, while excluding other conditions. A thorough history and physical as well as laboratory testing is typically needed to make an accurate diagnosis of OAB.21
The history should include patients’ baseline urinary function and the duration of patients’ current symptoms. A key component of the history is determining whether the patients are bothered by their symptoms. If there is minimum bother, intervention may not be necessary. An assessment of bladder storage and ease of emptying is also needed. It is important to keep in mind that bladder function is affected by the amount and type of fluid intake. Both inadequate and excessive fluid intake can lead to frequency and urgency symptoms. Low fluid intake makes the urine more concentrated and more acidic, thus acting as a bladder irritant, while excess fluid intake leads to more urine production. Caffeine, carbonated beverages, spicy food, artificial sweeteners, and alcohol can also exacerbate OAB symptoms.22,23 Asking the patients about their typical daily fluid intake and assessing for potential bladder irritants can provide the clinician with important information and also provide an opportunity to educate the patients about modifiable habits. A bladder diary is useful in gaining an objective measure of daily intake in terms of the type of fluids, the amount of fluid intake, and voiding habits. It is also important to explain normal voiding behaviors to patients. In community-dwelling healthy adults, normal frequency consists of voiding every 3–4 hours with a median of six to eight voids during the day. It is also normal to wake up once at night to void.24 Some patients may self-diagnose with OAB but may be within the normal range of voiding habits. Others may need advice in modifying their voiding patterns. All medications should be reviewed, and comorbidities such as sleep apnea, diabetes, and heart failure should be assessed, as all these can potentially contribute to lower urinary tract symptoms. Patients with significant comorbidities should be referred to a specialist for optimization if not already under routine care. Additional symptoms, such as hematuria, dysuria, dyspareunia, pelvic organ prolapse, pelvic pain, and neurological deficits, should lead the clinician to consider an alternative diagnosis.21
A focused physical examination is also needed, with special attention paid to the abdominal and genitourinary examination and lower extremity edema evaluation.25 In patients with multiple sclerosis, diabetes, stroke, or spinal injury, a neurological examination of the genital region may be considered. Neurologic disease can affect lower urinary tract function, including both voiding and urine storage. A postvoid residual should also be performed to evaluate bladder emptying in patients with obstructive symptoms, neurological disease, or prior surgery for incontinence, prolapse, or prostate issues.26
Laboratory testing should include a urinalysis to rule out both infection and hematuria. If the urinalysis is inconclusive, a urine culture should be sent, and if there is hematuria on urine dipstick, a microscopic urinalysis should be performed to screen for microscopic hematuria.25 Validated questionnaires can be used to quantify both bladder symptoms and amount of bother from these symptoms.25 Commonly used questionnaires include the Pelvic Floor Distress Inventory short form and the Pelvic Floor Impact Questionnaire short form.26 Each questionnaire evaluates the following three domains: bladder symptoms, bowel symptoms, and pelvic organ prolapse symptoms. The Pelvic Floor Distress Inventory assesses the degree of severity of these symptoms, and the Pelvic Floor Impact Questionnaire assesses the impact of these symptoms on activities of daily living and social functioning. These questionnaires can also be used to track improvement and to objectively assess the effectiveness of various treatment modalities.27 For more complicated or refractory patients, including patients with prior pelvic reconstructive surgery or those without symptom improvement with first- and second-line therapies, additional testing, including urodynamic evaluation, cystoscopy, and/or upper genitourinary tract imaging, can be used to differentiate between OAB and other etiologies.25
Conservative treatment option
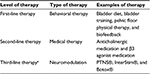
The American Urological Association has developed guidelines regarding treatment of OAB (Table 1).28 Treatment options are divided into three levels of care, ranging from most conservative to most specialized. First-line treatment is behavioral therapy. This includes bladder training and toileting habits, dietary changes, pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT), and biofeedback. Second-line treatment is medication, which includes both anticholinergic and β3 agonist therapy. Conservative therapy can be an effective treatment option and is recommended by the American Urological Association as a first-line intervention for OAB.28 The potential benefits of conservative therapy are significant and generally carry little to no risk of adverse effects. In general, there are two categories of conservative management options: 1) lifestyle modifications, which involve altering habits to alleviate bladder symptoms and promote bladder health, and 2) control techniques, which help patients to better control OAB symptoms.
Lifestyle modifications
Lifestyle modification includes a variety of behavioral changes that can reduce and even eliminate OAB symptoms. Most of these modifications are based on expert opinion with limited scientific evidence due to lack of trials.29 However, the benefit of a healthier lifestyle and the fact that these interventions often have little to no risk of adverse events favor the continued use of behavioral modification as an initial and ongoing therapy for OAB. Importantly, the foundation to achieving a successful behavioral change is patients’ education and investment in their own health. Thus, it is essential to have a discussion with your patients, educate them about these potential interventions, assess what they think are feasible options, and encourage them to initiate a change.30
An initial option for leakage control for patients with OAB is the use of absorbent products to help control symptoms. Studies have shown that in women with milder symptoms, disposable insert pads are preferred, while in women with more severe leakage, disposable pull-ups are the best overall option.31,32 Common lifestyle modifications include reducing fluid intake, avoiding bladder irritants, limiting intake of caffeine and other bladder irritants, avoiding constipation, optimizing overall health, and smoking cessation. Diet and fluid management is a common behavioral intervention that patients can institute at home independently or with the aid of a health care provider or nutritionist. There is also some evidence that weight loss in overweight women may reduce urinary incontinence symptoms and benefit overall health.29 Providers should educate patients on potential lifestyle changes such as weight loss, smoking cessation, and fluid intake adjustments that can lead to a significant impact in symptom control.
Diet and fluid management options
- Decrease fluid intake to six to eight glasses of water per day and avoid fluid intake for the 2–3 hours prior to bedtime to reduce urine production overnight;
- Reduce intake of bladder irritants such as caffeine, carbonated beverages, spicy food, artificial sweeteners, and alcohol;
- Avoid constipation by initiating a bowel regimen to achieve soft stools every 1–2 days, using fiber supplements, stool softeners, and/or laxatives and establishing a routine defecation schedule;
- Smoking cessation;
- Optimize overall health by improved control of hypertension, diabetes, sleep apnea, and other chronic health conditions to reduce urine production and improve bladder neurological function.
Control techniques
The most conservative control techniques include bladder retraining and scheduled toileting. Studies of prompted voiding have shown promising results in terms of reducing incontinence episodes and increasing self-initiated voiding over the short term.33,34 Urge control techniques can be taught in the office and are performed as follows: upon feeling a sense of urgency to void, the patients activate their pelvic floor musculature (kegel contraction) for ∼10 seconds or can do five to six rapid contractions until the urgency subsides and then they proceed to the bathroom. This technique can be used in combination with other relaxation techniques such as deep breathing. Bladder retraining involves scheduled toileting as well as urge control techniques described earlier. In order to increase the interval between voids, the patients are asked to delay urination for a short period, such as 1 minute. This interval is then increased slowly over time as the patients gain better bladder control. Bladder retraining has been shown to be an effective intervention to reduce OAB symptoms, with some studies showing a significantly higher quality of life and patient perception of cure when compared to drug therapy.35
PFMT has also been shown to improve urinary incontinence symptoms.36,37 PFMT involves improving pelvic floor control and muscle strength and reducing urgency sensations through a variety of techniques. In general, PFMT may be used to improve pelvic floor muscle strength (the maximum force generated by a single muscle contraction), endurance (ability to contract repetitively or sustain a single submaximal contraction over time), and coordination in order to reduce leakage or suppress urge. An individualized treatment plan is designed, and the patients are scheduled for regular visits with a physical therapist and are usually given an at-home exercise regimen, with intensity and difficulty progressing throughout the treatment period. Participants are also educated about the abdominal and pelvic anatomy at their initial visit and throughout the treatment period.
A recent study by Adams et al demonstrated significant quality of life improvement in patients who underwent PFMT in combination with myofascial release techniques one to two times per week for up to 10 weeks.38 The manual release techniques comprised trigger point release through direct pressure, contract–relax, strumming, sustained stretch, and fascial release through three-way stacking and skin rolling. Although there is no single optimal regimen for PFMT, studies suggest that patients benefit from regular supervision.39
All of these conservative and behavioral interventions can be used together to improve bladder control and optimize overall health.
Medical treatment
The mainstay of treatment for OAB is medical therapy, often coupled with behavioral and dietary modifications. Medication is considered second-line therapy for OAB.28 The primary class of pharmaceutical agents used to treat OAB is a subtype of anticholinergics known as antimuscarinics. Because muscarinic receptors are found throughout the body, the side effects of these agents are not only common but also widespread.40 The most commonly seen adverse effects due to antimuscarinic activity in other organ systems include dry mouth (salivary glands), dry eyes (cilia and iris), constipation (intestinal smooth muscle), heart palpitations (AV node), and cognitive impairment (forebrain). Each of these organ systems contains varying levels of all five muscarinic receptor subtypes. Newer antimuscarinic agents have been developed to target the bladder more specifically by selectively focusing on M2 and M3 receptors, which are both found in the detrusor muscle of the bladder wall. Although M2 receptors are predominant, M3 receptor is thought to play the most active role in detrusor muscle hyperreflexia.41 However, these agents have also demonstrated adverse effects in the body systems highlighted above, due to the fact that the M3 receptor is not unique to the bladder. The M1 receptor’s effect on cognitive impairment is thought to be due to its role in learning and memory.40 Cognitive effects that have been reported with antimuscarinic agents include changes in memory, blurred vision, somnolence, hallucinations, confusion, and delirium, all of which are more prevalent in the elderly population.42 Special consideration must be taken when prescribing antimuscarinic medications in this population.
There are six antimuscarinic agents available for the treatment of OAB worldwide: oxybutynin, tolterodine, fesoterodine, trospium, darifenacin, and solifenacin (Table 2). No one agent has clearly been shown to be more effective than another, but extended release versions have shown lower side effects compared to immediate release versions due to a decreased fluctuation in serum concentration.43 Extended release OAB drugs include oxybutynin ER, tolterodine XL, fesoterodine ER, darifenacin ER, solifenacin, trospium ER, and the oxybutynin transdermal patch. Trospium has a quaternary amine structure making it too large to cross the blood–brain barrier, thus having a decreased effect on cognitive function side effects.41 Tolerability and cost often dictate which agent is selected for treatment.44,45
Advances in understanding OAB pathophysiology have identified three β adrenoceptors (β1, β2, and β3) in the bladder. β3 adrenoceptors predominate in the bladder and are thought to be responsible for relaxation of the detrusor muscle during urine storage. Mirabegron is the only β3 adrenoceptor agonist available, and multiple trials support its clinical efficacy in patients with OAB.45 This medication can be used as a second-line therapy or in those who cannot or poorly tolerate antimuscarinic agents.46 The side effect profile is different from anticholinergics because β agonists work differently. β3 adrenoceptors may be present in cardiac and vascular tissue. In pooled Phase III clinical studies with a large number of patients, the change in the mean pulse rate for patients on mirabegron was ∼1 bpm compared to placebo. This was similar to the change from baseline pulse rate described for antimuscarinic agents, such as tolterodine, fesoterodine, and trospium, and the change was shown to be reversible with discontinuation.47 The increase in blood pressure associated with mirabegron was on average ≤1–3 mmHg, and the incidence of hypertension was similar to placebo and tolterodine ER.46,47 Given the different mechanism of action, it is possible to use mirabegron in conjunction with an anticholinergic medication. The Symphony trial is a Phase II study that sought to determine if solifenacin and mirabegron combination enhanced efficacy when compared to solifenacin alone.48 Efficacy was based on mean volume voided per micturition, as it strongly correlates with OAB symptoms. Combination therapy demonstrated significant improvement when compared to solifenacin 5 mg alone. The combination of mirabegron and an anticholinergic medication may allow providers to increase efficacy and minimize side effect burden.48 Botox® (onabotulinum toxin A) is another form of medication therapy, but it is delivered through injections in the bladder wall via cystoscopy. This will be further discussed in the next section, as this therapy is approved for the treatment of refractory OAB.
Treatment of refractory OAB
When patients do not improve with first- and second-line treatment for OAB, they are considered refractory. Specifically, patients must demonstrate lack of response to first-line therapy (behavioral therapy) and either inadequate response to second-line therapy (consisting of at least two medications) or intolerance of medications due to side effects or contraindications. If patients meet these criteria, they are eligible for third-line treatment. Third-line therapy includes neuromodulation of the nerves controlling bladder function. The following three distinct types of neuromodulation therapy exist: peripheral tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS), sacral neuromodulation, and temporary chemical denervation of the bladder detrusor muscle. All three therapies are based on Grade C recommendations by the American Urological Association.
PTNS was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2005 for the treatment of refractory OAB under the brand name Urgent PC® (Uroplasty, Minnetonka, MN, USA). Treatment is accomplished through a retrograduation stimulation from the posterior tibial nerve to the afferent nerves of the sacral plexus. A 34 G needle electrode is inserted into the skin 5 cm above the medial malleolus of the ankle. A surface electrode is attached to the skin near the medial aspect of the calcaneous bone. The needle electrode is attached to a handheld generator that creates a stimulation. The generator is turned on, and the stimulation is increased until the great toe curls, the toes fan out, or the entire foot extends. The amplitude is then reduced one level, and treatment continues for 30 minutes. Treatment extends for a period of 12 weekly sessions, followed by a tapering of treatment over several months. Ongoing therapy is continued as needed to maintain symptom relief. Treatment response can be seen as early as the first session, but may take up to six sessions. The recommendation is to complete all twelve sessions before reevaluating. No serious adverse events have been reported. FDA published common mild adverse events include mild pain and/or skin inflammation (33.3%), moderate pain (4.7%), and bleeding (3.2%). Contraindications to PTNS include patients with pacemakers or implantable defibrillators, excessive bleeding, nerve damage that can affect tibial nerve or pelvic floor function, and those pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
Peters et al49 compared PTNS with sham treatment of OAB in a randomized multicenter trial with 220 subjects undergoing 12 weekly treatment sessions. Based on a global response assessment (GRA), at week 13, 54.5% of subjects reported moderate or marked improvement in symptoms (based on an intent-to-treat model) compared with 20.9% in the sham group. Improvement in urgency, frequency, and urge leakage was observed in 42.7%, 47.6%, and 37.9% of patients, respectively, and all showed statistical significance compared to the sham group. The treatment group had a mean decrease in voids per day from 12.3 to 9.8 and in nighttime voids from 2.9 to 2.1. Episodes of moderate to severe urgency decreased from 8.3 to 3.7, and episodes of urge incontinence decreased from 3.0 to 0.3. The authors also reported long-term follow-up of 29 subjects who completed a 3-year follow-up on a tapered program.26 Three quarters (77%) maintained moderate or marked improvement on the GRA, with a significant improvement in daytime and nighttime voids as well as urge incontinence episodes, compared with baseline. Peters et al50 also performed a multicenter randomized trial in 100 subjects comparing 12 weeks of PTNS to drug therapy with tolterodine extended release 4 mg. They found that PTNS had a higher rate of improvement or cure based on GRA (79.5% vs 54.8%) and was noninferior to drug therapy based on mean reduction in daytime voids (both decreased from 12 to 9.8).
Sacral neuromodulation was FDA approved in 1997 and is manufactured under the name InterStim® (Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA). It is approved for the treatment of not only refractory OAB but also nonobstructive urinary retention and fecal incontinence. Similar to PTNS, sacral neuromodulation involves stimulation of the afferent neural pathways that control bladder function via the sacral nerve plexus in order to restore normal storage and voiding function. Unlike PTNS, this form of sacral neuromodulation is accomplished with a permanent surgical implant. The first step in this treatment is a test phase in order to test: 1) patients’ response to the therapy, 2) neural integrity of the patients’ sacral plexus, and 3) patient ability to successfully use the therapy. Patients must demonstrate at least a 50% improvement in baseline symptoms from the test phase before they can proceed with permanent implantation. Patients complete a baseline symptom diary that measures daytime and nighttime voiding frequency, degree of urgency, and frequency and severity of urge leakage episodes. A second diary is then completed during the test phase in order to measure the degree of improvement. Patients can qualify for sacral neuromodulation based on urgency/frequency symptoms alone and do not need to experience urge leakage to qualify for this therapy. The test phase involves the placement of a very thin wire through the skin of the lower back and into the S3 sacral foramen. The wire is then connected to a handheld generator that supplies continuous stimulation for a period of 7–14 days. This can be accomplished in one of the following two ways: 1) office peripheral nerve evaluation (PNE) and 2) intraoperative placement of lead wire (stage I). Both tests include wire placement, but PNE uses a temporary wire that is removed in 5–7 days, whereas stage I uses the permanent wire that can then be connected to an implantable generator (stage II). The benefit of PNE is that if the patients demonstrate at least 50% improvement in symptoms, they can go straight to a full implant (wire and generator), thus saving a surgical procedure. The benefit of stage I procedure is that the patients are testing the actual wire that they will keep and that this wire can be tested for a longer period (7–14 days) than the temporary PNE wire. Once implanted, a generator battery lasts 5 years on average, at which time the battery would need to be exchanged surgically. The lead wire has no expiration. Stage I procedures are preferred for patients with limited mobility and higher BMI or those not thought to tolerate an office procedure without sedation. For both PNE and stage I procedures, the patient lies prone and a spinal needle is inserted through the S3 foramen on each side. The needle is attached to a cable that is connected to a handheld generator that provides stimulation. As the stimulation is increased, the patient is instructed to describe the location of the stimulation. The patient is also observed for motor responses. S3 placement is best confirmed by sensation in the vagina, perineum, and/or rectum; and a motor response of great toe flexion and bellows of the perineum. Once correct location is confirmed, a wire is inserted through the needle and the needle is removed. The wire is taped to the skin of the back and covered with a clear occlusive dressing. The wire is attached to a handheld generator that is kept on for the duration of the test phase. Typically for stage I procedure, a wire is only placed on one side – the side with the most optimal sensory and motor response. While fluoroscopic guidance is necessary for stage I procedures, PNE can be performed solely with the use of bony landmarks. If at least 50% success is demonstrated and a permanent generator is implanted, the stimulation can be modified with the use of both a patient programmer and a clinician programmer, allowing flexibility with treatment even after implantation. Reported adverse events include pain at implantation site, lead migration, infection, technical or device problems, adverse change in bowel or voiding function, and undesirable stimulation. Contraindications to sacral neuromodulation include inadequate response to the test phase, need for frequent magnetic resonance imaging, use of diathermy, and pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
Siegel et al51 compared InterStim to standard medical therapy (SMT) in a randomized multicenter trial of 147 subjects over 6 months. SMT was based on physician preference, with a range of medications. Based on an intent-to-treat model, sacral neuromodulation demonstrated a significant improvement compared to SMT in terms of OAB symptoms (61% vs 42%), urge incontinence episodes (71% vs 47%), and urinary frequency (61% vs 37%). Sacral neuromodulation also demonstrated a significant improvement in quality of life scales regarding OAB impact on daily functioning compared to SMT.
The third type of therapy available to patients with refractory OAB is injection of a chemodenervation agent into the bladder. The agent used is Botox® (onabotulinum toxin A) (Allergan, Inc., Irvine, CA, USA), which was FDA approved in 2013 for idiopathic OAB. Botulinum toxin is derived from Clostridium botulinum and acts at the presynaptic membrane of the neuromuscular junction to prevent release of acetylcholine. This action leads to paralysis of muscle fibers until new fibrils can grow, thus creating a temporary effect on the myocytes in the bladder wall. The drug is stored in a powder form and is reconstituted in normal saline 30 minutes prior to the procedure. A cystoscope is used to distend and visualize the bladder wall. The bladder trigone is identified, and a needle is advanced through the cystoscope. The drug is injected in a series of 20 injection sites along the posterior wall of the bladder, above the trigone so as to avoid extreme paralysis and significant urinary retention. Therapeutic effect occurs within 7–10 days of injection and can last up to 12 months. However, injection can be repeated as early as 3 months. Patients must be willing to learn how to self-catheterize, as this is reported to occur at a rate of 5%–30% depending on dosage. Other adverse events include UTI, dysuria, and hematuria.
Brubaker et al52 performed a randomized multicenter trial of 43 subjects comparing 200 U of botulinum toxin to placebo, with primary outcome being patient global impression of improvement at 2 months after therapy. Based on patient global impression of improvement score, 60% of patients reported improvement, with a median duration of 373 days. The treatment group reported seven less leaks per day compared to 0.5 in the placebo group. However, 43% reported prolonged retention, which led to early termination of the study. Nitti et al performed a randomized trial of 557 subjects receiving a lower dose of 100 U of botulinum toxin compared to placebo.45 Patients in the treatment group reported a significant decrease in leaks per day compared with the placebo group (2.65 vs 0.87 less leaks per day). At 3 months posttreatment, 60.8% in the treatment group reported improvement compared to 29.2% in the placebo group. The rate of self-catheterization in the treatment group was lower than in the prior study by Brubaker et al52, at 8.3%. Based on this and other studies,46,53 100 U has become the standard starting dose for treatment. Higher doses may be used, but patients must be counseled about the proportional increased risk of retention and the need for catheterization.
When to refer?
From the information provided in this review, clinicians should be able to provide their patients with information regarding diagnosis and treatment options for OAB. Providers who wish to help manage OAB with their patients can offer first-line therapy, knowing that these treatment options have a low risk profile. Providers may also offer second-line therapy if they are comfortable in counseling patients and managing the potential side effects of pharmacotherapy. If providers do not have the time or interest in managing pharmacotherapy, they may refer to a specialist for medication management. For third-line therapy, such as neuromodulation and intravesical botulinum toxin, it is recommended to refer to a specialist who performs these procedures regularly. Patients are candidates for third-line therapy when they have failed conservative measures (first-line therapy), and either failed two medications (second-line therapy) or cannot tolerate medical therapy due to contraindications or side effects. There are also several helpful websites that can provide patients with information while they are considering the treatment options.
Self-advocacy
OAB can have a lasting effect on the lives of patients, and it is important to determine how OAB symptoms impact each individual’s quality of life. Explaining appropriate treatment options and resources, as well as creating realistic expectations, will allow the patients to make an informed decision on what interventions work best for them. Health self-advocacy is defined as “representing one’s own interest within the health care decision making process” and is associated with positive health outcomes.54 Hagan and Donovan’s review suggests that health self-advocacy is utilized in navigating the medical system, engaging in teamwork with providers, making informed decisions, utilizing available resources, and recognizing mindful nonadherence (the purposeful decision not to follow a provider’s recommendation based on personal knowledge or preferences).54 Empowering patients to be an active participant in their own health care can foster a strong patient–physician relationship. This is especially important when treating OAB, which can be a long-term and frustrating problem.
Conclusion
OAB is a prevalent condition that affects the lives of millions of adults in the US and around the world. It is important for providers to assess for OAB symptoms, especially in patients with risk factors, including older age, African American or Hispanic race, smoking, neurologic conditions, BMI >30 kg/m2, and recurrent UTI. As our population ages, the burden of OAB treatment and management will continue to increase. Currently, there are several options for treatment with first-line therapies including behavioral modification and pelvic floor physical therapy, progressing to second-line OAB medications and, for those who are poorly responsive or intolerant to prior treatment, neuromodulation techniques. OAB is a complex condition, but there are promising treatment options available. It is essential to recognize this diagnosis and to empower your patients to seek care.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Stewart WF, Van Rooyen JB, Cundiff GW, et al. Prevalence and burden of overactive bladder in the United States. World J Urol. 2003;20(6):327–336. | ||
Haylen BT, de Ridder D, Freeman RM, et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female pelvic floor dysfunction. Int Urogynecol J. 2010;21(1):5–26. | ||
Coyne KS, Sexton CC, Kopp ZS, Ebel-Bitoun C, Milsom I, Chapple C. The impact of overactive bladder on mental health, work productivity and health-related quality of life in the UK and Sweden: results from EpiLUTS. BJU Int. 2011;108(9):1459–1471. | ||
Scheife R, Takeda M. Central nervous system safety of anticholinergic drugs for the treatment of overactive bladder in the elderly. Clin Ther. 2005;27(2):144–153. | ||
Liberman JN, Hunt TL, Stewart WF, et al. Health-related quality of life among adults with symptoms of overactive bladder: results from a U.S. community-based survey. Urology. 2001;57(6):1044–1050. | ||
Sexton CC, Coyne KS, Thompson C, Bavendam T, Chen CI, Markland A. Prevalence and effect on health-related quality of life of overactive bladder in older americans: results from the epidemiology of lower urinary tract symptoms study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(8):1465–1470. | ||
Hu TW, Wagner TH. Health-related consequences of overactive bladder: an economic perspective. BJU Int. 2005;96(suppl 1):43–45. | ||
Hu TW, Wagner TH, Bentkover JD, Leblanc K, Zhou SZ, Hunt T. Costs of urinary incontinence and overactive bladder in the United States: a comparative study. Urology. 2004;63(3):461–465. | ||
Sexton CC, Coyne KS, Vats V, Kopp ZS, Irwin DE, Wagner TH. Impact of overactive bladder on work productivity in the United States: results from EpiLUTS. Am J Manag Care. 2009;15(4 suppl):S98–S107. | ||
Wein AJ, Rovner ES. Definition and epidemiology of overactive bladder. Urology. 2002;60(5 suppl 1):7–12. Discussion 12. | ||
Robinson D, Cardozo L, Milsom I, et al. Oestrogens and overactive bladder. Neurourol Urodyn. 2014;33(7):1086–1091. | ||
de Boer TA, Slieker-ten Hove MC, Burger CW, Vierhout ME. The prevalence and risk factors of overactive bladder symptoms and its relation to pelvic organ prolapse symptoms in a general female population. Int Urogynecol J. 2011;22(5):569–575. | ||
Coyne KS, Sexton CC, Bell JA, et al. The prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and overactive bladder (OAB) by racial/ethnic group and age: results from OAB-POLL. Neurourol Urodyn. 2013;32(3):230–237. | ||
Coyne KS, Margolis MK, Kopp ZS, Kaplan SA. Racial differences in the prevalence of overactive bladder in the United States from the epidemiology of LUTS (EpiLUTS) study. Urology. 2012;79(1):95–101. | ||
de Boer TA, Salvatore S, Cardozo L, et al. Pelvic organ prolapse and overactive bladder. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29(1):30–39. | ||
Abouassaly R, Steinberg JR, Lemieux M, et al. Complications of tension-free vaginal tape surgery: a multi-institutional review. BJU Int. 2004;94(1):110–113. | ||
Holmgren C, Nilsson S, Lanner L, Hellberg D. Frequency of de novo urgency in 463 women who had undergone the tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) procedure for genuine stress urinary incontinence – a long-term follow-up. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2007;132(1):121–125. | ||
WW Norton & Company. Female Pelvic Floor Disorders: Investigation and Management. New York: WW Norton & Company; 1992. | ||
Milne JL. Behavioral therapies for overactive bladder: making sense of the evidence. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2008;35(1):93–101. Quiz 102–103. | ||
Arya LA, Myers DL, Jackson ND. Dietary caffeine intake and the risk for detrusor instability: a case-control study. Obstet Gynecol. 2000;96(1):85–89. | ||
Lee UJ, Scott VC, Rashid R, et al. Defining and managing overactive bladder: disagreement among the experts. Urology. 2013;81(2):257–262. | ||
Davis NJ, Vaughan CP, Johnson TM 2nd, et al. Caffeine intake and its association with urinary incontinence in United States men: results from National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 2005-2006 and 2007-2008. J Urol. 2013;189(6):2170–2174. | ||
Gleason JL, Richter HE, Redden DT, Goode PS, Burgio KL, Markland AD. Caffeine and urinary incontinence in US women. Int Urogynecol J. 2013;24(2):295–302. | ||
van Haarst EP, Heldeweg EA, Newling DW, Schlatmann TJ. The 24-h frequency-volume chart in adults reporting no voiding complaints: defining reference values and analysing variables. BJU Int. 2004;93(9):1257–1261. | ||
Gormley EA, Lightner DJ, Burgio KL, et al; American Urological Association, Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction. Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. J Urol. 2012;188(6 suppl):2455–2463. | ||
Barber MD, Walters MD, Bump RC. Short forms of two condition-specific quality-of-life questionnaires for women with pelvic floor disorders (PFDI-20 and PFIQ-7). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;193(1):103–113. | ||
Bartley JM, Blum ES, Sirls LT, Peters KM. Understanding clinic options for overactive bladder. Curr Urol Rep. 2013;14(6):541–548. | ||
American Urological Association [webpage on the Internet]. Diagnosis & Treatment Algorithm: AUA/SUFU Guideline on Non-Neurogenic Overactive Bladder in Adults. 2014. Available from: https://www.auanet.org/common/pdf/education/clinical-guidance/Overactive-Bladder-Algorithm.pdf. Accessed February 2, 2016. | ||
Imamura M, Williams K, Wells M, McGrother C. Lifestyle interventions for the treatment of urinary incontinence in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(12):CD003505. | ||
Wyman JF, Burgio KL, Newman DK. Practical aspects of lifestyle modifications and behavioural interventions in the treatment of overactive bladder and urgency urinary incontinence. Int J Clin Pract. 2009;63(8):1177–1191. | ||
Fader M, Cottenden AM, Getliffe K. Absorbent products for light urinary incontinence in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;(2):CD001406. | ||
Fader M, Cottenden AM, Getliffe K. Absorbent products for moderate-heavy urinary and/or faecal incontinence in women and men. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;(4):CD007408. | ||
Eustice S, Roe B, Paterson J. Prompted voiding for the management of urinary incontinence in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD002113. | ||
Ostaszkiewicz J, Johnston L, Roe B. Timed voiding for the management of urinary incontinence in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD002802. | ||
Wallace SA, Roe B, Williams K, Palmer M. Bladder training for urinary incontinence in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD001308. | ||
Dumoulin C, Hay-Smith J, Habée-Séguin GM, Mercier J. Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women: a short version Cochrane systematic review with meta-analysis. Neurourol Urodyn. 2015;34(4):300–308. | ||
Hay-Smith EJ, Dumoulin C. Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(1):CD005654. | ||
Adams SR, Dessie SG, Dodge LE, McKinney JL, Hacker MR, Elkadry EA. Pelvic floor physical therapy as primary treatment of pelvic floor disorders with urinary urgency and frequency-predominant symptoms. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2015;21(5):252–256. | ||
Hay-Smith J, Herderschee R, Dumoulin C, Herbison P. Comparisons of approaches to pelvic floor muscle training for urinary incontinence in women: an abridged Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2012;48(4):689–705. | ||
Abrams P, Andersson KE, Buccafusco JJ, et al. Muscarinic receptors: their distribution and function in body systems, and the implications for treating overactive bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;148(5):565–578. | ||
Yamanishi T, Chapple CR, Yasuda K, Chess-Williams R. The role of M2 muscarinic receptor subtypes in mediating contraction of the pig bladder base after cyclic adenosine monophosphate elevation and/or selective M3 inactivation. J Urol. 2002;167(1):397–401. | ||
Biastre K, Burnakis T. Trospium chloride treatment of overactive bladder. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;43(2):283–295. | ||
Madhuvrata P, Cody JD, Ellis G, Herbison GP, Hay-Smith EJ. Which anticholinergic drug for overactive bladder symptoms in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;1:CD005429. | ||
Shamliyan T, Wyman J, Kane RL. Nonsurgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Adult Women: Diagnosis and Comparative Effectiveness. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2012. | ||
Nitti VW, Dmochowski R, Herschorn S, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of patients with overactive bladder and urinary incontinence: results of a phase 3, randomized, placebo controlled trial. J Urol. 2013;189(6):2186–2193. | ||
Chapple CR, Cardozo L, Nitti VW, Siddiqui E, Michel MC. Mirabegron in overactive bladder: a review of efficacy, safety, and tolerability. Neurourol Urodyn. 2014;33(1):17–30. | ||
Rosa GM, Ferrero S, Nitti VW, Wagg A, Saleem T, Chapple CR. Cardiovascular safety of β3-adrenoceptor agonists for the treatment of patients with overactive bladder syndrome. Eur Urol. 2016;69(2):311–323. | ||
Abrams P, Kelleher C, Staskin D, et al. Combination treatment with mirabegron and solifenacin in patients with overactive bladder: efficacy and safety results from a randomised, double-blind, dose-ranging, phase 2 study (Symphony). Eur Urol. 2015;67(3):577–588. | ||
Peters KM, Carrico DJ, Perez-Marrero RA, et al. Randomized trial of percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation versus Sham efficacy in the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome: results from the SUmiT trial. J Urol. 2010;183(4):1438–1443. | ||
Peters KM, Macdiarmid SA, Wooldridge LS, et al. Randomized trial of percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation versus extended-release tolterodine: results from the overactive bladder innovative therapy trial. J Urol. 2009;182(3):1055–1061. | ||
Siegel S, Noblett K, Mangel J, et al. Results of a prospective, randomized, multicenter study evaluating sacral neuromodulation with InterStim therapy compared to standard medical therapy at 6-months in subjects with mild symptoms of overactive bladder. Neurourol Urodyn. 2015;34(3):224–230. | ||
Brubaker L, Richter HE, Visco A, et al; Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Refractory idiopathic urge urinary incontinence and botulinum A injection. J Urol. 2008;180(1):217–222. | ||
Visco AG, Brubaker L, Richter HE, et al; Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Anticholinergic therapy vs. onabotulinumtoxinA for urgency urinary incontinence. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(19):1803–1813. | ||
Hagan TL, Donovan HS. Self-advocacy and cancer: a concept analysis. J Adv Nurs. 2013;69(10):2348–2359. |
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.