Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 14
Assessment of Post-Operative Pseudophakic Glaucoma by Ultrasound Biomicroscopy
Authors Ragab IT, Abdelkader AME , Kishk HM, Elshal AA
Received 7 April 2020
Accepted for publication 19 May 2020
Published 2 June 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1495—1501
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S255626
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Islam Taher Ragab, Amr Mohammed Elsayed Abdelkader, Hanem Mohammad Kishk, Abdelmohsen Abdelghany Elshal
Ophthalmology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt
Correspondence: Amr Mohammed Elsayed Abdelkader
Department of Ophthalmology, Mansoura University Ophthalmic Center, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, B.O:35516, Mansoura, Egypt
Tel +20 1004314242
Fax +20 502256104
Email [email protected]
Purpose: Pseudophakic glaucoma is a secondary glaucoma in which intra-ocular pressure is elevated following cataract removal. The current study aimed to evaluate the role of ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) in assessing post-operative pseudophakic glaucoma.
Patients and Methods: This is a case series, prospective, observational and analytical study. It included 29 eyes of 29 patients with post-operative pseudophakic glaucoma. The patients were evaluated by medical history, detailed ophthalmologic examination and UBM.
Results: UBM examination has unmasked different causes of pseudophakic glaucoma. The detected causes were classified into 3 main groups, including intraocular lens (IOL)-related causes, lens remnants and intra-ocular inflammation. Haptic-related causes were present in 9 eyes, while 6 eyes had decentered or tilted IOLs. Soemmering’s ring was the main cause in 3 eyes while in one eye the cause was lens particle in the anterior chamber (AC). Silicone oil in AC with seclusio pupillae was the main cause in one eye. Peripheral anterior synechiae were detected in 8 eyes while, posterior synechiae were evident in 7 eyes. Uveitis induced by anterior chamber IOL (ACIOL) was found in 3 eyes and one eye had peripheral anterior synechiae due to neovascular glaucoma.
Conclusion: UBM is a helpful diagnostic tool to evaluate causes of pseudophakic glaucoma through adequate visualization of different angle structures.
Keywords: ultrasound biomicroscopy, UBM, pseudophakic glaucoma, hyphaema, neovascularization
Introduction
Pseudophakic glaucoma is a secondary glaucoma in which intraocular pressure (IOP) is elevated following cataract removal. This diagnosis is given only if there was no glaucoma prior to cataract removal.1 Transient or permanent intraocular pressure elevation occurs in pseudophakic eyes as a result of several mechanisms including; vitreous filling the anterior chamber (AC), peripheral anterior synechia, lens particle glaucoma, corticosteroid-induced glaucoma,2 aqueous misdirection syndrome,3 capsular block syndrome,4 haptic-induced post-operative pseudophakic glaucoma,5 post-operative chronic inflammation,6 intraocular lens (IOL) dislocation,7 uveitis-glaucoma-hyphema (HUG) syndrome,8 pupillary block glaucoma,9 and pigment release glaucoma.10
Ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) is based on unique 50 to 100 MHz high-frequency ultrasound transducers, incorporated into a B-mode clinical scanner. Transducers of different frequencies have been used, depending on the region to be imaged. In general, higher-frequency transducers are used for fine resolution of more superficial structures. A computer program then converts these sound waves into a high-resolution image.11
UBM provides non-invasive, high-definition, reliable, and repeatable, cross-sectional images of the iris, posterior chamber IOL, lens zonule, ciliary body and even the anterior choroid.12 UBM provides measurements of several angle parameters, including the trabecular-iris angle, the trabecular-ciliary process distance, iris thickness, iris-ciliary process distance, iris-IOL contact distance, iris-zonular distance, AC angle, iris-IOL angle, and AC depth.11
UBM can be used to detect causes of pseudophakic glaucoma such as malposition of the IOL,5 pupillary block glaucoma,2 misplaced haptics, anterior and posterior synechiae, as well as occlusion of the trabecular meshwork by inflammatory cells and debris.13
Patients and Methods
This is a case series prospective, observational and analytical study. It included 29 eyes of 29 patients with postoperative pseudophakic glaucoma attending the outpatient clinics at Mansoura University Ophthalmic Center (a central university hospital and a tertiary referral center in Egypt), in the period from March 2017 to March 2019. The inclusion criteria included patients with elevated IOP after cataract extraction and intraocular lens implantation. Patients with chronic iridocyclitis or preoperative glaucoma were excluded from the study.
All the patients in this study were evaluated starting with medical history, detailed ophthalmologic examination including visual acuity measurement, slit lamp biomicroscopy, tonometry, fundus examination, gonioscopy and UBM.
UBM was used to examine the angle structures in which iris, ciliary body, and scleral spur can be recognized easily. The scleral spur is the only constant landmark used to interpret images and can be identified in the region where the radiopaque shadow of the sclera merges with the relatively radiolucent shadow of the cornea.
UBM scanning was performed in the supine position. Eye cup was used to separate the eyelids after applying a drop of benoxinate Hcl 0.4% and was filled with 2.5% methylcellulose as a coupling medium. Scanning was performed in eight directions, placing the probe close to the area of interest. Measurements were repeated five times to confirm reproducibility and eliminate artefacts.
Statistical Analysis
Data were coded, computed then analyzed using IBM SPSS (Statistical package for social science) version 24 for Windows. Descriptive statistics were calculated in the form of mean ± SD. The significance of difference in between groups was tested using Student’s t-test, Mann–Whitney, chi square test and Fisher Exact Test. P value less than 0.05 (5%) was considered to be statistically significant.
Results
The study included 29 eyes of 29 patients, 8 (27.6%) males and 21 (72.4%) females. The mean age was 52.4 ± 15.4 (mean ± SD) years. Twelve (41.3%) patients were diabetic, 4 (13.8%) of them had diabetic retinopathy. The study included 25 (86.2%) eyes with previous phaco-surgery, versus 4 (13.8%) eyes with extra capsular cataract extraction (ECCE). AIOLs were implanted in AC in 4 (13.8%) eyes and intra-bagal posterior chamber IOL (PCIOL) in 24 (82.8%) eyes while one (3.4%) eye was presented with sulcus PCIOL. The median time from cataract surgery till study inclusion was 12 months.
The mean IOP was 34.3 ± 7.5 mmHg. The C/D ratio was >0.8 in 2 (6.9%) cases, around 0.6 in 2 (6.9%) cases and 0.3 or less in 25 (86.2%) cases. Gonioscopy showed 10 (34.5%) eyes with open angle glaucoma and 19 (65.5%) eyes with closed angle glaucoma.
UBM was able to detect the possible causes of glaucoma in 28 (96.6%) eyes, while in one (3.4%) eye it could not offer a glaucoma explanation (Figure 1). Haptic-related causes were present in 9 (31%) eyes, with the haptic pushing the iris against the cornea (Figure 2) While 6 (20.6%) eyes had decentered or tilted IOL (Figures 3 and 4). Soemmering’s ring was found to be the main cause in 3 (10.3%) eyes (Figure 5). In 1 (3.4%) eye the detected cause was lens particle in AC. Silicone oil in AC with seclusio-pupillae was the main cause in 1 (3.4%) eye (Figure 6). Peripheral anterior synechiae were detected in 8 (27.5%) eyes (Figure 7), posterior synechiae were evident in 7 (24.1%) eyes. Uveitis induced by ACIOL haptics was found in 3 (10.3%) eyes (Figures 8) and 1 (3.4%) eye had peripheral anterior synechiae due to neovascular glaucoma (Figure 9). Data are shown in Table 1.
 |
Table 1 Causes of Pseudophakic Glaucoma Detected by UBM |
 |
Figure 1 No UBM explanation for elevated IOP. |
 |
Figure 2 IOL haptic pushing iris (arrow) leading to iridocorneal apposition and angle closure. |
 |
Figure 3 Decentered PCIOL, haptic impacted in ciliary body (arrow) leading to chronic uveitis. |
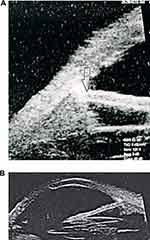 |
Figure 4 A, B Tilted IOL pushing iris anteriorly (arrow) causing peripheral anterior synechiae. |
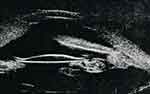 |
Figure 5 Soemmering’s ring (arrow), peripheral anterior synechiae. |
 |
Figure 6 Silicone oil in anterior chamber (arrow), seclusio pupillae. |
 |
Figure 7 Uveitis with iris bombe and peripheral anterior synechiae (arrow). |
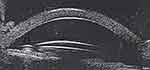 |
Figure 8 Haptic of ACIOL (arrow) inducing chronic irritation with pigment dispersion evident on slit lamp examination. |
 |
Figure 9 Peripheral anterior synechiae (arrow) due to neovascularization at angle. |
The study showed significant association (P ≤ 0.05) between pseudophakic glaucoma and types of cataract surgery. It was more common in cases having ECCE (100%) than cases having phaco-surgery (44%).
The anterior chamber angle morphology is affected by patient age, IOL type and the presence of synaechia. Open angle glaucoma was more evident in older age group (mean age was 60.4 ± 9.9 years) while closed angle glaucoma occurred in younger age group (mean age 48.2 ± 16.3 years). Also, open angle glaucoma was noted in all cases of ACIOL (100%) cases and 6 (24%) cases of PCIOL, while closed angle glaucoma occurred in 19 (76%) cases of PCIOL (P value ≤0.05). The incidence of synechiae detected by UBM was more common in cases of closed angle glaucoma (13 cases, 68.4%) than open angle glaucoma (2 cases, 20%) (P value ≤0.05).
Discussion
Traditionally, IOP is expected to decrease after cataract surgery. It is due to widening of the anterior chamber angle. This was reported by Hayashi et al, 2000,14 Slabaugh & Chen, 2014,15 and Bojikian & Chen, 2018.16
The current study analyzed cases with elevated IOP after either complicated or non-complicated cataract surgery. Similar literature research work focused on this paradoxical IOP response after cataract surgery like Hansen et al, 1995,17 Elfersy et al, 2016,18 and Annam et al, 2018.19 However, only a few of these previous studies made a good use of UMB and most of these studies were of small sample size, even some of them were merely case reports. Such studies are illustrated in Table 2. The aim of this prospective, case series, observational and analytical study was to evaluate the role of UBM in assessing causes of post-operative pseudophakic glaucoma.
 |
Table 2 UBM Finding of Other Studies for Pseudophakic Glaucoma |
In the current study, the IOP was found to be elevated in 4 eyes (13.8%) with ACIOL. The causes of IOP elevation in cases with ACIOL were presumed to be due to inflammation, pigment dispersion and HUG syndrome, this is also noted by Güell et al 2014,20 Sousa et al 2016,21 and Peralba et al 2018.22
On the other hand, IOP elevation was associated with PCIOL in 25 eyes (86.2%). PCIOL was reported to increase IOP due to IOL de-centration, haptic malposition, uveitis, synaechiae formation and micro-hyphaema. This is agreed by Alfaro-Juárez et al, 2015.8
Haptic malposition was evident in 9 (31%) cases leading to recurrent microhyphema due to continuous irritation of ciliary body, what is traditionally called “HUG syndrome”, this was reported by Mostafavi et al, 2013,5 Alniemi et al, 2018.23 Also, this malposition may lead to chronic postoperative inflammation and pushing iris anteriorly causing narrow angle, this is agreed by Lima et al, 2014.6
Arvind et al, 2005,24 Zhang et al, 2016,25 documented that prolonged iridocorneal apposition due to haptic malposition leads to peripheral anterior synechiae and angle closure glaucoma. This is reported in 5 cases in the current study.
Eight (27.6%) eyes had mainly uveitis as a leader cause in elevation of intra-ocular pressure. Lima et al, 2014,6 Aptel et al, 2017,26 and Peralba et al, 2018,22 emphasize that IOLs might lead to chronic inflammation and secondary glaucoma.
The studies conducted by Sathish et al, 2000,13 Zhang et al, 2016,25 and Zhang & Chen 2017,27 illustrated that intra-ocular inflammation after cataract surgery causes seclusio pupillae, pupillary block, iris bombe and angle closure that elevate IOP. This was evident in 5 cases in this study.
Soemmering’s ring was detected in three eyes (10.3%) in this study. Kobayashi et al 2000,28 and Suwan et al 20169 found that proliferation of remnants of lens epithelium and the peripheral part of the capsular bag leads to formation of Soemmering’s ring and pupillary block glaucoma. Remnants of lens particle were the cause of increase of IOP in one eye (3.4%) in this study. The study conducted by Kee & Lee 2001,29 documents that lens particles can obstruct trabecular meshwork and elevate IOP after cataract surgery.
Another cause of pseudophakic glaucoma detected in one (3.4%) eye in this study was silicone oil in anterior chamber after incomplete silicone oil removal in previous retinal surgery. IOP elevation was due to either blocking of trabecular meshwork by oil droplets or seclusio pupillae; this is also documented with Jawad et al 2016.30
One (3.4%) eye in the study had neovascular glaucoma in a diabetic patient with diabetic retinopathy. Eyes with diabetic retinopathy were associated with the development of rubeosis iridis and neovascular glaucoma after cataract surgery. Goyal et al 2017,31 Kelkar et al 2018,32 explained this by significant increase in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), interleukin-1 (IL-1), and pigment-epithelium-derived factor which lead to the formation of neo-vessels. Rodrigues et al 201633 refer the cause of IOP elevation in NVG to the development of neo-vascularization at angle and the traction of the iris to the cornea leading to peripheral anterior synechiae.
In this study there was one (3.4%) case with no UBM explanation for increased intra-ocular pressure, the most probable cause is trabeculitis. Assia et al 199234 explained similar conditions. Table 2 demonstrates UBM finding of different studies for pseudophakic glaucoma.
In the current study, The incidence of secondary angle closure glaucoma (19 out of 29 patients or 65.5%) was more than secondary open angle glaucoma (ten out of 29 patients or 34.5%). This could be explained by the presence of peripheral anterior synechiae in 27.5% of cases and posterior synechiae in 24.1% of cases as a complication of uveitis after cataract operation. This finding was in contrast to studies conducted by Mandal & Netland 2004,2 that reported more frequent open angle glaucoma than closed angle glaucoma after cataract surgery. This may be due to different age distribution between this study and current study. Suwan et al 20169 also reported less frequent cases of closed angle pseudophakic glaucoma due to peripheral laser iridotomy.
In this study, the site of implanted IOL has a significant association with the type of glaucoma (P = 0.009). Open angle glaucoma was associated with all 4 cases (100%) of ACIOL and only 6 cases (24%) of PCIOL cases. While closed angle glaucoma occurred with 19 cases (76%) of PCIOL cases.
In the current study, the mean age of patients has a significant association with the type of glaucoma (p = 0.04), as open angle glaucoma occurred in older age group (60.4 ± 9.9 years) than angle closure glaucoma (48.2 ± 16.3 years). In addition, intra-ocular synechiae has a significant association with type of glaucoma (P = 0.02), being higher with angle closure glaucoma.
Conclusion
UBM is a helpful diagnostic tool in pseudophakic glaucoma, as sound wave can penetrate behind iris and detect the possible causes of IOP elevation. UBM can detect changes which cannot be detected by clinical examination so it is recommended in all cases of pseudophakic glaucoma for better evaluation of the underlying cause which helps subsequent management.
Medical Ethics Approval
Prior approval of the institutional research ethics board (IRB), faculty of medicine, Mansoura University was obtained under code no.MS/17.02.79 on 12/3/2017 and informed consent was taken from all the patients. All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and Helsinki declaration.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Dosunmu EO, Freedman SF. Aphakic/Pseudophakic Glaucoma. Practical Management of Pediatric Ocular Disorders and Strabismus. Springer.N Y; 2016:459–470.
2. Mandal AK, Netland PA. Glaucoma in aphakia and pseudophakia after congenital cataract surgery. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2004;52:185.
3. Moinul P, Hutnik CM. Aqueous misdirection syndrome: an interesting case presentation. Clin Ophthalmol. 2013;9:183.
4. Srinivasan S, Hanumanthu S, Varikkara M. Angle-closure glaucoma secondary to inflammatory capsular block syndrome following routine cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013;39(3):471–474. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2012.11.034
5. Mostafavi D, Nagel D, Danias J. Haptic-induced postoperative complications,evaluation using ultrasound biomicroscopy. Can J Ophthalmol. 2013;48(6):478–481. doi:10.1016/j.jcjo.2013.03.017
6. Lima BR, Pichi F, Haydenv BC, Lowder CY. Ultrasound biomicroscopy in chronic pseudophakic ocular inflammation associated with misplaced intraocular lens haptics. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014;157(4):813–817. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2013.12.025
7. Zheng DY, Chen LN, Sun Y, Shao YF, Liang JL, Liu YZ. Out of the bag intraocular lens dislocation: outcomes of posterior chamber intraocular lens exchange, risk factors, and prevention. Chin Med J. 2010;123(18):2562–2567.
8. Alfaro-Juárez A, Vital-Berral C, Sánchez-Vicente J, Muñoz-Morales A, Muñoz-Morales A. Uveitis-glaucoma-hyphema syndrome associated with recurrent vitreous hemorrhage. Archivos de la Soc Esp de Oftalmología. 2015;90(8):392–394. doi:10.1016/j.oftal.2014.11.007
9. Suwan Y, Purevdorj B, Teekhasaenee C, Supakontanasan W, Simaroj P. Pseudophakic angle-closure from a Soemmering’s ring. BMC Ophthalmol. 2016;16(1):91. doi:10.1186/s12886-016-0257-6
10. Uy HS, Chan PS. Pigment release and secondary glaucoma after implantation of single piece acrylic intraocular lenses in the ciliary sulcus. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;142(2):330–332. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2006.02.033
11. Maslin JS, Barkana Y, Dorairaj SK. Anterior segment imaging in glaucoma: an updated review. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2015;63(8):630. doi:10.4103/0301-4738.169787
12. Tello C, Tran HV, Liebmann J, Ritch R angle closure: classification, concepts, and the role of ultrasound biomicroscopy in diagnosis and treatment.
13. Sathish S, Mackinnon JR, Atta HR. Role of ultrasound biomicroscopy in managing pseudophakic pupillary block glaucoma. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26(12):1836–1838. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(00)00520-4
14. Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Changes in anterior chamber angle width and depth after intraocular lens implantation in eyes with glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2000;107(4):698–703. doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(00)00007-5
15. Slabaugh MA, Chen PP. The effect of cataract extraction on intraocular pressure. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2014;25(2):122–126. doi:10.1097/ICU.0000000000000033
16. Bojikian KD, Chen PP. Intraocular pressure after phacoemulsification in open-angle glaucoma patients with uncontrolled or marginally controlled glaucoma and/or with severe visual field loss. J Glaucoma. 2018;27(2):108–114. doi:10.1097/IJG.0000000000000854
17. Hansen MH, Gyldenkerne GJ, Otland NW, Corydon L, Naeser K. Intraocular pressure seven years after extracapsular cataract extraction and sulcus implantation of a posterior chamber intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1995;21(6):676–678. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(13)80565-2
18. Elfersy AJ, Prinzi RA, Peracha ZH, et al. IOP elevation after cataract surgery: results for residents and senior staff at Henry Ford Health System. J Glaucoma. 2016;25(10):802–806. doi:10.1097/IJG.0000000000000421
19. Annam K, Chen AJ, Lee IM, Paul AA, Rivera JJ, Greenberg PB. Risk factors for early intraocular pressure elevation after cataract surgery in a cohort of united states veterans. Mil Med. 2018;183(9–10):427–433. doi:10.1093/milmed/usx113
20. Güell JL, Verdaguer P, Elies D, et al. Secondary iris-claw anterior chamber lens implantation in patients with aphakia without capsular support. Br J Ophthalmol. 2014;98(5):658–663. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2013-304035
21. Sousa DC, Leal I, Faria MY, Pinto LA. A rare manifestation of uveitis-glaucoma-hyphema syndrome. J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2016;10(2):76. doi:10.5005/jp-journals-10008-1205
22. Peralba RT, Lamas-Francis D, Sarandeses-Diez T, Martínez-Perez L, Rodríguez-Ares T. Iris-claw intraocular lens for aphakia: can location influence the final outcomes? J Cataract Refract Surg. 2018;44(7):818–826. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2018.05.010
23. Alniemi ST, Amin SR, Sculley L, Bakri SJ Ultrasound biomicroscopy in pseudophakic patients with unexplained recurrent hyphema or vitreous hemorrhage.
24. Arvind H, George R, Raju P, et al. Glaucoma in aphakia and pseudophakia in the Chennai glaucoma study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005;89(6):699–703. doi:10.1136/bjo.2004.056234
25. Zhang X, Soni N, Alexander J, Kalarn S, Saeedi O. Pupillary block due to reverse implantation of a sulcus intraocular lens. JCRS Online Case Reports. 2016;4(3):41–44. doi:10.1016/j.jcro.2016.06.002
26. Aptel F, Colin C, Kaderli S, et al. Management of postoperative inflammation after cataract and complex ocular surgeries: a systematic review and Delphi survey. Br J Ophthalmol. 2017;101:310–324.
27. Zhang X, Chen X. Postoperative Complications and Management. In Pediatric Lens Diseases. Singapore: Springer; 2017:309–328.
28. Kobayashi H, Hirose M, Kobayashi K. Ultrasound biomicroscopic analysis of pseudophakic pupillary block glaucoma induced by Soemmering’s ring. Br j Ophthalmol. 2000;84(10):1142–1146. doi:10.1136/bjo.84.10.1142
29. Kee C, Lee S. Lens particle glaucoma occurring 15 years after cataract surgery. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2001;15(2):137–139. doi:10.3341/kjo.2001.15.2.137
30. Jawad M, Khan B, Shah MA, Qayum I, Aftab M. Changes of intraocular pressure in vitrectomised eyes after removal of silicone oil. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2016;28:327–330.
31. Goyal S, Hardin J, Uwaydat SH, Ellabban AA, Warner DB, Sallam AB. Review and update of cataract surgery in the diabetic eye. Expert Rev Ophthalmol. 2017;12(5):359–371. doi:10.1080/17469899.2017.1351296
32. Kelkar A, Kelkar J, Mehta H, Amoaku W. Cataract surgery in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2018;66(10):1401. doi:10.4103/ijo.IJO_1158_17
33. Rodrigues GB, Abe RY, Zangalli C, et al. Neovascular glaucoma: a review. Int j Retina Vitreous. 2016;2(1):26. doi:10.1186/s40942-016-0051-x
34. Assia EI, Apple DJ, Lim ES, Morgan RC, Tsai JC. Removal of viscoelastic materials after experimental cataract surgery in vitro. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992;18(1):3–6. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(13)80376-8
35. Canlas OA, Tran HV, Ishikawa H, Liebmann JM, Ritch R, Ritch R. Ultrasound biomicroscopy in uveitis-glaucoma-hyphema syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002;133(6):839–841. doi:10.1016/S0002-9394(02)01386-7
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
