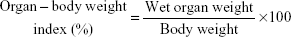Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 10 » Supplement 1 Challenges in biomaterials research
Acute and subchronic toxicity analysis of surface modified paclitaxel attached hydroxyapatite and titanium dioxide nanoparticles
Authors Venkatasubbu G, Ramasamy S, Gaddam PR, Kumar J
Received 8 January 2015
Accepted for publication 5 March 2015
Published 1 October 2015 Volume 2015:10(Supplement 1 Challenges in biomaterials research) Pages 137—148
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S79991
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Gopinath Devanand Venkatasubbu,1 S Ramasamy,2 Pramod Reddy Gaddam,3 J Kumar2
1Department of Biotechnology, University of Madras, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India; 2Crystal Growth Centre, Anna University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India; 3Department of Pharmacology, Siddha Central Research Institute, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Abstract: Nanoparticles are widely used for targeted drug delivery applications. Surface modification with appropriate polymer and ligands is carried out to target the drug to the affected area. Toxicity analysis is carried out to evaluate the safety of the surface modified nanoparticles. In this study, paclitaxel attached, folic acid functionalized, polyethylene glycol modified hydroxyapatite and titanium dioxide nanoparticles were used for targeted drug delivery system. The toxicological behavior of the system was studied in vivo in rats and mice. Acute and subchronic studies were carried out. Biochemical, hematological, and histopathological analysis was also done. There were no significant alterations in the biochemical parameters at a low dosage. There was a small change in alkaline phosphatase (ALP) level at a high dosage. The results indicate a safe toxicological profile.
Keywords: acute and subchronic toxicology, hematological analysis, biochemical analysis, histopathology
Introduction
Nanomedicine is defined as the application of nanotechnology for the treatment, diagnosis, monitoring, and control of biological systems. Nanomedicine utilizes nanotechnology concepts for imaging, therapeutic drug delivery, and targeted drug delivery. In traditional chemotherapy, toxicity to healthy cells is associated with anticancer drugs. Nanoparticles are used as a drug carrier for the specific delivery of drugs to cancer cells. In targeted drug delivery, the anticancer drug is delivered specifically to the cancer cells. This reduces the toxicity to normal cells. The physicochemical characteristics of nanocarriers, such as composition, particle size, surface charge, and the presence of ligands on their surface, will dictate their biodistribution and pharmacokinetics.1–3
Nanoparticles to be used in a targeted drug delivery system should be nontoxic in vivo. Surface modification is an important aspect of nanoparticle design for biomedical applications. Modulation of nanoparticle surfaces can influence particle uptake, biological responses, and biodistribution. After every modification performed on the nanoparticles, the biocompatibility of the particles has to be assessed. Surface functionalization can be utilized to increase the drug circulation time in blood, reduce non-specific distribution or specific targeting of tissues or cells by using a targeting ligand.4
Calcium apatites are biomaterials of interest in many fields. The general formula for calcium apatite is Ca5(PO4)3X, where X is a negative ion. Among the apatites, hydroxyapatite (HAp) is of much interest since it is the structural template for the mineral material in human and animal bones. HAp (Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2) is used in many biomedical applications including bone grafts and joint replacements. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles are bio-friendly and have good biocompatibility with weak or no toxicity in vitro and in vivo, which indicates their great potential for applications in the life sciences.5
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is used in targeted drug delivery systems because it is nontoxic, non-immunogenic, and nonantigenic. PEG has a general structure of HO-(CH2CH2O)nH encompassing a polyether backbone that is chemically inert with terminal hydroxyl groups. In this study, PEG 6000 was used to coat the nanoparticles. A low PEG concentration was preferred to avoid encapsulation of nanoparticles with a thicker layer of PEG.6 PEGylated nanocarriers have the ability to evade the reticuloendothelial system and extend the circulation time of encapsulated drugs in the bloodstream. When attached to the surfaces of nanoparticles, PEG has been shown to increase the biocompatibility, reduce the adsorption of proteins and blood components on the surface of nanoparticles, and reduce clearance by macrophages. Also it enables the nanoparticles to cross the cell membrane. PEG prevents the nanoparticles from agglomeration and prevents particle surface from oxidation. The major advantage of a PEG coating is that it increases the circulation time because of resistance to plasma protein deposition.7–10
Toxicity refers to unwanted effects on biological systems. It is difficult to define, since the biological entity could be a complex system in every mammalian animal (or a person), a single-cell organism such as a bacterium or cell, or a virus. Typical for biological toxicity is a “threshold dose”, which might be due to the organism’s ability to fight the toxin, such as in the case where the toxin is excreted, metabolized, or isolated, for example, by encapsulation into a vesicle. A threshold dose might also be due to the fact that the effect is too small to see or the observation time scale is too short to notice an effect. In order to analyze biological toxicity, it is very important to choose the correct system, since no effects may otherwise be seen. The release of toxic particle coatings inside a cell, which then interact with chromosomal DNA and transforms a cell into a cancer cell, is such a biological effect. Proving that such effects exist, especially when they stem from mixtures of compounds, may be very difficult and complex. Toxicity of a substance can be influenced by many factors, such as the pathway of administration (application of the toxin to the skin or ingestion, inhalation, or injection); the time of exposure (a brief, acute encounter versus long-term, chronic exposure); the number of exposures (a single dose versus multiple doses over a period of time); the physical form of the toxin (solid, liquid, or gas); the organ system involved (cardiovascular, nephro-, hemo-, nervous-, or hematopoietic-system); and even the genetic makeup and robustness of the target cells or organisms. The study of most general relationships in manifestations of the biological and toxic effects of nanoparticles depending on their shape, size, origin material, surface area, electric charge, physicochemical peculiarities of the structure, dosage, administration route, concentration in the target organ, and duration of interaction should be considered the most important and actual fundamental problem of nanoparticle toxicology.11
In vivo, nanoparticles will be translocated to and entrapped in other tissues or organs along the blood circulation. The small size and large surface area endow them with an active group or intrinsic toxicity. Even at a very small cellular level, they may pose potential long-term health hazards.12,13 Toxicity indicates the adverse effects due to the interaction between nanomaterials and cells. This interaction may vary depending on the chemical properties of the toxicants and the cell membrane, as it may occur on the cell surface or within the cell body. The evaluation of toxic properties of nanomaterials is crucial when considering them for use in biomedical science. In practice, the evaluation typically includes acute, subchronic, and chronic studies.14 The current status of toxicology due to nanoparticles has been reported by Becker.15
In our previous work, we reported the synthesis and surface modification of HAp16 and TiO217 nanoparticles. In vivo anticancer study of surface modified HAp and TiO2 nanoparticles was done in diethylnitrosamine induced hepatocarcinoma animal models. The in vivo analysis confirmed the efficacy of the surface modified nanoparticles. Biochemical and hematological parameters showed that the anticancer activity of the surface modified paclitaxel attached HAp and TiO2 nanoparticles was higher than the anticancer activity of pure paclitaxel.18 Although surface modified nanoparticles have anticancer activity, it is less than that of pure paclitaxel. The higher anticancer activity of surface modified paclitaxel attached HAp and TiO2 nanoparticles compared to pure paclitaxel may be because of the targeting of paclitaxel to the cancer cells.18
In this present study, the toxicological aspects of paclitaxel-loaded, surface modified HAp and TiO2 nanoparticles were analyzed. The anticancer drug paclitaxel was attached to folic acid functionalized PEG modified HAp and TiO2 nanoparticles. The individual components of the formulation, viz nanoparticles, folic acid, and PEG, are biocompatible materials. Paclitaxel represents the most significant advancement in chemotherapy drugs used to treat cancer. The attachment of paclitaxel to surface modified HAp and TiO2 nanoparticles will improve the pharmacological effects of the attached paclitaxel. The influence of this attachment is reported in this paper.
Experimental procedure
Animals
Healthy male and female Swiss Albino mice and rats (approximately 20–25 g body weight mice and 150–180 g body weight rats; Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Science University, Chennai, India) were housed in polypropylene cages with a maximum of three animals of the same sex per cage and placed in a ventilated, temperature-controlled room. The standard conditions were supplied and maintained at 20°C±2°C, 60%±10% relative humidity, and a 12-hour light/dark cycle. The cages contained autoclaved paddy husk as bedding that was replaced on a twice weekly basis. The commercial pellet diet and distilled water for rats and mice were available ad libitum. The experimental protocol involving animals was carefully reviewed and approved (111/PHARMA/SCRI/8 July 2011) by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of Siddha Central Research Institute, Chennai, India, where the studies were carried out in compliance with the guidelines of the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experimental Animals (CPCSEA), India. Animals were acclimated to their environment for 5 days prior to treatment.
Acute toxicity study (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development guideline; OECD, 1996)
Swiss albino mice (nine females) were assigned to the following three test groups: group I (250 mg/kg body weight of surface modified paclitaxel attached HAp and surface modified paclitaxel attached TiO2 [HAp-PEG-FA-PAC/TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC] nanoparticles in phosphate-buffered saline [PBS]); group II (500 mg/kg body weight of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC/TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticles in PBS); and group III (control, administered with PBS). The respective doses were suspended in PBS and were administered intraperitoneally. Thereafter, the animals were monitored for 14 days for clinical signs of toxicity or mortality. On completion of the treatment, the animals were sacrificed by cervical dislocation and necropsied to facilitate gross pathological examination of organs.
Subchronic toxicity (OECD guideline 407; OECD, 1995)
The animals (three males and three females) were assigned to the following four test groups: group I (vehicle control; distilled water); group II (25 mg/kg body weight of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC/TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC in PBS); group III (50 mg/kg body weight of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC/TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC in PBS); and group IV (100 mg/kg body weight of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC/TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC in PBS). The animals were gavaged with the respective doses of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC/TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC suspended in 0.5 mL of the vehicle, once daily, for a period of 28 days. Body weights were recorded on days 0, 7, 14, 21, 27, and 28. Feed consumption was measured per cage over successive periods of 3 days by weighing the feeders. Throughout the dosing, the animals were examined for any clinical signs of morbidity, mortality, changes in body weight, and changes in food consumption. At the end of the treatment, blood was collected from the animals from the orbital sinus for clinical pathology assessment, which included analysis of various hematology parameters and biochemical parameters. Consequently, the animals were sacrificed by cervical dislocation and necropsied for the gross evaluation of the various organs. The necropsy also included careful and consistent dissection of various target organs like liver and kidneys and calculation of organ–body index. The organ–body weight index was calculated according to the following formula:
|
|
We chose the administration of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC and TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticles by intraperitoneal injection as it is predominantly used for its ease compared to other parenteral methods during animal testing for the administration of systemic drugs and fluids. Additionally, one can administer a large volume of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC/TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticle suspensions (~400 μL) to the mice/rats if one chooses the intraperitoneal route compared to the intravenous method. One cannot inject this much drug via the intravenous route.
Blood biomarker assay
Blood samples were collected via the ocular vein. The serum was obtained by centrifugation of the whole blood at 3,000 rpm for 15 minutes. Liver function was evaluated based on the serum levels of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) as well as on blood glucose and cholesterol levels. Nephrotoxicity was determined by blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum creatinine, total protein, albumin, and globulin.
Hematological parameter determination
Blood samples were collected in tubes containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid as anticoagulant. Hemoglobin, platelets, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, packed cell volume, polymorphs, and lymphocytes were measured using a hematology Autoanalyzer, Mindray, BC 2800VET (Mindray Medical International Limited, Shenzhen, People’s Republic of China).
Histopathological examination
After sacrifice, liver and kidney were removed and placed into buffered formalin. For pathological studies, all histopathological tests were performed using standard laboratory procedures. The tissues were embedded in paraffin blocks, then sliced to 5 μm thickness and placed onto glass slides. After hematoxylin–eosin staining, the slides were observed and photos were taken using an optical microscope. The results were analyzed by a veterinary pathologist.
Statistical analysis
For statistical analysis, each of the experimental values was compared with its corresponding control. The results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Multi-group comparisons of the means were carried out by one-way analysis of variance test. Statistical significance for all tests was set at P<0.05.
Results and discussion
Acute toxicity analysis of surface modified paclitaxel attached HAp and TiO2 nanoparticles
No mortality was observed in the animals in any test group or in the control group. The animals did not show any abnormal behavior throughout the 14 days. Pathological examination of liver and kidney did not show any evidence of toxicity. Clinical signs of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC/TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticles over a period of 14 days are shown in Table 1. The nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery system was found to be safe for a single limit dose equivalent to 250 and 500 mg/kg of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC/TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC. All clinical symptoms were evaluated by comparing treated animals with controls (n=3). The toxicity of the nanoparticle formulation due to a single dose for less than 14 days was determined by acute toxicity analysis.19 The present study showed that intraperitoneal treatment of mice with HAp-PEG-FA-PAC/TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC did not induce mortality or significant clinical symptoms of toxicity.
Subchronic toxicity analysis of surface modified paclitaxel attached HAp and TiO2 nanoparticles
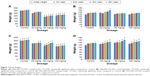
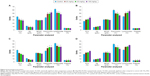
No animal mortality was observed in any of the test groups for the entire period of subchronic study for both HAp-PEG-FA-PAC and TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticles. The subchronic toxicity result shows that the nanoparticle formulations did not exhibit any adverse effect with long-term administration on the general health of the animals. The body weights of both male and female animals did not vary significantly. These results are given in Figure 1. There was no significant increase in the food consumption by the animals in the treatment group when compared with the control group except at 100 mg/kg body weight. These results are depicted in Figure 2. There was no change in the general systemic health of the animals. The organ–body weight indices are shown in Figure 3. The organ–body weight indices of liver and kidney for both sexes did not show any significant change.
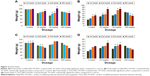
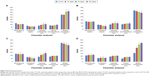
Changes in hematological parameters are used to find out the physiological and pathological changes in animals and humans. Figure 4 shows the hematological parameters. There was no significant change in platelets or mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration in either sex. In male animals, there was a significant change (P<0.05) in hemoglobin level and packed cell volume with increase in concentration of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC and TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticles, while insignificant changes were observed with increasing concentrations of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC and TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticles in the female animals. This suggests hemostasis and blood system damage in the male animals. There was a significant decrease (P<0.05) in the lymphocyte count in the male animals. This indicates a disturbance of cellular immune function and an inhibition of the immune response of the male animals. Lymphocytes circulate in the blood and migrate to injured tissues.20 This may account for the decrease in lymphocyte numbers at the highest dose of treatment. But in the female animals, there was a significant (P<0.05) increase in lymphocyte count. This may be attributed to local reactions at the injection site.21 In both male and female animals, there was a significant change (P<0.05) in the polymorphs. Polymorphs include neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils. A dose-dependent increase in the polymorphs may be due to the increased immune response. There was no significant change in the hematological parameters of the treated group when compared with the control group in both sexes. This indicates that the nanoparticle formulations are safe at 25 mg/kg body weight and 50 mg/kg body weight.
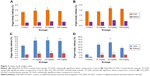
In the subchronic toxicity analysis, the biochemical, physiological, and/or pathological changes due to multiple administrations were analyzed. There will be a direct change in the hematological parameters when the test compound causes tissue injury. When there is damage to tissue, overproduction of red blood cells occurs. Changes in enzyme parameters are due to their leakage from intracellular sites or target tissues due to cellular/tissue injury. The biochemical parameters for male and female animals are given in Figure 5. There were no significant changes in blood glucose and cholesterol in both male and female animals. There was a slight change in AST values in males and ALP values in females (P<0.05) at a higher dose (100 mg/kg body weight). This may be due to the metabolism of HAp and TiO2, which was mainly through liver. The fact that all the animals survived throughout the investigation period indicated that the liver was not seriously damaged and neither formulation was fatal. The ALP levels were altered only at a higher dose, indicating that bone metabolism was not disturbed with the usage of HAp in the targeted drug delivery system at a low dose. HAp, which is the primary constituent of bone and teeth, affects bone absorption and metabolism.22 Liu et al observed liver damage by intraperitoneal injection of higher doses (50, 100, and 150 mg/kg body weight) of nanoparticulate TiO2 for 5 nm particles.23,24 Wang et al reported that after oral administration of 5 g/kg body weight of nanoparticulate TiO2 suspensions (25 and 80 nm), the liver enzymes AST and ALT were significantly increased.25 However, in our case, the elevated AST and ALT levels indicated that it is not fatal, and all the animals survived through the whole experiment. The discrepancy between our study and others is mainly due to the surface modification. The surface modification reduces the toxicity of the nanoparticle. The ALP levels are altered only at a higher dose. This shows that the metabolism was not disturbed with the usage of TiO2 in a targeted drug delivery system at a low dose.
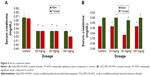
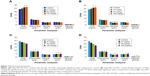
The serum creatinine values are given in Figure 6. There was no increase in the serum creatinine values. There was a significant difference in the level of BUN at higher dose, indicating renal toxicity.22 The BUN, globulin levels, and albumin-to-globulin ratio are given in Figure 7 for both sexes. Blood transportation excretes out serum BUN through the renal glomerulus. The renal glomerulus may have swelled and the renal tubule would have been filled with the proteinic liquid, which led to the high BUN concentration in the serum.26 Liver eliminates the side effects induced by nanoparticles; some proportion of these particles should be excreted by the kidneys. At high concentrations, it is difficult for nanoparticles to clear liver and kidney, and this would result in increased AST, ALP, and BUN. Liver enzymes are present within the liver cells. When the liver cells get damaged, they get spilled into blood. This causes an increase in the enzyme level. Albumin, the primary component of total protein, is made by liver. The change in albumin level was significant (P<0.05) at higher dosage in female animals. There was no change in albumin level in the male animals nor at low doses in the female animals when compared to untreated mice. This shows that there was no liver damage. If there is any damage in liver, albumin production will decrease. Total protein and blood clotting factors are also indicators of liver function. There was no change of total protein plasma proteins (albumin and globulins) between the control and nanoparticle-treated animals, indicating no abnormalities in liver even at the highest dose of nanoparticle treatment. Similarly, there was no change in blood sugar levels, which shows there were no dietary changes.27 The toxicity associated with TiO2 as reported previously28 was not found in our study, which may be due to the surface modification.
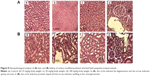
Histopathological analysis
The histopathological analysis of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC-treated animals is depicted in Figure 8. In the 25 and 50 mg/kg body weight HAp-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticle groups, there was no change in hepatocytes, portal area, or integrated hepatic sinusoidal endothelium when compared with control. In the 100 mg/kg body weight HAp-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticle group, however, histopathological changes were observed in the liver tissue. Fat degeneration of normal hepatocytes around central vein and spotty necrosis were induced by vacuoles around the central vein (Figure 8A). The ALT and AST are the most sensitive indicators of hepatic injury, showed an increase in the 100 mg/kg-treated group. The decreased liver weight and the hepatic necrosis in the physiological examination also indicated liver injury. The liver is the main detoxification tissue and became activated to eliminate side effects in the mass ingested-HAp-PEG-FA-PAC group. Similar to the observation in the liver, the kidney did not show any abnormal pathology changes in the 25 and 50 mg/kg HAp-PEG-FA-PAC groups. In the 100 mg/kg-treated group, proteinic liquids filled the renal tubule; in addition, swelling in the renal glomerulus was observed (Figure 8B). The increase in BUN levels at a high concentration of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticles was due to the renal dysfunction.
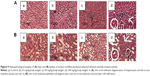
The histopathological analysis of TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC-treated animals is depicted in Figure 9. In the 25 and 50 mg/kg body weight TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticle groups, there was no change in hepatocytes, portal area, or integrated hepatic sinusoidal endothelium when compared with control. In the 100 mg/kg body weight TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticle group, however, histopathological changes were observed in the liver tissue. Hydropic degeneration of hepatocytes (indicated by circle), mononuclear cell infiltration, and spotty necrosis were observed (indicated by arrow). The ALT and AST showed an increase in the 100 mg/kg-treated group. The decreased liver weight and the hepatic necrosis in the physiological examination also indicated liver injury. The liver, the main detoxification tissue, became activated to eliminate side effects in the mass ingested-TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC group. Similar to the observation in liver, the kidney did not show any abnormal pathology changes at 25 and 50 mg/kg TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC. In the 100 mg/kg-treated group, tubular epithelial cell degeneration (indicated by circle), necrosis, and interstitial mononuclear cell infiltration (indicated by arrow) were observed. The increase in BUN levels at a high concentration of TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC nanoparticles was due to the renal dysfunction.25
Conclusion
Acute and subchronic toxicology analyses of HAp-PEG-FA-PAC and TiO2-PEG-FA-PAC confirmed the safety of the developed paclitaxel-loaded, surface modified HAp and TiO2 nanoparticles. Hematological and biochemical parameters showed no significant change when compared with normal animals, except slight elevation of ALP enzymes at high dosage. Acute and subchronic toxicity studies showed that there was no toxic effect in either male or female animals for the study duration. There was no change in the general health of the animals throughout the study. The results indicate that the nanoparticles did not exhibit any toxicity. The toxicological profile of the developed nanoparticles shows that they are safe and can be used as effective therapy against cancer.
Acknowledgments
Professor S Ramasamy, CSIR Emeritus Scientist, acknowledges the financial support given to him to carry out this work under CSIR Emeritus Scientist Scheme number 21(0714)/08/EMR-II dated April 28, 2008. Dr G Devanand Venkatasubbu, CSIR SRF, acknowledges CSIR for giving him SRF. The authors are grateful to Dr (Mrs) V Meenakumari, MA, MPhil, PhD, Professor, Department of English, Arulmigu Palaniandavar Arts College for Women, Palani, India (an autonomous college of Mother Theresa University) for making English corrections in the manuscript.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Sekhon BS, Kamboj SR. Inorganic nanomedicine – part 2. Nanomedicine. 2010;6:612–618. | ||
Park JH, Lee S, Kim JH, Park K, Kim K, Kwon IC. Polymeric nanomedicine for cancer therapy. Prog Polym Sci. 2008;33:113–137. | ||
Cirstoiu-Hapca A, Buchegger F, Bossy L, Kosinski M, Gurny R, Delie F. Nanomedicines for active targeting: physico-chemical characterization of paclitaxel-loaded anti-HER2 immunonanoparticles and in vitro functional studies on target cells. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2009;38:230–237. | ||
Kunzmann A, Andersson B, Thurnherr T, Krug H, Scheynius A, Fadeel B. Toxicology of engineered nanomaterials: focus on biocompatibility, biodistribution and biodegradation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1810(3):361–373. | ||
Devanand Venkatasubbu G, Ramasamy S, Avadhani GS, Palanikumar L, Kumar J. Size-mediated cytotoxicity of nanocrystalline titanium dioxide, pure and zinc-doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in human hepatoma cells. J Nanopart Res. 2012;14:819. | ||
Xie J, Xu C, Kohler N, Hou Y, Sun S. Controlled PEGylation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles for reduced non-specific uptake by macrophage cells. Adv Mater. 2007;19:3163–3166. | ||
Park DL, Bae JW, Park KD, et al. Surface modification of polyurethane using sulfonated PEG grafted polyrotaxane for improved biocompatibility. Macromol Res. 2006;14:73–80. | ||
Kim SY, Cho SH, Lee YM, Chu LY. Biotin-conjugated block copolymeric nanoparticles as tumor-targeted drug delivery systems. Macromol Res. 2007;15:646–655. | ||
Lee D, Singha K, Park J, Jo S, Kim WJ. Enhanced gene delivery by palmitic acid-conjugated low molecular weight polyethylenimine. Macromol Res. 2012;20:244–249. | ||
Mamaghani MY, Pishvaei M, Kaffashi B. Synthesis of latex based antibacterial acrylate polymer/nanosilver via in situ miniemulsion polymerization. Macromol Res. 2011;19:243–249. | ||
Mulder GJ, Dencker L, editors. Pharmaceutical Toxicology. London: Pharmaceutical Press; 2006. | ||
Dandekar P, Dhumal R, Jain R, Tiwari D, Vanage G, Patravale V. Toxicological evaluation of pH-sensitive nanoparticles of curcumin: acute, sub-acute and genotoxicity studies. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48:2073–2089. | ||
Olmedo DG, Tasat DR, Guglielmotti MB, Cabrini RL. Effect of titanium dioxide on the oxidative metabolism of alveolar macrophages: an experimental study in rats. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2005;73(2):142–149. | ||
Syahmi AR, Vijayarathna S, Sasidharan S, et al. Acute oral toxicity and brine shrimp lethality of Elaeis guineensis Jacq., (oil palm leaf) methanol extract. Molecules. 2010;15:8111–8121. | ||
Becker S. Nanotechnology in the marketplace: how the nanotechnology industry views risk. J Nanopart Res. 2013;15:1426. | ||
Devanand Venkatasubbu G, Ramasamy S, Avadhani GS, Ramakrishnan V, Kumar J. Surface modification and paclitaxel drug delivery of folic acid modified polyethylene glycol functionalized hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2013;235:437–442. | ||
Devanand Venkatasubbu G, Ramasamy S, Ramakrishnan V, Kumar J. Folate targeted PEGylated titanium dioxide nanoparticles as a nanocarrier for targeted paclitaxel drug delivery. Adv Powder Technol. 2013; 24:947–954. | ||
Venkatasubbu GD, Ramasamy S, Reddy GP, Kumar J. In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of surface modified paclitaxel attached hydroxyapatite and titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Biomed Microdevices. 2013;15:711–726. | ||
Rauckman EJ, Soiefer AI. Acute toxicology. In: Jacobson-Kram D, Keller KA, editors. Toxicological Testing Handbook: Principles, Applications and Data Interpretation. New York, NY: Informa Healthcare USA, Inc.,; 2006:135–146. | ||
Ansah C, Oppong E, Woode E. Subacute oral toxicity assessment of Alchornea cordifolia (Schumach and Thonn) Müll Arg (Euphorbiaceae) extract in rats. Trop J Pharm Res. 2011;10:587–594. | ||
Taniyama K, Fujiwara H, Kuno T, et al. Acute and subacute toxicity of 10B-paraboronophenylalanine. Pigment Cell Res. 1989;2:291–296. | ||
Limpeanchob N, Tiyaboonchai W, Lamlertthon S, Viyoch J, Jaipan S. Efficacy and toxicity of amphotericin B-chitosan nanoparticles in mice with induced systemic candidiasis. Naresuan University Journal. 2006;14:27–34. | ||
Liu HT, Ma L, Zhao JF, et al. Biochemical toxicity of mice caused by nano-anatase TiO2 particles. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2009;129: 170–180. | ||
Liu H, Ma L, Liu J, Zhao JF, Yan J, Hong F. Toxicity of nano-anatase TiO2 to mice: liver injury, oxidative stress. Toxicol Environ Chem. 2010;92:175–186. | ||
Wang J, Zhou G, Chen C, et al. Acute toxicity and biodistribution of different sized titanium dioxide particles in mice after oral administration. Toxicol Lett. 2007;168:176–185. | ||
International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS). Environmental Health Criteria 24: Titanium. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO); 1982. | ||
Keller KA, Banks C. Multidose general toxicology studies. In: Jacobson-Kram D, Keller KA, editors. Toxicological Testing Handbook: Principles, Applications and Data Interpretation. New York, NY: Informa Healthcare USA, Inc.; 2006:149–181. | ||
Duan Y, Liu J, Ma L, et al. Toxicological characteristics of nanoparticulate anatase titanium dioxide in mice. Biomaterials. 2010;31: 894–899. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.