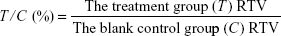Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 9
Design, synthesis, and antitumor evaluation of histone deacetylase inhibitors with L-phenylglycine scaffold
Authors Zhang Y , Li X, Hou J, Huang Y, Xu W
Received 8 August 2015
Accepted for publication 9 September 2015
Published 8 October 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 5553—5567
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S94037
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Wei Duan
Yingjie Zhang,1 Xiaoguang Li,1 Jinning Hou,1 Yongxue Huang,2 Wenfang Xu1
1Department of Medicinal Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, Shandong University, Ji’nan, 2Weifang Bochuang International Biological Medicinal Institute, Weifang, Shandong, People’s Republic of China
Abstract: In our previous research, a novel series of histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors with L-phenylglycine scaffold were designed and synthesized, among which amides D3 and D7 and ureido D18 were far superior to the positive control (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid [SAHA]) in HDAC inhibition, but were only comparable to SAHA in antiproliferation on tumor cell lines. Herein, further structural derivation of lead compounds D3, D7, and D18 was carried out to improve their cellular activities. Most of our newly synthesized compounds exhibited more potent HDAC inhibitory activities than the positive control SAHA, and several derivatives were even better than their parent compounds. However, compared with SAHA and our lead compounds, only secondary amine series compounds exhibited improved antiproliferative activities, likely due to their appropriate topological polar surface area values and cell permeabilities. In a human histiocytic lymphoma (U937) xenograft model, the most potent secondary amine 9d exhibited similar in vivo antitumor activity to that of SAHA.
Keywords: phenylglycine, histone deacetylases, inhibitor, antitumor
Introduction
Research and development of antitumor drugs targeting epigenetic mechanism has become a hot topic in the field of antitumor therapy. Among the epigenetics-related enzymes, histone deacetylases (HDACs) are drawing more and more attention from the academic community and the pharmaceutical industry because aberrant deacetylation of nucleosomal histone and other nonhistone substrates is closely related to tumorigenesis and because many HDAC inhibitors used alone or combined with other antitumor drugs demonstrate promising results in preclinical research and clinical trials.1–3
HDAC inhibitors could induce different phenotypes in various transformed cells, including cell-cycle arrest, mitotic cell death and senescence, autophagic cell death, activation of the extrinsic and/or intrinsic apoptotic pathways, DNA damage and oxidative stress, antiangiogenesis, disruption of chaperone function, etc.4,5
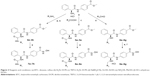
Currently, four HDAC inhibitors, including suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), FK228, PXD101, and LBH589 were approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, and one HDAC inhibitor CS005 was approved by the China Food and Drug Administration for cancer treatment (Figure 1A). Besides, approximately 20 small molecular HDAC inhibitors are in different phases of clinical trials (Figure 1B). It is worth noting that from the end of 2014 to the beginning of 2015, there were three HDAC inhibitors consecutively approved, which indicates the rapid development in the research field of HDACs and HDAC inhibitors.
  | Figure 1 The structures of five approved drugs (A) and HDAC inhibitors in clinical trials (B). |
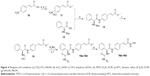
In order to find potent HDAC inhibitors, a virtual screening approach was performed in our lab, and we discovered a hit compound 1 (Figure 2).6 Structural modification and derivation of this hit compound generated a novel series of phenylglycine-based hydroxamic acids with potent HDAC inhibitory activity and antitumor potency.7,8 The general structure of these phenylglycine-based hydroxamic acids are represented in structure 2 (Figure 2). Although most of our previously discovered phenylglycine-based HDAC inhibitors exhibited more potent HDAC inhibitory activities than the approved drug SAHA, their in vitro antiproliferative potency was just similar to that of SAHA.8 Therefore, based on our previous lead compounds D18, D3, and D7,8 the main purpose of this work was to find HDAC inhibitors with more satisfying antiproliferative potency. Our compound design strategy mainly focused on the following three aspects (Figure 2).
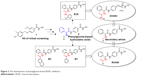  | Figure 2 The development of phenylglycine-based HDAC inhibitors. |
First, in our previous work, only two ureido analogs were synthesized and one of them, D18 exhibited approximately 20-fold more potent HDAC inhibition than the approved drug SAHA.8 In this work, comprehensive structure–activity relationship study of D18 was performed to develop ureido analogs with improved activity.
Second, the naphthyl group of D3 and phenyl group of D7 were replaced with several aromatic heterocycles to fine-tune their partition coefficient. We hope that introduction of nitrogen atoms could improve the water solubility and antiproliferative potency of D3 and D17.
Finally, considering that the antiproliferative potency of HDAC inhibitor is largely determined by their cell permeability, which is closely related to the topological polar surface area (tPSA) value,9 a series of secondary amine analogs were designed and synthesized, which should have preferable tPSA values due to their fewer polar atoms than the ureido and amide compounds.
Experimental materials and methods
Unless specified otherwise, all starting materials, reagents, and solvents were commercially available. All reactions except those in aqueous media were carried out by standard techniques for the exclusion of moisture. All reactions were monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) on 0.25 mm silica gel plates (60GF-254) and visualized with ultraviolet light, ferric chloride, or iodine vapor. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were determined using Bruker DRX or Varian INOVA spectrometers, chemical shift (δ) in parts per million and coupling constant (J) in hertz, using tetramethylsilane as an internal standard. Measurements were made in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-d6 solutions. Electrospray ionization–mass spectroscopy (ESI–MS) was carried out using an API 4000 spectrometer (MDS SCIEX, Concord, ON, Canada). High-resolution mass spectroscopy (HRMS) was conducted by Shandong Analysis and Test Center (Jinan, Shandong, People’s Republic of China). Silica gel was used for column chromatography purification. Melting points (Mps) were determined using an electrothermal Mp apparatus and were uncorrected.
Chemistry
The ureido compounds 7a–7k, amide compounds 8a–8e, and secondary amine compounds 9a–9g were synthesized according to the procedures described in Figure 3. The starting material, compound 3, was obtained according to our methods published in our previous study.8 Different kinds of aromatic amines were treated with triphosgene [bis(trichloromethyl) carbonate] to get corresponding isocyanates, and subsequently, the reaction of obtained isocyanates with compound 3 in the presence of Et3N afforded intermediates 4a–4k, which were treated with NH2OK in methanol to get target compounds 7a–7k. The starting material 3 was condensed with carboxylic acids or aldehydes to get intermediates 5a–5e and 6a–6g, respectively, which were finally transformed into target hydroxamate compounds 8a–8e and 9a–9g.
Target compounds 16a–16d were synthesized using the procedures described in Figure 4. Methyl ester protection and subsequent reduction of compound 10 provided intermediate 11. Condensation of 11 with Boc-phenylglycine 12, N-deprotection, followed by reaction with isocyanates led to compounds 15a–15d. The ester groups of 15a–15d were treated with NH2OK to get target compounds 16a–16b.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate hydrochloride (3)
Compound 3 was synthesized according to the methods described in our previous study.8
Methyl (S)-4-(2-(3-(3-methoxyphenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (4a)
At 0°C, 3-methoxyaniline (1.23 g, 10 mmol) was added to a solution of triphosgene (1.50 g, 5.0 mmol) in dioxane (50 mL). The reaction solution was stirred at 110°C for 6 hours, the solvent was then evaporated to give a crude residue, which was used for the following reaction without further purification. The residue was redissolved in CH2Cl2 (100 mL), and then, compound 3 (1.60 g, 5.0 mmol) and Et3N (0.61 g, 6.0 mmol) were added. After stirring the mixture at room temperature for 5 hours, CH2Cl2 was evaporated, with the residues being taken up in EtOAc (50 mL). The EtOAc solution was washed with saturated aqueous citric acid (3×20 mL), saturated aqueous NaHCO3 (3×20 mL), and brine (3×20 mL); dried over MgSO4; and concentrated under vacuum. The desired compound 4a was obtained as a white powder by crystallization from EtOAc (1.08 g, 50%). 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.76 (s, 1H), 8.78 (s, 1H), 7.92 (d, J =9.0 Hz, 2H), 7.73 (d, J =9.0 Hz, 2H), 7.30–7.52 (m, 5H), 7.09–7.15 (m, 3H), 6.82 (dd, J =8.1 Hz, 0.9 Hz, 1H), 6.49 (dd, J =7.8 Hz, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 5.56 (d, J =7.5 Hz, 1H), 3.81 (s, 3H), 3.68 (s, 3H). ESI–MS m/z: 434.2 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-(3-(3-chlorophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (4b)
Using the similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 3 and 3-chloroaniline gave 4b, a white powder (44% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 438.1 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-(3-(2-chlorophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (4c)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 3 and 2-chloroaniline gave 4c, a white powder (31% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 439.2 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-(3-(2-fluorophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (4d)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 3 and 2-fluoroaniline gave 4d, a white powder (36% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 422.2 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-(3-(2-bromophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (4e)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 3 and 2-bromoaniline gave 4e, a white powder (43% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 482.0 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-phenyl-2-(3-(o-tolyl)ureido)acetamido)benzoate (4f)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 3 and m-toluidine gave 4f, a white powder (45% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 418.2 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-phenyl-2-(3-(p-tolyl)ureido)acetamido)benzoate (4g)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 3 and p-toluidine gave 4g, a white powder (30% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 418.5 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (4h)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 3 and 2,4-dichloroaniline gave 4h, a white powder (46% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 472.1 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-(3-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (4i)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 3 and 3,5-dimethylaniline gave 4i, a white powder (39% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 432.2 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-(3-(2,6-diethylphenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (4j)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 3 and 2,6-diethylaniline gave 4j, a white powder (35% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 460.2 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-(3-(naphthalen-1-yl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (4k)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 3 and naphthalen-1-amine gave 4k, a white powder (57% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 454.3 [M + H]+.
(S)-N-Hydroxy-4-(2-(3-(3-methoxyphenyl) ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzamide (7a)
To a solution of compound 4a (0.87 g, 2.0 mmol) in 10 mL of anhydrous methanol, a solution of NH2OK (0.14 g, 6 mmol) in 3.5 mL of anhydrous methanol was added. The mixture was stirred for 1 hour and the solvent was evaporated under vacuum. The residues were acidified with 2 N HCl until pH 3–4, then extracted with EtOAc (3×10 mL). The organic layers were combined, washed with brine (3×10 mL), dried over MgSO4, and evaporated, with the residues being recrystallized with EtOH/EtOAc to give compound 7a, a white powder (0.57 g, 66% yield). Mp: 240°C–243°C. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.07 (s, 1H), 10.66 (s, 1H), 8.80 (s, 1H), 7.71 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.64 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.50 (d, J =7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.40 (t, J =7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.31–7.34 (m, 1H), 7.10–7.15 (m, 3H), 6.81–6.83 (m, 1H), 6.48 (dd, J =7.8 Hz, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 5.55 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H), 3.70 (s, 3H). HRMS (atmospheric pressure electrospray ionization [AP–ESI]) m/z: calcd for C23H23N4O5 [M + H]+, 435.1668; found, 435.1653.
(S)-4-(2-(3-(3-Chlorophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)-N-hydroxybenzamide (7b)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 4b gave 7b, a white powder (70% yield). Mp: 226°C–228°C. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.11 (s, 1H), 10.65 (s, 1H), 8.95 (s, 1H), 8.28 (s, 1H), 8.15 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.05 (dd, J =7.8 Hz, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.65 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.56 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.53 (d, J =7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.41 (t, J =7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.34 (t, J =7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.25–7.28 (m, 1H), 6.89–6.92 (m, 1H), 5.57 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C22H20ClN4O4 [M + H]+, 439.1173; found, 439.1170.
(S)-4-(2-(3-(2-Chlorophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)-N-hydroxybenzamide (7c)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 4c gave 7c, a white powder (50% yield). Mp: 228°C–231°C. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.12 (s, 1H), 10.66 (s, 1H), 8.95 (s, 1H), 8.45 (d, J =4.2 Hz, 1H), 8.14 (dd, J =8.4 Hz, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 8.09 (dd, J =7.8 Hz, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.92 (d, J =9.0 Hz, 1H), 7.74 (d, J =9.0 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.65 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.52–7.53 (m, 2H), 7.40–7.43 (m, 3H), 7.33–7.36 (m, 1H), 7.22 (td, J =7.8 Hz, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 6.96 (td, J =7.8 Hz, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 5.57 (d, J =7.2 Hz). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C22H20ClN4O4 [M + H]+, 439.1173; found, 439.1182.
(S)-4-(2-(3-(2-Fluorophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)-N-hydroxybenzamide (7d)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 4d gave 7d, a white powder (57% yield). Mp: 238°C–240°C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.61 (s, 1H), 8.77 (s, 1H), 8.11 (td, J =8.4 Hz, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.83–7.85 (m, 1H), 7.68 (d, J =8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.58 (d, J =8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.29–7.53 (m, 5H), 6.89–7.23 (m, 3H), 5.57 (d, J =8.1 Hz, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C22H20FN4O4 [M + H]+, 423.1469; found, 423.1466.
(S)-4-(2-(3-(2-Bromophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)-N-hydroxybenzamide (7e)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 4e gave 7e, a white powder (54% yield). Mp: 250°C–252°C. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.11 (s, 1H), 10.66 (s, 1H), 9.90 (s, 1H), 8.92 (s, 1H), 7.64–7.72 (m, 5H), 7.50 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.40 (t, J =7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.13–7.36 (m, 4H), 6.96 (dd, J =7.8 Hz, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 5.55 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C22H20BrN4O4 [M + H]+, 483.0668; found, 483.0624.
(S)-N-Hydroxy-4-(2-phenyl-2-(3-(o-tolyl)ureido)acetamido)benzamide (7f)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 4f gave 7f, a white powder (56% yield). Mp: 232°C–233°C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.11 (s, 1H), 10.66 (s, 1H), 8.93 (s, 1H), 8.03 (s, 1H), 7.83–7.90 (m, 1H), 7.63–7.73 (m, 5H), 7.30–7.53 (m, 5H), 6.84–7.13 (m, 3H), 5.58 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H), 2.18 (s, 3H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C23H23N4O4 [M + H]+, 419.1719; found, 419.1725.
(S)-N-Hydroxy-4-(2-phenyl-2-(3-(p-tolyl)ureido)acetamido)benzamide (7g)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 4g gave 7g, a white powder (50% yield). Mp: 208°C–211°C. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.11 (s, 1H), 10.65 (s, 1H), 8.95 (s, 1H), 8.66 (s, 1H), 7.71 (d, J =9.0 Hz, 2H), 7.64 (d, J =9.0 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.40 (t, J =7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.32 (t, J =7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.25 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.08 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.03 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 2H), 5.56 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H), 2.21 (s, 3H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C23H23N4O4 [M + H]+, 419.1719; found, 419.1723.
(S)-4-(2-(3-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)-N-hydroxybenzamide (7h)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 4h gave 7h, a white powder (67% yield). Mp: 213°C–215°C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.09 (s, 1H), 10.65 (s, 1H), 8.93 (s, 1H), 8.54 (s, 1H), 8.12–8.19 (m, 2H), 7.29–7.73 (m, 11H), 5.57 (d, J =7.5 Hz, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C22H19Cl2N4O4 [M + H]+, 473.0783; found, 473.0784.
(S)-4-(2-(3-(3,5-Dimethylphenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)-N-hydroxybenzamide (7i)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 4i gave 7i, a white powder (65% yield). Mp: 276°C–278°C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.54 (s, 1H), 8.91 (s, 1H), 7.86 (s, 1H), 7.21–7.68 (m, 10H), 7.02 (d, J =8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.47–6.53 (m, 1H), 5.50–5.54 (m, 1H), 2.19 (s, 6H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C24H25N4O4 [M + H]+, 433.1876; found, 433.1878.
(S)-4-(2-(3-(2,6-Diethylphenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)-N-hydroxybenzamide (7j)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 4j gave 7j, a white powder (% yield). Mp: 230°C–232°C. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.12 (s, 1H), 10.64 (s, 1H), 8.95 (s, 1H), 7.78 (s, 1H), 7.71 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.65 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.48–7.54 (m, 2H), 7.40 (t, J =7.2 Hz, 2H), 3.14 (t, J =7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.05–7.11 (m, 4H), 5.57 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 1H), 2.52 (q, J =9.6 Hz, 4H), 1.06 (t, J =9.6 Hz, 6H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C26H29N4O4 [M + H]+, 461.2189; found, 461.2194.
(S)-N-Hydroxy-4-(2-(3-(naphthalen-1-yl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzamide (7k)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 4k gave 7k, a white powder (50% yield). Mp: 218°C–221°C. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.14 (s, 1H), 10.78 (s, 1H), 8.99 (s, 1H), 8.96 (s, 1H), 8.20 (d, J =9.0 Hz, 1H), 8.04 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.89 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.82 (d, J =7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.68–7.73 (m, 4H), 7.49–7.59 (m, 5H), 7.32–7.43 (m, 4H), 5.66 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C26H23N4O4 [M + H]+, 455.1719; found, 455.1730.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-phenyl-2-(quinoline-6-carboxamido)acetamido)benzoate (5a)
At room temperature, to a solution of quinoline-6-carboxylic acid (0.17 g, 1.0 mmol) in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (20 mL), Et3N (0.11 g, 1.1 mmol) followed by 2-(1H-benzotriazole-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate (0.35 g, 1.1 mmol) was added. After 15 minutes, compound 3 (0.32 g, 1.0 mmol) and Et3N (0.11 g, 1.1 mmol) were added. Stirring was continued until compound 3 disappeared by TLC, then CH2Cl2 was evaporated with the residue being taken up in EtOAc (50 mL). The EtOAc solution was washed with saturated aqueous citric acid (3×20 mL), saturated aqueous NaHCO3 (3×20 mL), and brine (3×20 mL); dried over MgSO4; and evaporated with the residue being purified by flash column chromatography (petroleum/EtOAc 2:1) to give compound 5a, a white powder (0.23 g, 52% yield). 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.75 (s, 1H), 9.30 (d, J =7.2 Hz, 1H), 9.00 (dd, J =4.2, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 8.66 (d, J =1.8 Hz, 1H), 8.49 (d, J =7.2 Hz, 1H), 8.23 (dd, J =9.0, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 8.08 (d, J =9.0 Hz, 1H), 7.93 (d, J =8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.77 (d, J =8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.60–7.64 (m, 3H), 7.34–7.46 (m, 3H), 5.90 (d, J =7.2 Hz, 1H), 3.82 (s, 3H). ESI–MS m/z: 440.1 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-phenyl-2-(quinoxaline-6-carboxamido)acetamido)benzoate (5b)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 5a, compound 3 and quinoxaline-6-carboxylic acid gave 5b, a white powder (41% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 441.1 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-(1H-indole-6-carboxamido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (5c)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 5a, compound 3 and 1H-indole-6-carboxylic acid gave 5c, a white powder (37% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 428.7 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-(1H-indole-2-carboxamido)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (5d)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 5a, compound 3 and 1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid gave 5d, a white powder (53% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 428.7 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-phenyl-2-(pyrazine-2-carboxamido)acetamido)benzoate (5e)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 5a, compound 3 and pyrazine-2-carboxylic acid gave 5e, a white powder (76% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 391.0 [M + H]+.
(S)-N-(2-((4-(Hydroxycarbamoyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl)quinoline-6-carboxamide (8a)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 5a gave 8a, a white powder (64% yield). Mp: 222°C–225°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.13 (s, 1H), 10.67–10.80 (m, 2H), 9.39 (s, 1H), 9.10 (s, 1H), 8.67–8.74 (m, 2H), 8.15–8.33 (m, 2H), 7.37–7.90 (m, 10H), 5.93 (s, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C25H21N4O4 [M + H]+, 441.1563; found, 441.1569.
(S)-N-(2-((4-(Hydroxycarbamoyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl)quinoxaline-6-carboxamide (8b)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 5b gave 8b, a white powder (57% yield). Mp: 180°C–182°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.12 (s, 1H), 10.65 (s, 1H), 9.51–9.57 (m, 1H), 9.04–9.05 (m, 2H), 8.72–8.75 (m, 1H), 8.17–8.32 (m, 2H), 7.37–7.74 (m, 10H), 5.91 (d, J =7.2 Hz, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C24H20N5O4 [M + H]+, 442.1515; found, 442.1511.
(S)-N-(2-((4-(Hydroxycarbamoyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl)-1H-indole-6-carboxamide (8c)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 5c gave 8c, a white powder (47% yield). Mp: 146°C–148°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.34 (s, 1H), 11.17 (s, 1H), 10.56 (s, 1H), 8.78 (d, J =7.6 Hz, 1H), 8.27 (s, 1H), 7.40–7.71 (m, 13H), 6.54 (s, 1H), 5.88 (d, J =7.6 Hz, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C24H21N4O4 [M + H]+, 429.1563; found, 429.1573.
(S)-N-(2-((4-(Hydroxycarbamoyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxamide (8d)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 5d gave 8d, a white powder (59% yield). Mp: 231°C–233°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.74 (s, 1H), 11.18 (s, 1H), 10.93 (s, 1H), 9.14 (d, J =7.6 Hz, 1H), 8.97 (s, 1H), 7.61–7.74 (m, 7H), 7.05–7.45 (m, 7H), 5.96 (d, J =7.6 Hz, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C24H21N4O4 [M + H]+, 429.1563; found, 429.1566.
(S)-N-(2-((4-(Hydroxycarbamoyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl)pyrazine-2-carboxamide (8e)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 5e gave 8e, a white powder (63% yield). Mp: 150°C–152°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.15 (s, 1H), 10.77–10.81 (m, 2H), 9.21 (d, J =1.2 Hz, 1H), 9.08 (d, J =7.6 Hz, 1H), 8.94 (d, J =2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.81 (dd, J =2.4, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.73 (t, J =8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.67 (d, J =8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.35–7.59 (m, 5H), 5.89 (d, J =7.6 Hz, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C20H18N5O4 [M + H]+, 392.1359; found, 392.1375.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-((2-methoxybenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (6a)
To a solution of compound 3 (1.60 g, 5.0 mmol), Et3N (0.50 g, 5.0 mmol), and 2-methoxybenzaldehyde (0.81 g, 24.0 mmol) in EtOH (50 mL), acetic acid and sodium cyanoborohydride (1.98 g, 24.0 mmol) were added dropwise. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 hours, and the solvent was evaporated under vacuum. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography (petroleum ether/EtOAc 3:1) to give compound 6a (1.13 g, 56% yield), a white powder. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.40 (s, 1H), 7.90 (d, J =6.9 Hz, 2H), 7.75 (d, J =6.9 Hz, 2H), 7.20–7.50 (m, 7H), 6.90–6.96 (m, 2H), 4.40 (s, 1H), 3.81 (s, 3H), 3.73 (s, 3H), 3.68 (s, 2H), 3.06 (s, 1H). ESI–MS m/z: 405.5 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-((2-chlorobenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (6b)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 6a, reaction between compound 3 and 2-chlorobenzaldehyde gave 6b, a white powder (39% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 409.5 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-((2-bromobenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (6c)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 6a, reaction between compound 3 and 2-bromobenzaldehyde gave 6c, a white powder (40% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 453.0 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-((3-methoxybenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (6d)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 6a, reaction between compound 3 and 3-methoxybenzaldehyde gave 6d, a white powder (57% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 405.5 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-((4-chlorobenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (6e)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 6a, reaction between compound 3 and 4-chlorobenzaldehyde gave 6e as a light yellow oil (48% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 409.5 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-((4-hydroxybenzyl)amino)- 2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (6f)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 6a, reaction between compound 3 and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde gave 6f as a light yellow oil (64% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 391.2 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S)-4-(2-((4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)benzoate (6g)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 6a, reaction between compound 3 and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde gave 6g as a light yellow oil (65% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 421.2 [M + H]+.
(S)-N-Hydroxy-4-(2-((2-methoxybenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)benzamide (9a)
To a solution of compound 6a (0.81 g, 2.0 mmol) in 10 mL of anhydrous methanol, a solution of NH2OK (0.14 g, 6 mmol) in 3.5 mL of anhydrous methanol was added. The mixture was stirred for 1 hour and the solvent was evaporated under vacuum. The pH value of residues was adjusted with 2 N HCl and 1 N NaOH until the maximum precipitates were generated, which were then extracted with EtOAc (3×20 mL). The organic layers were combined, washed with brine (3×10 mL), dried over MgSO4, and concentrated, with the residues being stirred with EtOAc saturated by dry HCl (10 mL) for 20 minutes. The precipitates were filtered, with the filter being washed with EtOAc to get compound 9a (0.57 g, 64% yield), a white powder. Mp: 160°C–162°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.40 (s, 1H), 9.87–9.96 (m, 2H), 7.47–7.74 (m, 6H), 7.30–7.46 (m, 5H), 6.97–7.07 (m, 2H), 5.17 (t, J =6.0 Hz, 1H), 3.99–4.14 (m, 2H), 3.74 (s, 3H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C23H24N3O4 [M + H]+, 406.1767; found, 406.1742.
(S)-4-(2-((2-Chlorobenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)-N-hydroxybenzamide (9b)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 6b gave 9b, a white powder (70% yield). Mp: 200°C–202°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.39 (s, 1H), 10.22–10.36 (m, 2H), 7.65–7.81 (m, 7H), 7.42–7.54 (m, 6H), 5.32 (s, 1H), 4.23 (s, 2H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C22H21ClN3O3 [M + H]+, 410.1271; found, 410.1272.
(S)-4-(2-((2-Bromobenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)-N-hydroxybenzamide (9c)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 6c gave 9c, a white powder (54% yield). Mp: 220°C–222°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.39 (s, 1H), 11.25 (s, 1H), 10.22–10.39 (m, 2H), 8.93 (d, J =4.0 Hz, 1H), 7.66–7.72 (m, 8H), 7.47–7.50 (m, 5H), 5.32 (s, 1H), 4.24 (s, 2H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C22H21BrN3O3 [M + H]+, 454.0766; found, 454.0756.
(S)-N-Hydroxy-4-(2-((3-methoxybenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)benzamide (9d)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 6d gave 9d, a white powder (65% yield). Mp: 184°C–189°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.35 (s, 1H), 10.16–10.33 (m, 2H), 7.50–7.74 (m, 6H), 7.47–7.48 (m, 3H), 7.31–7.32 (m, 1H), 6.96–7.15 (m, 3H), 5.20 (t, J =6.0 Hz, 1H), 4.00–4.10 (m, 2H), 3.76 (s, 3H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C23H24N3O4 [M + H]+, 406.1767; found, 406.1743.
(S)-4-(2-((4-Chlorobenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)-N-hydroxybenzamide (9e)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 6e gave 9e, a white powder (58% yield). Mp: 193°C–195°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.47 (s, 1H), 10.22–10.37 (m, 2H), 7.66–7.75 (m, 6H), 7.46–7.55 (m, 7H), 5.27 (s, 1H), 4.02–4.12 (m, 2H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C22H21ClN3O3 [M + H]+, 410.1271; found, 410.1283.
(S)-N-Hydroxy-4-(2-((4-hydroxybenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)benzamide (9f)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 6f gave 9f, a white powder (46% yield). Mp: 240°C–242°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.35 (s, 1H), 10.30 (s, 1H), 10.00–10.08 (m, 2H), 7.30–7.91 (m, 6H), 7.44–7.49 (m, 3H), 7.27 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 2H), 6.81 (d, J =10.0 Hz, 2H), 5.16 (t, J =6.0 Hz, 1H), 3.89–3.97 (m, 2H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C22H22N3O4 [M + H]+, 392.1610; found, 392.1607.
(S)-N-Hydroxy-4-(2-((4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)benzamide (9g)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 6g gave 9g, a white powder (42% yield). Mp: 168°C–170°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.22 (s, 1H), 9.99–10.09 (m, 2H), 7.63–7.74 (m, 6H), 7.45–7.52 (m, 3H), 7.10 (s, 1H), 6.80 (s, 2H), 5.08 (t, J =6.0 Hz, 1H), 3.90–3.99 (m, 2H), 3.76 (s, 3H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C23H24N3O5 [M + H]+, 422.1716; found, 422.1718.
Methyl (E)-3-(4-aminophenyl)acrylate hydrochloride (11)
Compound 10 (9.66 g, 50.0 mmol) was dissolved in 200 mL of methanol; then acetyl chloride (11.78 g, 150.0 mmol) was added dropwise at 0°C; the mixed solution was refluxed at 70°C for 6 hours. The solvent was evaporated under vacuum to get crude methyl (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate, which was used for the following reaction without further purification. To a solution of methyl (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate (0.21 g, 1.0 mmol) in 30 mL of ethanol, stannous chloride dehydrate (1.13 g, 5.0 mmol) was added, and the mixture was refluxed at 75°C for 4 hours. The solvent was evaporated under vacuum followed by addition of 30 mL of distilled water, then saturated NaHCO3 was added until no more gas was generated. The mixture was extracted with EtOAc (3×20 mL). The organic layers were combined, washed with brine (3×10 mL), dried over MgSO4, and concentrated, with the residues being stirred with EtOAc saturated by dry HCl (10 mL) for 20 minutes. The precipitates were filtered, with the filter being washed with EtOAc to get compound 11 (0.19 g, 89% yield), a white powder. ESI–MS m/z: 178.0 [M + H]+.
(S)-2-((tert-Butoxycarbonyl)amino)-2-phenylacetic acid (12)
Compound 12 was synthesized according to the methods described in our previous study.5
Methyl (S, E)-3-(4-(2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-2-phenylacetamido)phenyl)acrylate (13)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 5a, reaction between compound 12 and 11 gave 13, a white powder (76% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 411.2 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S, E)-3-(4-(2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)phenyl)acrylate (14)
To a solution of compound 13 (0.41 g, 1.0 mmol) in dry EtOAc (15 mL), a solution of EtOAc (15 mL) saturated by dry HCl was added. The resulting solution was continuously stirred (for 5 hours) at room temperature until the precipitates appeared. The suspension was filtered, with the filter being washed with ether to give compound 14 (0.30 g, 86% yield), a white powder. ESI–MS m/z: 311.2 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S, E)-3-(4-(2-(3-(2-chlorophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)phenyl)acrylate (15a)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 14 and 2-chloroaniline gave 15a, a white powder (46% yield). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.73 (s, 1H), 8.46 (s, 1H), 8.10–8.14 (m, 2H), 7.66–7.68 (m, 4H), 7.59 (d, J =16.0 Hz, 1H), 6.80–7.55 (m, 8H), 6.53 (d, J =16.0 Hz, 1H), 5.59 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.71 (s, 3H). ESI–MS m/z: 464.1 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S, E)-3-(4-(2-(3-(2-fluorophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)phenyl)acrylate (15b)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 14 and 2-fluoroaniline gave 15b, a white powder (49% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 448.2 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S, E)-3-(4-(2-(3-(2-bromophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)phenyl)acrylate (15c)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 14 and 2-bromoaniline gave 15c, a white powder (51% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 408.0 [M + H]+.
Methyl (S, E)-3-(4-(2-phenyl-2-(3-(o-tolyl)ureido)acetamido)phenyl)acrylate (15d)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 4a, reaction between compound 14 and o-toluidine gave 15d, a white powder (45% yield). ESI–MS m/z: 444.2 [M + H]+.
(S, E)-3-(4-(2-(3-(2-Chlorophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)phenyl)-N-hydroxyacrylamide (16a)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 15a gave 16a, a white powder (66% yield). Mp: 184°C–186°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.78 (s, 1H), 10.73 (s, 1H), 10.10 (s, 1H), 8.19 (s, 1H), 6.95–8.14 (m, 15H), 6.53 (d, J =16.0 Hz, 1H), 5.60 (d, J =5.2 Hz, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C24H22ClN4O4 [M + H]+, 465.1330; found, 465.1334.
(S, E)-3-(4-(2-(3-(2-Fluorophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)phenyl)-N-hydroxyacrylamide (16b)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 15b gave 16b, a white powder (60% yield). Mp: 226°C–228°C. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.72 (s, 1H), 10.65 (s, 1H), 9.01 (s, 1H), 8.71 (s, 1H), 8.10 (td, J =8.4 Hz, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.73 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.64 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.50–7.52 (m, 4H), 7.32–7.42 (m, 4H), 7.17–7.20 (m, 1H), 7.07 (t, J =7.2 Hz, 1H), 6.91–6.95 (m, 1H), 6.36 (d, J =16.2 Hz, 1H), 5.58 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C24H22FN4O4 [M + H]+, 449.1625; found, 449.1620.
(S, E)-3-(4-(2-(3-(2-Bromophenyl)ureido)-2-phenylacetamido)phenyl)-N-hydroxyacrylamide (16c)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 15c gave 16c, a white powder (59% yield). Mp: 185°C–187°C. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.71 (s, 1H), 10.62 (s, 1H), 9.01 (s, 1H), 8.28 (s, 1H), 8.15 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.04 (dd, J =8.4 Hz, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.65 (d, J =8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.56 (dd, J =7.8 Hz, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.51–7.53 (m, 4H), 7.25–7.43 (m, 5H), 6.90 (td, J =7.2 Hz, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 6.35 (d, J =16.2 Hz, 1H), 5.57 (d, J =7.2 Hz, 1H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C24H22BrN4O4 [M + H]+, 509.0824; found, 509.0820.
(S, E)-N-Hydroxy-3-(4-(2-phenyl-2-(3-(o-tolyl)ureido)acetamido)phenyl)acrylamide (16d)
Using a similar synthetic method as for 7a, compound 15d gave 16d, a white powder (47% yield). Mp: 194°C–196°C. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.74 (s, 1H), 10.68 (s, 1H), 9.02 (s, 1H), 8.76 (s, 1H), 8.06–8.08 (m, 1H), 7.85 (d, J =7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.65–7.70 (m, 3H), 7.50–7.54 (m, 3H), 7.31–7.42 (m, 4H), 7.06–7.12 (m, 2H), 6.85–6.87 (m, 1H), 6.37 (d, J =16.2 Hz, 1H), 5.57 (d, J =7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.20 (s, 3H). HRMS (AP–ESI) m/z: calcd for C25H25N4O4 [M + H]+, 445.1876; found, 445.1866.
Biological materials and methods
In vitro HDAC inhibition fluorescence assay
In vitro HDAC inhibition assays were conducted as previously described.8,10–12 In brief, 10 μL of enzyme solution (HeLa cell nuclear extract) was mixed with different concentrations of tested compound (50 μL). The mixture was incubated at 37°C for 10 minutes, then substrate Boc-Lys (acetyl)-AMC (40 μL) was added. After incubation at 37°C for 30 minutes, the reaction was stopped by the addition of 100 μL of developer containing trypsin and Trichostatin A (a very potent HDAC inhibitor used here to completely stop the deacetylation reaction). Fluorescence intensity was measured after 20 minutes using a microplate reader at excitation and emission wavelengths of 390 and 460 nm, respectively. The inhibition ratios were calculated from the fluorescence intensity readings of inhibited wells relative to those of control wells, and the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values were determined using a regression analysis of the concentration/inhibition ratio.
In vitro antiproliferative assay
In vitro antiproliferative assays were determined by the MTT (3-[4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl]-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide) method as previously described.8,10–12 Briefly, human histiocytic lymphoma U937, human multiple myeloma U266, human acute myelogenous leukemia KG-1, human cervical cancer HeLa, human hepatoma H7402, and human colon carcinoma HCT116 cells were individually maintained in Roswell Park Memorial Institute-1640 (RPMI-1640) medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum at 37°C in 5% CO2 humidified incubator. Cells were passaged the day before dosing into a 96-well cell plate and allowed to grow for a minimum of 4 hours prior to addition of compounds. After addition of compounds, the plates were incubated for an additional 48 hours, and then 0.5% MTT solution was added to each well. After further incubation for 4 hours, the formazan formed from MTT was extracted by adding 200 μL of DMSO for 15 minutes. Absorbance was then determined using an ELISA reader at 570 nm. The inhibition ratios were calculated from the optical density readings of inhibited wells relative to those of control wells, and the IC50 values were calculated using a regression analysis of the concentration/inhibition ratio.
In vivo antitumor assay in U937 xenograft model
In vivo human tumor xenograft models were established as previously described.8,10–12 In brief, tumor cell line (U937) were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and maintained in a 5% CO2 humidified incubator at 37°C. For in vivo antitumor assays, the aforementioned cells were subcutaneously inoculated in the right flanks of male athymic nude mice (BALB/c-nu, 5–6 weeks old, Beijing HFK Bioscience Co., Ltd., People’s Republic of China). Approximately 10 days after injection, tumors were palpable (~100 mm3) and the mice were randomized into treatment and control groups (six mice per group). The treatment groups were dosed orally with either 9d (100 mg/kg once a day) or SAHA (100 mg/kg once a day) for 12 days, and the blank control group received an equal volume of phosphate-buffered saline solution. During treatment, subcutaneous tumors were measured using a vernier caliper every 3 days, and body weight was regularly monitored. Tumor volumes (V) were estimated using the equation, V = ab2/2, where a and b denote the longest and shortest diameter, respectively. Relative increment ratio (T/C) was calculated according to the following formula:
|
RTV, namely relative tumor volume = Vt/V0 (Vt: the tumor volume measured each time during the treatment; V0: the tumor volume measured at the time of randomization).
After treatment, mice were sacrificed and dissected to weigh the tumor tissues and to examine the internal organ injury by macroscopic analysis. All the obtained data were used to evaluate the antitumor potency and toxicity of compounds. Data were analyzed by Student’s two-tailed t-test. A P-level <0.05 was considered statistically significant. All experiments involving laboratory animals were performed with the approval of the Shandong University Laboratory Animal Center ethics committee.
Results and discussion
In vitro HDAC inhibitory activities of all synthesized compounds were evaluated using HeLa cell nuclear extracts as enzyme source.10–12 Results listed in Table 1 show that all ureido analogs 7a–7k except 7j exhibited more potent HDAC inhibitory activities than SAHA. Generally, ortho and para substitutions were well tolerated. For example, ortho-substituted 7c, 7e, 7f and para-substituted 7g were better than their lead compound D18, and the most potent analog 7h was ortho and para disubstituted. Compounds with larger R1 groups, such as 7j and 7k exhibited decreased potency. N-Hydroxycinnamamide is a very popular fragment in HDAC inhibitor design, which is contained in the structures of approved drug LBH-589, PXD101, and clinical compound SB-939 (Figure 1). Based on the N-hydroxycinnamamide fragment, we previously developed a series of HDAC inhibitors with remarkable in vitro and in vivo antitumor activities.10 However, introduction of N-hydroxycinnamamide fragment was detrimental to our compounds described here. N-Hydroxycinnamamide-based compounds 16a–16d exhibited much lesser rates of HDAC inhibition compared with their N-hydroxybenzamide analogs 7c–7f (Table 1).
  | Table 1 HDAC inhibitory activities of ureido series compounds |
HDAC inhibitory activities of amide series compounds (listed in Table 2) demonstrated that replacing the naphthyl group of D3 and the phenyl group of D7 with aromatic heterocycles was detrimental to their HDAC inhibitory activities.
  | Table 2 HDAC inhibitory activities of amide series compounds |
Encouraged by their potent HDAC inhibitory activities, several representative ureido compounds 7a, 7b, 7c, 7e, 7g, 7h, and 7i were selected to test their effects on the viability of U937 cell line. Considering the fact that amide compounds 8a–8d might have better water solubility than their parent compound D3, their antiproliferative potency were also evaluated even though their HDAC inhibitory activities were not satisfying. The results listed in Table 3 showed that all the tested ureido compounds, including 7c, 7e, 7g, and 7h, which possessed superior HDAC inhibition to their parent compound D18, exhibited less potent antiproliferative activities than that of D18. With respect to amide series compounds 8a–8d, introduction of aromatic heterocycles resulted in decreased antiproliferative potency relative to their parent compound D3, which was in line with their HDAC inhibitory activities (Table 2).
  | Table 3 In vitro antiproliferative activities against U937 cell line of representative ureido and amide series compounds |
We speculated that the main reason why enhanced enzymatic inhibition of ureido series compounds did not translate into antiproliferative potency is their poor cell permeabilities and high tPSA values resulting from abundant N and O atoms; so, we designed and synthesized secondary amine series compounds with less polar atoms and lower tPSA values. In vitro activity evaluation results showed that compared with ureido compound D18 and SAHA, the secondary amine series compounds 9a–9g exhibited similar and even more potent antiproliferative activities against several tumor cell lines, although their HDAC inhibitory activities were less potent (Table 4). It was remarkable that compound 9d was superior to D18 and SAHA in antiproliferative evaluation against all tested tumor cell lines, including U937, U266, KG-1, HeLa, H7402, and HCT116.
  | Table 4 HDAC inhibitory activities and antiproliferative activities of secondary amine series compounds |
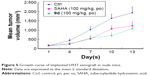
Encouraged by its very potent and promising in vitro antiproliferative activity against U937 cell line (IC50 =0.53 μM, Table 4), we then tested the effect of compound 9d in an in vivo U937 xenograft model with SAHA as the positive control. The tumor growth curve depicted in Figure 5 and the final tumor tissue size represented in Figure 6 explicitly showed that compound 9d exhibited potent oral antitumor activity, which is comparable with SAHA at the same dosage of 100 mg/kg. The relative increment ratio (T/C) of 9d and SAHA were 43% and 49%, respectively, both of which were significantly different from the control group (P<0.05) by Student’s two-tailed t-test. Furthermore, no significant body weight loss and no evident toxic signs in macroscopic analysis of liver and spleen were detected in the mice group treated by 9d.
  | Figure 6 Picture of dissected U937 tumor tissues. |
Currently, most HDAC inhibitors in the clinic, including the approved drugs SAHA, PXD101, and LBH589, are the so-called pan-HDAC inhibitors with similar inhibitory activities against broad-spectrum HDACs. Similarly, our representative amide compound D3 and ureido compound D18 exhibited no significant selectivity among class I (HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3) and class IIb HDACs (HDAC6).8 Such pan-HDAC inhibitors may be useful and acceptable in cancer treatment, but can be unacceptable and detrimental due to numerous side effects resulting from prolonged treatment of some chronic diseases such as neurologic disease and inflammatory disease. Therefore, class- or isoform-selective HDAC inhibitors with the expectation of better tolerance, fewer side effects, and broadened indications are also being developed in our lab.
Conclusion
In order to improve the antiproliferative activities of previously discovered lead compounds, 27 new L-phenylglycine-based HDAC inhibitors classified into ureido series, amide series, and secondary amine series were designed, synthesized, and evaluated. Although most of the ureido series compounds were quite effective at HDAC inhibition, their overall antiproliferative potency was disappointing. Substitution of N-hydroxycinnamamide for the N-hydroxybenzamide fragment of ureido series compounds was detrimental to their HDAC inhibitory activities. Introduction of N atoms to the amide series lead compounds got analogs with decreased enzymatic inhibition and antiproliferative potency. It is worth noting that secondary amine series compounds with less polar atoms and lower tPSA values exhibited promising antiproliferative activities, which indicated that poor cell permeability of ureido series compounds resulting from their higher tPSA values might be the reason for the discrepancy between enzymatic inhibition and antiproliferative potency. More importantly, at the same dosage of 100 mg/kg, secondary amine compound 9d exhibited comparable oral antitumor activity with SAHA in a U937 xenograft model.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National High-tech R&D Program of China, 863 Program (Grant number: 2014AA020523), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers: 21302111, 81373282, and 21172134), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (Grant numbers: 2013M540558 and 2014T70654).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Giannini G, Cabri W, Fattorusso C, Rodriquez M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of cancer: overview and perspectives. Future Med Chem. 2012;4:1439–1460. | ||
Thaler F. Current trends in the development of histone deacetylase inhibitors: a review of recent patent applications. Pharm Pat Anal. 2012;1:75–90. | ||
Gryder BE, Sodji QH, Oyelere AK. Targeted cancer therapy: giving histone deacetylase inhibitors all they need to succeed. Future Med Chem. 2012;4:505–524. | ||
Xu WS, Parmigiani RB, Marks PA. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: molecular mechanisms of action. Oncogene. 2007;26:5541–5552. | ||
Cea M, Cagnetta A, Gobbi M, et al. New insights into the treatment of multiple myeloma with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19:734–744. | ||
Zhang L, Li M, Feng J, Fang H, Xu W. Discovery of a novel histone deacetylase 8 inhibitor by virtual screening. Med Chem Res. 2012;21:152–156. | ||
Zhang L, Wang X, Li X, Xu W. Discovery of a series of small molecules as potent histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2014;29:333–337. | ||
Zhang L, Zhang Y, Chou CJ, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors with enhanced enzymatic inhibition effects and potent in vitro and in vivo antitumor activities. ChemMedChem. 2014;9:638–648. | ||
Ertl P, Rohde B, Selzer P. Fast calculation of molecular polar surface area as a sum of fragment-based contributions and its application to the prediction of drug transport properties. J Med Chem. 2000;43:3714–3717. | ||
Li X, Inks ES, Li X, et al. Discovery of the first N-hydroxycinnamamide-based histone deacetylase 1/3 dual inhibitors with potent oral antitumor activity. J Med Chem. 2014;57:3324–3341. | ||
Li X, Hou J, Li X, et al. Development of 3-hydroxycinnamamide-based HDAC inhibitors with potent in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;89:628–637. | ||
Duan W, Li J, Inks ES, et al. Design, synthesis and antitumor evaluation of novel histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors equipped with phenylsulfonylfuroxan module as nitric oxide (NO) donor. J Med Chem. 2015;89:4325–4338. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.