Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 9
Clinicopathological significance of matrix metalloproteinase-7 protein expression in esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis
Authors Miao S, Zhou S, Han C, Zhang L, Sun H, Yang B
Received 2 April 2015
Accepted for publication 14 May 2015
Published 20 July 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 3729—3740
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S85987
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Shu-Feng Zhou
Shuai Miao,1 Shi-Yao Zhou,2 Chun-Shan Han,3 Le-Ning Zhang,3 Hong-Bin Sun,3 Bin Yang3
1Department of Geriatrics, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, 2Department of Clinical Medicine, Jilin University, 3Department of Thoracic Surgery, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, People’s Republic of China
Background: The MMP-7 basement membrane and extracellular matrix may be essential for tumor invasion and metastasis, and the results presented herein showed a relationship between MMP-7 expression and esophageal cancer (EC). However, its clinicopathological value for EC patients remains inconsistent. To clarify their associations, a meta-analysis of the relevant published literature was conducted.
Materials and methods: Databases including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, CISCOM, CINAHL, and Google Scholar were electronically searched. Only those studies analyzing MMP-7 expression in EC patients with regard to series of different demographic variables and clinicopathological stages (TNM stage, differentiation and invasion grade, and lymph-node [LN] metastasis) were eligible for inclusion. Summary odds ratios (ORs) were pooled in accordance with the random-effect model.
Results: Fourteen clinical cohort studies (tumor samples =935) were incorporated into the current meta-analysis. Results revealed that increased MMP-7 expression in EC patients was positively correlated to TNM stage III–IV (OR 3.04, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.43–6.46; P=0.004). Similar connections were also detected in the differentiation grade, invasion grade, and LN metastasis (all P<0.05). Country-stratified analysis yielded significant association of elevated MMP-7 expression with EC in the People’s Republic of China (PRC) under both TNM III–IV versus I–II and differentiation low versus high comparisons (TNM stage, OR 2.01, 95% CI 1.55–2.59, P<0.001; differentiation grade, OR 1.32, 95% CI 1.11–1.57, P=0.002). With regard to invasion grade and LN metastasis, significant association was observed in all the experimental subgroups (all P-values [PRC and Japan] were lower than 0.05).
Conclusion: These data showed an obvious connection between MMP-7 and TNM stages, differentiation grade, invasive grade, and LN metastasis of EC, indicating that overexpression of MMP-7 may be a suitable diagnostic biomarker for variation in EC clinicopathological features.
Keywords: MMP-7, esophagus carcinoma, statistical analysis
Introduction
Esophageal cancer (EC) is regarded as a malignancy originating from the esophagus, which runs between the throat and the stomach.1 Generally speaking, the clinical symptoms of EC are composed of trouble swallowing, odynophagia, a hoarse voice, weight loss, a dry cough, enlarged lymph nodes (LNs) around the clavicle, and possibly coughing up or vomiting blood.2 EC, the eighth-most common malignancy globally, affects over 450,000 people around the world, and its prevalence is still increasing at a rapid speed.3 It was estimated that 18,170 new cases of EC were diagnosed, and 15,450 EC-related deaths occurred, in the US in 2014.4 In addition, the incidence of EC in such countries as Iran, India, South Africa, and the People’s Republic of China (PRC) is 10–100 times higher than that in the US, and in the EC it is approximately three times more prevalent in males than in females.5 Clinically, the etiology of EC is thought to result from multiple factors containing both environmental and genetic determinants.6,7 It is well established that a variety of risk factors, such as smoking, drinking, obesity, Barrett’s esophagus, nutritional imbalance, and gastroesophageal reflux, may lead to the development of EC.1 Recently, it has been described that the expression of MMP-7, which plays an essential part in tumor invasion, may be strongly implicated in esophageal tumorigenesis.7,8
MMP-7 is the only epithelium-specific product of the MMP family, which possess the ability to degrade the extracellular matrix (ECM) and have been illustrated to participate in the process of cancer invasion and metastasis via the degradation of the extracellular components.9,10 MMP-7, consisting of 267 amino acids, is also capable of degrading laminin, entactin, and type IV collagen, which mainly constitute the basement membrane, and responsible for the activation of other important MMPs, including MMP-1, MMP-2, and MMP-9.11,12 In recent studies, MMP-7 was noted to be expressed in EC, and its expression has been indicated to be connected with invasive grade, advanced TNM stage, and shorter overall survival, supporting the implication of MMP-7 expression in the progression of EC.7,13 As we all know, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells is a complex process in which the degradation of ECM and basement membrane is an essential procedure.14 Furthermore, ECM degradation is considered to depend largely on specific proteolytic enzymes like MMPs.9
As an important member of the MMP family, MMP-7 exhibits highly specific activity to degrade macromolecules, including the ECM, and thus also has a key impact on tumor invasion and metastasis.7 To be specific, overexpression of MMP-7 may result in the destruction of physical barriers surrounding tumor cells and promote the progress of tumor invasion and metastasis, due to the role of MMP-7 in ECM degradation.8 In this regard, it is rational to suppose that MMP-7 expression may be strongly involved in the pathogenesis of EC. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that MMP-7 overexpression may be linked to higher TNM stage and LN metastasis in EC patients, suggesting that there might be a close relationship between the expression of MMP-7 and clinicopathological features of EC.15,16 Nonetheless, contradictory findings have also been reported lately by other relevant studies.7,17 For the fact that such a discrepancy existed in previous studies, we carefully examined expression levels of MMP-7 in patients with EC, and sought to achieve a relatively comprehensive and accurate conclusion concerning the correlation of MMP-7 expression with the clinicopathological characteristics of EC in the current meta-analysis.
Materials and methods
Data sources and keywords
To identify all pertinent papers that assessed the relationship between MMP-7 protein expression and the clinicopathological features of EC, we comprehensively searched the PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, CISCOM, CINAHL, Google Scholar, CBM, and CNKI databases (last updated search in October 1, 2012), utilizing selected common keywords regarding the MMP-7 protein and EC. As for the keywords to be applied in our initial literature search, we selected “matrix metalloproteinase 7” or “MMP-7 protein, human” or “matrix metalloproteinase-7” or “MMP-7” or “MMP 7” or “matrilysin” for the exposure factors, and “esophageal neoplasms” or “esophagus cancer” or “esophageal cancer” or “esophagus neoplasms” or “esophagus carcinoma” or “esophageal carcinoma” or “esophageal tumor” or “esophagus tumor” or “oesophagus cancer” or “oesophagus tumor” or “oesophagus carcinoma” for the outcome factors. The words “human” and “cohort studies” were used for the literature search. MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) terms were also considered. No restriction was set on the language of the article. We also further scanned the bibliographies of relevant articles manually to identify additional potential relevant papers. When the enrolled papers supplied unclear additional data in their original publications, the first authors would be contacted and asked for clarifications.
Selection criteria
We searched throughout for all human-associated cohort studies providing available data for MMP-7 protein expression, including EC patients with different TNM stages, differentiation grades, invasive grades, and LN-metastasis situations, and reporting adjusted odd ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). We extracted only studies that supplied the sample number and sufficient information about MMP-7 protein expression, and excluded those articles with incomplete unavailable or inappropriate clinicopathologic data or those on EC not confirmed by histopathologic examinations. In addition, only studies with a minimum number of samples greater than 15 were enrolled. However, when the extracted studies had subjects overlapping more than 50% with two or more papers, we merely enrolled the one whose population was the most comprehensive. At the same time, only the latest or complete study was included when the extracted studies were published by the same authors, after careful reexamination.
Data extraction
In order to reduce bias and enhance credibility, two investigators extracted information from the retrieved papers according to the selection criteria separately, and arrived at a consensus on all the items through discussion and reexamination. The following relevant data were extracted from eligible studies prospectively in the final analyses: surname of first author, year of publication, source of publication, study type, study design, sample size, age, sex, ethnicity and country of origin, detection method for MMP-7 protein expression, protein expression of MMP-7 in EC patients with different TNM stage, differentiation grade, invasive grade, and LN-metastasis situation. All authors approved the final determinants of the studies to be enrolled.
Quality assessment
To decide whether the study in question was of high quality, Dr Stang used a set of predefined criteria based on Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) criteria to assess the studies independently.18 The NOS criteria are scored based on three aspects: 1) subject selection, 0–4; 2) comparability of subjects, 0–2; and 3) clinical outcome, 0–3. Total NOS scores range from 0 (lowest) to 9 (highest). According to the NOS scores, the included studies were classified into two levels: low quality (0–6), and high quality (7–9), respectively.19 Discrepancies in NOS scores of the enrolled articles were resolved by an additional reviewer discussing and consulting.
Statistical analysis
To calculate the effect size for each study, the summary ORs with 95% CIs were used for TNM stage III–IV versus TNM stage I–II, low-differentiation grade versus high-differentiation grade, invasive grade T3–4 versus invasive grade T1–2, and with-LN metastasis versus without-LN metastasis categories of MMP-7 protein expression with the utilization of the z-test. In order to supply quantitative evidence of all selected studies and minimize the variance of the summary ORs with 95% CIs, we conducted the current statistical meta-analyses by utilizing a random-effect model (DerSimonian and Laird method) or a fixed-effect model (Mantel–Haenszel method) of individual study results where data from independent studies could be combined. The random-effect model was applied when heterogeneity existed among studies, while the fixed-effect model was applied when there was no statistical heterogeneity.
Subgroup meta-analyses were also conducted by country and detection method to explore potential effect modification, and heterogeneity across the enrolled studies was evaluated by Cochran’s Q-statistic (P-values <0.05 were treated as statistically significant).20 As a result of the low statistical power of Cochran’s Q-statistic, the I2 test was also measured to reflect the possibility of heterogeneity between studies.21 I2 test values ranged from 0 (no heterogeneity) to 100% (maximal heterogeneity). One-way sensitivity analysis was conducted to assess whether the results could have been affected significantly through deleting a single study in our meta-analysis one by one to reflect the influence of the individual data set to the pooled ORs. Funnel plots were constructed to evaluate publication bias that might have affected the validity of the estimates. Symmetry of the funnel plots was further evaluated by Egger’s linear regression test.22 All tests were two-sided, and a P-value of <0.05 was regarded as statistically significant. To make sure that the results were credible and accurate, two investigators inputted all information in STATA software, version 12.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA) separately and arrived at an agreement.
Results
Included studies
Our present meta-analysis hit a total of 14 cohort studies that provided information on the correlation between MMP-7 protein expression and clinicopathological features of EC. Thirteen studies were conducted in populations of Asian descent, and only one in populations of Caucasian descent, including 899 subjects at all, which were published between 1999 and 2012. The characteristics and methodological quality of the extracted studies are presented in Table 1.7–9,13,15–17,23–29 Countries where studies were performed were the PRC (n=8), US (n=1), and Japan (n=5). Methods detecting MMP-7 protein expression in this current meta-analysis included streptavidin–peroxidase (SP; n=10), avidin–biotin–peroxidase complex (n=1), and streptavidin–biotin–peroxidase complex (n=3). Additionally, as for the step of screening, a flowchart of the study-selection process is displayed in Figure 1. Initially, 99 papers were selected from the nine databases through screening the title and keywords. After excluding the duplicates (n=1), letters, reviews, or meta-analyses (n=13), nonhuman studies (n=17), and studies not related to research topics (n=20), the remaining studies (n=48) were reviewed, and an additional 32 studies were excluded because they were not case-control or cohort studies (n=5), not relevant to the MMP-7 protein (n=10), or not relevant to EC (n=17). After the remaining 16 trails were further reviewed, 14 papers were enrolled in the final analysis. During the final selection process, the major reason for abandonment was not supplying enough information (n=2). All quality scores of the included studies were higher than 6 (high quality). The number of articles from 2001 to 2014 selected from the electronic databases is shown in Figure 2.
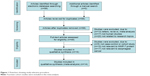  | Figure 1 Flowchart showing study-selection procedure. |
  | Figure 2 Distribution of topic-related literature in electronic databases over the last decade. |
Correlation between MMP-7 protein expression and EC clinicopathological features
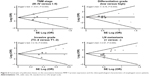
As shown in Figure 3, the major findings of the present meta-analysis revealed that MMP-7 protein expression in EC patients was positively correlated with TNM stage (OR 3.04, 95% CI 1.43–6.46; P=0.004). However, the chief results in Figure 3 suggested a negative association between MMP-7 protein expression in EC patients and differentiation grade (OR 1.55, 95% CI 1.07–2.23; P=0.020). Also displayed in Figure 3, MMP-7 protein expression in EC patients with invasive grade T3–4 was higher than that in patients with invasive grade T1–2 (OR 3.47, 95% CI 2.32–5.19; P<0.001). At the same time, the chief results in Figure 3 also suggest that MMP-7 protein was more highly expressed in EC patients with LN metastasis than in patients without LN metastasis (OR 2.55, 95% CI 1.61–4.04; P<0.001).
Subgroup analysis based on country implied that MMP-7 protein expression was positively related to EC TNM stage just in the PRC (OR 2.01, 95% CI 1.55–2.59; P<0.001), but not in Japan or the US (both P>0.05, Figure 4). In Figure 4, subgroup analysis by country also revealed a negative association of MMP-7 protein expression with differentiation grade in patients with EC only in the Chinese population (OR 1.32, 95% CI 1.11–1.57; P=0.002), while no such association was observed in the Japanese or American populations (both P>0.05). In addition, subgroup analysis based on country found that MMP-7 protein was more highly expressed in EC patients with invasive grade T3–4 than in patients with invasive grade T1–2 in both the Chinese (OR 2.00, 95% CI 1.58–2.53; P<0.001) and Japanese populations (OR 1.48, 95% CI 1.06–2.07; P=0.022; Figure 4). Furthermore, subgroup analysis by country (Figure 4) implied higher MMP-7 protein expression in EC patients with LN metastasis than in patients without LN metastasis in both the Chinese (OR 1.53, 95% CI 1.31–1.77, P<0.001) and Japanese subgroups (OR 1.51, 95% CI 1.12–2.02; P=0.006).
Further subgroup analysis based on detection method implied that MMP-7 protein expression was higher in EC patients with TNM stage III–IV than in patients with TNM stage I–II by using SP (OR 3.80, 95% CI 1.24–11.66; P=0.020) rather than non-SP (P>0.05, Figure 4). As for the correlation between EC differentiation and pathological grade, subgroup analysis by detection method (Figure 4) suggested that it was only found in the non-SP subgroup (OR 1.94, 95% CI 1.06–3.56; P=0.032), and not in the SP subgroup (P>0.05). Also, in the subgroup analysis by detection method (Figure 4), it was observed that MMP-7 protein expression was positively associated with invasive grade by both SP and non-SP methods (P<0.001). Furthermore, subgroup analysis by detection method showed that by using both SP and non-SP methods, the relationship between high MMP-7 protein expression in EC patients and LN metastasis existed (P<0.001, Figure 4).
Sensitivity analysis and publication bias
A leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was carried out to evaluate whether the present meta-analysis was stable. Each study enrolled in our meta-analysis was evaluated one by one to reflect the significance of pooled ORs. The overall statistical significance did not change when any single study was omitted. Therefore, the current meta-analysis data are relatively stable and credible (Figure 5). The funnel plots of those 14 studies were symmetrical, and Egger’s test showed no publication bias (all P>0.05, Figure 6).
Discussion
The relationship between MMP-7 overexpression and the clinicopathological features of EC was studied in this meta-analysis. From the main results of our analysis, we found and obvious connection between MMP-7 and TNM stages, differentiation grade, invasive grade, and LN metastasis of EC. MMPs are a family of enzymes containing Zn2+, contributing to macromolecule degradation from the ECM, connective tissue destruction, and tissue remodeling.9 MMP-7, also known as matrilysin, is the smallest family member, lacking the usual domain of hemopexin-like C-terminal found in other family members, and can be expressed in tumor cells, unlike other MMPs restricted to stromata.7 The substrate of MMP-7 is wide, including matrix proteins like elastin, fibronectin, proteoglycans, laminin, and type IV collagen, and nonmatrix proteins from the cell surface like pro-TNFα, E-cadherin, and Fas ligand.30 Besides, MMP-7 can also activate other MMPs, such as MMP-9, MMP-2, and MMP-1, and inactivate α1-antitrypsin to increase the activity of serine protease, thus indirectly leading to MMP activation.31
The overexpression of MMP-7 has been found in many tumors, and is connected with metastasis, progression, and poor prognosis of tumors, especially in gastrointestinal tract tumors, such as in the esophagus, liver, pancreas, and colon.10,12 Many studies have reported the relationship between overexpression of MMP-7 and the progression of EC in the TNM stage, differentiation grade, invasive grade, and LN metastasis: the expression of MMP-7 was found to be greater in stage III–IV than in stage I–II, indicating its role in the development of tumors;32 and MMP-7 is overexpressed in the early stages of tumor differentiation, suggesting that MMP-7 acts as a participant in tumor deterioration.33
Additionally, the increased MMP-7 expression is associated with a deeper invasive grade, proved by the fact that outer-membrane invasion is higher than invasion within the muscle, which could promote tumor development.34 Furthermore, a significant relationship has been found between MMP-7 expression and nodal metastasis, suggesting MMP-7 might be expressed at the front of the invasion, causing lymphatic permeation and the pattern of infiltrative growth and its role in basement-membrane degradation.8,14 In agreement with our study, Yamamoto et al demonstrated the role of matrilysin in esophageal carcinoma progression, suggesting its useful role in poor prognosis and recurrence prediction and a potential therapy for anti-MMPs.23 Salmela et al also proved that matrilysin was overexpressed in Barrett’s malignant cells and played an essential role in Barrett’s adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis.17
In view of the many other factors that may have an influence on the linkage between MMP-7 expression and EC clinicopathological features, a stratified analysis on the basis of different countries and detection methods was conducted. From the country-stratified analysis, we found a relationship between TNM stages, differentiation grade, invasive grade, LN metastasis, and MMP-7 expression is still significant in the PRC, and the relationship between invasive grade and LN metastasis and the expression of MMP-7 is also obvious in Japan, while the relationship involving the TNM stages and differentiation grade was not obvious in Japan or the US, which might be the result of living conditions and genetic background of different countries. In summary, partly in line with previous studies, our results showed that the high expression of MMP-7 could affect the EC clinicopathological features, showing MMP-7 could be an independent biomarker for the diagnosis of EC and thus improving the survival rate of EC patients.
These data at present available on MMP-7 protein expression and EC are somewhat promising; nevertheless, these results should be further confirmed by relatively larger prospective studies for several reasons, as follows. Firstly, the sample size in this study was relatively small, which may have had an influence on the introduction of selection bias with unbalanced confounding factors, and hence affecting the results of the present exploration. Most importantly, it was critical to predefine the cutoff values of MMP-7, and simply high- or low-expression levels would be extremely different. Also, different cutoff MMP-7 values between studies may have had an impact on the present results and been responsible for the inconclusive outcome. However, it was difficult to provide an accurate definition for these “high” or “low” expressions, considering that detection methods of MMP-7 expression differ from one another (SP, avidin–biotin–peroxidase complex, and streptavidin–biotin–peroxidase complex methods). Thirdly, though significance did not change after adjustment by the trim-and-fill method, some publication bias was still observed. Finally, stratified analyses cannot be performed only by country or method, mainly due to the apparent heterogeneity of EC stages and sex distribution among various types of studies.
MMP-7 is not a unique marker for EC. There are suitable other biomarkers in EC progression using meta-analysis apart from MMP-7. Among the biomarkers, p53 may be a potential molecule for meta-analysis.35 MMP-7 is overexpressed in cancers, so exploring MMP-7 inhibitors may help in preventing the development of EC.36
Collectively, the findings in this study are encouraging, though future exploration is warranted to evaluate the value of MMP-7 in clinicopathological characteristic screening of EC before its clinical application. Overall, increased expression levels of MMP-7 may be related to an advanced TNM stage, lower differentiation grade, aggressive invasive grade, and LN metastasis in EC patients, and the identification of MMP-7 is a promising molecular maker in EC progression.
Acknowledgment
We would like to acknowledge the reviewers for their helpful comments on this paper.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Mao WM, Zheng WH, Ling ZQ. Epidemiologic risk factors for esophageal cancer development. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12: 2461–2466. | ||
Layke JC, Lopez PP. Esophageal cancer: a review and update. Am Fam Physician. 2006;73:2187–2194. | ||
Zhang Y. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:5598–5606. | ||
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. | ||
González L, Magno P, Ortiz AP, et al. Esophageal cancer incidence rates by histological type and overall: Puerto Rico versus the United States Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results population, 1992–2005. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013;37:5–10. | ||
Holmes RS, Vaughan TL. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of esophageal cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17:2–9. | ||
Saeki H, Tanaka S, Sugimachi K, et al. Interrelation between expression of matrix metalloproteinase 7 and beta-catenin in esophageal cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;47:2738–2742. | ||
Tanioka Y, Yoshida T, Yagawa T, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 are associated with unfavourable prognosis in superficial oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2003;89:2116–2121. | ||
Ohashi K, Nemoto T, Nakamura K, Nemori R. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase 7 and 9 and membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer. 2000; 88:2201–2209. | ||
Bavi PP, Bu R, Uddin S, Al-Kuraya KS. MMP-7 polymorphisms – a new tool in molecular pathology to understand esophageal cancer. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:299–300. | ||
Yoshinaga K, Mimori K, Inoue H, et al. Activin A enhances MMP-7 activity via the transcription factor AP-1 in an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Int J Oncol. 2008;33:453–459. | ||
Zhou JH, Zhang B, Kernstine KH, Zhong L. Autoantibodies against MMP-7 as a novel diagnostic biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:1373–1378. | ||
Chiba T, Kawachi H, Kawano T, et al. Independent histological risk factors for lymph node metastasis of superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; implication of claudin-5 immunohistochemistry for expanding the indications of endoscopic resection. Dis Esophagus. 2010;23:398–407. | ||
Yamashita K, Mori M, Shiraishi T, Shibuta K, Sugimachi K. Clinical significance of matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression in esophageal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:1169–1174. | ||
Zhu ZH, Zhao YX, Shao LY, Qiu LL. [Expressions of MMP-26 and MMP-7 in esophageal cancer tissues and their significance]. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Hui. 2012;19:344–346. Chinese. | ||
Li YL, Yang XL. Expression of MMP-7 in esophageal carcinoma and clinical significance. Pract J Cancer. 2005;20:50–52. | ||
Salmela MT, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Puolakkainen P, Saarialho-Kere U. Upregulation and differential expression of matrilysin (MMP-7) and metalloelastase (MMP-12) and their inhibitors TIMP-1 and TIMP-3 in Barrett’s oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2001;85: 383–392. | ||
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25:603–605. | ||
Zhang P, Zhong ZH, Yu HT, Liu B. Significance of increased leptin expression in osteoarthritis patients. PloS One. 2015;10:e0123224. | ||
Jackson D, White IR, Riley RD. Quantifying the impact of between-study heterogeneity in multivariate meta-analyses. Stat Med. 2012;31:3805–3820. | ||
Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR, Rushton L. Comparison of two methods to detect publication bias in meta-analysis. JAMA. 2006;295:676–680. | ||
Zintzaras E, Ioannidis JP. HEGESMA: genome search meta-analysis and heterogeneity testing. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:3672–3673. | ||
Yamamoto H, Adachi Y, Itoh F, et al. Association of matrilysin expression with recurrence and poor prognosis in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1999;59:3313–3316. | ||
Yue J, Wang SY. Expression and significance of MMP-7 in esophageal carcinoma. J Xinxiang Med Coll. 2006;23:27–29. | ||
Yan ZQ, He RQ, Liu XQ, Yuan YC, Min H. Expression of MMP-7 in esophageal carcinoma and its clinical significance. Clin J Med Office. 2005;33:539–541. | ||
Wang YL, Wang JG, Liu L. Clinical pathological significance of the expression of nm23-H1 and matrixmetalloproteinase-7 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Xinxiang Med Coll. 2008;25:23–26. | ||
Wang YL, Li SL, Yin L. Expression of CD44V6 and MMP-7 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue. Zhengzhou Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2007;42:895–898. | ||
Li Z, Hao XJ, Chen J. Expression and significance of B-catenin and MMP-7 in esophagus squamous cell carcinoma. Hebei Med J. 2012;34:979–981. | ||
Gao JB, Chen YQ, Zhou ZG, et al. [Spiral CT features and expression of MMP-7 in esophageal carcinoma]. Chin J Med Imaging Technol. 2005;21:910–913. Chinese. | ||
Zhang J, Jin X, Fang S, et al. The functional polymorphism in the matrix metalloproteinase-7 promoter increases susceptibility to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, gastric cardiac adenocarcinoma and non-small cell lung carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:1748–1753. | ||
Malik MA, Sharma KL, Zargar SA, Mittal B. Association of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (-181A>G) polymorphism with risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Kashmir Valley. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:301–306. | ||
Ougolkov AV, Yamashita K, Mai M, Minamoto T. Oncogenic β-catenin and MMP-7 (matrilysin) cosegregate in late-stage clinical colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:60–71. | ||
Li YJ, Wei ZM, Meng YX, Ji XR. β-Catenin up-regulates the expression of cyclinD1, c-myc and MMP-7 in human pancreatic cancer: relationships with carcinogenesis and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:2117–2123. | ||
Mylona E, Kapranou A, Mavrommatis J, Markaki S, Keramopoulos A, Nakopoulou L. The multifunctional role of the immunohistochemical expression of MMP-7 in invasive breast cancer. APMIS. 2005;113: 246–55. | ||
Kandioler D, Schoppmann SF, Zwrtek R, et al. The biomarker TP53 divides patients with neoadjuvantly treated esophageal cancer into 2 subgroups with markedly different outcomes. A p53 Research Group study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;148:2280–2286. | ||
Long ZW, Wang JL, Wang YN. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 mRNA and protein expression in gastric carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:11415–11426. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.