Back to Journals » International Journal of General Medicine » Volume 13
Thyroid Dysfunctions Due to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Review
Authors El Sabbagh R, Azar NS, Eid AA, Azar ST
Received 6 May 2020
Accepted for publication 1 September 2020
Published 4 November 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1003—1009
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S261433
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Rawaa El Sabbagh,1 Nadim S Azar,2,3 Assaad A Eid,3 Sami T Azar1
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, American University of Beirut, Beirut, Lebanon; 2Department of Internal Medicine, American University of Beirut, Beirut, Lebanon; 3Department of Anatomy, Cell Biology and Physiological Sciences, American University of Beirut, Beirut, Lebanon
Correspondence: Sami T Azar
Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, American University of Beirut Medical Center, Beirut, Lebanon
Email [email protected]
Aim: Immune checkpoint inhibitors are anti-cancer drugs associated with adverse events that result from releasing the immune system against self-antigens while attacking cancer cells. Thyroid dysfunctions are among the most common associated adverse events.
Materials and Methods: We conducted a systematic search of the literature in 2 databases: PubMed and Medline. Articles that reported thyroid adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitors were reviewed. Thyroid disorders include hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism and are most commonly seen with programmed cell death protein 1 and programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitors.
Conclusions: Thyroid disorders are common side effects seen with check point inhibitors and are treated, depending on the clinical situation, by adequate hormonal replacement, thionamides, corticosteroids or observation only. The use of high dose corticosteroids has not been established as a treatment of thyroid toxicities. Thyroid function tests screening should be a part of baseline laboratory testing of all patients undergoing treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Keywords: immune check point inhibitors, thyroid dysfunction, anti-PD1, anti-PDL1
Prospectus
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are anti-cancer medications with wide range use in different types of cancer. The mechanism of action of these drugs results in some new types of adverse events related to the immune system. Thyroid dysfunctions are among the common adverse events observed. The increase in the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors and the improved survival of patients treated by these medications make the identification of these side effects more common. In fact, these disorders can affect the quality of life of the patients, and might be life-threatening in some cases if not promptly recognized and treated. The aim of this review is to summarize the current knowledge of the thyroid side effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors and their prevention, diagnose and treatment.
Introduction
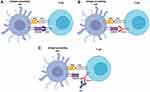
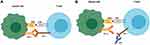
Over the recent years, the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICPi) has improved the management and prognosis of many solid tumors.1 These drugs are monoclonal antibodies that block immune checkpoints that are present on the surface of T-cells to ensure immune self-tolerance, resulting in an increase of the T-cells ability to attack the cancer cells2 (Figures 1 and 2).
Currently, seven ICPi are approved for the treatment of different solid tumors: a cytotoxic T-lymphocytes associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitor Ipilimumab;3 three programmed cell death protein (PD-1) inhibitors: Nivolumab,4 Pembrolizumab5 and Cemiplimab;6 and three programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitors: Atezolizumab,7 Avelumab8 and Durvalumab.9 Table 1 summarizes the different ICPi and their clinical indications.
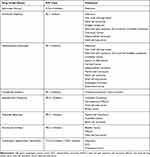 |
Table 1 Summary of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Their Clinical Indications |
ICPi are associated with immune-related adverse events (IrAEs), that result from unleashing the immune system against self-antigens while attacking neoplastic cells.10 Endocrine diseases are among the most common associated IrAEs, involving the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland, the pancreas, the adrenal gland and the parathyroid glands.11–13
The aim of this review is to describe the incidence, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and guidelines on the management and screening of thyroid disorders associated with ICPi.
Search Strategy
We conducted a systematic search of the literature in 2 databases: Medline and PubMed. Articles that reported thyroid adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitors were reviewed. We used the following keywords or corresponding Medical Subject Heading terms: “ipilimumab,” “nivolumab,” “pembrolizumab,” “atezolizumab,” “Cemiplimab” “Avelumab” “Durvalumab” “CTLA-4 inhibitors” “ PD-1 inhibitors” “PDL-1 inhibitors” “immune checkpoint inhibitors” “hypothyroidism” “hyperthyroidism” “thyroiditis” “Graves” “Hashimoto” “thyroid dysfunction” “thyroiditis” “thyroid disease”. We also reviewed references of published trials and review articles.
Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid dysfunction under ICPi can present as thyrotoxicosis or hypothyroidism.14 The incidence of thyroid dysfunction differs between different ICPi classes. In a meta-analysis of 37 studies, the predicted incidence of hyperthyroidism was estimated to be 3.2% with PD1-inhibitors and 8.0% with combination therapy.13 The median time to onset of hyperthyroidism is reported to be around 21 days in combination therapy and 47 days in monotherapy with PD1-inhibitors.13–15 For hypothyroidism, the incidence estimated by the same meta-analysis11 was higher with combination therapy 13.2%, and 7% with PDL-1 inhibitors alone. Median time to onset is comparable between the 2 regimens with 63 days in combination therapy and 70 days in PD-1 inhibitors monotherapy.16
The pathogenesis of thyroid disorders under ICPi is not completely known. Data from observational studies suggest that thyroid dysfunction induced by ICPi is due to a silent destructive thyroiditis that can evolve either to hypothyroidism or euthyroidism.17 However, few cases of thyrotoxicosis are due to Graves’ disease and have been described in the literature.18
In a case series study of nivolumab-induced thyroiditis, PD-L1 and PD-L2 were found in normal thyroid glands, which could possibly implicate that the administration of PD-1 inhibitors can disrupt the interaction between the PD-1 on the T-cells and the PDL-1/2 on the thyrocytes, leading to T-cell activation against the thyroid.19
The association between thyroid dysfunction due to ICPi and the presence of thyroid antibodies is not fully elucidated. In a study by Osorio et al anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) and anti-thyroglobulin were positive in 80% of patients with thyroid dysfunction due to pembrolizumab, while these antibodies were present in only 8% of patients without thyroid dysfunction (P <0.0001).20
In a recent case report of immunotherapy-induced thyroiditis, thyroid biopsy was performed in a woman with metastatic melanoma on nivolumab and ipilimumab who presented with hyperthyroidism. Unique features including abundant clusters of necrotic cells, lymphocytes and CD163-positive histiocytes were described.21
Data from a recent prospective cohort study of patients with ICI-induced thyroiditis showed T lymphocyte-mediated process with intra-thyroidal predominance of CD8+ and CD4−CD8− T lymphocytes.22
The clinical presentation of thyroid dysfunction with ICPi is similar to that of the general population, with thyrotoxicosis presenting with tachycardia, weight loss, fatigue and diarrhea and hypothyroidism presenting with bradycardia, weight gain, fatigue and constipation.24 These symptoms are not specific and might be overshadowed by the symptoms of the underlying neoplasm.16 The diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction due to immunotherapy is based on TSH and Free T4 levels to differentiate primary from central thyroid dysfunction. Total T3 measurement is necessary in cases of thyrotoxicosis. The interpretation of these levels should be done with caution due to the confounding factors in cancer therapy (steroids use, iodine contrast injection and non-thyroid illness) that might affect the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis.24 TSH elevation might be observed with cortisol deficiency without having true hypothyroidism.
In the setting of thyrotoxicosis, and when the etiology is uncertain, thyroid scintigraphy should be performed, since it can be a useful tool into distinguishing thyroid disruption from hyperfunction.23 The interpretation of this imaging modality should also be done with caution, especially in the setting of iodine injection.24 In inflammatory thyroiditis, doppler ultrasound of the thyroid is not routinely recommended but may help in the diagnosis by showing hypovascularization of the parenchyma.24
Since thyrotoxicosis is usually transient and self-limited, it is reasonable to monitor patients in this phase closely and manage them symptomatically, with beta blockers if needed.
Corticosteroids are the mainstay of the treatment of subacute thyroiditis and should be used when the symptoms of thyrotoxicosis are severe.12 Thionamides should be used when the diagnosis of Graves disease is established.12,24
The management of hypothyroidism depends on the degree of TSH elevation and the severity of symptoms.12 Adrenal insufficiency should be ruled out before the start of hormonal replacement to avoid adrenal crisis that could be lifethreatening12 Hormonal replacement with levothyroxine at a dose of 1–1.6mcg/kg/day (depending on the age and comorbidities) is the mainstay of the treatment.21 When the TSH below 10 mU/L, the decision on hormonal replacement should be evaluated on an individual basis (depending on the presence of symptoms or antibodies).12 Some experts recommend measuring anti-TPO in the setting of a high TSH between 5 and 10 mU/L to guide the decision for treatment.24 However, a TSH persistently higher than 10 mU/L or any level of TSH elevation in the presence of symptoms are indications for treatment. Patients with severe symptoms or signs of myxedema require admission for IV therapy.12 The discontinuation of therapy in the setting of thyroid disorders is not necessary except in cases of severe symptoms when therapy should be temporarily held and can be resumed once symptoms improve.12,24–27 The need for thyroid replacement seems permanent as the recovery of the thyroid gland has not been described.20,27,28 We recommend monitoring TSH and FT4 every 4 to 6 weeks starting from the initiation of treatment or from when the patient’s symptoms are suggestive of thyroid dysfunction.12
The recommendations for screening and monitoring of thyroid disorders in the setting of ICPi use are summarized in Table 2.
 |
Table 2 Thyroid Disorders Induced by ICPi Therapy – Screening and Monitoring Recommendations in Guidelines |
Conclusion
The use of ICPi in cancer treatment is currently increasing and will continue to increase in the future. This newly introduced modality of treatment is challenging for all specialists, including internists, oncologists and endocrinologists, due to the various patterns of adverse effects. Thyroid disorders are among the common side effects seen and should be adequately treated.
The use of corticosteroids has not been established as a treatment of thyroid toxicities, however, the available studies are limited by their retrospective nature and small sample size. Some studies have suggested a positive correlation between the development of various endocrine side effects, including thyroid abnormalities, and clinical cancer response18,20,29; however, larger prospective studies are needed to confirm this correlation.
It is not well understood why some patients are more prone than others to develop thyroid side effects. More investigations and research are needed to identify risk factors for these side effects and possibly tailor the treatment patients accordingly.
Finally, thyroid function tests including TSH and Free T4 and anti-TPO antibodies screening should be a part of baseline laboratory testing of all patients undergoing treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Patients should be educated about immunotherapy and the clinical profile of possible immune-related thyroid dysfunction adverse events.
Abbreviations
Anti-TPO, thyroid peroxidase antibodies; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocytes associated protein 4; ICPi, immune checkpoint inhibitors; IrAEs, immune-related adverse events; PD-1, programmed cell death protein; PDL-1, programmed death-ligand 1; PDL-2, programmed death-ligand 2; TRAb, TSH receptor antibodies; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone; TFT, thyroid function test.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sector.
Disclosure
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kreamer KM. Immune checkpoint blockade: a new paradigm in treating advanced cancer. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2014;5:418–431.
2. Pardoll DM. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:252–264.
3. Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF. Improved Survival with Ipilimumab in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(8):711–723. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1003466
4. Weber JS, D’Angelo SP, Minor D. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate 037): a randomised, controlled, open-label, Phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(4):375–384. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70076-8
5. Robert C, Schachter J, Long GV. Pembrolizumab versus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(26):2521–2532. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1503093
6. Migden MR, Rischin D, Schmults CD. PD-1 Blockade with Cemiplimab in Advanced Cutaneous Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(4):341–351. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1805131
7. Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer(OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10066):255–265. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32517-X
8. Patel MR, Ellerton J, Infante JR. Avelumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma after platinum failure (JAVELIN Solid Tumor): pooled results from two expansion cohorts of an open-label, Phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(1):51–64. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30900-2
9. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(20):1919–1929. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1709937
10. Postow MA, Sidlow R, Hellmann MD. Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(2):158–168. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1703481
11. Barroso-Sousa R, Ott PA, Hodi FS, Kaiser UB, Tolaney SM, Min L. Endocrine Dysfunction Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: practical Recommendations for Diagnosis and Clinical Management. Cancer. 2018;124(6):1111–1121. doi:10.1002/cncr.31200
12. Brahmer JR, Lacchetti C, Schneider BJ. Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: american Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(17):1714–1768. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6385
13. Barroso-Sousa R. Incidence of Endocrine Dysfunction Following the Use of Different Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Regimens: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMAONCOL. 2018;4(2):173–182.
14. Iyer PC, Cabanillas ME, Waguespack SG, et al. Immune-related thyroiditis with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Thyroid. 2018;28(10):1243–1251. doi:10.1089/thy.2018.0116
15. Chalan P, Di Dalmazi G, Pani F, De Remigis A, Corsello A, Caturegli P. Thyroid dysfunctions secondary to cancer immunotherapy.J. Endocrinol Invest. 2018;41(6):625–638. doi:10.1007/s40618-017-0778-8
16. Lee H, Hodi FS, Giobbie-Hurder A. Characterization of Thyroid Disorders in Patients Receiving Immune Checkpoint Inhibition Therapy. Cancer Immunol Res. 2017;5(12):1133–1140. doi:10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0208
17. De Filette J, Jansen Y, Schreuer M. Incidence of Thyroid-Related Adverse Events in Melanoma Patients Treated With Pembrolizumab. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(11):4431–4439. doi:10.1210/jc.2016-2300
18. Ruggeri RM, Campennì A, Giuffrida G, et al. Endocrine and metabolic adverse effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors: an overview (what endocrinologists should know). J Endocrinol Invest. 2019;42(7):745–756. doi:10.1007/s40618-018-0984-z
19. Yamauchi I, Sakane Y, Fukuda Y. Clinical Features of Nivolumab-Induced Thyroiditis: A Case Series Study. Thyroid. 2017;27(7):894–901. doi:10.1089/thy.2016.0562
20. Osorio JC, Ni A, Chaft JE, et al. Antibody-mediated thyroid dysfunction during T-cell checkpoint blockade in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(3):583–589. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdw640
21. Angell TE, Min L, Wieczorek TJ, Hodi FS. Unique cytologic features of thyroiditis caused by immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy for malignant melanoma. Genes Dis. 2018;5(1):46–48. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2017.11.002
22. Kotwal A, Gustafson M, Bornschlegl S, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced thyroiditis is associated with increased intrathyroidal T lymphocyte subpopulations. Thyroid. 2015:1050–7256.
23. Giuffrida G, et al. Thyroid dysfunction in patients treated with the immune checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab: different clinical features. APMB. 2017;105:2.
24. Illouz F. Expert opinion on thyroid complications in immunotherapy. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2018;79(5):555–561. doi:10.1016/j.ando.2018.07.007
25. Borodic G, Hinkle DM, Cia Y. Drug-induced graves disease from CTLA-4 receptor suppression. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;27(4):e87–8. doi:10.1097/IOP.0b013e3181ef72a1
26. Jonklaas J, Bianco AC, Bauer AJ. American Thyroid Association Task Force on Thyroid Hormone Replacement. Guidelines for the treatment of hypothyroidism: prepared by the american thyroid association task force on thyroid hormone replacement. Thyroid. 2014;24(12):1670–1751. doi:10.1089/thy.2014.0028
27. Illouz F, Briet C, Cloix L.Endocrine toxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitors: essential crosstalk between endocrinologists and oncologists. Cancer Med. 2017;6(8):1923–1929. doi:10.1002/cam4.1145
28. Delivanis DA, Gustafson MP, Bornschlegl S. Pembrolizumab-Induced Thyroiditis: comprehensive Clinical Review and Insights Into Underlying Involved Mechanisms. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(8):2770–2780. doi:10.1210/jc.2017-00448
29. Kotwal A, Kottschade L, Ryder M. PD-L1 inhibitor induced thyroiditis is associated with better overall survival in cancer patients. Thyroid. 2020;30:177–184. doi:10.1089/thy.2019.0250
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.