Back to Journals » Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity » Volume 14
The Impact of Vitamin D in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in Patients with Morbid Obesity
Authors Borges-Canha M , Neves JS, Mendonça F, Silva MM, Costa C, Cabral PM, Guerreiro V, Lourenço R, Meira P, Salazar D, Ferreira MJ, Pedro J , Leite AR, von-Hafe M, Vale C, Viana S, Sande A, Belo S, Lau E, Freitas P , Carvalho D
Received 12 October 2020
Accepted for publication 21 January 2021
Published 3 February 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 487—495
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S286334
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Konstantinos Tziomalos
Marta Borges-Canha,1,2 João Sérgio Neves,1,2 Fernando Mendonça,1 Maria Manuel Silva,1 Cláudia Costa,3 Pedro M Cabral,4 Vanessa Guerreiro,1 Rita Lourenço,5 Patrícia Meira,5 Daniela Salazar,1 Maria João Ferreira,1 Jorge Pedro,1 Ana Rita Leite,2 Madalena von-Hafe,2 Catarina Vale,2 Sara Viana,1 Ana Sande,1 Sandra Belo,1 Eva Lau,1 Paula Freitas,1,6 Davide Carvalho1,6
1Serviço de Endocrinologia, Diabetes e Metabolismo do Centro Hospitalar Universitário de São João, Porto, Portugal; 2Departamento de Cirurgia e Fisiologia, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal; 3Serviço de Endocrinologia do Instituto Português de Oncologia do Porto, Porto, Portugal; 4Serviço de Patologia Clínica do Centro Hospitalar Universitário Cova da Beira, Covilhã, Portugal; 5Faculdade de Ciências da Nutrição e Alimentação da Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal; 6Investigação e Inovação Em Saúde (I3s), Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal
Correspondence: Marta Borges-Canha
Serviço de Endocrinologia, Diabetes e Metabolismo do Centro Hospitalar Universitário de São João, Alameda Prof. Hernâni Monteiro, Porto, 4200-319, Portugal
Tel +351918935390
Email [email protected]
Purpose: We aimed to evaluate the association between vitamin D status and hepatic function parameters and scores: Fatty Liver Index (FLI, predictor of hepatic steatosis) and BARD (BMI, AST/ALT ratio and DM, predictor of hepatic fibrosis) in patients with morbid obesity.
Patients and Methods: Cross-sectional study including patients with morbid obesity followed in our centre between January 2010 and July 2018. Patients with missing vitamin D levels or hepatic profile parameters were excluded. We divided the population according to two cut-offs of vitamin D levels (12ng/mL and 20ng/mL).
Results: The included population (n=1124) had an average age of 43.3± 10.7 years and 84.3% were female. Seventy-point eight percent of the population had vitamin D levels lower than 20ng/mL and 34.8% lower than 12ng/dL. Patients with lower vitamin D levels (< 12ng/mL) had higher BMI, hip and waist circumferences and higher prevalence of hypertension. Higher FLI scores [OR= 0.77 (0.07), p< 0.01] and ALP levels [β= − 0.03 (− 0.06, − 0.01), p< 0.01] associated to lower vitamin D levels.
Conclusion: Vitamin D deficiency is associated with a higher risk of hepatic steatosis in individuals with morbid obesity. Correction of vitamin D deficiency may have a beneficial role in the management of NAFLD in patients with morbid obesity.
Keywords: vitamin D, fatty liver, NAFLD, obesity
Introduction
Vitamin D is classically recognized for its role in phospho-calcium metabolism and, therefore, in bone health. However, its receptors are present ubiquitously and vitamin D has been shown to have a myriad of pleiotropic effects in several other human organs and systems.1,2
In particular, vitamin D deficiency has been associated with several metabolic disturbances, such as obesity, dyslipidaemia, hypertension, type 2 diabetes (T2D) and metabolic syndrome (MS).3–5 Obesity, via pro-inflammatory adipokines, increases oxidative stress.6 The excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in obesity by the adipose tissue increases the risk of T2D, leading to a condition described as diabesity (combination of diabetes and obesity).7 Additionally, overproduction of ROS results in DNA, lipid, and protein damage induces endothelial dysfunction, favouring the development of other cardiovascular risk factors such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and NAFLD.6 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is considered the hepatic counterpart of MS. Vitamin D deficiency is highly prevalent among patients with NAFLD, however literature linking this hepatic disorder and vitamin D deficiency states have shown inconsistent results.8,9 It is biologically plausible that the relation is bidirectional. On one hand, vitamin D (either synthesised in the skin – cholecalciferol- or obtained from dietary – ergocalciferol) is metabolised within the liver to 25-hydroxyvitamin D and within the kidneys to the biologically active (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D).10 On the other hand, insulin resistance is at the root of both T2D and NAFLD, and vitamin D may have a significant impact on insulin sensibilization through its anti-inflammatory effects and its role in the regulation of insulin secretion.11 The presence of hepatic vitamin D receptors in various nonparenchymal cells reinforces the potential anti-proliferative, anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties of this hormone in this organ.12 Vitamin D is able to inhibit hepatic expression of several pro-fibrotic mediators and other liver fibrosis actors.13 In vitro and in vivo studies suggest that the protective effect of vitamin D in the liver may be, at least in part, mediated by acting on stellate cells and inhibiting fibrogenesis.3,14 The pathophysiology behind the association of vitamin D status and NAFLD is yet to be fully uncovered, making this a hot topic in current scientific research.3
NAFLD is a metabolic liver disease characterized by a continuum of liver dysfunction, ranging from simple steatosis to steatohepatitis and fibrosis, cirrhosis and even hepatocarcinoma.15–17 This metabolic liver disorder is typically asymptomatic at initial stages. Scores used to predict hepatic steatosis and fibrosis and measurement of serum liver enzymes are essential in clinical practice to screen and evaluate the progression of NAFLD. There are many scores available each with its strengths and limitations. The Fatty Liver Index (FLI) score is one of the best-validated scores for predicting steatosis. On the other hand, the BARD (BMI, AST/ALT ratio and presence of diabetes) score is reported as having a high negative predictive value, making it especially useful to exclude advanced fibrosis.17,18
In this study, we aimed to evaluate the association between vitamin D levels and hepatic function parameters and scores: Fatty Liver Index (FLI, predictor of hepatic steatosis), and BARD (BMI, AST/ALT ratio and DM, predictor of hepatic fibrosis), in a cohort of patients with morbid obesity.
Methods
Study Design and Participants
We performed a cross-sectional study according to Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement.19 We included patients with morbid obesity followed in our centre between January 2010 and July 2018. Patients missing measurements of vitamin D or hepatic profile parameters were excluded. From a total of 2595 patients 1124 were included in the analysis after applying the former inclusion and exclusion criteria (255 were excluded because of missing parameters of hepatic profile and 1216 because of missing measurement of vitamin D). This study was approved by the Ethics Committee for Health our centre, Centro Hospitalar Universitário de São João. For this type of study formal consent is not required in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.20 Privacy of the patients included was preserved along with this study and it was done according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Clinical and Biochemical Parameters Evaluated
The following parameters were evaluated: age, sex, weight, body mass index (BMI), waist and hip circumferences, history of diabetes, dyslipidaemia and hypertension. Diabetes was defined as fasting plasma glucose ≥126 mg/dL, glycated haemoglobin ≥6.5%, 2 hours plasma glucose after a 75g oral glucose tolerance test ≥200 mg/dL or the use of antihyperglycemic drugs.21 Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg, diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg or the use of antihypertensive drugs.22 Dyslipidaemia was defined as serum low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol ≥160 mg/dL, serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol <40 mg/dL, serum triglycerides ≥200 mg/dL, or the use of lipid-lowering agents.23 Vitamin D, albumin, triglycerides (TG), aspartate transaminase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), total bilirubin and direct bilirubin were measured in serum samples, obtained from the baseline clinical evaluation.
Predictors of Hepatic Fibrosis and Steatosis
FLI and BARD scores were used as predictors of hepatic steatosis and fibrosis, respectively. These were built based on the following formulas:
- FLI score: FLI=ey/(1+ ey) x 100, where y=0.953 x ln(triglycerides, mg/dL) + 0.139 x BMI, kg/m2 + 0.718 x ln(GGT, U/L) + 0.053 x waist circumference, cm – 15.745. FLI scores <30 indicate low risk of hepatic steatosis, 30–60 intermediate risk and ≥60 high risk.24
- BARD score: BMI≥28=1 point; AST/ALT ratio≥0.8=2 points, presence of diabetes=1 point. Low fibrosis risk patients are scored 0–1 points and higher risk patients are scored 2–4 points.17
Statistical Analysis
The population was divided according to two cut-offs of vitamin D levels (<12ng/mL and <20ng/mL). These cut-off values were chosen based on the Institute of Medicine stance on vitamin D status (levels ≥20ng/mL are sufficient and levels <12ng/mL represent a vitamin D deficiency state).25
For continuous variables, independent t-tests were performed. We used linear and ordered logistic regression models unadjusted and adjusted for possible confounders: 1) sex and age; 2) sex, age and body mass index (BMI); and 3) sex, age, BMI, diabetes and dyslipidaemia. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables and as percentages for categorical variables. Statistical analysis was performed with Stata software, version 14.1 (StataCorp). We considered a two-sided P value less than 0.05 to be statistically significant.
Results
Clinical and Demographic Population Characteristics
Clinical and demographic characteristics of the population included in this analysis are presented in Table 1. From the 1124 individuals, 84.3% were female. The average age of the population was 43.3±10.7 years and BMI was 43.3±10.7kg/m2. Seventy-point eight percent had vitamin D levels lower than 20ng/mL and 34.8% lower than 12ng/dL (43.5% of men and 33.16% of women had vitamin D levels below 12ng/mL). Six-point six percent of the participants were being supplemented with vitamin D. Patients supplemented with vitamin D had similar clinical and demographic characteristics in comparison with participants without supplementation, except for the waist circumference that was larger in the supplemented group (data not shown).
 |
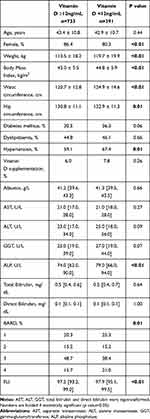
Table 1 Clinical and Demographic Characteristics of the Population Included (n=1124). Values are Shown as Mean ± Standard Deviation or as Median [95% Confidence Interval] |
Clinical, Demographic, Biochemical and Liver Scores Characteristics According to Vitamin D Levels
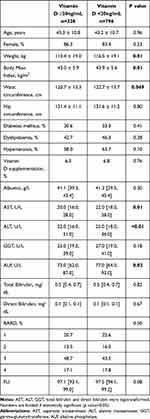
Table 2 (12ng/dL cut-off) and Table 3 (20ng/dL cut-off) show the clinical and demographic characteristics of the population according to vitamin D levels.
Considering Table 2, the group of patients with vitamin D <12ng/mL had a lower percentage of women (86.4% vs 80.3%, p<0.01), higher weight, BMI, hip and waist circumferences, and higher prevalence of hypertension. This group had higher levels of serum ALP and FLI score (97.2 [93.2; 99.0] vs 97.9 [95.1; 99.5], p<0.01) and a higher percentage of individuals with the highest BARD score (15.7% vs 21%).
Regarding Table 3, it is shown that patients with vitamin D <20ng/mL have higher weight, BMI, hip circumference, and ALT, AST and ALP levels. However, we did not find significant differences regarding FLI and BARD scores using 20ng/mL cut-off.
Results of the aforementioned linear and ordered logistic regression models are presented in Tables 4 and 5. Associations between vitamin D levels and FLI and BARD scores in uni- and multivariate logistic regression analysis are shown in Table 4. Patients with lower vitamin D levels have significantly higher FLI scores [OR= 0.77 (0.07), p<0.01]. This association was maintained when adjusting to sex and age (model 1) but was lost with further adjustments (Table 4). No significant association was found between vitamin D levels and BARD score (Table 4). In Supplementary Table 1, the 12 and 20ng/mL cut-offs were applied to this analysis. Similar results were found using the 12ng/mL cut-off but not the 20ng/mL cut-off.
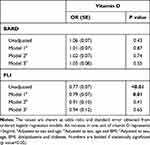 |
Table 4 Association of Vitamin D Levels with FLI and BARD Scores |
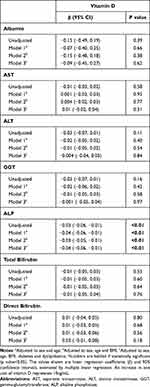 |
Table 5 Linear Association of Vitamin D Levels with Liver Function Tests |
Table 5 shows the linear association of vitamin D levels and biochemical liver parameters. A significant negative association between ALP and vitamin D levels was found [β= −0.03 (−0.06, −0.01), p<0.01], and was maintained in all models of adjustment. In Supplementary Table 2, the 12 and 20ng/mL cut-offs were applied to this analysis. Both patients with levels of vitamin D <12 and <20ng/mL had higher levels of ALP, in comparison with the groups of patients with levels of vitamin D >12 and >20ng/mL, respectively.
Discussion
In this study, performed in patients with morbid obesity, we showed that vitamin D deficiency is associated with higher weight, BMI, and hip and waist circumferences, and a higher risk of steatosis according to FLI score. While the anthropometric associations were present using both the 12ng/mL and the 20ng/mL cut-offs, the association of vitamin D deficiency with FLI score was only observed using the 12ng/mL cut-off.
Our results show that vitamin D deficiency seems to be associated with a higher risk of hepatic steatosis in patients with morbid obesity. Indeed, this is in agreement with several epidemiological studies that lean towards an association between low vitamin D levels and NAFLD, even though no causal relation can be established.26–28 Namely, Targher et al have shown that biopsy-proven NAFLD patients presented lower vitamin D levels, compared to healthy controls.9 Given the fact that vitamin D undergoes an important step of its biological activation in the liver, it is biologically plausible that chronic liver diseases, including NAFLD, can alter vitamin D metabolism and decrease its plasmatic levels.10 Another chronic liver disease which has been associated with vitamin D deficiency is hepatocellular carcinoma.29 However, similarly to vitamin D and NAFLD, this remains controversial and further research is necessary. We intend to explore this possible association in our population in future studies. Not only have other liver diseases been associated with vitamin D deficiency but also other vitamin deficiencies, such as A, C and E, have been associated with liver disease. Oxidative stress has been extensively described as a contributing factor for the development of liver disease. Antioxidant effects of vitamins A, C and E may help explain why their deficiencies may lead to liver disease.30 In future, it would be interesting to study the association between NAFLD and these three vitamins.
Recent studies have found that both patients with NAFLD and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) have lower levels of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol than patients without these diseases,8 and that levels of this hormone are negatively associated with NAFLD severity,31 raising the possibility of an association between vitamin D deficiency and the development and progression of NAFLD. Also, the expression of hepatic vitamin D receptors was found to be inversely associated with the severity of steatosis and lobular inflammation, in patients with NASH.32 It remains unclear whether vitamin D deficiency status is a contributing factor to NAFLD or simply a consequence of impaired liver function. Vitamin D has a well-established role as an anti-inflammatory molecule and is an important modulator of insulin sensitivity by inducing pancreatic β cells to release insulin and adipocytes to release adiponectin.33 These actions are important features in the prevention of fat accumulation in the liver and chronic inflammation.11 In our study, the association between vitamin D levels and hepatic steatosis, measured by FLI score, disappeared after adjustment for dyslipidaemia and diabetes. Indeed, these conditions might be important mediators and confounders of the association. Furthermore, its anti-fibrotic properties reinforce a potential beneficial effects of vitamin D in this organ.34 However, there is data contradicting these findings. Bozic et al showed that stimulation of hepatocyte vitamin D receptors in a mice model led to high-fat diet-associated liver steatosis.35 Also, in a mendelian randomization analysis, Wang et al found no causal association between vitamin D and NAFLD in a Chinese population with over 9000 participants.36 Barchetta et al performed a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial and concluded that high doses of oral vitamin D supplementation for a period of 24 weeks did not improve hepatic steatosis, measured by MRI and FLI score, nor hepatic function markers, such as liver enzymes, in patients with NAFLD and type 2 diabetes.12,37,38 Current evidence aiming to study the outcomes of high dose vitamin D supplementation in patients with NAFLD did not show any improvement in liver structure or function.39 It is important to take into account that the ideal vitamin D dose, frequency and formulation have not been determined yet.40 Some authors advocate the use of a loading dose instead of an oral daily vitamin D supplementation to achieve greater improvements in hepatic parameters.41
The controversy existing so far may rely on several factors. It may be due to the different populations studied and clinical heterogeneity of the studied populations, the variability of the diagnosis methodology used to define NAFLD, the follow-up periods and the variability of the criteria defining vitamin D deficiency. Longer intervention periods and standardized diagnostic criteria are required to clarify the disagreements in literature.
There are some limitations to our work that must be acknowledged. Firstly, this is a retrospective cross-sectional study and therefore we could not perform any imaging nor histological methods directed for NAFLD diagnosis. Also, we have not had access to data regarding other serological markers included in panels used to better predict hepatic fibrosis, nor hepatic biopsy (gold-standard to diagnose hepatic fibrosis).42 Due to its retrospective nature, no causal relation can be established. Furthermore, we only evaluated the parameters in one moment; the levels of the parameters analysed may vary according to acute events and offending factors.43,44 Nevertheless, as we evaluated a large population, we believe that our results are not strongly affected by these variations. Also, our study is clinically relevant as it involves a vast population of the frequently overlooked patients with morbid obesity, that enhances the external validity of this study.
Conclusion
Taking this in account, vitamin D deficiency seems to be associated to a higher risk of hepatic steatosis in individuals with morbid obesity. More studies, particularly prospective ones and ideally well-powered randomized controlled trials are needed to evaluate the potential role of vitamin D supplementation in the management of NAFLD.
Data Sharing Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Ethics Approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the São João Hospital Center.
Consent to Participate and for Publication
No formal consent is necessary for this type of study.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the CRIO group members for following these patients: John Rodrigues Preto; Eduardo Jorge Lima da Costa; Hugo Miguel Santos Sousa; André Manuel Costa Pinho; Selma de Maria Barbosa Souto; Carla Cristina Oliveira Rodrigues Teixeira Galego; Maria Flora Ferreira Sampaio Carvalho Correia; Cidália Fátima Castro Carção Gil; Diva Bizarro Figueiredo Melim; Eduardo Gil Ferreira Rodrigues Pinto; Marco António Costa Silva; Cristina Sarmento Pontes Martins; Luis Miguel Gonçalves Pereira; Inês Vasconcelos Sousa Magalhães; Isabel Maria Boavista Vieira Marques Brandão; Sertório Manuel Freitas Andrade and Patrícia Maria Lopes Nunes.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Disclosure
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
References
1. Alshahrani F, Aljohani N. Vitamin D: deficiency, sufficiency and toxicity. Nutrients. 2013;5(9):3605–3616. doi:10.3390/nu5093605.
2. DeLuca HF. Overview of general physiologic features and functions of vitamin D. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80(6):1689S–1696S. doi:10.1093/ajcn/80.6.1689S
3. Cimini FA, Barchetta I, Carotti S, et al. Relationship between adipose tissue dysfunction, vitamin D deficiency and the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(19):3407–3417. doi:10.3748/wjg.v23.i19.3407
4. Wimalawansa SJ. Associations of vitamin D with insulin resistance, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018;175:177–189. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.09.017
5. Prasad P, Kochhar A. Interplay of vitamin D and metabolic syndrome: a review. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2016;10(2):105–112. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2015.02.014
6. Gaman MA, Epingeac ME, Diaconu CC, et al. Evaluation of oxidative stress levels in obesity and diabetes by the free oxygen radical test and free oxygen radical defence assays and correlations with anthropometric and laboratory parameters. World J Diabetes. 2020;11(5):193–201. doi:10.4239/wjd.v11.i5.193
7. Riobo Servan P. Obesity and diabetes. Nutr Hosp. 2013;28(Suppl 5):138–143. doi:10.3305/nh.2013.28.sup5.6929
8. Wang X, Li W, Zhang Y, et al. Association between vitamin D and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: results from a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(10):17221–17234.
9. Targher G, Bertolini L, Scala L, et al. Associations between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 concentrations and liver histology in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2007;17(7):517–524. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2006.04.002
10. Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Bjelakovic M, et al. Vitamin D supplementation for chronic liver diseases in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;11:CD011564. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011564.pub2
11. Hosny S, Ali HM, Mohammed WA, El Ghannam MH. Study of relationship between total vitamin D level and NAFLD in a sample of Egyptian patients with and without T2DM. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019;13(3):1769–1771. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2019.04.002
12. Keane JT, Elangovan H, Stokes RA, Gunton JE. Vitamin D and the liver-correlation or cause? Nutrients. 2018;10(4):498. doi:10.3390/nu10040496
13. Beilfuss A, Sowa JP, Sydor S, et al. Vitamin D counteracts fibrogenic TGF-beta signaling in human hepatic stellate cells both receptor-dependently and independently. Gut. 2015;64(5):64. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307024
14. Beilfuss A, Sowa JP, Sydor S, et al. Vitamin D counteracts fibrogenic TGF-beta signalling in human hepatic stellate cells both receptor-dependently and independently. Gut. 2015;64(5):791–799. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307024
15. Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guidance from the American association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67:328–357. doi:10.1002/hep.29367
16. Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, et al. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64(1):73–84. doi:10.1002/hep.28431
17. Cheah MC, McCullough AJ, Goh GB. Current modalities of fibrosis assessment in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2017;5(3):261–271. doi:10.14218/JCTH.2017.00009
18. European Association for the Study of the L, European Association for the Study of D and European Association for the Study of O. EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64(6):1388–1402. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.004.
19. von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, et al. The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Int J Surg. 2014;12(12):1495–1499. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.07.013
20. Guimarães RRP, Santos A, Santos A, et al. Reuse of clinical records for scientific research: legal issues related to the authorization of the holders and anonymisation. Acta Med Port. 2018;31(6):299–302. doi:10.20344/amp.10147
21. American Diabetes A. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in Diabetes—2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(Supplement 1):S13–S28. doi:10.2337/dc19-S002.
22. Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W. 2018 ESC/ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:3021–3104. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339
23. Expert Panel on Detection E and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in A. Executive summary of the third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III). JAMA. 2001;285(19):2486–2497. doi:10.1001/jama.285.19.2486.
24. Bedogni G, Bellentani S, Miglioli L, et al. The fatty liver index: a simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006;6(1):33. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-6-33
25. Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(7):1911–1930. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0385
26. Eliades M, Spyrou E, Agrawal N, et al. Meta-analysis: vitamin D and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013;38(3):246–254. doi:10.1111/apt.12377
27. Liangpunsakul S, Chalasani N. Serum vitamin D concentrations and unexplained elevation in ALT among US adults. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56(7):2124–2129. doi:10.1007/s10620-011-1707-x
28. Eliades M, Spyrou E. Vitamin D: a new player in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(6):1718–1727. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i6.1718
29. Zhang Y, Jiang X, Li X, et al. Serum vitamin D levels and risk of liver cancer: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies. Nutr Cancer. 2020:1–9. doi:10.1080/01635581.2020.1797127.
30. Gheorghe GSA, Gaman MA, Gaman M-A, et al. The benefits and risks of antioxidant treatment in liver diseases. Rev Chim. 2019;70(2):651–655. doi:10.37358/RC.19.2.6977
31. Barchetta I, Angelico F, Del Ben M, et al. Strong association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and low 25(OH) vitamin D levels in an adult population with normal serum liver enzymes. BMC Med. 2011;9(1):85. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-9-85
32. Barchetta I, Carotti S, Labbadia G, et al. Liver vitamin D receptor, CYP2R1, and CYP27A1 expression: relationship with liver histology and vitamin D3 levels in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis or hepatitis C virus. Hepatology. 2012;56(6):2180–2187. doi:10.1002/hep.25930
33. Alfadda AA, Masood A, Shaik SA, et al. Association between osteocalcin, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular risk factors: role of total and undercarboxylated osteocalcin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int J Endocrinol. 2013;2013:197519. doi:10.1155/2013/197519
34. Abramovitch S, Sharvit E, Weisman Y, et al. Vitamin D inhibits development of liver fibrosis in an animal model but cannot ameliorate established cirrhosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015;308(2):G112–120. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00132.2013
35. Bozic M, Guzman C, Benet M, et al. Hepatocyte vitamin D receptor regulates lipid metabolism and mediates experimental diet-induced steatosis. J Hepatol. 2016;65(4):748–757. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2016.05.031
36. Wang N, Chen C, Zhao L, et al. Vitamin D and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: bi-directional mendelian randomization analysis. EBioMedicine. 2018;28:187–193. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.12.027
37. Barchetta I, Del Ben M, Angelico F, et al. No effects of oral vitamin D supplementation on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Med. 2016;14(1):92. doi:10.1186/s12916-016-0638-y
38. Han H, Cui M, You X, et al. A role of 1,25(OH)2D3 supplementation in rats with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis induced by choline-deficient diet. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015;25(6):556–561. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2015.02.011
39. Tabrizi R, Moosazadeh M, Lankarani KB, et al. The effects of vitamin D supplementation on metabolic profiles and liver function in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2017;11:S975–S982. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2017.07.025
40. Yodoshi T, Orkin S, Arce-Clachar AC, et al. Vitamin D deficiency: prevalence and association with liver disease severity in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2020;74(3):427–435. doi:10.1038/s41430-019-0493-y
41. Papapostoli I, Lammert F, Stokes CS. Effect of short-term vitamin d correction on hepatic steatosis as quantified by controlled attenuation parameter (CAP). J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2016;25(2):175–181. doi:10.15403/jgld.2014.1121.252.cap
42. Gheorghe G, Bungau S, Ceobanu G, et al. The non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis. J Formos Med Assoc. 2020. doi:10.1016/j.jfma.2020.08.019
43. Kaplowitz N. Drug-induced liver injury. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38(Suppl 2):S44–48. doi:10.1086/381446
44. Purkins L, Love ER, Eve MD, et al. The influence of diet upon liver function tests and serum lipids in healthy male volunteers resident in a Phase I unit. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004;57(2):199–208. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01969.x
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.