Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 8
The efficacy of bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.07% dosed once daily in achieving zero-to-trace anterior chamber cell severity following cataract surgery
Authors Silverstein S , Jackson M , Goldberg D, Muñoz M
Received 8 January 2014
Accepted for publication 6 February 2014
Published 16 May 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 965—972
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S60292
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Steven M Silverstein,1 Mitchell A Jackson,2 Damien F Goldberg,3 Mauricio Muñoz4
On behalf of the Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution 0.07% Once Daily Study Group
1Silverstein Eye Centers, Kansas City, MO, USA; 2Jacksoneye, Inc., Lake Villa, IL, USA; 3Wolstan & Goldberg Eye Associates, Torrance, CA, USA; 4Bausch + Lomb, Irvine, CA, USA
Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy of bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.07% dosed once daily in achieving zero-to-trace (0–5 cells) anterior chamber cells, following cataract surgery with posterior chamber intraocular lens implantation.
Methods: The study designed employed two Phase III, double-masked, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trials of 440 subjects, randomized to either bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.07% (n=222) or placebo (n=218). Subjects self-dosed once daily, beginning 1 day before undergoing cataract surgery with intraocular lens implantation (day −1) and again on the day of surgery (day 0) and for 14 days postoperatively. Follow-up was on days 1, 3, 8, and 15. The outcome measures included the percentage of subjects with zero-to-trace anterior chamber cells at each visit, as determined by the percentage of subjects with ≤5 anterior chamber cells, overall anterior chamber cell grades, and summed ocular inflammation score (SOIS) (combined anterior chamber cell and flare scores).
Results: The proportion of subjects with zero-to-trace anterior chamber cells was significantly higher in the bromfenac 0.07% group compared with the placebo group as early as day 3 (P=0.0007), continued at day 8 (P<0.0001), and through day 15 (P<0.0001). At day 15, 80.2% of subjects in the bromfenac 0.07% group achieved zero-to-trace anterior chamber cells compared with 47.2% of subjects who did so in the placebo group. The overall anterior chamber cell scores were significantly lower in the bromfenac 0.07% group compared with the placebo group at days 3, 8, and 15 (P<0.0001 at each visit). The SOIS were also significantly lower in the bromfenac group compared with the placebo group at days 3, 8, and 15 (P<0.0001 at each visit).
Conclusion: Bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.07%, dosed once daily was clinically effective in achieving zero-to-trace anterior chamber cell severity after cataract surgery and was superior to placebo in all anterior chamber cell severity and inflammation outcome measures.
Keywords: ocular inflammation, anterior chamber inflammation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, cells and flare
Introduction
Cataract surgery is the most frequently performed surgical procedure worldwide.1,2 With improvements in surgical techniques, patients’ expectations have risen proportionally;3 however, differences in surgical technique impact the severity of surgical trauma and postsurgical recovery.2 The amount of postsurgical ocular pain and inflammation a patient has will play a significant role in his/her perception of the surgical success. Prospective studies assessing the incidence of postoperative pain have reported that one-third of patients experience pain in the early hours following cataract surgery, and the majority of those patients (79%) continued to experience pain after leaving the surgical facility.4 Anterior chamber ocular inflammation, clinically assessed as anterior chamber cell counts and flare, is also common following cataract surgery. However, postoperative inflammation is frequently viewed as an acceptable risk that is largely outweighed by the numerous benefits of cataract surgery.3 The management of postoperative inflammation is essential, both to ensure rapid recovery following the surgery as well as to prevent or decrease the potential for long-term complications, such as cystoid macular edema.5
Postoperative pain and inflammation following phacoemulsification and intraocular lens (IOL) implantation are often managed with topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Recently, this management regimen has been extended to include dosing prior to and on the day of surgery, to potentially improve analgesia, reduce intra- and postoperative inflammation, and to minimize the risk of postoperative complications.6 Bromfenac ophthalmic solution has been evaluated in numerous clinical studies in both Japan and the United States (US)7–14 and has been shown to be a potent inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX). The COX enzyme promotes prostaglandin synthesis by converting arachidonic acid into prostaglandin, a necessary component for the onset of inflammation.15–19 By blocking both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, the release of potent inflammatory mediators located primarily in the iris and ciliary body, such as prostaglandin E2, is prevented. In vitro studies have shown the IC50 values (the concentration of NSAID needed to inhibit 50% of either COX-1 or COX-2) are even lower for COX-2, the inducible enzyme primarily responsible for prostaglandin E2, a potent inflammatory mediator in surgical trauma.16,18 Bromfenac sodium is designated chemically as sodium 2-amino-3-(4-bromobenzoyl) phenylacetate sesquihydrate.20 The addition of a bromine atom improves the absorption and penetration into ocular tissue and allows for an increased duration of effect.21,22 The inclusion of bromine also increases the potency against the COX-2 enzyme by providing an approximate tenfold greater lipophilicity.23 Bromfenac ophthalmic solution was first commercially available in Japan as Bronuck® (Senju Pharmaceuticals Co, Ltd, Osaka, Japan) and was approved for the treatment of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, scleritis, and postoperative inflammation.24 Bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.09% (Xibrom™; ISTA Pharmaceuticals Inc., Irvine, CA, USA), with no predosing and twice-daily administration for 14 days, was granted approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), in March 2005, for the treatment of ocular inflammation after cataract surgery with posterior chamber IOL implantation; this was amended, in January 2006, to include the reduction of postoperative ocular pain.25 This initial bromfenac 0.09% solution was formulated with a pH of 8.3.
The reduction of ocular inflammation in the bromfenac 0.09% twice-daily clinical trials assessed zero-to-trace inflammation (0−5 cells and no flare in the anterior chamber).9 Subsequent trials assessing the reduction of anterior chamber inflammation following cataract surgery, with bromfenac 0.09% dosed once daily (which also had a pH of 8.3), found the agent to be effective in the complete clearance of inflammation at all-time points (days 3, 8, and 15) compared with placebo, as well as in reducing ocular inflammation to zero-to-trace levels.10 The US FDA approved bromfenac 0.09% (Bromday®; ISTA Pharmaceuticals Inc.) on October 16, 2010; this was the first once-daily ophthalmic NSAID for the treatment of postoperative ocular inflammation and reduction of ocular pain in patients who have undergone cataract extraction with posterior chamber IOL implantation.20 Overall, since its initial approval, bromfenac has been a beneficial addition to the standard of care in the reduction of ocular inflammation.
Following the approval of Xibrom and Bromday, an advanced formulation of bromfenac ophthalmic solution was developed to improve ocular penetration, thereby allowing for a reduction of the concentration of the active ingredient, bromfenac, to 0.07%. The pH was reduced, from 8.3 in the 0.09% concentration to 7.8 in the 0.07% concentration, in order to increase the lipophilicity of the molecule. The reduction in pH to a more physiologic level, closer to that of normal tears, may also improve ocular comfort upon instillation. The hypothesis for the current clinical trials was that the once-daily bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.07% would be effective in reducing ocular inflammation and pain after cataract surgery. The specific intent of the analysis was to evaluate the efficacy of bromfenac 0.07% for reducing the level of postoperative anterior chamber inflammatory cells to trace or better. Of note: at the time of these studies, bromfenac 0.09% once daily (Bromday) was marketed in the United States; since the US regulatory approval of bromfenac 0.07% (PROLENSA®; Bausch + Lomb, Bridgewater, NJ, USA), Bromday has been discontinued.
Subjects and methods
Subjects and study design
The current analyses comprised of two multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled, clinical trials (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01367249;26 approval received from Sterling Institutional Review Board, Atlanta, GA, USA) that evaluated 440 subjects. The clinical trials27 were split geographically into an east and a west region of the US (Study S00124-ER and Study S00124-WR, respectively). Each clinical trial enrolled subjects using separate randomization sequences, and each was comprised of a minimum of 75 subjects in order to generate sufficient data to demonstrate statistical significance.
The clinical trials were conducted in accordance and adherence with the Declaration of Helsinki (Edinburgh 2000), the Code of Federal Regulations, and the International Conference on Harmonisation, and maintained patient confidentiality and complied with the US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.27 Written informed consent was received from each subject prior to any study-related procedure.
Sample size calculations
A sample size of 75 subjects per treatment arm provided 80% power to detect a treatment effect equivalent to that seen with a previous bromfenac formulation.10 This calculation was based on a two-sided Fisher’s exact test of independent proportions conducted with an alpha =0.05 and was performed using PASS (version 2005; NCSS, Kaysville, UT, USA). In order to account for a potential dropout rate of 30%, the required sample size was increased to 200 subjects, 100 per group.
This current study is a subset analysis of a larger study on the safety and efficacy of bromfenac 0.07% that used those same sample size calculation parameters.27
Study protocol
These post hoc analyses were based on Phase III clinical trials conducted between May 2011 and July 2011; the results of the primary endpoints have been previously reported.27 Briefly, all the subjects were randomized to receive either bromfenac 0.07% or placebo; the subjects and study personnel were masked to treatment.27 Dosing of the test agent began 1 day prior to surgery (day −1), and continued on the day of surgery (day 0) and for 14 days after surgery, for a total of 16 drops of the investigational eye drop. Subjects self-instilled the topical eye drops into the inferior conjunctival cul de sac of the study eye. A follow-up visit was scheduled on days 1, 3 (±1), 8 (±1), and 15 (±1) after cataract surgery. A safety follow-up visit was performed on day 22 (±3) or on day 7 (±3) if the subject prematurely discontinued the eye drops.27
Topical antibiotics were permitted per the investigators’ standard practice of postcataract surgery treatment. No other ocular, topical, or systemic NSAIDs were allowed. Ocular, topical, or systemic gentamicin was not allowed. No form of opioid, narcotic or any other pain-relieving medication that could have interfered with the interpretation of the study results, (eg, gabapentin, pregabalin, or COX-2 inhibitors) was allowed. The use of acetaminophen (up to 4,000 mg/day) during the study and/or an opioid during surgery (ie, fentanyl) was allowed. Topical cyclosporine 0.05% was not allowed. The use of ocular, topical, inhaled, or oral corticosteroids within 15 days prior to the initiation of dosing with the investigational study medication or depot corticosteroids within 45 days prior to initiation of dosing with the investigational study medication or throughout the duration of the study was also prohibited.
Outcome measures
Efficacy
The outcome measures in the analyses included the proportion of subjects with ≤5 anterior chamber cells, overall anterior chamber cell grades, anterior chamber cell grades by frequency/severity, and overall anterior chamber inflammation. Anterior chamber cell grades were determined twice per study visit and were based on a manual count of cells using a slit lamp biomicroscope (Table 1). Each of the aforementioned endpoints was assessed at days 1, 3, 8, and 15.
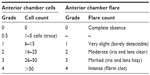  | Table 1 Ocular inflammation grading scale |
Safety
As with the earlier published study,27 the safety factors were assessed by the incidence and frequency of ocular and systemic adverse events (AEs), ophthalmological evaluations (visual acuity, slit lamp examination, intraocular pressure [IOP], and dilated funduscopic examination), as well as the Ocular Comfort Grading Assessment (OCGA) that subjects completed within 1 hour after instilling the investigational product into their study eye.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
For this analysis, the inclusion and exclusion criteria were the same as in the pivotal Phase III clinical trials.27 Some key inclusion criteria included subjects ≥18 years of age scheduled for unilateral cataract surgery with posterior chamber IOL implantation and no other concurrent ophthalmic surgical procedures. Visual acuity at baseline had to be logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution (logMAR) 0.6 or better in the nonstudy eye. The primary exclusion criterion was extraocular/intraocular inflammation (any cell or flare in the anterior chamber, as assessed using slit lamp biomicroscopy examination) in either eye at screening, including ongoing, unresolved uveitis. Subjects were also excluded if they had administered ocular, topical, or systemic NSAIDs within 1 week of the study initiation or administered ocular, topical, inhaled, or systemic corticosteroids within 15 days of the study initiation. Finally, the IOP had to be between 5−22 mmHg in the study eye at screening.
Study medications
The study medications were provided by the study sponsor (Bausch + Lomb) and included bromfenac 0.07% (Bausch + Lomb) and placebo (vehicle-controlled ophthalmic solution; Bausch + Lomb and JHP Pharmaceuticals, LLC, Parsippany, NJ, USA). The ophthalmic solutions were identically formulated, with the exception that the placebo did not include bromfenac. The study medications were supplied in identical bottles with trial-specific labels, and each of the bottles was placed into a tamper-evident carton. Both the bottles and the cartons were masked to all study participants and investigators.
Adverse events, safety, and analysis
The AEs included the incidence and frequency of both ocular and systemic AEs. Safety was assessed on study day 22 and included all subjects who received at least one dose of the study medication. All subjects were included in the intent-to-treat population; investigators used the last observation carried forward (LOCF) for efficacy outcomes if a follow-up visit was missed.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was performed, comparing the bromfenac 0.07% once daily data with placebo data, at each study visit. The P-values were derived from a Fisher’s exact test, adjusted for multiple comparisons using Hochberg’s method. The treatment difference was calculated by subtracting the placebo percentage from the bromfenac percentage.
Results
A total of 440 subjects were enrolled and randomized to receive bromfenac 0.07% (n=222) or placebo (n=218). The disposition of the subjects has been previously reported.27 The mean age in the bromfenac 0.07% arm was 68.4 years compared with 68.5 years in the placebo arm; these were not statistically different. There were significantly more females enrolled in both arms (141/222 in the bromfenac arm and 146/218 in the placebo arm). Table 2 provides an overview of the completion rates in the two arms.
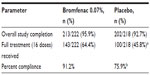  | Table 2 Subject completion |
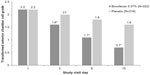
In the LOCF population, at day 15, the proportion of subjects with ≤5 anterior chamber cells was significantly higher in the bromfenac 0.07% group (80.2%) compared with those in the placebo group (47.2%) (P<0.0001). The proportion of subjects with ≤5 anterior chamber cells was also significantly higher in the bromfenac 0.07% group at days 3 and 8 compared with the placebo group (P=0.0007 and P<0.0001 respectively) (Figure 1).
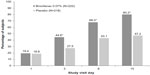  | Figure 1 Trace anterior chamber cells (cell count ≤5) at each visit day. |
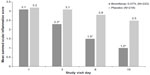
The overall anterior chamber cell grades were significantly lower in the bromfenac group by as early as day 3 and continued through days 8 and 15 (all P<0.0001) (Figure 2). When the anterior chamber cell grades were assessed by severity, a significantly higher proportion of subjects in the bromfenac group had low severity scores at days 3, 8, and 15 compared with subjects in the placebo group (all P<0.001). Conversely, there was a significantly higher proportion of subjects in the placebo group with high severity scores at days 3, 8, and 15 compared with those in the bromfenac group (Figure 3). Finally, the summed ocular inflammation score (SOIS), which took into account anterior chamber cell count and flare, were significantly lower in the bromfenac group at days 3, 8, and 15 compared with the placebo group (all P<0.0001) (Figure 4).
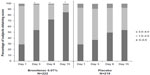  | Figure 3 Severity of anterior chamber cell scores. |
Safety endpoints
There were 416 subjects who met the criteria for inclusion in the safety analysis (received at least one eye drop). The safety and tolerability of bromfenac 0.07% has been previously reported;27 the incidence of AEs was significantly lower in the bromfenac 0.07% group than in the placebo group (P=0.0041).
Adverse events
Overall, 31.3% (130/416) of subjects experienced an AE affecting the study eye. There was a significantly lower incidence of AEs affecting the study eye in the bromfenac 0.07% group (48/212 [22.6%]) than in the placebo group (82/204 [40.2%]) (P=0.0001). A lower proportion of subjects in the bromfenac 0.07% group (15/212 [7.1%]) experienced AEs related to the eye drop in the study eye compared with those in the placebo group (21.6%, 44/204). Ocular AEs related to the instilled drops occurred in ≥2% of subjects, as follows: eye pain (7.8%, placebo; 2.8%, bromfenac), anterior chamber inflammation (5.4%, placebo; 2.4%, bromfenac), conjunctival hyperemia (3.9%, placebo; 0.9%, bromfenac), photophobia (3.9%, placebo; 0.5%, bromfenac), corneal edema (2.5%, placebo; 0.5%, bromfenac), increased lacrimation (2.5%, placebo; 0.5%, bromfenac), foreign body sensation (2.5%, placebo; 0%, bromfenac), and ocular hyperemia (2%, placebo; 0% bromfenac).
Discussion
Physicians are aware that clinical FDA studies mandate that the efficacy endpoint of NSAID trials include the proportion of subjects with an SOIS of 0, yet in practical daily experience, a noteworthy percentage of patients have 1−5 anterior chamber cells for longer than 2 weeks following cataract surgery. By reporting trace cell data, this study more aptly reflects the experience of the nontrial environment. In these analyses of the zero-to-trace anterior chamber cell severity and inflammation in the bromfenac 0.07% Phase III clinical trials, the findings consistently demonstrated that bromfenac 0.07% effectively reduced anterior chamber cell and flare compared with placebo, beginning as early as study visit day 3 and continuing through study visit day 15. Additionally, there were significantly fewer AEs reported in the bromfenac 0.07% group compared with participants in the placebo group.
The clinical results are similar to other trials evaluating higher concentrations of bromfenac.9,10,28 In a twice-daily dosing study, bromfenac 0.09% was able to reduce ocular inflammation to trace or cleared levels by day 3.9 In a more recent study evaluating bromfenac 0.09% dosed once daily, a post hoc analysis found that 78.7% of the bromfenac 0.09% once-daily group reached zero-to-trace inflammation by day 15, compared with only 42% who did so in the placebo group.10
Direct comparisons of bromfenac 0.07% with other versions of bromfenac are not possible as other currently approved formulations are of a higher concentration, have different pH levels, and/or the clinical trials on those formulations did not necessarily include predosing. However, the overall results with both the once- and twice-daily versions of bromfenac 0.09%, as well as the once-daily dosing of bromfenac 0.07%, reconfirm the potency of the bromfenac molecule in reducing inflammation in the postcataract surgery population. This analysis also indicates that a lower concentration of bromfenac solution could be as efficacious in reducing cell and flare as a higher concentration of bromfenac solution.
Most importantly, by maintaining the efficacy of already-approved bromfenac 0.09% formulations and potentially improving the absorption across the hydrophobic corneal barrier, via the pH adjustment, to a more physiologic pH, once-daily bromfenac 0.07% solution may improve comfort and tolerability, particularly at the corneal and/or ocular surface level. The incidence of adverse events was significantly lower in the bromfenac 0.07% group than in the placebo group and similar to those of earlier formulations of bromfenac.
Safety profiles among ophthalmic NSAIDs are important as the early 1990s taught us a valuable lesson about topical NSAID safety in terms of corneal AEs, such as corneal melts.29 Corneal infiltrates and ulcerative keratolysis were associated, in 117 cases, to either diclofenac (27%−61%) or ketorolac (12%) in the early 2000s.6 The reported incidence of serious AEs over the course of 6 years in patients who used bromfenac has been found to be extremely low, at 0.0002%.30,31
The limitations of the current clinical trials have been previously reported27 and include a smaller sample size than in other clinical trials evaluating higher concentrations of bromfenac and an overwhelming number of Caucasian subjects in the bromfenac 0.07% arm. These factors prevent us from making direct comparisons with other clinical trial results.
In summary, the clinical trials clearly demonstrated that the proportion of subjects with zero-to-trace anterior chamber cells was significantly higher in the bromfenac 0.07% group, while the overall anterior chamber cell severity and SOIS were significantly lower in the bromfenac 0.07% group compared with placebo. Based in part on these results of the Phase III clinical trials, on April 5, 2013, the US FDA approved once-daily use of bromfenac 0.07% (PROLENSA®) for the treatment of postoperative inflammation and reduction of ocular pain in patients who have undergone cataract surgery.32 In future clinical assessments, bromfenac 0.07% may be further evaluated in other ocular inflammatory disorders where NSAID use may be potentially beneficial.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sharon M Klier, MD, for contributions to the protocol conception and design, and data acquisition; and Michelle Dalton, BS, ELS, for medical writing assistance. These clinical trials were supported by Bausch + Lomb.
The Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution 0.07% Once Daily Study Group members were:
S00124-WR; Jason Bacharach, MD; Donald Beahm, MD; James Boyce, MD; E Randy Craven, MD; Jung Dao, MD; Michael Depenbusch, MD; Eran Duzman, MD; Joseph Gira, MD; Damien Goldberg, MD; Kerry Hagen, MD; Michael Korenfeld, MD; Ryan McKinnon, MD; Karl Olsen, MD; James Peace, MD; Kenneth Sall, MD; David L Schwartz, MD; Steven Silverstein, MD; Robert Smyth-Medina, MD; Jon-Marc Weston, MD.
S00124-ER; Mark Bergmann, MD; Robert Berry, MD; Leonard Cacioppo, MD; David Cooke, MD; Thomas Elmer, MD; William Flynn, MD; Ronald Frenkel, MD; Marvin Greenberg, MD; Brennan Greene, MD; Mitchell Jackson, MD; Lawrence Katzen, MD; John Lim, MD; Parag Majmudar, MD; Bernard Perez, MD; Francis Price, Jr, MD; Eugene Protzko, MD; Harvey Reiser, MD; Stephen Smith, MD; W Colby Stewart, MD; Thomas Walters, MD.
Disclosure
Study support was provided by Bausch + Lomb, Irvine, CA, USA. The sponsor participated in the design of the study, data collection, data management, data analyses, data interpretation, preparation, review, and approval of the manuscript. The authors report no other conflicts of interest.
References
Harrer A, Gerstmeyer K, Hirnschall N, Pesudovs K, Lundström M, Findl O. Impact of bilateral cataract surgery on vision-related activity limitations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013;39(5):680–685. | |
Porela-Tiihonen S, Kaarniranta K, Kokki H. Postoperative pain after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013;39(5):789–798. | |
Monnet D, Tépenier L, Brézin AP. Objective assessment of inflammation after cataract surgery: comparison of 3 similar intraocular lens models. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35(4):677–681. | |
Porela-Tiihonen S, Kaarniranta K, Kokki M, Purhonen S, Kokki H. A prospective study on postoperative pain after cataract surgery. Clin Ophthalmol. 2013;7:1429–1435. | |
Gulkilik G, Kocabora S, Taskapili M, Engin G. Cystoid macular edema after phacoemulsification: risk factors and effect on visual acuity. Can J Ophthalmol. 2006;41(6):699–703. | |
O’Brien TP. Emerging guidelines for use of NSAID therapy to optimize cataract surgery patient care. Curr Med Res Opin. 2005;21(7):1131–1137. | |
Ahuja M, Dhake AS, Sharma SK, Majumdar DK. Topical ocular delivery of NSAIDs. AAPS J. 2008;10(2):229–241. | |
Cho H, Wolf KJ, Wolf EJ. Management of ocular inflammation and pain following cataract surgery: focus on bromfenac ophthalmic solution. Clin Ophthalmol. 2009;3:199–210. | |
Donnenfeld ED, Holland EJ, Stewart RH, Gow JA, Grillone LR; Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution 0.09% (Xibrom) Study Group. Bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.09% (Xibrom) for postoperative ocular pain and inflammation. Ophthalmology. 2007;114(9):1653−1662. | |
Henderson BA, Gayton JL, Chandler SP, Gow JA, Klier SM, McNamara TR; Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution (Bromday) Once Daily Study Group. Safety and efficacy of bromfenac ophthalmic solution (Bromday) dosed once daily for postoperative ocular inflammation and pain. Ophthalmology. 2011;118(11):2120–2127. | |
Ridgway D. Analgesics for acute pain: Meeting the United States Food and Drug Administration’s requirements for proof of efficacy. Clin J Pain. 2004;20(3):123–132. | |
Silverstein SM, Cable MG, Sadri E, et al; Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution Once Daily (Bromday) Study Group. Once daily dosing of bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.09% for postoperative ocular inflammation and pain. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011;27(9):1693–1703. | |
Miyake K, Ogawa T, Tajika T, Gow JA, McNamara TR. Ocular pharmacokinetics of a single dose of bromfenac sodium ophthalmic solution 0.1% in human aqueous humor. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2008;24(6):573–578. | |
Mukai K, Matsushima H, Gotoh N, et al. Efficacy of ophthalmic nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in suppressing anterior capsule contraction and secondary posterior capsule opacification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35(9):1614–1618. | |
Colin J. The role of NSAIDs in the management of postoperative ophthalmic inflammation. Drugs. 2007;67(9):1291–1308. | |
Csukas S, Paterson CA, Brown K, Bhattacherjee P. Time course of rabbit ocular inflammatory response and mediator release after intravitreal endotoxin. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1990;31(2):382–387. | |
Koay P. The emerging roles of topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents in ophthalmology. Br J Ophthalmol. 1996;80(5):480–485. | |
Warner TD, Mitchell JA. Cyclooxygenases: new forms, new inhibitors, and lessons from the clinic. FASEB J. 2004;18(7):790–804. | |
Walters T, Raizman M, Ernest P, Gayton J, Lehmann R. In vivo pharmacokinetics and in vitro pharmacodynamics of nepafenac, amfenac, ketorolac, and bromfenac. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33(9):1539–1545. | |
Bromday® (bromfenac ophthalmic solution) 0.09% [package insert]. Irvine, CA: ISTA Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2011. | |
Sancilio LF, Nolan JC, Wagner LE, Ward JW. The analgesic and antiinflammatory activity and pharmacologic properties of bromfenac. Arzneimittelforschung. 1987;37(5):513–519. | |
Walsh DA, Moran HW, Shamblee DA, et al. Antiinflammatory agents. 3. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of 2-amino-3-benzoylphenylacetic acid and analogues. J Med Chem. 1984;27(11):1379−1388. | |
Ruiz J, López M, Milà J, Lozoya E, Lozano JJ, Pouplana R. QSAR and conformational analysis of the antiinflammatory agent amfenac and analogues. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 1993;7(2):183–198. | |
Bronuck® (bromfenac ophthalmic solution) 0.1% [package insert]. Osaka, Japan: Senju Pharmaceutical Co, 2009. | |
Xibrom™ (bromfenac ophthalmic solution) 0.09% [package insert]. Irvine, CA: ISTA Pharmaceuticals, 2010. | |
Bausch & Lomb Incorporated. Efficacy of Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution in Patients Undergoing Cataract Surgery. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01367249. NLM identifier: NCT01367249. Accessed March 3, 2014. | |
Walters TR, Goldberg DF, Peace JH, Gow JA; Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution 0.07% Once Daily Study Group. Bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.07% dosed once daily for cataract surgery: results of 2 randomized controlled trials. Ophthalmology. 2014;121(1):25–33. | |
Miyake-Kashima M, Takano Y, Tanaka M, et al. Comparison of 0.1% bromfenac sodium and 0.1% pemirolast potassium for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2004;48(6):587−590. | |
Price FW. New pieces for the puzzle: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corneal ulcers. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26(9):1263–1265. | |
Carreño E, Portero A, Galarreta DJ, Herreras JM. Update on twice-daily bromfenac sodium sesquihydrate to treat postoperative ocular inflammation following cataract extraction. Clin Ophthalmol. 2012;6:637–644. | |
Donnenfeld ED, Donnenfeld A. Global experience with Xibrom (bromfenac ophthalmic solution) 0.09%: the first twice-daily ophthalmic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2006;46(4):21–40. | |
Prolensa™ (bromfenac ophthalmic solution) 0.07% [package insert]. Tampa, FL: Bausch Lomb, 2013. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.