Back to Journals » Cancer Management and Research » Volume 13
The Efficacy and Toxicity of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Regimens of Epirubicin Plus Cyclophosphamide Followed by Docetaxel or Paclitaxel in Female Breast Cancer Patients
Authors Wu X, Ye C, Wang X, Cai R, Yang J, Yu X, Zhou Y, Shen L, Zhu Y, Liu X
Received 30 September 2020
Accepted for publication 25 January 2021
Published 15 February 2021 Volume 2021:13 Pages 1517—1527
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S284638
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Xian Wu,1,* Chaoran Ye,1,* Xingmeng Wang,2 Ruyu Cai,1 Junzhe Yang,1 Xiafei Yu,1 Yi Zhou,1 Li Shen,1 Yanhui Zhu,1 Xiaoan Liu1
1Department of Breast Surgery, The First Affiliated HospitalofNanjing Medical University, Nanjing, 210029, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of General Surgery, The First People’s Hospital of Yancheng City, Yancheng, 224006, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Correspondence: Yanhui Zhu; Xiaoan Liu Tel +86-25-68308152
Email [email protected]; [email protected]
Purpose: To retrospectively analyze the efficacy and toxicity of epirubicin plus cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel (EC-D) and epirubicin plus cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel (EC-P) efficacy as neoadjuvant chemotherapy regiments by pathological complete response (pCR) in this study.
Methods: In total, 455 patients diagnosed with breast cancer who received NAC from January 2014 to January 2019 were enrolled. Of which, 109 patients received EC-D (E: 90, C: 600, D: 80, all in mg/m2) and 346 were treated with EC-P (E: 90, C: 600, D: 175, all in mg/m2). Efficacy of NAC regimens was evaluated by pCR, and the toxicity was studied. Chi-squared test was used at p=0.05.
Results: In EC-D, 11 patients received ypT0/isN0, and 6 of them got ypT0N0. Analogously, 67 patients receiving received EC-P obtained ypT0/isN0, and 43 people of them acquired ypT0N0. The rate of pCR in EC-P was higher than EC-D. Patients with ER (-), PR (-), Her-2 (+) and high Ki-67 index were easier to were more likely to acquire pCR. Two pCRs were described, the pCR of NAC differed according to the definition. In terms of side effects, there was no significant difference in platelet and urea, but the decrease of hemoglobin and creatinine levels after EC-P treatment was more significant than that after EC-D treatment.
Conclusion: The efficacy of EC-P is better than EC-D if pCR is to be determined as a surrogate end-point for prognosis. The patients with anemia or renal insufficiency who need to receive NAC should choose EC-D.
Keywords: neoadjuvant chemotherapy, pathological complete response, EC-D, EC-P, toxicity of anticancer drugs
Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common tumor in women and the second cause of cancer-related mortality globally.1 So far, a growing number of therapies have been investigated to treat breast carcinomas. Among them, neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is very important, as it can observe chemosensitivity and reduce micrometastasis for locally advanced breast malignancy.2 Most significantly, it can reduce the size of the tumor and provide patients with more surgical options.
NAC has many regimes. As reported, adding taxanes to an anthracycline-based regime further reduces recurrence and mortality,3 and thus, plays an important role in NAC. However, the optimal dose and interval period of this regime remain to be discussed.
The principal outcome endpoint of NAC is the pathological complete response (pCR) rate, which has two main explanations.4 One explanation (ypT0/isN0) is that surgical specimens have no invasive tumour cells, but ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) can be allowed in breast is permissible. The other one (ypT0N0) is that no tumor cell can appear in the breast and lymph nodes, including DCIS. In this retrospective study, these two explanations of pCR were discussed separately.
Firstly, the efficacy and adverse effects were compared between two groups: (1) epirubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel every 3 weeks (EC-D) and (2) epirubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel every 2 weeks (EC-P) in NAC. Then, the correlations among different curative effects and factors (eg age, menstrual status, molecular type) were investigated in order to dig out the therapy and individualized treatment of breast cancer.
Methods
Patients
This retrospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China, and the Helsinki Declaration. In addition, written and informed consents were received from the patients. Totally 455 patients diagnosed with breast cancer who received NAC at the tested Hospital from January 2014 to January 2019 were recruited.
Inclusion criteria were as follows:
(1) Gender: female
(2) Age: ≥18 years old
(3) Diagnosis of breast cancer by pathology
(4) Preoperative chemotherapy
(5) Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) grade: 0–1
Exclusion criteria were as follows:
(1) Gender: male
(2) Age: <18 years old
(3) ECOG grade: 2 and above
(4) Surgery during chemotherapy interval
(5) Incomplete postoperative pathological data
(6) Patients with kidney disease and blood disease
Evaluation Parameters
Histological diagnosis, estrogen receptor (ER) status, progesterone receptor (PR) status, Her-2 status and Ki-67 index were detected via standard immunohistochemistry (IHC), Her-2 status would be confirmed by fluorescence in situ hybridization If 2+ IHC staining was present. The molecular typing was divided into four types: luminal A-like, luminal B-like, Her-2 overexpression, and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). The definitions of pCR were the same as above. Furthermore, we compared the effects of different NAC regimens on hemoglobin, platelets and renal function, and provided these results using Sysmexs-800i hematology analyzer (Sysmex Corporation, Kobe, Japan).
Treatment
The doses of NAC were decided based on the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) guidelines for breast cancer: (1) epirubicin plus cyclophosphamide (E:90 mg/m2, C:600 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by docetaxel (D:80 mg/m2,) every 3 weeks for four cycles; (2) epirubicin plus cyclophosphamide (E:90 mg/m2, C:600 mg/m2) every 2 weeks for four cycles followed by paclitaxel (D:175 mg/m2) every 2 weeks for four cycles. Patients with Her-2 (+) disease were concomitantly treated with trastuzumab in the four cycles and then with trastuzumab for 1 year totally. All people received systematic granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) 48 hours after chemotherapy.
Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed on SPSS 22.0. Mean and standard deviation (SD) were evaluated using an independent sample t-test. In the univariate analysis, the predictive factors influencing pCR in NAC were acquired via Chi-square test. Independent predictors of pCR were identified by multivariate binary logistic regression. The levels of hemoglobin, platelets, serum creatinine and blood urea were compared via two-sample Wilcoxon rank-sum (Mann–Whitney) test. P<0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Patients
A total of 455 patients (EC-D: 109, EC-P: 346) were included from January 2014 to January 2019. Table 1 summarizes patient characteristics. In the EC-D group, 11 patients were ypT0/isN0, and of them 6 got ypT0N0. Analogously, 67 patients in the EC-P group were ypT0/isN0, and of them 43 acquired ypT0N0.
 |
Table 1 Patient and Tumor Features |
The baseline characteristics were well balanced between groups. The median age was 50 years (range: 24 to 75 years old).
Exposure to Treatment
According to several key prognostic factors (eg age of diagnosis, menstrual status, molecular type, ER status, PR status, Her-2 status, Ki-67 index), we compared the efficacy between EC-D and EC-P. Details can be found in the following tables.
The univariable analysis for ypT0/isN0 in NAC showed the significant prognostic factors were chemotherapy scheme, molecular type, ER status, PR status, Her-2 status, and Ki-67 index (P<0.05; Table 2). When these factors were incorporated into the multivariate regression analysis, molecular type was retained as the independent predictor of pCR of ypT0/isN0 (odds ratio (OR): 9.495,95% CI: 0.492–36.176) along with ER status (OR: 0.085, 95% CI: 0.013–0.561) and Her-2 status (OR: 0.055, 95% CI: 0.017–0.183) (all P<0.05). Multivariate regression analysis proved chemotherapy scheme (OR: 1.797, 95% CI: 0.882–3.660), PR status (OR: 1.395, 95% CI: 0.46–4.23) and ki-67 index (OR: 0.444, 95% CI: 0.089–2.219) had no predictive value for ypT0/isN0 (all P>0.05).
 |
Table 2 The Analysis of ypT0/isN0 |
The univariable analysis for pCR of ypT0N0 in NAC found that the significant prognostic factors were chemotherapy scheme, molecular type, ER status, and PR status (P<0.05; Table 3). In the multivariable regression analysis, chemotherapy scheme (OR: 3.379, 95% CI: 1.373–8.314), molecular type (OR: 21.3, 95% CI: 3.651–124.264) and ER status (OR:0.104,95% CI: 0.011–0.991) (P<0.05) were identified as the significant independent predictors.
 |
Table 3 The Analysis of ypT0N0 |
Tables 4 and 5 show the two types of pCR in the chemotherapy of EC-D. Clearly, ER status and Her-2 status were prognostic factors of ypT0/isN0, while ER status and Her-2 status were not the independent predictors of ypT0/isN0 (both P>0.05). However, none of the factors mentioned above can affect ypT0N0 in the chemotherapy of EC-D. Similarly, the univariable analysis showed the prognostic factors for ypT0/isN0 in the chemotherapy of EC-P were molecular type, ER status, PR status, Her-2 status, and Ki-67 index (P<0.05; Table 6). Then, the multivariable regression analysis uncovered molecular type (OR:4.214, 95% CI: 1.105–16.065) and Her-2 status (OR: 0.126, 95% CI: 0.038–0.414) were the independent predictors.
 |
Table 4 The ypT0/isN0 Rate Analysis of EC-D |
 |
Table 5 The ypT0N0 Rate Analysis of EC-D |
 |
Table 6 The ypT0/isN0 Rate Analysis of EC-P |
Finally, prognostic factors of ypT0N0 in the EC-P chemotherapy were molecular type, ER status, and PR status (P<0.05; Table 7). Nevertheless, molecular type (OR: 11.571, 95% CI: 1.838–72.83) was found as the independent predictor.
 |
Table 7 The ypT0N0 Rate Analysis of EC-P |
Some OR and 95% CI in the table are blank, which is meaningless because the chi-square test proved that these factors do not have independent influences, so this article did not fill it into the tables.
Side Effects
Due to the limitations of data collection, we only collected blood data from 317 patients, who received either EC-D (n=87) or EC-P (n=230). No significant difference was found in platelet count in patients treated with EC-D (27.4%) or EC-P (72.6%) (P=0.7683) (Table 8). No significant difference was identified in proportions of urea in patients treated with EC-D (27.4%) or EC-P (72.6%) (P=0.399). The hemoglobin levels were significantly different between EC-D and EC-P (P=0.0021). EC-P had a greater impact on the decline of hemoglobin level than EC-D. Furthermore, the creatinine levels were significantly different between treatment with EC-D and EC-P (P=0.0004). Also, EC-P had a greater impact on the decline of creatinine level than EC-D.
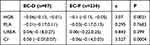 |
Table 8 Blood and Kidney Marker Analysis |
Trastuzumab Treatment
A total of 178 patients showed Her-2 (+) (Table 9), and 126 received trastuzumab, in them 40 (31.75%) patients got ypT0/isN0, and 23 (18.25%) patients obtained ypT0N0. The remaining 52 patients did not use trastuzumab, only 9 (17.31%) got ypT0/isN0, and 4 (7.69%) obtained ypT0N0. The pCR rate of patients who used trastuzumab was significantly higher than that of patients who were not used, whether it was ypT0/isN0 nor ypT0N0(p<0.05).
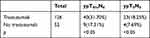 |
Table 9 Trastuzumab Analysis |
Discussion
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous malignant tumor. Although the clinical and pathological types are similar, the prognosis and survival rate of cancer may be completely different.5
Therefore, the accurate chemotherapy is significant, especially in NAC. IHC has been used to distinguish the molecular type of breast cancer and assess the link between pathological response6–8 and long-term survival.9,10 As reported, response to preoperative chemotherapy can predict the prognosis of breast cancer11–13 which makes pCR become an evaluation method for the efficacy of preoperative chemotherapy.
The two pCRs of NAC were associated with chemotherapy scheme, molecular type, ER status, and PR status. Differently, ypT0/isN0 was also linked with Her-2 status and ki-67 index. Further analysis suggested that patients receiving EC-P with ER negativity and Her-2 gene amplification more easily reach the pCR of ypT0/isN0. And these patients with negative ER would more easily reach the pCR of ypT0N0. Our conclusions were also consistent with previous research. In a study involving 1731 patients treated with different neoadjuvant regimens, the pCR rates in the patients with ER (-) tumors versus ER (+) tumors were significantly higher (24% vs 8%), no matter what treatment was taken.14 In addition, patients with basal-like and HER2 (+) diseases reached the higher rate of pCR, whereas the luminal tumors had a lower pCR rate.6 Furthermore, the Ki-67 index was extraordinarily lower after treatment, suggesting chemotherapy has an effective anti-proliferative effect on tumors.15
In the arm of EC-D, 11 of 109 (10.0%) patients were ypT0/isN0, which was similar to another study that 4 of 41 (9.8%) patients had a pCR to chemotherapy.16 Moreover, 6 of 109 (5.5%) patients were ypT0N0. These results implied that the pCR of ypT0/isN0 can be more easily reached. This is a good explanation that DCIS is insensitive to chemotherapy. But we did not find the difference of EC-D with the pCR of ypT0/isN0 or ypT0N0.
In the arm of EC-P, 67 (19.4%) and 43 (12.4%) of 346 patients accepted ypT0/isN0 and ypT0N0 respectively. In terms of molecular type, no luminal A patients achieved pCR. Moreover, 23 (12.9%) and 9 (5.0%) of 178 luminal B patients accepted ypT0/isN0 and ypT0N0 respectively. Also, 25 (34.7%) and 17 (23.6%) of 72 patients with Her-2 overexpression were ypT0/isN0 and ypT0N0 respectively. About 19 (25.7%) and 17 (23.0%) of 74 triple-negative patients were ypT0/isN0 and ypT0N0 respectively. About 20.8% of breast cancer patients exhibited HER-2 overexpression, which was similar to other studies (15–25%)17–19. In terms of ER (+) tumors, the rate of pCR in anthracycline and taxane combined NAC was between 6% and 12%,20 which was slightly higher than our rate. Probably we prioritized surgery for luminal tumors because of the low rate of pCR, and the patients included in this study had locally more advanced tumor, so these patients relatively achieved pCR difficultly.
The two pCRs of EC-P were both linked with molecular type, ER status, and PR status. The ypT0/isN0 of EC-P was also associated with both Her-2 status and Ki-67 index. The patients with Her-2 gene amplification achieved pCR more easily. This finding was the same as that of EC-D.
The rate of pCR of EC-P was higher than that of EC-D. Moreover, EC-P shortened the medication time, and increased dose density, and then made patients to accept surgery in time. Some small-sized uncontrolled studies demonstrated breast cancer women with poor-prognosis can benefit from high-dose chemotherapy, which prolonged disease-free survival and overall survival.21,22 The increased dose intensity and total dose of adjuvant chemotherapy can improve the outcomes of breast cancer patients.23 In addition, the higher dose intensity with the adjunction of filgrastim can significantly improve the survival of node-positive patients.22 Although there is no clear clinical trial in NAC for shortening the chemotherapy interval and increasing the dose of chemotherapy, theoretical basis previously obtained in adjuvant chemotherapy implies these studies benefit some patients with NAC and call for new clinical studies.
We showed differences in two definitions of pCR whether DCIS was left in breasts or not. Therefore, it is necessary to reach a consensus on the definition of PCR in NAC, especially if PCR is determined as an alternative end-point of prognosis.24 No obvious difference in platelet or urea was found between EC-D and EC-P, implying that patients with similar platelet or urea can choose and benefit from NAC of EC-P. However, a significant difference was identified in creatinine level and hemoglobin level, indicating EC-P can more significantly reduce the creatinine level than EC-D. Thus, patients with anemia or renal insufficiency should choose NAC more cautiously. The hemoglobin levels of patients after chemotherapy were lower than those of the healthy group. During chemotherapy, the patients will experience a decrease in hemoglobin level, but the hemoglobin level will reverse after the treatment.25 Reportedly, the tumor characteristics such as tumor stage or hormone-receptor status had no significant influence on the occurrence of anemia.26 Thus, the decline of hemoglobin level was only linked to chemotherapy. Most hematological parameters remained constant throughout the treatment period, but creatinine and hemoglobin levels were slightly regulated at different stages.27 In summary, EC-P has a shorter interval between chemotherapy, so it more considerably impacts hemoglobin and creatinine levels.
In the patients with Her-2 (+), the PCR rate of patients who used trastuzumab was significantly higher than that of patients who were not used, whether it was ypT0/isN0 nor ypT0N0. The NOAH trial28 divided the enrolled HER-2 positive breast cancer patients into a chemotherapy alone group and a chemotherapy combined trastuzumab group. The results showed that the pathological complete remission of the trastuzumab group was achieved. pCR rate is higher than that of the chemotherapy alone group, and in patients receiving trastuzumab, Event-free survival (EFS) is closely related to pCR. These results indicated that neoadjuvant therapy with trastuzumab can improve the prognosis of patients with Her-2 (+) locally advanced or inflammatory breast cancer. This proves the unshakable status of trastuzumab in the neoadjuvant treatment of Her-2 (+) breast cancer.
This study has some limitations. Firstly, systematic G-CSF was applied to every patient, so we cannot clearly understand the myelosuppressive effects of chemotherapy and thus cannot choose chemotherapy according to myelosuppression. Secondly, we did not investigate survival. Nevertheless, this is the first study to examine the efficacy of EC-D and EC-P as NAC regimens.
In conclusion, the efficacy of EC-P is better than EC-D in NAC, especially in patients with ER (-), PR (-), Her-2 (+) and high Ki-67 expression. Patients with Her-2 overexpression and triple negativity can more easily accept pCR in EC-P, regardless of the definition of pCR. Consensus on the definition of pCR in NAC is urgently needed, especially if pCR is to be determined as a surrogate end-point for Prognosis. In terms of toxicity, patients with a similar platelet or urea can benefit from EC-P, and patients with anemia or renal insufficiency should choose EC-P more cautiously.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81572602).
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interests in this work.
References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30. doi:10.3322/caac.21442
2. Mieog JS, van der Hage JA, van de Velde CJ. Preoperative chemotherapy for women with operable breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;CD005002.
3. Peto R, Davies C, Godwin J, et al. Comparisons between different polychemotherapy regimens for early breast cancer: meta-analyses of long-term outcome among 100 000 women in 123 randomised trials. Lancet. 2012;379(9814):432–444. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61625-5
4. Vriens BE, Aarts MJ, de Vries B, et al., Breast Cancer Trialists’ Group of the Netherlands (BOOG). Doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide with concurrent versus sequential docetaxel as neoadjuvant treatment in patients with breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(15):3102–3110. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2013.06.012
5. Wu J, Li S, Jia W, Su F. Response and prognosis of taxanes and anthracyclines neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137(10):1505–1510. doi:10.1007/s00432-011-1029-6
6. Rouzier R, Perou CM, Symmans WF, et al. Breast cancer molecular subtypes respond differently to preoperative chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(16):5678–5685. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2421
7. Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, et al. The triple negative paradox: primary tumor chemosensitivity of breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(8):2329–2334. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1109
8. Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(8):1275–1281. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.14.4147
9. Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA, Caggiano V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: a population-based study from the California cancer Registry. Cancer. 2007;109(9):1721–1728. doi:10.1002/cncr.22618
10. Smid M, Wang Y, Zhang Y, et al. Subtypes of breast cancer show preferential site of relapse. Cancer Res. 2008;68(9):3108–3114. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5644
11. Wolmark. N, Wang. J, Mamounas. E, Bryant. J, Fisher B. Preoperative chemotherapy in patients with operable breast cancer: nine-year results from national surgical adjuvant breast and bowel project B-18. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2001;2001(30):96–102. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jncimonographs.a003469
12. Bear HD, Anderson S, Brown A, et al. The effect on tumor response of adding sequential preoperative docetaxel to preoperative doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide: preliminary results from national surgical adjuvant breast and bowel project protocol B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(22):4165–4174. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.12.005
13. Rastogi P, Anderson SJ, Bear HD, et al. Preoperative chemotherapy: updates of national surgical adjuvant breast and bowel project protocols B-18 and B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(5):778–785. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.15.0235
14. Guarneri V, Broglio K, Kau SW, et al. Prognostic value of pathologic complete response after primary chemotherapy in relation to hormone receptor status and other factors. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(7):1037–1044. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.02.6914
15. Burcombe RJ, Makris A, Richman PI, et al. Evaluation of ER, PgR, HER-2 and Ki-67 as predictors of response to neoadjuvant anthracycline chemotherapy for operable breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2005;92(1):147–155. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602256
16. Schott. AF, Hayes DF. Defining the benefits of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(15):1747–1749. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.41.3161
17. Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuIRE WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of theHER-2lneu oncogene. Science. 1987;235(4785):177–182. doi:10.1126/science.3798106
18. Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989;244(4905):707–712. doi:10.1126/science.2470152
19. Kathleen MD, Pritchard I, Shepherd LE, O’Malley FP, Andrulis IL. HER2 and responsiveness of breast cancer to adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(20):2103–2111. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa054504
20. Gianni L, Zambetti M, Clark K, et al. Gene expression profiles in paraffin-embedded core biopsy tissue predict response to chemotherapy in women with locally advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(29):7265–7277. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.02.0818
21. Schrama JG, Faneyte IF, Schornagel JH, et al. Randomized trial of high-dose chemotherapy and hematopoietic progenitor-cell support in operable breast cancer with extensive lymph node involvement: final analysis with 7 years of follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2002;13(5):689–698. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdf203
22. Citron ML, Berry DA, Cirrincione C, et al. Randomized trial of dose-dense versus conventionally scheduled and sequential versus concurrent combination chemotherapy as postoperative adjuvant treatment of node-positive primary breast cancer: first report of intergroup trial C9741/cancer and leukemia group B trial 9741. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(8):1431–1439. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.09.081
23. BONADONNA MDGIANNI, PINUCCIA VALAGUSSA BS, Moliterni Mdangela. Adjuvant cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil in node-positive breast cancer: the results of 20 years of follow-up. N Engl J Med. 1995;332(14):901–906. doi:10.1056/NEJM199504063321401
24. von Minckwitz G, Untch M, Blohmer JU, et al. Definition and impact of pathologic complete response on prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(15):1796–1804. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.38.8595
25. Loo WT, Yip MC, Chow LW, et al. A pilot study: application of hemoglobin and cortisol levels, and a memory test to evaluate the quality of life of breast cancer patients on chemotherapy. Int J Biol Markers. 2013;28(4):e348–356. doi:10.5301/JBM.5000053
26. Denison. U, Baumann J, Peters-Engl C, Samonigg H. Incidence of anaemia in breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003;79(3):347–353. doi:10.1023/A:1024016508925
27. Paz M, Gomes ALJ, Islam MT, et al. Assessment of chemotherapy on various biochemical markers in breast cancer patients. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(3):2923–2928. doi:10.1002/jcb.26487
28. Luca Gianni WE, Semiglazov V, Lluch A, et al. Neoadjuvant and adjuvant trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive locally advanced breast cancer (NOAH): follow-up of a randomised controlled superiority trial with a parallel HER2-negative cohort. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15.
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
