Back to Journals » Cancer Management and Research » Volume 13
The Effect of Subsequent Pregnancy on Prognosis in Young Breast Cancer Patients (≤35 Years Old) According to Hormone Receptor Status
Authors Li Y, Zhang Y, Wang S, Lu S, Song Y, Liu H
Received 12 November 2020
Accepted for publication 18 January 2021
Published 15 February 2021 Volume 2021:13 Pages 1505—1515
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S290566
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Video abstract of "Effect of pregnancy on prognosis in YBC patients with HR positive" [ID 290566].
Views: 121
Yang Li,1 Yuhan Zhang,1 Shuaibing Wang,2 Su Lu,1 Yixuan Song,1 Hong Liu1
1The Second Surgical Department of Breast Cancer, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy, Tianjin’s Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin, 300060, People’s Republic of China; 2Oncology Department, China National Petroleum Corporation Central Hospital, Langfang, Hebei Province, 065000, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Hong Liu
The Second Surgical Department of Breast Cancer, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Huanhu West Road, Hexi District, Tianjin, 300060, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86-18622221169
Email [email protected]
Purpose: We aimed to examine the effect of pregnancy on prognosis in young breast cancer (YBC) patients with hormone receptor (HR) positive after surgery and the safety of interrupting endocrine therapy (ET).
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was performed in patients who became pregnant after BC surgery under the age of 35 and were matched (1:4) to nonpregnant patients from 2006 to 2014. The primary endpoints were disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) in HR-positive BC patients, and the secondary endpoints were DFS and OS in HR-negative BC patients and the whole population. Subgroup analyses included the DFS of patients who became pregnant within 5 years after surgery and DFS according to the ET interval time (≤ 30 months v > 30 months) in the pregnant group.
Results: A total of 1323 YBC patients were collected in our study, which included 68 pregnant patients and 264 matched nonpregnant patients. There were no statistically significant differences in DFS and OS among HR-positive patients (P=0.657, P=0.250, respectively) and the whole population (P=0.058, P=0.152, respectively). A BC pregnancy interval ≤ 5 years showed a better DFS (P=0.042), and an ET interval ≤ 30 months had a worse DFS (P = 0.01).
Conclusion: This study did not observe a worse prognosis in patients with HR-positive disease who became pregnant after BC surgery, and an ET interval less than 30 months in pregnant patients led to a worse outcome. Patients were able to become pregnant within 5 years after surgery.
Keywords: young breast cancer, prognosis, pregnancy, hormone receptor positive, endocrine therapy
Introduction
There was an estimated 278,900 new breast cancer (BC) cases in China in 2014, accounting for 16.51% of all new cases in females and ranking first in the incidence of female malignant tumors.1 It has been reported that BC patients had the lowest fertility rate after diagnosis among cancer patients, such as cervical carcinoma, thyroid cancer and malignant melanoma patients.2 YBC patients also have problems such as premenopausal ovarian function failure, psychological disease caused by tumor treatment and fertility decline.3 A study showed that 40% to 50% of women wanted to become pregnant after BC treatment.4 HR-positive patients have a further reduction in fertility when they completed at least five years of endocrine therapy owing to the natural failure of ovaries.5,6 Therefore, increasing attention should be paid to the quality of life and fertility needs of YBC patients after surgery.7,8
Previous studies have suggested that there was a better prognosis among women who became pregnant after BC diagnosis, and a large meta-analysis found that subsequent pregnancy in BC patients could reduce the risk of death by 41%.9–12 Nevertheless, patients who became pregnant after treatment tended to be in an early clinical stage and had no evidence of relapse, which is also known as the “healthy mother effect”.5,9,13 The Swedish scholar Valachis et al conducted a large meta-analysis of 20 studies involving 49,370 premenopausal BC patients and found that pregnancy in early BC patients did not impact prognosis and might actually have improved survival benefits. This analysis corrected for the selection bias of the “healthy mother effect”14 Although large prospective clinical studies are lacking, a number of retrospective studies have shown that pregnancy after BC diagnosis does not affect prognosis; therefore, in terms of safety, pregnancy should not be a contraindication for YBC patients.
There are some reasons for HR-positive BC patients forgoing the chance to reproduce. On the one hand, ET for at least five years causes some young patients lose fertility. On the other hand, some studies have reported that patients treated with tamoxifen were less likely to have children in the future than those who did not.15,16 The lack of prospective clinical data increases the uncertainty regarding fertility in HR-positive BC patients. A study showed that 56.5% of women with a diagnosis of BC who subsequently conceived miscarried or underwent abortion.13 The higher rate of abortion is also a common concern for physicians and patients. Fertility concerns affected treatment decisions in HR-positive YBC patients, and 12% of them chose to take ET for fewer than 5 years.17 A web-based survey on oncologists revealed that more than half of the respondents did not recommend the interruption of ET in patients, underscoring the need for prospective data regarding the safety of ET interruption.18 Currently, no previous studies have been conducted on the safety of temporarily halting ET to achieve pregnancy in YBC patients.
There are still few studies on the safety of postoperative pregnancy in young patients with HR-positive BC. The purpose of this article was to explore the effect of pregnancy on the prognosis of HR-positive YBC patients after surgery and the safety of interrupting ET on the basis of previous studies.
Patients and Methods
Patients
A retrospective cohort study was conducted to evaluate the effect of pregnancy on prognosis in young patients with HR-positive BC after surgery. We defined YBC patients as patients younger than or equal to 35 years old. Patients were enrolled in the study from January 1, 2006, to December 31, 2014. The inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) all included patients were histologically diagnosed with breast malignancy, and their molecular subtypes were grouped as luminal type, HER2 overexpression and triple-negative; 2) no occurrence of distant metastasis prior to surgery; 3) no pregnancy-associated breast cancer (PABC); and 4) no local recurrence or distant metastasis before pregnancy in the pregnant group. The exclusion criteria were as follows: 1) no medical records on treatment after surgery at our institution; and 2) unable to be contacted by telephone or mail to confirm whether they became pregnant any time after BC treatment (Figure 1).
 |
Figure 1 Schematic diagram for patient selection. |
Molecular subtypes were defined by immunohistochemical staining features of ER, PR, and HER2. We defined ER and PR staining < 10% as negative and ≥ 10% as positive before 2010, while the threshold changed to 1% in 2010 in our study.19 HER2 0/1 was considered negative. HER2 2+ was defined as negative or positive, depending on fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and HER2 3+ was considered positive.
Methods
The pregnant group was matched (1:4) to nonpregnant patients with similar tumor sizes, lymph node statuses, molecular subtypes and years of diagnosis. If one pregnant patient was matched to multiple nonpregnant patients, the random number table method was used to randomly select four matched nonpregnant patients. To include as many pregnant patients as possible, the admission criteria of the matched group could be relaxed appropriately, such as years of diagnosis plus or minus 1 year; if there was still no match after the relaxing the admission criteria, patients in the pregnant group could also match to three or two nonpregnant patients. The disease-free interval of each nonpregnant patient was at least equal to the time elapsed between BC surgery and the date of conception of the matched pregnant patient to adjust for time bias. The primary purpose of this study was to investigate the difference in DFS and OS between pregnant and nonpregnant HR-positive YBC patients. The secondary objectives were to examine DFS and OS in HR-negative patients and the whole population. Subgroup analysis examined differences in DFS between patients who became pregnant within five years and their matched groups and the safety of time to interrupting ET among the pregnant group (≤30 months v > 30 months). The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital. The patients were not required to sign an informed consent form because this was a retrospective study.
Follow-Up and Clinical Assessment
All patients were followed up from the date of surgery to January 1st, 2019, the date of death or the last date recorded in electronic medical records. The median follow-up time was 101 months (29 to 156 months). DFS time was measured from the date of surgery until the follow-up date, first local recurrence, distant recurrence, second primary tumor or any cause of death. The OS time was calculated from the date of surgery until death, and living patients were examined at the time of the last follow-up. Whether patients became pregnant was confirmed by electronic medical records, paper medical documents, telephone and mail. If the patients died by the time of contact, available family members provided the needed information. In the first 2 years after the operation, patients were followed up every 3 months. The interval was extended to 6 months from year 2 to year 5 and once a year thereafter. The patient content that was reviewed included breast tumor markers, breast ultrasound, mammography, X-ray or computed tomography (CT) of the chest, whole abdominal ultrasound and bone scans, and head magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), as necessary.
Statistical Methods
Statistics were used to characterize clinicopathologic and treatment characteristics. Categorical variables are summarized using frequencies and percentages, and the χ2 test and Fisher’s exact test were used to compare the differences between two groups. We used medians and ranges to describe continuous variables, and a Mann–Whitney U-test was run to compare differences in ages between the pregnant group and the nonpregnant group. Calculations of survival times and rate distributions were performed with the Kaplan-Meier method. The Log rank test and univariate analyses were used to assess the relationship between survival and potential prognostic factors. We used multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression to further compare variables and outcomes. P values <0.05 were considered statistically significant, and all tests were two tailed. Analyses were conducted using the Statistical Package for Social Science program (SPSS for Windows, version 22.0, SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL)
Results
Patient Characteristics
A total of 332 YBC patients were enrolled in this study, which included 68 (20.5%) who became pregnant after BC surgery and 264 (79.5%) who were nonpregnant. Sixty-eight patients who became pregnant after the operation (pregnant group), which included 2 patients who chose abortion, 3 who were pregnant and 63 who had delivered, were enrolled in the study. Correspondently, another 264 nonpregnant patients were randomly collected for matching (control group). All the patients in our study underwent surgery. The two groups were compared in terms of the time of surgery, breast cancer family history, tumor size, regional lymph node metastasis, pathological type, histological grade, hormone receptor, HER2 overexpression status, postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy, adjuvant hormonal therapy, targeted therapy, ovarian function suppression and molecular subtypes. There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups (P > 0.05). The baseline characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1. The median age of the patients who became pregnant was younger than that of nonpregnant patients (median age, 28 vs 33 years; p < 0.01), and it was more likely that there was no procreation or lactation before the operation in the pregnant group (80.9% vs 16.7% and 82.4% vs 24.6%, respectively; P<0.01). In comparison with the patients who did not become subsequently pregnant, the pregnant patients were found to have significantly higher rates of breast-conserving surgery (44.1% vs 24.6%; p=0.002). The ratio of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (20.6% vs 7.2%; p = 0.001) and postoperative radiotherapy (55.9% vs 37.5%; p=0.012) in the pregnant group was higher than that in the control group. A total of 206 (62.0%) patients were estrogen receptor-positive, with 43 in the pregnant group and 163 in the nonpregnant group. The differences were not statistically significant (p=0.821). The follow-up information of the 68 pregnant patients is shown in Table 2.
 |
Table 1 Clinicopathological Characteristics of Patients in the Two Groups |
 |
Table 2 Basic Information of 68 Pregnant Patients in the Follow-Up Visit |
Survival Analysis
In the pregnant group, the median DFS time was 102.5 months (ranging from 33 to 156 months), while in the nonpregnant group, it was 94 months (ranging from 17 to 155 months). The OS time was 106 months in the pregnant group (ranging from 50 to 156 months), and in the other group, the median value was 100 months (ranging from 29 to 155 months). Thirty-five patients relapsed in our study, including 3 patients in the pregnant group and 32 in the other group. No one died by the end of the follow-up in the pregnant group, and 7 patients died in the control group. No statistically significant differences were found in DFS and OS between the two groups (P=0.058 and P=0.152, respectively, Figure 2A and B).
 |
Figure 2 Disease-free survival (DFS) of patients in the pregnant group and control group (A) and overall survival (OS) of patients in the pregnant group and control group (B). |
For HR-positive YBC patients, we did not find any statistically significant difference in DFS or OS between the HR-positive pregnant group and their matched group (P=0.657 and P=0.250, respectively, Figure 3A and B). Regarding HR-negative patients, there was no difference in OS between the pregnant group and the control group (P=0.389; Figure 4B). Nevertheless, the pregnant group showed a better DFS than the matched group (P=0.026; Figure 4A).
Subgroup Analysis
Time to Pregnancy After BC Surgery
We investigated differences in DFS between patients who became pregnant within 5 years after the operation and their matched control group. As shown below (Figure 5), a better DFS was found in patients with a pregnancy interval ≤ 5 years after surgery than their control group (log rank P=0.042). Multiple Cox proportional hazard regression was used to investigate whether pregnancy was an independent factor affecting prognosis. The results showed that pregnancy was not an independent factor impacting DFS (HR=0.080; 95% CI, 0.022 to 1.237; P=0.080).
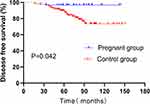 |
Figure 5 Disease-free survival (DFS) of patients with pregnancy intervals ≤ 5 years after surgery and their control group. |
Time to Interrupting ET
Forty-three patients who became pregnant after surgery received ET. We compared if DFS was affected by the time to interrupting ET (≤ 30 months v > 30 months) among pregnant patients after surgery. There were 11 (25.6%) patients whose duration of endocrine therapy was less than or equal to 30 months, of whom 2 patients relapsed after surgery, and the other 32 (74.4%) patients received ET for more than 30 months after surgery, one of whom recurred. A statistically significant difference was observed for DFS in women whose duration of ET was more than or less than 30 months in the pregnant group (P = 0.01) (Figure 6), and women with more than 30 months of endocrine therapy had a better outcome.
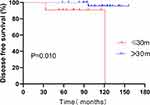 |
Figure 6 Disease-free survival (DFS) of patients with endocrine therapy intervals (≤ 30 months vs >30 months) after surgery in the pregnant group. |
Discussion
This study suggested that pregnancy in YBC patients did not increase the risk of recurrence or death. A number of retrospective studies on the fertility of BC patients have reported similar findings, as shown below. Sankila R et al reported that pregnancy after the diagnosis of BC can significantly reduce the risk of death, but this result might be affected by the healthy mother effect.13,20 Some meta-analysis studies concluded that pregnancy after surgical treatment did not increase the risk of BC recurrence and might actually improve OS.21,22 The same conclusion was reported by Von Schoultz after the inclusion of 50 pregnant patients whose pregnancy had no adverse effect on the prognosis of BC treatment.23 Kroman N included 371 pregnant patients, and after multivariate analysis, it was concluded that having a child after BC reduced the risk of death.24 The most recent large retrospective analysis also found better survival in the pregnant group, even in the case of strict matching.12 Therefore, despite the lack of prospective studies, pregnancy after the diagnosis of BC in young patients is safe based on well-designed retrospective studies.
In the present study, we found that most of the young patients who gave birth after surgery were younger, had no childbearing history before disease and were more likely to have undergone breast-conserving surgery than patients who did not become pregnant. As a result, the ratio of postoperative radiotherapy was significantly higher in the pregnant group than the control group. Some prospective cohort studies of young women with newly diagnosed BC revealed that younger age and not having children were associated with a greater likelihood of fertility concern.17,25 It is not unexpected that women in the pregnant group were younger, and most of them did not have children. The reason for the higher ratio of breast-conserving surgery in the pregnant group might be the consideration of the need for breastfeeding in the future.
In this study, no differences in DFS and OS were found between pregnant and nonpregnant HR-positive YBC patients. This has important clinical implications because the effects of tamoxifen treatment for at least five years on follicular reserve function in HR-positive YBC patients have been controversial for a long time. It has been reported that tamoxifen does not reduce ovarian reserve function in YBC patients. Therefore, the authors suggested that tamoxifen had no direct effect on reproductive function.15 However, Partridge AH et al reported that BC patients who received tamoxifen after surgery had lower levels of anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) and antral follicle counts (AFCs) in 2010.26 Although there have been few studies on postoperative pregnancy in HR-positive BC patients, a well-designed retrospective cohort study and a meta-analysis by Lambertini M et al suggested that patients who became pregnant after the diagnosis of BC with HR positivity did not have an increased risk of relapse.11,12,27 Subsequently, the research team revealed that pregnancy after BC in patients with germline BRCA mutations was safe with no detrimental prognostic effects.28 Unfortunately, the lack of BRCA information in our study limits our ability to further study this specific cohort of patients. In addition, the decrease in ER expression after pregnancy in YBC patients might be associated with the long-term protective effect of pregnancy in terms of gene expression.29 Animal experiments have also shown that increased estrogen and progesterone levels might have a preventive effect on BC.30,31 Despite that, many physicians are concerned about a possible negative impact of subsequent pregnancy in HR-positive YBC patients because of endocrine stimulation.32,33 Moreover, we found that the pregnant group showed a better DFS than the matched group among HR-negative patients. To investigate whether this was a true protective effect of postoperative pregnancy in HR-negative YBC patients or just caused by some confounding factors or selective bias, we compared the DFS of HR-positive and HR-negative nonpregnant YBC patients. The result was that the nonpregnant group of HR-negative patients who were matched to the pregnant cohort had a lower DFS (P=0.018) than HR-positive patients. Although the selection of HR-negative nonpregnant patients was random, it seemed that HR-negative BC patients tended to have molecular subtypes such as HER2 overexpression or triple-negative BC, which usually had worse prognoses than others. Moreover, a similar study was performed in the pregnant group, and we observed no difference in DFS (P=0.210), which might be due to the selection effect of healthy mothers. Therefore, the better DFS in the HR-negative pregnant group might be due to selection bias rather than a real protective effect of pregnancy.
In subgroup analysis, our retrospective investigation observed a better DFS in women who became pregnant within five years than in women who did not become pregnant. In regard to the appropriate time to conceive after the diagnosis of BC in young patients, different studies have suggested different times to conception. Lambertini M et al showed that patients who became pregnant within 2 years after BC diagnosis had a better DFS than patients in their matched group, while the authors suggested that this protective effect might have been influenced by selection bias, and it was concluded that there was no significant difference in relapse within 2 years of pregnancy.11,12 Another study conducted by Lauren Nye found no difference in DFS among HR-positive premenopausal female BC patients who became pregnant within 5 years of their diagnosis,34 which was different from our study, which showed that pregnancy might be a beneficial prognostic factor. A retrospective study from the United States reported that women who conceived within 12 months of the diagnosis of BC experienced slightly worse survival outcomes than their matched cases, while those who delayed pregnancy tended to have improved survival. However, these results were not significant.35 In addition, a population-based cohort study in Canada suggested that compared with nonpregnant women, women who gave birth 6 months or more after BC had a significantly lower risk of death.36
HR-positive YBC patients were recommended to receive five years of ET, and this was further increased to ten years according to the ATLAS trial, which demonstrated potential recurrence-free and survival benefits of continuing ET for 10 years.37 This therefore further limits the possibility of future conception among YBC patients, and the appropriate time to interrupting ET for patients who plan to become pregnant after surgery urgently needs to be determined. This study showed that pregnant patients with an ET duration of less than 30 months had a worse DFS than those with an ET duration of more than 30 months; thus, we suggest that HR-positive YBC patients conceive after having completed at least 30 months of endocrine therapy. The result needs to be further confirmed by large and well-designed clinical studies due to the small number of recurrences or metastases in pregnant YBC patients after surgery and restricted by the number of samples. A global collaboration: The BIG-NABCG recently launched the IBCSG-coordinated trial, evaluating the pregnancy outcomes and safety of interrupting endocrine therapy for premenopausal women with endocrine responsive breast cancer (POSITIVE) who desire pregnancy and are actively involved in assessing the safety of pregnancy after interrupting ET.38,39 We look forward to obtaining more reliable results in the future.
The strengths of this study are described below. First, the subjects of the study were young patients who became pregnant after surgery, which are the patients with the highest probability of fertility, and there are limited data on pregnancy outcomes of YBC patients under the age of 35 in existing clinical studies.40 Second, this was the first study on the safety of ET ≤ 30 months for becoming pregnant in HR-positive YBC patients. Finally, the pregnant group was matched strictly to the control group according to a similar tumor size, lymph node status, years of diagnosis and even molecular subtype to increase the comparability between the two groups. However, this study also had some limitations. First, the sample size of pregnant patients was relatively small, and data on the precise date of pregnancy and the duration of ET might have been limited by the memory bias of some patients or their relatives in this retrospective study. On the other hand, the short follow-up time did not reflect the real effect of pregnancy after the diagnosis of BC on the long-term survival of patients. It is important to note that addressing the effect of postoperative pregnancy on BC outcomes in a prospective randomized trial is nearly impossible, and thus larger and better-designed retrospective studies are needed to explore this problem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we found that pregnancy after BC surgery in young patients was safe in this study, and patients who became pregnant within five years had a better outcome. For HR-positive YBC patients, this study did not demonstrate a worse prognosis after surgery. Moreover, there was worse prognosis in pregnant patients with a duration of ET ≤ 30 months, but further validation is required in prospective clinical trials. We believe that young women who desire pregnancy after BC diagnosis should be well informed of various potential and unknown risks through careful discussion with their physicians.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institution and Hospital (Approval no. bc2020201). The need for informed patient consent was waived because of the retrospective nature of the study. As a retrospective study, waiver of informed consent was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institution and Hospital. This study protected patient data confidentiality and was in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Acknowledgment
The authors want to acknowledge Sijia Zhai for her help in processing figures and Jiajun Fu for his great contributions to statistics of this study.
Funding
This research was supported by Tianjin Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for Major Disease Prevention and Control [19ZXDBSY00090].
Disclosure
The authors have stated that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Li H, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, et al. [Incidence and mortality of female breast cancer in China, 2014]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018;40(3):166–171. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2018.03.002
2. Stensheim H, Cvancarova M, Moller B, Fossa SD. Pregnancy after adolescent and adult cancer: a population-based matched cohort study. Int J Cancer. 2011;129(5):1225–1236. doi:10.1002/ijc.26045
3. Ademuyiwa FO, Cyr A, Ivanovich J, Thomas MA. Managing breast cancer in younger women: challenges and solutions. Breast Cancer. 2016;8:1–12.
4. Letourneau JM, Smith JF, Ebbel EE, et al. Racial, socioeconomic, and demographic disparities in access to fertility preservation in young women diagnosed with cancer. Cancer. 2012;118(18):4579–4588. doi:10.1002/cncr.26649
5. Azim HA
6. Abusief ME, Missmer SA, Ginsburg ES, Weeks JC, Partridge AH. The effects of paclitaxel, dose density, and trastuzumab on treatment-related amenorrhea in premenopausal women with breast cancer. Cancer. 2010;116(4):791–798. doi:10.1002/cncr.24835
7. Howard-Anderson J, Ganz PA, Bower JE, Stanton AL. Quality of life, fertility concerns, and behavioral health outcomes in younger breast cancer survivors: a systematic review. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104(5):386–405. doi:10.1093/jnci/djr541
8. Mayer EL, Gropper AB, Neville BA, et al. Breast Cancer survivors‘ perceptions of survivorship care options. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(2):158–163. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.36.9264
9. Azim HA
10. Rippy EE, Karat IF, Kissin MW. Pregnancy after breast cancer: the importance of active counselling and planning. Breast. 2009;18(6):345–350. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2009.08.003
11. Azim HA
12. Lambertini M, Kroman N, Ameye L, et al. Long-term safety of pregnancy following breast cancer according to estrogen receptor status. JNCI. 2018;110(4):426–429. doi:10.1093/jnci/djx206
13. Ives A, Saunders C, Bulsara M, Semmens J. Pregnancy after breast cancer: population based study. BMJ. 2007;334(7586):194. doi:10.1136/bmj.39035.667176.55
14. Valachis A, Tsali L, Pesce LL, et al. Safety of pregnancy after primary breast carcinoma in young women: a meta-analysis to overcome bias of healthy mother effect studies. Obstetrical Gynecol Survey. 2010;65(12):786–793. doi:10.1097/OGX.0b013e31821285bf
15. Shandley LM, Spencer JB, Fothergill A, et al. Impact of tamoxifen therapy on fertility in breast cancer survivors. Fertil Steril. 2017;107(1):243–252. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.10.020
16. Cordoba O, Bellet M, Vidal X, et al. Pregnancy after treatment of breast cancer in young women does not adversely affect the prognosis. Breast. 2012;21(3):272–275. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2011.10.001
17. Ruggeri M, Pagan E, Bagnardi V, et al. Fertility concerns, preservation strategies and quality of life in young women with breast cancer: baseline results from an ongoing prospective cohort study in selected European Centers. Breast. 2019;47:85–92. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2019.07.001
18. Rosenberg SM, Gelber S, Gelber RD, et al. Oncology Physicians‘ Perspectives on Practices and Barriers to Fertility Preservation and the Feasibility of a Prospective Study of Pregnancy After Breast Cancer. J Adolescent Young Adult Oncol. 2017;6(3):429–434. doi:10.1089/jayao.2017.0031
19. Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College Of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(16):2784–2795. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.6529
20. Sankila R, Heinävaara S, Hakulinen T. Survival of breast cancer patients after subsequent term pregnancy: “healthy mother effect”. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;170(3):818–823. doi:10.1016/S0002-9378(94)70290-X
21. Luo M, Zeng J, Li F, He L, Li T. Safety of pregnancy after surgical treatment for breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2014;24(8):1366–1372. doi:10.1097/IGC.0000000000000242
22. Hartman EK, Eslick GD. The prognosis of women diagnosed with breast cancer before, during and after pregnancy: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016;160(2):347–360. doi:10.1007/s10549-016-3989-3
23. von Schoultz E, Johansson H, Wilking N, Rutqvist LE. Influence of prior and subsequent pregnancy on breast cancer prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13(2):430–434. doi:10.1200/JCO.1995.13.2.430
24. Kroman N, Jensen M-B, Wohlfahrt J, Ejlertsen B. Pregnancy after treatment of breast cancer – a population-based study on behalf of Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group. Acta Oncol. 2008;47(4):545–549. doi:10.1080/02841860801935491
25. Ruddy KJ, Gelber SI, Tamimi RM, et al. Prospective study of fertility concerns and preservation strategies in young women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(11):1151–1156. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.52.8877
26. Partridge AH, Ruddy KJ, Gelber S, et al. Ovarian reserve in women who remain premenopausal after chemotherapy for early stage breast cancer. Fertil Steril. 2010;94(2):638–644. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.03.045
27. Eva Blondeaux MP, Bruzzone M. Chances of pregnancy after breast cancer, reproductive and disease outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
28. Lambertini M, Ameye L, Hamy A-S, et al. Pregnancy After Breast Cancer in Patients With Germline BRCA Mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(26):3012–3023. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.02399
29. Asztalos S, Gann PH, Hayes MK, et al. Gene expression patterns in the human breast after pregnancy. Cancer Prev Res. 2010;3(3):301–311. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0069
30. Rajkumar L, Guzman RC, Yang J, Thordarson G, Talamantes F, Nandi S. Prevention of mammary carcinogenesis by short-term estrogen and progestin treatments. Breast Cancer Res. 2003;6(1):R31–R37. doi:10.1186/bcr734
31. Medina D, Sivaraman L, Hilsenbeck SG, et al. Mechanisms of hormonal prevention of breast cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;952(1):23–35. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb02725.x
32. Lambertini M, Di Maio M, Pagani O, et al. The BCY3/BCC 2017 survey on physicians‘ knowledge, attitudes and practice towards fertility and pregnancy-related issues in young breast cancer patients. Breast. 2018;42:41–49. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2018.08.099
33. Lambertini M, Peccatori FA, Demeestere I, et al. Fertility preservation and post-treatment pregnancies in post-pubertal cancer patients: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines†. Ann Oncol. 2020;31(12):1664–1678. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.09.006
34. Nye L, Rademaker A, Gradishar WJ. Breast Cancer Outcomes After Diagnosis of Hormone-positive Breast Cancer and Subsequent Pregnancy in the Tamoxifen Era. Clin Breast Cancer. 2017;17(4):e185–e189. doi:10.1016/j.clbc.2016.12.014
35. Kranick JA, Schaefer C, Rowell S, et al. Is pregnancy after breast cancer safe? Breast J. 2010;16(4):404–411. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4741.2010.00939.x
36. Iqbal J, Amir E, Rochon PA, Giannakeas V, Sun P, Narod SA. Association of the timing of pregnancy with survival in women with breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(5):659–665. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0248
37. Davies C, Pan H, Godwin J, et al. Long-term effects of continuing adjuvant tamoxifen to 10 years versus stopping at 5 years after diagnosis of oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: ATLAS, a randomised trial. Lancet. 2013;381(9869):805–816. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61963-1
38. Pagani O, Ruggeri M, Manunta S, et al. Pregnancy after breast cancer: are young patients willing to participate in clinical studies? Breast. 2015;24(3):201–207. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2015.01.005
39. Pagani O. Pregnancy outcome and safety of interrupting therapy for women with endocrine responsive breast cancer (POSITIVE). Available from: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02308085.
40. Blakely LJ, Buzdar AU, Lozada JA, et al. Effects of pregnancy after treatment for breast carcinoma on survival and risk of recurrence. Cancer. 2004;100(3):465–469. doi:10.1002/cncr.11929
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.


