Back to Journals » Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology » Volume 8
Spectrum of dermatophyte infections in Botswana
Authors Thakur R
Received 27 November 2014
Accepted for publication 5 January 2015
Published 5 March 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 127—133
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S78237
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jeffrey Weinberg
Rameshwari Thakur
Department of Microbiology, Muzzaffarnagar Medical College, Uttar Pradesh, India
Background: Dermatophyte infections are a common cause of superficial fungal infection in different geographical locations of the world. Usually, it involves superficial invasion of keratinized tissue, eg, skin, nails, and hair, but in immunosuppressed individuals, it may cause atypical, extensive and deep lesions, which may pose serious diagnostic and therapeutic challenges.
Aim: To find out the causative dermatophyte species responsible for the various clinical types of dermatophyte infection.
Results: Trichophyton violaceum was found to be the predominant species, being the causative organism responsible for all the clinical types.
Conclusion: T. violaceum was found to be the most common species responsible for most of the clinical forms of dermatophytosis (96; 80%). Tinea unguium was found to be the most frequent clinical type of dermatophytosis (33; 27.50%).
Keywords: Trichophyton violaceum, Trichophyton interdigitale, Trichophyton tonsurans, Trichophyton ferrugineum, tinea unguium, tinea corporis
Introduction
The three closely related genera of dermatophytes: Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton usually cause superficial infections of skin, hair, and nail. The various clinical forms caused by dermatophytes are tinea capitis, tinea faciei, tinea unguium, tinea manuum, tinea corporis, tinea pedis, tinea barbae, tinea cruris and tinea gladiotorum. An article on ‘Tinea capitis in Botswana’ has already been published by the author.1 One of the most prevalent species of this group is Trichophyton rubrum.2,3 Rarely these pathogens may cause a more aggressive and invasive infection.4,5 Dermatophyte infections are common in HIV patients and occur at some point during their illness.6,7 It has been estimated that these infections may not occur any more frequently in HIV patients than in control groups.8 One study has reported an apparently higher prevalence of onychomycosis in HIV-positive patients relative to general patients visiting dermatologic clinics.9
The severity and variability of presentation are more common in HIV/AIDS.10,11 In severely immunosuppressed patients with AIDS, lesions may have little inflammation and often lack the elevated border and central clearing typical of tinea (anergic tinea).7 They may resemble sharply marginated lesions of dry skin. Goodman et al observed that the prevalence of dermatophytosis was four times higher amongst HIV infected individuals.12 Bizarre presentations and failure to respond to treatment should alert care providers to the possibility of an underlying immunologic problem.13 Some of the dermatophyte species are cosmopolitan in distribution, but some species, which are confined to a particular geographical region, can no longer remain geographically restricted, because of frequent travel and migration. An infection acquired in any geographical region, can manifest itself in another country. So knowledge of the distribution of various species of dermatophyte is important. Though T. rubrum is a very common cause of dermatophyte infection all over the world, it can be rare in some geographical regions. In some regions of Africa, T. rubrum is rare.14
Material and methods
From January 2009 to December 2010, samples were collected from 450 patients with a clinical diagnosis of dermatophytosis.
A total of 120 patients were found to be culture positive for dermatophyte.
Samples were collected in the microbiology section of the National Health Laboratory, Gaborone, Botswana. The suspicious area was cleaned with 70% alcohol on gauze. The samples were collected either in a sterile petri dish or a container.
All the samples were submitted for potassium hydroxide (KOH) 10%–20% mount (Figure 1) and fungal culture.
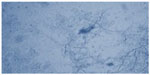  | Figure 1 Potassium hydroxide 10% mount. |
Skin scrapings and nail clippings were collected after cleaning the suspicious area with 70% alcohol.
In case of tinea capitis, samples were collected from three suspicious sites after cleaning the area with 70% alcohol. We used a scalpel blade and the wet swab for collecting hair and scales.1
For the collection of samples from the suppurative lesions, especially from children suffering from tinea capitis, sterile swabs were used.
In case the lesions had vesicles and bullae, the top of the vesicles and bullae was clipped off and added to the sample.
Diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor was made on the typical morphology of skin scrapings in 10% KOH, which resembles “spaghetti and meatball”.
For suspected deeper lesions like Majocchi’s granuloma, punch biopsy was collected in a sterile container for KOH and culture, and the remaining tissue was sent to the histology section in formol saline.
Sabouraud dextrose agar and Dermasel media were used for the inoculation of the samples. Sabouraud plates were incubated in duplicate at 25°C and 37°C. Dermasel plates were incubated for 4 weeks, before declaring it culture negative.
Incubation of Sabouraud plate at 37°C was done for 5–7 days to identify yeasts (Candida). Germ tube test, morphological characteristics on corn meal agar, and CHROMagar™ Candida were performed for speciation.
A non-dermatophyte fungus was considered relevant only when on microscopic examination, fungal hyphae, spores or yeast cells were seen on repeat culture, and the same species of non-dermatophyte fungus was isolated.
If direct microscopy was negative but cultures positive, the case was included. Cases with positive direct microscopy and with a negative culture were excluded. Where more than one site yielded the same organism, the case was counted as a single infection. Where more than one species was found in different sites or at the same site both species were counted.
Teased mount preparations were made in lacto phenol cotton blue stain to study the microscopic structures. Urease test and in vitro hair perforation tests were done for the confirmation of Trichophyton interdigitale species. Also, other standard tests required for the identification of the dermatophyte species were done in accordance with the textbooks, manuals, and journals.15–19
Results
Trichophyton violaceum was found to be the most common species responsible for most of the clinical forms of dermatophytosis (n=96 [80%]) (Tables 1 and 2 and Figures 2–5). Next in frequency was T. interdigitale (n=16 [3.33%]) (Figures 6–8).
  | Table 1 Causative dermatophytes in 120 patients |
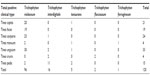  | Table 2 Clinical types and causative dermatophytes in 120 patients |
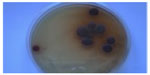  | Figure 2 Trichophyton violaceum (violet pigment). |
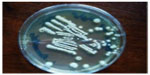  | Figure 3 Trichophyton violaceum (white variant). |
  | Figure 4 Trichophyton violaceum (lacto phenol cotton blue mount). |
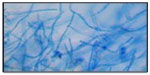  | Figure 5 Trichophyton violaceum. |
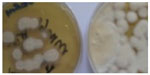  | Figure 6 Trichophyton interdigitale. |
  | Figure 7 Trichophyton interdigitale (lacto phenol cotton blue mount). |
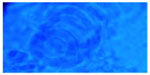  | Figure 8 Trichophyton interdigitale. |
Other species isolated were Trichophyton tonsurans (n=5 [4.16%]) (Table 1 and Figure 9), Epidermophyton floccossum (n=2 [1.66%]) (Table 1) and only one case of Microsporum ferrugineum 0.83% (Table 1 and Figure 10).
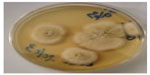  | Figure 9 Trichophyton tonsurans. |
  | Figure 10 Microsporum ferrugineum (lacto phenol cotton blue mount). |
Tinea unguium was found to be the predominant clinical form (n=33 [27.50%]) (Figures 11 and 12). Though tinea unguium is common in older people and the incidence increases with age, but in our study, no such association was found (Table 3) and it was statistically insignificant.
  | Table 3 Association between age-groups of clinical forms |
Other clinical forms in descending order were tinea corporis (n=24 [20%]) (Figures 11 and 13), tinea capitis (n=21 [17.50%]) (Figures 11 and 14), tinea faciei (n=19 [15.83%]), (Figure 11), tinea pedis 15 (12.50%) (Figure 15), tinea manuum (n=4 [3.33%]) and also tinea cruris (n=4 [3.33%]).
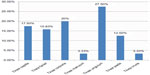  | Figure 11 Bar diagram of clinical forms. |
Involvement of all the nails of both hands (Figure 12A) was found in three cases, but in one case KOH mount and culture was negative, so it was excluded from the study. All these three cases were HIV positive. We isolated T. violaceum from the remaining two cases and the involvement of nails was of endonyx type (Figure 12).
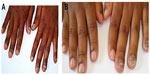  | Figure 12 Tinea unguium. |
Tinea capitis was the most common clinical form in children below 10 years (76.2%)1 (Figure 14). Tinea capitis is common in younger age groups, below 20 years (Table 3) and statistically significant.
Extensive lesions of tinea corporis without central clearing were seen in few HIV/AIDS patients (Figure 13).
  | Figure 13 Tinea corporis (right knee). |
  | Figure 14 Hair loss, marked crusting and Kerion formation. |
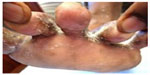  | Figure 15 Tinea pedis due to Trichophyton interdigitale. |
One of the patients suffering from tinea manuum appears to have acquired the infection in South Africa. He gave the history of having played soccer in South Africa, and within 2 weeks of returning from there, he started complaining of itching, and was prescribed steroid cream. His condition did not improve and skin scrapings were collected and cultured, which yielded growth of T. tonsurans (Figure 9). Most cases of tinea pedis were due to T. interdigitale (Figure 15). Positive cases for superficial fungal infections:
- Dermatophytes (120 cases)
- Candida (five cases)
- Malassezia species (five cases)
- Non-dermatophyte moulds in onychomycosis (four cases)
Discussion
T. violaceum was found to be the predominant species, and was found to be the causative organism for most of the clinical forms. Tinea unguium of the fingernails was found to be due to T. violaceum, and in two HIV cases ten fingers’ involvement was found. Two cases of tinea unguium of the toenails were due to T. interdigitale and one was due to T. tonsurans.
Various studies have been conducted from time to time. It has been observed that there has been a rise and fall of certain species of dermatophytes. This could have been due to the change of habitat, war, better medical facilities, and more effective drugs.
There has not been any major study in Botswana before and after the HIV/AIDS era. The only relevant information available is in Vismer and Findlay’s published data about Botswana, and in which, they reported Trichophyton schoenleinii and T. violaceum.20 We did not isolate T. schoenleinii in our study, but T. violaceum was found to be the predominant species. Botswana has got high prevalence of HIV/AIDS, and dermatophytic lesions in HIV/AIDS patients can be deep, widespread, and atypical. So it presents some diagnostic challenges. We did not isolate T. rubrum in any of the samples.
Since we did not isolate T. rubrum from any of the patients in our study or in any samples referred to our laboratory from various hospitals and clinics, we can assume, that T. rubrum could be rare. The reason for the less involvement of the toenails could be due to either absence or rarity of T. rubrum in Botswana.
T. rubrum is the most prevalent species of dermatophyte in many geographical regions of the world. It has been found responsible for causing tinea pedis and tinea unguium in a vast majority of cases. The history of onychomycosis is analogous to that of T. rubrum, the major causative fungal pathogen involved in the pathogenesis of onychomycosis and tinea pedis.21
Increased population mobility that resulted from world wars, mass migration, and recreational travel led to the translocation and subsequent distribution of T. rubrum from its original endemic regions to the new ecological environments in Europe and America.21,22 In the United States, the first documented case of onychomycosis is said to have been reported in 1928.21,23 World War II and the Korean and Vietnam wars, increased participation in fitness activity, the occlusive footwear and periodic and migratory movement of populations, have contributed towards the increased prevalence of tinea pedis and onychomycosis in the 20th century.24 After the Vietnam War, T. rubrum surpassed T. interdigitale as the most commonly isolated dermatophyte worldwide.24
So, the involvement of the toenail is more common in the countries, where, T. rubrum is the predominant species, and involvement of finger nails could be more prevalent in our study because of T. violaceum being the predominant species. In brief, tinea pedis is the source of infection for the toenail infections; and tinea capitis and tinea corporis could be the source of infection for the fingernails in our study. We did not report onychomycosis of the toenails due to T. violaceum. Also, in the literature, there is only one case report of toenail onychomycosis due to T. violaceum.25
Since we did not know the HIV status of all the patients, we cannot know if tinea unguium was more prevalent in HIV infected individuals. A larger study is needed in which the HIV status of all enrolled cases should be known.
Conclusion
T. violaceum was found to be the predominant dermatophyte species and tinea unguium was found to be the most frequent clinical type. In our study, involvement of fingernails was more frequent as compared to toenails, 26 and three respectively. Involvement of fingernails in all the cases was found due to T. violaceum, which presented both unilateral; involving 2–4 fingers; and bilateral, involving all ten fingers (Figure 12A and B).
It appears that the source of infection for tinea unguium of fingernails is the scalp. It has been mentioned by Mapelli et al.25
Both the scalp and fingernails can remain potential sources of infection to the person himself and to others, because it can be transmitted easily to others. These clinical forms can lead to cosmetic embarrassment and social stigma. Both these conditions require both dermatological and mycological expertise for the appropriate treatment and follow-up.
Disclosure
The author has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
Thakur R. Tinea capitis in Botswana. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;3(6):37–41. | |
Evans EG. Causative pathogens in onychomycosis and the possibility of treatment resistance: a review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;38(5 Pt 3):S32–S36. | |
Summerbell RC. Epidemiology and ecology of onychomycosis. Dermatology. 1997;194 (Suppl 1):32–36. | |
Akiba H, Motoki Y, Satoh M, Iwatsuki K, Kaneko F. Recalcitrant trichophytic granuloma associated with NK-cell deficiency in a SLE patient treated with corticosteroids. Eur J Dermatol. 2001; 11(1):58–62. | |
Chastain MA, Reed RJ, Pankey GA. Deep dermatophytosis: report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Cutis. 2001;67(6):457–462. | |
Coldrion BM, Bergstresser PR. Prevalence and clinical spectrum of skin disease in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125(3):357–361. | |
Aly R, Berger T. Common superficial fungal infections in patients with AIDS. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;22 Suppl 2:S128–S132. | |
Singh A, Thappa DM, Hamide A. The spectrum of mucocutaneous manifestations during the evolutionary phases of HIV disease: An emerging Indian scenario. J Dermatol. 1999;26(5):294–304. | |
Gupta AK, Taborda P, Taborda V, et al. Epidemiology and prevalence of onychomycosis in HIV-positive individuals. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39(10):746–753. | |
Dover JS, Johnson RA. Cutaneous manifestations of human immunodeficiency virus infection Part II. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127(10):1549–1558. | |
Torssander J, Karlsson A, Morfeldt–Mason L, Putkonen PO, Wasserman J. Dermatophytosis and HIV infection: a study in homosexual men. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;68(1):53–56. | |
Goodman DS, Teplitz ED, Wishner A, Klein RS, Burk PG, Hershenbaum E. Prevalence of cutaneous disease in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or AIDS-related complex. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;17(2 Pt 1):210–220. | |
Crissey JT, Lang H, Parish LC. Manual of Medical Mycology. Cambridge: Blackwell Science; 1995. | |
Havlickova B, Czaika VA, Friedrich M. Epidemiological trends in skin mycoses worldwide. Mycoses. 2008;51 Suppl 4:2–15. | |
Rippon JW. Dermatophytosis and Dermatomycosis. In: Medical Mycology: The Pathogenic Fungi and Pathogenic Actinomycetes. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 1988:169–275. | |
Kwon-Chung KJ, Bennett JE. Dermatophytoses (Ringworm, Tinea, Dermatomycoses). In: Medical Mycology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lea and Febige; 1992:105–170. | |
Larone DH. Dermatophytes. In: Medically Important Fungi: A Guide to Identification. 4th ed. Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology (ASM) Press; 2002:229–253. | |
Vena GA, Chieco P, Posa F, Garofalo A, Bosco A, Cassano N. Epidemiology of dermatophytoses: retrospective analysis from 2005 to 2010 and comparison with previous data from 1975. New Microbiol. 2012;35(2):207–213. | |
Weitzman I, Summerbell RC. The Dermatophytes. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1995;8(2):240–259. | |
Vismer HF, Findlay GH. Superficial fungal infections in the Transvaal A contemporary analysis of dermatophytes in this region. S Afr Med J. 1988;73(10):587–592. | |
Charif MA, Elewski BE. A historical perspective on onychomycosis. Dermatologic Therapy. 1997;3:43–45. | |
Weidman FD. The laboratory aspects of dermatophytosis. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1927;15:415–450. | |
Salgo PL, Daniel CR, Gupta AK, Mozena JD, Joseph SW. Onychomycosis disease management. Medical Crossfire: Debates, Peer Exchange and Insights in Medicine. 2003;4:1–17. | |
Elewski BE. Tinea pedis and tinea manuum. In: Demis JD, editor. Clinical Dermatology. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott Co; 1993:1–10. | |
Mapelli ET, Colombo L, Crespi E, Menni S. Toenail onychomycosis due to Trichophyton violaceum complex. (An unusual, emerging localization of this anthropophilic dermatophyle). Mycoses. 2012;55(2):193–194. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
