Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 12
Small-aperture intraocular lens tolerance to induced astigmatism
Authors Ang RE
Received 28 April 2018
Accepted for publication 10 July 2018
Published 4 September 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 1659—1664
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S172557
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Robert Edward Ang
Department of Cornea and Refractive Surgery, Asian Eye Institute, Makati City, Philippines
Purpose: This prospective, single-site study aimed to assess the corresponding change in monocular visual acuity with induced astigmatic defocus in subjects implanted with a small-aperture intraocular lens (IOL).
Patients and methods: Ten subjects with a mean age of 65.1 years were recruited. Eleven eyes of these 10 subjects were implanted (9 unilaterally, 1 bilaterally) with an IC-8 small-aperture IOL. Baseline manifest refraction and best-corrected distance visual acuity were measured with a Snellen chart (Tumbling E chart). Astigmatic defocus was induced in the same axis as the manifest sphere-cylinder refraction or at 180° for a spherical refraction. Cylinder defocus was reduced in 0.50 D steps from -2.50 D, and distance visual acuity was measured at each level of defocus.
Results: Mean distance visual acuity was 0.08 logarithm of minimum angle of resolution (logMAR) ±0.08 (20/24) at 1.50 D of defocus, 0.18 logMAR ±0.08 (20/30) at 2.00 D of defocus, and 0.24 logMAR ±0.07 (20/35) at 2.50 D of defocus. Eight out of 10 subjects achieved 20/25 or better vision with 1.50 D of cylinder defocus, and all subjects were 20/30 or better. Ten out of 11 subjects were 20/40 or better with 2.50 D of defocus.
Conclusion: The IC-8 IOL shows good tolerance to astigmatic defocus with minimal effect on visual acuity. Overall, 20/25 or better distance acuity was maintained through 1.50 D cylinder defocus.
Keywords: multifocal intraocular lenses, extended depth of focus lenses, refractive errors, cataract
Introduction
The IC-8 small-aperture intraocular lens (IOL; AcuFocus, Inc., Irvine, CA, USA) is an aspheric monofocal IOL embedded with an opaque mini-ring that is intended to extend depth of focus by decreasing the size of the blur circle at the retina. The relation between decreasing pinhole size and increasing acuity in ametropia has been well established.1,2 This principle is already being used successfully by the KAMRA corneal inlay (CorneaGen, Seattle, WA, USA), which is US Food and Drug Administration-approved for presbyopia correction.3,4 Likewise, the unilateral implantation of the IC-8 IOL with an aspheric monofocal IOL in the fellow eye provides reduced spectacle dependence by extending the depth of focus from far through near in the IC-8 eye.5,6 Subjects implanted contralaterally in a prospective clinical trial achieved uncorrected binocular visual acuities of 20/18, 20/22, and 20/29 for distance, intermediate, and near, respectively.6
Residual refractive error in an eye implanted with an IOL is one of the primary factors influencing postoperative visual acuity and patient satisfaction. Multifocal IOLs can tolerate up to 0.75 diopters (D) of astigmatism, beyond which visual acuity, spectacle independence, and patient satisfaction are compromised.7 Similarly, the Symfony IOL (J&J Vision, Costa Mesa, CA, USA) has been shown to tolerate up to 1.00 D of astigmatism.8 Laser in situ keratomileusis, photorefractive keratectomy arcuate corneal incisions, piggy-back IOLs, and IOL exchange are some of the techniques used to correct residual refractive error when spectacle independence is desired after cataract surgery.9–11
In contrast, a small aperture is able to provide good uncorrected distance, intermediate, and near vision while being more tolerant to sphero-cylindrical residual refractive errors as a result of its extended depth of focus.6,12 In a recently published prospective clinical trial, patients with up to 1.75 D of corneal astigmatism that were treated with an IC-8 IOL without any additional astigmatic management were able to tolerate up to 1.50 D of refractive astigmatism.6
Thirty-two percent of patients present for cataract surgery with between 0.75 and 2.00 D of corneal astigmatism before cataract surgery.13 For eyes with >0.50 D of corneal astigmatism, a toric IOL may be needed.14 The IC-8 IOL has the potential to bridge the gap between the monofocal and monofocal toric IOLs for correcting low-grade astigmatism and/or to have greater tolerance for residual postoperative astigmatism. This pilot evaluation was designed to investigate the tolerance of the IC-8 IOL to increasing levels of induced astigmatism.
Patients and methods
This was a prospective, single-center, single-visit, observational pilot study on 11 eyes implanted with the IC-8 IOL. Nine subjects were contralaterally implanted with an IC-8 IOL in conjunction with a monofocal IOL in the fellow eye and 1 subject was implanted bilaterally with the IC-8 IOL (both eyes from this subject were enrolled in the study). The study was performed at the Asian Eye Institute in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the ethics committee of the investigational site. Subjects were screened for eligibility, and written informed consents were obtained from all eligible subjects.
Eligibility criteria included eyes with best-corrected distance visual acuity (BCDVA) of 20/25 or better and clear intraocular media with no posterior capsular opacification. Eyes with any pathology resulting in loss of BCDVA were excluded from the study.
The baseline manifest refraction and BCDVA were measured in all eyes using a Snellen chart (Tumbling E chart). With the manifest refraction in place, −2.50 D of astigmatic defocus was induced in the IC-8 IOL eye either in the same axis as that of the manifest sphere-cylinder refraction or at the 180° axis in eyes with a spherical refraction. The amount of astigmatism induced was decreased in 0.50 D steps from −2.50 to −0.50 D. Distance visual acuity was recorded at each defocus level with the Snellen chart. No spherical adjustments were made in order to isolate the astigmatic defocus effect.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using JMP statistical software version 13.0 (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Snellen visual acuity data were converted to logarithm of minimum angle of resolution (logMAR) for analysis. The mean and SD of visual acuity at each level of induced astigmatic defocus were calculated. Continuous parameters were compared using the Wilcoxon test. A P-value of <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Change in mean visual acuity with an increase in induced astigmatic defocus was plotted to generate astigmatic defocus curve.
Results
Demographics and baseline characteristics
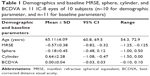
The mean age ± SD was 65.1 years ±6.1 (range: 54.3–72.9 years, n=10). Of the 10 subjects analyzed, 60% (n=6) subjects were female and 40% (n=4) subjects were male. All (100%) subjects were Asian. Demographics results and the baseline sphere, cylinder, and manifest spherical equivalent refraction, BCDVA for the IC-8 IOL eyes (n=11) are presented in Table 1.
Visual acuity with induced astigmatic defocus
Figure 1 shows the mean far visual acuity in logMAR at different levels of induced astigmatic defocus. The baseline mean logMAR ±95% CIs ([min, max]; mean Snellen equivalent) visual acuity was 0.00±0.03 ([−0.01, 0.10]; 20/20) at 0.00 D defocus, ie, BCDVA with manifest refraction. Visual acuity was 0.02±0.05 ([−0.10, 0.18]; 20/21) with −0.50 D, 0.07±0.05 ([0.00, 0.18]; 20/24) with −1.00 D, 0.08±0.05 ([0.00, 0.18]; 20/24) with −1.50 D, 0.19±0.07 ([0.00, 0.40]; 20/31) with –2.00 D, and 0.26±0.08 ([0.10, 0.54]; 20/36) with −2.50 D of defocus. The mean logMAR visual acuity showed a statistically significant difference from baseline at −1.00 D (P=0.0025), −1.50 D (P=0.0009), −2.00 D (P<0.0001), and −2.50 D (P<0.0001) of induced astigmatism. There was no statistically significant difference in visual acuity between −0.50 and −1.00 D (P=0.0767) and between −1.0 and −1.50 D (P=0.73) of astigmatic defocus. Figure 2 shows the distribution of visual acuity scores. For astigmatism defocus up to −1.50 D, 73% and 100% of subjects had 20/25 or better and 20/30 or better visual acuity, respectively. At 2.50 D, 46% and 91% of eyes had acuity of 20/30 or better and 20/40 or better, respectively.
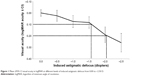  | Figure 1 Mean ±95% CI visual acuity in logMAR at different levels of induced astigmatic defocus from 0.00 to −2.50 D. |
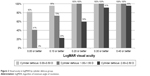  | Figure 2 Visual acuity in logMAR by cylinder defocus group. |
The change in visual acuity at each incremental step of induced astigmatic defocus was not constant. A gradual change of <1 line was observed from the baseline to −1.50 D of defocus, followed by a 1 line loss from −1.50 to −2.00 D of defocus and approximately another line of loss from −2.00 to −2.50 D of defocus. Figure 3 shows the mean change in visual acuity from baseline by cylinder axis: with-the-rule, oblique, and against-the-rule. Change in visual acuity was similar between all 3 groups. Eyes with astigmatism in the oblique axis or with-the-rule showed slight better maintenance of visual acuity at −1.00 and −1.50 D of induced cylinder defocus than eyes with against-the-rule astigmatism.
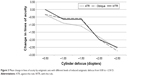  | Figure 3 Mean change in lines of acuity by astigmatic axis with different levels of induced astigmatic defocus from 0.00 to −2.50 D. |
Discussion
Patient satisfaction with presbyopia correcting lenses such as multifocal IOLs is largely linked to patient expectations of spectacle independence following lens surgery.15,16 While 80% of the patients experienced spectacle independence,17 a common complaint among dissatisfied multifocal IOL patients is blurred vision due to residual refractive error that may require secondary management using refractive surgery or IOL exchange.9 Residual refractive astigmatism is reported in 29%–64% of complaints of blurred vision with a mean residual cylinder amount of 1.00–1.50 D.18,19 In the presence of astigmatism, the light split between different foci of a multifocal lens further decreases in intensity, along with interference of the astigmatic focal lines between different foci.20 The IC-8 IOL is an extended depth of focus IOL that combines an aspheric monofocal IOL optic and a small aperture to elongate depth of focus. By virtue of this design, the IC-8 IOL should be more tolerant of residual astigmatic refractive error.
A mean acuity of 20/24 was observed at 1.50 D of induced astigmatic defocus with the IC-8 IOL. According to the American Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgery (ASCRS) committee guidelines for multifocal IOL patient selection, the threshold for astigmatic defocus is placed at 0.75 D, beyond which satisfactory functional visual acuity and spectacle independence may be compromised.7 Astigmatism exceeding 0.75 D compromised distance visual acuity to 20/40 or less with diffractive multifocal and 20/30 or less with refractive multifocal.21,22 This doubling of tolerance to astigmatism was also observed with computational eye modeling of the small-aperture inlay. Vilupuru et al12 observed in 20 eyes, if 1.00 D of astigmatism remained uncorrected for a pupil diameter of 3.00 mm in an untreated eye, the equivalent value with the small-aperture inlay implanted was 1.90 D (ie, an increase of 0.90 D of tolerance to astigmatism).
When comparing induced astigmatism up to 1.00 D with minus cylinder, the effect of astigmatic defocus on acuity with the IC-8 IOL agrees well with the Symfony IOL.8 BCDVA was 20/24 with the IC-8 IOL and 20/25 with the Symfony IOL for 1.00 D induced cylinder. The impact on acuity for the same diopter of induced astigmatism in multifocal IOLs ranges from 20/29 to 20/40.8 For astigmatic defocus >1.00 D, acuity results, at least in this series and as reported by Dick et al,6 appear to be better with the IC-8 IOL compared to the Symfony IOL or multifocal IOLs. Acuity with 1.50 D cylinder was 20/24 with the IC-8 IOL, 20/29 with the Symfony IOL, and worse than 20/30 with multifocals IOLs.8
Carones et al8 compared the impact of induced astigmatism with 2 multifocals (AcrySof ReSTOR +2.50 D and AcrySof ReSTOR +3.00 D; Alcon, Fort Worth, TX, USA), a trifocal (AcrySof PanOptix, Alcon), and the extended range of vision (Tecnis Symfony ZRX00, J&J Vision, Santa Ana, CA, USA) IOLs. The results of the study showed the Symfony IOL to be tolerant to up to 1.00 D of astigmatism and be the least sensitive to induced blurriness and change in satisfaction scores, when compared to the multifocals and the trifocal IOLs. At 1.50 D of astigmatic defocus, the average visual acuities with the multifocals, trifocal, and Symfony IOLs were 20/33, 20/40, and 20/29, respectively. In contrast, with 1.50 D of astigmatic defocus, the average visual acuity was 20/24 with the IC-8 IOL. At 1.50 D of induced astigmatic defocus, the multifocals, trifocal, and Symfony IOLs, on average, lost 3, 4, and 2 lines of visual acuity from their baseline visual acuity, respectively. In contrast, with 1.50 D of astigmatic defocus, eyes implanted with the IC-8 IOL lost <1 line of visual acuity. Additionally, at 1.00 D of induced astigmatic defocus, the Symfony IOL, on average, lost 2 lines of visual acuity, while eyes with the IC-8 IOL, lost <1 line of visual acuity.
Hayashi et al21 recommended that residual astigmatism be within 1.00 D with multifocal IOLs to achieve a functional distance visual acuity of 20/40 required for most tasks such as driving. In this study, all eyes except 1 achieved 20/40 or better acuity with 2.50 D of induced defocus.
The individual defocus curves of the 11 eyes showed some differences in response to astigmatic defocus between subjects. We observed that some subjects implanted with the IC-8 IOL had a change in baseline acuity at 1.00 D while others did not have any change in baseline acuity until 2.00 D. If the eyes had a baseline refraction that was categorized to be mixed or simple astigmatism and if the astigmatism was against-the-rule, the eyes tended to exhibit lower tolerance to induced astigmatic defocus.
Residual astigmatism after cataract surgery is difficult to control as a result of conditions like corneal curvature changes induced by a corneal incision and possible postoperative IOL tilt and rotation. In addition, toric IOL power calculation, reference marking, IOL axis placement intraoperatively, and monitoring of IOL rotation postoperatively can be tedious and time-consuming. In the event of toric IOL misalignment, every degree of off-axis rotation results in a loss of up to 3.3% of IOL cylindrical power. This means with a 10° off-axis rotation, the toric IOL provides only 0.66 D of effective cylinder power and hence one-third of the cylindrical effect is lost.23 The small-aperture lens design is symmetric, with the small aperture placed at the IOL optic center. With no axis to align, astigmatism management is less complex and the potential for postoperative rotational misalignment is eliminated.
Dick et al6 compared visual acuity results by cylinder power in the European postmarket study on the IC-8 IOL. They showed that subjects who had 1.50 D or less uncorrected astigmatism achieved mean visual acuity of 20/22 where subjects with more than 1.50 D of uncorrected astigmatism achieved 20/38. While this prior study compared groups based on preexisting corneal astigmatism, this study evaluated the influence of increasing amounts of cylinder defocus in a consistent cohort of IC-8 IOL eyes. This study provides additional support for astigmatism tolerance of the IC-8 IOL up to 1.50 D and new information about influence of cylinder axis. The IC-8 IOL expands the surgical options for the treatment of low-level corneal astigmatism without the inconveniences associated with toric alignment, surgically induced astigmatism, and postoperative lens rotation with axis misalignment.
While the results are promising, this study is limited by the sample size. Further studies are required on a larger cohort for a more precise determination of tolerance to astigmatic defocus with the IC-8 IOL. Additional measures of patient satisfaction scores and contrast sensitivity can help to complement acuity data in subjects. Other future modifications to the study include inducing astigmatism at horizontal, vertical, and oblique axes as well as use of optotypes such as Landolt C without any orientation bias rather than linear optotypes such as Tumbling E.
Conclusion
Induced astigmatic defocus up to 1.50 D may be reasonably compensated for with the IC-8 IOL, and up to 2.00 D in some subjects following monocular implantation of the IC-8 IOL in the nondominant eye. The IC-8 IOL may provide improved tolerance to blur from residual induced astigmatism compared to multifocals, with minimal impact on distance acuity of 20/25 or better. With each type of IOL having its benefits and trade-offs, this knowledge will be clinically useful for surgeons in considering IOL options for cataract and refractive lens exchange patients with astigmatism. Additional study is ongoing to fully describe the benefits and limitations of a small-aperture IOLs tolerance to corneal astigmatism.
Disclosure
The author is the clinical investigator of this study and a member of AcuFocus’ medical advisory board. The author reports no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Atchison DA, Smith G, Efron N. The effect of pupil size on visual acuity in uncorrected and corrected myopia. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1979;56(5):315–323. | ||
Wang B, Ciuffreda KJ. Depth-of-focus of the human eye: theory and clinical implications. Surv Ophthalmol. 2006;51(1):75–85. | ||
Dexl AK, Seyeddain O, Riha W, et al. Reading performance and patient satisfaction after corneal inlay implantation for presbyopia correction: 2-year follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012;38(10):1808–1816. | ||
Vilupuru S, Lin L, Pepose JS. Comparison of contrast sensitivity and through focus in small-aperture inlay, accommodating intraocular lens, or multifocal intraocular lens subjects. Am J Ophthalmol. 2015;160(1):150.e1–162.e1. | ||
Grabner G, Ang RE, Vilupuru S. The small-aperture IC-8 intraocular lens: a new concept for added depth of focus in cataract patients. Am J Ophthalmol. 2015;160(6):1176.e1–1184.e1. | ||
Dick HB, Piovella M, Vukich J, et al. Prospective multicenter trial of a small-aperture intraocular lens in cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2017;43(7):956–968. | ||
Braga-Mele R, Chang D, Dewey S, et al. Multifocal intraocular lenses: relative indications and contraindications for implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014;40(2):313–322. | ||
Carones F. Residual astigmatism threshold and patient satisfaction with bifocal, trifocal and extended range of vision intraocular lenses (IOLs). Open J Ophthalmol. 2017;7(1):1–7. | ||
Macsai MS, Fontes BM. Refractive enhancement following presbyopia-correcting intraocular lens implantation. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008;19(1):18–21. | ||
Alio JL, Abdelghany AA, Fernández-Buenaga R. Management of residual refractive error after cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2014;25(4):291–297. | ||
Sáles CS, Manche EE. Managing residual refractive error after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015;41(6):1289–1299. | ||
Vilupuru A, Tabernero J, Artal P. Tolerance to astigmatism with a small aperture corneal inlay. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013;54:4280. | ||
Ferrer-Blasco T, Montés-Micó R, Peixoto-de-Matos SC, González-Méijome JM, Cerviño A. Prevalence of corneal astigmatism before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35(1):70–75. | ||
Villegas EA, Alcón E, Artal P. Minimum amount of astigmatism that should be corrected. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014;40(1):13–19. | ||
de Silva SR, Evans JR, Kirthi V, Ziaei M, Leyland M. Multifocal versus monofocal intraocular lenses after cataract extraction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;12:CD003169. | ||
Hawker MJ, Madge SN, Baddeley PA, Perry SR. Refractive expectations of patients having cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31(10):1970–1975. | ||
Rosen E, Alió JL, Dick HB, Dell S, Slade S. Efficacy and safety of multifocal intraocular lenses following cataract and refractive lens exchange: metaanalysis of peer-reviewed publications. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2016;42(2):310–328. | ||
de Vries NE, Webers CA, Touwslager WR, et al. Dissatisfaction after implantation of multifocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37(5):859–865. | ||
Woodward MA, Randleman JB, Stulting RD. Dissatisfaction after multifocal intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35(6):992–997. | ||
Ravalico G, Parentin F, Baccara F. Effect of astigmatism on multifocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1999;25(6):804–807. | ||
Hayashi K, Manabe S, Yoshida M, Hayashi H. Effect of astigmatism on visual acuity in eyes with a diffractive multifocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36(8):1323–1329. | ||
Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Influence of astigmatism on multifocal and monofocal intraocular lenses. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000;130(4):477–482. | ||
Novis C. Astigmatism and toric intraocular lenses. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2000;11(1):47–50. |
 © 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.