Back to Journals » Cancer Management and Research » Volume 11
Sinonasal/nasopharyngeal pleomorphic adenoma and carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma: a report of 17 surgical cases combined with a literature review
Authors Li W, Lu H, Zhang H, Lai Y , Zhang J , Ni Y, Wang D
Received 20 December 2018
Accepted for publication 26 April 2019
Published 17 June 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 5545—5555
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S198942
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Wanpeng Li, Hanyu Lu, Huankang Zhang, Yuting Lai, Jia Zhang, Yang Ni, Dehui Wang
Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Affiliated Eye Ear Nose and Throat Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200031, People’s Republic of China
Objective: The aim of this study was to review demographic data, location, clinical symptoms, therapeutic methods, pathological features and relapse in sinonasal/nasopharyngeal pleomorphic adenoma (PA) and carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma (CXPA).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of 17 patients who were referred to our hospital during a 5-year period from 2013 to 2018.
Results: In this series, there were 7 males and 10 females. The tumors originated from the nasal septum in 4 cases, from the lateral wall of the nasal cavity in 2 cases, from the maxillary sinus in 1 case, and from the nasopharynx in 7 cases. The origin sites of 3 cases were not clear. The main symptoms were usually unilateral nasal congestion and epistaxis. All patients underwent endoscopic resection surgery. The postoperative period was uneventful. Ten patients were diagnosed with benign PA, and 7 patients were diagnosed with CXPA, including 5 cases of adenocarcinoma, 1 patient with mucoepidermoid carcinoma, and 1 patient with adenoid cystic carcinoma. After a mean follow-up period of 2.2 years (6 months–5.3 years), the recurrence rate of benign PA was 10% (1/10); the rate of malignant recurrence was 42.8% (3/7).
Conclusion: Sinonasal/nasopharyngeal PA and CXPA are rare neoplasms, and the most common primary site of PA and CXPA is the nasopharynx. As any salivary carcinoma type can arise in PA, these PA sites should be thoroughly sampled and closely examined to exclude the possibility of malignant transformation. Furthermore, PA and CXPA should be treated as soon as possible after definitive diagnosis, and endoscopic resection of tumor-negative margins may be helpful in preventing recurrence.
Keywords: sinonasal, nasopharyngeal, pleomorphic adenoma, carcinoma ex- pleomorphic adenoma, endoscopic
Introduction
Salivary gland neoplasms mostly occur in major salivary glands but less in minor salivary glands (10–15%). Approximately 75% of the pleomorphic adenomas (PAs) are located in the parotid gland and 15% in the submandibular gland; only 10% of the PAs originate from the small salivary glands, though they can develop at any site where these glands are located, including the hard and soft palates, upper lip, floor of the mouth, lacrimal gland, larynx, and trachea.1–3 PA is rare in the sinonasal and nasopharyngeal areas, with the majority of cases occurring more frequently in women in their third to sixth decades of life.4,5
A carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma (CXPA) is a malignant epithelial neoplasm arising from a primary or recurrent benign PA. Tumors of this variety account for approximately 3.6–4% of all salivary gland neoplasms, which in turn account for 12% of all salivary gland malignancies.6 CXPA is extremely rare in the sinonasal and nasopharyngeal regions, and only a few cases have been reported in the literature (Table 1).5–14 CXPA is divided into noninvasive, minimally invasive, and invasive categories according to the degree of invasion of carcinoma beyond PA. This distinction is important for determining prognosis and guiding appropriate treatment. Noninvasive and minimally invasive CXPA rarely occur in a malignant fashion, and invasive CXPA has a 5-year survival rate of approximately 30%.15
 | Table 1 Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma in the sinonasal and nasopharyngeal region |
Patients and methods
We retrospectively collected data for all patients presenting with PA and CXPA involving the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses (sphenoid, maxillary, ethmoid, and frontal sinuses), and nasopharynx. The cases were retrieved from the Department of Otorhinolaryngology of the Affiliated Eye Ear Nose and Throat Hospital (AEENTH), Fudan University, during a 5-year period from 2013 to 2018. The patients’ medical records were analyzed for demographic data, location, previous surgical history, clinical symptoms, therapeutic method, pathological features, and relapse. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of AEENTH at Fudan University. All patients provided informed consent with regard to clinical information and photographs for research.
Results
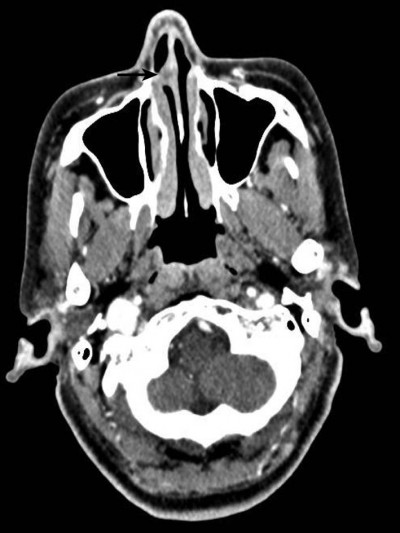
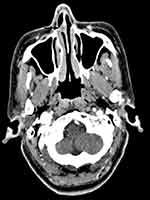
A summary of the patients in this series is depicted in Table 2. Of the 17 patients identified, 7 were male and 10 were female. The age at the time of surgery ranged from 37 years to 77 years, with a mean age of 55.2 years. The tumors originated from the nasal septum in 4 cases, from the lateral wall of the nasal cavity in 2 cases, from the maxillary sinus in 1 case, and from nasopharynx in 7 cases. The origin sites of 3 cases were not clear. Imaging computed tomography (CT) showed an aspect of osteolysis in 6 patients: 1 case of benign IP and 5 cases of CXPA. In addition, enhanced CT for patient 1 revealed flaky, thickened soft tissue lesions on the right side of the nasal septum (Figure 1). Enhanced CT for patient 9 showed a soft tissue mass in the left nasal cavity and maxillary sinus with an unclear boundary; the nasal septum was compressed and obviously deviated to the right (Figure 2). Based on an MRI for patient 13, the soft tissue mass occupied the top of the nasopharynx; TIWI showed a moderate signal and T2W1 showed a slightly high signal (Figure 3A and B).
 | Table 2 Features of 17 cases with sinonasal/nasopharyngeal PA and CXPA |
 | Figure 1 Enhanced CT showed flaky, thickened soft tissue lesions (black arrow) on the right side of the nasal septum. |
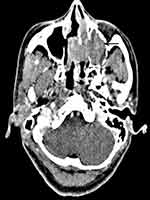 | Figure 2 Enhanced CT demonstrated a neoplasm on the left maxillary sinus (black arrow); the size was 4.5 cm*4.0 cm. The nasal septum was obviously compressed, with a right deviation. |
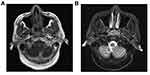 | Figure 3 MRI showed that the soft tissue mass occupied the top of the nasopharynx (black arrow). TIWI showed a moderate signal (A) and T2W1 showed a slightly high signal (B). |
All patients with PA and CXPA underwent endoscopic resection surgery; 4 cases of CXPA were treated with adjuvant radiotherapy after surgical exeresis, and no cases were managed with chemotherapy. The tumors in 12 patients (70.6%) were completely resected at our institution as the initial surgery; residual tumors were found in 5 patients (29.4%). The postoperative period was uneventful, and no serious complications were observed in any patients. The final diagnosis was based on pathological findings. Ten patients were diagnosed with PA, and 7 patients were diagnosed with CXPA, including 5 cases of adenocarcinoma (not otherwise specified, NOS), 1 case of mucoepidermoid carcinoma, and 1 case of adenoid cystic carcinoma. Postoperatively, PA and CXPA patients were observed by nasal endoscopy for tumor recurrence. The follow-up time was every three months in the first year after the operation, followed by every other year. No patient was lost to follow-up. After the mean follow-up period of 2.2 years (6 months–5.3 years), 4 patients (4/17, 23.5%) had postoperative recurrence; the recurrence rate of benign PA was 10% (1/10), and the rate of malignant recurrence was 42.8% (3/7). Patient 11 and patient 15 underwent one more surgical resection, patient 10 underwent two more surgical resections, and patient 12 did not undergo reoperation because of the high risk but did receive further radiotherapy.
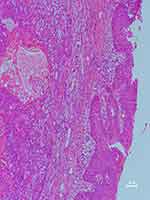
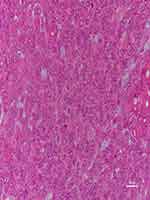
A microscopy histopathological examination of patient 1 revealed the lesion to be the benign PA (Figure 4). Immunohistochemical staining indicated the following: CKpan(+), CK8 (+), P63(+), Vimentin(+), SMA(+), Calponin(+), S100(+), Ki67(2%+), and CK(+). A histopathological examination of patient 15 demonstrated that lesion was CXPA (Figure 5), with immunohistochemical staining revealing CKpan(+), CK8 (+), P63(+), Vimentin(+), HHF35(+), SMA(+), and Ki67(15%+).
Discussion
Many theories have been proposed for the origin of PA of the nasal cavity. PA may arise from residues in the vomeronasal organs, the epithelial lining ducts found in the septa regenerated in early embryonic life.16 Another study considered that the abnormal origin of PA from the nasal septum mucosa may be caused by dislocated embryonic epithelial cells originating from the ectoderm and carried into the septal region via the nasal pits.17 Evans et al. proposed that sinonasal PA originates from the mature salivary gland.18
We conducted a comprehensive MEDLINE search for all cases of sinonasal/nasopharyngeal PA and CXPA, and 45 articles were identified in our literature review.2,4–17,19–48 The earliest report of the disease was a single case report published in 1971.40 Including our 17 patients, a total of 115 cases were included in this review. The distribution of primary sites is depicted in Figure 6. The most common primary site was the nasal septum (61/115, 53.0%), followed by the lateral wall of the nasal cavity (16/115, 13.9%) and the nasopharynx (13.9%, Table 3). Involvement of the paranasal sinuses was found to be extremely rare, with only 10 documented cases of PA and CXPA (10/115, 11.5%): 9 from the maxillary sinus and 1 from the frontal sinus (Table 4). In our series, 7 cases stemmed from the nasopharynx, it was the largest reported series of PA in the nasopharynx, and nasopharyngeal CXPA was found in 4 cases. The main symptoms of sinonasal/nasopharyngeal PA and CXPA are usually unilateral nasal congestion and epistaxis; other symptoms may include nasal swelling, mucous purulent rhinorrhea, external deformities, otalgia, hearing loss, and otitis media.6,11,16,47 Patients with sinonasal CXPA may also have the following symptoms as a result of invading surrounding structures: visual change, headache, facial pain, or facial paresthesia. In our study, 3 patients experienced decreased olfactory sensation, and 2 patients with nasopharyngeal PA had tinnitus and ear stuffiness. In addition, patient 15 developed facial numbness, right orbital pain, and decreased vision due to CXPA.
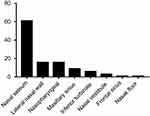 | Figure 6 Distribution of primary sites among patients with sinonasal/nasopharyngeal PA and CXPA. |
 | Table 3 Summary of all reported cases of PA and CXPA arising in the paranasal sinuses |
 | Table 4 Summary of all reported cases of PA and CXPA arising in the nasopharynx |
The diagnosis of PA and CXPA in the sinonasal/nasopharyngeal regions is challenging because symptoms are not characteristic and radiologic findings are usually nonspecific. CT generally shows bony alterations and expansive or destructive type changes, providing reliable clues for differentiating between benign and malignant lesions. PA usually presents with well-defined, homogeneous soft tissue masses and expansile bony changes. An aspect of osteolysis is an indirect sign of malignancy. MRI manifestations are varied but often well defined. The signal intensity of T1-weighted images is low to moderate and that of T2-weighted images is high.34 In this series, the proportion of CXPA and benign IP with osteolysis presentation was 71.4% and 10%, respectively. This appears to indicate that osteolysis may suggest the malignancy of IP.
There are epithelial and mesenchymal components in the pathology of PA. Sinonasal and nasopharyngeal PA differ from mixed neoplasms of major salivary glands in that they have more cytoplasm and predominant epithelial components; they are also devoid of capsules and have few stromal components.33,35 Occasionally, PA is composed almost entirely of epithelial cells, with few or no stromata. Thus, microscopically, PA resembles malignant tumors, such as malignant mixed tumors, which can make the diagnosis of intranasal PA more challenging. The presence of infiltrating carcinoma and disruptive growth patterns in juxtaposition with PA is the diagnostic criterion for CXPA. For example, in the surgical specimens of approximately 75% of the cases, CXPA clearly appears in PA. However, the proportion of malignant components varies greatly, and in some cases, it is difficult to locate the original benign PA.33 The diagnosis of CXPA depends on careful sampling of the resected tumor to identify any coexisting benign adenomatous components.
The histological diagnosis of PA can be confirmed by immunohistochemical staining for positive expression of such factors as cytokeratins, Vimentin, S100 protein, smooth muscle actin (SMA), and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP).32 This finding describes the “mixed” nature of neoplasms, namely, mesenchymal and epithelial lines. In addition, overexpression of the p53 protein, HER-2, and proliferation marker Ki-67 (MIB-1) may serve as a target for identifying malignant areas in PA.49 In recent years, molecular genetic analysis has also been applied to identify CXPA; human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) and TP53 genes and proteins are involved in the early stages of malignant transformation of PA.
Any salivary carcinoma type can arise from a PA, and poorly differentiated or undifferentiated adenocarcinoma (not otherwise specified, NOS) is reportedly the most common.50 Other varieties are classically reported, including cystic adenoid carcinoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, epidermoid carcinoma, myoepithelial carcinoma, and metastatic tumor. Our analysis included 7 cases of sinonasal and nasopharyngeal CXPA reported in our study and 20 cases described in the literature,5–14 and the subtypes were as follows: adenoid cystic carcinoma (n=12), adenocarcinoma (n=10), myoepithelial carcinoma (n=1), squamous cell carcinoma (n=1), mucoepidermoid carcinoma (n=1), mucoepidermoid and squamous cell carcinoma (n=1), and histologic subtype not reported (n=1). The adenoid cystic carcinoma subtype of CXPA is more common than the adenocarcinoma subtype in the nasopharynx and nasal regions.
The two classic clinical manifestations of CXPA are recent rapid growth in a long-term neoplasm and malignant transformation following repeated resection of PA. Thus, PA and CXPA should be treated as soon as possible after definitive diagnosis. For sinonasal/nasopharyngeal PA and CXPA, there are several surgical approaches to achieve extensive local removal described in the literature, including endoscopic surgery, external rhinoplasty, lateral rhinotomy, and facial degloving. As external approaches for removing sinonasal PA and CXPA may lead to significant postoperative complications, we prefer to use endoscopic surgery to resect neoplasms. The use of endoscopy provides a broad surgical field and excellent visibility, thereby avoiding surgical morbidity. Endoscopy also prevents blindness and destruction of adjacent structures.30
Recurrence is not frequent in benign PA in the sinonasal/nasopharyngeal regions. Compagno and Wong reported that intranasal mixed tumors have a relatively low rate of recurrence (10%) compared with recurrence rates as high as 25% for intraoral mixed tumors and 50% for parotid gland mixed tumors.33 Vento et al. reported 10 cases of benign PA of the nasal cavity, and all tumors were surgically resected with no recurrence during various follow-up periods; regretfully, the follow-up time for 6 cases was less than 1 year.16 Rha et al. performed endoscopic surgery for sinonasal PA in 7 patients, one of whom (1/7, 14.3%) experienced recurrence within the mean follow-up period of 34.4 months.4 The recurrence rate of CXPA is much higher than that of benign PA. Toluie et al studied a series of 9 patients with adenoid cystic carcinoma ex-PA in the sinonasal tract and reviewed 6 patients with CXPA from the literature; 55% of the patients experienced recurrence, and they all died of the disease after an average overall survival time of 8.4 years.11
We performed endoscopic resection of sinonasal/nasopharyngeal PA and CXPA without serious postoperative complications. Within the mean follow-up period of 2.2 years, the recurrence rate of benign PA was 10% (1/10), and the malignant recurrence rate was 42.8% (3/7). The postoperative recurrence rate was similar to that reported in the literature. It was possible that the tumor-negative margin could not be completely reached during surgery, which may be a reason for recurrence in 4 patients. Patient 10, with a tumor originating from the nasal septum, was treated with three endoscopic resections and had no recurrence in the follow-up period of 3 years and 5 months. Patient 11 had a tumor involving the left maxillary sinus, ethmoid sinus, and orbit; most of the lesions were removed, and the lamina papyracea was invaded by the tumor. The lesion could not be completely resected, and recurrence occurred 18 months after the operation. In patient 12, the CXPA exhibited nasopharynx and skull base occupancy and recurred at 4 years after resection; the disease eventually extended to the pterygopalatine fossa, infraorbital fissure, posterior nostril, and sphenoid sinus. This patient did not undergo reoperation because of the high risk but received further radiotherapy. The neoplasms of patient 15 invaded the right paranasal sinus and anterior skull base, and there was obvious adhesion between the tumor and dura mater during the procedure. Part of the dura mater was resected, and the septum and nasal base mucosa were used as a mucosal flap to repair it; the symptoms were relieved, but there was recurrence 13 months later. Therefore, our clinical experience suggests that relapse is more likely in those with tumors invading the orbit or skull base.
Conclusion
Sinonasal/nasopharyngeal PA and CXPA are rare neoplasms, and the most common primary site of PA and CXPA is the nasopharynx. Because any salivary carcinoma type can arise in PA, these PA sites should be thoroughly sampled and closely examined to exclude the possibility of malignant transformation. Thus, PA and CXPA should be treated as soon as possible after definitive diagnosis, and endoscopic resection of tumor-negative margins may be helpful in preventing recurrence.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81870703)
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Manucha V, Ioffe OB. Metastasizing pleomorphic adenoma of the salivary gland. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008;132(9):1445–1447. doi:10.1043/1543-2165(2008)132[1445:MPAOTS]2.0.CO;2
2. Unlu HH, Celik O, Demir MA, Eskiizmir G. Pleomorphic adenoma originated from the inferior nasal turbinate. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2003;30(4):417–420.
3. Pons Vicente O, Almendros Marques N, Berini Aytes L, Gay Escoda C. Minor salivary gland tumors: a clinicopathological study of 18 cases. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2008;13(9):E582–E588.
4. Rha MS, Jeong S, Cho HJ, Yoon JH, Kim CH. Sinonasal pleomorphic adenoma: a single institution case series combined with a comprehensive review of literatures. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2018;46(2):223–229.
5. Kuan EC, Diaz MF, Chiu AG, Bergsneider M, Wang MB, Suh JD. Sinonasal and skull base pleomorphic adenoma: a case series and literature review. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015;5(5):460–468. doi:10.1002/alr.21500
6. Cimino-Mathews A, Lin BM, Chang SS, Boahene KD, Bishop JA. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal cavity. Head Neck Pathol. 2011;5(4):405–409. doi:10.1007/s12105-011-0262-2
7. Cho KJ, el-Naggar AK, Mahanupab P, Luna MA, Batsakis JG. Carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal cavity: a report of two cases. J Laryngol Otol. 1995;109(7):677–679.
8. Chimona TS, Koutsopoulos AV, Malliotakis P, Nikolidakis A, Skoulakis C, Bizakis JG. Malignant mixed tumor of the nasal cavity. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2006;33(1):63–66. doi:10.1016/j.anl.2005.07.018
9. Freeman SR, Sloan P, de Carpentier J. Carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal septum with adenoid cystic and squamous carcinomatous differentiation. Rhinology. 2003;41(2):118–121.
10. Liao PW, Chen YL, Chen JW. Pedunculated carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal cavity: a unique case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(39):e5004. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000004864
11. Toluie S, Thompson LD. Sinonasal tract adenoid cystic carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma: a clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic study of 9 cases combined with a comprehensive review of the literature. Head Neck Pathol. 2012;6(4):409–421. doi:10.1007/s12105-012-0381-4
12. Kariya S, Kosaka M, Orita Y, Akagi H, Nishizaki K. Adenocarcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the head and neck: report of five cases. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2006;33(1):43–46. doi:10.1016/j.anl.2005.07.001
13. Sreedharan S, Prasad KC, Hegde MC, Sahoo K, Alva A. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the maxillary sinus: a case report. Ear Nose Throat J. 2012;91(12):E1–E3. doi:10.1177/014556131209101211
14. Gupta A, Manipadam MT, Michael R. Myoepithelial carcinoma arising in recurrent pleomorphic adenoma in maxillary sinus. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2013;17(3):427–430. doi:10.4103/0973-029X.125213
15. Olsen KD, Lewis JE. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma: a clinicopathologic review. Head Neck. 2001;23(9):705–712.
16. Vento SI, Numminen J, Kinnunen I, et al. Pleomorphic adenoma in the nasal cavity: a clinicopathological study of ten cases in Finland. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273(11):3741–3745. doi:10.1007/s00405-016-4023-4
17. Gana P, Masterson L. Pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal septum: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2008;2:349. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-2-349
18. Evans RW, Cruickshank AH. Epithelial tumours of the salivary glands. Major Probl Pathol. 1970;1:1–299.
19. Sen S, Saha S, Basu N. Pleomorphic adenoma of nasal septum. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;57(2):163–166. doi:10.1007/BF02907682
20. Castello E, Caligo G, Pallestrini EA. [Case report: pleomorphic adenoma of the lateral nasal wall]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 1996;16(5):433–437.
21. Wakami S, Muraoka M, Nakai Y. [Two cases of pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal cavity]. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 1996;99(1):38–45.
22. Motoori K, Takano H, Nakano K, Yamamoto S, Ueda T, Ikeda M. Pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal septum: MR features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000;21(10):1948–1950.
23. Jackson LE, Rosenberg SI. Pleomorphic adenoma of the lateral nasal wall. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002;127(5):474–476. doi:10.1067/mhn.2002.129808
24. Mackle T, Zahirovic A, Walsh M. Pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal septum. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2004;113(3 Pt 1):210–211. doi:10.1177/000348940411300307
25. Uguz MZ, Onal K, Demiray U, Ekinci N. Tumoral mass presenting in the nasomalar region arising from the lateral nasal wall: pleomorphic adenoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2007;264(11):1377–1379. doi:10.1007/s00405-007-0359-0
26. Sciandra D, Dispenza F, Porcasi R, Kulamarva G, Saraniti C. Pleomorphic adenoma of the lateral nasal wall: case report. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2008;28(3):150–153.
27. Acevedo JL, Nolan J, Markwell JK, Thompson D. Pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal cavity: a case report. Ear Nose Throat J. 2010;89(5):224–226.
28. Olajide TG, Alabi BS, Badmos BK, Bello OT. Pleomorphic adenoma of the lateral nasal wall–a case report. Niger Postgrad Med J. 2009;16(3):227–229.
29. Baron S, Koka V, El Chater P, Cucherousset J, Paoli C. Pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal septum. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2014;131(2):139–141. doi:10.1016/j.anorl.2013.03.007
30. Cho Y, Kim YG, Shin E, Kim BY. Transnasal endoscopic resection of a pleomorphic adenoma originate from nasal floor. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(7):e717–e719. doi:10.1097/SCS.0000000000003778
31. Shetty S, Nayak DR, Jaiprakash P. Pleomorphic adenoma of nasal septum: a rare case. BMJ Case Rep. 2018.
32. Wierzchowska M, Bodnar M, Burduk PK, Kazmierczak W, Marszalek A. Rare benign pleomorphic adenoma of the nose: short study and literature review. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2015;10(2):332–336. doi:10.5114/wiitm.2014.47370
33. Compagno J, Wong RT. Intranasal mixed tumors (pleomorphic adenomas): a clinicopathologic study of 40 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977;68(2):213–218. doi:10.1093/ajcp/68.2.213
34. Fushiki H, Morijiri M, Maruyama M, Motoshima H, Watanabe Y. MRI of intranasal pleomorphic adenoma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006;126(8):889–891. doi:10.1080/00016480500527243
35. Baglam T, Durucu C, Cevik C, Bakir K, Oz A, Kanlikama M. Giant pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal septum. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;63(4):393–395. doi:10.1007/s12070-011-0229-3
36. Chew YK, Brito-Mutunayagam S, Chong AW, et al. Pleomorphic adenoma of the frontal sinus masquerading as a mucocele. Ear Nose Throat J. 2015;94(12):E4–E6. doi:10.1177/014556131509401202
37. Facon F, Paris J, Ayache S, Chrestian MA, Dessi P. [Pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal cavity: a case arising from the wall of the maxillary sinus]. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord). 2002;123(2):103–107.
38. Lee KC, Chan JK, Chong YW. Ossifying pleomorphic adenoma of the maxillary antrum. J Laryngol Otol. 1992;106(1):50–52. doi:10.1017/S0022215100118596
39. Berenholz L, Kessler A, Segal S. Massive pleomorphic adenoma of the maxillary sinus. A case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998;27(5):372–373.
40. Martis CS, Karakasis DT. Pleomorphic adenoma arising in the maxillary sinus. Case report. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1971;47(3):290–292.
41. Ray D, Mazumder D, Ray J, Bhattacharya S. Massive ossifying pleomorphic adenoma of the maxillary antrum: a rare presentation. Contemp Clin Dent. 2015;6(1):139–141. doi:10.4103/0976-237X.149312
42. Roh JL, Jung BJ, Rha KS, Park CI. Endoscopic resection of pleomorphic adenoma arising in the nasopharynx. Acta Otolaryngol. 2005;125(8):910–912.
43. Lee SL, Lee CY, Silver SM, Kuhar S. Nasopharyngeal pleomorphic adenoma in the adult. Laryngoscope. 2006;116(7):1281–1283. doi:10.1097/01.mlg.0000221972.07176.38
44. Thakur JS, Mohindroo NK, Mohindroo S, Sharma DR, Thakur A. Pleomorphic adenoma of minor salivary gland with therapeutic misadventure: a rare case report. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord. 2010;10:2. doi:10.1186/1472-6815-10-2
45. Martinez-Capoccioni G, Martin-Martin C, Espinosa-Restrepo F. Transnasal endoscopic resection of a nasopharyngeal pleomorphic adenoma: a rare case report. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;269(8):2009–2013. doi:10.1007/s00405-012-2003-x
46. Berrettini S, Fortunato S, De Vito A, Bruschini L. A rare case of nasopharyngeal pleomorphic adenoma. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2013;2013:712873.
47. Maruyama A, Tsunoda A, Takahashi M, Kishimoto S, Suzuki M. Nasopharyngeal pleomorphic adenoma presenting as otitis media with effusion: case report and literature review. Am J Otolaryngol. 2014;35(1):73–76. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2013.08.019
48. Yazici ZM, Yegin Y, Erdur O, Celik M, Kayhan FT. Management of pleomorphic adenoma in the nasopharynx: a case report. Balkan Med J. 2015;32(1):118–120. doi:10.5152/balkanmedj.
49. Di Palma S. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma, with particular emphasis on early lesions. Head Neck Pathol. 2013;7(Suppl 1):S68–S76. doi:10.1007/s12105-013-0454-z
50. Antony J, Gopalan V, Smith RA, Lam AK. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma: a comprehensive review of clinical, pathological and molecular data. Head Neck Pathol. 2012;6(1):1–9. doi:10.1007/s12105-011-0281-z
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.