Back to Journals » Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology » Volume 14
Simultaneous Infection of the Skin Surface and Dermal Tissue with Two Different Fungus Mimicking Pyoderma Gangrenosum: A Case Report
Authors Jia QY , Song YG, Li XQ , Mu ZL, Li RY, Li HM
Received 24 October 2020
Accepted for publication 26 January 2021
Published 15 February 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 163—167
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S286582
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jeffrey Weinberg
Qiu-Yu Jia,1 Ying-Gai Song,2 Xiang-Qian Li,1 Zhang-Lei Mu,1 Ruo-Yu Li,2 Hou-Min Li1
1Department of Dermatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Dermatology, Peking University the First Hospital, Beijing, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Hou-Min Li
Department of Dermatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, No. 11 Xizhimen South Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, 100044, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86 (424) 390-2625
Email [email protected]
Abstract: Mucormycosis is an opportunistic fungal infection driven by subphylum Mucormycotina. Cutaneous mucormycosis is the third most common presentation of mucormycosis, and its characterized presentation is an indurated plaque that rapidly evolves to necrosis. Trichophyton rubrum is one of the most common dermatophytes that mainly cause superficial infections and seldom induce deep infections. The present report presents a case of cutaneous fungal infection, in which two kinds of fungus were isolated, and the skin lesion mimicked pyoderma gangrenosum. Trichophyton rubrum was isolated from the crust and hyphae of subphylum Mucormycotina were found in dermal tissue. The irregular systemic and topical use of steroid therapy is the possible cause of the mixed fungal infection in this patient, suggesting the importance of regular steroid therapy.
Keywords: cutaneous mucormycosis, Trichophyton rubrum infection, cutaneous infection, lower leg, steroid therapy
Introduction
Mucormycosis is an opportunistic fungal infection of the fungi of subphylum Mucormycotina, which can cause various types of infections.1,2 Cutaneous mucormycosis is the third most common presentation of mucormycosis after rhinocerebral and pulmonary mucormycosis, and the skin lesions are mostly localized.3 Furthermore, the clinical presentation is nonspecific, and an indurated plaque that rapidly evolves to necrosis is commonly found.1 Trichophyton rubrum (T. rubrum) is one of the most common dermatophytes, which usually causes superficial skin infection, such as tinea corporis and cruris, tinea manus and pedis, and onychomycosis. In some immunocompromised patients, T. rubrum can also cause deep fungal infection.4
Case Report
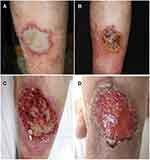
A 58-year-old male presented to our clinic with a one-month history of ulcer on the left lower leg (Figure 1). One month ago, an off-white patch with an erythematous halo appeared on his left lower leg during the treatment of autosensitization dermatitis. Approximately eight weeks ago, the patient topically administered traditional Chinese medicine on the lower legs to prevent eczema. In the next few days, red patches appeared on the lower legs, accompanied by pruritus. The patient was diagnosed with drug eruption and was treated with antibiotics and antihistamine for approximately three weeks at a local hospital. During the subsequent three weeks, erosion appeared on the left lower leg, and the skin lesions extended to the trunk and upper extremity, accompanied by intense itching. The patient was admitted to the Inpatient Department and was diagnosed with autosensitization dermatitis. This patient was treated with betamethasone by intramuscular injection, venous antibiotics, oral antihistamine, and topical glucocorticoid. One month ago, the previous lesions in the trunk and upper extremity improved, but a new off-white patch with an erythematous halo appeared on the left lower leg, with a size of 5×6 cm. This patient did not have diabetes mellitus or other immunosuppressive conditions.
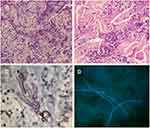
Based on the skin manifestation, pyoderma gangrenosum (PG) was considered. Meanwhile, oral glucocorticoids were started, betamethasone was injected into the lesion, and a pathological examination was performed. However, the lesion aggravated to a painful ulcer with rapid growth in the next few days. After broad non-septate hyphae with right-angled branches were found in the dermis in the skin pathology examination, the patient was diagnosed with suspected skin mucormycosis. Interestingly, the KOH examination of the crust on the ulcer revealed a thin septate hypha (Figure 2). The crust culture under 25°C revealed T. rubrum growth.
The disease was confirmed as mixed fungal infection caused by T. rubrum and fungi of subphylum Mucormycotina. Based on this, the investigators decided to start treatment with oral itraconazole of 200 mg bid and topical amphotericin B solution. In addition, surgical debridement was performed, and all devitalized tissues were removed. After two months, the improvement on the lesion was significant. After five months, the lesion totally healed.
Laboratory Examinations
The pathological examination showed partial epidermal loss, hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis of the remaining stratum corneum, and pan-dermal infiltration of abundant inflammatory cells such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, and plasma cells. Broad non-septate hyphae were found in the dermis, both in the hematoxylin-eosin and periodic acid-Schiff staining (Figure 2). In order to detect the species of the pathogen in the patient, the DNA was extracted from the paraffin-embedded tissues, and the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) gene was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using primer ITS1 and ITS4. However, no PCR products were obtained. The immunohistochemical staining of the M. oryzae antibody revealed positive results, with colored hypha in the dermis (Figure 2). However, the fungal culture of tissues taken by the debridement was negative. For fungal identification, the crust was inoculated and cultured on Sabouraud’s Agar (SDA) at 25°C. After two days, a white filamentous colony appeared. This fungus was identified as T. rubrum through morphological features and was further confirmed by ITS gene sequencing. Meanwhile, the specimens taken from the patient’s toenails and interdigital web spaces were subjected to fungal culture, and T. rubrum was also identified.
Discussion
Two different types of fungus were found in the skin lesion of the present patient. The lesion, which appeared as an off-white patch and ulcer, did not resemble the common cutaneous mucormycosis and dermatophyte infection. The patient was misdiagnosed with PG based on the appearance of the skin lesion before the pathological examination. The initial patch was off-white, with the rapid formation of ulcer. A large number of colorless septum hyphae were found in the crust of the ulcer. The culture of the crust revealed T. rubrum growth, which usually causes superficial skin infection, such as tinea corporis, tinea cruris, tinea manus and pedis, and onychomycosis. In some immunocompromised patients, T. rubrum can also cause deep fungal infection. The forms of deep infections include faveolate folliculitis, kerion, Majocchi’s granuloma, abscess, mycetoma, verrucous hyperplasia, and disseminated infection.4 Physical trauma of the skin and immunocompromise were considered to be the cause of the fungal invasion. Dermatophytes have keratin-philic properties. Invasion occurs when the epidermal barrier’s integrity becomes damaged or the follicular is disrupted. Thus, dermatophyte, along with keratin and necrotic materials, can enter the dermis.5 For the present patient, no hypha of T. rubrum was found in the deep tissue of the biopsy specimen, indicating that T. rubrum only colonized on the surface of ulcer and surrounding skin. The lack of stratum corneum on the ulcer was not helpful for the T. rubrum to invade into the deep tissues. Interestingly, the patient had tinea pedis and onychomycosis. Hence, the T. rubrum in the superficial crust may have been inoculated from the patient’s own feet.
Cutaneous mucormycosis is a fungal infection caused by opportunistic fungi of the phylum Mucormycotina. This mainly occurs in poorly controlled diabetic patients or immunosuppressed individuals. The common underlying conditions include solid organ transplantation, deferoxamine therapy, drug injections, renal failure, infant low birth weight, malnutrition, HIV infection, systemic lupus erythematosus, burns, trauma, aplastic anemia, and steroid use.1 The most frequently affected areas of the skin are the arms and legs. Cutaneous mucormycosis is usually acquired by direct inoculation through trauma.6 The clinical presentation is nonspecific, but an indurated plaque that rapidly evolves to necrosis is common.1,7 The lesions may mimic PG, bacterial synergistic gangrene, or other infections.6 The treatment consists of surgical debridement, the use of antifungal drugs, and the reversal of underlying risk factors.6 The common findings in the biopsy specimens of cutaneous mucormycosis are edema, thrombosis, infarctions, necrosis, and an inflammatory reaction. The investigators reached a conclusion that the previous injection of betamethasone was the main reason for the mixed fungal infection, since the present patient did not have diabetes mellitus or other immunosuppressive conditions. Several cases of cutaneous mucormycosis under special circumstances of corticosteroid therapy have been reported.8–10 For the present patient, hyphae were hardly found, and no thrombosis was revealed by the pathological examination. This result suggested that the patient’s immunity was normal, and this explained the reason why the result of the tissue culture appeared to be negative.
The percentage of fungal cultures reported positive in mucormycosis is between 50%–82%.6 There are several causes for false-negative results: the hyphae of the Mucormycotina are too broad; the disposed tissues subjected to culture are too small; the amount of hyphae in the tissues is not sufficient. For the present patient, the culture was not performed before the pathological examination, since PG was considered. After fungal elements were found in the pathological section, surgical debridement was performed in the patient. The fungal culture of tissues taken from the debridement was also negative. This was likely due to the use of oral antifungal agents. In order to detect the pathogen in the present patient, the DNA was extracted from paraffin-embedded tissues, and the ITS gene was amplified by PCR using primer ITS1 and ITS4. The result was negative, and this was possibly correlated to the insufficient amount of DNA or the sensitivity of the technique.11 Since the broad non-septate hyphae found in the dermis and immunohistochemical staining with the M. oryzae antibody was positive, the investigators confirmed that the dermal tissue was infected with the fungi of subphylum Mucormycotina.
The present patient was not an immunocompromised host. Hence, the cause of mixed fungal infection could be correlated to the irregular systemic and topical steroid use, reminding the importance of regular steroid therapy. On one hand, steroids may influence a patient’s immunity. Hence, it should be noted that unusual manifestations also suggest the possibility of opportunistic fungal infection in patients using steroids. On the other hand, attention should always be given to opportunistic fungal infections, especially when treating patients with steroid therapies.
Funding
Project 81772160 supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Disclosure
No conflicts of interest in this work. Written informed consent was provided by the patient to have the case details and any accompanying images published. Institutional approval was not required to publish the case details.
References
1. Castrejón-Pérez AD, Welsh EC, Miranda I, Ocampo-Candiani J, Welsh O. Cutaneous mucormycosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92(3):304–311. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20176614
2. Petrikkos G, Skiada A, Lortholary O, Roilides E, Walsh TJ, Kontoyiannis DP. Epidemiology and clinical manifestations of mucormycosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54(Suppl 1):S23–S34. doi:10.1093/cid/cir866
3. Vulsteke J, Deeren D. Cutaneous mucormycosis. Transpl Infect Dis. 2019;21(2):e13039. doi:10.1111/tid.13039
4. Liang GZ, Xu WQ, Zheng XL, et al. Successful treatment by surgery of a primary cutaneous mucormycosis caused by mucor irregularis. Mycopathologia. 2018;183(2):445–449. doi:10.1007/s11046-017-0219-4
5. Boral H, Durdu M, Ilkit M. Majocchi’s granuloma: current perspectives. Infect Drug Resist. 2018;11:751–760. doi:10.2147/IDR.S145027
6. Skiada A, Rigopoulos D, Larios G, Petrikkos G, Katsambas A. Global epidemiology of cutaneous zygomycosis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30(6):628–632. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2012.01.010
7. Bonifaz A, Vázquez-González D, Tirado-Sánchez A, Ponce-Olivera RM. Cutaneous mucormycosis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30(4):413–419. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2011.09.013
8. Geisen M, Fodor P, Eich G, Zollinger A, Dzemali O, Blumenthal S. Disseminated cutaneous mucormycosis in a patient on high-dose steroid therapy for severe ARDS. Intensive Care Med. 2011;37(11):1895–1896. doi:10.1007/s00134-011-2347-5
9. Sahni K, De D, Dogra S, Kanwar A, Saikia UN. Cutaneous mucormycosis: a fatal complication of immunosuppressant therapy for pemphigus vulgaris. Skinmed. 2017;15(6):467–469.
10. Fujimoto A, Nagao K, Tanaka K, Yamagami J, Udagawa S-I, Sugiura M. The first case of cutaneous mucormycosis caused by Rhizopus azygosporus. Br J Dermatol. 2005;153(2):428–430. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06593.x
11. Dannaoui E. Molecular tools for identification of Zygomycetes and the diagnosis of zygomycosis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009;15:66–70. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02983.x
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.