Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 10 » Issue 1
Silver-coated carbon nanotubes downregulate the expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes: a potential mechanism for their antimicrobial effect
Authors Dosunmu E, Chaudhari A, Singh SR, Dennis V, Pillai S
Received 21 March 2015
Accepted for publication 26 May 2015
Published 5 August 2015 Volume 2015:10(1) Pages 5025—5034
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S85219
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Ejovwoke Dosunmu, Atul A Chaudhari, Shree R Singh, Vida A Dennis, Shreekumar R Pillai
Center for NanoBiotechnology Research, Alabama State University, Montgomery, AL, USA
Abstract: The antimicrobial activity of silver-coated carbon nanotubes (AgCNTs) and their potential mode of action against mucoid and nonmucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was investigated in vitro. The results showed that AgCNTs exhibited antimicrobial activity against both strains with minimum inhibitory concentrations of approximately 8 µg/mL, indicating a high sensitivity of P. aeruginosa to AgCNTs. AgCNTs were also bactericidal against both strains at the same minimum inhibitory concentration. Scanning and transmission electron-microscopy studies further revealed that a majority of the cells treated with AgCNTs transformed from smooth rod-shape morphology to disintegrated cells with broken/damaged membranes, resulting in leakage of cytoplasmic contents to produce ghost cells. The molecular effects of AgCNTs on P. aeruginosa genes involved in virulence and pathogenicity, stress response, and efflux pumps were evaluated for changes in their expression. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) showed that after exposure to AgCNTs, the expression levels of the rpoS, rsmZ, and oprD genes were significantly downregulated in both strains of P. aeruginosa compared to the untreated samples. These results suggest that the mechanism of action of AgCNTs may be attributed to their effect on cell-membrane integrity, downregulation of virulence-gene expression, and induction of general and oxidative stress in P. aeruginosa.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, AgCNT, antimicrobial activity, qRT-PCR
Introduction
One area of rapidly growing interest in the development of new antimicrobials is the use of nanoparticles coupled with metals. Silver, for example, has shown antimicrobial activity against a wide range of microorganisms.1 Therefore, silver-based nanomaterials are being used for their bactericidal activity.2,3 Although the antimicrobial activity of silver is well known, its mechanism of action is not yet fully understood. Several mechanisms have been proposed, such as a loss of the replication ability of DNA4 and changes in membrane structure.5
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are used in many nanocomposites, because they possess distinct mechanical and electronic properties.6 CNTs also possess antimicrobial activity, possibly resulting from physical damage to bacterial cells that inhibits the growth of biofilm-forming microbes on surfaces. However, drawbacks to their antimicrobial applications include instability, aggregation, and lack of bioavailability of the NTs.7 Some of these issues may be mitigated by hybrid nanocomposites of silver and CNTs, which may have enhanced antimicrobial activity while reducing aggregation. Silver-coated carbon nanotubes (AgCNTs) are highly attractive as water-disinfecting materials, due to their ability to remain insoluble. Other antimicrobial hybrid materials, such as dendritic poly(amidoamine) combined with silver, are soluble in water and contaminate treatment feeds when used as antimicrobials.8
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes a wide array of human infections. Normally, it is harmless; however, if the immune system is compromised, it gains access to submucosal tissues, becoming a persistent opportunist pathogen.9 P. aeruginosa is a human pathogen of major public health significance, causing approximately 16% of nosocomial pneumonia infections, 12% of hospital-acquired urinary tract infections, and 8% of surgical wound infections.10 It is one of the most fatal pathogens. Mortality rates among patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia range from 33% to 61%, and bacteremia associated with this pathogen is responsible for 50% of deaths in HIV-infected patients.11 Also, it colonizes the respiratory tracts of cystic fibrosis patients, contributing to morbidity and mortality in this disease,12–15 and it is associated with ventilator-acquired pneumonia in intubated patients.16 Treatment of P. aeruginosa is problematic, due to its high intrinsic resistance to antibiotics, such as β-lactams and fluoroquinolones.17
This resistance is coordinated by a variety of virulence genes that enable its persistence and pathogenicity in vivo. A well-known mechanism enabling antibiotic resistance in P. aeruginosa is the outer-membrane protein OprD, the narrow channels of which reduce outer-membrane permeability.18 The OprD protein is the main reason for resistance to carbapenems, due to bacterial alteration in the expression of the oprD gene. Other systems of virulence include quorum sensing (QS) and efflux pumps.19
QS is a major determinant of persistence and pathogenicity in P. aeruginosa, and inhibitors of this system may act as antimicrobial agents by enabling the bacterium’s susceptibility to antibiotics. The efflux pumps, MexAB-OprM and MexEF-OprN, which are regulated by the mexR and mexT genes, respectively, are recognized as significant antibiotic-resistance complexes, involved in removing toxic substances, such as antibiotics, from the bacterium.20 In addition to the inherent difficulty in treating P. aeruginosa infections, the organism also has the ability to convert from a nonmucoid to a mucoid state. The mucoid matrix enables the formation of protected biofilm microcolonies,21–23 and provides increased resistance to opsonization, phagocytosis, and digestion.24 The mucoid phenotype is characterized by the synthesis of a large quantity of alginate exopolysaccharide, which allows consistent infections25 and poor prognosis for infected patients,26,27 because this phenotype is rarely eradicated.
To our knowledge, the effects of AgCNTs on the virulence genes of P. aeruginosa involved in pathogenicity and persistence have not been determined. Therefore, the objectives of this study were to evaluate the antimicrobial activity of AgCNTs against P. aeruginosa and to determine their effects on the expression of virulence genes of P. aeruginosa.
Materials and methods
Silver-coated single-wall nanotubes
AgCNTs were purchased from NanoLab Inc (Waltham, MA, USA). The AgCNTs had an outer diameter of 1–5 μm and a length of 1–2 μm. AgCNTs were dispersed in a mixture of sterile distilled water and dispersant (Nanosperse AQ; NanoLab). Portions (1 mg) of AgCNTs were suspended in 1 mL aliquots of water and dispersant mixture according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and then immediately sonicated for 1 hour to obtain AgCNT dispersion of 1 mg/mL.
Bacteria, media, and antibiotics
Mucoid (ATCC 39324) and nonmucoid (ATCC 27318) strains of P. aeruginosa were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). Cation-adjusted Müller–Hinton broth CA-MHB from BD (Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) was used to grow P. aeruginosa for determination of in vitro antimicrobial activity and time-kill assays. Todd–Hewitt media supplemented with yeast extract was used for scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis. Gentamicin sulfate and polymyxin B were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA).
Antimicrobial activity
Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) against both strains of P. aeruginosa were measured according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) M7-A7 method.28 Briefly, serial twofold dilutions of AgCNTs in dispersant, starting at 64 μg/mL, were added into Costar untreated polystyrene 96-well plates, and each well was inoculated with 20 μL (1×106 CFU/mL) of either strain of P. aeruginosa in CA-MHB to a final concentration of approximately 1×105 CFU/mL. Positive control wells were inoculated with bacteria alone, whereas negative control wells had only media to ensure sterility. The MIC was determined as the lowest concentration of AgCNTs or antibiotic (polymyxin B and gentamicin sulfate) that showed no visible growth after 24 hours of incubation at 37°C. The dilution representing the MIC and two concentrations above the MIC were then plated on Luria agar plates and viable CFU/mL were enumerated to obtain the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC).29 The MBC was determined as the lowest concentration of the AgCNTs yielding a 99.9% reduction in the initial colony count after 24 hours’ incubation.
Time-kill analysis
Time-kill studies of AgCNTs against each strain of P. aeruginosa were carried out based on the M26-A guidelines of the CLSI.30 The assay was conducted by incubating an initial inoculum of approximately 1×105 CFU/mL of either strain into Costar untreated polystyrene 96-well plates with AgCNTs at their respective MICs, two dilutions above the MIC (2× and 4× MIC) and one dilution below (0.5× MIC) in CA-MHB. Viable cell counts were determined after 2, 4, 8, and 24 hours of incubation at 37°C by plating serially diluted samples on Luria agar. Antimicrobial activity was defined as ≥3 log10 decrease in CFU compared to the initial inoculum.30
Scanning electron microscopy
Exponential phase bacteria (1×109 CFU/mL) were exposed to AgCNTs at approximately 4× MIC for 4 hours at 37°C, before being centrifuged at 2,000× g (Sorvall ST 40R; Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 10 minutes. The pellets were then washed in 0.1% phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and fixed overnight in a mix of 2.5% glutaraldehye and 1% formaldehyde in 0.1% PBS. Samples were treated with 1% osmium tetroxide in 0.1% PBS, before stepwise dehydration in increasing concentrations of ethanol in water. The dehydrated samples (5 μL each) were then placed on SEM stubs (Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA, USA), and air-dried and sputter-coated with gold in a sputter-coat device (EMS 550X; Electron Microscopy Sciences) prior to performing SEM (EVO 50 variable pressure scanning; Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, Jena, Germany) analysis.
Transmission electron microscopy
For TEM sample preparation, a similar processing method was used as described earlier for SEM, until achieving dehydration in 100% ethanol. After dehydration, the samples were passed through propylene oxide and infiltrated with Embed 812 resin (Electron Microscopy Sciences) and polymerized overnight. Ultrathin sections were collected on copper grids stained with 2% uranyl acetate and lead citrate, and imaged using the TEM (EM10; Carl Zeiss Meditec AG).
RNA extraction and quantitative real-time PCR
For qRT-PCR analysis, untreated and treated bacteria (1×109 CFU/mL) were exposed to either 4× MIC of AgCNTs or gentamicin for 4 hours at 37°C. Total RNA was purified using an RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen NV, Venlo, the Netherlands), and quantified using a spectrophotometer (NanoDrop 2000c; Thermo Fisher Scientific). The complementary DNA synthesis was carried out in 20 μL reaction volumes using the Applied Biosystems High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcriptase Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). A total of 1 μg of RNA was used to amplify the oprD, lasA, creD, lecA, lecB, rpoS, creB, rsmZ, ampD, ampP, ampG, mexT, and mexR genes of P. aeruginosa using the Applied Biosystems ViiA 7 real-time PCR system. Primer pairs for each gene are shown in Table S1. The amplification conditions used were one cycle of initial denaturation at 95°C for 2 minutes, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 seconds, 56°C for 25 seconds, and 72°C for 30 seconds. The relative changes in gene expression were calculated using the equation 2−ΔΔCT, where all values were normalized with respect to the 16S messenger RNA levels. Each real-time PCR assay was performed in triplicate from three independent cultures, and the results are expressed as means ± standard deviation.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed by Student’s t-test using SigmaPlot software. Significance was established at P<0.05 and P<0.01.
Results
Antibacterial activity of AgCNTs
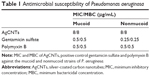
Susceptibility of the mucoid and nonmucoid strains P. aeruginosa to AgCNTs was determined by the micro-broth dilution assay. Both strains displayed susceptibility to AgCNTs at an MIC of 8 μg/mL compared to gentamicin or polymyxin B controls, with MICs between 0.25 and 0.5 μg/mL (Table 1). The MIC and MBC concentrations were the same for both strains. We further conducted time-kill experiments to evaluate microbial reduction by AgCNTs over time.
AgCNTs are bactericidal at the MBC and above
Time-kill analysis showed rapid killing occurred at the MBC and above, as the viable cell count decreased by 5 log10 CFU/mL in the first 2 hours (Figure 1A and B). The MBC was at the MIC. These results show that AgCNTs are effective in killing both mucoid and nonmucoid strains of P. aeruginosa.
AgCNTs cause morphological changes to the cell membrane of P. aeruginosa
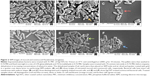
We employed both SEM and TEM to understand the mechanisms by which AgCNTs exert their antimicrobial effects against P. aeruginosa. The effect of AgCNTs on P. aeruginosa cell morphology was examined after 4 hours’ treatment of 5 mL of exponential phase bacteria (1×109 CFU/mL) of either strain of P. aeruginosa with 4× MIC of AgCNTs. Both strains showed broken cell membranes, cell-membrane disintegration, and the formation of irregular cell surfaces, in contrast to the smooth surfaces of the untreated samples (Figure 2). These images suggest a probable mechanism of action whereby AgCNTs interact with the cell membrane, causing membrane permeabilization and degradation, with accompanying changes in cell morphology.
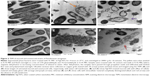
TEM analysis confirmed the SEM findings, with treated cells showing complete loss of cell membranes (Figure 3), along with dispersed and disintegrated intracellular material of both strains. Together, these results suggest that AgCNTs caused loss of membrane integrity with lethal effects on both strains of P. aeruginosa.
Virulence-gene expression in response to AgCNT treatment
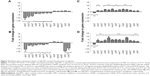
To study the molecular effects of AgCNTs against the mucoid and nonmucoid strains of P. aeruginosa, virulence genes involved in resistance, stress response, motility, pathogenicity, attachment, and redox regulation were selected for quantification of their transcriptional expression using qRT-PCR, and then compared to the molecular effects of gentamicin. Both strains exhibited similar gene-expression patterns (Figure 4A and B) for the AgCNT samples, except for a few exceptions, such as downregulation of expression of lasA and creD, which are essential for attachment to eukaryotic cells and the development of resistance, respectively. Their expression was significantly downregulated in the nonmucoid strain, but remained unchanged in the mucoid strain. By contrast, the expression of the mexT gene was downregulated in the mucoid strain, but showed no significant change in the nonmucoid strain. As expected, the presence of AgCNTs significantly downregulated expression of the outer-membrane porin oprD gene by ten- and elevenfold in the mucoid and nonmucoid strains, respectively. The rpoS gene expression (encoding sigma factor RpoS, a regulator of cellular response to oxidative stress) was also significantly downregulated: six- and fourfold for the mucoid and nonmucoid strains, respectively. The lasA gene expression (encoding a QS-regulating factor LasA, an endopeptidase) was also downregulated four- and 14-fold for the mucoid and nonmucoid strains, respectively. Other virulence factors that were downregulated in both strains included the prtR (encoding a negative regulator of pyocin genes) and mexR (negative regulator of MexAB-OprM) genes. In contrast to the AgCNT-treated samples, gentamicin-treated samples of both strains showed upregulation of gene-expression patterns for all genes analyzed, except for downregulation of oprD gene expression (Figure 4, C and D). Collectively, these results show that AgCNTs deregulate a number of virulence genes of P. aeruginosa, which may be linked to their antimicrobial properties, which appear to be different from the mechanism of action of the gentamicin. Virulence genes and function are shown in Table 2.
  | Table 2 Genes, gene product, and product function |
Discussion
AgCNT hybrid nanoparticles have a broad spectrum of activities against microbial pathogens, such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Escherichia coli, and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.31 In this study, we investigated the antimicrobial activity and mechanistic effect of AgCNTs against mucoid and nonmucoid strains of P. aeruginosa, a major opportunist pathogen of immunocompromised patients.32 To our knowledge, this is the first investigation of the antimicrobial activity of AgCNTs against a mucoid variant of P. aeruginosa, a more virulent phenotype, which fosters the formation of biofilms and enables resistance against antimicrobials.33
Our results showed that AgCNTs are bactericidal against both strains of P. aeruginosa, with no recovery of AgCNT-treated cells on Luria agar plates at MIC concentrations or higher. Although the antimicrobial activity of AgCNTs against P. aeruginosa has been investigated,3 their mechanism of action is not well established. However, the antimicrobial effect has been attributed to membrane damage caused by direct or electrostatic interaction between AgCNTs and cell membranes. An examination of the effects of AgCNTs on cell morphology by SEM revealed obvious membrane damage, as evidenced by changes from a smooth morphology to irregular cell surfaces with membrane disintegration, suggesting membrane damage as a probable mechanism of action. TEM confirmed the effect of AgCNTs on P. aeruginosa membranes, showing rupture with subsequent leakage and efflux of cytoplasmic contents.
One of the major drawbacks to treating and preventing P. aeruginosa infection is the ability of the organism to develop resistance to an array of antimicrobial agents; this is not unusual for bacteria, which adapt quickly to change or stress by regulating the synthesis of defensive or resistance proteins in order to ensure survival. In P. aeruginosa, the lower outer-membrane permeability to antibiotics has been attributed to the narrower structure of the OprD protein compared to the OmpF of Escherichia coli,18 which makes this pathogen recalcitrant to treatment. Therefore, we studied a number of genes that enable P. aeruginosa pathogenicity and protection from antibiotics. Resistance in P. aeruginosa is enabled by the synergistic effect of the overexpression of efflux pumps and reduced expression of the oprD gene. The OprD protein plays a critical role as a channel for basic amino acids, peptides, and carbapenems, and is a major mediator of resistance of P. aeruginosa to carbapenems. To eliminate antimicrobial compounds, the organism reduces its expression of oprD, in order to prevent entry of antimicrobials, and to develop resistance to antimicrobial agents.18 It is known that MexT, a possible indirect regulator of oprD and a positive regulator of the multidrug efflux pump MexEF-OprN, and MexR, a negative regulator of the MexAB-OprM pump, enable the organism to acquire resistance by the increased expression of mexT and reduced expression of mexR and oprD.18,34
Analyses of these genes in P. aeruginosa treated with AgCNTs or gentamicin in this study showed that the expression of oprD was significantly downregulated in both strains for both treatments. In contrast, the expression of mexR was downregulated in the AgCNT-treated strains but upregulated in the gentamicin-treated strains. On the other hand, mexT was also downregulated in the AgCNT-treated mucoid strain, but remained unaffected in the AgCNT-treated nonmucoid strain, while it was upregulated in both gentamicin-treated strains. This may indicate that AgCNTs cause stress and inhibit P. aeruginosa by their effect on the expression of the resistance-response genes. A reduced expression of rpoS in the presence of AgCNTs in both strains may suggest a decreased ability for survival under stress imposed by AgCNTs, whereas an increased expression in the presence of gentamicin may suggest the opposite. It is known that the general oxidative stress regulator and alternative sigma factor, RpoS35 regulates the expression of more than 35 genes, many of which are involved in the general stress response. RpoS also plays a role as an intermediary regulator of catalase activity and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) tolerance. RpoS has been shown to mediate protection against H2O2 killing, as differential sensitivity to H2O2 in a parent and mutant rpoS strain was the result of a 60% reduction in catalase activity in the latter.36 Other stress-related genes include the small regulatory RNA genes rsmY and rsmZ, the expression of which are essential to enhance population density under environmental stress,37 and also for biofilm formation.38 In this study, we observed a significantly reduced expression of the rsmZ gene in AgCNT-treated samples and an upregulation in gentamicin-treated samples. A study has shown that upregulation of these regulatory RNAs resulted in more biofilm formation, by increasing expression of the QS gene lasR. Another prior study has shown that biofilm production was markedly impaired in rsmZ-, gacA-, and rsmY-mutant strains.37 Therefore, our findings suggest that AgCNTs may interfere with biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa.
Other genes essential for pathogenicity and resistance include lecB and prtR. prtR expression is upregulated in the presence of (ROS), resulting in increased type III secretory system gene expression and increased bacterial tolerance of stress.39 lecB gene expression has been identified to be critical in P. aeruginosa pathogenesis, as it plays a role in adhesion of P. aeruginosa to the A549 lung epithelial cell line. lecA and lecB mutation decrease bacteria dissemination,40 and in this study a significant downregulation of the lecA gene was observed for both strains treated with AgCNTs. We also found that the creD gene was significantly downregulated – eightfold – in the nonmucoid strain, but remained unchanged in the mucoid strain. The creD gene encodes an inner-membrane protein, and is regulated by a dual creBC gene system involved in β-lactam resistance/tolerance.41 The outer membrane of the mucoid strain is enclosed in alginate, a complex polysaccharide that may mitigate the damaging effects of AgCNTs on the inner-membrane protein.
In contrast to creD, creB gene expression was significantly downregulated in both strains. The QS-regulated gene lasA, which encodes the LasA protease,42 an exotoxin produced by P. aeruginosa, was significantly downregulated in the nonmucoid strain, suggesting an impaired QS system, and subsequent decreased pathogenicity in the nonmucoid strain. By comparison, lasA expression was significantly upregulated in the gentamicin-treated P. aeruginosa. However, the ampP and ampG genes, which encode permease43 and are critical for β-lactamase induction, remained unchanged in both strains. From these experiments, it appears that the antimicrobial activity of AgCNTs may include several mechanisms, such as membrane damage, affecting antibiotic-resistance genes, downregulating virulence genes, and inducing oxidative and general stress. The downregulation of virulence genes may also suggest a decreased pathogenicity of P. aeruginosa after AgCNT treatment. The downregulation of these virulence genes in AgCNT-treated samples is in contrast to the upregulation of these genes in the gentamicin-treated samples, which suggests that not only do the mechanisms of action differ between AgCNTs and gentamicin but upregulation of these virulence genes may indicate the ability of P. aeruginosa to respond to the presence of gentamicin. For example, upregulation of stress-regulator and efflux-pump genes may indicate the organism’s ability to adapt and develop resistance to gentamicin over time and with continuous usage.
We have previously examined the cytotoxicity of AgCNTs.44 In that study, the toxicity of pegylated and naked AgCNTs were analyzed, together with their antimicrobial effect. Although the pegylated AgCNTs were comparatively less toxic, antimicrobial activity remained unchanged, thereby indicating that the cytotoxicity of AgCNTs can be reduced while maintaining antimicrobial activity and effect. Further, at their MIC, AgCNTs were nontoxic to eukaryotic cells.
In summary, AgCNTs showed antimicrobial activity and bactericidal effects against both the mucoid and nonmucoid strains of P. aeruginosa at low concentrations. AgCNTs also induced significant morphological changes and membrane disruption. Based on these results and changes in gene expression, a probable mechanism of AgCNT bactericidal effect involves direct interaction between AgCNTs and cell membrane, whereby the cell membrane is affected and nanoparticle entry induces stress in the bacteria, resulting in growth inhibition and death. These data suggest that AgCNTs may be applicable as an antimicrobial agent against P. aeruginosa, especially for antimicrobial coatings. AgCNTs may also be useful for disinfecting surfaces, water treatment, and purification due to their insolubility. Membrane disintegration and deregulation of virulence-gene expression could contribute to the rapid bactericidal activity of AgCNTs.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation Centers of Research Excellence in Science and Technology (HRD-1241701), NSF-HBCU-UP (HRD-1135863), and National Institutes of Health Minority Biomedical Research Support Research Initiative for Scientific Enhancement (1R25GM106995-01). We thank Yvonne Williams, Lashaundria Lucas, and Amber Grace for excellent administrative assistance.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Liau SY, Read DC, Pugh WJ, Furr JR, Russell AD. Interaction of silver nitrate with readily identifiable groups: relationship to the antibacterial action of silver ions. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1997;25(4):279–283. | ||
Seo Y, Hwang J, Kim J, Jeong Y, Hwang MP, Choi J. Antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with silver nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:4621–4629. | ||
Neelgund GM, Oki A. Deposition of silver nanoparticles on dendrimer functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes: synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011;11(4):3621–3629. | ||
Valappil SP, Pickup DM, Carroll DL, et al. Effect of silver content on the structure and antibacterial activity of silver-doped phosphate-based glasses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51(12):4453–4461. | ||
Nover L, Scharf KD, Neumann D. Cytoplasmic heat shock granules are formed from precursor particles and are associated with a specific set of mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989;9(3):1298–1308. | ||
Terada M, Abe S, Akasaka T, Uo M, Kitagawa Y, Watari F. Multiwalled carbon nanotube coating on titanium. Biomed Mater Eng. 2009;19(1):45–52. | ||
Li Q, Mahendra S, Lyon DY, et al. Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: potential applications and implications. Water Res. 2008;42(18):4591–4602. | ||
Yuan W, Jiang GH, Che JF, et al. Deposition of silver nanoparticles on multiwalled carbon nanotubes grafted with hyperbranched poly(amidoamine) and their antimicrobial effects. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2008;112(48):18754–18759. | ||
Eckert R, Brady KM, Greenberg EP, et al. Enhancement of antimicrobial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa by coadministration of G10KHc and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50(11):3833–3838. | ||
Van Delden C, Iglewski BH. Cell-to-cell signaling and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Emerg Infect Dis. 1998;4(4):551–560. | ||
Mendelson MH, Gurtman A, Szabo S, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia in patients with AIDS. Clin Infect Dis. 1994;18(6):886–895. | ||
Delaval M, Boland S, Solhonne B, et al. Acute exposure to silica nanoparticles enhances mortality and increases lung permeability in a mouse model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2015;12:1. | ||
Govan JR, Deretic V. Microbial pathogenesis in cystic fibrosis: mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia. Microbiol Rev. 1996;60(3):39–74. | ||
Stover CK, Pham XQ, Erwin AL, et al. Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature. 2000;406(6799):959–964. | ||
Lodise TP Jr, Patel N, Kwa A, et al. Predictors of 30-day mortality among patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa bloodstream infections s: impact of delayed appropriate antibiotic selection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51(10):3510–3515. | ||
Dunn, M, Wunderink RG. Ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by Pseudomonas infection. Clin Chest Med. 1995;16(1):95–109. | ||
Li XZ, Nikaido H, Poole K. Role of MexA-MexB-OprM in antibiotic efflux in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995;39(9):1948–1953. | ||
Li H, Luo YF, Williams BJ, Blackwell TS, Xie CM. Structure and function of OprD protein in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: from antibiotic resistance to novel therapies. Int J Med Microbiol. 2012;302(2):63–68. | ||
Balasubramanian D, Schneper L, Merighi M, et al. The regulatory repertoire of Pseudomonas aeruginosa AmpC β-lactamase regulator AmpR includes virulence genes. Plos One. 2012;7(3):e34067. | ||
Poole K, Tetro K, Zhao Q, Neshat S, Heinrichs DE, Bianco N. Expression of the multidrug resistance operon mexA-mexB-oprM in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: mexR encodes a regulator of operon expression. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996;40(9):2021–2028. | ||
Murray TS, Egan M, Kazmierczak BI. Pseudomonas aeruginosa chronic colonization in cystic fibrosis patients. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2007;19(1):83–88. | ||
Li Z, Kosorok MR, Farrell PM, et al. Longitudinal development of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and lung disease progression in children with cystic fibrosis. JAMA. 2005;293(5):581–588. | ||
Fegan M, Francis P, Hayward AC, Davis GH, Fuerst JA. Phenotypic conversion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990;28(6):1143–1146. | ||
Lam J, Chan R, Lam K, Costerton JW. Production of mucoid microcolonies by Pseudomonas aeruginosa within infected lungs in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1980;28(2):546–556. | ||
Pier GB, Coleman F, Grout M, Franklin M, Ohman DE. Role of alginate O acetylation in resistance of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa to opsonic phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 2001;69(3):1895–1901. | ||
Hodges NA, Gordon CA. Protection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa against ciprofloxacin and beta-lactams by homologous alginate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991;35(11):2450–2452. | ||
Koch C, Høiby N. Pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1993;341(8852):1065–1069. | ||
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically: Approved Standard M07-A9. 9th ed. Wayne (PA): CLSI; 2012. | ||
Peterson LR, Shanholtzer CJ. Tests for bactericidal effects of antimicrobial agents: technical performance and clinical relevance. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1992;5(4):420–432. | ||
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Determining Bactericidal Activity of Antimicrobial Agents: Approved Guideline M26-A. Wayne (PA): CLSI; 1999. | ||
Rangari VK, Mohammad GM, Jeelani S, et al. Synthesis of Ag/CNT hybrid nanoparticles and fabrication of their nylon-6 polymer nanocomposite fibers for antimicrobial applications. Nanotechnology. 2010;21(9):095102. | ||
Gooderham WJ, Hancock RE. Regulation of virulence and antibiotic resistance by two-component regulatory systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009;33(2):279–294. | ||
Pritt B, O’Brien L, Winn W. Mucoid Pseudomonas in cystic fibrosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007;128(1):32–34. | ||
Vaez H, Faghri J, Isfahani BN, et al. Efflux pump regulatory genes mutations in multidrug resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from wound infections in Isfahan hospitals. Adv Biomed Res. 2014;3:117. | ||
Khakimova M, Ahlgren HG, Harrison JJ, English AM, Nguyen D. The stringent response controls catalases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and is required for hydrogen peroxide and antibiotic tolerance. J Bacteriol. 2013;195(9):2011–2020. | ||
Suh SJ, Silo-Suh L, Woods DE, Hassett DJ, West SE, Ohman DE. Effect of rpoS mutation on the stress response and expression of virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1999;181(13):3890–3897. | ||
Zhao K, Li Y, Yue B, Wu M. Genes as early responders regulate quorum-sensing and control bacterial cooperation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Plos One. 2014;9(7):e101887. | ||
Li K, Xu C, Jin Y, et al. SuhB is a regulator of multiple virulence genes and essential for pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. MBio. 2013;4(6):e00419-13. | ||
Sun Z, Shi J, Liu C, et al. PrtR homeostasis contributes to Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis and resistance against ciprofloxacin. Infect Immun. 2014;82(4):1638–1647. | ||
Chemani C, Imberty A, de Bentzmann S, et al. Role of LecA and LecB lectins in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced lung injury and effect of carbohydrate ligands. Infect Immun. 2009;77(5):2065–2075. | ||
Moya B, Dötsch A, Juan C, et al. β-Lactam resistance response triggered by inactivation of a nonessential penicillin-binding protein. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5(3):e1000353. | ||
Balasubramanian D, Schneper L, Kumari H, Mathee K. A dynamic and intricate regulatory network determines Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(1):1–20. | ||
Kong KF, Aguila A, Schneper L, Mathee K. Pseudomonas aeruginosa β-lactamase induction requires two permeases, AmpG and AmpP. BMC Microbiol. 2010;10:328. | ||
Chaudhari AA, Jasper SL, Dosunmu E, et al. Novel pegylated silver coated carbon nanotubes kill Salmonella but they are non-toxic to eukaryotic cells. J Nanabiotechnology. 2015;13:23. |
Supplementary material
  | Table S1 Gene and primers used for quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (sequence 5′ → 3′) |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.