Back to Journals » International Journal of General Medicine » Volume 14
Seroprevalence of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Among Patients Attending at Addis Alem Primary Hospital, Bahir Dar, Northwest Ethiopia
Authors Geta M, Yizengaw E , Getaneh Z , Getahun T
Received 22 December 2020
Accepted for publication 27 January 2021
Published 10 February 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 405—411
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S298586
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Mekuanint Geta,1 Endalew Yizengaw,2 Zegeye Getaneh,3 Tamyalew Getahun4
1Department of Medical Microbiology, School of Biomedical and Laboratory Sciences, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia; 2Departments of Microbiology, Immunology and Parasitology, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Bahir Dar University, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia; 3Department of Hematology and Immunohematology, School of Biomedical and Laboratory Sciences, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia; 4Laboratory Department, Addis Alem Hospital, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia
Correspondence: Mekuanint Geta
Department of Medical Microbiology, School of Biomedical and Laboratory Sciences, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Gondar, PO Box 196, Gondar, Ethiopia
Email [email protected]
Background: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) causes severe liver disease, such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and life-threatening liver disease. Hepatitis B virus infection is one of the most dominant public health problems these days. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the seroprevalence of HBV infection among patients attending Addis Alem Hospital, Bahir Dar, Northwest Ethiopia.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted from January to February 2019 on HBV registered from January 2016 to December 2018 for three years period. The presence of HBsAg in serum was detected using the One Step Cassette Style HBsAg test kit. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 20. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the characteristics of participants with HBV infection. Statistical association of the determinants with HBV infection was determined by the X2 test.
Results: In this study, a total of 2010 participants of HBsAg rapid test records in the laboratory logbook were included. The median age of women was 25 years. The overall seroprevalence of HBsAg was 78 (3.9%). There was a general increment of HBV infection from 2016 to 2018, X2 =7.52; P=0.023. Age (X2 =8.19; P= 0.042) and sex (X2 =37.77; P < 0.001) were associated with HBsAg positivity.
Conclusion and Recommendations: An intermediate seroprevalence of HBV infection was detected among participants in our study area. This figure raises significant public health concerns. Therefore, implementing strategies for routine screening of women for HBV and hospital attendants would be critical.
Keywords: HBV, HBsAg, Addis Alem, Bahir Dar
Background
Hepatotropic viruses cause most cases of hepatitis worldwide. Hepatitis B virus (HBV), a Hepadnaviridae,1 is one of these viruses which causes severe liver disease, such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and life-threatening liver disease. Hepatitis remains one of the most dominant public health problems these days. Hepatitis B virus infection is the critical cause of diseases and death worldwide.2,3
Hepatitis B virus infection is limited to the liver cells of humans and causes cirrhosis and HCC. This infection is still accounting for a significant proportion of morbidity and mortality. Globally, 2 billion people are infected with HBV, 350 million people are estimated to be chronically infected,4,5 and 50 million people are newly infected with hepatitis B every year.6 The prevalence of chronic HBV infection is variable throughout the world, ranging from <1% in areas of low endemicity to over 30% in highly endemic areas. Africa has the second largest number of chronic carriers of HBsAg (>8%) next to Asia, which is considered a region of high endemicity.5,7,8 Ethiopia, being part of this region, is ranked as an area with medium to high endemicity for HBV infection.9,10 Worldwide, HBV infection is estimated to be the cause of 50% of reported cases of cirrhosis and 30% of liver cancer, and over 500,000 people die from them each year.11 Cirrhosis, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma develop in 15–40% of chronically HBV infected individuals.2,12
In highly endemic settings, perinatal, and horizontal (exposure to chronically infected household members) routes are responsible for most disease transmission.13 But in low prevalence countries, the Hepatitis B virus is transmitted parenterally.14 Adults infected with HBV usually develop acute hepatitis and recover. Infected children rarely develop the acute disease, but 25 to 90% become chronic carriers.15 Infection with HBV is highest among developing countries. Ethiopia is among the high burden countries for HBV infection,16 7.4% in the general population.17 Therefore, this study aimed to determine the seroprevalence of HBV for the last three years using laboratory recorded data (log book) to fill the existing epidemiologic gap in the area.
Methods
Study Area, Period and Design
From January to February 2019, a retrospective cross-sectional study was conducted on HBsAg test results registered from January 2016 to December 2018 for three years period. The research was done in Northwest Ethiopia, in Bahir Dar. Bahir Dar is situated 556 kilometers from Addis Ababa, Ethiopia’s capital city. The study was conducted at Addis Alem Primary Hospital found in this town. The Hospital has 52 beds for inpatients and delivery services. In the Hospital, a total of 4 specialist physicians and 17 general practitioners served an average of 104, 700 attendants annually.
Population
The study population consisted of all clients who had request for HBV screening from the respective clinics and gave blood for HBV screening, and recorded in the laboratory logbook at the Addis Alem Hospital from January 2016 to December 2018.
Data Collection Tool
The checklist was used to obtain information on HBV status, gender, age, and the department that requested the exam. Further data on different factors associated with HBV infection were problematic because the logbook contained small variables.
Laboratory Investigation
The hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) was requested as part of the antenatal care panel and for clinical suspicion of liver disease. The presence of HBsAg in serum was detected using a One Step Cassette Style HBsAg test kit (Nantog genes Biotech Co. Ltd, China) by following the Manufacturer’s instructions.
Quality Control
To ensure the consistency of the data, the necessary data were obtained from the laboratory logbook and reviewed thoroughly every day for completeness and accuracy. Software data have been tested carefully for errors, implausible values, and discrepancies that may be due to encoding, input, typing, and other errors. HBsAg positive clients’ serum was double-checked using ELISA in the referral laboratory located in the city.
Data Processing, Analysis and Interpretation
Data were entered and analyzed using version 20 of the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS). Descriptive statistics (frequency, median, percentage) were used to define the characteristics of HBV participants. The Pearson Chi-square (X2) test was used to determine the relationship between categorical variables. The Chi-square trend test was used to analyze year-by-year changes in patterns.
Results
Among 2010 screened patients, 616 (30.6%), 1151 (57.3%) and 243 (12.1%) patients were screened for HBV in 2016, 2017 and 2018, respectively. Among the screened patients, 1893 (94.2%) were females, and 117 (5.8%) were males with a median age of 25 years (Table 1). Within the year 2016, 2017, and 2018 screened patients, 591 (95.9%), 1068 (92.8%), and 234 (96.3%) were females, respectively. The majority of participants 427 (69.3%), 735 (63.9), and 168 (69.1%) patients were in the age group of 21–30 years screened in 2016, 2017, and 2018, respectively. Most of the participants (95%) in this study were from urban residency (Table 2).
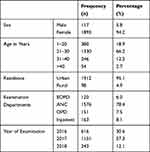 |
Table 1 Socio-Demographic Characteristics of Study Participants Screened for HBV from 2016 to 2018 (n=2010), Northwest Ethiopia, 2019 |
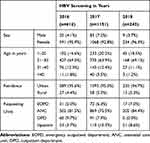 |
Table 2 The Distribution of Participants Characteristics Within Consecutive Three Years (n = 2010), Northwest Ethiopia, 2019 |
From all patients screened, the total prevalence of HBsAg in this study was 78/2010 (3.9% with 95% CI 3.1, 4.8). The seroprevalence of HBV infection in each consecutive year was 16/616 (2.6%), 46/1151 (4.0%), and 16/243 (6.6%), respectively (Figure 1). The trend of HBV infection was increasing and statistically significant change in seropositivity from the year 2016 to 2018 (Table 3). The positivity rate was higher in females 61/2010 (3.0%) than males 17/2010 (0.8%). This difference was statistically significant with HBV infection, X2 = 37.7; P< 0.001.
 |
Table 3 Seroprevalence of HBV Infection with Respect to Socio-Demographic Characteristics and Different Years of Screening (N=2010), Northwest Ethiopia, 2019 |
 |
Figure 1 Trends of HBsAg positivity from 2016 to 2018 at Addis Alem Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia, 2019. |
From the total patients requested for HBV screening in the hospital, 76 (3.8%) were positive for HBsAg in urban patients, whereas 2 (0.1%) were positive in rural patients. The seroprevalence of HBV infection was higher in the age group of 21–30 years, 48/2010 (2.4%) than their counterparts. This was statistically significant with HBsAg seropositivity, X2 = 8.2; P = 0.042. Among the requested patients from different examination departments, the highest prevalence reported from the antenatal care unit 44/2010 (2.2%) followed by the emergency outpatient department accounts for 22/2010 (1.1%), but the least HBsAg positivity were inpatients 4 (0.1%). This was statistically significant with X2 =73.9; P < 0.001 (Table 2).
Discussion
The cases selected for our study were all patients who seek screening for HBV infection. The lab tests employed were all standard and reliable. It is easy to compare our findings with other hospital-based similar studies where the cases selected are the clinically suspected ones coming to the hospital seeking treatment.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) including HBV are widespread in developing countries and constitute a major public health problem in sub-Saharan Africa.18 Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is the main marker indicating endemicity of HBV infection in the general population of a particular geographical area.13 The classification of low, intermediate, and high endemicity for HBV infection has been defined as HBsAg less than 2%, 2 to 7%, and greater than 7% in an adult population, respectively.19
In the present study, we found 3.9% (95% CI, 3.0–4.7%) of the overall seroprevalence of HBsAg among patients screened for HBV infection in Addis Alem primary Hospital. Based on the WHO classification, the prevalence of HBV infection in this study was classified as “intermediate”. This figure is still high if we compute the general population of Ethiopia as these days it is close to 100 million. In addition, it is assumed that the rate might be increased more if this study is done in different geographical areas. Therefore, HBV infection was a particular problem that might be due to the possibility all the population are at risk for HBV infection.20
In our study, the prevalence rate of HBsAg was comparable with a study conducted in Gondar University Teaching Hospital on blood donors 4.7%21 and Addis Ababa 3.0%.22 However, our study finding was lower than when compared to study done in Gondar, Ethiopia among street dwellers 10.9%23 and among medical waste handlers 6%,24 on donors at Bahir Dar, Ethiopia 25%,25 among blood donors in Amhara and Tigray regional states, Ethiopia 6.2%,26 among patients with chronic hepatitis, southeast Ethiopia 22.3%,27 among VCT clients, southern Ethiopia 5.7%,28 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia among medical waste handlers 6.3%29 and among general population higher than 7%,9 and Jigjiga, Ethiopia (10.9),30 in Nigeria among blood donors 10.9%31 and 18.6%.32 In contrast, our study was higher than a study conducted in Eretria on blood donors 2.6%33 and 2.0%,34 and the study reported Japan 0.8%.5
These differences might be suggested to sample size difference, geographical variation, method of detection, cultural practice difference, and behavioural divergences for the risk factors, and the degree of HBV endemicity often correlates with the predominant mode of transmission. Furthermore, the variation might be also due to different study designs and methods for the assay of HBV infection used.
In this study, the highest prevalence was recorded among the age group between 21–30 years 48 (2.4%), which was higher than the seroprevalence of all other age groups participants 30 (1.5%). The infectivity of HBV seems to be skewed towards persons younger than 30 years of age as the majority of the clients in this age group were HBsAg positive. In our opinion, the reason behind the high rate of HBV in this age group is most probably the high infectivity potential of the virus, immunization status, cultural practices, which could expose to HBV infection like circumcisions, tattooing, bloodletting exercises to treat different diseases.35 But a study conducted in Ghana on blood donors, revealed that the highest seroprevalence was among the 30–39 years age group 8.9%36 which was not in agreement with our study. Sixty-one (3.0%) females were tested positive as compared to 17 (0.8%) males. This was supported by another study done by Walana et al (14.3%) of females as compared to (6.7%) males.36 Almost all, 76/78 (97.4) of all HBsAg positives were from urban.
The trend analysis performed showed that HBV infection significantly increased from 16 (2.6%), 46 (4.0%), and 16 (6.6%) for the last three consecutive years. This might be due to an increased focus and frequent HBV screening for all suspected attendants in the hospital. The limitation of our study is the method that we employed. HBsAg detection method can also be questioned because it used a rapid chromatographic immunoassay for the first 3 years. Another limitation is that laboratory tests have been limited to the detection of HBsAg, without checking the markers of viral replication, as HBeAg or HBV DNA, for financial reasons. So, our results would have been more genuine if we had been able to perform ELISA and Nucleic Acid Amplification Technique (NAAT) as a screening method.
Conclusions
An intermediate prevalence of HBV infection was detected among study participants in our study area. Because hospital attendant clients are among vulnerable population groups, the figure raises serious public health concerns. Therefore, implementing strategies for routine screening of all patients attending Hospitals for HBV would be critical.
Abbreviations
DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; NAAT, nucleic acid amplification technique; STI, sexually transmitted infection; VCT, voluntary counselling and testing.
Data Sharing Statement
The original data used for this study are available at the corresponding author, so that interested reader can get the data from the corresponding author with reasonable request.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical approval was received from the Ethical Committee of the University of Gondar, College of Medicine and Health Science, Biomedical School and Laboratory Sciences Research. The Hospital Administration and clinical management committee have waived the requirement to seek patient consent from participants. Since our study was on hospital attendants who were not able to address them, we review the record of the patients, and the research poses no more than minimal risks to participants. The study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. The confidentiality of the data was kept through locking the computer data with password, hard copy with locker, and by preventing of disclosure for unauthorized individuals.
Acknowledgments
We have a great appreciation to University of Gondar for giving the technical support during analysis and write-up of this article. We would also like to acknowledge Addis Alem Hospital.
Laboratory staffs who actively participated in the collection of these data.
Author Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Funding
There is no funding to report.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Lavanchy D. Hepatitis B, virus epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, and current and emerging prevention and control measures. J Viral Hepat. 2004;11(2):97–107. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2893.2003.00487.x
2. Gunn RA, Murray PJ, Ackers ML, Hardison WG, Margolis HS. Screening for chronic hepatitis B and C virus infections in an urban sexually transmitted disease clinic: rationale for integrating services. Sex Transm Dis. 2001;28(3):166–170. doi:10.1097/00007435-200103000-00008
3. Lok A. Chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1682–1683. doi:10.1056/NEJM200205303462202
4. Seid M, Gelaw B, Assefa A. Sero-prevalence of HBV and HCV infections among pregnant women attending antenatal care clinic at Dessie Referral Hospital, Ethiopia. Adv Life Sci Health. 2014;1(2):109–120.
5. Merican I, Guan R, Amarapuka D, et al. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Asian countries. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;15(12):1356–1361. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1746.2000.0150121356.x
6. Lamberth JR, Reddy SC, Pan JJ, Dasher KJ. Chronic hepatitis B infection in pregnancy. World J Hepatol. 2015;7(9):1233–1337. doi:10.4254/wjh.v7.i9.1233
7. Ryder S, Beckingham I. ABC diseases of liver, pancreas, and biliary system: acute hepatitis. Br Med J. 2001;322(7279):151–153. doi:10.1136/bmj.322.7279.151
8. Hwang E, Cheung R. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. N Am J Med Sci. 2011;4(1):7–13. doi:10.7156/v4i1p007
9. Abebe A, Nokes D, Dejene A, Enquselassie F, Messele T, Cutts F. Sero epidemiology of hepatitis B virus in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: transmission patterns and vaccine control. Epidemiol Infect. 2003;131(1):757–770. doi:10.1017/S0950268803008574
10. Tsega E, Mengesha B, Hansson BG, Lindberg J, Nordenfelt E. Hepatitis A, B, and delta infection in Ethiopia: a serologic survey with demographic data. Am J Epidemiol. 1986;123(2):344–351. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114243
11. Lavanchy D. Worldwide epidemiology of HBV infection, disease burden, and vaccine prevention. J Clin Virol. 2005;34:S1–3. doi:10.1016/S1386-6532(05)00384-7
12. Alavian M, Masoud H, Asl A, Ali K, Lankarani B. Hepatitis B virus infection in Iran. Soc Inf Disp. 2008;8(4):281–294.
13. Shepard CW, Simard EP, Finelli L, Fiore AE, Bell BP. Hepatitis B virus infection: epidemiology and vaccination. Epidemiol Rev. 2006;28(1):112–125. doi:10.1093/epirev/mxj009
14. Chienyc J, Kuo H, Chenc J. Nationwide hepatitis B vaccination program in Taiwan: effectiveness in the 20 years after it was launched. Epidemiology. 2006;28(1):126–135. doi:10.1093/epirev/mxj010
15. Juszczyk J. Clinical course and consequences of hepatitis B infection. Vaccine. 2000;18:S23–25. doi:10.1016/S0264-410X(99)00457-0
16. WHO. Media centre/fact sheets. http://www.who.int/. Jul 2014.
17. Belyhun Y, Maier M, Mulu A, Diro E, Liebert UG. Hepatitis viruses in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16(1):761. doi:10.1186/s12879-016-2090-1
18. Olokoba AB, Salawu FK, Damburam A, et al. Hepatitis B virus infection amongst pregnant women in North-Eastern: a call for action. Niger J Clin Pract. 2011;14(1):10–13. doi:10.4103/1119-3077.79232
19. Uneke CJ, Ogbu O, Inyama PU, Anyanwu GI, Njoku MO, Idoko JH. Prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen among blood donors and human immunodeficiency virus infected patients in Jos, Nigeria. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2005;100:13–16. doi:10.1590/S0074-02762005000100002
20. CDC. Viral hepatitis: hepatitis B information. July 28, 2020. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hbv/bfaq.htm.
21. Tessema B, Yismaw G, Kassu A, et al. Seroprevalence of HIV, HBV, HCV and syphilis infections among blood donors at Gondar University Teaching Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia: declining trends over a period of five years. BMC Infect Dis. 2010;10(1):111. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-10-111
22. Tegegne D, Desta K, Tegbaru B, Tilahun T. Seroprevalence and transmission of hepatitis B virus among delivering women and their new born in selected health facilities, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2014;7(1):239. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-7-239
23. Moges F, Kebede Y, Kassu A, et al. Seroprevalence of HIV, hepatitis B infections and syphilis among street dwellers in Gondar city, Northwest Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Dev. 2006;20(3):160–165.
24. Anagaw B, Shiferaw Y, Anagaw B, et al. Seroprevalence of hepatitis B and C viruses among medical waste handlers at Gondar town Health institutions, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2012;5(1):55. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-5-55
25. Dessie A, Abera B, Wale F. Seroprevalence of major blood-borne infections among blood donors at Felege Hiwot referral hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Dev. 2007;21(1):68–69. doi:10.4314/ejhd.v21i1.10034
26. Gelaw B, Mengitsu Y. The prevalence of HBV, HCV and malaria parasites among blood donor in Amhara and Tigray regional states. Ethiop J Health Dev. 2008;22(1):3–7. doi:10.4314/ejhd.v22i1.10056
27. Taye S, Abdulkerim A, Hussen M. Prevalence of hepatitis B and C virus infections among patients with chronic hepatitis at Bereka Medical Center, Southeast Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2014;7:272. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-7-272
28. Negero A, Sisay Z, Medhin G. Prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) among visitors of Shashemene General Hospital voluntary counseling and testing center. BMC Res Notes. 2011;4(1):35. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-4-35
29. Shiferaw Y, Abebe T, Mihret A. Hepatitis B virus infection among medical waste handlers in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. 2011;4(1):1–7. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-4-479
30. Mohammed Y, Bekele A. Seroprevalence of transfusion transmitted infection among blood donors at Jijiga blood bank, Eastern Ethiopia: retrospective 4 years study. BMC Res Notes. 2016;9(1):129. doi:10.1186/s13104-016-1925-6
31. Nwankwo E, Momodu I, Umar I, Musa B, Adeleke S. Sero-prevalence of major blood-borne infections among blood donors in Kano, Nigeria. Turk J Med Sci. 2012;42(2):337–341.
32. Buser FI, Muhibi MA, Jeremiah ZA. Sero-epidemiology of transfusion transmissible infectious diseases among blood donors in Osogbo, southwest Nigeria. Blood Transfus. 2009;7(4):293–299. doi:10.2450/2009.0071-08
33. Fessehaye N, Naik D, Fessehaye T. Transfusion transmitted infections: a retrospective analysis from the national blood transfusion service in Eritrea. Pan Afr Med J. 2011;9(1):1–6. doi:10.4314/pamj.v9i1.71219
34. Siraj N, Achila OO, Issac J, et al. Seroprevalence of transfusion-transmissible infections among blood donors at national blood transfusion service, Eritrea. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):264. doi:10.1186/s12879-018-3174-x
35. National Foundation of Infectious Disease. Infectious disease: hepatitis and adults: hepatitis B. Available from: https://www.nfid.org/infectious-diseases/hepatitis-b-are-you-at-risk-infographic/.
36. Walana W, Ahiaba S, Hokey P, et al. Sero-prevalence of HIV, HBV and HCV among blood donors in the Kintampo Municipal Hospital, Ghana. Br Microbiol Res J. 2014;4(12):1491–1499. doi:10.9734/BMRJ/2014/12160
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
