Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 9
Selective use of vandetanib in the treatment of thyroid cancer
Authors Fallahi P, Di Bari F, Ferrari SM, Spisni R, Materazzi G, Miccoli P, Benvenga S, Antonelli A
Received 25 March 2015
Accepted for publication 12 May 2015
Published 3 July 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 3459—3470
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S72495
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Shu-Feng Zhou
Poupak Fallahi,1 Flavia Di Bari,2 Silvia Martina Ferrari,1 Roberto Spisni,3 Gabriele Materazzi,3 Paolo Miccoli,3 Salvatore Benvenga,2 Alessandro Antonelli1
1Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, University of Pisa, Pisa, 2Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Section of Endocrinology, University of Messina, Messina, 3Department of Surgical, Medical, Molecular Pathology and Critical Area, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy
Abstract: Vandetanib is a once-daily orally available tyrosine kinase inhibitor that works by blocking RET (REarranged during Transfection), vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3), and epidermal growth factor receptor and to a lesser extent VEGFR-1, which are important targets in thyroid cancer (TC). It is emerging as a potentially effective option in the treatment of advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) and in dedifferentiated papillary thyroid cancer not responsive to radioiodine. The most important effect of vandetanib in aggressive MTC is a prolongation of progression-free survival and a stabilization of the disease. Significant side effects have been observed with the vandetanib therapy (as fatigue, hypertension, QTc prolongation, cutaneous rash, hand-and-foot syndrome, diarrhea, etc), and severe side effects can require the suspension of the drug. Several studies are currently under way to evaluate the long-term efficacy and tolerability of vandetanib in MTC and in dedifferentiated papillary TC. The efficacy of vandetanib in patients with MTC in long-term treatments could be overcome by the resistance to the drug. However, the effectiveness of the treatment could be ameliorated by the molecular characterization of the tumor and by the possibility to test the sensitivity of primary TC cells from each subject to different tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Association studies are evaluating the effect of the association of vandetanib with other antineoplastic agents (such as irinotecan, bortezomib, etc). Further research is needed to determine the ideal therapy to obtain the best response in terms of survival and quality of life.
Keywords: vandetanib, medullary thyroid cancer, papillary thyroid cancer, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, adverse events
Introduction
Thyroid cancer (TC) accounts for about 1% of all cancers1 and is the most common malignant endocrinological tumor.2 In the last few decades, an increased TC incidence has been shown (from 10.3 per 100,000 individuals in 2000 to 21.5 per 100,000 individuals in 2012),3 especially for papillary carcinoma, while mortality seems not changed.
The increased incidence of TC is probably due to more sophisticated diagnostic procedures (ultrasonography, fine-needle aspiration [FNA], etc), but also environmental factors have been implicated (radiation exposure, pollutants, etc). Furthermore, new risk factors have emerged in the last decade.4,5 Histologically, TCs include different subtypes (Table 1).6–16
Molecular pathways in TC
In the last few decades, several molecular pathways involved in the development of TC have been identified.17
Rat sarcoma
Rat sarcoma (RAS) genes encode proteins activating MAPK and PI3K pathways (Figure 1). RAS activation depends on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and is often overexpressed if mutated. RAS mutations are more frequent in follicular thyroid cancer (FTC) and in half of anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) and poorly differentiated thyroid cancer (PDTC), while they are present in only 10%–15% of papillary thyroid cancer (PTC; especially in follicular variant).16,18,19 Somatic RAS mutations are also found in medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) without RET (REarranged during Transfection) mutations.20
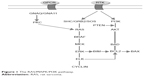  | Figure 1 The RAS/MAPK/PI3K pathway. |
BRAF is a member of RAF family proteins that binds RAS and activates MAPK cascade. Valine to glutamate amino acid substitution at residue 600 (V600E) is the most frequent point mutation (45% of PTC, 10%–20% of PDTC, 20% of ATC, rarely in FTC) that is associated with tumor recurrence, absence of tumor capsule, and loss of response to radioiodine (RAI).21 Other BRAF mutation or rearrangements (as AKP9/BRAF) are less frequent.
RET (REarranged during Transfection)
RET is a proto-oncogene (10q11.2), which codes for a tyrosine kinase transmembrane receptor and is expressed on tissues deriving from the neural crest including thyroid C cells but not in normal thyroid follicular cells.22,23 In thyroid tumors, RET can be activated by point mutations in C cells or by rearrangements (fusion to other genes) in epithelial cells.16
RET/PTC rearrangements (the 3′ portion of RET gene is fused to the 5′ portion of various genes) activate transcription of the RET tyrosine kinase domain inducing uncontrolled proliferation.24,25 Approximately 20%–40% of sporadic PTC are found RET/PTC rearrangements,26 that are also present in thyroid adenomas and benign lesions.27,28 Among 13 RET/PTC rearrangements reported, RET/PTC1 (by the fusion with the CCDC6, formerly H4) and RET/PTC3 (by the fusion with the NCOA4, formerly ELE1) are the most common.29
Some authors have suggested a role of RET/PTC in the initial step of childhood PTC or in PTC arising after exposure to ionizing radiations (mainly RET/PTC3).30,31 RET/PTC3 appears to be related with poor prognostic factors, such as a greater tumor size and a more advanced stage at diagnosis.32
Activating mutations involving RET have been identified in 98% of hereditary MTC and 50% of sporadic MTC.33 Germ line gain of function RET mutations are found in 98% multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A (MEN2A) families, 85% familial medullary thyroid cancer (FMTC), and more than 98% multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B (MEN2B).34 In MEN2A, the most frequent mutation of RET is in cysteine 634,35 while the most common mutations associated with MEN2B are M918T and A883F.35–37
In sporadic MTC, the substitution of methionine by threonine at codon 918 (M918T) is the most common mutation and is associated with a more aggressive disease and poorer prognosis.38,39
Rearrangements of PAX8/peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ is detected in 30%–40% of FTC and 2%–13% of follicular adenomas.40,41
Vascular endothelial growth factor
Angiogenesis plays a crucial role for growth and metastasis of a tumor; in fact, several studies showed correlation between angiogenesis and tumor aggressiveness.42,43 The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family includes VEGF A-C and placental growth factor (P1GF) and stimulates angiogenesis, endothelial cell proliferation, migration, survival, and vascular permeability binding to the VEGF receptors: VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, and VEGFR-3.44 VEGF signal is mediated mainly by VEGFR-2 receptor, expressed at high levels by endothelial cells involved in angiogenesis.45 VEGFR-2 stimulation results in activation of different pathways, including MAPK and PI3K-Akt.46 An overexpression of VEGF and angiopoietin-247 has been shown in DTC, while in MTC, overexpression of VEGF and VEGFR-2 was found.48 Also, there is an increased expression of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 in metastatic MTC.49 Increased VEGF expression is associated with a worse prognosis in many DTC.50 Furthermore, overexpression and activation of VEGFR-2 in MTC correlate with metastasis.39 In experimental models, drugs interfering with VEGF block the growth of DTC and PDTC.51–53 These discoveries have led to the development of systemic antiangiogenic drugs that act on VEGF-A pathway, for the treatment of patients with various types of cancers including TC.54
Epidermal growth factor
Epidermal growth factor is also important for the growth and metastasis ability of the tumor and acts by binding to EGFR, thus stimulating VEGF expression.55 In TC, EGFR (ErbB-1; HER1 in human beings) mutations contribute to RET kinase activation and favor growth and spread of tumor; in turn, activation of RET/PTC1 and RET/PTC3 induces expression of EGFR.56,57
The incidence of EGFR mutations in TC was previously thought to be low, but more recently, it has been suggested that EGFR mutations are almost 30%.58 EGFR is overexpressed and correlated with tumor progression and lymph node metastasis in ATC and PDTC, compared to normal thyroid tissue.59–61 Lote et al have described a case of metastatic PDTC with an EGFR mutation, treated with erlotinib (selective EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor [TKI]) and responsive to therapy, suggesting the importance of EGFR as therapeutic target in PDTC.62 In PTC, the expression of EGFR-1 protein is absent or poor. It suggests that overexpression of EGFR-1 can favor progression toward an angiogenic, poorly differentiated, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)-independent phenotype.63
Thyroid carcinoma therapy
Differentiated thyroid carcinoma
DTC is treated by surgery, followed by RAI in selected patients and levothyroxine therapy in all patients.64 Generally, patients with DTC have a good prognosis, with a 5-year survival rate of 97.8%, when properly treated.65 However, 5% of patients have distant metastasis at the diagnosis or recurrent disease that cannot be treated with surgery and/or are resistant to RAI (because during progression, tumor cells lose RAI uptake ability).66,67
For patients with metastatic disease, the NCCN Thyroid Carcinoma Panel recommends individualized treatment based on tumor location. Although not curative, systemic and/or locoregional therapy may be recommended for patients with symptomatic and/or progressive disease who cannot be treated with RAI.68 Systemic therapy (including cytotoxic chemotherapy) can be considered for tumors not surgically resectable, not responsive to RAI, and not treatable with external beam radiation therapy or that have shown progression during the past 6–12 months.15 However, conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy often have a modest effect on aggressive TC.6
TKIs represent an option of systemic treatment in case of progressive, aggressive refractory cancers.69
Medullary thyroid carcinoma
MTC prognosis varies in relation to the extension of the tumor and RET mutations. MEN2A and FMTC patients commonly have a better treatment outcome than those with sporadic MTC, who are frequently diagnosed at a more advanced stage. Three risk levels related RET mutations have been identified. Level 1 (low risk) includes patients with RET codon 768, 790, 791, 804, and 891 mutations; level 2 (high risk), patients with MEN2A/FMTC-related mutations (codon 609, 611, 618, 620, 630, and 634); and level 3 (very high risk), patients with MEN2B mutations in codon 883 or 918.26
Generally, MTC is curable by surgery in an early stage, followed by postoperative levothyroxine therapy. No curative systemic therapy exists for locally advanced and metastatic progressive MTC that does not respond to conventional cytotoxic chemotherapy. TKIs are actually recommended for selected patients with recurrent or persistent aggressive MTC.15,69,70
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
TKIs act by blocking the ATP site of the tyrosine kinase receptors, preventing tyrosine kinase activation.19 Already, several TKIs are used in the treatment of various advanced cancers.
Whereas TKIs do not act selectively on pathways specific for a tumor, they have been tested on different tumors including DTC, MTC, and ATC.71 TKIs improve progression-free survival (PFS) and stable disease (SD) rates in TC.72
It has been demonstrated that TKIs have a clinically significant activity in randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials in locally recurrent unresectable and metastatic MTC and in RAI refractory DTC. Particularly, in aggressive DTC, or MTC, several studies have evaluated the use of axitinib, lenvatinib, motesanib, pazopanib, sorafenib, sunitinib, cabozantinib, and vandetanib.73 Sorafenib and lenvatinib are currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and EMA for the treatment of aggressive DTC, while vandetanib and cabozantinib are used for the treatment of aggressive advanced MTC.74–76
Cabozantinib is an oral once-daily multitarget TKI of MET, VEGFR-2, RET, acting against KIT, AXL, FLT3, and Tie-2.77 In a Phase III clinical study, cabozantinib improved PFS of patients with MTC, and it is actually approved by FDA and EMA for the treatment of aggressive MTC.76 Cabozantinib has also been evaluated in metastatic DTC patients, because they have activation on tyrosine kinases, including MET, VEGFR-2, and RET, suggesting the possible use of cabozantinib in metastatic DTC.78
Actually, studies focus on refining combination treatment strategies and determining which patients will obtain the best benefit from TKIs (with the least toxicity).79
Vandetanib
Vandetanib (Caprelsa, ZD6474; AstraZeneca) is an oral once-daily TKI that works by blocking RET, VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, and EGFR and to a lesser extent VEGFR-1, which are important targets in TC (Figure 2).80
Initially, it was shown that vandetanib blocks the enzymatic activity of RET-derived oncoproteins and in vivo phosphorylation and signaling of the RET/PTC3 and RET/MEN2B oncoproteins and of an epidermal growth factor-activated EGFR/RET chimeric receptor. Vandetanib inhibited the proliferation of two human PTC cell lines that carry spontaneous RET/PTC1 rearrangements. Finally, it blocked formation of tumors in vivo after injection of RET/PTC3-transformed NIH3T3 fibroblasts into nude mice.81
Also, most of the mutant oncoproteins (RET/E768D, RET/L790F, RET/Y791F, RET/S891A, and RET/A883F) were found sensitive to vandetanib, while mutations substituting valine 804, either to leucine or to methionine (as occur in some cases of MEN2A), were significantly resistant.82
Furthermore, it was shown that vandetanib was able to inhibit the growth of a transplantable MTC (from a sporadic human MTC carrying a RET C634R mutation) in nude mice.83
The most important antitumoral effect of vandetanib, in vivo, is an “indirect” effect on angiogenesis, interfering with EGFR-induced production of angiogenic growth factors.84,85
Several clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of vandetanib in patients with TC (Table 2).
Phase I trials
The first Phase I trial was conducted on 77 patients with advanced solid tumors (not including MTC), treated with vandetanib; this study concluded that 500 mg/day was the maximum tolerated dose and once-daily oral dosing of 300 mg/day was generally well tolerated.86 A Phase I trial, carried on 18 patients, established the maximum tolerated dose at 400 mg/day. In both trials, the authors recommended a dose of 300 mg/day.87
Phase II trials
Medullary thyroid cancer
A Phase II, single-arm trial evaluated the efficacy of treatment with vandetanib (300 mg/day) in 30 adult patients with unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic hereditary MTC. In this study, the majority of patients had MEN2A (70%); RET mutations were located in codons: 634 (33% of patients), 618 (27%), 620 (13%), 918 (13%), 791 (7%), 768 (3%), and 891 (3%). In this study, objective partial response (PR) was observed in 20% of patients and 53% of patients had SD for a median of 24 weeks with a manageable adverse event (AE) profile. There was no apparent association between RET germ line mutation and response to vandetanib treatment.88
Another trial investigated efficacy and safety of vandetanib at 100 mg/day (or up to 300 mg/day in cases with disease progression) in 19 patients with advanced hereditary MTC and the results were similar to the previous study (PR in 16% and SD in 53% of patients for 24 weeks).89 Both trials showed important reduction (≥50%) in CEA and calcitonin levels; the latter did not correlate with the degree of tumor growth inhibition. It was suggested that CEA levels may be a better marker of tumor response to vandetanib.
Recently, a Phase I/II trial has been conducted for adolescents (13–18 years) and children (5–12 years) with metastatic or locally advanced MTC. In this trial, 16 patients were treated with vandetanib 100 mg/m2/day, concluding that this dosage is a well-tolerated and highly active treatment for adolescents and children with locally advanced or metastatic MTC and MEN2B.90
Differentiated thyroid cancer
Leboulleux et al91 carried out a double-blind, Phase II, randomized trial, in 145 patients with metastatic or locally advanced DTC (papillary, follicular, or poorly differentiated) evaluating efficacy of vandetanib (300 mg/day) vs placebo (72 patients were allocated in vandetanib arm and 73 patients in placebo arm). PFS (primary endpoint) in vandetanib group was 11.1 months compared to 5.9 months in placebo group, while PR was 8% and 5% respectively, and SD 57% vs 42%. Better results have occurred in PTC than in FTC and PDTC.91
Phase III trials
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter Phase III trial (ZETA trial) was conducted in 331 advanced (5% of all patients) or metastatic (95%) MTC patients.92 In this study, all MTC patients were offered the option of receiving vandetanib (300 mg daily administered until disease progression) in an open-label phase. Ten percent of patient had hereditary MTC, while 90% sporadic or unknown origin MTC. Also, 56% of patients were RET mutation positive, 2% RET mutation negative, and 41% unknown. The results of this study showed better PFS in the vandetanib group compared to placebo (30.5 vs 19.3 months; P<0.001), while OS was not significantly changed and calcitonin (69% vs 3%) and CEA (52% vs 2%) response rates were higher (P<0.001) in patients receiving vandetanib. Patients with sporadic MTC (RET positive) benefited from vandetanib and there was a good response in patients with M918T-negative tumors and in RET unknown status.92
Because vandetanib is effective in stabilizing symptomatic and/or progressive disease, it was approved, since April (FDA) and November (European Union) 2011, for the treatment of unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic MTC in patients with symptomatic or progressive disease, in Europe and the United States.93
Recently, a retrospective study showed efficacy of vandetanib in the treatment of eleven progressive metastatic MTC patients with 36% PR.94
Moreover, a recent French study conducted to describe the toxicity profile and efficacy of vandetanib treatment outside any trial showed vandetanib efficacy in advanced MTC patients, but in consideration of the appearance of at least one AE in all patients, a careful monitoring was recommended.95
Actually, a new randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter Phase III study is ongoing in DTC patients.96
Also, a first Phase IV randomized trial is ongoing to evaluate differences in the response in MTC patients treated with 300 mg/day vs 150 mg/day of vandetanib.97
Safety and tolerability
Clinical studies showed that vandetanib treatment is associated with several AEs but it has an acceptable tolerability because AEs are generally mild and manageable. The most frequent AEs in vandetanib-treated patients are diarrhea, rash and folliculitis, nausea, QTc prolongation, hypertension and fatigue, headache, decreased appetite, and acne (diarrhea, hypertension, prolongation QTc, and fatigue were the most common AEs of at least grade 3).88–92 In the management of AEs, it is important to remember that the half-life of vandetanib is 19 days.98,99 Dose reduction can induce AEs grade 1 or 2 improvement, but for AEs grade 3 or 4, it is advisable to interrupt vandetanib until AEs resolve, then therapy might be resumed but at a lower dose.89
Moreover, vandetanib treatment requires increased thyroxine, calcium, and vitamin D analog.100
Dermatological AEs
Several trials showed a high incidence of dermatological AEs in patients treated with vandetanib. In the ZETA trial, in fact, these AEs occurred in 45% of cases.92 Vandetanib, as other EGFR inhibitors, is associated especially with a papulopustular eruption. The development of the rash is related to EGFR inhibition by vandetanib (in fact, EGFRs are abundantly expressed in the epidermis and its appendages)101,102 that induces hyperkeratosis, follicle obstruction, and then inflammation of the pilosebaceous follicle.103
In a review of 2,961 MTC patients treated with vandetanib, incidence of all-grade and high-grade rash was 46.1% and 3.5%, respectively.104
Other dermatological AEs associated to the treatment with vandetanib are photosensitivity (observed in all patients), xerosis, hair changes, paronychia, genital skin reactions, finger clefts, subungual splinter hemorrhages, and blue dots.105,106 AEs less frequently observed are mucositis, erythrodysesthesia, and pruritus,107 and in one case, Stevens-Johnson syndrome has been described.108
Recently, a study confirmed that dermatologic AEs in children treated with target anticancer therapy (including vandetanib) are similar to those in adults.109
Generally, dermatological AEs are easily manageable, but given the high incidence of these dermatological AEs, their prevention and early management are important to reduce the risk of vandetanib dose reduction or interruption.110
Gastrointestinal AEs
Diarrhea is the most frequent gastrointestinal AE in patients treated with vandetanib during ZETA trial (56% of all patients), followed by nausea (33% of cases), decreased appetite (21%), vomiting (14%), and abdominal pain (14%).92 Often, these AEs (especially diarrhea) cause poor patient compliance and treatment interruption. Patient education is important with dietary measures.
Sometimes, diarrhea in MTC may be due to excessive hormone production by tumor, which accelerates intestinal transit; in these cases, it improves with vandetanib treatment. In most cases, treatment with vandetanib causes diarrhea, which can be rectified by correct hydration and possibly by administering loperamide.
For the treatment of nausea, the use of 5-HT3 antagonists (ondansetron) is not recommended as it might increase the risk of prolongation of the QTc interval.111 For the same reason, metoclopramide should also be used with caution.102 In the antiemetic therapy, an alternative may be palonosetron.112
When gastrointestinal AEs are severe, vandetanib should be stopped until symptoms improve.102,113
Cardiovascular AEs
Vandetanib treatment may induce development of cardiovascular AEs including hypertension, bleeding, arterial thrombosis, ventricular dysfunction, fatal cardiac failure, and QTc interval prolongation.114,115
In a systematic review and meta-analysis of 3,154 patients treated with vandetanib, incidences of all-grade and high-grade hypertension in patients were 24.2% (95% confidence interval, 18.1%–30.2%) and 6.4% (95% confidence interval, 3.3%–9.5%), respectively, with a higher incidence of all-grade hypertension in MTC patients than non-MTC patients.116 Because of this risk of hypertension, adequate blood pressure monitoring and therapy with ACE inhibitors (if necessary) is recommended in patients being treated with vandetanib. If blood pressure is not controlled, calcium antagonist and beta blockers can be used.102
A cardiological very important AE in vandetanib treatment (and TKIs therapy) is QTc prolongation. Particularly QTc >500 ms was observed in 14% of patients treated with vandetanib in the ZETA trial; two cases of death in patients with QTc >550 ms have been reported (one due to sepsis and one due to heart failure).99
Before starting vandetanib treatment, ECG and echocardiogram are recommended and vandetanib must not be started in patients with QTc >450 ms (US) or >480 ms (European Union). During therapy, coadministration of drugs which prolong QTc interval should be avoided. Also, electrolyte levels and serum TSH should be maintained in normal range. Usually, QTc interval prolongation is relatively mild at clinical doses and has not led to appreciable morbidity clinically,115 although because of the potential for QT prolongation, torsades de pointes, and sudden death, vandetanib is restricted via a Risk Evaluations and Mitigation Strategy program.93
Other AEs
Other common side effects of vandetanib include fatigue, headache, hypocalcemia, hypoglycemia, increased transaminase levels, and thyroid dysfunction.102,117,118
Limits, drug resistance, and combination studies
Although therapy with TKIs is less toxic than chemotherapy, severe AEs require discontinuation of the drug. Furthermore, TKIs block tumor growth but do not eliminate it. Clinical trials have given contrasting results regarding the efficacy of TKIs in DTC patients: probably, these discordant results depend on mechanisms of drug resistance, via activation of alternative mitogenic signals.119 For this reason, studies are evaluating the combinations of TKIs targeting different pathways.120 Mechanisms of primary and acquired resistance to vandetanib have been investigated; actually, RET mutations cannot be used clinically to predict response in MTC.121
ZETA trials confirmed the clinical efficacy of vandetanib in patients with sporadic MTC tumors harboring the M918T mutation; while, the clinical efficacy of vandetanib in patients harboring other RET mutations needs other studies.
In vitro studies showed that the RET V804M and V804L mutations (that are rare and occur in sporadic and hereditary MTC) confer resistance to vandetanib82 and result clinically in primary or acquired resistance to vandetanib. However, sorafenib has shown activity against the V804 mutant in vitro.122
Moreover, other studies are needed to evaluate if Ras mutations, identified in 60%–80% of RET-negative sporadic MTC,123 confer clinical resistance to vandetanib. However, it has been shown (in vitro) that cell lines with acquired resistance to vandetanib present persistent activation of the Ras/Raf/MEK pathway (that can be abrogated by sorafenib).124
The response to therapy could be improved by testing the sensitivity of TC cells to different TKIs. In fact, in vitro drug screening with human primary neoplastic cells has a 60% positive predictive value of clinical response in vivo in the same patient and a 90% negative predictive; thus, the administration of inactive drugs could be avoided.125–129 More recently, it has been demonstrated that primary TC cell cultures from ATC (ANA) may be obtained from FNA opening the possibility to the use of FNA-ANA to test the chemosensitivity to different drugs in each patient (avoiding unnecessary surgical biopsies, until now used to obtain ANA).129–135
Combination studies
Several studies have evaluated the effectiveness of the synergic action of different antineoplastic drugs in combination studies.
It has been shown that combined therapy with bortezomib (proteasome inhibitor) and EGFR inhibitors (gefitinib, vandetanib, and cetuximab) induced (in EGFR-expressing human cancer cell lines) a synergic inhibition of neoplastic growth.136 Currently, nonrandomized, Phase I/II trial of the combination of vandetanib plus bortezomib is recruiting patients with solid tumors (including MTC).137
Other studies have evaluated the combination of vandetanib and irinotecan. Preclinical data showed that vandetanib has antiproliferative antitumor activity in vitro, which acts in a sequence-dependent manner with chemotherapeutic agents, such as irinotecan, in colon cancer cell lines.138 A subsequent study was conducted in a murine xenograft model of human colon cancer treated with vandetanib in combination with irinotecan that showed an additive synergic effect of these drugs.139 Another study evaluated the response to vandetanib, radiotherapy, and irinotecan of human LoVo colorectal tumoral cells, demonstrating that vandetanib significantly increases the antineoplastic effects of irinotecan and radiation when given in combination, resulting in a reduction of tumor growth.140 Recently, a Phase I trial was conducted in 27 patients with metastatic colorectal cancer refractory to cytotoxic chemotherapy, treated with vandetanib, cetuximab, and irinotecan, showing no apparent increase of the efficacy with this combination.141 Several studies have recently suggested that the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway is implicated in the pathogenesis and progression of neuroendocrine tumors and MTC. The deregulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway seems to contribute to the tumorigenic activity of RET proto-oncogene mutations. Targeting this pathway through specific inhibitors at simple or multiple sites may represent an attractive potential therapeutic approach for patients with advanced MTCs. It has been recently suggested that the concomitant targeting of RET and mTOR may represent another innovative therapeutic strategy in MTC.142
Conclusion
Vandetanib is emerging as a potentially effective option in the treatment of advanced MTC. Furthermore, vandetanib seems to be a promising therapeutic option in patients with advanced dedifferentiated PTC that is not responsive to traditional therapies or RAI. The most important effect of vandetanib in aggressive MTC is a prolongation of PFS and a stabilization of the disease, while overall survival is not changed. Significant side effects have been observed with vandetanib therapy (as fatigue, hypertension, QTc prolongation, cutaneous rash, mucositis, hand-and-foot syndrome, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and thyroid dysfunction), and severe side effects can require the suspension of the drug. Several studies are currently under way to evaluate the long-term efficacy and tolerability of vandetanib in MTC, and in dedifferentiated PTC, because progression can be slow. The efficacy of vandetanib in patients with MTC in long-term treatments could be overcome by the resistance to the drug that could arise from the activation of alternate mitogenic signals. The effectiveness of the treatment could be ameliorated by the possibility to test the sensitivity of primary TC cells from each subject to different TKIs. In fact, disease-orientated in vitro drug screening permit to predict in vivo effectiveness in 60% of cases, while a negative chemosensitivity test in vitro is associated with a 90% ineffectiveness of the chemotherapy in vivo, avoiding the administration of inactive (potentially toxic) drugs to these patients. Moreover, association studies are evaluating the effect of the association of vandetanib with other antineoplastic agents (such as irinotecan, bortezomib, etc), in patients with various types of cancer. Further research is needed to determine the ideal targeted therapy, based on molecular characterization of the tumor and of the host factors, to obtain the best response in terms of survival and quality of life.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Tuttle R, Ball D, Byrd D. Thyroid Carcinoma. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) Version 2. 2013. Fort Washington, PA: National Comprehensive Cancer Network; 2013. | ||
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. | ||
Zevallos JP, Hartman CM, Kramer JR, Sturgis EM, Chiao EY. Increased thyroid cancer incidence corresponds to increased use of thyroid ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration: a study of the veterans affairs health care system. Cancer. 2015;121(5):741–746. | ||
Antonelli A, Ferri C, Fallahi P, et al. Thyroid cancer in HCV-related chronic hepatitis patients: a case-control study. Thyroid. 2007;17(5):447–451. | ||
Antonelli A, Ferri C, Fallahi P, et al. Clinical and subclinical autoimmune thyroid disorders in systemic sclerosis. Eur J Endocrinol. 2007;156(4):431–437. | ||
Antonelli A, Ferri C, Ferrari SM, et al. New targeted molecular therapies for dedifferentiated thyroid cancer. J Oncol. 2010;2010:921682. | ||
Burman KD. Is poorly differentiated thyroid cancer poorly characterized? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(4):1167–1169. | ||
Patel KN, Shaha AR. Poorly differentiated thyroid cancer. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014;22(2):121–126. | ||
Keating GM, Lyseng-Williamson KA, Frampton JE. Vandetanib: a guide to its use in advanced medullary thyroid cancer. Bio Drugs. 2012;26(6):431–435. | ||
Pusztaszeri MP, Bongiovanni M, Faquin WC. Update on the cytologic and molecular features of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Adv Anat Pathol. 2014;21(1):26–35. | ||
Maia AL, Siqueira DR, Kulcsar MA, Tincani AJ, Mazeto GM, Maciel LM. Diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of medullary thyroid carcinoma: recommendations by the Thyroid Department of the Brazilian Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2014;58(7):667–700. | ||
Gomez K, Varghese J, Jimenez C. Medullary thyroid carcinoma: molecular signaling pathways and emerging therapies. J Thyroid Res. 2011;2011:815826. | ||
Roman S, Lin R, Sosa JA. Prognosis of medullary thyroid carcinoma: demographic, clinical, and pathologic predictors of survival in 1,252 cases. Cancer. 2006;107(9):2134–2142. | ||
Moley JF. Medullary thyroid carcinoma: management of lymph node metastases. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2010;8(5):549–556. | ||
Tuttle RM, Haddad RI, Ball DW, et al. Thyroid carcinoma, version 2. 2014. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2014;12(12):1671–1680. | ||
Alonso-Gordoa T, Díez JJ, Durán M, Grande E. Advances in thyroid cancer treatment: latest evidence and clinical potential. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2015;7(1):22–38. | ||
Nikiforov YE, Nikiforova MN. Molecular genetics and diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;7(10):569–580. | ||
Handkiewicz-Junak D, Czarniecka A, Jarzab B. Molecular prognostic markers in papillary and follicular thyroid cancer: current status and future directions. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;322(1–2):8–28. | ||
Nikiforova MN, Nikiforov YE. Molecular genetics of thyroid cancer: implications for diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2008;8(1):83–95. | ||
Agrawal N, Jiao Y, Sausen M, et al. Exomic sequencing of medullary thyroid cancer reveals dominant and mutually exclusive oncogenic mutations in RET and RAS. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(2):E364–E369. | ||
Fallahi P, Giannini R, Miccoli P, Antonelli A, Basolo F. Molecular diagnostics of fine needle aspiration for the presurgical screening of thyroid nodules. Curr Genomics. 2014;15(3):171–177. | ||
Santoro M, Rosati R, Grieco M, et al. The ret proto-oncogene is consistently expressed in human pheochromocytomas and thyroid medullary carcinomas. Oncogene. 1990;5(10):1595–1598. | ||
Fallahi P, Ferrari SM, Mazzi V, Vita R, Benvenga S, Antonelli A. Personalization of targeted therapy in advanced thyroid cancer. Curr Genomics. 2014;15(3):190–202. | ||
Antonelli A, Fallahi P, Ferrari SM, et al. RET TKI: potential role in thyroid cancers. Curr Oncol Rep. 2012;14(2):97–104. | ||
Nikiforov YE. Thyroid carcinoma: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Mod Pathol. 2008;21(suppl 2):S37–S43. | ||
de Groot JW, Links TP, Plukker JT, Lips CJ, Hofstra RM. RET as a diagnostic and therapeutic target in sporadic and hereditary endocrine tumors. Endocr Rev. 2006;27(5):535–560. | ||
Corvi R, Martinez-Alfaro M, Harach HR, Zini M, Papotti M, Romeo G. Frequent RET rearrangements in thyroid papillary microcarcinoma detected by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization. Lab Invest. 2001;81(12):1639–1645. | ||
Sapio MR, Guerra A, Marotta V, et al. High growth rate of benign thyroid nodules bearing RET/PTC rearrangements. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(6):E916–E919. | ||
Santoro M, Dathan NA, Berlingieri MT, et al. Molecular characterization of RET/PTC3; a novel rearranged version of the RETproto-oncogene in a human thyroid papillary carcinoma. Oncogene. 1994;9(2):509–516. | ||
Romei C, Elisei R. RET/PTC translocations and clinico-pathological features in human papillary thyroid carcinoma. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012;3:54. | ||
Hamatani K, Eguchi H, Ito R, et al. RET/PTC rearrangements preferentially occurred in papillary thyroid cancer among atomic bomb survivors exposed to high radiation dose. Cancer Res. 2008;68(17):7176–7182. | ||
Powell DJ Jr, Russell J, Nibu K, et al. The RET/PTC3 oncogene: metastatic solid-type papillary carcinomas in murine thyroids. Cancer Res. 1998;58(23):5523–5528. | ||
Zarif Yeganeh M, Sheikholeslami S, Dehbashi Behbahani G, Farashi S, Hedayati M. Skewed mutational spectrum of RET proto-oncogene Exon10 in Iranian patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma. Tumour Biol. Epub 2015 Feb 20. | ||
Zbuk KM, Eng C. Cancer phenomics: RET and PTEN as illustrative models. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(1):35–45. | ||
Drosten M, Pützer BM. Mechanisms of disease: cancer targeting and the impact of oncogenic RET for medullary thyroid carcinoma therapy. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2006;3(10):564–574. | ||
Hennige AM, Lammers R, Arlt D, et al. Ret oncogene signal transduction via a IRS-2/PI 3-kinase/PKB and a SHC/Grb-2 dependent pathway: possible implication for transforming activity in NIH3T3 cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000;167(1–2):69–76. | ||
Murakami H, Iwashita T, Asai N, et al. Enhanced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and high phosphorylation state of its downstream signalling molecules mediated by Ret with the MEN 2B mutation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;262(1):68–75. | ||
Elisei R, Cosci B, Romei C, et al. Prognostic significance of somatic RET oncogene mutations in sporadic medullary thyroid cancer: a 10-year follow-up study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(3):682–687. | ||
Rodríguez-Antona C, Pallares J, Montero-Conde C, et al. Overexpression and activation of EGFR and VEGFR2 in medullary thyroid carcinomas is related to metastasis. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010;17(1): 7–16. | ||
Marques AR, Espadinha C, Catarino AL, et al. Expression of PAX8-PPAR gamma 1 rearrangements in both follicular thyroid carcinomas and adenomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87(8):3947–3952. | ||
Omur O, Baran Y. An update on molecular biology of thyroid cancers. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014;90(3):233–252. | ||
Turner HE, Harris AL, Melmed S, Wass JA. Angiogenesis in endocrine tumors. Endocr Rev. 2003;24(5):600–632. | ||
Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature. 2000;407(6081):249–257. | ||
Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev. 2004;25(4):581–611. | ||
Shibuya M, Claesson-Welsh L. Signal transduction by VEGF receptors in regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(5):549–560. | ||
Kerbel RS. Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(19):2039–2049. | ||
Minucci S, Pelicci PG. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(1):38–51. | ||
Capp C, Wajner SM, Siqueira DR, Brasil BA, Meurer L, Maia AL. Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2, in medullary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid. 2010;20(8):863–871. | ||
Bunone G, Vigneri P, Mariani L, et al. Expression of angiogenesis stimulators and inhibitors in human thyroid tumors and correlation with clinical pathological features. Am J Pathol. 1999;155(6): 1967–1976. | ||
Peng XG, Chen ZF, Zhang KJ, et al. VEGF Trapon inhibits tumor growth in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(2):235–240. | ||
Soh EY, Eigelberger MS, Kim KJ, et al. Neutralizing vascular endothelial growth factor activity inhibits thyroid cancer growth in vivo. Surgery. 2000;128(6):1059–1065. | ||
Schoenberger J, Grimm D, Kossmehl P, Infanger M, Kurth E, Eilles C. Effects of PTK787/ZK222584, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, on the growth of a poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma: an animal study. Endocrinology. 2004;145(3):1031–1038. | ||
Younes MN, Yazici YD, Kim S, Jasser SA, El-Naggar AK, Myers JN. Dual epidermal growth factor receptor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibition with NVP-AEE788 for the treatment of aggressive follicular thyroid cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(11 pt 1):3425–3434. | ||
Cao Y. VEGF-targeted cancer therapeutics-paradoxical effects in endocrine organs. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10(9):530–539. | ||
Politti U. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of papillary thyroid cancer. Clin Ther. 2014;165(6):e452–e463. | ||
Croyle M, Akeno N, Knauf JA, et al. RET/PTC-induced cell growth is mediated in part by epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation: evidence for molecular and functional interactions between RET and EGFR. Cancer Res. 2008;68(11):4183–4191. | ||
Fallahi P, Mazzi V, Vita R, et al. New therapies for dedifferentiated papillary thyroid cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(3):6153–6182. | ||
Masago K, Asato R, Fujita S, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2009;124(11):2744–2749. | ||
Knauf JA. Does the epidermal growth factor receptor play a role in the progression of thyroid cancer? Thyroid. 2011;21(11):1171–1174. | ||
Hoffmann S, Burchert A, Wunderlich A, et al. Differential effects of cetuximab and AEE 788 on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGF-R) in thyroid cancer cell lines. Endocrine. 2007;31(2):105–113. | ||
Tang C, Yang L, Wang N, et al. High expression of GPER1, EGFR and CXCR1 is associated with lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(6):3213–3223. | ||
Lote H, Bhosle J, Thway K, Newbold K, O’Brien M. Epidermal growth factor mutation as a diagnostic and therapeutic target in metastatic poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Oncol. 2014;7(2):393–400. | ||
Landriscina M, Pannone G, Piscazzi A, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor 1 expression is upregulated in undifferentiated thyroid carcinomas in humans. Thyroid. 2011;21(11):1227–1234. | ||
Tiedje V, Schmid KW, Weber F, Bockisch A, Führer D. Differentiated thyroid cancer. Internist (Berl). 2015;56(2):153–168. | ||
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2011. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2013. | ||
Baudin E, Schlumberger M. New therapeutic approaches for metastatic thyroid carcinoma. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8(2):148–156. | ||
Antonelli A, Fallahi P, Ferrari SM, et al. Dedifferentiated thyroid cancer: a therapeutic challenge. Biomed Pharmacother. 2008;62(8):559–563. | ||
Schlumberger M, Brose M, Elisei R, et al. Definition and management of radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2(5):356–358. | ||
Kapiteijn E, Schneider TC, Morreau H, Gelderblom H, Nortier JW, Smit JW. New treatment modalities in advanced thyroid cancer. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(1):10–18. | ||
Links TP, Verbeek HH, Hofstra RM, Plukker J. Endocrine tumours: progressive metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma: first- and second-line strategies. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015;172(6):R241–R251. | ||
Wells SA Jr, Santoro M. Update: the status of clinical trials with kinase inhibitors in thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(5):1543–1555. | ||
Haugen BR, Sherman SI. Evolving approaches to patients with advanced differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocr Rev. 2013;34(3):439–455. | ||
Gruber JJ, Colevas AD. Differentiated thyroid cancer: focus on emerging treatments for radioactive iodine-refractory patients. Oncologist. 2015;20(2):113–126. | ||
Thornton K, Kim G, Maher VE, et al. Vandetanib for the treatment of symptomatic or progressive medullary thyroid cancer in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease: U.S. Food and Drug Administration drug approval summary. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(14):3722–3730. | ||
Traynor K. Cabozantinib approved for advanced medullary thyroid cancer. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2013;70(2):88. | ||
Elisei R, Schlumberger MJ, Müller SP, et al. Cabozantinib in progressive medullary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(29):3639–3646. | ||
Hoy SM. Cabozantinib: a review of its use in patients with medullary thyroid cancer. Drugs. 2014;74(12):1435–1444. | ||
Cabanillas ME, Brose MS, Holland J, Ferguson KC, Sherman SI. A phase I study of cabozantinib (XL184) in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2014;24(10):1508–1514. | ||
Jasim S, Ozsari L, Habra MA. Multikinase inhibitors use in differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Biologics. 2014;8:281–291. | ||
Frampton JE. Vandetanib: in medullary thyroid cancer. Drugs. 2012;72(10):1423–1436. | ||
Carlomagno F, Vitagliano D, Guida T, et al. ZD6474, an orally available inhibitor of KDR tyrosine kinase activity, efficiently blocks oncogenic RET kinases. Cancer Res. 2002;62(24):7284–7290. | ||
Carlomagno F, Guida T, Anaganti S, et al. Disease associated mutations at valine 804 in the RET receptor tyrosine kinase confer resistance to selective kinase inhibitors. Oncogene. 2004;23(36):6056–6063. | ||
Johanson V, Ahlman H, Bernhardt P, et al. A transplantable human medullary thyroid carcinoma as a model for RET tyrosine kinase-driven tumorigenesis. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007;14(2):433–444. | ||
Ryan AJ, Wedge SR. ZD6474: a novel inhibitor of VEGFR and EGFR tyrosine kinase activity. Br J Cancer. 2005;92(suppl 1):S6–S13. | ||
Morabito A, Piccirillo MC, Falasconi F, et al. Vandetanib (ZD6474), a dual inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinases: current status and future directions. Oncologist. 2009;14(4):378–390. | ||
Holden SN, Eckhardt SG, Basser R, et al. Clinical evaluation of ZD6474, an orally active inhibitor of VEGF and EGF receptor signaling, in patients with solid, malignant tumors. Ann Oncol. 2005;16(8):1391–1397. | ||
Tamura T, Minami H, Yamada Y, et al. A phase I dose-escalation study of ZD6474 in Japanese patients with solid, malignant tumors. J Thorac Oncol. 2006;1(9):1002–1009. | ||
Wells SA Jr, Gosnell JE, Gagel RF, et al. Vandetanib for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic hereditary medullary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(5):767–772. | ||
Robinson BG, Paz-Ares L, Krebs A, Vasselli J, Haddad R. Vandetanib (100 mg) in patients with locally advanced or metastatic hereditary medullary thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(6):2664–2671. | ||
Fox E, Widemann BC, Chuk MK, et al. Vandetanib in children and adolescents with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B associated medullary thyroid carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(15): 4239–4248. | ||
Leboulleux S, Bastholt L, Krause T, et al. Vandetanib in locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(9):897–905. | ||
Wells SA Jr, Robinson BG, Gagel RF, et al. Vandetanib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer: a randomized, double-blind phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(2): 134–141. | ||
Cooper MR, Yi SY, Alghamdi W, Shaheen DJ, Steinberg M. Vandetanib for the treatment of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Ann Pharmacother. 2014;48(3):387–394. | ||
Massicotte MH, Brassard M, Claude-Desroches M, et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatments in patients with metastatic thyroid carcinomas: a retrospective study of the TUTHYREF network. Eur J Endocrinol. 2014;170(4):575–582. | ||
Chougnet CN, Borget I, Leboulleux S, et al. Vandetanib for the treatment of advanced medullary thyroid cancer outside a clinical trial: results from a French cohort. Thyroid. 2015;25(4):386–391. | ||
AstraZeneca Evaluation of Efficacy, Safety of Vandetanib in Patients With Differentiated Thyroid Cancer (VERIFY). Available from: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01876784. Accessed February 27, 2015. | ||
AstraZeneca to Compare the Effects of Two Doses of Vandetanib in Patients with Advanced Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Available from: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01496313. Accessed February 27, 2015. | ||
US Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Caprelsa (vandetanib) Tablets: US Prescribing Information, March 2014. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DrugSafety/UCM250399.pdf. Accessed February 27, 2015. | ||
European Medicines Agency. Caprelsa (vandetanib): Summary of Product Characteristics. Available from: http://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/medicines/human/medicines/002315/human_med_001529.jsp&mid=WC0b01ac058001d124. Accessed February 27, 2015. | ||
Brassard M, Neraud B, Trabado S, et al. Endocrine effects of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor vandetanib in patients treated for thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(9):2741–2749. | ||
Macdonald JB, Macdonald B, Golitz LE, LoRusso P, Sekulic A. Cutaneous adverse effects of targeted therapies: part I: inhibitors of the cellular membrane. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72(2):203–218. | ||
Grande E, Kreissl MC, Filetti S, et al. Vandetanib in advanced medullary thyroid cancer: review of adverse event management strategies. Adv Ther. 2013;30(11):945–966. | ||
Peuvrel L, Bachmeyer C, Reguiai Z, et al. Semiology of skin toxicity associated with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors. Support Care Cancer. 2012;20(5):909–921. | ||
Rosen AC, Wu S, Damse A, Sherman E, Lacouture ME. Risk of rash in cancer patients treated with vandetanib: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(4):1125–1133. | ||
Giacchero D, Ramacciotti C, Arnault JP, et al. A new spectrum of skin toxic effects associated with the multikinase inhibitor vandetanib. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148(12):1418–1420. | ||
Sibaud V, Robert C. Pigmentary disorders induced by anticancer agents. Part II: targeted therapies. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2013;140(4):266–273. | ||
Ensslin CJ, Rosen AC, Wu S, Lacouture ME. Pruritus in patients treated with targeted cancer therapies: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(5):708–720. | ||
Yoon J, Oh CW, Kim CY. Stevens–Johnson syndrome induced by vandetanib. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23(suppl 3):S343–S345. | ||
Belum VR, Washington C, Pratilas CA, Sibaud V, Boralevi F, Lacouture ME. Dermatologic adverse events in pediatric patients receiving targeted anticancer therapies: a pooled analysis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015;62(5):798–806. | ||
Lacouture ME, Ciccolini K, Kloos RT, Agulnik M. Overview and management of dermatologic events associated with targeted therapies for medullary thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2014;24(9):1329–1340. | ||
Hafermann MJ, Namdar R, Seibold GE, Page RL 2nd. Effect of intravenous ondansetron on QT interval prolongation in patients with cardiovascular disease and additional risk factors for torsades: a prospective, observational study. Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2011;3:53–58. | ||
Eisenberg P, MacKintosh FR, Ritch P, Cornett PA, Macciocchi A. Efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of palonosetron in patients receiving highly emetogenic cisplatin-based chemotherapy: a dose-ranging clinical study. Ann Oncol. 2004;15(2):330–337. | ||
Krajewska J, Jarzab B. Novel therapies for thyroid cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014;15(18):2641–2652. | ||
Scheffel RS, Dora JM, Siqueira DR, Burttet LM, Cerski MR, Maia AL. Toxic cardiomyopathy leading to fatal acute cardiac failure related to vandetanib: a case report with histopathological analysis. Eur J Endocrinol. 2013;168(6):K51–K54. | ||
Shah RR, Morganroth J, Shah DR. Cardiovascular safety of tyrosine kinase inhibitors: with a special focus on cardiac repolarisation (QT interval). Drug Saf. 2013;36(5):295–316. | ||
Qi WX, Shen Z, Lin F, et al. Incidence and risk of hypertension with vandetanib in cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;75(4):919–930. | ||
Alemán JO, Farooki A, Girotra M. Effects of tyrosine kinase inhibition on bone metabolism: untargeted consequences of targeted therapies. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21(3):R247–R259. | ||
Fallahi P, Ferrari SM, Vita R, et al. Thyroid dysfunctions induced by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014;13(6):723–733. | ||
Gild ML, Bullock M, Robinson BG, Clifton-Bligh R. Multikinase inhibitors: a new option for the treatment of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;7(10):617–624. | ||
Liu R, Liu D, Xing M. The Akt inhibitor MK2206 synergizes, but perifosine antagonizes, the BRAF(V600E) inhibitor PLX4032 and the MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 in the inhibition of thyroid cancer cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(2):E173–E182. | ||
Chau NG, Haddad RI. Vandetanib for the treatment of medullary thyroid cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;19(3):1–6. | ||
Carlomagno F, Anaganti S, Guida T, et al. BAY 43-9006 inhibition of oncogenic RET mutants. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98(5):326–334. | ||
Moura MM, Cavaco BM, Pinto AE, Leite V. High prevalence of RAS mutations in RET-negative sporadic medullary thyroid carcinomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:E863–E868. | ||
Morgillo F, Martinelli E, Troiani T, Orditura M, De Vita F, Ciardiello F. Antitumor activity of sorafenib in human cancer cell lines with acquired resistance to EGFR and VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28841. | ||
Schroyens W, Tueni E, Dodion P, Bodecker R, Stoessel F, Klastersky J. Validation of clinical predictive value of in vitro colorimetric chemosensitivity assay in head and neck cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1990;26(7):834–838. | ||
Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Fallahi P, et al. Thiazolidinediones and antiblastics in primary human anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2009;70(6):946–953. | ||
Antonelli A, Bocci G, La Motta C, et al. CLM94, a novel cyclic amide with anti-VEGFR-2 and antiangiogenic properties, is active against primary anaplastic thyroid cancer in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(4):E528–E536. | ||
Antonelli A. Molecular profiling and ways towards personalized medicine in advanced differentiated thyroid cancer. Curr Genomics. 2014;15(3):161. | ||
Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Fallahi P, et al. Evaluation of the sensitivity to chemotherapeutics or thiazolidinediones of primary anaplastic thyroid cancer cells obtained by fine-needle aspiration. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008;159(3):283–291. | ||
Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Fallahi P, et al. Primary cell cultures from anaplastic thyroid cancer obtained by fine-needle aspiration used for chemosensitivity tests. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2008;69(1):148–152. | ||
Ferrari SM, Fallahi P, La Motta C, et al. Antineoplastic activity of the multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitors CLM3 and CLM94 in medullary thyroid cancer in vitro. Surgery. 2014;156(5):1167–1176. | ||
Antonelli A, Bocci G, La Motta C, et al. CLM29, a multi-target pyrazolopyrimidine derivative, has anti-neoplastic activity in medullary thyroid cancer in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014;393(1–2):56–64. | ||
Antonelli A, Bocci G, Fallahi P, et al. CLM3, a multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor with antiangiogenic properties, is active against primary anaplastic thyroid cancer in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(4):E572–E581. | ||
Antonelli A, Bocci G, La Motta C, et al. Novel pyrazolopyrimidine derivatives as tyrosine kinase inhibitors with antitumoral activity in vitro and in vivo in papillary dedifferentiated thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(2):E288–E296. | ||
Uchida N, Suda T, Inoue T, Fujiwara Y, Ishiguro K. Needle track dissemination of follicular thyroid carcinoma following fine-needle aspiration biopsy: report of a case. Surg Today. 2007;37(1):34–37. | ||
Cascone T, Morelli MP, Morgillo F, et al. Synergistic anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic activity of combined therapy with bortezomib, a proteasome inhibitor, with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) drugs in human cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 2008;217(1):290. | ||
AstraZeneca A Targeted Phase I/II Trial of ZD6474 (Vandetanib; ZACTIMA) Plus the Proteasome Inhibitor, Bortezomib (Velcade), in Adults with Solid Tumors With a Focus on Hereditary or Sporadic, Locally Advanced or Metastatic Medullary Thyroid Cancer (MTC). Available from: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00923247. Accessed February 27, 2015. | ||
Troiani T, Lockerbie O, Morrow M, Ciardiello F, Eckhardt SG. Sequence-dependent inhibition of human colon cancer cell growth and of prosurvival pathways by oxaliplatin in combination with ZD6474 (Zactima), an inhibitor of VEGFR and EGFR tyrosine kinases. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5(7):1883–1894. | ||
Troiani T, Serkova NJ, Gustafson DL, et al. Investigation of two dosing schedules of vandetanib (ZD6474), an inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling, in combination with irinotecan in a human colon cancer xenograft model. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(21):6450–6458. | ||
Wachsberger P, Burd R, Ryan A, Daskalakis C, Dicker AP. Combination of vandetanib, radiotherapy, and irinotecan in the LoVo human colorectal cancer xenograft model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;75(3):854–861. | ||
Meyerhardt JA, Ancukiewicz M, Abrams TA, et al. Phase I study of cetuximab, irinotecan, and vandetanib (ZD6474) as therapy for patients with previously treated metastastic colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38231. | ||
Manfredi GI, Dicitore A, Gaudenzi G, Caraglia M, Persani L, Vitale G. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in medullary thyroid cancer: a promising molecular target for cancer therapy. Endocrine. 2015;48(2):363–370. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.