Back to Journals » OncoTargets and Therapy » Volume 13
RNA-Binding Motif Protein 38 as a Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer
Authors She X, Lin Y, Liang R , Liu Z, Gao X, Ye J
Received 31 August 2020
Accepted for publication 27 November 2020
Published 24 December 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 13225—13236
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S278755
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Xiaomin She, Yan Lin, Rong Liang, Ziyu Liu, Xing Gao, Jiazhou Ye
Medical Oncology, Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, Nanning, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Jiazhou Ye Tel +86 7715301253
Email [email protected]
Abstract: RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) act as a key factor in gene regulation by governing RNA metabolism. They contribute to the expression and functions of most RNAs by binding to them and forming complexes. RNA-binding motif protein 38 (RBM38), a member of the RBP family, alters the stability and translation of targeted mRNAs to affect various biological processes, such as cell proliferation, cell cycle arrest, and myogenic differentiation. RBM38 contains a highly conserved RNA recognition motif (RRM) consisting of two subunits, RNP1 and RNP2, which specifically bind to RNAs. Recent studies have revealed that RBM38 regulates the mRNA stability of several tumor-related genes, such as p53, mdm2, p63, p73, p21, and c-Myc, by binding to their 3′ untranslated regions (3′ UTRs); thus, RBM38 modulates targeted gene expression and affects the biological processes of tumors. In addition, abnormal RBM38 expression in some malignant tumors and its correlation with prognosis have been documented in many studies, indicating its value for potential clinical applications. In this review, we present an overview of RBM38, specifically highlighting its relationship with tumor manifestation and development. A brief overview of the potential use of RBM38 in cancer therapy is also included to provide ideas for further research on RBM38.
Keywords: RBM38, malignant tumors, p53 family, posttranscriptional regulation
Introduction
Regulation of gene expression, which is the molecular basis of cell differentiation, morphogenesis, and ontogeny, occurs at the levels of gene expression, namely, transcription, posttranscriptional processing, translation, and posttranslational modifications.1,2 Recently, posttranscriptional regulation, which includes RNA splicing, transport, stability, translation and so on, has become a hot topic in oncology.3,4
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) play a vital role in posttranscriptional events. As an unstable and easily degraded biological macromolecule, mRNAs bind to a specific RBP and form a complex to maintain their stability in cells.5 RBPs are described as “RNA clothes”. By binding to and covering different RNA regions, RBPs control the localization, stability, translation and degradation of RNAs.6 The attachment of RBPs to RNAs contributes to RNA metabolism in different stages and regulates their subsequent functions. Posttranscriptional modifications and interactions involving RBPs are a major RNA regulatory mechanism that is crucial for intracellular homeostasis.7 An increasing number of studies indicate that RBPs are dysregulated in diverse tumors and affect the expression and function of tumor-related proteins by binding to different receptors, thus engaging in different biological roles in tumor tissues.6–8 For example, human antigen R (HuR) is a tumor-promoting gene in breast cancer, cervical cancer and colon cancer that promotes tumor angiogenesis, avoids immune surveillance, evades apoptosis and so on.9,10 HnRNPs are another RNA-binding protein family that is regarded to have a complicated relationship with tumors such as breast, liver, and lung cancer. They participate in tumor promotion or inhibition by deregulating cellular energetics, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), genomic imbalance and so on.7,11,12 In conclusion, the RBP family regulates the metabolism of transcription by combining with RNA domains, thus affecting tumorigenesis, invasion and metastasis.
RNA-binding motif protein 38 (RBM38, also known as RNPC1), a member of the RBP family, was first discovered in a study of Xenopus by Fetka et al in 2000. It was found to be expressed in bone marrow, lymph nodes, blood, brain, breast, colorectal, lung and other organs in humans.13 Studies have shown that RBM38 contains the classical RRM domain and regulates numerous downstream targets in different ways to play a key role in posttranscriptional regulation. For example, RBM38 positively or negatively regulates the mRNA stability and translation of targeted genes to intensively control of the cell status.14,15 RBM38 is also intricately related to p53, p63, and p73 to form several feedback loops.16–18 In recent years, posttranscriptional regulation has been increasingly regarded as a pivotal regulatory step in tumorigenesis and development, in which RBPs play an essential role. As a member of the RBP family, RBM38 has attracted our attention owing to its abnormal performance in some pathological conditions. It has been reported that abnormal RBM38 expression is associated with high malignancy and poor prognosis in several malignant tumors, and its target genes play an important role in regulating processes that contribute to the malignant phenotype of tumors, such as cell growth, invasion and metastasis.14,16,19–24 These data suggest that targeting RBM38 and related pathways is a potential strategy for molecular-based cancer therapy. Therefore, we review the molecular mechanism of RBM38 in tumors with the aim of providing a theoretical basis for further research and the clinical application of RBM38.
The History of RBM38
In the study of Fetka et al in 2000, a novel gene SEB-4 with a RRM domain was found in Xenopus firstly, which is the homologous gene of RBM38 in human.25 In the later Human Genome Project (2001), Deloukas et al sequenced human chromosome 20 and identified RBM38 in human genome for the first time.26 Soon after, Krackhardt et al27 and Scanlan et al28 found that there was an obvious binding reaction between RBM38 antigen and the serum from patients with leukemia and colon cancer. In the following study of Chen et al, RBM38 was found to be induced by p53 family and acted as a potential common target of the p53 family,29 which was later verified by Shu et al.30 Due to its regulatory role in the stability of various mRNAs and the correlation between p53 family and tumors, RBM38 was speculated to be a tumor-related gene, which was confirmed in subsequent studies.
The Structure of RBM38
The RBM38 gene is located on chromosome 20q13.31 and contains 6 exons. It encodes two alternatively spliced isoforms, as shown in Figure 1: RBM38a (239 amino acids) and RBM38b (121 amino acids), both of which contain an intact RRM. Both forms are expressed in the nucleus and cytoplasm, and the N-terminal sequences are identical. The RBM38 protein contains a highly conserved RRM (amino acids 35–107)31 and four introns (amino acids 79, 120, 138 and 239). In the human RBM38 gene, 34 functional single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have been identified, 14 of which cause missense mutations, 12 of which cause nonsense mutations, and 8 of which cause exon splicing enhanced mutations.13
 |
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of RBM38 protein. RBM38 contains an RRM domain comprising two submotifs, RNP1 and RNP2, which are capable of binding to a single RNA strand. |
Physiological Functions of RBM38
Current studies have shown that RBM38 is widely involved in biological processes, including proliferation, cell cycle arrest, myogenic differentiation, invasion, migration and senescence.16,17,21 RBM38 mainly participates in the posttranscriptional regulation of genes, namely, RNA processing and metabolism. RBM38 can positively or negatively affect the stability of the mRNA of a target gene by binding to its 3′UTR. In addition, various studies have also found abnormal RBM38 expression in different tumors, which suggests that RBM38 plays an important role in human tumors and is a target for the treatment of malignant tumors.
The Regulatory Mechanism of RBM38
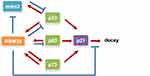
As research on RBM38 continues to deepen, an increasing number of molecular mechanisms have been explored and confirmed. As shown in Figure 2, RBM38 participates in RNA metabolism by regulating its transport, stability and competitive binding to other macromolecules. RBM38 binds to AU-rich elements (AREs) of the 3′UTR of the following transcribed genes: p21, p53, p63, HuR, GDF15, c-Myc, p73 and mdm2. However, RBM38 has specific regulatory mechanisms and produces different results for each gene. RBM38 binds to and stabilizes the RNA of p21, p73, and HuR, thus increasing their protein expression,30,32 while its interaction with macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1) mRNA inhibits cell growth.33 RBM38 can also decrease the protein levels of p53 and p60 by reducing translation levels,16 and it can reduce the expression levels of p63 and double minute-2 (mdm2) by destabilizing their mRNA.15,17,34
As shown in Table 1, the mechanisms of RBM38 on different target genes are extremely complicated, and each pathway related to RBM38 may be an effective target for tumor gene therapy. Therefore, the differential regulatory mechanisms of RBM38 targets need to be further explored. Very likely, the specific biological functions will provide a theoretical basis for targeting RBM38 in clinical practice.
 |
Table 1 The Target Genes of RBM38 |
Feedback Loops of RBM38-P53 Family
The p53 family, which includes p73, p63, p53CP, p53 and other members, is closely related to the occurrence and development of a considerable number of tumors. As shown in Figure 3, RBM38 is involved in the posttranscriptional regulation of the p53 family; RBM38 inhibits the translation of p53 and destabilizes the p63 mRNA yet stabilizes the p73 transcript.
RBM38-P53 Feedback Loop
Under normal conditions in humans, p53, as a regulator of cell proliferation, maintains genomic stability by inducing cell cycle arrest, promoting apoptosis and regulating cell senescence, which avoids the accumulation of damaged DNA.36 However, p53 inactivation has been reported in more than 50% of human cancers, and this is widely believed to be closely related to the development of tumors.37,38
RBM38 plays an important regulatory role in the negative feedback loop of p53-mdm2. The study by Xu et al15 in HCT116 and SW480 cells found that RBM38 independently inhibited mdm2 expression by decreasing its mRNA stability: overexpression of RBM38 shortened the half-life of the mdm2 transcript in a p53-independent manner. In addition, they also reported that RBM38 can destabilize mdm2 transcripts by binding to multiple AU-/U-rich elements in its 3′UTR, resulting in decreased levels of mdm2 transcripts and subsequently reduced protein expression. Similarly, Ye et al16 confirmed that RBM38 destabilizes mdm2 transcripts by binding to multiple AU-/U-rich elements in the mdm2 3ʹUTR in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). At the same time, they also found that upregulation of RBM38 not only inhibits mdm2 but also restores wild-type p53 expression, thereby inducing apoptosis and senescence of cancer cells and inhibiting cell proliferation, colony growth, migration and invasion.
RBM38 also suppresses p53 translation via the PEP8 pathway. PEP8 is a peptide derived from RBM38; it contains 8 amino acids and is part of the binding interface between RBM38 and the translation initiation factor eIF4E.When p53 is activated, RBM38 binds to eIF4E on p53 mRNA, thereby inhibiting p53 translation.39 Lucchesi et al39 found that when serine 195 (Ser195) of RBM38 was phosphorylated, Ser6 in PEP8 can form a hydrogen bond with Asp202 in eIF4E, thus inhibiting the interaction between RBM38 and eIF4E; this interaction prevents the RMB38-mediated inhibition of p53 mRNA translation, resulting in increased expression of p53.
Moreover, p53 can regulate the production of miRNA, and RBM38 is essential for this regulation. First, p53 induces the expression of RBM38.40 There are miRNA-binding sites on the 3′UTR of the p53 target gene transcript. p53-induced protein expression of RBM38 can relieve the repression of miRNA by blocking this binding site, thereby influencing the expression of p53 target genes. Moreover, RBM38 is selective in terms of which miRNAs it restricts, and this selective antagonism of miRNAs provides favorable conditions for the differential regulation of gene expression and of the cell cycle, thereby enhancing p53 function. In addition, this target selectivity is related to the uracil-rich region surrounding the miRNA target site. For example, RBM38 can effectively counteract the repression of miR-17 on the p21-3′UTR, miR-125b on the RBM38-3′UTR, and miR-153 on the DDIT4-3′UTR. However, the SIRT1-3′UTR, which is a downstream target of miR-34a, is not significantly affected by RBM38.41
RBM38-P63 Feedback Loop
p63 is a tumor suppressor gene in the p53 family that has high homology with p53 in its DNA binding, activation and tetramerization domains.42 It not only participates in the induction of cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, differentiation and other processes but also plays a key role in skin development, aging, metabolism and tumorigenesis.43 p63 is expressed as two isoforms via the P1 and P2 promoters: TAp63 and ΔNp63, respectively. Initiation at both promoters produces multiple isoforms via alternative splicing at the C-terminus. The TAp63 isoform is transcribed from the upstream promoter, whereas the ΔNp63 isoform is transcribed from an alternate promoter in intron.44,45
Mice deficient in the ∆Np63 isoforms die due to developmental defects shortly after birth. Mice lacking TAp63 can survive after birth experience accelerated aging and increased susceptibility to spontaneous tumors. They are also present defective lipid metabolism and glucose tolerance and are prone to liver steatosis.46,47
Related experiments have found that RBM38 affect the activity of p63 by regulating the stability of its mRNA. Zhang et al34 conducted experiments showing that RBM38 overexpression reduced transcription and protein expression of p63, whereas knockdown of RBM38 increased p63 expression by changing the half-life of the p63 transcript. In addition, they also found that RBM38 binds to AU-/U-rich elements in the p63 3′UTR in vitro and in vivo, and the RRM domain in RBM38 is required for binding to the p63 transcript and regulating its stability.
Recently, Jiang et al17 established RBM38- and TAp63-deficient mouse models and monitored their lifespans. Mice deficient in either RBM38 or TAp63 alone died mostly from spontaneous tumors, and they had shorter lifespans and more aging-related phenotypes than their wild-type counterparts. Furthermore, the levels of inflammatory cytokines were also increased in the models. However, in mice with simultaneous knockout of RBM38 and TAp63, the loss of RBM38 increased TAp63 expression, thereby delaying premature aging, inhibiting tumorigenesis and hepatic steatosis, reducing aging-related phenotypes and the levels of inflammatory cytokines (IL17D and Tnfsf15) in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and the liver, and prolonging the lifespan of mice.
RBM38-P73 Feedback Loop
p73 shares homology with the p53 gene, and the structure and function of the two proteins are not much different. They participate in the activation of target genes, regulation of the cell cycle, and induction of apoptosis.48 Similar to the p63 gene, the p73 gene also has two isoforms that exist due to differences in promoters: TAp73 and ∆Np73. TAp73 is expressed via the P1 promoter located upstream of the first exon, whereas ∆Np73 is expressed via the P2 promoter in intron 3.32 TAp73 contains an N-terminal activation domain that is homologous to the N-terminal activation domain in p53, but ∆Np73 lacks this activation domain yet carries a unique activation domain in its N-terminus. Therefore, TAp73 has activity similar to that of p53, but ∆Np73 has activity in opposition of that of TAp73.40
A number of studies have shown that p73 gene expression correlates with the formation, occurrence and prognosis of various tumor diseases, such as colorectal, gastric, breast and cervical cancer.49,50 It has also been found that mice deficient in TAp73 are prone to developing spontaneous tumors, while mice deficient in Np73 are susceptible to neurological defects.51,52
Similar to p53 and p63, Yan et al32 found that RBM38 affects p73 expression by regulating the stability of p73 mRNA in SW480 and HCT116 cells. Knocking down or knocking out RBM38 decreased p73 expression, while overexpression of RBM38 elicited the opposite effect. Moreover, qRT-PCR analysis indicated that RBM38a increased p73 expression by prolonging the half-life of p73 mRNA. The integrity of the RNA-binding domain and the 118 C-terminal residues in RBM38 are essential for the regulation of p73 mRNA stability. Studies have also found that knocking down TAp73 and p21 either alone or in combination can block the ability of RBM38 to inhibit growth and induce senescence. p73 is also a member of the p53 family of RBM38-target genes. Yan and colleagues proposed a new feedback loop based on the mutual regulation between p73 and RBM38: under certain stress signals, p73 was induced to transcribe and then activate the expression of target genes, such as p21 and RBM38. In turn, RBM38 binds to and stabilizes the p73 and p21 transcripts. This positive feedback loop is expected to be an effective target for overcoming tumor defects in the p53 pathway.
RBM38 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest by Stabilizing the P21 Transcript
p21 is a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that is transcriptionally regulated by the p53 family to induce cell cycle arrest. It plays a key role in regulating the transition of cells from G1 to S phase and from G2 to M phase.53
In the study by Shu et al30 of RKO and MCF7 cells, RBM38 was required to maintain the stability of the p53-induced expression of p21 transcript. After DNA damage, p53 first mediates the elevation of RBM38 expression, which can then induce high levels of p21 expression. This process is necessary for p21-mediated cell cycle arrest. Conversely, the lack of RBM38 expression inhibits p21 accumulation caused by DNA damage. RBM38 is also able to induce cell cycle arrest in G1 phase by inhibiting miRNA activity and stabilizing the p21 transcript. Both RBM38a and RBM38b can bind directly to the 3′UTR of p21 mRNA, but only RBM38a is capable of stabilizing the basal and stress-induced expression of p21 transcript. RBM38a both promotes the transport of p21 transcripts from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and protects transcripts from cytosolic RNase degradation. RBM38b is thought to help with this process. In addition, the unique 108 residues in RBM38a may interact with other proteins to regulate the stability of p21 mRNA.
RBM38 and c-Myc Mutually Antagonize Each Other in Breast Cancer
c-Myc is an oncogenic transcription factor involved in many cellular processes, such as cell growth, cell cycle control, metabolism, adhesion, differentiation and apoptosis, and it plays an important role in the development of cancer.54
Studies have shown that RBM38 and c-Myc form a mutually antagonistic RBM38-c-Myc feedback loop in breast cancer. RBM38 contributes to the direct inhibition of c-Myc expression, and inhibition of c-Myc in turn inhibits RBM38 expression. RBM38 inhibits the protein expression of c-Myc by directly targeting AREs in the 3′UTR of c-Myc mRNA, thereby disrupting the stability of the c-Myc transcript. Conversely, c-Myc regulates RBM38 expression in breast cancer cells by directly binding to the E-box in the promoter region of the RBM38 gene.14
RBM38, a Target of E2F1, Restricts E2F1-Induced Proliferation
In higher eukaryotes, the E2F family of transcription factors plays a pivotal role in regulating cell proliferation. These factors modulate cell cycle progression by modulating the expression of S phase-associated genes, which have the ability to induce exit from G1 phase and entry into S phase.46 The dysregulation of E2F activity caused by pathway mutations is common in human tumors and leads to uncontrolled cell proliferation, which is one of the hallmarks of cancer.55,56
Feldstein et al57 studied the complex regulatory relationship between RBM38 and E2F1. RBM38 is a direct transcriptional target of E2F1, which regulates RBM38 expression by binding to its promoter. However, RBM38 is an E2F1-regulated transcriptional target that limits E2F1-induced proliferation. RBM38 restricts the activity of E2F1 by arresting cell cycle progression at the G1-S transition. These results showed that there is a negative feedback loop between E2F1 and RBM38 that modulates E2F1 activity: E2F1 directly activates RBM38 expression, which in turn limits the proliferative function of E2F1. This feedback loop was supported in subsequent experiments in which inhibiting RBM38 expression increased E2F1-mediated cell cycle progression, whereas activating E2F1 resulted in an increase in RBM38 expression. In addition, an analysis of patients with ovarian cancer showed that this negative feedback cycle can restrict tumor aggressiveness and promote the survival of patients.
RBM38 Inhibits Cell Growth by Enhancing MIC-1 Stability
MIC-1 is a secreted cytokine directly regulated by p53, and it plays an important role in cell proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis and angiogenesis via autocrine and paracrine processes.58 MIC-1 exhibits two opposing effects in tumors: tumor suppression and tumor promotion. In the early stages of tumor development, MIC-1 inhibits tumor growth, whereas in more advanced disease stages, MIC-1 tends to promote tumor development.59
Studies by Yin et al33 showed that RBM38 is a positive regulator of MIC-1 posttranscriptional expression. They found that RBM38 overexpression increased MIC-1 transcript and protein levels, while knockdown or knockout of RBM38 decreased MIC-1 transcript and protein expression in RKO and MCF7 cells. In addition, overexpression and knockdown of RBM38 had no effect on MIC-1 pre-mRNA levels, suggesting that RBM38 regulates MIC-1 at the posttranscriptional level. In addition, they discovered that RBM38 enhances the stability of MIC-1 mRNA and inhibits cell proliferation by binding to the ARE region within the 3′UTR of MIC-1 mRNA. However, knockdown of MIC-1 reduced RBM38-induced inhibition of cell proliferation, and this process was at least partially mediated by p21.
The Role of RBM38 in Malignant Tumors
RBM38 participates in the expression of genes involved in biological processes in tumors through the above molecular mechanisms and thus participates extensively in the development and metastasis of various tumors by playing a role in tumor progression. Moreover, RBM38 expression is distinct in different types of cancer, suggesting that the role of RBM38 in tumors is multidimensional. As shown in Table 2, exhaustive research on RBM38 in recent years has revealed an important link between aberrant RBM38 expression and the development of cancer, resulting in clarification of cancer formation mechanisms and providing a theoretical basis for treatment, suggesting that RBM38 contributes to the assessment of disease development. Thus, RBM38 has potential value in clinical applications as a therapeutic target and provides a new developmental direction for cancer research.
 |
Table 2 RBM38 and Tumors |
RBM38 and Breast Cancer
Prior to the discovery of RBM38, Ginestier et al60 observed amplification of 20q13 in a large number of breast cancer tissues. Subsequent studies have confirmed that the RBM38 gene is located at 20q13.31.26
Recently, many studies have reported that RBM38 acts as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer. Xue et al19 found that RBM38 expression is silenced in breast cancer and is associated with poor prognosis. Their study also showed that knockdown of RBM38 promoted the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells in vivo and in vitro. When RBM38 is overexpressed, it inhibits the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by inducing cell cycle arrest and inhibiting mutant p53-induced EMT. The analysis of clinical breast cancer tissue samples showed that low mRNA expression of RBM38 was associated with a late clinical stage and high p53 mutation level, while low protein expression of RBM38 corresponded to a large number of lymph node metastases, a high level of p53 mutation and negative progesterone receptor (PR) expression.
It is currently believed that RBM38 exerts anticancer effects through the regulation of its downstream targets in breast cancer. Zhou et al22 conducted in vivo and in vitro experiments showing that RBM38 can stabilize the expression of the estrogen receptor (ER) and PR, thereby regulating the proliferation of breast cancer. There was a significant correlation between RBM38 and ERα expression in breast cancer tissues, and there existed a regulatory feedback loop between them: ectopic RBM38 expression increased ERα transcription and expression in breast cancer cells, while ERα overexpression reduced RBM38 transcription and protein levels. This feedback loop suggests that RBM38 plays an important role in the regulation of ERα in ER-positive breast cancer.
In addition, studies by Nicloas et al41 suggested that RBM38 expression on adjacent CpG islands is silenced by DNA methylation, which subsequently inhibits the ability of p53 to activate its target genes and promotes tumor development in wild-type p53 breast cancer.
PTEN is a tumor suppressor located on chromosome 10 and is a key regulator of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway. Its expression is closely related to the phenotype, prognosis and drug selection in breast cancer.61,62 Zhou et al22 suggested that PTEN expression was positively correlated with RBM38 expression in breast cancer tissues. RBM38 stabilizes PTEN transcripts by binding to multiple AREs in their 3′UTRs. The increased expression of PTEN, in turn, impairs RBM38-mediated growth inhibition, suggesting that RBM38 may exert tumor suppressive effects by upregulating PTEN expression.
The above studies show that RBM38 is a functional tumor suppressor in breast tumorigenesis and metastasis and may be a potential target for breast cancer treatment or prognosis.
RBM38 and Liver Cancer
In recent years, studies have also shown that RBM38 plays a tumor suppressor role in liver cancer development.
The mdm2-p53 pathway is frequently dysregulated in HCC. A number of studies have reported that mutations in the mdm2 and p53 genes usually lead to mdm2 stabilization and p53 degradation, thereby destroying the mdm2-p53 balance and promoting HCC.15,63 Ye et al16 found that RBM38 was a core molecule stabilizing p53-mdm2 loop function; in HCC samples, RBM38 was inactivated, mdm2 expression was increased, and wild-type p53 expression was decreased, all of which eventually disrupted the balance of the p53-mdm2 feedback loop. Conversely, increased RBM38 expression inhibits mdm2 expression and restores wild-type p53 expression in hepatoma cells. RBM38 also directly suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of liver cancer cells in vitro. In vivo experiments showed that RBM38 exerts a certain inhibitory effect on the tumorigenicity of liver cancer in nude mice. The above in vitro and in vivo studies show that upregulation of RBM38 expression may alter the biological activities and progression of liver cancer in part by inhibiting mdm2 expression and rescuing wild-type p53 levels.
In a study of liver cancer by Ding et al64 the expression level of RBM38 in liver cancer tissues was significantly lower than that in paired adjacent tissues and was negatively correlated with serum alpha fetoprotein (AFP) levels, further confirming that RBM38 plays a tumor suppressive role in liver cancer. The authors also thought that RBM38 was a target of inhibition by HORAIR. HORAIR is a long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) that can promote the migration and invasion of liver cancer by inhibiting RBM38. This indicates that RBM38 exerts a tumor-suppressive effect through various mechanisms in the progression of liver cancer.
RBM38 and Lung Cancer
Shang et al65 found that the mRNA and protein expression levels of RBM38 and p53 in lung adenocarcinoma tissues were higher than those in adjacent noncancerous tissues, and the expression of both genes showed a correlation with TNM staging. With increasing RBM38 protein expression, p53 protein expression decreases. It is speculated that RBM38 promotes the development of lung cancer by inhibiting the translation of p53 mRNA, suggesting that RBM38 has potential application value as a therapeutic target for lung adenocarcinoma.
RBM38 and Gastric Cancer
In a study of gastric cancer, Wang et al23 found that the proportion of gastric cancer tissues with high RBM38 protein expression was significantly lower than that of adjacent tissues, and the protein expression of RBM38 was related to tumor size, depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis and TNM stage. In addition, low RBM38 expression was associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. The results of this experiment suggest that RBM38, as a tumor suppressor gene, plays a vital role in the development of gastric cancer and is a potential marker in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer.
RBM38 and Hematological Malignancies
In recent studies, abnormal RBM38 expression was observed in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), lymphoma and other malignant hematological diseases, suggesting that RBM38 likely plays a critical regulatory role in the pathogenesis of these diseases. AML is a myelopoietic stem cell disease that causes differentiation disorders at different stages of myelopoiesis. Wampfler et al20 found that RBM38 mRNA levels were significantly lower in AML blasts than in healthy mature neutrophils, suggesting that RBM38 has a potential role in the pathogenesis of AML. However, knockdown of RBM38 attenuated NB4 neutrophil differentiation, suggesting that RBM38 is required for neutrophil differentiation. At the same time, knockdown of RBM38 also decreased the mRNA expression of p21CIP1, a cell cycle inhibitor that is stabilized by RBM38 and is capable of inducing normal differentiation of APL cells.66 RBM38 may antagonize the activity of AML tumor cells by protecting p21CIP1 and also act as an essential factor in the normal differentiation of neutrophils.20
RBM38 is presumed to play a role in the progression of lymphoma. Canine lymphoma is clinically and morphologically similar to human lymphoma and has been used as a clinical research model for studying cancer treatment and prevention. Zhang et al24 found that RBM38 was frequently overexpressed in canine lymphomas and was associated with a decrease in p53 expression. Their study demonstrated that the RBM38-p53 regulatory loop is conserved in dogs and that RBM38 may play a procancer role in the development of lymphoma by contributing to p53 inactivation. Overall, RBM38 may play a central role in hematological malignancies and has potential as a target of future treatment.
RBM38 and Kidney Cancer
Similarly, RBM38 has also been found to act as a suppressor of kidney cancer. Huang et al21 observed that RBM38 is decreased in renal cell carcinoma tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of RBM38 can reduce the growth rate of renal cell carcinoma and the number of colonies formed by renal cell carcinoma cell lines, whereas knockout of RBM38 can elicit opposing effects. In vivo experiments showed that the incidence of tumors in the RBM38-positive group was lower than that in the control group, and the anticancer effect was induced by RBM38 binding to p21 in renal cell carcinoma cells to induce cell cycle arrest at G1 phase.
In addition, the same research group found that RBM38 inhibited EMT by upregulating E-cadherin expression and downregulating β-catenin expression, thereby suppressing the migration and invasion of renal cancer cells. Moreover, patients with low RBM38 expression had a shorter survival time than those with higher expression, suggesting that RBM38 can be used as an independent prognostic indicator for the survival of patients with renal cancer.21
Conclusions
In summary, RBM38 is an RBP that plays an important role in the posttranscriptional translation of multiple RNAs. At present, RBM38 is known to bind to the ARE on the 3ʹUTR of various mRNAs, thereby regulating the expression of related genes and thus providing an important influence on the occurrence and development of malignant tumors. Therefore, RBM38 is expected to become a potential target for cancer diagnosis and treatment in the clinic as well as a specific biomarker for estimating prognosis. In recent years, some progress has been made in RBM38 research; however, due to the complexity of the RBM38 regulatory mechanisms and tumor development, there are still many issues that require attention. It is believed that the in-depth study of RBM38 in the future will further clarify its molecular mechanisms, which could be applied to the development and clinical use of targeted drugs.
Abbreviations
RBM38, RNA-binding motif protein 38; 3′UTR, 3′ untranslated region; RBPs, RNA-binding proteins; RRM, RNA recognition motif; SNPs, single nucleotide polymorphisms; AREs, AU-rich elements; HuR, human antigen R; GDF15, growth and differentiation factor 15; MIC-1, macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1; mdm2, double minute-2; eif4E, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; miRNA, microRNA; SIRT1, Silent information regulator factor 2-related enzyme 1; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR; E2F, early region 2 factor; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; ER, estrogen receptor; PR, progesterone receptor; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; PTEN, Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; AFP, alpha-fetoprotein; lncRNA, long noncoding RNA; HOTAIR, lncRNA HOX transcript antisense RNA; AML, acute myeloid leukemia, APL, acute promyelocytic leukemia, CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Funding
The sudy was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO.81803007, 82060427 and 81660498), Guangxi Key Research and Development Plan (NO.GUIKEAB19245002), Guangxi Scholarship Fund of Guangxi Education Department, General Program of GuangXi Natural Science Foundation (NO. 2020GXNSFAA259080), Youth Talent Fund Project of GuangXi Natural Science Foundation (NO. 2018GXNSFBA281030, 2018GXNSFBA281091), Guangxi Medical and Health Appropriate Technology Development and Application Project (NO. S2017101, S2018062), Guangxi Medical University Training Program for Distinguished Young Scholars, Science and Technology Plan Project of Qingxiu District, Nanning (NO. 2020037, 2020038).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest for this work and declare that the research presented here was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. Leavitt JM, Alper HS. Advances and current limitations in transcript-level control of gene expression. Curr Opinion Biotech. 2015;34:98–104. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2014.12.015
2. Lackner DH, Bähler J. Translational control of gene expression from transcripts to transcriptomes. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2008;271:199–251.
3. Sanchez-Diaz P, Penalva LO. Post-transcription meets post-genomic: the saga of RNA binding proteins in a new era. RNA Biol. 2006;3(3):101–109.
4. Orphanides G, Reinberg D. A unified theory of gene expression. Cell. 2002;108(4):439–451.
5. Hentze MW, Castello A, Schwarzl T, Preiss T. A brave new world of RNA-binding proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(5):327–341.
6. Lunde BM, Moore C, Varani G. RNA-binding proteins: modular design for efficient function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(6):479–490.
7. Pereira B, Billaud M, Almeida R. RNA-Binding Proteins in Cancer: old Players and New Actors. Trends Cancer. 2017;3(7):506–528.
8. Gerstberger S, Hafner M, Tuschl T. A census of human RNA-binding proteins. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(12):829–845.
9. Wu M, Tong C, Yan W, To K. The RNA Binding Protein HuR: A Promising Drug Target for Anticancer Therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2019;19(5):382–399.
10. Grammatikakis I, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M. Posttranslational control of HuR function. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017;8(1):1. doi:10.1002/wrna.1372
11. David CJ, Chen M, Assanah M, Canoll P, Manley JL. HnRNP proteins controlled by c-Myc deregulate pyruvate kinase mRNA splicing in cancer. Nature. 2010;463(7279):364–368.
12. Hussey GS, Chaudhury A, Dawson AE, et al. Identification of an mRNP complex regulating tumorigenesis at the translational elongation step. Mol Cell. 2011;41(4):419–431. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2011.02.003
13. Ding Z, Yang H-W, Xia T-S, Wang B, Ding Q. Integrative genomic analyses of the RNA-binding protein, RNPC1, and its potential role in cancer prediction. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(2):473–484. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2015.2237
14. Li -X-X, Shi L, Zhou X-J, et al. The role of c-Myc-RBM38 loop in the growth suppression in breast cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36(1):49. doi:10.1186/s13046-017-0521-5.
15. Xu E, Zhang J, Chen X. MDM2 expression is repressed by the RNA-binding protein RNPC1 via mRNA stability. Oncogene. 2013;32(17):2169–2178. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.238
16. Ye J, Liang R, Bai T, et al. RBM38 plays a tumor-suppressor role via stabilizing the p53-mdm2 loop function in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):212. doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0852-x.
17. Jiang Y, Xu E, Zhang J, et al. The Rbm38-p63 feedback loop is critical for tumor suppression and longevity[J]. Oncogene. 2018;37(21):2863–2872. doi:10.1038/s41388-018-0176-5.
18. Ozaki T, Nakagawara A. p73, a sophisticated p53 family member in the cancer world. Cancer Sci. 2005;96(11):729–737. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00116.x
19. Xue J-Q, Xia T-S, Liang X-Q, et al. RNA-binding protein RNPC1: acting as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2014;14(1):322. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-322
20. Wampfler J, Federzoni EA, Torbett BE, et al. The RNA binding proteins RBM38 and DND1 are repressed in AML and have a novel function in APL differentiation[J]. Leuk Res. 2016;41:96–102. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2015.12.006.
21. Huang W, Wei X-L, Ni W, Cao M, Meng L, Yang H. The expression of RNA-binding protein RBM38 decreased in renal cell carcinoma and represses renal cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Tumour Biol. 2017;39(5):1010428317701635. doi:10.1177/1010428317701635
22. Zhou X-J, Wu J, Shi L, et al. PTEN expression is upregulated by a RNA-binding protein RBM38 via enhancing its mRNA stability in breast cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36(1):149. doi:10.1186/s13046-017-0620-3.
23. Wang P, Gu J, Li X, et al. RNA-binding protein RBM38 acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017;10(11):11130–11136.
24. Zhang J, Cho SJ, Shu L, et al. Translational repression of p53 by RNPC1, a p53 target overexpressed in lymphomas[J]. Genes Dev. 2011;25(14):1528–1543. doi:10.1101/gad.2069311.
25. Fetka I, Radeghieri A, Bouwmeester T. Expression of the RNA recognition motif-containing protein SEB-4 during Xenopus embryonic development. Mech Dev. 2000;94(1–2):283–286.
26. Deloukas P, Matthews LH, Ashurst J, et al. The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 20[J]. Nature. 2001;414(6866):865–871. doi:10.1038/414865a.
27. Krackhardt AM, Witzens M, Harig S, et al. Identification of tumor-associated antigens in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by SEREX. Blood. 2002;100(6):2123–2131.
28. Scanlan MJ, Welt S, Gordon CM, et al. Cancer-related serological recognition of human colon cancer: identification of potential diagnostic and immunotherapeutic targets. Cancer Res. 2002;62(14):4041–4047.
29. Mazloomian A, Araki S, Ohori M, et al. Pharmacological systems analysis defines EIF4A3 functions in cell-cycle and RNA stress granule formation. Commun Biol. 2019;2(1):165.
30. Shu L, Yan W, Chen X. RNPC1, an RNA-binding protein and a target of the p53 family, is required for maintaining the stability of the basal and stress-induced p21 transcript. Genes Dev. 2006;20(21):2961–2972.
31. Qian K, Li M, Wang J, Zhang M, Wang M. Structural basis for mRNA recognition by human RBM38. Biochem J. 2020;477(1):161–172.
32. Yan W, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Jung YS, Chen X. p73 expression is regulated by RNPC1, a target of the p53 family, via mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32(13):2336–2348.
33. Yin T, Cho SJ, Chen X. RNPC1, an RNA-binding protein and a p53 target, regulates macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1) expression through mRNA stability[J]. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(33):23680–23686. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.480186.
34. Zhang J, Jun Cho S, Chen X. RNPC1, an RNA-binding protein and a target of the p53 family, regulates p63 expression through mRNA stability[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(21):9614–9619. doi:10.1073/pnas.0912594107.
35. Brázda V, Fojta M. The Rich World of p53 DNA Binding Targets: the Role of DNA Structure. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:22.
36. Xue W, Zender L, Miething C, et al. Senescence and tumour clearance is triggered by p53 restoration in murine liver carcinomas. Nature. 2007;445(7128):656–660.
37. Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science. 2004;303(5659):844–848.
38. Muller PA, Vousden KH, Norman JC. p53 and its mutants in tumor cell migration and invasion. J Cell Biol. 2011;192(2):209–218.
39. Lucchesi CA, Zhang J, Ma B, et al. Disruption of the Rbm38-eIF4E Complex with a Synthetic Peptide Pep8 Increases p53 Expression[J]. Cancer Res. 2019;79(4):807–818. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2209.
40. Vilborg A, Glahder JA, Wilhelm MT, et al. The p53 target Wig-1 regulates p53 mRNA stability through an AU-rich element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(37):15756–15761.
41. Léveillé N, Elkon R, Davalos V, et al. Selective inhibition of microRNA accessibility by RBM38 is required for p53 activity[J]. Nat Commun. 2011;2:513. doi:10.1038/ncomms1519.
42. Levrero M, De Laurenzi V, Costanzo A, Gong J, Melino G, Wang JY. Structure, function and regulation of p63 and p73. Cell Death Differ. 1999;6(12):1146–1153.
43. Gonfloni S, Caputo V, Iannizzotto VP. 63 in health and cancer. Int J Dev Biol. 2015;59(1–3):87–93.
44. Hall C, Muller P. The Diverse Functions of Mutant 53, Its Family Members and Isoforms in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20.
45. Ferraiuolo M, Di Agostino S, Blandino G, Oncogenic Intra-p SS. 53 Family Member Interactions in Human Cancers. Front Oncol. 2016;6:77.
46. Romano RA, Smalley K, Magraw C, et al. ΔNp63 knockout mice reveal its indispensable role as a master regulator of epithelial development and differentiation. Development. 2012;139(4):772–782.
47. Su X, Chakravarti D, Cho MS, et al. TAp63 suppresses metastasis through coordinate regulation of Dicer and miRNAs. Nature. 2010;467(7318):986–990.
48. Ichimiya S, Nakagawara A, Sakuma Y, et al. p73: structure and function. Pathol Int. 2000;50(8):589–593.
49. Orzol P, Holcakova J, Nekulova M, Nenutil R, Vojtesek B, Coates PJ. The diverse oncogenic and tumour suppressor roles of p63 and p73 in cancer: a review by cancer site. Histol Histopathol. 2015;30:503–521.
50. Inoue K, Fry EA. Alterations of p63 and p73 in human cancers. Subcell Biochem. 2014;85:17–40.
51. Wilhelm MT, Rufini A, Wetzel MK, et al. Isoform-specific p73 knockout mice reveal a novel role for delta Np73 in the DNA damage response pathway. Genes Dev. 2010;24(6):549–560.
52. Tomasini R, Tsuchihara K, Wilhelm M, et al. TAp73 knockout shows genomic instability with infertility and tumor suppressor functions. Genes Dev. 2008;22(19):2677–2691.
53. Mansilla SF, de la Vega MB, Calzetta NL, Siri SO, Gottifredi VCDK. Independent and PCNA-Dependent Functions of p21 in DNA Replication. Genes (Basel. 2020;11:6.
54. Bhawe K, Roy D. Interplay between NRF1, E2F4 and MYC transcription factors regulating common target genes contributes to cancer development and progression. Cell Oncol. 2018;41(5):465–484.
55. Fischer M, Müller GA. Cell cycle transcription control: DREAM/MuvB and RB-E2F complexes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2017;52(6):638–662.
56. Schaal C, Pillai S, Chellappan SP. The Rb-E2F transcriptional regulatory pathway in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Adv Cancer Res. 2014;121:147–182.
57. Feldstein O, Ben-Hamo R, Bashari D, et al. RBM38 is a direct transcriptional target of E2F1 that limits E2F1-induced proliferation[J]. Mol Cancer Res. 2012;10(9):1169–1177. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0331.
58. Bauskin AR, Brown DA, Kuffner T, et al. Role of macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 in tumorigenesis and diagnosis of cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66(10):4983–4986.
59. Khaled YS, Elkord E, Ammori BJ. Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1: a review of its pleiotropic actions in cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2012;11(5):183–190.
60. Ginestier C, Cervera N, Finetti P, et al. Prognosis and gene expression profiling of 20q13-amplified breast cancers[J]. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(15):4533–4544. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2339.
61. Chen CY, Chen J, He L, Stiles BL. PTEN: tumor Suppressor and Metabolic Regulator. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:338.
62. Worby CA, Dixon JE. PTEN. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014;83:641–669.
63. Yoon YJ, Chang HY, Ahn SH, et al. MDM2 and p53 polymorphisms are associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29(6):1192–1196.
64. Ding C, Cheng S, Yang Z, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes cell migration and invasion via down-regulation of RNA binding motif protein 38 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):4060–4076. doi:10.3390/ijms15034060.
65. Lin QY, Yin HL. RBM38 induces SIRT1 expression during hypoxia in non-small cell lung cancer cells by suppressing MIR34A expression. Biotechnol Lett. 2020;42:35–44.
66. Peterson LF, Yan M, Zhang DE. The p21Waf1 pathway is involved in blocking leukemogenesis by the t(8;21) fusion protein AML1-ETO. Blood. 2007;109(10):4392–4398.
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.