Back to Journals » Pediatric Health, Medicine and Therapeutics » Volume 10
Risk Factors Of Stunting Among Children Under 5 Years Of Age In The Eastern And Western Provinces Of Rwanda: Analysis Of Rwanda Demographic And Health Survey 2014/2015
Authors Habimana S , Biracyaza E
Received 6 July 2019
Accepted for publication 25 September 2019
Published 25 October 2019 Volume 2019:10 Pages 115—130
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PHMT.S222198
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Roosy Aulakh
Samuel Habimana,1 Emmanuel Biracyaza2
1Rwanda Resilience and Grounding Organization (RRGO), Kigali, Rwanda; 2Department of Community Health, School of Public Health, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Rwanda, Kigali, Rwanda
Correspondence: Samuel Habimana
Rwanda Resilience and Grounding Organization, P.O. Box 4285, Kigali, Rwanda
Tel +250788765133
Email [email protected]
Background: Stunting is one of the most public health burdens in Rwanda. Most deaths due to stunting are associated with inappropriate feeding practices that occur in the first 5 years of life. This study aimed at determining the risk factors for stunting in children under 5 years of age in the Eastern and Western provinces of Rwanda.
Method: Cross-sectional study using secondary data from Rwanda Demographic Health Survey 2014/2015.
Results: Stunting was highly prevalent in eastern province compared to Western province. It was also highly prevalent in rural area in both provinces. Results indicated a significant association between maternal education and stunting (x2=6.868; p=0.001), maternal age group (x2=15.44; p=0.017), maternal occupation (x2=30.012; p=0.000), wealth index (x2=14.327; p=0.006), sex of child (x2=2.91; p=0.008) and giving child fortified food (x2=4.256; p=0.039). Results indicated that antenatal care visits were significantly associated with stunting (x2=6.653; p=0.01). Sharing a toilet was significantly associated with stunting (x2=25.88; p=0.000). Multiple logistic regression indicated that the gender of child [OR=1.08; 95% CI (1.057–1.093), p=0.008], household wealth index [OR=0.386; 95% CI (0.357–0.414)] and breastfeeding [OR=0.02; 95% CI (0.004–0.036), p=0.013] were the risk factors of stunting in eastern and western provinces.
Conclusion: Immediate and appropriate interventions targeted at community management of acute malnutrition and stunting are needed to manage the associated morbidity and mortality. Strengthening the health system for improving child health through prioritizing maternal and child by addressing poverty and increase food access is mostly needed. These tactics yield more sustainable improvement in child nutrition within Eastern and Western provinces.
Keywords: stunting, children, under 5 years, malnutrition, province
Background
Poor nutrition during childhood impedes physical and mental development of children, which propagates the vicious cycle of intergenerational under nutrition. The developing world generally and Sub-Saharan African countries are experiencing momentous socio-demographic, economic, and nutritional transitions. These transitions are predictors of continued, highly prevalent stunting. Stunting is a public health concern that increases morbidity and mortality worldwide. It is higher in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).1 Every day stunting increases physiological, psychological and social consequences that lessen the quality of life nationally and societally.2 Researchers have demonstrated how nutrients relate to health and disease, and have explored why people choose particular foods and types of diet3–6 and have shown that nutrition is central to promoting health and development.7 Protein-energy malnutrition refers to the measure of stunting, wasting or both. Stunting refers to linear growth retardation resulting from long-term chronic under nutrition manifesting as faltering growth.8 Wasting is defined as the tendency to be too thin for one’s height, sometimes called weight-for-height.9
Malnutrition is an obstacle to socio-economic development due to its harmful effects on gross domestic product (GDP). In most countries, several synergies are needed to overcome the outcomes of malnutrition which jeopardize the health of children.10 For example, recent studies have found that as we strive to minimize under 5 malnutrition, another nutritional problem, obesity, has emerged which in combination with under nutrition, is referred to as the double burden effect of malnutrition and needs to be considered in the development plans of all economies.11 In 2008, the World Bank (WB) noted that a county cannot be considered industrialized if stunting rates are above 30%.9 Global statistics on stunting are alarming with the substantial impact being felt in Asian countries where 87 million under 5 children are stunted.12 One in three children in Africa is stunted; as of 2016, 59 million children in Africa are stunted with the highest rate in East African at 36.7%.13
In November 2014, the International Conference on Nutrition, jointly organized by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and WHO, announced the Rome Declaration on Nutrition which indicated different preventive measures for all forms of malnutrition including stunting. The global resolution on stunting and its devastating effect on human development are the first of its kind and is now used in African countries as an appropriate approach to prevent stunting.14 The previous study conducted in Tanzania revealed that maternal education, mother’s age at birth, water supply and other factors were associated with stunting.5 These results were confirmed in other studies.6,7 A child whose mother works as a merchant or a farmer is more likely to be stunted than one whose mother works as a housewife. It has been documented that this is due to decreased contact time between child and mother, limited exclusive breastfeeding, early cessation of breastfeeding, bottle feeding usage, and untimely introduction of complementary food. Certainly, stunting was found to be higher among children who exclusively breastfed for less or higher than 6 months of ages compared with those who exclusively breastfed for 6 months.11,15,16 Inappropriate timing for the introduction of some kinds of complementary food may affect a child’s nutritional status because his/her digestive and immune systems are not yet mature. Introducing supplementary food earlier, especially under unhygienic conditions, could be an important cause of malnutrition.16,17 Another study confirmed that feeding complementary food using a bottle or by hand both increase the risk of stunting among children.18
Antenatal care is an important determinant of child under nutrition. Through this period, the pregnant are provided the health education based on nutrition that influence the health of child; therefore, proper nutrition for mothers during the prenatal and postnatal period is essential in order to improve child growth.11,19 Several factors contribute to stunting; key among them are nutritional deprivation or adverse fetal environment during pregnancy, poor quality diets during the complementary feeding period and frequent infections. Stunting has origins in the fetal stages. Surveys on the causes of stunting have shown that stunting peaks during complementary feeding periods. This period also coincides with frequent infections as children are no longer exclusively breastfed.6,19 Stunted children may suffer irreversible brain damages due to lack of iodine and iron which prevents them from reaching their full potential.12,13,20 Stunted children face many disabilities such as learning deficiencies which affect their productivity for economic prosperity.9 In addition, stunted children are more likely to be obese adults and suffer the risk of nutrition-related non-communicable diseases referred to as the double burden of malnutrition.6
Poor linear growth, or stunting (<2 SD length/height for age), is an appropriate proxy for children’s general health and nutritional well-being. Stunting is considered to be the outcome of a multifaceted combination of proximal and distal biological and socio-environmental influences.2,4,21 Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) number 2 aims to limit stunting in under-5 children: targets 2.1 and 2.2, aspire to end malnutrition and hunger, are specifically intended to be achieved by 2025.4 This makes our study important as it will shed light on areas that need improvement in other parts of the world like Rwanda by looking at comparative risk factors for stunting in the Eastern and Western provinces of the country.
Stunting in Rwandan children under 5 years of age is a serious health issue that is still being discussed. However, the strategic measures taken for its prevention in 2010 reported that 21.9% of mortality among children in Rwanda was related to under nutrition.19 The government of Rwanda has made efforts to limit stunting rates through Scaling up Nutrition (SUN), Multiple Sectorial Strategies and being part of the Comprehensive Africa Agriculture Development Program of 2007 (CAADP), upon which Rwanda’s feed the Future Multi-Year Strategy rests. With these efforts, stunting declined from 44% in 2010 to 38% in 2015 in country.18,19 Previous studies indicated that several factors, including limited accessibility of food, breastfeeding and poor nutrient intakes, contributed to stunting in Rwanda.19 Stunting in the Eastern and Western provinces of Rwanda in 2010 was at 44% and 50% and by 2015 declined to 35% and 45%, respectively.
There is also variation of cross-sectional studies regarding the underlying the risk factors associated with childhood stunting. We conducted this study after finding that the stunting is the serious public health concern among the children of Eastern and Western provinces of Rwanda and there was no study conducted for discovering its risk factors associated. The main rationale of this study is discovering the risk factors associated with the stunting in these two provinces. Basing on the results, we disseminate the findings and then provide the appropriate recommendations to the policy makers for reducing the risk factors and promote health of the children. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no study has been done to identify factors associated with stunting in Eastern and western provinces on children under 5 years old in Rwanda. Therefore, the present study aims to determine the risk factors for stunting among children 5 years old in both Eastern and Western provinces of Rwanda.
Methods
Study Setting
Rwanda is located in East Africa and has a population of about 10.5 million. It is a land-locked country of 26,338 km.2 The Eastern and Western provinces of Rwanda share borders with Tanzania and Democratic Republic of Congo. Rwanda has a single city and four provinces: there are 30 districts, 416 sectors, 2148 cells, and 14,837 villages. The Rwandan climatic conditions are the predictors of some public health issues. Rwandans speak Kinyarwanda in addition to English and French. The eastern and western provinces were presented.
Study Design
An analytical cross-sectional study was conducted using secondary data from the Rwanda Demographic Health Survey (RDHS) 2014/2015 to compare risk factors for stunting among children under five in the Eastern and Western provinces.
Target Population
The target population was children under five from the Eastern and Western provinces of Rwanda during the period 2011 to 2015. The study included children whose mothers were interviewed and whose anthropometric measurements were taken. Children whose mothers were pregnant or who had given birth in the preceding 2 months were not included. Children who did not fit the inclusion criteria were excluded from the study. The study randomly selected children aged 6–59 months and their mothers or care givers living in the selected provinces.
Ethical Consideration
Rwanda Demographic Health Survey 2014/2015 is publicly available and therefore this research did not need approval from a research ethics committee. For the multi-country assessment, Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) data are available on DHS website: https://dhsprogram.com. Rwanda is one of the 35 Sub-Saharan countries that has DHS data on the DHS website.
Sample Size
A total of 961 children under 5 years from the Eastern province and 944 from the Western province were recruited giving a total sample of 1905. The sample included children and mothers who had stayed in their household on the night before the interview. The body mass index (BMI; weight/height2; kg/m2) of children was used and expressed weight, height and BMI as z-scores using age and sex-specific references. Weight, height and BMI z-scores were calculated using the 2006 WHO Child Growth Standards. Children with weight-for-age-z-score <-2 were considered to be underweight, those with height-for-age-z-score <-2 were considered to be stunted, and those with BMI-z-score >+1, >+2, >+3 as at risk, overweight and obese, respectively. The people at-risk category (BMI-z-score >+1 and ≤+2SD) was presented for children younger than 5 years. Biologically implausible values were identified and discarded using cut-off points from the WHO Anthro software (version 3.2.2, January 2011) for the Child Growth Standards (grow-up).
Potential Risk Factors
In this study, the ecological model of childhood obesity included the potential risk factors associated with childhood malnutrition. These factors were categorized into child, parental, household and community factors that were the determinants of stunting for children. The child factors consisted of child’s age (2.0–2.9, 3.0–3.9, and 4.0–4.9 years), sex, diarrhea in the 2 weeks before survey, anemia level, anthropometry (birth weight [low, healthy, and high birth weight], current weight and height), and nutrition history (ever breastfed, age of weaning [cessation of breastfeeding], and age of starting complementary foods [less or equal to/more than 6 months]). The parental and household factors included parental age, months when pregnancy ended, parental education, parental occupation, marital status, giving food in the first 3 days of life (milk, liquid, eggs, plain water and gripe water), anthropometry (weight and height) and maternal antenatal care history (ever/never had check-up during pregnancy).
The household factors of stunting comprised parental education, number of children under five in the household, who the child lives with, household wealth index, access to electricity, access to toilet facilities, and cooking facilities. The household wealth index comprised the ranking for all households across the survey which was conducted nationwide. The index variable was categorized into five quintiles: poorest, poorer, middle, richer and richest). The community factors of stunting included residence, religion and child play with household objects.
Data Collection And Sampling Technique
Concerning the sampling techniques used in the current study, sampling frame was used in this study where we used it in the current study. The sampling frame consisted of the list of enumeration areas (EAs) that enclosed the whole country, provided by the National Institute of Statistics of Rwanda (NISR), the implementing agency for the RDHS 2014–15. The EA refers to a natural village formed for the RPHC 2012 which served as a counting unit for the census conducted in Rwanda. In this study, each EA had the identification information of the participants, administrative belongings and a measure of size which is the number of residential households residing in each EA. It is in that regard, we classified all EAs using the types of the residence including urban and rural areas. Within this study, we used both stratified sampling that helped us to select Eastern and Western provinces that were considered as the strata. In addition to this sampling method, sampling weights were also used. We extracted data for the Eastern and Western provinces after obtaining information on stunting for the whole of Rwanda. This helped the researchers to ensure the actual representative of the survey results at provincial level. Since the RDHS sample is a two-stage stratified cluster sample, sampling weights were calculated based on sampling probabilities separately for each sampling stage and for each cluster.22 The eligible households with children under five were included in the present study. Measurement tools like the SECA scale were used to check the weight of children that had mostly been estimated by parents and a short measuring board was used to measure children’s height. All measures were developed from the United Nations Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF) Standards and measurements were taken according to the WHO 2006 standards. The outcome variables were anthropometric determinants including height and age.
Data Analysis
In the present study, data were analyzed using STATA version 13. Arc GIS version 11.0 was used to design the map that represented the study area. Both descriptive and analytical analyses were computed. Children’s weight, antenatal care, post-natal care, height and BMI within each wave were described using means and standard deviations. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed. In the multivariable model, a staged modeling technique was employed. Descriptive and analytical analyses were also performed.
In the first modeling stage, community factors were first entered into the model to assess their associations with stunting. A manually executed backward elimination method was used to select factors significantly associated with stunting. In the second model, the significant factors from the first stage were added to parental and household factors and this was followed by the backward elimination procedure. An analogous tactic was used for the child factors in the third stage. A staged stepwise regression was executed to avoid the degree of correlation between the significant predictors. It was also used to produce better models and a better understanding of the data and produce the best estimation for the current study and was important to avoid reporting redundant predictors. The stepwise regression went from the most distal set of community factors to the most proximate set of child factors, because the child is a subset of the community and any future population health intervention would start at the community level and work towards the individual level. To avoid statistical bias, collinearity was tested and reported in the final model. The odds ratios with 95% confidence interval (CIs) were calculated for assessing the adjusted risk of explanatory factors, and those with p < 0.05 were retained in the final model of the study. The Chi-square test was performed for examining the association between stunting and socio-demographic data in Eastern and Western provinces of Rwanda. The researchers that participated in the RDHS 2014/15 were not involved in the present study and we did not make any efforts to identify the study participants.
Results
Descriptive Analysis For Stunting Factors In The Eastern And Western Provinces
Of the 1905 children screened from the Eastern and Western provinces, 47.93% (n=913) were female and 52.07% (n=992) were male. Among these children, 84.41% (n=1608) lived in rural areas while 15.59% (n=297) lived in urban areas. Of the screened children, 50.45% (n=961) were from the Eastern province and 49.55% (n=944) from the Western province. The average age of participants’ mothers at their first birth was around 21.2 years (SD 3.3, min=12, max=49). The 15.11% and 20.6% of the mothers of the recruited children had received no education in both provinces, respectively. The average age of the participants was 36.79 months (SD=7.4; min=15 & max=49). Moreover, the household wealth index for each child was screened and classified as follow: poorest 25.88% (n=493), poorer 23.94% (n=456), middle 20.58% (n=392), richer 17.69% (n=337), and richest 11.92% (n=229). Of the screened children, 55.22% (n=1052) came from 5 to 8 member families, 38.95% (n=742) from 1 to 4 member families, and 5.83% (n=111) from 9 to 13 member families. The mothers of 27.98% (n=5330), of the children were aged 30–34, 25.88% (n=498) of them were aged 25–29 years while who were aged 15–19 and 2.05% (n=39) were aged 45–49. Of the participant households, 81.89% (n=1560) were headed by men and 18.11% (n=343) by women. A total of 1388 children were assessed for being given milk 3 days after birth (other than breast milk). We found that 98.20% (n=1363) were not given milk three days after birth and 1.8% (n=25) were. Among the total study population, we found 86.77% (n=1653) are stunted and 13.23% (n= 252) are not [Table 1].
 |
Table 1 Selected Socio-Demographic Characteristics Of Children Who Formed The Analysis Sample In Eastern And Western Provinces |
The bivariate analysis indicated that the stunted children born to women aged 25–29 years in the Eastern province was 28.78%. This prevalence was higher than the results found in Western province (25.76%). Among the stunting among children born to women aged 30–34 years was 23.86%. This was also higher than the Western province where we found the prevalence of 27.35%. Most of the participant households used unimproved toilets. Comparing toilets between the Eastern and Western provinces, the results indicated that majority used pit latrine with slab (69.56% versus 57.29%), pit latrine without slab (21.56% versus 28.07%), no facility or bush or field (2.76% versus 2.92%). Only the recommended toilet facility or VIP (3.65% versus 8.5%) was found.
Of the households headed by women in the Eastern and Western provinces, 18.47% versus 1.48% had stunted children. The proportion of heads of the household was males to females (81.53% versus 83.52%). This gave a p-value of 0.590 for the Eastern and 0.039 for the Western provinces. Similarly, among stunted children, 52.04% versus 52.14% were male and 47.96% versus 47.86% were females giving p-values of 0.610 and 0.637. Among the families of stunted children, 54.74% versus 5.80% were Protestant and 29.05% versus 29.67% were Roman Catholic giving a p-value of 0.493 versus 0.081. Of the families, 19.23% shared a toilet (p=0.007) versus 29.41% (p=0.002). This analysis shows that among stunted children, 42.21% versus 36.02% are from 1 to 4 member families, 53.24% versus 56.12% are from 5 to 8 member families and 4.56% versus 7.81% are from 9 to 13 member families giving p-values of 0.644 versus 0.971 [Table 3].
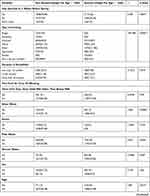 | 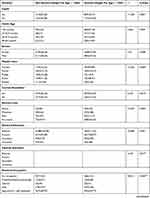 | 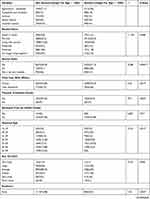 |  |
Table 2 Distribution Of Children By Explanatory Factors Associated With Stunting |
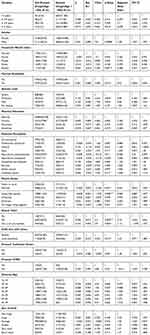 |
Table 3 Multiple Logistic Regression Estimates Of The Effect Of The Explanatory Variables On Stunting In Western And Eastern Provinces Of Rwanda |
The results about the household wealth index of stunted children in the Eastern and Western provinces indicated the majority (33.21%) of the stunted children were born to the poorest in Western province while in Eastern province the majority (24.22%) of stunted children were born to the poorer households. But the stunting among children was lowly prevalent in the richest households (10.74% versus 12.47%). Of the stunted children in the Eastern and Western provinces, the majority of stunted children under 5 years (73.38% versus 70.70%) were born to the mother with primary education. This was followed by the prevalence of 15.11% versus 20.63% of the stunting among the children born to the illiterate women. Among the participants, 42.54% were aged 0–23 months, 20.23% aged 24–36 months, 20.85% aged 36–48 months and 16.39% aged 48–60 months. Of the total-stunted children, the majority, 42.8% were aged less than 24 months, 20.17% were 2–2.9 years, 20.82% were 3–3.9 years and 16.4% were 4–5 years. The younger the age group, the more children were stunted. Basing on the residences, stunting was 22.8% among the poorest families, 23.7% in the poorer families, 22.4% in middle families, 19.4% in richer families and 6.9% in the richest families [Table 1].
Analytical Analysis
The diarrhea in the 2 weeks before the survey was significantly associated with stunting (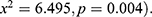 The results indicated that the type of cooking was significantly associated with stunting (
The results indicated that the type of cooking was significantly associated with stunting (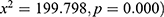 . The findings of this study indicate that the maternal and paternal education was significantly associated with stunting
. The findings of this study indicate that the maternal and paternal education was significantly associated with stunting 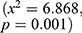 and (
and (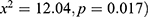 , respectively. Household Wealth Index was significantly associated with stunting (
, respectively. Household Wealth Index was significantly associated with stunting (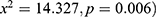 . Anemia level and maternal occupation were significantly associated with nutritional status (
. Anemia level and maternal occupation were significantly associated with nutritional status (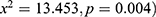 and
and 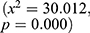 , respectively [Table 2]. The results indicated a significant association between stunting and residence (
, respectively [Table 2]. The results indicated a significant association between stunting and residence (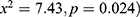 , shared toilets facilities ended (
, shared toilets facilities ended (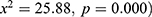 and months when the pregnancy (
and months when the pregnancy (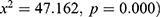 . The gender of children under 5 years was found to significantly associated with stunting (
. The gender of children under 5 years was found to significantly associated with stunting (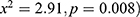 . Child’s age at introduction of complementary foods for children had a highly significant association with long-term nutritional. Basing on the findings related to nutritional status, the significant associations between stunting and liquid (
. Child’s age at introduction of complementary foods for children had a highly significant association with long-term nutritional. Basing on the findings related to nutritional status, the significant associations between stunting and liquid (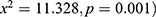 were found. The results indicated the significant association between stunting and eggs (
were found. The results indicated the significant association between stunting and eggs (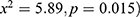 . The significant association between stunting and plain water (
. The significant association between stunting and plain water (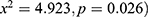 , and gripe water (
, and gripe water (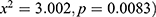 was found. The results indicated a significant association between stunting and children who were breastfed during the survey (
was found. The results indicated a significant association between stunting and children who were breastfed during the survey (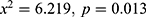 ). The results indicated that the household electricity (
). The results indicated that the household electricity (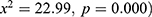 and fortified food were significantly associated with stunting
and fortified food were significantly associated with stunting 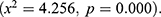 The number of the children in the household was significantly associated with the nutritional status of the child
The number of the children in the household was significantly associated with the nutritional status of the child 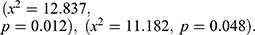 The findings also indicated that there was the significant association between the marital status and playing with household objects were significantly associated with the nutritional status of the child
The findings also indicated that there was the significant association between the marital status and playing with household objects were significantly associated with the nutritional status of the child 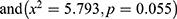 respectively. Religion was significantly associated with stunting
respectively. Religion was significantly associated with stunting 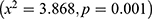 . Results indicated that antenatal care visits were significantly associated with stunting (
. Results indicated that antenatal care visits were significantly associated with stunting (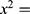 6.653; p=0.01) [Table 3].
6.653; p=0.01) [Table 3].
Multiple Logistic Regression Estimates Of The Effect Of The Explanatory Variables On Stunting
The adjusted odds ratios for all identified potential risk factors for stunting in the Eastern and Western provinces. The multivariate analysis yielded similar results for the two forms of under nutrition: stunting and underweight. In the final model, the factors related to the higher probability of being stunted and underweight were lower birth weight (<2.5 kg), being breastfed for 6 months or more, having a mother or father who was underweight or had short stature, and having a mother who had never attended formal education. The only difference between the two was that the probability of being stunted was also higher when a child lived in a rural area. Children had a greater probability of being at risk, or overweight/obese when they were in the youngest age group (2–2.9 years), were male, had a mother and father who was overweight/obese or had a father who had attended university [Table 3].
After adjusting for stunting in the model, at 95% CI and 0.03 of significance level, the analysis showed that male children were 1.08 (1.057–1.093) times more likely to be stunted than female children under 5 years. The risk for children aged 0-23months, 24-35months and 36-60months was OR [2.697 (2.654–2.739), 2.7 (2.658–2.742) and 2.678 (2.632–2.723)], respectively. Children from the poorest families had a higher risk of being stunted compared to other wealth groups. Children from the richest families were 0.386 (0.357–0.414) less at risk of being stunted than children from the poorest families. Children who were breastfed were less at risk to be stunted 0.02 (0.004–0.036) than children who are not breastfed [Table 3]. Moreover, logistic regression analyses identified the risk of stunting according to the educational status of mother as [OR=0.362 (0.376–0.333)] for primary school education, [OR=0.337 (0.0413–1.039)] for secondary education [OR=0.34 (0.409–1.077)] for university education. The risk of stunting according to maternal anemia level was [OR=0.89 (0.766–1.004)] for moderate, [OR=0.9 (0.788–1.015)] for mild and [OR=1.05 (0.937–1.161)] for children with no anemia. Risk of stunting according to maternal occupation was high among household and domestic workers [OR=1.15 (1.04–1.26)], agricultural employee [OR=1.006 (0.974–1.046)], clerical [OR=1.156 (0.811–1.501)], sales [OR=1.003 (0.957–1.048)], unskilled manual [OR=1.036 (0.953–1.118)] and services [OR=1.063 (0.967–1.159)].
Discussion
In this study, we noted that the educational status of mothers, family size and occupation of mother were significantly associated with stunting. In the multivariable logistic regression analysis, having a mother with no-formal education was associated with stunting. The results revealed these children born to illiterate mothers had a higher risk of stunting than those whose mothers studied at primary (OR=0.365), secondary (OR=0.337) or university level (OR=0.34). Mother’s occupation was significantly associated with stunting. The results confirmed that children whose mothers were skilled worker, professional worker or self-employed were less likely to be stunted than children whose mothers had other occupations. These results also showed that children with unemployed mothers were more likely to be stunted than those whose mothers were employed. The findings showed that children over the age of 24 months were at significantly higher risk of stunting than children in other age groups. Compared with children aged 0–24 months, the risk of stunting was more than two times higher for children in all other age groups. The logistic model showed that the likelihood of being stunted was highest for the age groups 24–35 months, 36–47 months and 48–60 months while the lowest was observed for age group 0–24 months.
Children who were breastfed were 0.02 less likely to be stunted than children who were not breastfed. These findings accorded with previous studies that showed that children who are not breastfed are more likely to become stunted than children who are.7 Children who were given food such as plain water, gripe water, liquid and fortified food in the first 6 months after birth were more likely to become stunted than children who were only given milk or who were breastfed. These findings accorded with previous studies that indicated that children who started eating solid food before 6 months were more likely to become stunted than those who only had milk or were breastfed.23 Children whose mothers had moderate and mild maternal anemia were less likely to be stunted compared than children whose mothers had severe anemia and those mothers with no anemia. The current results were similar to previous findings indicating that maternal malaria, underweight, anemia and biomass fuel use are risk factors for stunting.7,24 Male children were 1.08 times as likely to be stunted as female children. These results support previous studies that indicated that the males are more likely to become stunted than females.25 Wealth index was found to be an important risk factor for stunting. Children from the poorest household were highly likely to be stunted compared to the children from the poorer, middle, richer, and richest families.26
This study found that stunting was higher in rural settings than in urban settings in the two provinces. This was similar to previous studies showing rural area as a significant risk factor.6,8 We found that children whose mothers were in the middle age group (25–34) were more likely to be stunted than those with young mothers (under 25). However, the findings are contrary to those of a Tanzanian study where stunting was associated with young maternal age (under 25 years). These findings were similar to the previous studies conducted in Tanzania and indicated that the children born in rural residence had higher risk to become stunted compared to those born in an urban area.1,27 Our study showed that children whose mothers had higher education levels were less likely to be stunted than those whose mothers had no education or no education beyond preschool. However, this may be explained by the better earning power of an educated woman compared to one who has little or no education and thus more capacity to meet the nutritional needs of her families. These findings also accord with the Tanzanian study which found that children under 5 years whose mothers are illiterate are at higher risk of stunting than those with educated mothers.27
This study revealed that early introduction of complementary food was not a significant factor for stunting in the either province which was contrary to the findings of some previous studies which indicated that inappropriate timing of the introduction of complementary food to a child affected the nutritional status of children because their digestive and immune systems were not yet mature.16,17 Education level and sex of household head were contributory factors in the Eastern and Western provinces. These findings were relevant to other studies.3 The study found that leaving child alone for more than an hour in the previous week was a contributory factor for stunting in both Eastern and Western provinces. In addition, sharing toilet facilities was found to be a significant predictor for stunting in the Western province. Despite its prediction for stunting, we were unable to find the reason for its significance.
The study data had some limitations. Firstly, there were missing values such as age at which the child ceased breastfeeding, accompanied by many confounding factors. Secondly, the fact that data for the study were collected 4 years previously posed a drawback to this study. Regardless of the limitations, however, it was possible to indicate the risk factors of stunting in the Eastern and Western Provinces of Rwanda, multivariate linear regressions or adjusted for all missing confounders, presented which factors contributed most significantly to stunting.
Conclusion
The stunting is a serious public health concern associated with various factors including poor socio-demographic factors in Rwanda. The foremost factors of stunting among children under 5 years old in Eastern and Western provinces of Rwanda were inadequate nutrition, child sex, child-age, residence, maternal education, source of drinking water, maternal age, maternal occupation, duration of breastfeeding, household wealth index and sharing toilets. The factors associated with childhood stunting were multifactorial and interdependent.
There is a need for effective strategies to prevent and treat stunting in both Eastern and Western provinces of Rwanda. The health strategies like Community-based Interventions are mostly needed for managing the risk factors of stunting. The multidisciplinary approach that includes both national and international health institutions are certainly needed to be reinforced for lessening the burden of stunting among children under 5 years. The Rwandan government is recommended to keep empowering and encouraging health facilities to provide health education to pregnant and non-pregnant women about how to behave for reducing and adjusting stunting among children. The further researcher should be carried out to explore the biological and psychosocial effects of stunting on the children under five, their families, communities and the country. The other further study should be carried out for understanding the effect of childhood stunting and malnutrition on children’s epistemological and cognitive development in Rwanda. The other recommended further research should be carried out among the children under 5 years for comparing the risk factors for stunting between the Rwandan provinces.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Vonaesch P, Tondeur L, Bata P, et al. Factors associated with stunting in healthy children aged 5 years and less living in Bangui (RCA). PLoS One. 2017;12:1–17.
2. Norris A. Stunting has adverse long-term consequences for children’s immune function and survival, risk of nutrition-related chronic diseases, cognitive and behavioral development, and human capital. Africa in transition: growth trends in children and implic. Ann Nutr Metab. 2014;64:142–148.
3. Handayani F, Siagian A, Aritonang EY. Mother’s education as A determinant of stunting among children of age 24 to 59 months in North Sumatera province of Indonesia. J Humanit Soc Sci. 2017;22:58–64.
4. Frison S, Kerac M, Checchi F, Prudhon C. Anthropometric indices and measures to assess change in the nutritional status of a population : a systematic literature review. BMC Nutr. 2016;2:1–11. doi:10.1186/s40795-016-0104-4
5. Age M, District G, Zone EW. Prevalence of stunting and associated factors of children among 6-59 prevalence of stunting and associated factors of children among 6-59 months age in Guto Gida District, East Wollega Zone. Food Sci Qual Manag. 2016;29:1–17.
6. Francisco J, Ferrer L, Serra-Majem L. Factors associated with stunting among children. Nutrients. 2017;9:1–16.
7. Danaei G, Andrews KG, Sudfeld CR, et al. Risk factors for childhood stunting in 137 developing countries: a comparative risk assessment analysis at global, regional, and country levels. PLoS Med. 2016;13:1–18. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002164
8. Semali IA, Tengia-Kessy A, Mmbaga EJ, Leyna G. Prevalence and determinants of stunting in under-five children in central Tanzania : remaining threats to achieving Millennium development goal 4. BMC Public Health. 2015;4–9. doi:10.1186/s12889-015-2507-6
9. Nutrition National Alliance for Improved (NAFIN). Malnutrition in Namibia: The Time to Act Is Now!; 2010.
10. Lartey A. Conference on ‘Food and nutrition security in Africa: new challenges and opportunities for sustainability’ What would it take to prevent stunted growth in children in sub-Saharan Africa? Proceedings of the Nutrition Society. Proc Nutr Soc. 2015;74:449–453. doi:10.1017/S0029665115001688
11. Akombi BJ. Stunting, wasting and underweight in Sub-Saharan Africa : a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014;14:1–18.
12. Wirth J. Determinants of stunting in East Africa. Université De Montpellier; 2018.
13. WHO. Global Nutrition Targets 2025: Stunting Policy Brief. WHO; 2012.
14. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO). The Second International Conference on Nutrition; The United Nations Children's Fund: 2014.
15. Mangani C, Maleta K, Phuka J, et al. Original Article Effect of complementary feeding with lipid-based nutrient supplements and corn–soy blend on the incidence of stunting and linear growth among 6- to 18-month-old infants and children in rural Malawi. Matern Child Nutr. 2015;11:132–143. doi:10.1111/mcn.12068
16. Fikadu T, Assegid S, Dube L. Factors associated with stunting among children of age 24 to 59 months in Meskan district, Gurage Zone, South Ethiopia: a case-control study. BMC Public Health. 2014;14:1–7. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-14-800
17. Keino S, Plasqui G, Ettyang G, Van Den BB. Determinants of stunting and overweight among young children and adolescents in sub-Saharan Africa. Food Nutr Bull. 2014;35:167–177. doi:10.1177/156482651403500203
18. Cumming O, Cairncross S. Review Article Can water, sanitation and hygiene help eliminate stunting? Current evidence and policy implications. Matern Child Nutr. 2016;12:91–105. doi:10.1111/mcn.12258
19. USAID. Rwanda: Nutrition Profile; Publisher name" The United States for Agency International Development: 2014. Available from: https://www.usaid.gov/sites/default/files/documents/1864/USAID-Rwanda_NCP.pdf.
20. Prendergast AJ, Humphrey JH. The stunting syndrome in developing countries. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2014;34:254–264. doi:10.1179/2046905514Y.0000000158
21. SUNRAY. Challenges for Nutrition in Sub-Saharan Africa; ustainable Nutrition Research for Africa in the Years to come: 2012.Available from: http://sunrayafrica.co.za/sunray_cms/downloads/dynamic/compound_text_content/sunray_background_papers_english_0d1fe7c4b9d1c53e38a94f6ea689eb07.pdf.
22. National Institute of Statistics of Rwanda (NISR) [Rwanda], Ministry of Health (MOH) [Rwanda], ICF International. 2015. Rwanda Demographic and Health Survey 2014-15: Rockville, MD: NISR, MOH and ICF International.
23. Kuo AA, Inkelas M, Slusser WM, Maidenberg M, Halfon N. Introduction of Solid Food to Young Infants. Matern Child Heal J. 2011;15:1185–1194. doi:10.1007/s10995-010-0669-5
24. Thorne CJ, Roberts LM, Edwards DR, Haque MS, Cumbassa A, Last AR. Europe PMC Funders Group Anaemia and malnutrition in children aged 0–59 months on the Bijagós Archipelago, Guinea-Bissau, West Africa: a cross-sectional, population-based study. Paediatr Int Child Heal. 2017;33:151–160. doi:10.1179/2046905513Y.0000000060
25. Islam MM, Sanin KI, Mahfuz M, et al. Risk factors of stunting among children living in an urban slum of Bangladesh: findings of a prospective cohort study. BMC Public Health. 2018;18:1–13. doi:10.1186/s12889-018-5101-x
26. Tiwari R, Ausman LM, Agho KE. Determinants of stunting and severe stunting among under-fives: evidence from the 2011 Nepal Demographic and Health Survey. BMC Pediatr. 2014;14:1–15. doi:10.1186/1471-2431-14-82
27. Yisak H, Gobena T, Mesfin F. Prevalence and risk factors for under nutrition among children under five at Haramaya district, Eastern Ethiopia. BMC Pediatr. 2015;15:1–7. doi:10.1186/s12887-015-0535-0
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
