Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 13
Results of switchback from ranibizumab to aflibercept in patients with exudative age-related macular degeneration
Authors Koike N, Otsuji T, Tsumura A, Miki K, Sakai Y, Nishimura T, Takahashi K
Received 27 February 2019
Accepted for publication 27 June 2019
Published 15 July 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1247—1251
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S206910
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Naoko Koike,1 Tsuyoshi Otsuji,1 Akiko Tsumura,1 Katsuaki Miki,1 Yukio Sakai,1 Tetsuya Nishimura,1 Kanji Takahashi2
1Department of Ophthalmology, Kansai Medical University Medical Center, Osaka, Japan; 2Department of Ophthalmology, Kansai Medical University, Osaka, Japan
Purpose: Intravitreal injection of anti-VEGF drugs has become standard therapy for patients with exudative age-related macular degeneration (AMD). However, some patients do not exhibit sufficient response to the drugs for suppression of choroidal neovascularization activity. We investigated the efficacy of switchback from ranibizumab to aflibercept in patients with AMD who could not achieve further benefit beyond initial therapy of aflibercept injection.
Methods: Eleven eyes of eleven patients were included in this study. Two patients were nonresponders, and nine exhibited tachyphylaxis to aflibercept. All patients received three monthly injections of ranibizumab as an initial phase of switching and received aflibercept as a switchback drug. We investigated changes in injection interval, visual acuity, and central retinal thickness.
Results: In four patients (36.4%), injection interval was extended. The interval was 6.73 weeks before switch and 9.27 weeks after switchback (P=0.96). LogMAR visual acuity was 0.22 before switch and 0.24 after switchback (P=0.62). Central retinal thickness was 306.8 μm before switch and 256.1 after switchback (P=0.13). In all patients who were nonresponders to aflibercept, injection interval could not be extended.
Conclusion: A switchback from ranibizumab to aflibercept may be beneficial in some patients with AMD who exhibit tachyphylaxis to aflibercept.
Keywords: AMD, aflibercept, ranibizumab, switchback, anti-VEGF drugs
Introduction
Anti-VEGF drugs are used worldwide for patients with age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Aflibercept has been proven effective for the suppression of choroidal neovascularization (CNV) activity in AMD. The effect of bimonthly intravitreal injections of aflibercept (IVA) is comparable to that of monthly intravitreal injections of ranibizumab (IVR). However, some patients do not show initial response to IVA (nonresponders). In some patients, the response to IVA gradually deteriorates after repeated injections (tachyphylaxis, short-term tolerance). In patients with tachyphylaxis, suspending the treatment (drug holiday) is sometimes effective to restore response to the drug. However, during drug holidays, CNV activity can increase, due to the cessation of treatment for AMD. This study was undertaken to investigate switchback from ranibizumab to aflibercept, in order to regain the effectiveness of aflibercept without the use of drug holidays, for patients who did not exhibit sufficient response to initial aflibercept injections.
Methods
Patients with no improvement in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and no decrease in central retinal thickness (CRT) >10% measured by optical coherence tomography (OCT) after initial therapy were defined as nonresponders. Patients who showed improvement in VA and decrease in CRT >10% after initial therapy and those whose response deteriorated after following injections were defined as patients with tachyphylaxis. Eleven eyes of eleven patients (nine males and two females, average age 71.5±6.3 years) were included in this study. Baseline characteristics of these patients are shown in Table 1. Ten eyes exhibited typical AMD, and one eye exhibited polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. All typical AMD patients demonstrated occult CNV. They received three initial injections of aflibercept and continued to receive injections in accordance with the treat-and-extend method. For patients with difficulty in extending their aflibercept-treatment intervals, switchback from ranibizumab to aflibercept was considered. After the switch from aflibercept to ranibizumab, three monthly injections of ranibizumab were performed, followed by switchback to aflibercept. This retrospective study was performed with written informed patient consent after approval by the Kansai Medical University Medical Center Institutional Review Board, and conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Patients were followed up for >12 months after switchback. A comprehensive ophthalmic examination, including BCVA and spectral domain OCT imaging using the RTVue-100 (Optovue, Fremont, CA, USA), was performed at every visit. BCVA was measured with a Japanese standard decimal visual chart, and the logarithm of minimum angle of resolution (logMAR) scale was used for statistical analysis. Comparisons were made of the interval of administration of aflibercept, VA, and CRT measured by OCT before switch and after switchback. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare VA, CRT, and interval of administration of aflibercept before and after switchback, because these data did not exhibit normal distribution.
 |
Table 1 Baseline characteristics |
Results
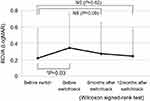
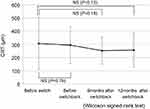
Changes in VA are shown in Figure 1. BCVA before switch was 0.22, whereas it was 0.24 at 12 months after switchback. These values did not significantly differ (P=0.62). BCVA deteriorated after switching (P=0.03), but had recovered at 6 months after switchback (P=0.09). Changes in CRT are shown in Figure 2. CRT decreased from 306.8 µm before switching to 256.1 µm at 12 months after switchback (P=0.13). Intervals between administration of aflibercept changed from 6.73 weeks before switching to 9.27 weeks after switchback (Figure 3). These did not significantly differ (P=0.96). Numbers of IVA injections in 1 year are shown in Figure 4. These decreased from 8.6 before switch to 6.7 after switchback (P=0.11). Four eyes (36.4%) exhibited an extended interval for administration of aflibercept after switchback. Notably, all four exhibited tachyphylaxis to initial aflibercept injections. Among seven eyes that did not demonstrate an extended interval after switchback, two were eyes of nonresponders; moreover, two of the seven had exhibited persistent exudation before switch, which fully resolved after switchback. In other words, all eleven eyes showed exudation before switch, and complete fluid absorption was achieved after switchback in six eyes (55%). If we regard eyes with dry maculae after switchback as those in which switchback was effective and those without dry maculae as eyes in which switchback was not effective, there was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of AMD type, greatest linear dimension (GLD), or period from initiation of therapy to switch. Nonresponders and tachyphylaxis cases are shown in Table 2.
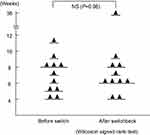 |
Figure 3 Interval of aflibercept administration before switch and after switchback. |
 |
Table 2 There was no significant difference between the two groups (effective and ineffective) in terms of AMD type, GLD, or period from initiation of therapy to switch |
Discussion
There have been recent reports regarding patients who were nonresponders to anti-VEGF drugs.1,2 In one report on nonresponders to aflibercept, nonresponders to aflibercept in treatment-naïve and treatment-switched groups comprised 8.1% and 15.5% determined by BCVA and 12.9% and 8.5% via fundus findings. Generally, tachyphylaxis is a condition in which the response to drugs gradually deteriorates after repeated administration over a short period.2 Acquisition of drug tolerance and drug resistance are caused by upregulation of target cells and elevation in the number of drug-tolerant cells. The use of drug holidays has been reported as effective with respect to preventing and resolving drug tolerance and resistance in patients with melanoma,3 breast cancer,4 and lung cancer.5 To regain drug effectiveness, the use of drug holidays is also considered useful for anti-VEGF therapy in patients with AMD; however, the use of drug holidays may increase CNV activity. Rather than using drug holidays, continuation of treatment with other anti-VEGF drugs may provide suppression of CNV exudation. In the present study, we administered IVR in place of a drug holiday. Ranibizumab is an anti-VEGF antibody and a Fab fragment of humanized monoclonal antibody. Aflibercept is a recombinant fusion glycoprotein with an Fc portion of human IgG1 to which the extracellular domains of human VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 are fused. It has high affinity with not only VEGFA but also other factors in the VEGF family, such as VEGFB and placenta growth factor. Moreover, Platania et al reported that aflibercept–VEGFA and ranibizumab–VEGFA complexes considerably differed considerably in terms of both molecular interactions and stabilizing energy.6 We thought this result might explain the effects of switchback. A prior study on switchback from aflibercept to ranibizumab for AMD showed a short-term benefit.7 Waibel et al reported that switchback from aflibercept to ranibizumab may improve morphological parameters and stabilize VA in patients with AMD.8
In this study, the interval of injection was extended in four eyes. Dry macula was achieved in two of seven eyes in which extension was not obtained after switchback. Therefore, switchback was effective in six of eleven eyes (54.8%). Notably, we found a benefit of switchback in eyes with tachyphylaxis to aflibercept (six of nine, 66.7%). In contrast, in nonresponders, we did not find any benefit of switchback. We suspect that in nonresponders, there is an intrinsic lack of responsiveness to anti-VEGF drugs, eg, because ofmaturity of vessels and atrophy of retinal pigment epithelium, which is not affected by switchback. We may need to consider options for treatment of nonresponders other than anti-VEGF drugs. This study had limitations of a small number of cases and being retrospective. Additional studies are needed to confirm the benefit of switchback from ranibizumab to aflibercept for AMD patients.
Conclusion
The present study showed that switchback from ranibizumab to aflibercept might be beneficial in some patients with AMD for whom responsiveness to aflibercept has deteriorated after repeated drug administration. Switchback is not necessarily effective for all AMD patients, but it might be worth a try for patients who have inadequate responses to drugs.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Otsuji T, Nagai Y, Sho K, et al. Initial non-responders to ranibizumab in the treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Clin Ophthalmol. 2013;7:1487–1490. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S46317
2. Nagai N, Suzuki M, Uchida A, et al. Non-responsiveness to intravitreal aflibercept treatment in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: implications of serous pigment epithelial detachment. Sci Rep. 2016;6:29619. doi:10.1038/srep29619
3. Ravindran Menon D, Das S, Krepler C, et al. A stress-induced early innate response causes multidrug tolerance in melanoma. Oncogene. 2015;34(34):4448–4459. doi:10.1038/onc.2014.372
4. Gómez-Miragaya J, Palafox M, Paré L, et al. Resistance to taxanes in triple-negative breast cancer associates with the dynamics of a CD49f+ tumor-initiating population. Stem Cell Rep. 2017;8(5):1392–1407. doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.03.026
5. Yap TA, Macklin-Doherty A, Popat S. Continuing EGFR inhibition beyond progression in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2017;70:12–21. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.10.014
6. Platania CB, Di Paola L, Leggio GM, et al. Molecular features of interaction between VEGFA and anti-angiogenic drugs used in retinal diseases: a computational approach. Front Pharmacol. 2015;6:248. doi:10.3389/fphar.2015.00248
7. Despreaux R, Cohen SY, Semoun O, et al. Short-term results of switchback from aflibercept to ranibizumab in neovascular age-related macular degeneration in clinical practice. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016;254(4):639–644. doi:10.1007/s00417-015-3084-1
8. Waibel S, Matthé E, Sandner D. Results of re-switch from intravitreal aflibercept to ranibizumab in patients with exudative age-related macular degeneration. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2018;235(5):616–621. doi:10.1055/s-0043-106308
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.