Back to Journals » OncoTargets and Therapy » Volume 14
Research Progress on Regulating LncRNAs of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Stem Cells
Received 28 October 2020
Accepted for publication 21 January 2021
Published 10 February 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 917—927
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S289064
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Nicola Silvestris
Xiaoli Zhang, Ying Zhu
Liver Disease Center of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Liaoning, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Ying Zhu Email [email protected]
Abstract: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most prevalent malignancies around the world. The self-renewal, proliferation, differentiation, and tumorigenic potential of liver cancer stem cells (LCSCs) may account for the high recurrence rate and the refractory feature of HCC. Despite extensive researches, the underlying regulatory mechanism of LCSCs has not been fully disclosed. Long nonprotein coding RNAs (lncRNAs) may exert an essential role in regulating various biological functions of LCSCs, such as maintaining the stemness of cancer stem cells (CSCs) and promoting tumor development. Therefore, it is highly critical to determine which lncRNAs can control LCSCs functions and understand how LCSCs are regulated by lncRNAs. Herein, we summarized lncRNAs and the main signaling pathways involved in the regulation of LCSCs found in recent years. Moreover, we shed light on the existence of the network system of lncRNAs and LCSCs, which may provide valuable clues on targeting LCSCs.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC, liver cancer stem cells, LCSCs, long nonprotein coding RNAs, lncRNAs, signaling pathways, network
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accounts for approximately 75% to 85% of primary hepatic malignancies, ranking the third-largest cause of cancer-related death worldwide.1,2 Liver cancer stem cells (LCSCs) are a subpopulation of cells with stem cell properties, which can not only renew and expand vigorously and further differentiate into heterogeneous tumor cells, but also cause malignant changes of normal stem cells or progenitor cells, causing the invasion, drug resistance, relapse, metastasis, and poor prognosis of HCC.3,4 However, it is not well understood how LCSCs maintain self-renewal and promote malignant progression.
Long nonprotein coding RNAs (LncRNAs) are a subclass of noncoding genes with a length of more than 200 nucleotides, participating in regulating the biological processes of cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and metabolism.5–7 Moreover, lncRNAs manipulate the downstream gene expression by introducing chromatin modification complexes and interacting with miRNAs, mRNA, or proteins.8,9 Accumulated evidence shows that lncRNAs are often dysregulated as carcinogens or tumor suppressors in various cancers.10,11 At present, increasing studies suggest that lncRNAs participate in the self-renewal and proliferation of LCSCs through different mechanisms and play a vital role in the deterioration of HCC. Thus, further investigation and verification of the role of lncRNAs expressed in LCSCs aberrantly may provide new ideas for the treatment of HCC.
LncRNAs Involved in the Regulation of LCSCs
Recently, massive investigations support that lncRNAs are essential for sustaining CSCs properties. According to the expression levels in LCSCs, lncRNAs are briefly classified into up-regulated lncRNAs and down-regulated lncRNAs, which not only provide new clues to the pathogenesis of HCC but also may become new markers and therapeutic targets for HCC. Some lncRNAs involved in the regulation of LCSCs are summarized below (Table 1).
 |
Table 1 LncRNAs Participating in the Regulation of Liver CSCs |
Up-Regulated LncRNAs Expressed in LCSCs
HULC
HULC is located on chromosome 6p24.3, containing about 1600 nucleotides and two exons. The promoter and the first exon of HULC are situated at a long terminal repeat (LTR) reverse transposon.12 Via miR675, HULC enhances Sirt1 expression, which in turn induces cell autophagy. Thus, HULC can enhance CyclinD1 through the autophagy-mir675-pkm2 pathway, thereby increasing pRB and inhibiting the expression of P21 and WAF1/CIP1 in the LCSCs. Depending on CyclinD1, HULC accelerates the progress and the growth of human LCSCs, especially the CD44+CD24+EpCAM+ LCSCs.13
LINC00324
LINC00324 is situated in chromosome 17p13.1 and is uniformly distributed in the nucleus. Pathologically, LINC00324 regulates cell proliferation and participates in cancer development by combining HUR and FAM83B family.14 LINC00324 is highly expressed in the EpCAM+CD24+CD133+ LCSCs, with a lower survival rate of HCC patients. Interestingly, it is related to tumor size, stage, differentiation degree, and lymph node metastasis but has nothing to do with gender, age, and AFP. LINC00324 can promote FasL expression by attracting PU.1 to the FasL promoter region, ultimately maintaining the biological characteristics of LCSCs and inhibiting cell apoptosis.15
SAMMSON
SAMMSON is a target of the transcription factor SOX10 on chromosome 3p13-3p14, mainly accumulating in the nucleus. The carcinogenic effect of SAMMSON can be enhanced by interacting with p32.16 SAMMSON is overexpressed in CDl33+ LCSCs and liver cancer cells, which is closely associated with poor prognosis. Interestingly, its expression level in advanced liver cancer is higher than that in early liver cancer. By regulating the translations of c-MYC and CCND2 proteins, SAMMSON activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to promote the self-renewal of LCSCs, the invasion and tumorigenic ability of hepatoma cell lines, and the occurrence of HCC.17
LncHDAC2
Human chromosome 9 contains a gene named lncHDAC2, which is 834 kb in length. LncHDAC2 is expressed immoderately in liver cancer and CD13+CD133+ liver CSCs. Mechanically, the interaction between lncHDAC2 and HDAC2 can recruit the NuRD complex to the promoter of PTCH1. Ultimately, the inhibition of PTCH1 expression and the activation of the Hh signal can drive the self-renewal, expansion, and tumor progression of LCSCs. Furthermore, lncHDAC2 combines with the 1200–1400 base pair region on the PTCH1 promoter in a non-sequence complementary manner to regulate its transcription. Meaningfully, HDAC2 and PTCH1 have completely opposite relationships with the severity of HCC.18
LncARSR
LncARSR is a gene on chromosome 9, composed of 4 exons and 591 nucleotides.19 The expression of lncARSR is significantly increased in EpCAM+CD133+ liver CSCs. Moreover, it can promote the dedifferentiation of liver cancer cells and the expansion of LCSCs by targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway. LncARSR is one of the controllers of HCC cells lying upstream of STAT3. S3I-201, a STAT3 inhibitor, makes lncARSR-knockout liver cancer cells and control cells the same in the ratio and self-renewal capacity of LCSCs, further confirming that lncARSR requires STAT3 to promote the expansion of LCSCs. Also, when interfering with lncARSR, the sensitivity of HCC to sorafenib and cisplatin remarkably increases, suggesting that lncARSR may play a role in HCC resistance treatment.20
DLX6-AS1
DLX6-AS1 is a regulatory factor of the DLX gene family, located on chromosome 7q21.3.21 The abnormal expression of DLX6-AS1 may be related to the poor prognosis of HCC patients through the DLX6-AS1/miR-203a/MMP-2 pathway.22 DLX6-AS1 is highly expressed in CD133+CD13+ LCSCs and hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Its down-regulation results in a reduction of the CADM1 promoter methylation to further enhance the expression of CADM1 inactivating the STAT3 signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting the autophagy and amplification of LCSCs, inhibiting the proliferation of cancer cells, colony formation, and tumor formation, attenuating the expression of stemness-related genes (CD133, CD13, OCT-4, SOX2 and Nanog) in LCSCs, and inhibiting the occurrence and development of tumors in vivo.23
THOR
The study found that the ectopic expression of human THOR accelerates the occurrence of melanoma in zebrafish, so it is called an oncogene.24 In HCC cells, β-catenin is located downstream of THOR. THOR is upregulated in OV6+ or EpCAM+ liver tissues and CSC-riched hepatoma cell spheres through β-catenin signaling, thereby promoting dedifferentiation of hepatoma cells and self-renewal and expansion of LCSCs. The downstream genes of TGF-β/SMAD include β-catenin and THOR in liver CSCs. Therefore, the mediated chain of TGF-β/SMAD-THOR-β-catenin participates in the regulation of LCSCs. Besides, THOR also increases the resistance of liver cancer cells to sorafenib.25
HAND2-AS1
HAND2-AS1 is spanning nearly 8.3 kb with four exons. It is a conservative locus on human chromosome 4.26 Studies have reported that HAND2-AS1 can suppress tumor migration, invasion, and metastasis.27,28 The expression of HAND2-AS1 is significantly increased in CD13+CD133+ liver CSCs. It recruits the INO80 chromatin remodeling complex to the promoter of BMPR1A, thereby inducing its expression and leading to the activation of the BMP signal that can promote the self-renewal of LCSCs and the development of liver cancer. Knocking down HAND2-AS1 and silencing BMPR1A also have a synergistic antitumor effect on the human liver cancer model.26
PTV1
PTV1 lies in chromosome 8q24, which plays an integral part in CSC self-differentiation, proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. PVT1 can act as a transcription regulator by cooperating with the chromatin remodeling complex in HCC.29 PVT1 promotes the expression of SWI and SNF proteins by activating the SWI/SNF complex, which can further start the downstream Wnt signaling pathway to increase the Wnt protein expression, ultimately encouraging the self-renewal of LCSCs and the proliferation of tumors. The research results reveal that the expression level of PTV1 is positively and negatively correlated with monoclonals formation and apoptosis rate, respectively.30
NEAT1
NEAT1 is a lncRNA transcribed from chromosome 11, activated in EpCAM+CD24+ LCSCs. NEAT1 and the AKAP8 protein bind to each other so that the PKA C subunit in the cytoplasm is reduced dramatically. In contrast, the R subunit and C subunit are significantly increased in the nucleus, inhibiting the phosphorylation of LATS and YAP, key molecules of the Hippo signaling pathway, which contributes to the expansion and self-renewal of LCSCs.31 Meantime, NEAT1v1 is required for the expression of CD44, a marker of LCSCs.32 Alarmingly, evidence indicates that liver cancer patients with high expression of NEAT1 have poorer overall survival and tumor-free survival.
CUDR
CUDR is encoded on chromosome 19p13.1, about 2.2 kb in length. CUDR plays a vital part in tumor progression and patients’ prognosis. Furthermore, the transcription of CUDR is higher in CD133+/CD44+/CD24+/EpCAM+ LCSCs, contributing to the malignant proliferation of stem cells and the tumorigenic effect. Hu Pu et al reported that CUDR overexpression + CyclinD1 overexpression/CUDR overexpression + PTEN depletion synergistically boost the expression of H19 in LCSCs, thereby increasing telomere length.33 The cascade of CUDR-HULC/CUDR-β-catenin has also been reported.34 CUDR changes the gene expression of human embryonic stem cell-like hepatocytes by inhibiting the surface modification of H3K27me3. Meantime, it can inhibit HULC promoter methylation to induce HULC expression. CTCF encourages the formation of β-catenin promoter-enhancer DNA loops, which makes CUDR recruit more RNApolII and P300, resulting in a unique expression of β-catenin. Shengxian Yuan et al also discovered SET1A-CUDR-pRB-h3k4me3-trf2 -telomere, a new regulatory chain in HCC and LCSCs.35 CUDR enhances the interaction between SET1A and pRB1, and joints SET1A and pRB1 to increase H3K4me3, boosting the activity of TRF2 specifically. Eventually, the telomere length is extended. Clearly, through various genetic molecules, CUDR can promote the malignant transformation of LCSCs and the occurrence and development of HCC synergistically.
DANCR
DANCR is a tumor-associated lncRNA on chromosome 4. Studies have found that it is necessary for the dedifferentiation of epidermal cells.36 DANCR is upregulated in EpCAM+CD90+CD133+ LCSCs. Besides, DANCR significantly increases the stem characteristics of liver cancer cells, the proliferation of CSCs, and the proliferation and metastasis of HCC. The function of DANCR primarily depends on the association and regulation with CTNNB1. Some miRNAs can bind to CTNNB1 to suppress the effect of CTNNB1, while DANCR possesses the capacity of competitive combination. Consequently, DANCR reverses the inhibitory effect of miRNAs.37 To some extent, DANCR may be a key oncogene for the occurrence and development of HCC and can predict the prognosis of HCC.
ICR (Lnc24236)
ICR is associated with the incidence and the prognosis of HCC patients with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT). The expressions of ICR and ICAM-1 are up-regulated and linearly related in PVTT tissues, which reduces the overall survival rate of patients. ICR and ICAM-1 mRNAs have a continuous complementary sequence of 812 bp. The two form an RNA double strand that reinforces the stability of ICAM-1 mRNA and the expression of ICAM-1, thereby regulating the stem cell characteristics of HCC and promoting HCC growth and metastasis. ICR is controlled by Nanog in hepatoma cells, which is involved in the stemness maintenance of EpCAM+CD24+ CSCs. Moreover, a remarkable relationship between the expression of ICR/ICAM-1 and the clinical indicators of liver cancer patients, including tumor size, intrahepatic metastasis rate, PVTT incidence, TNM stage, and DFS/OS, was detected. Valuably, both may also be used as prognostic indicators and may have a higher predictive potential than AFP.38
LncBRM
LncBRM contains 1321 nucleotides and six exons, positioned between ACTBL2 and PLK2 genes on the human chromosome 5. It is a moderately conserved site, assembling in the nucleus.39 LncBRM expression markedly enhances in HCC and CD13+CD133+ LCSCs, facilitating the proliferation of xenograft tumors and the self-renewal of LCSCs. Mechanically, lncBRM isolates BRM to initiate BRG1-biased BAF complexes in LCSCs, adjusting the BRG1/BRM switch. Moreover, the BAF complex embedded in BRG1 is involved in the activation of YAP1 signaling in a KLF4-dependent manner.39 YAP1 is a crucial factor for self-renewal, maintenance of stemness, and tumorigenesis of liver CSCs. The BRG1 and YAP1 targets are closely correlated with liver cancer severity and prognosis.
LncCAMTA1
LncCAMTA1, a gene on chromosome 1, is oriented to CAMTA1 in the antisense direction. LncCAMTA1 is a critical tumor suppressor in various human cancers, functioning in the nucleus.40–42
LncCAMTA1 is highly expressed in CD13+CD133+ LCSCs and HCC. The higher the expression, the higher the recurrence rate, and the worse the prognosis of liver cancer, suggesting that it may be an oncogene. Studies show that lncCAMTA1 advances the formation of spheres, the expression of stem cell markers and transcription factors in vitro, the proliferation of liver cancer cells, and tumor development in vivo. Significantly, the mechanism of maintaining the properties of CSC-like cells is the inhibition of CAMTA1 mRNA and protein expression by reducing tissue markers in the CAMTA1 promoter region and changing the chromatin structure on the CAMTA1 promoter, suggesting that lncCAMTA1 transcription level is negatively relevant to the CAMTA1 mRNA level in HCC tissues. CAMTA1 is required to the effect of lncCAMTA1 on HCC cell proliferation and CSC-like properties, and silencing CAMTA1 can destroy the effects of lncCAMTA1 knockout.43
Lnc-β-Catm
Lnc-β-Catm situates in between genes of the IRF2BP2 and TOMM20 on chromosome 1q, possessing two exons and 2281 nucleotides. It is a gene with a moderately conserved site, chiefly in the nucleus. Lnc-β-Catm is overexpressed in HCC and CD13+CD133+ LCSCs, which accelerates LCSCs self-renewal, tumorigenesis, and tumor dissemination in vivo. The 9 and 6 fragments of lnc-β-Catm are connected to the N-terminus of β-catenin and EZH2, respectively, and the three combine to form an RNA-protein complex. The combination of β-catenin and EZH2, which mechanism is that EZH2 methylates β-catenin at K49 of N-terminus, promotes tumor balls formation that can be disrupted by lnc-β-Catm knockout, illustrating that the ball-forming ability of the combination depends on lnc-β-Catm. Furthermore, lnc-β-Catm augments the mutual effect between EZH2 and β-catenin, boosting the methylation and stability of β-catenin. Lastly, Wnt signaling is initiated.44 Notably, the positive connection between the expression levels of lnc-β-Catm, EZH2, and Wnt/β-catenin target genes and the severity and prognosis of liver cancer patients is significant.
LncTCF7
LncTCF7 locates between HSPA4 and TCF7 genes on human chromosome 5, composed of 3 exons and 3.6 kb. The enhancive expression of lncTCF7 promotes pluripotent transcription factors (Sox2 and Nanog) expression and tumor development in HCC tissues and CD13+CD133+ liver CSCs. The mechanism is that lncTCF7 recruits the SWI/SNF complex to the 3ʹ terminus and binds to it, starting lncTCF7 expression and activating the Wnt signaling pathway. Experiments found that TCF7 and Wnt7a can reverse the knockout effect of lncTCF7. Nevertheless, the impact of lncTCF7 can be destroyed by DKK1, a Wnt signaling inhibitor. Knocking out lncTCF7 disrupts the bind of BAF170 and the 1160 to 1048 bp fragment of TCF7 promoter. Hence, the deletion of BAF170 significantly represses the activity of downstream target genes of TCF7, Nanog, and Wnt, such as Sox2, CCND1, and CCND2. Additionally, the 5-year survival rate is reduced in HCC patients with upregulated TCF7.45
HOTAIR
HOTAIR sits in the HOXC gene cluster, which is on chromosome 12. To a certain degree, HOTAIR can accelerate tumorigenesis and the malignant proliferation of CD133+CD44+CD24+EpCAM+ human LCSCs in a SETD2 reduction way. HOTAIR overexpression enhances the interaction of HOTAIR, CREB, P300, and RNApolII, blocking the recruitment of the CREB-P300-RNApolII complex in the SETD2 promoter region. Due to the SETD2 promoter region containing CREB binding elements that support RNApolII activity, the catalytic function of RNApolII is blocked to inhibit the expression and phosphorylation of SETD2. HOTAIR strengthens the binding ability of pSTED2 and HOTAIR, which makes the interaction between pSETD2 and histone H3 and the levels of H3K36me1/2/3 suppressed, thereby reducing the formation of the hMSH6-hMSH2-H3k36me3-Skp2 complex. The hMSH6-H3k36me3-Skp2 has excellent effects on repairing broken DNA and old proteins. HOTAIR prevents hMSH2/6-H3k36me3-Skp2 complex from binding DNA damage sites to ruin DNA damage repair and enhance MSI, triggering the abnormal expression of genes, such as CyclinE, CyclinD1, CDK2, CDK4, ppRB, E2F1, and PCNAs.46
LncRNAs Down-Regulated in Liver Cancer Stem Cells
H19
H19 is a 2.3 kb lncRNA with 35 small open reading frames encoded on 11p15.5. It may preserve cells from oxidative stress in cancer tissues by motivating the activity of NF-KB. In HCC, H19, participating in the epigenetic mechanism of tumorigenesis and tumor development, can inhibit and improve the transcription of genes related to apoptosis and chemical reactions, respectively.47–49 Evidence obtained indicates an enlargement of H19 expression in HCC tissues by initiating the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Astonishingly, the down-regulation of H19 accelerates cell activity and decelerates cell apoptosis and resistance in CD133+ LCSCs in an oxidative stress (OS) dependent manner. Furthermore, ROS, MDA, and SOD are induced up-regulation through blocking MAPK/ERK signaling pathway, which stimulates OS.50
DILC
DILC is a noncoding protein gene seated in chromosome 13q34, with a full-length of 2394nt.51 DILC down-regulation enlarges the expression of markers and stem-related transcription factors and the formation of spheroid colonies in LCSCs, strengthening cancer cell tumorigenesis and tumor growth, advancing the tumor size and volume as well. DILC modulates the signal of IL-6/JAK2/STAT3/autocrine in EpCAM+CD24+ LCSCs. When DILC is down-regulated, IL-6 transcription and IL-6 autocrine signal are boosted by reducing the hybrid of DILC and IL-6 promoter to activate the IL-6/STAT3 pathway. Further, DILC controls the cross-linked signal between TNF-α/NF-κB and autocrine/IL-6/STAT3 cascade. NF-κB is activated in dependence on inflammatory factors and induced to the IL-6 promoter region. Low DILC expression reduces the competitive combination of DILC and the IL-6 promoter region, promoting IL-6 transcription and LCSCs expansion. Accordingly, DILC may exert an enormous function in joining liver inflammation and LCSCs expansion.51 Furthermore, emerging data support that a higher expression level of DILC has a lower recurrence rate and a higher survival rate.
Signaling Pathways of LncRNAs Regulating LCSCs
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
According to research reports, the evolutionary conserved Wnt/β-catenin pathway can mediate the regulation of varieties of lncRNAs on LCSCs, such as SAMMSON, lnc-β-Catm, lncPTV1, lncTCF7, and THOR.17,25,30,44,45 When the Wnt signal is absent, β-catenin is destroyed by the multi-protein complex containing two kinases of APC, Axin, WTX, and phosphorylated β-catenin. Then, it is ubiquitinated and eventually degraded by the proteasome. When the Wnt signal reaches the cell surface, the phosphorylation of β-catenin is sedated. Then β-catenin collects and is transferred to the nucleus furtherly. Finally, it integrates with the LEF/TCF factor to govern the expression of target genes.52–54 The active Wnt signaling pathway is associated with the HCC microenvironment and the stem cell characteristics obtained by tumor cells.55
Hedgehog Signaling Pathway
The Hedgehog pathway manages cell proliferation and differentiation during carcinogenesis.56 The competence of this pathway facilitates the expression of target genes about proliferation, angiogenesis, and stem cell self-renewal. Typically, in the absence of Hh ligands (IHh, SHh, and DHh), the PTCH1 protein restrains the Smo protein by inhibiting the transcription factor Gli. However, when the Hh ligand is present, the signaling pathway is activated, and the negative effect of PTCH1 on Smo is released. Next, multiplied expressed Gli is transferred to the nucleus furtherly to reinforce the transcription of the target genes.57,58 The Shh pathway sensitizes the expression of downstream genes of cell migration and invasion (SNAIL, MMPs, CHSY1), cell cycle tumor growth (cyclin B1, CDK, Bcl2), and CSCs markers (CD133).59 Several lines of evidence have testified that the Shh pathway is stimulated in many tumors and participates in the stemness maintenance of CSCs and drug tolerance, such as breast cancer, colon cancer, and liver cancer. Wu et al found that lncHDAC2 participates in governing LCSCs through this pathway.18 After the Shh pathway is activated in CSCs, the low expression of Shh mRNA and the high expression of Smo mRNA make HCC cells have more increased colony proliferation and clonal formation and help maintain the stemness of LCSCs.60
STAT3 Signaling Pathway
STAT3 exhibits a strong role in the generation, metastasis, drug resistance, and immune evasion of HCC and participates in the maintenance of the properties of LCSCs, which are principally modulated by different oncogenes. Recently, studies have found that lncARSR, lncDLX6-AS1, lncDILC can control LCSCs leaning on the STAT3 signaling pathway.20,23,51 STAT3 is provoked by multiple cytokines, including IL-6, IL-10, EGF, FGF, IGF, and other growth factors. Once these factors attach to the corresponding receptors, JAKs will also be excited, which phosphorylate STAT3 and the tyrosine residues of the receptor. Then, the SH2 domain of STAT3 links to the tyrosine residue of the receptor to form a homodimer that enters the nucleus, thereby exchanging the signals between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. After translocation to the nucleus, pSTAT3 forms a complex with some co-activators, including p68, to activate the transcription of the target genes.61
BMP Signaling Pathway
LncHAND2-AS1 is an activator of the BMP signaling pathway to maintain cell stemness and improve LCSCs proliferation, suggesting that BMP signaling mediates the regulation of lncRNAs on LCSCs.26 Evidence indicates that not only BMP2 and BMP4 are the key regulators of normal SCs and CSCs, but also BMP-9 can directly affect LCSCs.62 There are two ways to excite the BMP signaling pathway. In the classical pathway, mature BMP dimers bind to receptors, resulting in the transphosphorylation of the receptors. SMADs1/5/8 are recruited to the activated receptor complex and are phosphorylated. Subsequently, SMADs1/5/8 connect with SMAD4 to form a heterologous complex transported to the nucleus as a transcription factor. In the case of SMAD4 missing, BMPs can stimulate a non-classical pathway. The complexes of TAK1 and TAB 1 exert effect via BMP receptors (XIAP, BRAM1). TAK1 is a versatile MAPKKK that mediates p38-MAPK, ERK1/2-MAPK, JNK-MAPK, and NF-jB signaling pathways. Generally, stimulation of these pathways can accelerate tumor growth and drug resistance. Additionally, the PI3K/AKT pathway is activated by non-standard BMP signals either to promote cancer cell invasion and diffusion.63 BMP ligands also manipulate tumor differentiation, angiogenesis, and immune response and promote CSC expansion and survival.64
MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway
The MAPK/ERK signaling pathway pushes forward an immerse influence on numerous cancers, including inducing cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, making the components of the MAPK/ERK pathway potential targets of cancer treatment. The MAPK/ERK signaling pathway is also involved in the biological process of several lncRNAs acting on LCSCs, such as H19.50 The MAPK/ERK pathway, composed of three kinases, RAF, MEK, and ERK, is a signal transduction pathway, which mainly transmits extracellular signals into the cell. There are four different MAPK signal cascades involved in delivering extracellular stimuli, including ERK1/2, p38, JNK1/2/3, and ERK5, which perform functions through the small g protein RAS. RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK, the most important cascade, ultimately phosphorylates and activates JNK1/2/3. However, the effector protein p38, consisting of RAC (or Cdc42)-TAK1 (or MTK1)-MKK3/6 protein, is eventually provoked through the other parallel MAPK pathways. ERK1/2 kinase functions on the final signaling node of the MAPK/ERK pathway, regulating cell growth, differentiation, and metabolism.65–67
Hippo Signaling Pathway
The Hippo pathway is an evolutionarily conserved pathway. Remarkably, the excessive activation of transcriptional co-activator YAP/TAZ leads to uncontrolled cell growth and malignant transformation.68 NEAT1, one of the lncRNAs, work on LCSCs via this pathway.31 When the Hippo pathway is encouraged, Lats1/2-Mob1 is phosphorylated and started by Mst1/2. Eventually, YAP/TAZ is phosphorylated. Phosphorylated YAP/TAZ does not enter the nucleus to function, but it is degraded by 14-3-3 proteins. When the Hippo pathway is closed, YAP/TAZ gathers and combines with TEADs to form functional hybrid transcription factors that initiate targeted gene expression.69 Amounts of data highlight that YAP/TAZ can play a tumorigenic effect by enhancing the properties of CSCs, including drug resistance, EMT, and metastasis.70 LncRNAs influence mutually with the downstream effector YAP/TAZ or the upstream kinase MST1/LATS of the Hippo pathway, thereby acting on HCC and LCSCs.71 The impact of YAP/TAZ-lncRNAs interaction on LCSCs emphasizes its potential in a drug intervention.
LncRNAs and Signaling Pathways on LCSCs
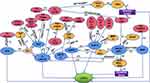
Notably, the regulation of lncRNAs on LCSCs is not independent but interrelated and constitutes a relatively complex regulatory network (Figure 1).
The GLI molecule as a communication medium between the SHH signaling pathway and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway has been reported.72 Moreover, through DP1, the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway inhibits the interaction between NOTCH signaling and YAP/TAZ of the HIPPO signaling pathway. In addition, the HIPPO signaling pathway can start the STAT3 signal.73,74 The dephosphorylation of STAT3 can be aroused by BMP10 in means of PTPRS, suggesting the positive relationship between the STAT3 signal and BMP signal.75 Evidence proves that through the TAK1/TAB 1 molecular mechanism, the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway is inspired by BMP, thereby interacting with the Hippo/Yap1 pathway in a C-MYC-dependent manner.63,76 Of note, accumulating investigations have demonstrated that the MAPK/ERK pathway is also cross-linked with other signaling pathways. For example, the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways can be motivated attributing to IN/IGF signaling molecules, and subsequently, the WNT/β-catenin and Notch signaling pathways are further animated.77 Several lncRNAs act on LCSCs through the above pathways. Consistently, lncRNAs have also been shown to interplay with each other, like HULC, H19, CUDR, and so on.33,34
Significantly, this complex network exerts an essential part in our understanding of the regulatory mechanism of lncRNAs on LCSCs that may arise from two-dimensional to three-dimensional.
Conclusions
LCSCs are considered to be responsible for the poor prognosis, recurrence, and incurability of HCC.4 However, the mechanism of self-renewal and malignant progression of LCSCs is not yet clear. Currently, accumulating studies have shown that lncRNAs may play a significant role in regulating the biological functions of LCSCs through the interaction of multiple molecules or signal transduction pathways. This article summarized the 20 lncRNAs involved in regulating LCSCs and the six signal pathways that mediate their regulatory effects discovered in the past six years. Surprisingly, we found that lncRNAs and various signaling pathways formed an across-linked network, allowing us to understand further the complexity of lncRNAs’ regulatory mechanism on LCSCs. However, the connection between LINC00324, DANCR, ICR, lncCAMTA1, HOTAIR, and this network needs to be further verified. Moreover, why the reverse differential expression of H19 on HCC and LCSC is still unknown. In this network system, the specific molecular mechanisms of the interactions between lncRNAs, molecules, and signaling pathways and how they precisely participate in the regulation of LCSCs are still great conundrums.
We believe that other lncRNAs and regulatory pathways or molecular mechanisms have not yet been unveiled. Undoubtedly, it requires us to do lots of research to enrich the complex network regulating LCSCs. Prospectively, the network system provides us a new treatment direction on LCSCs. Combination targeting therapy on the lncRNAs or molecular signaling pathways may become a new treatment method or a new adjuvant remedy to prolong survival and reduce the recurrence of HCC.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 81673728.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. doi:10.3322/caac.21492
2. Qin G, Dang M, Gao H, Wang H, Luo F, Chen R. Deciphering the protein-protein interaction network regulating hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017;1865(9):1114–1122. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2017.06.005
3. Batlle E, Clevers H. Cancer stem cells revisited. Nat Med. 2017;23(10):1124–1134. doi:10.1038/nm.4409
4. Nagano H, Ishii H, Marubashi S, et al. Novel therapeutic target for cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2012;19(6):600–605. doi:10.1007/s00534-012-0543-5
5. Rinn JL, Chang HY. Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81(1):145–166. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-051410-092902
6. Li X, Wu Z, Fu X, Han W. lncRNAs: insights into their function and mechanics in underlying disorders. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2014;762:1–21. doi:10.1016/j.mrrev.2014.04.002
7. Di Gesualdo F, Capaccioli S, Lulli M. A pathophysiological view of the long non-coding RNA world. Oncotarget. 2014;5(22):10976–10996. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.2770
8. Amaral PP, Leonardi T, Han N, et al. Genomic positional conservation identifies topological anchor point RNAs linked to developmental loci. Genome Biol. 2018;19(1):32. doi:10.1186/s13059-018-1405-5
9. Geisler S, Coller J. RNA in unexpected places: long non-coding RNA functions in diverse cellular contexts. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(11):699–712. doi:10.1038/nrm3679
10. Fernández-Ruiz I. Atherosclerosis: a new role for lncRNAs in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018;15(4):195. doi:10.1038/nrcardio.2018.18
11. Wu Q, Guo L, Jiang F, Li L, Li Z, Chen F. Analysis of the miRNA–mRNA–lncRNA networks in ER+ and ER− breast cancer cell lines. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(12):2874–2887. doi:10.1111/jcmm.12681
12. Kapusta A, Kronenberg Z, Lynch VJ, et al. Transposable elements are major contributors to the origin, diversification, and regulation of vertebrate long noncoding RNAs. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(4):e1003470. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003470
13. Wang C, Jiang X, Li X, et al. Long noncoding RNA HULC accelerates the growth of human liver cancer stem cells by upregulating CyclinD1 through miR675-PKM2 pathway via autophagy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):8. doi:10.1186/s13287-019-1528-y
14. Zou Z, Ma T, He X, et al. Long intergenic non-coding RNA 00324 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation via binding with HuR and stabilizing FAM83B expression. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(7):717. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0758-8
15. Gao J, Dai C, Yu X, Yin XB, Zhou F. Long noncoding RNA LINC00324 exerts protumorigenic effects on liver cancer stem cells by upregulating fas ligand via PU box binding protein. FASEB J. 2020;34(4):5800–5817. doi:10.1096/fj.201902705RR
16. Leucci E, Vendramin R, Spinazzi M, et al. Melanoma addiction to the long non-coding RNA SAMMSON. Nature. 2016;531(7595):518–522. doi:10.1038/nature17161
17. Xiaopeng L. The Role and Molecular Mechanisms of Long Non-Coding RNA SAMMSON Maintains Self-Renewal in Human Liver Cancer Stem Cells. Nanchang University; 2019.
18. Wu J, Zhu P, Lu T, et al. The long non-coding RNA LncHDAC2 drives the self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells via activation of hedgehog signaling. J Hepatol. 2019;70(5):918–929. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2018.12.015
19. Qu L, Ding J, Chen C. Exosome-transmitted lncARSR promotes sunitinib resistance in renal cancer by acting as a competing endogenous RNA. Cancer Cell. 2016;29(5):653–668. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.004
20. Yang C, Cai WC, Dong ZT, et al. lncARSR promotes liver cancer stem cells expansion via STAT3 pathway. Gene. 2019;687:73–81. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2018.10.087
21. Wang P, Mokhtari R, Pedrosa E, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated heterozygous knockout of the autism gene CHD8 and characterization of its transcriptional networks in cerebral organoids derived from iPS cells. Mol Autism. 2017;8(1):11. doi:10.1186/s13229-017-0124-1
22. Zhang L, He X, Jin T, Gang L, Jin Z. Long non-coding RNA DLX6-AS1 aggravates hepatocellular carcinoma carcinogenesis by modulating miR-203a/MMP-2 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;96:884–891. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.056
23. Wu DM, Zheng ZH, Zhang YB, et al. Down-regulated lncRNA DLX6-AS1 inhibits tumorigenesis through STAT3 signaling pathway by suppressing CADM1 promoter methylation in liver cancer stem cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):237. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1239-3
24. Hosono Y, Niknafs YS, Prensner JR, et al. Oncogenic role of THOR, a conserved cancer/testis long non-coding RNA. Cell. 2017;171(7):1559–1572.e1520. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.040
25. Cheng Z, Lei Z, Yang P, et al. Long non-coding RNA THOR promotes liver cancer stem cells expansion via β-catenin pathway. Gene. 2019;684:95–103. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2018.10.051
26. Yang Y, Chen L, Gu J, et al. Recurrently deregulated lncRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):14421. doi:10.1038/ncomms14421
27. Yang X, Wang CC, Lee WYW, Trovik J, Chung TKH, Kwong J. Long non-coding RNA HAND2-AS1 inhibits invasion and metastasis in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma through inactivating neuromedin U. Cancer Lett. 2018;413:23–34. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.10.028
28. Wang Y, Zhu P, Luo J, et al. LncRNA HAND2-AS1 promotes liver cancer stem cell self-renewal via BMP signaling. EMBO J. 2019;38(17):e101110. doi:10.15252/embj.2018101110
29. Guillou S, Beaumont J, Tamareille S, et al. Direct rivaroxaban-induced factor XA inhibition proves to be cardioprotective in rats. Shock. 2020;53(6):730–736. doi:10.1097/SHK.0000000000001412
30. Zhou L, Zhou X, Nie H, Xing R. Regulation of long non-coding RNA PVT1 on self-renewal of hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells through the activation of wnt signaling pathway. J China Pharm. 2019;22:1997–2002.
31. Cheng Z. Long Non-Coding RNA NEAT1 Regulate the Self-Renewal of Liver Cancer Stem Cells via the Hippo Signal Pathway. The Second Military Medical University; 2019.
32. Koyama S, Tsuchiya H, Amisaki M, et al. NEAT1 is required for the expression of the liver cancer stem cell marker CD44. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(6):1927. doi:10.3390/ijms21061927
33. Pu H, Zheng Q, Li H, et al. CUDR promotes liver cancer stem cell growth through upregulating TERT and C-Myc. Oncotarget. 2015;6(38):40775–40798. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.5805
34. Gui X, Li H, Li T, Pu H, Lu D. Long noncoding RNA CUDR regulates HULC and β-catenin to govern human liver stem cell malignant differentiation. Mol Ther. 2015;23(12):1843–1853. doi:10.1038/mt.2015.166
35. Li T, Zheng Q, An J, et al. SET1A cooperates with CUDR to promote liver cancer growth and hepatocyte-like stem cell malignant transformation epigenetically. Mol Ther. 2016;24(2):261–275. doi:10.1038/mt.2015.208
36. Kretz M, Webster DE, Flockhart RJ, et al. Suppression of progenitor differentiation requires the long noncoding RNA ANCR. Genes Dev. 2012;26(4):338–343. doi:10.1101/gad.182121.111
37. Yuan SX, Wang J, Yang F, et al. Long noncoding RNADANCR increases stemness features of hepatocellular carcinoma by derepression of CTNNB1. Hepatology. 2016;63(2):499–511. doi:10.1002/hep.27893
38. Guo W, Liu S, Cheng Y, et al. ICAM-1-related noncoding RNA in cancer stem cells maintains ICAM-1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(8):2041–2050. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-3106
39. Zhu P, Wang Y, Wu J, et al. LncBRM initiates YAP1 signalling activation to drive self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells. Nat Commun. 2016;7(1):13608. doi:10.1038/ncomms13608
40. Schraivogel D, Weinmann L, Beier D, et al. CAMTA1 is a novel tumour suppressor regulated by miR-9/9* in glioblastoma stem cells. EMBO J. 2011;30(20):4309–4322. doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.301
41. Henrich KO, Bauer T, Schulte J, et al. CAMTA1, a 1p36 tumor suppressor candidate, inhibits growth and activates differentiation programs in neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2011;71(8):3142–3151. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3014
42. Ha SY, Choi IH, Han J, et al. Pleural epithelioid hemangioendothelioma harboring CAMTA1 rearrangement. Lung Cancer. 2014;83(3):411–415. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.12.015
43. Ding LJ, Li Y, Wang SD. Long noncoding RNA lncCAMTA1 promotes proliferation and cancer stem cell-like properties of liver cancer by inhibiting CAMTA1. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(10):1617. doi:10.3390/ijms17101617
44. Zhu P, Wang Y, Huang G, et al. lnc-β-Catm elicits EZH2-dependent β-catenin stabilization and sustains liver CSC self-renewal. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016;23(7):631–639. doi:10.1038/nsmb.3235
45. Wang Y, He L, Du Y, et al. The long noncoding RNA lncTCF7 promotes self-renewal of human liver cancer stem cells through activation of Wnt signaling. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(4):413–425. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2015.03.003
46. Li H, An J, Wu M, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR promotes human liver cancer stem cell malignant growth through downregulation of SETD2. Oncotarget. 2015;6(29):27847–27864. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.4443
47. Raveh E, Matouk IJ, Gilon M, Hochberg A. The H19 long non-coding RNA in cancer initiation, progression and metastasis - a proposed unifying theory. Mol Cancer. 2015;14(1):184. doi:10.1186/s12943-015-0458-2
48. Yang ZW, Meng XX, Xu P. Central role of neutrophil in the pathogenesis of severe acute pancreatitis. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(11):2513–2520. doi:10.1111/jcmm.12639
49. Collins JF. Long noncoding RNAs and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(2):291–294. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2014.12.011
50. Ding K, Liao Y, Gong D, Zhao X, Ji W. Effect of long non-coding RNA H19 on oxidative stress and chemotherapy resistance of CD133+ cancer stem cells via the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;502(2):194–201. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.143
51. Wang X, Sun W, Shen W, et al. Long non-coding RNA DILC regulates liver cancer stem cells via IL-6/STAT3 axis. J Hepatol. 2016;64(6):1283–1294. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2016.01.019
52. Zhong Y, Katavolos P, Nguyen T, et al. Tankyrase inhibition causes reversible intestinal toxicity in mice with a therapeutic index. Toxicol Pathol. 2016;44(2):267–278. doi:10.1177/0192623315621192
53. Mariotti L, Pollock K, Guettler S. Regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signalling by tankyrase-dependent poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation and scaffolding. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(24):4611–4636. doi:10.1111/bph.14038
54. Tian Y, Mok MT, Yang P, Cheng AS. Epigenetic activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in NAFLD-associated hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancers (Basel). 2016;8(8):8. doi:10.3390/cancers8080076
55. Dhanasekaran R, Bandoh S, Roberts LR. Molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma and impact of therapeutic advances. F1000Res. 2016;5:879. doi:10.12688/f1000research.6946.1
56. Petrova R, Joyner AL. Roles for hedgehog signaling in adult organ homeostasis and repair. Development. 2014;141(18):3445–3457. doi:10.1242/dev.083691
57. Holtz AM, Griffiths SC, Davis SJ, Bishop B, Siebold C, Allen BL. Secreted HHIP1 interacts with heparan sulfate and regulates hedgehog ligand localization and function. J Cell Biol. 2015;209(5):739–757. doi:10.1083/jcb.201411024
58. Zhao Z, Lee RT, Pusapati GV, Iyu A, Rohatgi R, Ingham PW. An essential role for Grk2 in hedgehog signalling downstream of smoothened. EMBO Rep. 2016;17(5):739–752. doi:10.15252/embr.201541532
59. Jeng KS, Jeng CJ, Jeng WJ, et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway as a potential target to inhibit the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(5):4377–4384. doi:10.3892/ol.2019.10826
60. Tian F, Mysliwietz J, Ellwart J, Gamarra F, Huber RM, Bergner A. Effects of the hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449 on lung cancer cell lines are mediated by side populations. Clin Exp Med. 2012;12(1):25–30. doi:10.1007/s10238-011-0135-8
61. Siveen KS, Sikka S, Surana R, et al. Targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer: role of synthetic and natural inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1845(2):136–154. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2013.12.005
62. Jung JW, Yoon SM, Kim S, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-9 is a potent growth inhibitor of hepatocellular carcinoma and reduces the liver cancer stem cells population. Oncotarget. 2016;7(45):73754–73768. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.12062
63. Alarmo EL, Kallioniemi A. Bone morphogenetic proteins in breast cancer: dual role in tumourigenesis? Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010;17(2):R123–139. doi:10.1677/ERC-09-0273
64. Pickup MW, Owens P, Moses HL. TGF-β, bone morphogenetic protein, and activin signaling and the tumor microenvironment. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017;9(5):a022285. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a022285
65. Kurtzeborn K, Kwon HN, Kuure S. MAPK/ERK signaling in regulation of renal differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(7):1779. doi:10.3390/ijms20071779
66. Chappell WH, Steelman LS, Long JM, et al. Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR inhibitors: rationale and importance to inhibiting these pathways in human health. Oncotarget. 2011;2(3):135–164. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.240
67. Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, et al. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathways in controlling growth and sensitivity to therapy-implications for cancer and aging. Aging (Albany NY). 2011;3(3):192–222. doi:10.18632/aging.100296
68. Johnson R, Halder G. The two faces of hippo: targeting the Hippo pathway for regenerative medicine and cancer treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13(1):63–79. doi:10.1038/nrd4161
69. Zhang S, Zhou D. Role of the transcriptional coactivators YAP/TAZ in liver cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019;61:64–71. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2019.07.006
70. Park JH, Shin JE, Park HW. The role of hippo pathway in cancer stem cell biology. Mol Cells. 2018;41(2):83–92. doi:10.14348/molcells.2018.2242
71. Pan D. The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev Cell. 2010;19(4):491–505. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2010.09.011
72. Steinway SN, Zañudo JG, Ding W. Network modeling of TGFβ signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition reveals joint sonic hedgehog and Wnt pathway activation. Cancer Res. 2014;74(21):5963–5977. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0225
73. Kim W, Khan SK, Yang Y. Interacting network of Hippo, Wnt/β-catenin and notch signaling represses liver tumor formation. BMB Rep. 2017;50(1):1–2. doi:10.5483/BMBRep.2017.50.1.196
74. Kim W, Khan SK, Gvozdenovic-Jeremic J, et al. Hippo signaling interactions with Wnt/β-catenin and notch signaling repress liver tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(1):137–152. doi:10.1172/JCI88486
75. Yuan YM, Ma N, Zhang EB, et al. BMP10 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PTPRS-STAT3 axis. Oncogene. 2019;38(48):7281–7293. doi:10.1038/s41388-019-0943-y
76. Kapil S, Sharma BK, Patil M, et al. The cell polarity protein scrib functions as a tumor suppressor in liver cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(16):26515–26531. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.15713
77. Chung W, Kim M, de la Monte S, et al. Activation of signal transduction pathways during hepatic oncogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2016;370(1):1–9. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.09.016
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.