Back to Archived Journals » Botanics: Targets and Therapy » Volume 6
Remission roles of the herbal formula B401 in mice with manganese-induced neurotoxicity
Authors Hsu C , Wang S, Lin C , Sheu S, Wu C
Received 16 March 2016
Accepted for publication 7 June 2016
Published 25 August 2016 Volume 2016:6 Pages 75—88
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/BTAT.S108648
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Ayse Kuruuzum-Uz
Chih-Hsiang Hsu,1 Sheue-Er Wang,2 Ching-Lung Lin,1 Shuenn-Jyi Sheu,3 Chung-Hsin Wu1
1Department of Life Sciences, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei City, 2Department of Pathological Inspection, Saint Paul’s Hospital, Taoyuan City, 3Brion Research Institute of Taiwan, New Taipei City, Taiwan
Abstract: Excessive exposure to manganese (Mn), mainly by occupational inhalation, may cause brain and motor defects that are known as manganism. There are a few pharmacological studies aimed at treating the symptoms of manganism. The herbal formula B401 may serve as a new lead in ameliorating Mn-induced neurotoxicity. In this study, we aimed to investigate the possible protective mechanisms of the herbal formula B401 against Mn-induced neurotoxicity. Thirty-two ICR mice were divided into four groups that were administered sham treatment, B401 treatment, Mn treatment, and B401 plus Mn treatment, respectively (n=8 for each group). Rotarod performance was used in these mice to compare their motor coordination. In addition, chemiluminescence analysis was used to examine the reactive oxygen species in their blood. Furthermore, immunostaining and Western blotting techniques were used to examine the expression of dopaminergic receptors, dopamine, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and oxidative stress and apoptosis-related protein markers in their brain tissue. We found that the mice given Mn treatment showed brain and motor defects in comparison to the mice undergoing sham treatment. Immunostaining and Western blotting revealed that the mice given Mn treatment had reduced dopaminergic and BDNF expressions, but enhanced oxidative stress and apoptosis-related protein markers in their brain tissue. While the mice administered B401 plus Mn treatment had significantly improved motor coordination and enhanced dopaminergic and BDNF expressions, they showed reduced oxidative stress and apoptosis-related protein markers in their brain tissue in comparison with the mice given Mn treatment. Our findings provide evidence that oral B401 treatment may alleviate the symptoms of Mn-induced neurotoxicity in mice by enhancing dopaminergic and BDNF expressions and suppressing oxidative stress and apoptosis in their brain tissue. Therefore, we suggest that the herbal formula B401 may be developed as a potential health supplement for ameliorating Mn-induced neurotoxicity.
Keywords: manganism, neurodegeneration, motor disorder, dopaminergic receptor, dopamine, brain-derived neurotrophic
factor, oxidative stress, apoptosis
Introduction
Manganese (Mn) is an essential nutrient that functions as a cofactor in numerous enzymes that are critical to metabolic homeostasis in the brain. However, excessive exposure to Mn, mainly through occupational inhalation, may cause brain and motor defects that are known as manganism or Mn-induced parkinsonism.1–4 In addition, those people involved in the manufacturing of dry batteries, steel, aluminum, and welding metals are at a higher risk of Mn intoxication.5,6
The clinical symptoms of patients with Mn-induced neurotoxicity are monotone speech, tremor, rigidity, decreased hand dexterity, and gait and balance problem.7–9 As observed in animal and human studies, Mn-induced neurotoxicity is clearly associated with damage to basal ganglia structures.10–12 It has been reported that patients with Mn-induced neurotoxicity show markedly decreased dopaminergic levels in the striatum.13 In addition, it has been reported that Mn-induced neurotoxicity is mediated by enhanced free radical reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation, NMDA-mediated excitotoxicity, and neuronal apoptosis.14,15 Although there are many studies exploring the possible pathology of manganism in humans and animals, quite a few pharmacological studies focus on the clinical treatment of Mn-induced neurotoxicity.
In Taiwan, traditional Chinese medicines that are a composite formula of herbs have been used historically for treating a wide variety of brain disorders. The herbal formula B401 is a Taiwan–US patent formula and consists of six herbal ingredients. Currently, the herbal formula B401 has been widely used as a health supplement in supporting healthy neurovascular and cardiovascular functions. The neuroprotective function of the herbal formula B401 has been reported in Huntington’s disease, wherein it was found to protect the R6/2 mice from brain atrophy by enhancing the level of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), but suppressing the expression of markers of excitotoxicity, inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis.16,17 In our earlier studies, the herbal formula B401 was shown to alleviate penile toxicity by enhancing the synthesis of nitric oxide and angiogenesis, but suppressing the expression of markers of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in penile corpus cavernosum of Mn-treated mice with erectile dysfunction.18 In this sense, the herbal formula B401 may serve as a new lead in treating Mn-induced neurotoxicity.
Therefore, we aimed to study the protective potential of the herbal formula B401 against brain damage in mice with Mn-induced neurotoxicity. We used behavioral, immunohistochemical, and biochemical studies to assess the beneficial effects of the herbal formula B401 in complementary or integrated therapy for brain and motor defects in manganism.
Materials and methods
Chromatographic fingerprint analysis
A high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) fingerprint analysis was performed with acetonitrile from Burdick & Jackson (Gyeonggi-do, South Korea) and methanol from Avantor (Center Valley, PA, USA). All chemicals used were of analytical grade and were solubilized in distilled H2O/MeOH. Moreover, water purified from Milli-Q water purification system (EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) was used to dissolve the ingredients of the herbal formula B401 (US patent, No 7838048B2, November 23, 2010; Brion Research Institute of Taiwan, New Taipei City, Taiwan).
Cell viability assay
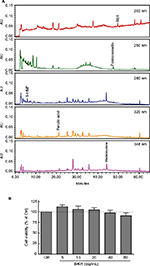
Human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells were grown at a density of 3.0×104 cells/well in 100 μL culture medium in a 96-well plate for 24 hours to reach ~60% confluence. Then the neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells were treated with vehicle, the herbal formula B401 (5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 mg/mL; Brion Research Institute of Taiwan). The number of viable cells was compared between the control and treated conditions. The culture medium was supplemented with 0.5 mg/mL of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT; Sigma-Aldrich Co., St Louis, MO, USA) for 3 hours, and then 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate/HCl buffer was added to each well. The number of viable cells was determined by the measurement of MTT absorbance at 570 nm using a microplate reader (Bio-Tek u-Quant Instrument, Winooski, VT, USA). The half-maximal inhibitory concentration of the herbal formula B401 was evaluated by MTT assay. Figure 1B shows that SH-SY5Y cells treated with the herbal formula B401 at a dose of <80 mg/mL had very less cytotoxicity. The cell viability assay was approved by the Committee on Biological Research of National Taiwan Normal University (NTNU) and implemented under the guidelines of the committee.
Animal preparation and monitoring
In this study, a total of 32 ICR mice at 4 months of age were divided into sham treatment group (n=8), Mn treatment group (n=8), the herbal formula B401 treatment group (n=8), and the herbal formula B401plus Mn treatment group (n=8). All mice were housed and maintained in a 12:12 hour light–dark cycle with water and food ad libitum. The mice in sham treatment group were fed with the same amount of distilled water without the herbal formula B401 and Mn. The mice in Mn treatment group were given an intraperitoneal injection of a single high dose of manganese chloride (100 mg/kg/day, the pH value was close to 7.0; Sigma-Aldrich Co.) for 5 days without oral B401 treatment. The mice in the herbal formula B401plus Mn treatment group were orally fed with B401 formulation (50 mg/kg, the pH value was close to 7.0; Brion Research Institute of Taiwan) twice per day for 5 days and then given an intraperitoneal injection of single high dose of manganese chloride (100 mg/kg/day, the pH value was close to 7.0; Sigma-Aldrich Co.) for 5 days. During the intraperitoneal injection of manganese chloride, these mice were fed with herbal formula B401 continuously. All doses of the herbal formula B401 were adjusted according to individual weight and water consumption, which was much lower than the dosage of half-maximal inhibitory concentration. Following treatments under different conditions, the motor performance was observed, the blood ROS was measured, and immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining and Western blotting were performed at the same time for the brain tissue. All protocols in this study were executed according to the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care International Animal Care (AAALAC) and Use Committee Guidebook. Animal experiment and drug trials on animals were approved by the Committee on Research of National Taiwan Normal University (Authorization NO. NTNU-104022) and implemented under the guidelines of the committee.
Rotarod performance
Rotarod performance was used to examine the motor coordination of the mice subjected to different treatments. The mice were tested on a rotarod apparatus (Ugo Basile, Varese, Italy) starting at 5 rpm and accelerating to 10 and 20 rpm over a period of 2 minutes, and then maintaining a constant speed of 5, 10, and 20 rpm. The mice were rested for 30 minutes between trials, and they were trained at 5 rpm for 10 minutes per day for 3 days after they were subjected to respective treatments, in order to become acquainted with the rotarod apparatus. The mice were tested three times per day for 3 days, and the latency period was recorded before the mice fell off the rotating rod.
ROS analysis
For determining the blood ROS levels in the mice undergoing different treatments, lucigenin- and luminol-amplified chemiluminescence (CL) methods were used to measure O2− radical and H2O2 activity. As described previously,17 the lucigenin-enhanced CL method provides a reliable assay for ROS. A heparinized 0.2 mL sample of whole blood was taken from the left femoral artery of each mouse. The blood ROS levels in mice were measured with a CL analyzer (CLA-ID3 chemiluminescence analyzer; Tohoku Electronic Industrial, Sendai, Japan) after mixing 1.0 mL of 0.1 mM lucigenin in phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.4) into the tested samples. The assay was duplicated for each sample, and the total CL counts in 180 seconds were calculated by integrating the area under the curve.
Histological and IHC stains
For brain histological and IHC stains, the anesthetized mice from different treatment groups were first cardiac perfused with phosphate-buffered saline containing 4% formaldehyde. Then the brain tissues of the mice were removed and fixed with 4% formaldehyde (EM grade). Brain specimens were embedded in paraffin and cut into tissue sections of thickness 5 μm. These brain tissue sections were then mounted on slides for histological and IHC stains. Brain morphology of the mice was assessed by using hematoxylin and eosin staining with a kit-based approach (Sigma-Aldrich Co.). By using the heat-induced epitope retrieval method, brain tissue sections were separately stained at room temperature for 1 hour with antibodies of D1 dopaminergic receptor (Abcam Cambridge, UK), BDNF (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA), superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) (Cell Signaling Technology Inc., Danvers, MA, USA), 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT) (Cell Signaling Technology Inc.), B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.), Bcl-2 associated X protein (BAX) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and caspase 3 (Cell Signaling Technology Inc.). As immunostaining controls for each antibody, serial 5 μm cross-sections were treated with the unanimous staining protocol. Immunostaining detection was performed by incubation with biotinylated secondary antibodies (NovolinkÔ polymer detection system l; Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd, Newcastle, UK) at room temperature for 30 minutes, and then by incubation with avidin–biotin–horseradish peroxidase complex (NovolinkÔ polymer detection system l) for an additional 30 minutes. Immunostaining visualization was performed with DAB Chromogen (NovolinkÔ polymer detection system l) and counterstained with hematoxylin (NovolinkÔ polymer detection system l).
Western blotting of brain
The removed brain tissue was homogenized in a buffer solution that was placed on ice for 1 hour and then centrifuged at 13,000 rpm at 4°C for another 20 minutes, causing the supernatant solution to separate. The separated solution was quantified by using a BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Proteins were separated on 12.5% or 15% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels (Bionovas Pharmaceuticals Inc., Washington, DC, USA) and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Barrington, IL, USA). The antibodies used in this study were α-tubulin (Thermo Fisher Scientific), dopamine and D1 dopaminergic receptor (Abcam Inc.), BDNF (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.), SOD 2 and 3-NT (Cell Signaling Technology Inc.), Bcl-2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.), BAX (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and caspase 3 (Cell Signaling Technology Inc.). Antibodies were detected using suitable horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.). The proteins’ immunoreactive bands were visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence (EMD Millipore) and the band intensities were quantified with ImageJ analysis software (version 1.48t, Wayne Rasband, Bethesda, Maryland, USA).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed with one- or two-way analysis of variance tests followed by Student–Newman–Keuls multiple comparisons post-test, and the results are shown as mean ± standard error of mean values. Results were considered significant at P<0.05. The number of samples was at least six independent experiments for cell viability assay and Western blotting analysis.
Results
Chromatographic fingerprint analysis of the herbal formula B401
The herbal formula B401 is composed of six herbal ingredients, including the extracts from Panax ginseng, Astragalus membranaceus, Angelica sinensis, Rehmannia glutinosa, Ligustri fructus, and Eclipta prostrata in specific ratios. HPLC charts of the ingredients of herbal formula B401 are shown in Figure 1A. These charts include ginsenoside Rb1 (molecular formula: C54H92O23; molecular weight: 1,109.3 g/mol; extracts from P. ginseng), formononetin (molecular formula: C16H12O4; molecular weight: 268.3 g/mol; extracts from As. membranaceus), 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (molecular formula: C6H6O3; molecular weight: 126.1 g/mol; extracts from R. glutinosa), ferulic acid (molecular formula: C10H10O4; molecular weight: 194.2 g/mol; extracts from L. fructus), and wedelolactone (molecular formula: C16H10O7; molecular weight: 314.3 g/mol; extracts from E. prostrata).
Oral B401 treatment improves motor coordination of Mn-treated mice
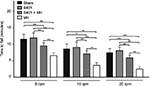
Effects of the herbal formula B401 on motor coordination were studied by examining the fall time records of rotorod test in accelerating mode. In the rotorod test with the speed accelerated gradually (5, 10, and 20 rpm), the fall time of all the mice shortened gradually irrespective of the treatment given. We observed that the fall time of Mn-treated mice was significantly shorter than that of mice in the sham group, B401-treated group, and B401 + Mn-treated group (Figure 2) (Mn vs sham, Mn vs B401, Mn vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01 for rotorod test speed at 5, 10, and 20 rpm). Also, we observed that the fall time of B401-treated mice was significantly longer than that of mice given B401 + Mn treatment (Figure 2) (B401 vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01–0.05 for rotorod test speed at 5, 10, and 20 rpm).
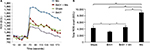
Oral B401 treatment enhances brain dopaminergic expressions of Mn-treated mice
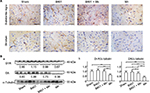
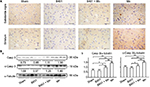
We examined the effects of the herbal formula B401 on brain dopaminergic expressions of Mn-treated mice (Figure 3). IHC staining showed that the expression of D1 receptors was obvious in the substantia nigra and the striatum of mice in the sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups, while it was not obvious in the same areas of Mn-treated mice (Figure 3A). Western blotting analysis showed that the quantified brain D1 receptor expression levels of Mn-treated mice were significantly lower than those of mice in the sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 3B) (Mn vs sham, Mn vs B401, Mn vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01). Also, we observed that the quantified brain D1 receptor expression levels in B401-treated mice were significantly higher than those of mice in the sham and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 3B) (B401 vs sham, B401 vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01).
We further compared the dopamine expression levels in the brain of mice subjected to different treatments (Figure 3B). Western blotting analysis showed that the quantified brain dopamine expression levels in Mn-treated mice were significantly lower than those in mice of sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 3B) (Mn vs sham, Mn vs B401, Mn vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01). Also, we observed that the quantified brain dopamine expression levels in B401-treated mice were significantly higher than in mice of sham and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 3B) (B401 vs sham, B401 vs B401 + Mn, P<0.05).
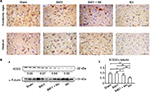
Oral B401 treatment enhances brain BDNF expression of Mn-treated mice
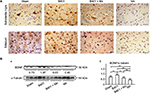
We evaluated the effects of the herbal formula B401 on brain BDNF expression levels of Mn-treated mice (Figure 4). IHC staining showed that the expression of BDNF was obvious in the substantia nigra and the striatum of mice in sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups, while they were not obvious in the same areas of mice subjected to Mn treatment (Figure 4A). Western blotting analysis showed that the quantified brain BDNF expression levels of Mn-treated mice were significantly lower than those in mice of sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 4B) (Mn vs sham, Mn vs B401, Mn vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01). Also, we observed that the quantified brain BDNF expression levels of B401-treated mice were significantly higher than those of mice in sham and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 4B) (B401 vs sham, B401 vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01).
Oral B401 treatment reduces blood ROS levels of Mn-treated mice
While comparing the effects of oral B401 treatment on oxidative stress, we examined blood ROS levels in Mn-treated mice with oral B401 treatment (Figure 5). We observed that blood ROS levels were much increased in Mn-treated mice than in mice of sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 5A). Furthermore, total counts of blood ROS were significantly increased in Mn-treated mice than in mice of sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 5B) (Mn vs sham, Mn vs B401, Mn vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01). Also, we observed that total counts of blood ROS were significantly decreased in B401-treated mice than in mice of sham and B401 + Mn-treated groups (Figure 5B) (B401 vs sham, B401 vs B401 + Mn, P<0.05).
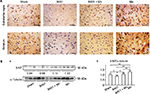
Oral B401 treatment alleviates brain oxidative stress of Mn-treated mice
Effects of the herbal formula B401 on brain oxidative stress were studied by comparing the brain SOD2 and 3-NT expressions in Mn-treated mice with and without oral B401 treatment (Figures 6 and 7). We compared the brain SOD2 expression levels of mice in the sham, B401, Mn, and B401 + Mn treatment groups. IHC staining showed that the SOD2 expression was obvious in the substantia nigra and the striatum of mice in the sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups, while it was not obvious in the same areas of Mn-treated mice (Figure 6A). Western blotting analysis showed that the quantified brain SOD2 expression levels of Mn-treated mice were significantly lower than those of mice in sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 6B) (Mn vs sham, Mn vs B401, Mn vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01). Also, we observed that the quantified brain SOD2 expression levels of sham- and B401-treated mice were significantly higher than those of mice given B401 + Mn treatment (Figure 6B) (sham vs B401 + Mn, B401 vs B401 + Mn, P<0.05).
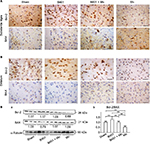
We further compared brain 3-NT expression levels of mice subjected to different treatments (Figure 7). IHC staining showed that 3-NT expression was obvious in the substantia nigra and the striatum of mice in Mn treatment group, while it was not obvious in the same areas of mice belonging to sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 7A). Western blotting analysis showed that the quantified brain 3-NT expression levels of Mn-treated mice were significantly higher than those of mice in sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 7B) (Mn vs sham, Mn vs B401, Mn s B401 + Mn, P<0.01). Also, we observed that the quantified brain 3-NT expression levels of B401-treated mice were significantly lesser than those of mice subjected to sham and B401 + Mn treatments (Figure 7B) (B401 vs sham, B401 vs B401 + Mn, P<0.05).
Oral B401 treatment alleviates brain apoptosis of Mn-treated mice
We examined the effects of the herbal formula B401 on apoptosis by comparing the ratio of Bcl-2/BAX and the expression levels of caspase 3 in the brain of Mn-treated mice (Figures 8 and 9). IHC staining revealed that Bcl-2 expression was obvious in the substantia nigra and the striatum of mice of sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups, while it was not obvious in the same areas of mice given Mn treatment (Figure 8A). On the contrary, BAX expression was obvious in the substantia nigra and the striatum of mice given Mn treatment, while it was not obvious in the same areas of mice of sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 8A). Western blotting analysis showed that the quantified brain Bcl-2/BAX ratios of Mn-treated mice were significantly lesser than those of mice in sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 8B) (Mn vs sham, Mn vs B401, Mn vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01). In addition, the quantified brain Bcl-2/BAX ratios of B401-treated mice were significantly higher than those of mice in sham and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 8B) (sham vs B401 + Mn, B401 vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01).
We further compared brain caspase 3 expression levels of mice subjected to different treatments (Figure 9). IHC staining showed that caspase 3 expression was obvious in the substantia nigra and the striatum of Mn-treated mice, while it was not obvious in the same areas of mice in sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 9A). Western blotting analysis showed that the quantified brain caspase 3 expression levels of Mn-treated mice were significantly higher than those of mice in sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 9B) (Mn vs sham, Mn vs B401, Mn vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01). In addition, the quantified brain caspase 3 expression levels of B401 + Mn-treated mice were significantly higher than those of mice in sham and B401 treatment groups (Figure 9B) (B401 + Mn vs sham, B401 + Mn vs B401, P<0.05). We further observed that the quantified brain cleaved caspase 3 expression levels were significantly higher than those of mice in sham, B401, and B401 + Mn treatment groups (Figure 9B) (Mn vs sham, Mn vs B401, Mn vs B401 + Mn, P<0.01). The quantified brain cleaved caspase 3 expression levels of B401 + Mn-treated mice were significantly higher than those of mice given B401 treatment (Figure 9B) (B401 + Mn vs B401, P<0.05).
Discussion
In this study, we demonstrated that chronic exposure to Mn induced oxidative and apoptotic signaling pathways and triggered behavioral dysfunction. Moreover, we showed that the herbal formula B401, a potent antioxidant, significantly attenuated blood ROS generation, and alleviated oxidative stress and apoptosis in the substantia nigra and the striatum. Therefore, our study could be profitably directed to determine the therapeutic efficacy of this agent in reducing Mn-induced neurotoxicity.
Mn is an essential metal for living organisms, but excessive Mn may lead to pathological processes characterized by irreversible damage in the brain.19 Mn is often accumulated in the basal ganglia, and in adults, it may cause parkinsonism.20 Compared to adults, younger people may accumulate more Mn in the brain and are more vulnerable to its toxicity.21,22 In this study, we found that Mn-treated mice had worsened motor coordination as shown by reduced fall time of the rotarod test. It was reported that Mn-induced neurotoxicity is characterized by extrapyramidal symptoms resembling idiopathic parkinsonism.23 Our study demonstrated that following Mn exposure, the mice showed a significant reduction of dopaminergic D1 receptors and dopamine levels in the substantia nigra and the striatum. These findings are consistent with a previous report demonstrating that Parkinson’s patients showed a significant decrease in dopamine synthesis and dopamine transporter levels in the substantia nigra.24
It has been reported that BDNF has potent effects on survival and morphology of dopaminergic neurons, and BDNF loss may contribute to death of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s patients.25 We also observed that mice with Mn-induced neurotoxicity had significantly reduced BDNF expression levels in the substantia nigra and the striatum. Reduction of BDNF expression might be one of the reasons for reduced dopaminergic D1 receptors and dopamine levels in the substantia nigra and the striatum of mice with Mn-induced neurotoxicity. Reduction of dopaminergic receptors and dopamine levels in the substantia nigra and the striatum may cause motor dysfunction. A previous study has reported that rats with Mn-induced neurotoxicity had motor impairment as shown by a reduction in fall time of the rotarod test and enhanced levels of oxidative stress due to increase in ROS generation.26 Even though the mechanisms are not fully understood, Mn-induced parkinsonism may be associated with mitochondrial dysfunction that causes ROS generation and oxidative stress in dopaminergic cells.27–30 In this study, we observed that mice with Mn-induced parkinsonism had increased blood ROS generation and reduced SOD2 expression, but elevated 3-NT expression in the substantia nigra and the striatum. SOD2 is an important antioxidant enzyme for oxidative stress, but 3-NT is a marker of oxidative damage.31 Therefore, oxidative stress is accepted as the critical factor in the pathogenesis of Mn-induced neurotoxicity.
Mn-induced oxidative stress may cause mitochondrial permeability transition and then leads to cell death in dopaminergic neurons.32 In the present study, we characterized the apoptotic mechanisms associated with Mn-induced parkinsonism in the brain tissue. We observed that Mn treatment targets the mitochondria and shifts the balance of Bcl-2 family proteins to favor apoptotic death in the neurons of the substantia nigra and the striatum. Immunoblotting and Western blotting analysis revealed that chronic exposure to Mn causes a decrease in the antiapoptotic Bcl-2 protein, but an increase in the proapoptotic BAX protein in the substantia nigra and the striatum. Furthermore, the Bcl-2/BAX ratio was also decreased significantly. To determine if the mitochondrial dysfunction would activate effector caspases, we assayed the activity of caspase 3 in the brain tissue of mice following chronic exposure to Mn. As shown in Figure 9, chronic exposure of mice to Mn causes a significant increase in caspase 3 expression in the substantia nigra and the striatum. Our results provide evidences that mitochondria-mediated apoptosis involves caspase cascades in the brain tissue of mice with Mn-induced parkinsonism. It has been reported that more active caspase 3–positive neurons were observed among dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s patients.33
Alternative medical applications of traditional Chinese medicines in neurodegenerative disease remission are becoming popular because of their reputed safety and clinical efficacy for chronic conditions. The most widely used type of herbal treatment is formulas that are composed of specific mixtures of several herbs. It is believed that complex interactions produce synergistic effects and a reduction in side effects and toxicity. For example, the herbal formula B401 contains six herbal ingredients, including the extracts from P. ginseng, As. membranaceus, An. sinensis, R. glutinosa, L. fructus, and E. prostrata in specific ratios. By MTT assay, we found less cytotoxicity in the herbal formula B401-containing SH-SY5Y cell culture at any concentration (not more than 80 mg/mL). In addition, we also found that the herbal formula B401 may alleviate excitotoxicity by increasing the cell viability in B401-containing glutamate-treated SH-SY5Y cell culture. As illustrated in HPLC fingerprint shown in Figure 1A, the active ingredients of the herbal formula B401 include ginsenoside Rb1 from P. ginseng, formononetin from A. membranaceus, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from R. glutinosa, ferulic acid from L. fructus, and wedelolactone from E. prostrata. Some of these compounds have been verified to have neuroprotective properties. For example, ginsenoside Rb1, which has been widely used as a traditional herbal medicine, has antioxidative and antiapoptotic effects in brain function.34 Furthermore, formononetin has been used to protect the brain by suppressing cellular excitotoxicity.35 It is unknown whether mixtures of the herbal formula B401 have more advantages than a single ingredient. Therefore, further studies are required to clarify the underlying molecular mechanism of components’ interaction and develop an appropriate system to allow evaluation of the ameliorative potential of such a herbal formula against Mn-induced neurotoxicity.
Conclusion
Here, we used oral treatment with the herbal formula B401 as an alternative medical application in remission of Mn-induced neurotoxicity. As summarized in Figure 10, we found that oral administration of B401 in Mn-treated mice significantly improved the motor coordination, reduced blood ROS, and enhanced the expression levels of dopaminergic receptors, dopamine, and BDNF, but suppressed oxidative stress (by upregulating SOD2 expression and downregulating 3-NT expression) and apoptosis (by upregulating Bcl-2/BAX ratio and downregulating caspase 3 expression) in the brain, especially in the substantia nigra and the striatum. Therefore, we suggest that the herbal formula B401 may be developed as a potential health supplement for ameliorating Mn-induced neurotoxicity.
Highlights
- We found that the herbal formula B401 alleviates neurotoxicity in Mn-treated mice.
- Neurotoxicity is alleviated by B401 in Mn-treated mice by enhancing the expression of dopaminergic receptor, dopamine, and BDNF, and suppressing oxidative stress and apoptosis.
- The herbal formula B401 can be developed as a potential health supplement for ameliorating Mn-induced neurotoxicity.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Industry-University Cooperative Grant of Brion Research Institute of Taiwan, Top University Project of NTNU, the foundation of Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST 104-2320-B-003-004), and the Transnational Research Centers Grant from NTNU (104T3040B04). The funding agency had no role in the study design, data collection, and analysis, and the decision to publish the manuscript.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Couper J. On the effects of black oxide of manganese when inhaled into the lungs. Br Ann Med Pharmacol. 1837;1:41–42. | ||
Huang CC, Chu NS, Lu CS, et al. Chronic manganese intoxication. Arch Neurol. 1989;46(10):1104–1106. | ||
Kawamura R, Ikuta H, Fukuzumi S, Yamada R, Tsubaki S, Kodama T, Kurata S. Intoxication by manganese in well water. Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1941;18:145–169. | ||
Mergler D, Huel G, Bowler R, et al. Nervous system dysfunction among workers with long-term exposure to manganese. Environ Res. 1994;64(2):151–180. | ||
Hauser RA, Zesiewicz TA, Rosemurgy AS, Martinez C, Olanow CW. Manganese intoxication and chronic liver failure. Ann Neurol. 1994;36(6):871–875. | ||
Krieger D, Krieger S, Jansen O, Gass P, Theilmann L, Lichtnecker H. Manganese and chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet. 1995;346(8970):270–274. | ||
Calne DB, Chu NS, Hung CC, Lu CS, Olanow W. Manganism and idiopathic parkinsonism: similarities and differences. Neurology. 1999;44(9):1583–1586. | ||
Olanow CW. Manganese-induced parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1012:209–223. | ||
Pal PK, Samii A, Calne DB. Manganese neurotoxicity: a review of clinical features, imaging and pathology. Neurotoxicity. 1999;20(2–3):227–238. | ||
Bernheimer H, Birkmayer W, Hornykiewicz O, Jellinger K, Seitelberger F. Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington. J Neurol Sci. 1973;20(4):415–455. | ||
Eriksson H, Magiste K, Olantin LO, et al. Effects of manganese oxide on monkeys as revealed by a combined neurochemical, histological and neurophysiological evaluation. Arch Toxicol. 1987;61:46–52. | ||
Yamada M, Ohno S, Okayasu I, et al. Chronic manganese poisoning: a neuropathological study with determination of manganese distribution in the brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;70(3–4):273–278. | ||
Mena I, Court J, Fuenzalida S, Papavasiliou PS, Cotzias GC. Modification of chronic manganese poisoning. N Engl J Med. 1970;282(1):5–10. | ||
Brouillet EPL, Shinobu U, McGarvey F, et al. Manganese injection into the rat striatum produces excitotoxic lesions by impairing energy metabolism. Exp Neurol. 1993;120(1):89–94. | ||
Maynard LS, Cotzias GC. The partition of manganese among organs, and intracellular organelles of the rat. J Biochem Chem. 1955;214(1):489–495. | ||
Wang SE, Lin CL, Hsu CH, Sheu SJ, Chien CT, Wu CH. Treatment of a herbal formula B401 enhances neuroprotection and angiogenesis in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:887–900. | ||
Wang SE, Lin CL, Hsu CH, Sheu SJ, Wu CH. Oral treatment with the herbal formula B401 protects against aging-dependent neurodegeneration by attenuating oxidative stress and apoptosis in the brain of R6/2 mice. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:1825–1837. | ||
Hsu CH, Lin CL, Wang SE, Sheu SJ, Chien CT, Wu CH. Oral treatment of a herbal formula B401 alleviates penile toxicity for aging mice with manganism via enhancing synthesis of nitric oxide and angiogenesis, and suppressing oxidative stress, inflammation and apotosis. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:1173–1187. | ||
Lazrishvili IL, Shukakidze AA, Chkhartishvili NN, Bikashvili TZ. Morphological changes and manganese content in the brains of rat pups subjected to subchronic poisoning with manganese chloride. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2009;39(1):7–12. | ||
Cordova FM, Aguiar AS Jr, Peres TV, et al. Manganese-exposed developing rats display motor deficits and striatal oxidative stress that are reversed by Trolox. Arch Toxicol. 2013;87(7):1231–1244. | ||
Keen CL, Ensunsa JL, Clegg MS. Manganese metabolism in animals and humans including the toxicity of manganese. Metal Ions Biol. 2000;37:89–121. | ||
Mergler D, Huel G, Bowler R, et al. Nervous system dysfunction among workers with long-term exposure to manganese. Environ Res. 1994;64(2):151–180. | ||
Roth JA. Are there common biochemical and molecular mechanisms controlling manganism and parkinsonism. Neuromolecular Med. 2009;11(4):281–296. | ||
Cummings JL, Henchcliffe C, Schaier S, Simuni T, Waxman A, Kemp P. The role of dopaminergic imaging in patients with symptoms of dopaminergic system neurodegeneration. Brain. 2011;134(Pt 11):3146–3166. | ||
Howells DW, Porritt MJ, Wong JY, Batchelor PE, Kalnins R, Hughes AJ, Donnan GA. Reduced BDNF mRNA expression in the Parkinson’s disease substantia nigra. Exp Neurol. 2000;166(1):127–135. | ||
Cordova FM, Aguiar AS Jr, Peres TV, et al. In vivo manganese exposure modulates erk, akt and darpp-32 in the striatum of developing rats, and impairs their motor function. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(3):e33057. | ||
Pennathur S, Jackson-Lewis V, Przedborski S, Heinecke JW. Mass spectrometric quantification of 3-nitrotyrosine, ortho-tyrosine, and o,o’-dityrosine in brain tissue of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3, 6-tetrahydropyridine-treated mice, a model of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(49):34621–34628. | ||
Tamm C, Sabri F, Ceccatelli S. Mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in neural stem cells exposed to manganese. Toxicol Sci. 2008;101(2):310–320. | ||
Yin Z, Aschner JL, dos Santos AP, Aschner M. Mitochondrial dependent manganese neurotoxicity in rat primary astrocyte cultures. Brain Res. 2008;1203:1–11. | ||
Zhang F, Xu Z, Gao J, Xu B, Deng Y. In vitro effect of manganese chloride exposure on energy metabolism and oxidative damage of mitochondria isolated from rat brain. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2008;26(2):232–236. | ||
Chong ZZ, Li F, Maiese K. Oxidative stress in the brain: novel cellular targets that govern survival during neurodegenerative disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2005;75(3):207–246. | ||
Tatton WG, Chalmers-Redman R, Brown D, Tatton N, Apoptosis in Parkinson’s disease: signals for neuronal degradation. Ann Neurol. 2003;53(Suppl 3):S61–S70. | ||
Hartmann A, Hunot S, Michel PP, et al. Caspase-3: A vulnerability factor and final effector in apoptotic death of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(6):2875–2880. | ||
Chen XC, Zhu YG, Zhu LA, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates dopamine-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by suppressing oxidative stress. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;473(1):1–7. | ||
Yu S, Li S, Yang H, Lee F, Wu JT, Qian MG. A novel liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry based depletion method for measuring red blood cell partitioning of pharmaceutical compounds in drug discovery. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2005;19(2):250–254. |
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.