Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 16
Recent Advances in Macrophage-Mediated Drug Delivery Systems
Authors Liang T, Zhang R, Liu X, Ding Q, Wu S, Li C, Lin Y, Ye Y, Zhong Z, Zhou M
Received 19 December 2020
Accepted for publication 14 February 2021
Published 7 April 2021 Volume 2021:16 Pages 2703—2714
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S298159
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Tiantian Liang,1,* Rongtao Zhang,1,* Xianbin Liu,1,* Qian Ding,1 Siqiong Wu,1 Chunhong Li,2 Yan Lin,2 Yun Ye,1 Zhirong Zhong,2 Meiling Zhou1
1Department of Pharmacy, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, 646000, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, 646000, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Correspondence: Meiling Zhou
Department of Pharmacy, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, No. 25, Taiping Street, Luzhou, Sichuan, 646000, People’s Republic of China
Email [email protected]
Zhirong Zhong
Department of Pharmaceutical, Sciences School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, No. 319 Zhongshan Road Jiangyang District, Luzhou, Sichuan, 646000, People’s Republic of China
Email [email protected]
Abstract: Macrophages have been extensively used in the development of drug delivery systems, as they can prolong the circulation and release of drugs, extend their half-life, increase their stability and targeting ability, and reduce immunogenicity. Moreover, they have good biocompatibility and degradability and offer abundant surface receptors for targeted delivery of a wide variety of drugs. Macrophage-mediated drug delivery systems can be prepared by loading drugs or drug-loaded nanoparticles into macrophages, macrophage membranes or macrophage-derived vesicles. Although such systems can be used to treat inflammation, cancer, HIV infection and other diseases, they require further research and optimization since they have been assembled from diverse sources and therefore can have quite different physical and chemical properties. Moreover, potential cell-drug interactions can limit their application, and the biological activity of membrane proteins might be lost during membrane extraction and storage. In this review, we summarize the recent advances in this field and discuss the preparation of macrophage-mediated drug delivery systems, their advantages over other delivery systems, their potential applications and future lines of research.
Keywords: macrophage, macrophage membranes, drug delivery systems, inflammation, tumor, biomimetic
Introduction
Most drugs used in the clinic have short half-lives, their concentration in blood fluctuates widely, they are not easily eliminated from the body, they show low targeting ability, and they elicit adverse reactions. To address these disadvantages, several chemical and biological carriers have been developed to serve as drug delivery systems. Among them, nano-drug delivery systems have attracted particular attention as drug, gene, or vaccine carriers because of their good biocompatibility, low toxicity, and controllable release in vivo.1 However, their applications have been limited so far because nanoformulations, like other exogenous biomaterials, are recognized by the immune system as invaders and are quickly eliminated from the circulation by the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS).2,3 Currently, the most common method to reduce clearance by MPS is to modify the surface of nanoparticles (NPs) with polyethylene glycol (PEG).4–6 However, PEGylated NPs may also induce the “accelerated blood clearance” (ABC) phenomenon in experimental animal models, which can greatly reduce their safety and effectiveness.7 Therefore, several challenges that hinder the clinical application of nano-agents, such as rapid clearance from the blood circulation and limited ability to overcome multiple physiological barriers, still need to be addressed.
In recent years, new biomimetic carriers have been developed for drug delivery to overcome the inherent limitations of nanomaterials, avoid recognition by the MPS, and prolong circulation time. In particular, cell-mediated drug delivery using red blood cells, neutrophils, macrophages, stem cells, lymphocytes and tumor cells has attracted extensive attention,8,9 as these cells can target blood vessels while evading immune system clearance, they remain relatively inert in the circulation, and they perform specific functions such as nutrient delivery to tissues, pathogen elimination, and targeted drug delivery.10 Biodegradable NPs coated with natural red blood cell membranes have also been developed, which persist in circulation for a long time and prevent the ABC effect of PEG.11,12
The pathogenesis of most diseases involves innate and adaptive immune responses, especially those related to the infiltration and transport of immune tissue cells. Macrophages are immune cells involved mainly in innate and adaptive immunity. In response to inflammation, macrophages are activated and they concentrate at the inflammation site, where their main function is to phagocytose and digest cell debris and pathogens, as well as activate lymphocytes or other immune cells.13–15 A large number of macrophages infiltrates the tumor microenvironment, significantly affecting tumor growth, metastasis, and drug therapy.16,17
These properties make macrophages good carriers of small-molecule drugs or macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Biomimetically modified drug delivery systems using macrophages, macrophage membranes or macrophage-derived vesicles harness the long circulation time, abundant surface receptors, and active targeting ability of macrophages. They show great potential to overcome the low biocompatibility, short cycle time, and undesirable immunogenicity of common carrier materials. In this review, we summarize the development, sources, advantages, drug-loading methods, and potential clinical applications of macrophage-mediated drug delivery systems. This may provide a reference for further research.
Development of Macrophage-Mediated Drug Delivery Systems
A macrophage-mediated nanoparticle delivery system for antiretroviral drugs was first reported in 2006.18 A similar approach using mononuclear macrophages was also applied to transport therapeutic NPs to tumor sites,19 as well as to deliver drugs for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.20 Nanoporous silicon particles were later encapsulated with purified mononuclear macrophage membranes, resulting in materials with macrophage-like functions.21 Based on these encouraging findings, the application of macrophages as carriers for the delivery of drugs with different properties has been significantly expanded in order to study and treat various conditions such as cancer,22 inflammation,23 and HIV infection24 (Table 1).
 |
Table 1 Macrophage-Mediated Drug Delivery Systems |
Sources of Macrophages
Monocytes circulate in the blood and can cross the endothelial barrier to differentiate into tissue macrophages, also known as mononuclear macrophages.25,26 Two major classes of macrophages have been studied: primary macrophages extracted from animals, which include mainly bone marrow-derived macrophages,27,28 alveolar macrophages,29 and peritoneal macrophages;30 and macrophages cultured in cell banks, including mouse mononuclear macrophage leukemia cells (RAW 264.7),31,32 mouse mononuclear macrophages (J774A.1),33 and human acute mononuclear leukemia cells (THP-1).34
Advantages of Macrophage-Mediated Drug Delivery Systems
Prolongation of Drug Circulation Time and Half-Life
Generally, the lifespan of macrophages ranges from several months to years, which is longer than the circulation time of conventional drug carriers in the body. Macrophages, as immune circulating cells, are part of the MPS, so macrophage-mediated drug delivery systems can be recognized as “self” by the host.23 Therefore, drug-carrying macrophages can escape host defense mechanisms, thus extending a drug’s circulation time and half-life. For instance, NPs encapsulated in macrophage-derived microvesicles prepared for the targeted treatment of rheumatoid arthritis remained at the lesion site for more than 24 h after administration, significantly longer than that of naked NPs, indicating that they can extend the half-life of the drug.23 In another approach, gold nanoshells coated with macrophage membranes were used to enhance the photothermal treatment effect of tumors.35 Naked nanoshells disappeared nearly completely from the blood by 24 h post-injection, but 30% of membrane-coated nanoshells could still be detected after 48 h (Figure 1). Therefore, macrophages can be used effectively as drug carriers to prolong the circulation time and half-life of drugs, reducing the frequency of drug administration.
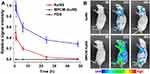 |
Figure 1 (A) In vivo circulation time and (B) accumulation of naked or membrane-coated gold nanoshells at tumor sites. Abbreviations: AuNS, naked gold nanoshells; MPCM-AuNS, gold nanoshells coated with macrophage membranes; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline. Notes: Reprinted with permission from Xuan M, Shao J, Dai L, Li J, He Q. Macrophage cell membrane camouflaged Au nanoshells for in vivo prolonged circulation life and enhanced cancer photothermal therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(15):9610–9618. Copyright (2016) American Chemical Society.35 |
Good Biocompatibility and Biodegradability
Nano-drug delivery systems based on polymer materials have always attracted attention for biomedical applications because of their potential biocompatibility and biodegradability. However, existing polymer materials are not completely inert, which prevents their clinical application as drug carriers.36 Therefore, macrophages have been used to replace polymer materials due to their potentially higher biocompatibility and ability to be fully metabolized into safe, non-toxic products. For example, iron oxide NPs coated with macrophage membranes have been found not to affect body weight or blood biochemistry of ICR mice up to 30 days after intravenous injection, nor did pathology reveal obvious toxicity to major organs.37
Improvement of Drug Stability and Low Immunogenicity
Given that macrophages, as immune cells, can escape phagocytosis by MPS, loading drugs into those cells can also protect the drugs from phagocytosis. In addition, the macrophage cell membranes can protect the loaded drugs from premature inactivation and degradation by endogenous factors. Studies have shown that membrane-wrapped nanoporous silicon particles can effectively escape immune system surveillance, avoid the action of opsonins, delay uptake by MPS, bind preferentially to inflammatory endothelial cells, and promote the transport of drugs to endothelial cells while avoiding the lysosomal pathway.21 Recently, loading doxorubicin (DOX) into mesoporous silica nanocapsules encapsulated by macrophage cell membranes was shown to reduce uptake of the drug and allow the NPs to evade the immune response.38 Therefore, biomimetic drug delivery systems based on macrophage membrane-wrapped drugs can increase drug stability and reduce immunogenicity.
Sustained Drug Release
Macrophage cell membranes are flexible, semi-permeable and composed of phospholipids. Their main function is to selectively exchange substances, absorb nutrients, discharge metabolic waste, as well as secrete and transport proteins.39 Τhe loading of drugs into macrophages can result in slow and continuous drug release. For example, loading DOX into mesoporous silica nanocapsules resulted in sustained release of the drug for more than 72 h due to the diffusion barrier provided by the macrophage membranes.38 Loading the enzyme catalase into a macrophage-nanozyme delivery system, which may be a treatment against Parkinson’s disease, allowed it to be released in a catalytically active form for more than 24 h, whereas naked catalase was rapidly degraded.20 Indeed, macrophages can serve as “nanozymes” to allow slow release of enzymes into the blood.27 Therefore, macrophage-mediated drug delivery systems can be used to effectively prolong the release time of a drug, significantly reduce the fluctuation of drug concentration in the blood, and improve drug efficacy.
Improvement of Drug Targeting Ability
The targeting ability of most drugs is low, causing a series of toxic side effects. Loading drugs into NPs may reduce such effects, but naked NPs can be easily phagocytosed and cleared by MPS, as they lack active targeting properties. Macrophages, as circulating guards, can home to inflammatory sites and tumors, while helping their cargo avoid the body’s defense mechanisms.40 Macrophage-mediated drug delivery systems display the same surface receptors and proteins as the original macrophages from which they were produced, and these surface proteins can interact with desired targets. For instance, the membrane proteins CD14 and TLR4 bind lipopolysaccharide,41 and CD44 and Mac-1 bind inflamed endothelium expressing abundant P-selectin and ICAM-1.23 Several membrane receptors bind proinflammatory cytokines: CD120a and CD120b bind tumor necrosis factor (TNF); CD126 and CD130, interleukin 6 (IL-6); and CD119, interferon-γ (IFN-γ).41 These interactions help recruit macrophages to tumor sites, since the tumor microenvironment often resembles a situation of chronic inflammation.42 Through such surface receptors, macrophage-mediated drug delivery systems can deliver their cargo deep into the hypoxic regions of tumors.43 In one study, wrapping drug-loaded liposomes with macrophage cell membrane led to anti-breast tumor activity that was nearly double that of naked liposomes.44 Another study confirmed the ability of the macrophage membrane to target NPs to tumors by comparing the intratumor fluorescence signal between “upconversion” NPs with or without a membrane wrapping.45
Delivery of Various Substances
Several studies have demonstrated that macrophages can be used to efficiently deliver a wide variety of substances. For example, macrophage membranes can encapsulate poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) NPs,41 liposomes,44 chitosan,46 Au NPs,35 Fe3O4 NPs,37 and SiO2 NPs.38 Macrophages can also be loaded with nanozymes20 and various natural small-molecule drugs under conditions that preserve their biological activity.
Drug-Loading Methods for Macrophage-Mediated Drug Delivery Systems
Direct Loading of Drugs or Drug-Loaded NPs into Macrophages
Incubation
Incubation is the oldest and most commonly used method to load drugs into macrophages. Macrophages are incubated with drugs or drug-loaded NPs under appropriate culture conditions, and the macrophages phagocytose the drugs.20,29
Adhesion
In order to develop drug delivery systems that can successfully encapsulate and release drugs in a controlled manner, researchers used a phagocytosis-resistant “cellular backpack”, which is a thin film prepared via a layer-by-layer spray deposition technique.47,48 Different backpack layers were loaded with different substances and attached to macrophages, forming cell nanocomplexes that not only retained the native cell functions, but also targeted solid tumors47 and brain disorders.48 Backpack adhesion did not affect macrophage health or proliferation, suggesting that the approach does not show undesired toxicity.
Low Permeability Resealing
Target-specific delivery systems limit the in vivo degradation of antioxidant enzymes, which are good therapeutic agents. For example, the membrane-impermeable enzyme catalase was packaged into THP-1 cells using this method.49 The enzyme’s antioxidant activity was boosted by the resulting targeting ability.
Electroporation
Electroporation can increase drug loading without requiring cells to phagocytose it. In one study, for example, macrophages were suspended in electroporation buffer containing DOX and transferred to an electroporation tube.50 The cells were electroporated, and DOX diffused into the cells through the small pores. This system can be quite reproducible, fast and cost-effective.
Encapsulation of Drugs or Drug-Loaded NPs Within Macrophage Membranes or Macrophage-Derived Vesicles
Encapsulation Within Macrophage Membranes
There are about 1000 types of proteins in the macrophage membrane, many of which recognize specific inflammatory factors and tumor cells and play a leading role in biological functions.51 The structure and activity of these proteins must be maintained during extraction and purification of the membranes in order to ensure that the resulting drug delivery system acquires macrophage properties.41 Since macrophages contain nuclei, numerous organelles, and lysozymes, the extraction of the macrophage membrane requires a combination of hypo-osmotic swelling, mechanical destruction, and several gradient centrifugation steps to remove unruptured cells and cell contents. Protease inhibitors should also be added to prevent degradation of the membrane proteins, while the entire extraction process should be performed at low temperature to prevent inactivation of the membrane proteins.41 Subsequently, the membranes are wrapped onto the surface of the drug or drug-loaded NPs using ultrasonication and/or multiple mechanical extrusions, and the spherical core–shell structure can be observed by transmission electron microscopy. Hence, macrophage membrane-mediated drug delivery systems combine the drug core with the macrophage membrane, which not only compensates for the rapid clearance of drugs in vivo, but also exploits the functional properties of the membrane.41,52
Encapsulation Inside Macrophage-Derived Vesicles
In order to avoid the complex and inefficient macrophage membrane extraction method, which involves cell fragmentation, density gradient centrifugation, and ultracentrifugation steps, macrophage-derived vesicles can be used.53,54 Macrophages are cultured in serum-free medium and stimulated using cytochalasin B to secrete macrophage-derived vesicles.23 The vesicles are purified through multiple gradient centrifugation cycles. Using this approach, researchers have encapsulated drug-loaded NPs into vesicles for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Proteomic analysis showed that their membrane proteins were similar to those of the macrophage membrane, suggesting that their biological activities would also be similar. Macrophage vesicle-encapsulated DOX and paclitaxel (PTX) may be effective against triple-negative breast cancer.53
Applications of Macrophage-Mediated Drug Delivery Systems
Anti-Inflammatory Treatment
Inflammation is the body’s main defense against injury. When inflammation occurs, a large number of monocytes move to the lesion site and differentiate into macrophages, which regulate inflammatory processes.26 Macrophages have been used as therapeutic agents or drug carriers to target inflammatory sites and regulate the inflammatory response.
Therapeutic Agents
When inflammation occurs, macrophages at the site of inflammation produce a large number of pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-6 and INF-γ, which recruit more macrophages in the circulatory system. Macrophage-mediated drug delivery systems can retain the key membrane proteins of the source cells, such as CD14 and TLR4, as well as the related cytokine binding receptors, which can be confirmed using Western blot analysis. In fact, the membrane derivatization process leads to the significant enrichment of these molecules.41 Therefore, macrophage membrane-coated empty NPs can, like the source macrophages, bind endotoxins and cytokines, inhibiting downstream inflammatory cascades. Such NPs as therapeutic agents can, for example, improve the survival of septic mice previously injected intraperitoneally with Escherichia coli.41 In another study with septic mice, macrophage-derived biomimetic NPs without any drug, called leukosomes, interacted with macrophages to down-regulate pro-inflammatory genes (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α) and up-regulate anti-inflammatory genes (IL-10 and TGF-β), thereby prolonging survival.55
Drug Delivery
A dexamethasone-loaded drug delivery system, prepared using the incubation method, inhibited NF-κB activity and therefore inflammation to a similar extent as a 5-fold higher concentration of dexamethasone.56 The dexamethasone-loaded system also significantly reduced kidney inflammation and fibrosis in mice with nephropathy, and it significantly reduced the side effects of chronic glucocorticoid therapy. Li et al prepared macrophage-derived microvesicle-coated tacrolimus-loaded nanoparticles (MNPs).23 CD44 and Mac-1 on the surface of the MNPs bound to P-selectin and ICAM-1 on endothelial cells in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis (Figure 2). In this way, MNPs increased the anti-inflammatory effect of tacrolimus and significantly inhibited arthritis progression. These results illustrate how macrophage-mediated drug delivery systems can enhance the anti-inflammatory efficacy of drugs.
 |
Figure 2 Schematic of the macrophage-derived microvesicle-coated tacrolimus-loaded nanoparticles (MNPs). MNPs could target sites of rheumatoid arthritis through bound to P-selectin or ICAM-1 on endothelial cells. Notes: Reprinted with permission from Li R, He Y, Zhu Y, et al. Route to rheumatoid arthritis by macrophage-derived microvesicle-coated nanoparticles. Nano letters. 2019; 19(1):124–134. Copyright (2019) American Chemical Society.23 |
Anti-Tumor Therapy
Macrophages can phagocytose and digest foreign substances, thus removing harmful substances, including cell debris and tumor cells. The tumor microenvironment includes a large number of infiltrated macrophages, known as tumor-associated macrophages, which significantly affect tumor growth, metastasis, and drug therapy.42,57 At present, clinical anti-tumor drugs lack tumor targeting and cause substantial side effects. To limit these disadvantages, the encapsulation of common anti-tumor drugs such as PTX and DOX into macrophages has been investigated.53,58,59 Macrophages on their own have been explored as therapeutic agents. Appropriately loaded macrophages have also been explored for drug delivery, photothermal therapy (PTT) against tumors and for tumor imaging.
Anti-Tumor Therapeutic Agents
Macrophages are highly plastic and have different phenotypes in different environments, leading them to different functions. M1 and M2 are important phenotypes of macrophages.60,61 M1 macrophages initiate cytokine production in the tumor microenvironment, recruiting immune cells that promote an immune response against tumor cells. In contrast, M2 macrophages regulate the extracellular matrix, promote angiogenesis and suppress immune responses and thereby promote tumor progression and metastasis.
Sun et al demonstrated how macrophage phenotype could be exploited to exert anti-tumor effects: treating macrophages with an inhibitor of the colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor polarized them to the M1 phenotype, stimulating phagocytosis of tumor cells.62 Bioinformatics studies have suggested that macrophages can influence multicellular gene networks in the microenvironment of gliomas.63,64 Transmembrane TNF-α is an important cytokine with anti-proliferation activity. In one study, empty chitosan NPs were encapsulated inside the membrane of TNF-α-expressing macrophages, and the resulting particles significantly inhibited cancer proliferation.46 These examples illustrate how macrophages on their own can act as therapeutic agents in the tumor microenvironment.
Anti-Tumor Drug Delivery
Due to the intrinsic homing characteristics of macrophages, they can pass through the endothelial barrier and migrate to tumor sites. DOX has been loaded into a macrophage biomimetic delivery system to allow its controlled release without affecting its activity, and this system effectively inhibited growth and metastasis of 4T1 breast cancer cells in mice and prolonged their survival.65 Macrophage membrane-camouflaged liposomes and hollow bismuth selenide NPs were prepared as drug delivery systems and shown to effectively inhibit breast cancer lung metastasis.44,66 An M1 macrophage-biomimetic drug delivery system was able to treat glioma, and its efficacy reflected the strong phagocytic ability and good drug loading characteristic of the M1 phenotype.67 By exploiting the extracellular vehicles known as exosomes, which are secreted by nearly all cells and have specific surface markers,68 one study prepared exosomes from M1 macrophages and loaded them with PTX to prepare the nano-formulation PTX-M1-Exos.69 The formulation enhanced the antitumor efficacy of PTX by activating the nuclear factor-κB pathway and creating a proinflammatory environment. Another study used electroporation to prepare cisplatin-loaded exosomes from M1 macrophages, which enhanced the free drug’s efficacy against lung cancer.70
Photothermal Therapy (PTT)
In photothermal therapy, materials with high photothermal conversion efficiency are used to convert light into heat energy after irradiation with an external light source (usually near-infrared light), and the heat kills nearby cancer cells.71 Various nanomaterials with good photothermal conversion properties have been reported, such as graphene oxide nanosheets,72 carbon nanotubes,73 and gold nanorods.74 Encapsulating such materials with macrophage membranes can lead to drug delivery systems with good photothermal conversion ability, biocompatibility, ability to escape immune responses, and ability to target tumors. This has been demonstrated using gold nanoshells against breast cancer (Figure 3),35 and using reduced graphene oxide loaded with DOX.75 In the latter case, chemical modification of the graphene oxide nanosheets increased their photothermal conversion efficiency.
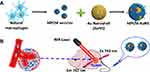 |
Figure 3 (A) Schematic illustration of the preparation and (B) in vivo photothermal cancer therapy of macrophage cell membrane (MPCM)-camouflaged Au nanoshells (MPCM-AuNS). Notes: Reprinted with permission from Xuan M, Shao J, Dai L, Li J, He Q. Macrophage cell membrane camouflaged Au nanoshells for in vivo prolonged circulation life and enhanced cancer photothermal therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(15):9610–9618. Copyright (2016) American Chemical Society.35 |
Tumor Imaging
Fluorescence-based imaging of tumors is of great significance for the early detection of cancer and the study of cancer metastases. However, traditional imaging agents rely mainly on tumor penetration and retention effects to achieve passive tumor targeting in vivo, which greatly limits the possibilities for tumor imaging. Wrapping upconversion NPs with macrophage vesicles allows them to adhere to macrophages and thereby target tumors, improving tumor imaging.45
Anti-HIV Therapy
The HIV virus can decimate the population of CD4 T-lymphocytes in the human immune system, significantly reducing immune function. Indinavir, a specific inhibitor of HIV protease, has been encapsulated within bone marrow-derived macrophages, and in one study in mice, this formulation led to continuously increasing drug levels in tissues, serum, and urine for 10 days, giving rise to a sustained antiretroviral response and immune reconstitution that lasted up to 14 days.18 This formulation also reduced the load of HIV-1 virus in the mouse brain,76 which may reduce the risk of neurological complications of HIV infection.
Treatment of Other Diseases
Macrophages have been used for the delivery of catalase, which effectively crosses the blood–brain barrier and significantly reduces the neuroinflammation and degeneration of substantia nigra in mice with Parkinson’s disease, thus achieving active targeting therapy.20,27,77
Bacterial recognition receptors on the macrophage membrane can recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns in bacteria. Therefore, macrophages have been co-cultured with bacteria to significantly increase the expression of recognition receptors on the macrophage membrane.78 These membranes were then wrapped around gold–silver nanocages to generate a biocompatible nano-drug delivery system that targeted those bacteria at sites of infection after local or systemic injection.
Atherosclerosis is a typical vascular disease, and macrophages play an important role in the pathological progression of atherosclerosis.79 Macrophage-mediated drug delivery can be targeted to atherosclerotic lesions by exploiting the specific recognition between integrin α4β1 on the macrophage membrane and the atherosclerotic vascular adhesion molecule VCAM-1. In one study, this system targeted endothelial cells, in which it eliminated more than 90% of reactive oxygen species.49 Subsequently, macrophage membranes were found to improve not only the targeted delivery of NPs to the lesion site, but also to scavenge pro-inflammatory factors and thereby treat atherosclerosis.80
Amphotericin B has been encapsulated in macrophage membrane vesicles for the treatment of intracellular parasites.81 This system showed excellent biocompatibility and reduced the drug’s inherent toxicity, while allowing a lower dose to be used to achieve the same therapeutic effect.
Summary
Macrophages are phagocytic cells in the human immune system with key roles in injury, inflammation, and cancer. Macrophage-mediated drug delivery offers many advantages over traditional drug delivery methods, but the heterogeneity among macrophages used to build such delivery systems has limited their clinical application. In addition, how macrophages interact with drug cargo is unclear, so it is difficult to predict whether the drug will be degraded by endolysin. To ensure that macrophage-mediated delivery systems retain the inherent functions of macrophages, membrane surface proteins must be protected during extraction of the macrophage membrane, and more research is needed into how to achieve this. Storing macrophages in a way that preserves their biological activity remains a major obstacle to large-scale production. Future work addressing these challenges may bring macrophage-mediated drug delivery closer to the clinic.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2018RZ0120, 2020YFS0313), the Key Program of Southwest Medical University (2019ZZD020), and the Collaborative Project of Luzhou Government and Southwest Medical University (2018LZXNYD-PT02).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Patra JK, Das G, Fraceto LF, et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J Nanobiotechnol. 2018;16. doi:10.1186/s12951-018-0392-8
2. García KP, Zarschler K, Barbaro L, et al. Zwitterionic coatings: zwitterionic-coated “stealth” nanoparticles for biomedical applications: recent advances in countering biomolecular corona formation and uptake by the mononuclear phagocyte system. Small. 2014;13:2516–2529. doi:10.1002/smll.201303540
3. Tsoi KM, Macparland SA, Ma X-Z, et al. Mechanism of hard-nanomaterial clearance by the liver. Nat Mater. 2016;15(11):1212–1221. doi:10.1038/nmat4718
4. Kolate A, Baradia D, Patil S, et al. PEG — a versatile conjugating ligand for drugs and drug delivery systems. J Control Release. 2014;192:67–81. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.06.046
5. Li C, Wang X, Li R, et al. Resveratrol-loaded PLGA nanoparticles functionalized with red blood cell membranes as a biomimetic delivery system for prolonged circulation time. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2019;54:101369. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101369
6. Zhang Z, Chu Y, Li C, et al. Anti-PEG scFv corona ameliorates accelerated blood clearance phenomenon of PEGylated nanomedicines. J Control Release. 2020;330:493–501. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.12.047
7. Elsadek NE, Lila ASA, Emam SE, et al. Pegfilgrastim (PEG-G-CSF) induces anti-PEG IgM in a dose dependent manner and causes the accelerated blood clearance (ABC) phenomenon upon repeated administration in mice. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020;152:56–62. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.04.026
8. Ayer M, Klok HA. Cell-mediated delivery of synthetic nano- and microparticles. J Control Release. 2017;259:92–104. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.01.048
9. Yu H, Yang Z, Li F, Xu L, Sun Y. Cell-mediated targeting drugs delivery systems. Drug Deliv. 2020;27(1):1425–1437. doi:10.1080/10717544.2020.1831103
10. Anselmo AC, Mitragotri S. Cell-mediated delivery of nanoparticles: taking advantage of circulatory cells to target nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2014;190:531–541. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.03.050
11. Hu CMJ, Zhang L, Aryal S, Cheung C, Fang RH, Zhang L. Erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged polymeric nanoparticles as a biomimetic delivery platform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(27):10980–10985. doi:10.1073/pnas.1106634108
12. Rao L, Bu LL, Xu JH, et al. Red blood cell membrane as a biomimetic nanocoating for prolonged circulation time and reduced accelerated blood clearance. Small. 2015;11(46):6225–6236. doi:10.1002/smll.201502388
13. Wynn TA, Chawla A, Pollard JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013;496(7446):445–455. doi:10.1038/nature12034
14. Tacke F. Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases. J Hepatol. 2017;66(6):1300–1312. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2017.02.026
15. Moghaddam AS, Mohammadian S, Vazini H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425–6440. doi:10.1002/jcp.26429
16. Noy R, Pollard JW. Tumor-associated macrophages: from mechanisms to therapy. Immunity. 2014;41(1):49–61. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.010
17. Guo Q, Zhichao J, Yuan Y, et al. New mechanisms of tumor-associated macrophages on promoting tumor progression: recent research advances and potential targets for tumor immunotherapy. J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:9720912. doi:10.1155/2016/9720912
18. Dou H, Destache CJ, Morehead JR, et al. Development of a macrophage-based nanoparticle platform for antiretroviral drug delivery. Blood. 2006;108:2827–2835. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-03-012534
19. Choi MR, Stanton-Maxey KJ, Stanley JK, et al. A cellular trojan horse for delivery of therapeutic nanoparticles into tumors. Nano Lett. 2007;7(12):3759–3765. doi:10.1021/nl072209h
20. Batrakova EV, Li S, Reynolds AD, et al. A macrophage-nanozyme delivery system for parkinson’s disease. Bioconjug Chem. 2007;18:1498–1506. doi:10.1021/bc700184b
21. Parodi A, Quattrocchi N, Van D, et al. Biomimetic functionalization with leukocyte membranes imparts cell like functions to synthetic particles. Nat Nanotechnol. 2013;8(1):61. doi:10.1038/nnano.2012.212
22. Wayne EC, Long C, Haney MJ, et al. Targeted delivery of siRNA lipoplexes to cancer cells using macrophage transient horizontal gene transfer. Adv Sci. 2019;6(21):1900582. doi:10.1002/advs.201900582
23. Li R, He Y, Zhu Y, et al. Route to rheumatoid arthritis by macrophage-derived microvesicle-coated nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2019;19(1):124–134. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b03439
24. Nowacek AS, Balkundi S, Mcmillan JE, et al. Analyses of nanoformulated antiretroviral drug charge, size, shape and content for uptake, drug release and antiviral activities in human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Control Release. 2011;150(2):204–211. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.11.019
25. Gordon S, Taylor PR. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(12):953–964. doi:10.1038/nri1733
26. Shi C, Pamer EG. Monocyte recruitment during infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11(11):762–774. doi:10.1038/nri3070
27. Zhao Y, Haney MJ, Mahajan V, et al. Active targeted macrophage-mediated delivery of catalase to affected brain regions in models of parkinson’s disease. J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2011;S4:003. doi:10.4172/2157-7439.S4-003
28. Evans M, Huang PJ, Iwamoto Y, et al. Macrophage-mediated delivery of light activated nitric oxide prodrugs with spatial, temporal and concentration control. Chem Sci. 2018;9:3729–3741. doi:10.1039/C8SC00015H
29. Madsen SJ, Christie C, Hong SJ, et al. Nanoparticle-loaded macrophage-mediated photothermal therapy: potential for glioma treatment. Laser Med Sci. 2015;30:1357–1365. doi:10.1007/s10103-015-1742-5
30. Choi J, Kim H-Y, Ju EJ, et al. Use of macrophages to deliver therapeutic and imaging contrast agents to tumors. Biomaterials. 2012;33:4195–4203. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.02.022
31. Nguyen VD, Min HK, Kim DH, et al. Macrophage-mediated delivery of multifunctional nanotherapeutics for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy of solid tumors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(9):10130–10141. doi:10.1021/acsami.9b23632
32. Cao X, Tan T, Zhu D, et al. Paclitaxel-loaded macrophage membrane camouflaged albumin nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:1915–1928. doi:10.2147/IJN.S244849
33. Zhou X, Luo B, Kang K, et al. Leukocyte-repelling biomimetic immunomagnetic nanoplatform for high-performance circulating tumor cells isolation. Small. 2019;15(17):e1900558. doi:10.1002/smll.201900558
34. He W, Frueh J, Wu Z, He Q. Leucocyte membrane-coated janus microcapsules for enhanced photothermal cancer treatment. Langmuir. 2016;32(15):3637–3644. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b04762
35. Xuan M, Shao J, Dai L, Li J, He Q. Macrophage cell membrane camouflaged Au nanoshells for in vivo prolonged circulation life and enhanced cancer photothermal therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(15):9610–9618. doi:10.1021/acsami.6b00853
36. Su H, Wang Y, Gu Y, Bowman L, Zhao J, Ding M. Potential applications and human biosafety of nanomaterials used in nanomedicine. J Appl Toxicol. 2018;38(1):3–24. doi:10.1002/jat.3476
37. Meng QF, Rao L, Zan M, et al. Macrophage membrane-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for enhanced photothermal tumor therapy. Nanotechnology. 2018;29(13):134004. doi:10.1088/1361-6528/aaa7c7
38. Xuan M, Shao J, Dai L, He Q, Li J. Macrophage cell membrane camouflaged mesoporous silica nanocapsules for in vivo cancer therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(11):1645–1652. doi:10.1002/adhm.201500129
39. Casares D, Escribá PV, Rosselló CA. Membrane lipid composition: effect on membrane and organelle structure, function and compartmentalization and therapeutic avenues. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(9):2167. doi:10.3390/ijms20092167
40. Dong X, Chu D, Wang Z. Leukocyte-mediated delivery of nanotherapeutics in inflammatory and tumor sites. Theranostics. 2017;7(3):751–763. doi:10.7150/thno.18069
41. Thamphiwatana S, Angsantikul P, Escajadillo T, et al. Macrophage-like nanoparticles concurrently absorbing endotoxins and proinflammatory cytokines for sepsis management. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(43):11488–11493. doi:10.1073/pnas.1714267114
42. Combes F, Meyer E, Sanders NN. Immune cells as tumor drug delivery vehicles. J Control Release. 2020;327:70–87. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.07.043
43. Choi M-R, Bardhan R, Stanton-Maxey KJ, et al. Delivery of nanoparticles to brain metastases of breast cancer using a cellular trojan horse. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2012;3(1–6):47–54. doi:10.1007/s12645-012-0029-9
44. Cao H, Dan Z, He X, et al. Liposomes coated with isolated macrophage membrane can target lung metastasis of breast cancer. ACS Nano. 2016;10(8):7738–7748. doi:10.1021/acsnano.6b03148
45. Rao L, He Z, Meng QF, et al. Effective cancer targeting and imaging using macrophage membrane-camouflaged upconversion nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(2):521–530. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.35927
46. Srirupa B, Sankar GS. Transmembrane TNFα-expressed macrophage membrane-coated chitosan nanoparticles as cancer therapeutics. ACS Omega. 2020;5:1572–1580. doi:10.1021/acsomega.9b03531
47. Doshi N, Swiston AJ, Gilbert JB, et al. Cell-based drug delivery devices using phagocytosis-resistant backpacks. Adv Mater. 2011;23(12):H105–H109. doi:10.1002/adma.201004074
48. Klyachko NL, Polak R, Haney MJ, et al. Macrophages with cellular backpacks for targeted drug delivery to the brain. Biomaterials. 2017;140:79–87. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.06.017
49. Lee S. Monocytes: a novel drug delivery system targeting atherosclerosis. J Drug Target. 2014;22(2):138–145. doi:10.3109/1061186X.2013.844158
50. Evangelopoulos M, Yazdi IK, Acciardo S, et al. Biomimetic cellular vectors for enhancing drug delivery to the lungs. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):172. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-55909-x
51. Lemke G. How macrophages deal with death. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19(9):539–549. doi:10.1038/s41577-019-0167-y
52. Zhang Y, Cai K, Li C, et al. Macrophage-membrane-coated nanoparticles for tumor-targeted chemotherapy. Nano Lett. 2018;18(3):1908–1915. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b05263
53. Haney MJ, Zhao Y, Jin YS, et al. Macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems for triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) therapy. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019;15:2. doi:10.1007/s11481-019-09884-9
54. Rayamajhi S, Nguyen TDT, Marasini R, Aryal S. Macrophage-derived exosome-mimetic hybrid vesicles for tumor targeted drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2019;94:482–494. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.054
55. Molinaro R, Pastò A, Corbo C, et al. Macrophage-derived nanovesicles exert intrinsic anti-inflammatory properties and prolong survival in sepsis through a direct interaction with macrophages. Nanoscale. 2019;11(28):13576–13586. doi:10.1039/c9nr04253a
56. Tang TT, Lv LL, Wang B, et al. Employing macrophage-derived microvesicle for kidney-targeted delivery of dexamethasone: an efficient therapeutic strategy against renal inflammation and fibrosis. Theranostics. 2019;9(16):4740–4755. doi:10.7150/thno.33520
57. Arneth B. Tumor microenvironment. Medicina. 2019;56(1):15. doi:10.3390/medicina56010015
58. Zhang W, Wang M, Tang W, et al. Nanoparticle-laden macrophages for tumor-tropic drug delivery. Adv Mater. 2018;30(50):e1805557. doi:10.1002/adma.201805557
59. Kim MS, Haney MJ, Zhao Y, et al. Engineering macrophage-derived exosomes for targeted paclitaxel delivery to pulmonary metastases: in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Nanomedicine. 2017;14(1):195–204. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2017.09.011
60. Ngambenjawong C, Gustafson HH, Pun SH. Progress in tumor-associated macrophage (TAM)-targeted therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;114:206–221. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2017.04.010
61. Wu K, Lin K, Li X, et al. Redefining tumor-associated macrophage subpopulations and functions in the tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1731. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01731
62. Zheng Y, Bao J, Zhao Q, Zhou T, Sun X. A spatio-temporal model of macrophage-mediated drug resistance in glioma immunotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018;17(4):814–824. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0634
63. Zhang J, Guan M, Wang Q, Zhang J, Zhou T, Sun X. Single-cell transcriptome-based multilayer network biomarker for predicting prognosis and therapeutic response of gliomas. Brief Bioinform. 2020;21(3):1080–1907. doi:10.1093/bib/bbz040
64. Sun X, Liu X, Xia M, Shao Y, Zhang XD. Multicellular gene network analysis identifies a macrophage-related gene signature predictive of therapeutic response and prognosis of gliomas. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):159. doi:10.1186/s12967-019-1908-1
65. Fu J, Wang D, Dong M, et al. Macrophage mediated biomimetic delivery system for the treatment of lung metastasis of breast cancer. J Control Release. 2015;204:11–19. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.01.039
66. Zhao H, Zhang J, Zheng C, et al. C–C chemokine ligand 2 (CCl2) recruits macrophage-membrane-camouflaged hollow bismuth selenide nanoparticles to facilitate photothermal sensitivity and inhibit lung metastasis of breast cancer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(37):31124–31135. doi:10.1021/acsami.8b11645
67. Pang L, Zhu Y, Qin J, Zhao W, Wang J. Primary M1 macrophages as multifunctional carrier combined with PLGA nanoparticle delivering anticancer drug for efficient glioma therapy. Drug Deliv. 2018;25(1):1922–1931. doi:10.1080/10717544.2018.1502839
68. Liu J, Wu F, Zhou H. Macrophage-derived exosomes in cancers: biogenesis, functions and therapeutic applications. Immunol Lett. 2020;227:102–108. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2020.08.003
69. Wang P, Wang H, Huang Q, et al. Exosomes from M1-polarized macrophages enhance paclitaxel antitumor activity by activating macrophages-mediated inflammation. Theranostics. 2019;9(6):1714–1727. doi:10.7150/thno.30716
70. Li J, Li N, Wang J. M1 macrophage-derived exosome-encapsulated cisplatin can enhance its anti-lung cancer effect. Minerva Med. 2020. doi:10.23736/S0026-4806.20.06564-7
71. Joan E, Maria B. Iron oxide nanoparticles in photothermal therapy. Molecules. 2018;23:1567. doi:10.3390/molecules23071567
72. Cheon YA, Bae JH, Chung BG. Reduced graphene oxide nanosheet for chemo-photothermal therapy. Langmuir. 2016;32(11):2731–2736. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b00315
73. Han S, Kwon T, Um JE, Haam S, Kim WJ. Highly selective photothermal therapy by a phenoxylated-dextran-functionalized smart carbon nanotube platform. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(10):1147–1156. doi:10.1002/adhm.201600015
74. Choi WI, Sahu A, Kim YH, Tae G. Photothermal cancer therapy and imaging based on gold nanorods. Ann Biomed Eng. 2012;40(2):534–546. doi:10.1007/s10439-011-0388-0
75. Qiang L, Cai Z, Jiang W, et al. A novel macrophage-mediated biomimetic delivery system with NIR-triggered release for prostate cancer therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2019;17:83–98. doi:10.1186/s12951-019-0513-z
76. Dou H, Grotepas CB, McMillan JM, et al. Macrophage delivery of nanoformulated antiretroviral drug to the brain in a murine model of NeuroAIDS. J Immunol. 2009;183(1):661–669. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900274
77. Haney MJ, Klyachko NL, Zhao Y, et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for parkinson’s disease therapy. J Control Release. 2015;207:18–30. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.03.033
78. Wang C, Wang Y, Zhang L, et al. Pretreated macrophage-membrane-coated gold nanocages for precise drug delivery for treatment of bacterial infections. Adv Mater. 2018;30(46):e1804023. doi:10.1002/adma.201804023
79. Peng R, Ji H, Jin L, et al. Macrophage-based therapies for atherosclerosis management. J Immunol Res. 2020;2020:8131754. doi:10.1155/2020/8131754
80. Gao C, Huang Q, Liu C, et al. Treatment of atherosclerosis by macrophage-biomimetic nanoparticles via targeted pharmacotherapy and sequestration of proinflammatory cytokines. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):2622. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-16439-7
81. Kumar P, Bose PP. Macrophage ghost entrapped amphotericin B: a novel delivery strategy towards experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018;9:249–259. doi:10.1007/s13346-018-00602-1
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
