Back to Journals » OncoTargets and Therapy » Volume 7
Recall radiation dermatitis by sorafenib following stereotactic body radiation therapy
Authors Hsieh C , Lin S, Shueng P, Kuo D
Received 24 March 2014
Accepted for publication 23 April 2014
Published 18 June 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 1111—1114
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S64706
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Chen-Hsi Hsieh,1,3,4 Shih-Chiang Lin,2 Pei-Wei Shueng,1,5,6 Deng-Yu Kuo1
1Division of Radiation Oncology, Department of Radiology, 2Division of Medical Oncology and Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, Far Eastern Memorial Hospital, New Taipei City, Taiwan; 3Department of Medicine, 4Institute of Traditional Medicine, School of Medicine, National Yang-Ming University, 5Department of Radiation Oncology, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan; 6Oriental Institute of Technology, New Taipei City, Taiwan
Abstract: We report on a 63-year-old man with a history of hepatitis B virus–related hepatocellular carcinoma with a thrombus extending into the inferior vena cava, who received image-guided stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) with helical tomotherapy, followed by sorafenib. A total tumor dose of 48 Gy was delivered by 6 fractions within 2 weeks. The tumor responded dramatically, and the patient tolerated the courses well. Ten days after SBRT, sorafenib (200 mg), at 1.5 tablets twice a day, was prescribed. One week later, grade 2 recall radiation dermatitis subsequently developed in the previous SBRT off-target area. SBRT followed by sorafenib for the treatment of a portal vein thrombosis provided effective results, but the potential risk of enhanced adverse effects between radiation and sorafenib should be considered with caution, especially under a SBRT scheme.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, recall radiation dermatitis
Background
Portal vein thrombosis and inferior vena cava tumor thrombosis are common complications in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) that limit the application of surgical resection or transarterial chemoembolization to HCC.1,2 Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is a
“treatment method to deliver a high dose of radiation to the target, utilizing either a single dose or a small number of fractions with a high degree of precision within the body.”3
SBRT has substantial activity against HCC, with a local control rate of 87% at 1 year.4 Use of helical tomotherapy (HT) for the treatment of HCC with portal vein thrombosis is clinically feasible and has been investigated.5
Sorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor that has been shown to induce tumor cell apoptosis in HCC.6 HCC cells damaged by irradiation in vitro show enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)7 that can be inhibited by sorafenib and may enhance the efficacy of the radiation, when sorafenib is given following radiation treatment.7 However, the side-effects caused by drugs or irradiation are unpredictable. Here, we report a case of triggered recall radiation dermatitis (RRD) from sorafenib administered following SBRT.
Case presentation
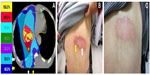
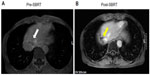
A 63-year-old man with a history of hepatitis B virus–related HCC with diaphragm invasion (pT4N0M0, according to the tumor–node–metastasis classification)8 was treated surgically with an extended right lobectomy and cholecystectomy. One year later, recurrent HCC, at the junction of segments 2 and 3, was noted and treated by transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. In 2013 September, magnetic resonance imaging showed local recurrence of the HCC, with a thrombus extending into the inferior vena cava. HT liver SBRT with 48 Gy, in six fractions, was delivered within 2 weeks, without complications (Figure 1A). Ten days after SBRT, sorafenib (200 mg), at 1.5 tablets twice a day, was prescribed in a sequential radiation therapy (RT)–sorafenib regimen, which has been demonstrated to provide greater efficacy against HCC than a concurrent RT–sorafenib regimen, both in vitro and in vivo.9 One week later, grade 2 RRD10 subsequently developed in the previous SBRT off-target area (Figure 1B). The patient was given clobetasol propionate topical use ointment three times a day, and the sorafenib prescription was withheld, with symptoms resolving 10 days later (Figure 1C). In the subsequent magnetic resonance imaging report, a partial response of recurrent HCC after SBRT was noted (Figure 2A and B). The highest level of glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase after SBRT was 83 (IU/L).
Conclusion
HT liver SBRT delivers doses in an image-guided technique and can be a noninvasive and safe alternative treatment for unresectable HCC.11 The main pattern of hepatic toxicity after SBRT includes elevations in serum liver enzyme or bilirubin levels.12,13 Other toxicities reported after SBRT have included hepatic pain, gastric ulcer, fatigue, and hematologic dysfunction.13,14 After SBRT, a partial response with mild elevation in glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase was noted in this patient (Figure 2). No other complications were noted. However, RRD subsequently developed in the 40%−50% isodose area (Figure 1B). RRD is characterized by an inflammatory reaction within a previously irradiated volume after administration of certain promoting agents, such as antineoplastic drugs. It was first described by D’Angio et al15 and was found to be triggered by dactinomycin. One possible mechanism of action may be that the radiation induces the expression of certain cytokines that are responsible for an inflammatory response, such as interleukin 1, interleukin 6, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), tumor necrosis factor alpha, and transforming growth factor beta. These cells continue to secrete low levels of cytokines after radiation, and when a precipitating agent is then introduced, these cytokines are upregulated, causing a recall reaction.16 Sorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor that targets Raf serine/threonine kinases, VEGF receptor (VEGFR)-2 and -3, and PDGF receptor (PDGFR)-β, which has been shown to induce tumor cell apoptosis in a HCC model.6 Previous reports have touched on the possibility of photosensitivity in sorafenib.17,18 The histopathological analysis of a sorafenib-induced hand–foot skin reaction revealed keratinocyte damage, keratinocyte vacuolar degeneration, intracytoplasmic eosinophilic bodies, and confluent keratinocyte necrosis, leading to intraepidermal cleavage.19
VEGF would be increased in a time- and dose-dependent manner after sublethal irradiation damage to HCC cells in vitro, translating to enhanced intratumor angiogenesis in vivo and correlating well with serum VEGF levels.7 Sorafenib, as an inhibitor of the Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase and VEGFR pathways, might enhance the efficacy of radiation, when administered following radiation. In HCT116 xenograft tumor growth delay experiments in mice, sorafenib altered the radiation response in a schedule-dependent manner.20 Additionally, radiation treatment followed sequentially by sorafenib was found to be associated with the greatest tumor growth delay.20 The current report also shows the benefit of sorafenib following SBRT (Figure 2A and B).
SBRT with HT allows for the maximum dose to the targeting area, with minimization of normal tissue volume exposure to high radiation dose.21 However, off-target organs at risk can be impacted by arc therapy, due to the “low-dose bath” phenomenon, and be magnified by agents associated with recall effects.22,23 Irradiation, both target dose and off-target dose, can modulate the systemic pharmacokinetics in rat’s model24,25 and a deeper investigation of the molecular mechanisms showed that there was an enhanced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-8 when combined treatments of irradiation and 5-fluorouracil were made.26 Further study of RT–PK phenomenon persistence in target therapy drugs is warranted.
The clinical effects and toxicities of sorafenib administered concurrently or sequentially with RT were reported recently. For hand-foot syndrome, grade 2 or 3 toxicities were higher in the concurrent treatment than in the sequential management.27 Erythematous patch matching the previously irradiated treatment area was also reported after prescription of sequential sorafenib.28 Moreover, there was a significant correlation between serious bowel injury and VEGF inhibitor within 3 months of SBRT.29
After discontinuation of the triggering drug, RRD will subside, but the resolution time is not understood, and the occurrence of RRD may be unpredictable. The role of steroids in managing RRD is unclear; however, they are commonly used for symptom control. The effect of dose reduction on reducing the chance of RRD recurrence also remains unknown. Nevertheless, targeting the tumor and minimizing the exposure of normal tissue will potentially avoid skin complications.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Far Eastern Memorial Hospital (grant numbers FEMH-2014-C-045 and FEMH 101-2314-B-418-010-MY3).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Pawlik TM, Poon RT, Abdalla EK, et al. Hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma with major portal or hepatic vein invasion: results of a multicenter study. Surgery. 2005;137(4):403–410. | |
Kim JH, Yoon HK, Kim SY, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization vs chemoinfusion for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with major portal vein thrombosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009;29(12):1291–1298. | |
Potters L, Steinberg M, Rose C, et al; American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology; American College of Radiology. American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology and American College of Radiology practice guideline for the performance of stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;60(4):1026–1032. | |
Bujold A, Massey CA, Kim JJ, et al. Sequential phase I and II trials of stereotactic body radiotherapy for locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(13):1631–1639. | |
Hsieh CH, Liu CY, Shueng PW, et al. Comparison of coplanar and noncoplanar intensity-modulated radiation therapy and helical tomotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiat Oncol. 2010;5:40. | |
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, et al. Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res. 2006;66(24):11851–11858. | |
Chung YL, Jian JJ, Cheng SH, et al. Sublethal irradiation induces vascular endothelial growth factor and promotes growth of hepatoma cells: implications for radiotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(9):2706–2715. | |
AJCC: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor. In: Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, et al., editors. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer; 2010:181–189. | |
Wild AT, Gandhi N, Chettiar ST, et al. Concurrent versus sequential sorafenib therapy in combination with radiation for hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e65726. | |
National Cancer Institute. CTC v2.0 and Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v3.0 (CTCAE). Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2006. Available from http://ctep.info.nih.gov/reporting/ctc.html. Accessed June 5, 2014. | |
Baisden JM, Reish AG, Sheng K, Larner JM, Kavanagh BD, Read PW. Dose as a function of liver volume and planning target volume in helical tomotherapy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy-based stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatic metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66(2):620–625. | |
Tse RV, Hawkins M, Lockwood G, et al. Phase I study of individualized stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26(4):657–664. | |
Andolino DL, Johnson CS, Maluccio M, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81(4):e447–e453. | |
Bibault JE, Dewas S, Vautravers-Dewas C, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: prognostic factors of local control, overall survival, and toxicity. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e77472. | |
D’angio GJ, Farber S, Maddock CL. Potentiation of x-ray effects by actinomycin D. Radiology. 1959;73:175–177. | |
Johnston CJ, Piedboeuf B, Rubin P, Williams JP, Baggs R, Finkelstein JN. Early and persistent alterations in the expression of interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA levels in fibrosis-resistant and sensitive mice after thoracic irradiation. Radiat Res. 1996;145(6):762–767. | |
Hsieh CH, Jeng KS, Lin CC, et al. Combination of sorafenib and intensity modulated radiotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Drug Investig. 2009;29(1):65–71. | |
Magné N, Chargari C, Auberdiac P, Moncharmont C, Merrouche Y, Spano JP. Ultraviolet recall dermatitis reaction with sorafenib. Invest New Drugs. 2011;29(5):1111–1113. | |
Yang CH, Lin WC, Chuang CK, et al. Hand-foot skin reaction in patients treated with sorafenib: a clinicopathological study of cutaneous manifestations due to multitargeted kinase inhibitor therapy. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158(3):592–596. | |
Plastaras JP, Kim SH, Liu YY, et al. Cell cycle dependent and schedule-dependent antitumor effects of sorafenib combined with radiation. Cancer Res. 2007;67(19):9443–9454. | |
Goodman KA, Wiegner EA, Maturen KE, et al. Dose-escalation study of single-fraction stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;78(2):486–493. | |
Shueng PW, Lin SC, Chang HT, et al. Toxicity risk of non-target organs at risk receiving low-dose radiation: case report. Radiat Oncol. 2009;4:71. | |
Hsieh CH, Chang HT, Lin SC, et al. Toxic risk of stereotactic body radiotherapy and concurrent helical tomotherapy followed by erlotinib for non-small-cell lung cancer treatment – case report. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:696. | |
Hsieh CH, Hsieh YJ, Liu CY, et al. Abdominal irradiation modulates 5-Fluorouracil pharmacokinetics. J Transl Med. 2010;8:29. | |
Hsieh CH, Hou ML, Chiang MH, et al. Head and neck irradiation modulates pharmacokinetics of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin. J Transl Med. 2013;11:231. | |
Hsieh CH, Liu CY, Hsieh YJ, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 mediates the unfavorable systemic impact of local irradiation on pharmacokinetics of anti-cancer drug 5-Fluorouracil. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21000. | |
Chen SW, Lin LC, Kuo YC, Liang JA, Kuo CC, Chiou JF. Phase 2 study of combined sorafenib and radiation therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;88(5):1041–1047. | |
Oh D, Park HC, Lim HY, Yoo BC. Sorafenib-triggered radiation recall dermatitis with a disseminated exanthematous reaction. Radiat Oncol J. 2013;31(3):171–174. | |
Barney BM, Markovic SN, Laack NN, et al. Increased bowel toxicity in patients treated with a vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor (VEGFI) after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;87(1):73–80. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.