Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 10 » Issue 1
Protein immobilization onto electrochemically synthesized CoFe nanowires
Authors Torati SR, Reddy V, Yoon SS, Kim C
Received 1 November 2014
Accepted for publication 26 November 2014
Published 14 January 2015 Volume 2015:10(1) Pages 645—651
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S76850
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Sri Ramulu Torati,1 Venu Reddy,1 Seok Soo Yoon,2 CheolGi Kim1
1Department of Emerging Materials Science, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology, Daegu, South Korea; 2Department of Physics, Andong National University, Andong, South Korea
Abstract: CoFe nanowires have been synthesized by the electrodeposition technique into the pores of a polycarbonate membrane with a nominal pore diameter of 50 nm, and the composition of CoFe nanowires varying by changing the source concentration of iron. The synthesized nanowire surfaces were functionalized with amine groups by treatment with aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) linker, and then conjugated with streptavidin-Cy3 protein via ethyl (dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide and N-hydroxysuccinimide coupling chemistry. The oxide surface of CoFe nanowire is easily modified with aminopropyltriethoxysilane to form an amine terminating group, which is covalently bonded to streptavidin-Cy3 protein. The physicochemical properties of the nanowires were analyzed through different characterization techniques such as scanning electron microscope, energy dispersive spectroscopy, and vibrating sample magnetometer. Fluorescence microscopic studies and Fourier transform infrared studies confirmed the immobilization of protein on the nanowire surface. In addition, the transmission electron microscope analysis reveals the thin protein layer which is around 12–15 nm on the nanowire surfaces.
Keywords: electrodeposition, biofunctionalization, streptavidin
Introduction
In recent years, there has been significant interest in the surface modification of nanowires with chemicals and biomolecules for the application of biosensing, bioelectronics, and biodevices.1–8 Especially, the surface-modified magnetic nanowire is more important in the field of magnetic biosensing and magnetic separation.9,10 The direct surface modification of magnetic nanowire is quite a difficult task for researchers. However, the surface modification of magnetic nanowire through oxide surfaces could be an alternative method for the immobilization of biomolecules. Here, the oxide surfaces of nanowires are modified by an amine terminating group of a chemical linker like aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES), and then ultimately coupled with biomolecules.11 There are some reports on the surface modification of magnetic Fe3O4 and NiO nanowires with different linkers for biological application.12,13 The surface modification of CoFe nanowires could be more advantageous for biosensing applications because of its high saturation magnetization and magnetic moment. However, there is no such report on surface modification of CoFe nanowires. In addition, the functionalized CoFe nanowires can be used as a magnetic carrier that offers significant advantages in manipulation applications. Hence, we tried to functionalize the CoFe nanowires through APTES linker.
The important techniques to obtain nanowires are template-assisted electrochemical deposition, electron beam lithography, vapor–liquid–solid mechanism, solvothermal synthesis, and chemical vapor deposition.14–18 Among these methods, electrochemical deposition offers an efficient physical and chemical property of the synthesized nanowires with a controllable aspect ratio.19,20 In addition, electrodeposition method is considered a promising alternative technique for high throughput fabrication on a large surface area because it is simple, cost-effective, operates at room temperature, and is able to tailor the properties of the nanowires by adjusting the deposition conditions.21
In this paper, we report on the synthesis of CoFe nanowires by an electrochemical technique using polycarbonate as a template with a nominal pore diameter of 50 nm. We varied the percentage of Fe content in the vicinity of the nanowires by changing the electrolyte concentration. The synthesized nanowires are characterized with field emission-scanning electron microscope, energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), and vibrating sample magnetometer. The synthesized nanowires were immobilized by streptavidin-Cy3 in the presence of ethyl (dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) activators. The confirmation of protein immobilization on magnetic nanowires was observed through Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), fluorescence microscopy, and field emission transmission electron microscope.
Experimental details
Chemicals and materials
The track-etched polycarbonate membrane with 50 nm diameter and 6–9 μm thickness was purchased from Whatmann. All the chemicals such as CoSO47H2O, FeSO47H2O, H3BO3, APTES, CH2Cl2 Na2HPO4, NaH2PO4, and NaCl were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Co. (St Louis, MO, USA) and used without any further purification. Also, the streptavidin-Cy3 from Streptomyces avidin was procured from Sigma-Aldrich Co. The phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (0.05 M) was prepared using Na2HPO4 and NaH2PO4 with 0.9% NaCl and adjusted to pH 7.4 by HCl. Deionized water obtained from a Milli-Q water purification system was used throughout the experiments.
Synthesis of CoFe nanowires
The CoFe nanowires were electrochemically deposited using a potentiostat (SP-150; BioLogic, Claix, France) into the track-etched polycarbonate membrane with a nominal pore diameter of 50 nm. The room-temperature electrolyte bath for the CoFe contained CoSO47H2O 0.05 M, FeSO47H2O varied from 0.01 to 0.1 M, and H3BO3 0.5 M. The pH for the deposition of CoFe was adjusted to be around 3 by using 1 M NaOH. Initially, one side of the polycarbonate membrane was coated with metallic Au by magnetron sputtering system under the working pressure of 3 mTorr with a base pressure of ~1.0×10−7 Torr for electric conduction. The deposition of the nanowires was conducted potentiostatically by a three electrode configuration with a one-side-gold-coated polycarbonate membrane, platinum sheet, and Ag/AgCl as the working, counter, and reference electrodes, respectively. The deposition of CoFe nanowires was carried out at a constant potential of −1.0 V with respect to the reference electrode for 30 minutes. After deposition, the nanowires were released from the polycarbonate membrane by dissolving it in dichloromethane for a few minutes. The suspended nanowires in dichloromethane were washed several times with distilled water and dried at 100°C.
Amine functionalization onto CoFe nanowires
Figure 1 shows the schematic procedure for immobilization of streptavidin-Cy3 protein on the nanowire surface. One hundred micrograms of CoFe nanowires were mixed with 1 mL of APTES (2 mM) dissolved in ethanol. The resultant solution was kept in an ultrasonic bath for a few minutes to avoid the aggregation of nanowires and expose all surface areas of individual nanowires to the APTES solution. After that, the dispersed nanowire solution was kept at room temperature for 12 hours, followed by washing with PBS buffer (pH 7.4) and purification by repeated magnetic purification method using a hard magnet.
Streptavidin-Cy3 protein immobilization
The amine functionalized nanowires were suspended in PBS buffer (500 μL, pH 7.4) contained in an Eppendorf tube. To this, 100 μL of EDC (0.1 M), 100 μL of NHS (0.1 M), and 10 μL of streptavidin-Cy3 protein (0.0105 mg/mL) was added. Then, the tube was placed on a vortex shaker and gently agitated for 12 hours at 8°C followed by repeated washing in PBS buffer (500 μL, pH 7.4), and was finally dispersed in 500 μL of PBS buffer (pH 7.4) for further characterization.
Characterization of nanowires and protein-loaded nanowires
The morphological structures of nanowires were observed by FE-SEM (Nova-230; FEI Company) with an operating voltage of 10 kV. The nominal elemental composition of CoFe nanowires was analyzed by EDS coupled with the FE-SEM. The applied voltage and probe current for the EDS measurement system was 20 kV and 1.5 nA, respectively. The as-deposited nanowires embedded in the polycarbonate membrane were used for the measurement of magnetic properties by a vibrating sample magnetometer (Lake-Shore 7,400) at room temperature with an applied field range of 10 kOe to −10 kOe and a sensitivity of 10−6 EMU. The protein-loaded nanowires were characterized by FT-IR spectra which was recorded by an attenuated total reflectance instrument equipped with diamond crystal reflection element (Brucher Optic GmbH, Ettligen, Germany). The FT-IR spectra were acquired using 32 scans over the spectral range from 4,000 to 500 cm−1 with a maximum resolution of 0.9 cm−1 at room temperature. The morphology and microstructure of the as-grown and coated nanowires were characterized through field emission transmission electron microscope (Technai F20; Philips, Eindhoven, the Netherlands) with an accelerating voltage of 200 kV. Fluorescence microscopy of the streptavidin-Cy3 protein functionalized nanowires was performed using a confocal laser scanning microscope (LSM 5 live; Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, Jena, Germany). The fluorescence images were taken with confocal FL detector with a scan speed of 120–1,010 fps.
Results and discussion
Synthesis and physicochemical characterization of nanowires
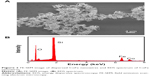
The structural morphology of the CoFe nanowires, determined by SEM, is shown in Figure 2A, where a high density of nanowires is observed. The average length of the nanowires was found to be around 4 μm and the diameter was slightly greater than the pore diameter of the template, which may be due to the nonuniform pore diameter of the polycarbonate membrane.22 Figure 2B shows the EDS spectrum of CoFe nanowires, indicating the presence of Co and Fe elements in the vicinity of the nanowire. The average atomic composition of Co and Fe in the nanowire was found to be 30% and 70%, respectively. In addition, the presence of oxygen element peak is clearly observed in the EDS spectrum, which is considered as an indication of native oxide surface formation on CoFe nanowires.
Various CoFe alloy nanowires were fabricated with different compositions in order to observe the influence of the iron content by changing the iron source concentration in an electrolyte bath, and the average composition of the nanowires with respect to the electrolyte bath is presented in Table 1. The EDS data presented in Table 1 revealed that the atomic percentage of nanowires is significantly influenced by the source concentration of Co and Fe ions in the electrolyte bath. Hence, the composition of CoFe nanowires can be monitored by varying the ratio of iron to cobalt ions in the electrolyte.
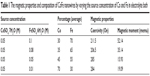  | Table 1 The magnetic properties and composition of CoFe nanowires by varying the source concentration of Co and Fe in electrolyte bath |
The magnetic properties of as-deposited CoFe nanowires embedded in a polycarbonate membrane were measured in the magnetic field parallel to the nanowire axis at room temperature. Figure 3 shows the magnetization curves for different composition of CoFe nanowires. The CoFe nanowire with 70:30 Fe to Co (Fe70Co30) had the highest magnetization. The change in saturation magnetization and coercivity of CoFe nanowires by varying the Fe concentration are shown in Table 1. The magnetic properties were significantly changed by varying the composition of CoFe nanowires.
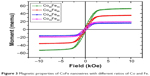  | Figure 3 Magnetic properties of CoFe nanowires with different ratios of Co and Fe. |
Streptavidin-Cy3 protein immobilization onto CoFe nanowire
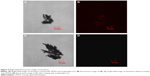
A drop of solution containing CoFe nanowires conjugated with streptavidin-Cy3 protein was spread onto the glass slide for the analysis of fluorescence properties to assess the efficiency of protein binding on the nanowire surfaces. The bright-field and fluorescence images are shown in Figure 4A and B, respectively. For the comparative studies, the CoFe nanowires were functionalized with and without amine functional groups and then conjugated with streptavidin-Cy3 protein. The CoFe nanowires which were functionalized with amine groups and conjugated with streptavidin-Cy3 protein in the presence of EDC and NHS activators showed fluorescence (Figure 4A). The mechanism of streptavidin-Cy3 immobilized onto CoFe nanowires surface is shown in Figure 1A. The presence of a high quantity of oxygen in the vicinity of the nanowires was observed by EDS analysis. This indicates that the nanowire surface has native oxide surfaces. The oxygen from the native surface of the nanowires is easily bonded to APTES to form terminal amine groups on the nanowire surface.23 The amine functionalized nanowires were conjugated by carboxylic groups presented in the streptavidin-Cy3 protein via covalent amide bond between amine functionalized nanowires and streptavidin-Cy3 protein.14 However, sometimes there may be possibilities for weak nonspecific attachment of protein on the nanowire surfaces. This nonspecific attachment was eliminated by repeated washings of the functionalized nanowires with PBS buffer.
However, to further confirmation of origin of the fluorescence from the nanowire surface rather than the carrier solution is analysed without functionalization of amine and exposed to streptavidin-Cy3 protein in the presence of EDC and NHS. As expected, no fluorescence for nanowires was observed (Figure 4C and D). The reason may be due to the repellence of the negative oxide surface of CoFe, which contains a negative charge (O− species), to the streptavidin-Cy3 protein which also has a negative charge at pH 7.4.23 This observation confirms that the fluorescence comes from the nanowire surface, which is functionalized with amine group by treating with APTES linker.
The morphology of the nanowires immobilized with streptavidin-Cy3 was examined through TEM. The images were taken near the edge of the nanowire surfaces. Figure 5A and B show the TEM images of streptavidin-Cy3 protein-immobilized nanowires and bare nanowire surfaces, respectively. Figure 5A shows a clear indication of the organic layer formation on the nanowire surface indicating the immobilization of protein. Similar results for the immobilization of streptavidin protein on silicon nanowire surfaces were obtained by Williams et al.23 The wrapped organic layer around the nanowire surface was found to be 10–15 nm. However, the nanowires which were not functionalized with protein did not show any organic layer on the nanowire surface (Figure 5B). The above studies reveal that the CoFe nanowire surface is good for the protein immobilization.
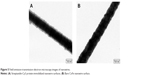  | Figure 5 Field emission-transmission electron microscopy images of nanowires. |
Figure 6 (curve a and b) shows the FT-IR spectra of bare CoFe nanowires and streptavidin-Cy3-immobilized nanowire. Curve b shows some characteristic peaks related to streptavidin where as there are no such peaks in curve a. The broad absorbance peak observed at 3,340 cm−1 was assigned to the stretching vibrations of −NH2. The absorption peak represented at 1,540 cm−1 is the amide bond of streptavidin molecules immobilized on the nanowire surfaces.25 It can be seen that the stretching vibration of C–H absorption bands are observed at 2,922 and 2,810 cm−1. In addition, the absorption peaks near 1,040 and 1,085 cm−1 are attributed to the phosphate stretching vibration from the PBS buffer used for the dissolution of nanowires. The FT-IR spectroscopic study confirmed the immobilization of streptavidin-Cy3 on nanowire surfaces.
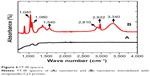  | Figure 6 FT-IR spectra. |
Conclusion
A biofunctionalization method for streptavidin protein conjugation to CoFe nanowires via APTES linker was developed and confirmed through different characterization techniques. The nanowires were fabricated using a template-assisted electrochemical technique. The developed method includes the functionalization of the nanowire surface with amine, followed by the covalent binding of streptavidin through EDS-NHS coupling chemistry. Fluorescence studies confirmed the immobilization of protein on the nanowire surface, whereas TEM analysis revealed a thin layer of protein wrapping around the nanowire surface. Further confirmation of protein functionalization on the nanowire was observed by FT-IR studies. These functionalized nanowires are useful as magnetic labels for magnetic biosensor applications.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2013R1A1A2065222).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Hsiao CY, Lin CH, Hung CH, et al. Novel poly-silicon nanowire field effect transistor for biosensing application. Biosens Bioelectron. 2009;24:1223–1229. | ||
Garcia M, Escarpa A. Disposable electrochemical detectors based on nickel nanowires for carbohydrate sensing. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011;26:2527–2533. | ||
Wang J, Li S, Zhang Y. A sensitive DNA biosensor fabricated from gold nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, and zinc oxide nanowires on a glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim Acta. 2010;55:4436–4440. | ||
Miao R, Mu L, Zhang H, et al. Modified silicon nanowires: a fluorescent nitric oxide biosensor with enhanced selectivity and stability. J Mater Chem. 2012;22:3348–3353. | ||
Ramulu TS, Venu R, Sinha B, Yoon SS, Kim CG. Electrodeposition of CoPtP/Au multisegment nanowires: synthesis and DNA functionalization. International Journal of Electrochemical Science. 2012;7:7762–7769. | ||
Ramulu TS, Venu R, Sinha B, et al. Nanowires array modified electrode for enhanced electrochemical detection of nucleic acid. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;40:258–264. | ||
Abumaree MH, Zhu L, Bardeen CJ, Al-Suwaidan SD, Al-Kaysi RO. Fabrication of biologically active surface-modified Taxol nanowires using anodic aluminum oxide templates. RSC Adv. 2011;1:884–892. | ||
Lee MH, Lee KN, Jung SW, Kim WH, Shin KS, Seong WK. Quantitative measurements of C-reactive protein using silicon nanowire arrays. Int J Nanomed. 2008;3:117–124. | ||
Hultgren A, Tanase M, Chen CS, Meyer GJ, Reich DH. Cell manipulation using magnetic nanowires. J Appl Phys. 2003;93:7554–7556. | ||
Lee KB, Park S, Mirkin CA. Multicomponent magnetic nanorods for biomolecular separations. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2004;43:3048–3050. | ||
Tanase M, Bauer LA, Hultgren A, et al. Magnetic alignment of fluorescent nanowires. Nano Lett. 2001;1(3):155–158. | ||
Demin AM, Krasnov VP, Charushin VN. Covalent surface modification of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles with alkoxy silanes and amino acids. Mendeleev Communications. 2013;23:14–16. | ||
Salem AK, Searson PC, Leong KW. Multifunctional nanorods for gene delivery. Nat Mater. 2003;2:668–671. | ||
Ramulu TS, Venu R, Anandakumar S, Sudha Rani V, Yoon SS, Kim CG. Structure, growth and magnetic property of hard magnetic CoPtP nanowires synthesized by electrochemical deposition. Thin Solid Films. 2012;520:5508–5511. | ||
Martin JI, Vélez M, Morales R, et al. Fabrication and magnetic properties of arrays of amorphous and polycrystalline ferromagnetic nanowires obtained by electron beam lithography. J Magn Magn Mater. 2002;249(1–2):156–162. | ||
Morber JR, Ding Y, Haluska MS, et al. PLD-assisted VLS growth of aligned ferrite nanorods, nanowires, and nanobelts-synthesis, and properties. J Phys Chem B. 2006;110:21672–21679. | ||
Liu Z, Zhang Q, Shi G, Li Y, Wang H. Solvothermal synthesis and magneto-optical properties of Zn1–XNiXO hierarchical microspheres. J Magn Magn Mater. 2011;323:1022–1026. | ||
Barth S, Estrade S, Hernandez-Ramirez F, et al. Studies on Surface Facets and Chemical Composition of Vapor Grown One-Dimensional Magnetite Nanostructures. Cryst Growth Des. 2009;9:1077–1081. | ||
Anandakumar S, Sudha Rani V, Ramulu TS, et al. Electrodeposition of multi-segmented CoNiP-Au nanowires for bio-barcodes. J Electrochem Soc. 2011;158:E124–E127. | ||
Sahu G, Gordon SW, Tarr MA. Synthesis and application of core-shell Au–TiO2 nanowire photoanode materials for dye sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv. 2012;2:573–582. | ||
Yoo B, Xiao F, Bozhilo KN, Herman J, Ryan MA, Myung NV. Electrodeposition of thermoelectric superlattice nanowires. Adv Mater. 2007;19:296–299. | ||
Schönenberger C, van der Zande BMI, Fokkink LGJ, et al. Template synthesis of nanowires in porous polycarbonate membranes: electrochemistry and morphology. J Phys Chem B. 19997;101:5497–5505. | ||
Williams EH, Schreifels JA, Rao MV, et al. Selective streptavidin bioconjugation on silicon and silicon carbide nanowires for biosensor applications. J Mater Res. 2013;28:68–77. | ||
Venu R, Lim B, Hu XH, Jeong I, Ramulu TS, Kim CG. On-chip manipulation and trapping of microorganisms using a patterned magnetic pathway. Microfluid Nanofluidics. 2013;14:277–285. | ||
Jung SM, Kim HJ, Kim BJ, Kim YS, Yoon TS, Lee HH. Electrical charging of Au nanoparticles embedded by streptavidin-biotin biomolecular binding in organic memory device. Appl Phys Let. 2010;97:153302. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.