Back to Journals » International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease » Volume 13
Prevalence of smoking in a psychiatric hospital and its relationship with respiratory symptoms and the prevalence of COPD
Authors Lores L , Monje A, Bergada M, Arellano E, Rodríguez-Larrea J, Miravitlles M
Received 19 February 2018
Accepted for publication 2 June 2018
Published 7 September 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 2797—2804
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S165880
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Luis Lores,1 Alfonso Monje,2 Manel Bergada,2 Elisabeth Arellano,1 Julian Rodríguez-Larrea,3 Marc Miravitlles4
1Pneumology Department, Hospital General Parc Sanitari Sant Joan de Déu, Sant Boi de Llobregat, Barcelona, Spain; 2Mental Health Services, Parc Sanitari Sant Joan de Déu, Sant Boi de Llobregat, Barcelona, Spain; 3Cardiology Department, Hospital General Parc Sanitari Sant Joan de Déu, Sant Boi de Llobregat, Barcelona, Spain; 4Pneumology Department, Hospital Universitari Vall d’Hebron, CIBER de Enfermedades Respiratorias (CIBERES), Barcelona, Spain
Purpose: Psychiatric patients present an elevated rate of smoking, and the smoking habit is related to a high morbidity and mortality in this collective. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of smoking in patients admitted for psychiatric disorders and its relationship with respiratory disease, the prevalence of COPD, and alterations in the quality of life.
Patients and methods: A cross-sectional, observational study was conducted and detailed information on smoking and respiratory symptomatology was obtained. The study participants underwent the following tests: spirometry with bronchodilator test, Fagerström test, determination of physical activity using the LCADL questionnaire, and evaluation of quality of life with the EuroQoL-5 Dimensions EQ-5D questionnaire.
Results: Two hundred seventy-six patients (mean age 56.8 years) were included: 155 with schizophrenia (87.7% smokers), 46 with depressive or anxiety disorders (54.3% smokers), and 49 and 25 with intellectual disability and dementia (43.2% smokers), respectively. The mean Fagerström test score was 5.75 points. Smokers presented with cough (47.6%), expectoration (41.4%), and chronic bronchitis (36.6%). The prevalence of COPD in the total population was 28.9%. The EQ-5D and LCADL scores were better in smokers because of their younger age and lesser psychiatric involvement. A high prevalence of smoking was observed in the psychiatric population studied, and 28.9% were diagnosed with COPD.
Conclusion: Smokers presented many more respiratory symptoms and chronic bronchitis but did not present a worse quality of life or physical activity due to their younger age and milder psychiatric involvement.
Keywords: smoking, psychiatric patients, spirometry, quality of life, COPD, physical activity
Introduction
It is well known that the life expectancy of adults with severe psychiatric disorders admitted to mental health institutions is reduced by up to 25 years compared to the general population,1,2 despite the causes of death being the same: cardiovascular and respiratory diseases and cancer. Among others, the factors influencing early mortality include: deficient alimentation, sedentarism, and smoking. Indeed, a reduction of 12–13 years in the life expectancy of these patients has been attributed to smoking.3 Up to 70% of patients with schizophrenia and other severe mental disorders smoke, with this frequency being double or triple that of the general population.4,5 In addition, patients with mental illness smoke more frequently, with patients with schizophrenia generally smoke more than 20–30 cigarettes/day.6 Therefore, the impact of smoking on the high mortality rate of the population with schizophrenia is not surprising.7
COPD has been described to have an important effect on the quality of life and the physical activity of patients even in early stages of the disease.8 However, there are very few studies on the relationship of smoking and health-related quality of life and physical activity in psychiatric patients. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to determine the prevalence of smoking in patients with long-term admission to a mental health institution for a psychiatric disorder and its relationship with respiratory disease, quality of life, and physical activity.
Patients and methods
Study design
A cross-sectional, observational study was conducted with the aim of analyzing the smoking habit, respiratory symptoms, and alterations in spirometric results of patients admitted for a long term with psychiatric disorders and to determine the relationship of smoking with the quality of life and physical activity of these patients.
This study was approved by the Research and Ethics Committee of the Fundació Sant Joan de Déu (Barcelona, Spain). The confidentiality of the data of the patients and the legal guardians was maintained, and informed consent was obtained from all the patients included in the study.
Setting
The study was conducted at the Mental Health Centre of the Parc Sanitari Sant Joan de Déu de Sant Boi de Llobregat (Barcelona, Spain).
Participants
All adult patients with psychiatric disorders admitted to the study center for more than 6 months were included in the study. Patients or those with legal guardians who did not provide written informed consent or who did not cooperate during the tests were excluded from the study.
Variables
The clinical history of the patients was first collected to determine the possible presence of known respiratory disease, previous hospitalizations, and length of admission for respiratory problems. Moreover, detailed information related to smoking was obtained, including the Fagerström dependence test.9 A smoker was defined as a patient who smoked at least one cigarette per day and an ex-smoker was defined as a person who had not smoked for at least 6 months. The patients were classified by their psychiatric diagnosis (according to the International Classification of Diseases, ninth revision [ICD-9]).10
The usual physical activity was evaluated using the London Chest Activity of Daily Living (LCADL) questionnaire, which has been translated and validated in Spanish.11,12 The LCADL is a specific questionnaire made up of 15 items and four domains of activity: self-care, household activities, physical activity, and leisure activities. An overall score is obtained as well as a score for each group of activity.
Respiratory symptoms were evaluated using the Spanish version of the European Commission for Steel and Coal (ECSC) respiratory symptom questionnaire.13 As in previous epidemiological studies,8,14 an individual was considered to have a usual cough with an affirmative response to at least one of the following questions: “Do you usually cough when you get up in the morning?” and “Do you cough every day during 3 months of the year?” An individual was considered to usually expectorate, if they had an affirmative answer to any of the following questions: “Do you usually expectorate when you get up in the morning?”, “Do you expectorate during the day or the night?”, or “Do you expectorate almost every day or night during 3 months of the year?” A patient was considered to have dyspnea if they had an affirmative answer to the question, “Do you become breathless when you climb the stairs at a normal pace?” Wheezing was evaluated with the following question: “Have you noticed wheezing in your chest?” Chronic bronchitis was considered if the patient presented with cough and expectoration during more than 3 months a year for over more than 2 consecutive years. Asthma was diagnosed with an affirmative answer to the question, “Has a doctor told you that you have asthma?” Similar to previous epidemiological studies, a diagnosis prior to COPD was considered when a patient disclosed having been diagnosed with chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or COPD.8,14
The Medical Research Council (MRC) scale was used to evaluate the intensity of dyspnea that classifies dyspnea into five grades of intensity (0, absence of dyspnea up to 5, dyspnea while resting).15 The presence of significant comorbidity was quantified with the Charlson Index,16 which takes into account the number and severity of the most frequent chronic diseases. Health-related quality of life was measured using the 5-dimension EuroQoL (EQ-5D) questionnaire translated and validated into Spanish.17 This is a generic questionnaire, which includes a descriptive system that enables the respondent to classify his/her health according to three levels in five dimensions: mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression. The data may be used to represent a profile of health status or may be converted into a single summary index (EQ-5D index) by applying scores from a valuation set. Higher EQ-5D scores represent a more favorable health status. The minimally important clinical difference for the EQ-5D index has been estimated to be 0.051.17
Spirometry and bronchodilator tests (Datospir 200 Sibel Med, Barcelona, Spain) were carried out by specialized personnel according to the guidelines of the Spanish Society of Pneumology and Thoracic Surgery (SEPAR).18 A post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC <0.7 was considered diagnostic of COPD. Exercise capacity was measured with the 6-minute walk test (6MWT) according to international guidelines.19,20
Data sources
Data were obtained from revision of the clinical records and direct interview with the participating patients. Questionnaires were either self-administered or administered by the investigators according to their instructions of use. Spirometry with bronchodilator test and the 6MWT were conducted during the clinical visit.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive analysis of the different variables of interest collected was made using the mean and SD or medians with the interquartile range (IQR) for continuous variables and absolute frequencies and percentages for categorical variables. The Student’s t-test was used to compare continuous variables with a normal distribution between smokers and non-smokers, whereas variables with a non-normal distribution were compared with the Mann–Whitney U test. Categorical variables were compared with the chi-square or Fisher’s exact test, when appropriate. A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant. The SPSS (SPSS for Windows, IBM Static version 22, Chicago, IL, USA) statistical package was used for the statistical analyses.
Results
Participants
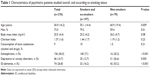
Of the 350 adult patients admitted to the center, 74 did not provide consent or were unable to complete the tests or fill out the questionnaires of the study; therefore, 276 patients (78.8%) were included and constituted the study population. Of these, 204 were men (72.6%; mean age 56.8 [SD=16.1] years; mean body mass index [BMI] 25.4 [SD=4.1]). The characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1.
The psychiatric diagnoses of the patients included were: 156 (56.5%) cases of chronic schizophrenia, 46 (16.4%) cases with affective or personality disorders, 49 (17.4%) with intellectual disability, and 25 (8.9%) with dementia (Figure 1).
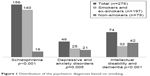  | Figure 1 Distribution of the psychiatric diagnoses based on smoking. |
Of the patients studied, 181 (65.6%) were active smokers, and 15 (5.4%) were ex-smokers. Among smokers, 96.9% (189/196) smoked cigarettes, five smoked cigars, and only one smoked a pipe. Of the smokers, 87.7% (172/196) had schizophrenia with a mean tobacco consumption of 24.5 pack-years (SD=10.5), 54.3% (106/196) had a depressive or anxiety disorder with a consumption of 21.6 pack-years (SD=9.7), and 43.2% (85/196) had dementia or intellectual disability with a consumption of 18.3 pack-years (SD=9.1), and an overall mean tobacco consumption of 23.8 pack-years (SD=11.9). The mean score in the Fagerström test was 5.75 (SD=2.86) points, and only four active smokers had a history of attempting to cease smoking.
Analysis of patient history and respiratory symptoms
Table 2 shows the previous respiratory diagnoses, previous admissions, the MRC dyspnea scale score obtained, and the main respiratory symptoms presented by the patients as well as a comparison of the differences between smokers and non-smokers. The main symptoms presented by smokers and non-smokers were: cough (47.6% [93/196] vs 2.4% [2/79], respectively; p=0.03) and expectoration (41.4% [81/196] vs 2.4% [2/79], respectively; p=0.01). Among the smokers, 36.6% (72/196) fulfilled criteria of chronic bronchitis vs only 2.4% (2/79) of the non-smokers (p=0.001). The prevalence of a previous diagnosis of COPD and asthma was significantly greater in smokers compared to non-smokers. No significant differences were observed between the two groups of patients only in relation to the presence of dyspnea (Table 2).
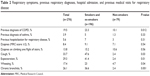  | Table 2 Respiratory symptoms, previous respiratory diagnoses, hospital admission, and previous medical visits for respiratory disease |
Prevalence of COPD
It was impossible to conduct spirometry in 18 patients. In 83 patients, the spirometries were not evaluable because of incorrect maneuvers (many patients were not able to perform maximal inspiration or complete expiration), and finally, 175 spirometries with a bronchodilator test were considered acceptable (63.4%). Among the smokers, spirometry was possible in 71% (139/196) compared to only 43% (34/79) among non-smokers. The diagnosis of COPD was determined in 50 cases (28.7%), 37 of whom had been diagnosed previously. The results are shown in Table 3.
Analysis of health-related quality of life and physical activity
A mean score of 0.74 (SD=0.21) was obtained by smokers in the EQ-5D questionnaire compared to 0.57 (SD=0.16) in non-smokers (p=0.001). In regards to physical activity, the total scores and those of the different dimensions of the LCADL questionnaire were significantly better in the smokers. The 6MWT was successfully completed by 236 patients (85.5%). The mean distance walked was 289 (SD=56) m, being greater, albeit not significantly, for smokers. Table 4 shows the main results of the EQ-5D and LCADL questionnaires.
Discussion
This study found that the prevalence of smoking in a long-stay psychiatric hospital was 62.5%. Indeed, among the patients with schizophrenia, this percentage rose to up to 87.7%. Of note were the strong dependence on tobacco, the scarce frequency of attempts to cease smoking, and the elevated prevalence of respiratory symptoms in the smoker psychiatric population, with more than one fourth of the patients developing COPD. These results are in contrast with the better scores obtained in the questionnaires on quality of life and physical activity in smoker patients. One explanation for these better results may be that the smoker population was significantly younger and patients with schizophrenia predominated, whereas the non-smoker population included a higher percentage of patients with intellectual disability or dementia, which may have an important impact on different aspects of health, activity, and autonomy.
The first aspect of note in the results of this study was that the prevalence of smoking in the psychiatric population studied was more than double that observed in the general Spanish adult population,14,21 and was even slightly higher than the percentage reported in studies including similar populations.6 Although a higher prevalence of smoking was observed among patients with schizophrenia, 54.3% of patients admitted for depressive and anxiety disorders smoked, which was a similar frequency to that described in other studies.22 The percentage of patients with dementia and/or intellectual disability who smoked (43.2%) can also be considered as being very high, although there are no previous studies with which these results can be compared. However, the mean tobacco consumption (23.8 pack-years), seems low for this special population with a mean age of 56 years and a high prevalence of COPD. It is likely that this consumption may be underestimated due to self-reporting.
Beyond the elevated prevalence of smoking, the high grade of nicotine dependence and the low number of attempts to cease smoking were of note among the patients included in the present study. The mean score in the Fagerström test was 5.75, which is higher than the score of 4.77 obtained in the group of smokers with COPD in the IBERPOC epidemiological study conducted in Spain.23 In fact, only four admitted patients had attempted to give up smoking at some time. Our results concur with the 5.6 score observed in a recent study among inpatients with schizophrenia in Croatia.24 The grade of nicotine dependence together with the intensity of the smoking habit and the measurement of CO in exhaled air is a prognostic marker of the development of COPD in smokers.25 Therefore, the incidence of cases of COPD in this population can be expected to be especially elevated, as shown in the present study.
One possible explanation for this high dependence is that nicotine modulates numerous neurotransmitter systems including dopamine, acetylcholine, endogenous opioid peptides, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), norepinephrine, and serotonin that are related to the pathogenesis of mental disorders.26,27 In addition, this high dependence is increased by genetic and environmental factors,28 and by a reduction of the symptoms and secondary effects of psychiatric treatment, which seems to occur with smoking.29,30
Smoker patients were found to present significantly more respiratory symptoms, especially cough and expectoration, compared to non-smokers. Thus, 36.6% of the smokers fulfilled clinical criteria of chronic bronchitis, which is more than double the prevalence observed among smokers in the general adult population in Spain.8,31 However, the sensation of dyspnea reported by the smokers was similar to that of non-smokers, and this may be due to a possible reduction in their perception.32 Furthermore, smokers presented a greater number of admissions for respiratory problems despite being younger.
The prevalence of COPD observed in the present study was 28.9%, being higher than the 10.2% observed in the population over 40 years of age in Spain,8 and similar to the 26.3% reported in adult smokers.33 Moreover, previous studies have shown an increase in the risk of developing COPD and chronic bronchitis in patients with schizophrenia, with ORs of 4.2 and 2.8, respectively.34–36
Surprisingly, smoker patients showed significantly and clinically better scores in the quality of life and physical activity questionnaires and they also reported fewer problems with mobility, self-care, and usual activities and had better pain/discomfort scores compared with non-smokers. A possible explanation for these paradoxical results is that the study included two groups of patients who were heterogeneous with respect to age and psychiatric diagnosis. The group of smokers was younger and included a higher percentage of schizophrenic patients and a lower number of patients with intellectual disability or dementia. The latter present a high dependence for basic daily life activities (even the impossibility of smoking), which worsens the parameters of quality of life and mobility. Interestingly, the 0.74 utility value obtained in smokers and ex-smokers is almost identical to the 0.73 found in a group of patients with COPD in a previous study in Spain.37 The low number of patients with schizophrenia among the non-smokers did not allow comparison of the differences in quality of life and physical activity with smoker patients with schizophrenia, although other studies have described a clear relationship between low levels of physical activity and a worse quality of life in these patients,6 similar to what occurs in the non-psychiatric population.38 The low mean walking distance in the 6MWT was of note, suggesting that this test may not be valid in this type of patients because it cannot be ensured that they have made maximum effort in performing the test.20
It has been reported that tobacco is the main cause of death in people with psychiatric disorders.39 Smoking is also related to increased suicide risk, and a recent study indicated that suicide may be almost as important as a cause of death as cancer,40 leading to increasingly more suggestions that psychiatric centers should be tobacco free.41 Some of the reasons why smoking continues in psychiatric centers are cultural habits (tobacco makes up part of the idiosyncrasy of these institutions) and the idea that change results in resistance. This latter idea is held not only by the patients but also by the relatives as well as the personnel in the center, including physicians and caregivers, who defend the right of patient choice and suggest possible social and psychiatric benefits, although not demonstrated, derived from continuing to smoke. These possible benefits include facilitation of socialization or a reduction in the secondary effects of the treatment, among others.42 However, in a study carried out in a psychiatric center in Melbourne (Australia), when the patients were asked if they would like to stop smoking or reduce their consumption, only 22.5% answered no.43
Although it is complex and difficult, smoking cessation by psychiatric patients is possible. In a review by Moss et al, it was concluded that with the application of consensus measures among the caregivers,41 the family, and the patients themselves, acceptable rates of smoking cessation could be achieved with the available therapeutic measures, and this would lead to tobacco-free psychiatric centers.
Strengths and limitations
Our study has the strength of a comprehensive evaluation of the whole population of patients admitted to a long-term psychiatric hospital; however, it has a series of limitations. First, it is a unicenter study, which means that the results may not be fully representative of patients in other centers or countries. Second, this was a cross-sectional descriptive study and, therefore, we did not perform any adjusted models to evaluate associations. Moreover, this design makes it impossible to establish any cause–effect relationship. Third, we did not have any objective measure of tobacco consumption available and, therefore, despite the high prevalence of smoking the recorded consumption may have been underestimated. In addition, the number of spirometer tests performed in the non-smoking population was low due to the more severe cognitive impairment in this population.
Conclusion
The prevalence of smoking in the psychiatric population studied was more than double that described in the general population. On comparing smoker and non-smoker patients, it was found that the smokers presented significantly more respiratory symptoms and chronic bronchitis. Surprisingly, compared with non-smokers, the smoker patients presented better scores in the questionnaires on quality of life and physical activity, which may be explained by their different characteristics and baseline disease.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank all the personnel in the Área de Salut Mental del Parc Sanitari Sant Joan de Déu for their essential and altruistic collaboration which enabled the conduct of this study.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Lutterman T, Ganju V, Schacht L, Shaw R, Monihan K, Huddle M. Sixteen State Study on Mental Health Performance Measures. DHHS pub no (SMA) 03-3835. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Center for Mental Health Services; 2003. | ||
Parks J, Svendensen D, Singer P, Foti ME. Morbidity and Mortality in People with Serious Mental Illness. 13th Technical Report. Alexandria, Va, National Association of State Mental Health Program Directors 2006. Available from: www.nammhpd.org/publicationsmeddir.efm. Accessed February 2, 2018. | ||
Ziedonis DM, Zammarelli L, Seward G, et al. Addressing tobacco use through organizational change: a case study of addiction treatment organization. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2007;39(4):451–459. | ||
de Leon J, Diaz FJ. A meta-analysis of worldwide studies demonstrates and association between schizophrenia and tobacco smoking behaviors. Schizophr Res. 2005;76(2–3):135–157. | ||
Tanskanen A, Viinamaki H, Koivumaa-Honkanen HTJ, Lehtonen J. Smoking among psychiatric patients. Eur Psychiatry. 1997;11:179–188. | ||
Dixon L, Meodff DR, Wohlheiter K, et al. Correlates of severity of smoking among persons with severe mental illness. Am J Addict. 2007;16(2):101–110. | ||
Olfson M, Gerhard T, Huang C, Crystal S, Stroup TS. Premature mortality among adults with schizophrenia in the United States. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72(12):1172–1181. | ||
Miravitlles M, Soriano JB, García Rio F, et al. Prevalence of COPD in Spain: impact of undiagnosed COPD on quality of life and daily life activities. Thorax. 2009;64(10):863–868. | ||
Fagerström KO. Measuring degree of physical dependence to tobacco smoking with reference to individualization of treatment. Addict Behav. 1978;3(3–4):235–241. | ||
Clasificación Internacional de Enfermedades 9ª revisión Modificación Clínica, CIE-9-MC, 7ª edición. Enero 2010. Ministerio Sanidad, Política Social e Igualdad. [International Classification of Diseases 9th revision Clinical Modification, ICD-9-MC, 7th ed. Madrid: Ministry of Health, Social Policy and Equality; 2010]. Spanish. | ||
Garrod R, Bestall JC, Paul EA, Wedzicha JA, Jones PW. Development and validation of a standardized measure of activity of daily living in patients with severe COPD: the London Chest Activity of Daily Living scale (LCADL). Respir Med. 2000;94(6):589–596. | ||
Vilaró J, Gimeno E, Sánchez Férez N, et al. Actividades de la vida diaria en pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica: validación de la traducción española y análisis comparativo de 2 cuestionarios [Activities of daily life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: validation of the Spanish translation and comparative analysis of 2 questionnaires]. Med Clin (Barc). 2007;129(9):326–332. Spanish [with English abstract]. | ||
Minette A. Questionnaire of the European Community for Coal and Steel (ECSC) on respiratory symptoms. 1987 – updating of the 1962 and 1967 questionnaires for studying chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Eur Respir J. 1989;2(2):165–177. | ||
Peña VS, Miravitlles M, Gabriel R, et al. Geographic variations in prevalence and underdiagnosis of COPD: results of the IBERPOC multicentre epidemiological study. Chest. 2000;118(4):981–989. | ||
Bestall JC, Paul EA, Garrod R, Garnham R, Jones PW, Wedzicha JA. Usefulness of the Medical Research Council (MRC) dyspnoea scale as a measure of disability in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 1999;54(7):581–586. | ||
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373–383. | ||
Badia X, Roset M, Montserrat S, Herdman M, Segura A. La versión española del EUROQoL: descripción y aplicaciones [The Spanish version of EuroQol: a description and its applications. European Quality of Life scale]. Med Clin (Barc). 1999;112(Suppl 1):79–85. Spanish [with English abstract]. | ||
García-Río F, Calle M, Burgos F, et al; Spanish Society of Pulmonology and Thoracic Surgery (SEPAR). Normativa Espirometría SEPAR [Spirometry. Spanish Society of Pulmonology and Thoracic Surgery (SEPAR)]. Arch Bronconeumol. 2013;49(9):388–401. Spanish [with English abstract]. | ||
ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories. ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(1):111–117. | ||
Celli B, Tetzlaff K, Criner G, et al; COPD Biomarker Qualification Consortium. The 6-minute-walk distance test as a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease stratification tool. Insights from the COPD biomarker qualification consortium. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;194(12):1483–1493. | ||
Soriano JB, Miravitlles M, Borderías L, et al. Diferencias geográficas en la prevalencia de EPOC en España: relación con hábito tabáquico, tasas de mortalidad y otros determinantes [Geographical variations in the prevalence of COPD in Spain: relationship to smoking, death rates and other determining factors]. Arch Bronconeumol. 2010;46(10):522–530. Spanish [with English abstract]. | ||
Olivier D, Lubman DI, Fraser R. Tobacco smoking with psychiatric inpatient settings: biopsychosocial perspective. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2007;41(7):572–580. | ||
Jiménez-Ruiz CA, Masa F, Miravitlles M, et al. Smoking characteristics: differences in attitudes and dependence between healthy smokers and smokers with COPD. Chest. 2001;119(5):1365–1370. | ||
Šagud M, Vuksan-Ćusa B, Jakšić N, et al. Nicotine dependence in Croatian male inpatients with schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry. 2018;18(1):18. | ||
Jiménez-Ruiz C, Miravitlles M, Sobradillo V, et al. Can cumulative tobacco consumption, FTND score, and carbon monoxide concentration in expired air be predictors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Nicotine Tob Res. 2004;6(4):649–653. | ||
Dalack GW, Healy DJ, Meador-Woodruff JH. Nicotine dependence in schizophrenia: clinical phenomena and laboratory findings. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155(11):1490–1501. | ||
Picciotto MR. Nicotine as modulator behaviour: beyond the inverted U. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24(9):493–499. | ||
Kalman D, Kahler CW, Tirch D, Kaschub C, Penk W, Monti PM. Twelve-week outcomes from an investigation of high-dose nicotine patch therapy for heavy smokers with a past history of alcohol dependence. Psychol Addict Behav. 2004;18(1):78–82. | ||
Sacco KA, Bannon KL, George TP. Nicotinic receptor mechanisms and cognition in normal states and neuropsychiatric disorders. J Psychopharmacol. 2004;18(4):457–474. | ||
Morisano D, Bacher I, Audrian Mc-Govern J, George TP. Mechanisms underlying the comorbidity of tobacco use in mental health an addictive disorders. Can J Psychiatry. 2009;54(6):356–367. | ||
Miravitlles M, de la Roza C, Morera J, et al. Chronic respiratory symptoms, spirometry and knowledge of COPD among general population. Respir Med. 2006;100(11):1973–1980. | ||
Laurin C, Moullec G, Bacon SL, Lavoie KL. The impact of psychological distress on exacerbation rates in COPD. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2011;5(1):3–18. | ||
Llordés M, Jaén A, Almagro P, et al. Prevalence, risk factors and diagnostic accuracy of COPD among smokers in primary care. COPD. 2015;12(4):404–412. | ||
Hsu JH, Chien IC, Lin CH, Chou YJ, Chou P. Increased risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in patients with schizophrenia: a population-based study. Psychosomatics. 2013;54(4):345–351. | ||
Schoepf D, Uppal H, Potluri R, Heun R. Physical comorbidity and its relevance on mortality in schizophrenia: a naturalistic 12-year follow-up in general hospital admissions. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;264(1):3–28. | ||
Partti K, Vasankari T, Kanervisto M, et al. Lung function and respiratory diseases in people with psychosis: population-based study. Br J Psychiatry. 2015;207(1):37–45. | ||
Miravitlles M, Huerta A, Fernández-Villar JA, et al. Generic utilities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients stratified according to different staging systems. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014;12:120. | ||
Ramon MA, Esquinas C, Barrecheguren M, et al. Self-reported daily walking time in COPD: relationship with relevant clinical and functional characteristics. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:1173–1181. | ||
Hurt RD, Offord KP, Croghan IT, et al. Mortality following inpatient addictions treatment. Role of tobacco use in a community-based cohort. JAMA. 1996;275(14):1097–1103. | ||
Kõks G, Fischer K, Kõks S. Smoking-related general and cause-specific mortality in Estonia. BMC Public Health. 2017;18(1):34. | ||
Moss TG, Weinberger AH, Vessicchio JC, et al. A tobacco reconceptualization in psychiatry: toward the development of tobacco-free psychiatric facilities. Am J Addict. 2010;19(4):293–311. | ||
George TP, Ziedonis DM. Addressing tobacco dependence in psychiatric practice: promises and pitfalls. Can J Psychiatry. 2009;54(6):353–355. | ||
Moeller-Saxone K. Cigarette smoking and interest in quitting among consumers at a Psychiatric Disability Rehabilitation and Support Service in Victoria. Aust N Z J Public Health. 2008;32(5):479–481. |
 © 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.