Back to Journals » Patient Preference and Adherence » Volume 13
Nurse-led follow-up to outpatients with cancer pain treated with opioids at home—telephone calls plus WeChat versus telephone calls only: a quasi-experimental study
Authors Qiao S, Tang L, Zhang W, Tian S, Liu M, Yang L, Ye Z
Received 2 February 2019
Accepted for publication 30 April 2019
Published 7 June 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 923—931
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S203900
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Shina Qiao*, Leiwen Tang*, Weibo Zhang, Suming Tian, Minjun Liu, Lili Yang, Zhihong Ye
Affiliated Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Background: Recently, cancer pain management has come increasingly to be provided in outpatient settings, requiring health-care providers and outpatients to take on responsibilities. Pain is among the most distressing symptoms of cancer.
Objectives: To compare the effectiveness of nurse-led telephone calls plus WeChat versus telephone calls only for the pain management of outpatients with cancer.
Methods: 231 outpatients with cancer pain were classified into two groups (group 1, N=125; group 2, N=106). Group 1 was followed up with weekly telephone calls for eight weeks, and group 2 with weekly telephone calls combined with the booklets through WeChat for eight weeks. Differences between groups in pain level, side effects, medication adherence, and satisfaction with pain management were analyzed, and statistical differences were tested usingan independent-sample t-test and a chi-squared test.
Results: Group 2 had a significantly lower rest pain (p<0.01), and lower move pain but there was no statistical difference between the two groups. Among patients in group 2, constipation, nausea and vomiting, and dizziness were less (p<0.01), while medication adherence (p<0.05) and pain management satisfaction were higher (p<0.01) than patients in group 1.
Conclusion: Nurse-led follow-up telephone calls combined with WeChat significantly reduced opioid-related health problems, such as pain intensity, side effects and medication adherence.
Keywords: nurse, follow-up, telephone, WeChat, outpatient, cancer pain
Introduction
Pain is one of the most feared symptoms in cancer patients.1 While patients can be relieved of most of the cancer pain effectively using the World Health Organization analgesic ladder, 10–20% of them fail to respond to conventional treatment.2 Patients who present with cancer pain are often complex, and as chronic cancer pain can be difficult to manage, these patients often require more than a single interaction with a physician or other health-care professional to achieve even adequate control over their pain. Participation of anesthetists who are interested in the field of interventional cancer pain management has been highlighted as a key to achieving successful control over cancer pain.3,4 A combination of conventional medical management with intraspinal drug delivery resulted in significant pain relief and reduced side effects.5 However, invasive procedures are used only as a last resort in cancer pain management.6
Unfortunately, disease progression, tolerance to opioids, or increased side effects can prevent patients from attaining adequate long-term pain control. Authors suggest that frequent follow-ups, telephone calls, and other medical strategies can have better results. Transitional care programs have proven to be effective in supporting post-discharge patients, with positive outcomes including reduced readmission rates,7,8 enhanced quality of life,9 self-efficacy,7,9 and satisfaction.5,8 Home visits and telephone calls are the two most common approaches used in transitional care programs. A study by McEwan and Billings10 has shown that a telephone counseling service is an effective way of communicating with patients and a fast way to answer patients’ questions. Patients receiving this counseling can have their wrong beliefs corrected, be made aware of treatment choices, and receive support.11 One study has suggested that following up on a patient’s condition via telephone after discharge is a quick and cost-effective way to address their physical and psychosocial concerns, thus improving their quality of life.12 However, one randomized controlled trial (RCT) has shown that merely a single telephone call did not have an effect on the outcome measures of patient satisfaction.13
Does this indicate the need to provide repeated calls? Recently, many different social media technologies have been widely used as educational health promotion strategies for disease management. In the UK, mobile applications are used to actively engage cancer survivors in publicly available physical fitness programs.14 WeChat is a popular smartphone-based social media application that has emerged as an effective medium and an established interactive educational platform through which to deliver health education to patients. WeChat-based health education programs have been found more effective than traditional methods, and can increase follow-up rate and improve satisfaction in patients with chronic illness.15 One RCT16 showed that an eight-week intervention with education through WeChat was much more effective in facilitating medication adherence than telephone calls with booklets, although there was no difference in pain level.
In China, in order to manage opioids and keep patients safe, the government has a policy for outpatients who have been requested to establish a special medical chart for the use of opioids for a long time (more than two weeks) at home, a situation very different from that of other countries. Patients treated with opioids in hospitals take medications according to their physicians’ prescription, under the strict supervision of the health-care providers. For outpatients, lacking this supervision and the support that comes with it, there are some added obstacles to effective pain management, related to addiction, side effects, expenses, and extremely strict control of analgesics.
In our hospital, since 2009, nurses assisting in pain management have been guiding outpatients with cancer pain once or twice a month through telephone follow-ups in order to improve outpatients’ pain control outcomes. However, there were still many opioid-related problems even when the frequency of contact was upped to a weekly telephone call. Based on that, we decided to implement some strategies to solve or reduce these health problems. In March 2017, we established the WeChat platform and a WeChat group for outpatients with cancer pain.
To our knowledge, prolonged intervention with the use of telephone calls combined with WeChat has not been evaluated in outpatients with cancer pain. We intended to test a follow-up approach involving nurse-led telephone calls combined with WeChat, to determine its potential to improve the patients’ pain situation after discharge. The hypothesis underlying this study is that an approach involving nurse-led telephone call follow-up combined with WeChat for outpatients with cancer pain has the potential to longitudinally decrease pain level, reduce side effects caused by opioids, and enhance satisfaction with information on pain management.
Theoretical framework
The cognitive theory of multimedia learning was popularized by the work of Richard E. Mayer and other cognitive researchers who argue that multimedia supports the way that the human brain learns.17 They assert that people learn more deeply from words and pictures than words alone. The words can be spoken or written, and the pictures can be any form of graphical imagery including illustrations, photos, or video.18
Mayer’s Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning was used during our design of the WeChat element of this study. This theory was utilized to promote engagement of outpatients as they navigate available health information using WeChat. Based on this theory, audio and visual components were incorporated, with videos on the WeChat platform, and a WeChat communication group within which patients can send text messages to health-care providers was established.
Objectives
The purpose of the study was to determine the effects of delivering follow-ups combined with WeChat on cancer pain outpatients’ opioid-related outcomes. Specific research questions included the following:
Are there differences in pain intensity, side effect, and medication adherence outcomes for outpatients with cancer pain between the two groups?
Is the follow-up combined with WeChat an effective way to improve pain management?
Methods
Sample and setting
A convenience sample was obtained by recruiting clinic patients from Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, a public hospital in Southeastern China. Patients were eligible to participate if they had newly established the special medical charts during this study, were being treated with opioids with no previous history of opioid use, not satisfied with pain control for cancer pain management, were able to speak and write Mandarin, were able to report pain score by themselves, could be reached through telephone and communicated over WeChat, and had consented to participate in this study. Patients were excluded if the diagnosis was not cancer, had been treated with opioids for cancer pain for no more than 2 weeks, or if they refused to participate. As shown in Figure 1, of the 257 patients who were screened, 246 were eligible to participate, 130 and 116 eligible patients seen at clinics in March–December 2016 (group 1) and in March–December 2017 (group 2), respectively. Patients included in group 2 all had newly established special medical charts from March–December 2017 and did not overlap the patients from group 1.
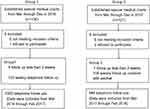 | Figure 1 Flowchart of the study. |
Intervention
All patients were followed up for eight weeks unless they stopped using opioids. Patients from group 2 were invited to join in the WeChat group, and the WeChat platform was shared with them. The WeChat platform was put in a public place in clinics, and patients could easily share with other patients. We recruited patients at different time periods and divided them into two groups in order not to contaminate the data. Education booklets on pain management, side effects, and coping skills, which included “Common Misunderstandings about Painkillers,” “Ways to Cope with Side Effects,” and “the Numerical Rating Scale,” and two videos entitled “The story of Mrs Zhao” and “The story of Mr Li,” were distributed weekly on WeChat. Patients could send text messages in the WeChat group to ask questions as needed related to pain management, and three health-care providers would give them some suggestions. Patients from group 1 could gain knowledge on cancer pain management during telephone calls, and could call back as needed. After this study, there were also invited to join in WeChat.
Data collection
There were two components of the data: one component was collected as patients’ baseline data from the special medical charts at the patients’ first clinics, and included age, gender, education, cancer status and pain status; the other component included pain status, side effects and medication adherence, which were provided through weekly telephone calls. The overall satisfaction with pain control support was provided at the last telephone call of each group. The demographic data items were based on the literature19 and factors that could influence the variables, as mentioned above. In order to avoid patients sharing WeChat with each other, we recruited patients at different time periods and divided them into two groups. Because patients were recruited one by one, not all the patients were recruited at the same time. As we needed at least eight weeks for the last patients (recruited in December 2016) to receive the follow-up intervention and in order not to overlap the data, we stopped collecting data for this study from group 1 until February 2017. The intervention period for group 2 was the same as that for group 1, we stopped collecting data by follow-ups from group 2 until February 2018.
Instruments and procedure
Patients were identified by clinic staff and screened for eligibility by the researcher, who then approached eligible patients, explained the study, and obtained written informed consent. Telephone follow-up calls were made by the same nurse. Calls lasted for about 3–5 min, and a standard telephone call form was used. This brief standard telephone call form was designed based on the Brief Pain Inventory – Chinese version20 (BPI-C) and revised by four experts in pain management; it was much shorter than BPI-C and included these questions: 1) How do you scale your rest pain on average in the last week? 2) How do you scale your move pain on average in the last week? 3) Did you feel uncomfortable in the last week, such as constipation, dizziness, nausea or vomiting? 4) How often do you take the medication? 5) Are you satisfied with the pain management in the last week? The nurse should record pain intensity, side effects of analgesics, adherence situation, and satisfaction with pain management.
Pain was assessed using the Numerical Rating Scale.21 In groups 1 and 2, 1,000 and 848 telephone calls were made, respectively, by the nurse in this study, and the total rest/move pain score in group 1 equal to the sum of all the scores of rest/move pain in group 1, the same calculation with the total pain score in group 2.
Details of side effects were collected through weekly telephone calls after patients’ first clinics. The incidences of side effects of analgesics were calculated at the end of the research. The incidence of each side effect was equal to the number of patients who had the side effect during this study divided by the total number of patients of each group. Patient satisfaction with pain control was recorded as “satisfied” or “not satisfied” and calculated at the last telephone follow-up.
Medication adherence was calculated from the telephone call reports, and the nurse would also calculate according to the medical chart. Medication possession ratio (MPR) was adapted to calculate medication adherence. An MPR score of 1 would indicate that a patient had medication in their possession 100% of the time for the calculated time period.22 A lower MPR would indicate that there were days in which the patient did not have their medication in their possession and would, therefore, indicate a lower adherence rate. In this study, MPR equal to medication all days take divided by eight weeks. Caro et al tested different adherence thresholds by creating a multilevel adherence variable of 50% (poor adherence), 50–90% (moderate adherence), and >90% (high adherence).23
The education booklets distributed through the WeChat platform included “Common Misunderstandings about Painkillers,” “Ways to Cope with Side Effects,” “The Numerical Rating Scale,” shown as education articles and two videos entitled “The story of Mrs Zhao” and “The story of Mr Li,” each lasting for 4–8 min. The education booklets included information on using the Numerical Rating Scale to evaluate the intensity of pain, common side effects, and ways to cope with them, such as taking fluids, positioning, massage, or medications, and the two videos about correct and incorrect beliefs about pain. Based on the experience of the early telephone calls, we found that side effects were one of the main causes of patients discontinuing or reducing opioids themselves. Constipation in particular was a stubborn side effect, and from our early telephone calls, we found that honey or milk was valuable for some patients to relieve constipation, so we included this information in the booklet. A panel of experts validated the content of the booklet.
Data analysis
All data were analyzed using SPSS 19.0. The Fisher’s exact test and independent-samples t-tests were used to compare differences between the two groups on demographic, cancer status, and pain variables at baseline. Independent-samples t-tests were also used to compare the differences between the two groups on pain intensity. The data were presented as the mean ± SD or n (%). The independent-samples t-test was used for statistical analysis of the continuous data, the chi-square test was used for statistical analysis of the categorical data, and p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
There were 125 and 106 patients included in group 1 and group 2, respectively. All of them were followed up for eight weeks. The nurse implemented a total of 1,000 and 848 telephone follow-ups, respectively, in group 1 and group 2.
Baseline patient characteristics
Table 1 shows that the two groups’ patients were comparable with regard to demographic and disease-related variables. The mean age of the patients was 64.82±5.03 years, the mean pain score at rest was 2.29±1.46, and the mean pain score at movement was 4.51±1.32 in group 1. The mean age of the patients was 61.04±6.35 years, the mean pain score at rest was 2.42±1.56, and the mean pain score at movement was 3.75±1.55 in group 2. There was no significant difference in age, education, pain score or cancer status between the two groups at baseline. The flow chart of this study is shown in Figure 1.
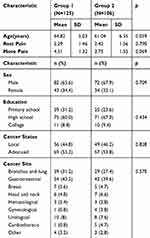 | Table 1 Sample characteristics by group at baseline |
Pain severity
Compared with group 1, the pain score at rest of the patients in group 2 was decreased (p<0.01); and also, the pain score at movement in group 2 was decreased even there was no significant difference in pain score between the two groups (p>0.05), as shown in Table 2. Pain increased in group 1 after intervention both at rest and with movement, but there was no significant difference in pain score between pre- and post-intervention (p>0.05), as shown in Table 3. Pain score in group 2 decreased after intervention (p<0.05).
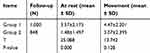 | Table 2 Total pain score |
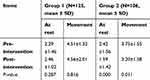 | Table 3 Pain score pre- and post-intervention |
Side effects of analgesics
In group 2, 37.7% of patients had no side effects, while the percentage was 28.8% in group 1.
Side effects recorded included nausea and vomiting, dizziness, pruritus, urinary retention, and constipation. Constipation, nausea and vomiting, and dizziness were the most common side effects in this study. The incidence of urinary retention (group 1: 2.4%; group 2: 4.7%) and pruritus (group 1: 0.8%; group 2: 0.9%) was higher in group 2, but there was no statistical difference between them. The incidence of dizziness, constipation and nausea and vomiting in group 2 was much lower than in group 1 (p<0.01), as shown in Table 4.
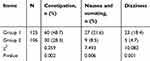 | Table 4 Side effects |
Medication adherence
Medication adherence (Table 5) was recorded at each telephone call, and at the end of the data collection, a value of MPR was calculated. According to Caro et al, MPR higher than 90% is high adherence, and most of the patients got a high adherence. The percentage of patients’ high adherence was 79.2% in group 1 and increased to 89.6% in group 2 (p<0.05).
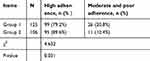 | Table 5 Medication adherence |
Satisfaction with pain control
Each patient’s rate of satisfaction with pain control (Table 6) was recorded at each telephone follow-up, and calculated respectively at the end of the data collection. Statistical differences between the two groups were tested using the chi-squared test. The results showed that patients’ satisfaction with pain control rose from 57.6% to 93.4% (p<0.01).
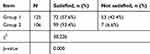 | Table 6 Satisfaction with pain control |
Discussion
Pain is one of the most common symptoms in cancer patients, with an incidence of about 59% overall and for advanced cancer patients as high as 64%.24 It is easier for health-care providers to manage cancer pain of inpatients, but cancer pain may last throughout the course of the disease, and some discharged patients may discontinue their medications due to their worries about side effects or about getting addicted to the medications.
Recently, studies have shown the positive impact that supportive care programs provided by nurses can have on patients.25,26 Telephone follow-ups can serve as a way to exchange information, provide health education and advice, manage symptoms, recognize complications early, reassure patients, and provide high-quality care.27 An RCT found that just a single telephone call did not have an effect on the outcome measures of patient satisfaction and sense of security and suggested that multiple calls may be more satisfying for patients.13 From our previous experience of follow-ups, we concluded that telephone calls only were not effective for cancer pain management, and might lead to lower medication adherence, incorrect pain beliefs, and inability to tolerate side effects, amounting to poor pain management.
When first taking their medications, patients often receive a large amount of information about them from their health-care providers. Patients often cannot digest and assimilate all this information in a short time,28 or may forget what they have learned. Outpatients may not return to health-care providers due to such confusions. WeChat currently has 600 million active users out of the 1.12 billion registered users.29 WeChat can provide consistent health support through the communication and dissemination of disease-related information, overcoming many time and location constraints.30,31
In this study, we adopted telephone calls combined with booklets provided through WeChat. The results showed an increase in pain severity both at rest and with movement in group 1 post-intervention, which may be because patients from group 1 had a lower medication adherence and a higher pain score as the disease progressed. The pain severity also limited the scope of patients’ movements to some extent. In contrast, pre-intervention pain severity reduced both at rest and with movement in group 2 (Table 3). As shown in Table 2, the total rest pain score had a reduction of 2.09 in group 2. This difference of pain score between two groups not only reached statistical significance but can be considered clinically meaningful.32
Providing health education on managing pain in this way played an important role; information could be reinforced, thereby increasing medication adherence and reducing self-scored pain. Through continuous follow-up calls combined with WeChat, patients can find effective ways to deal with their own problems, and the booklets delivered over the WeChat platform can provide them with videos to answer the questions that they worried about. Patients in group 2 were thus able to learn from WeChat according to their needs, and were able to solve the problems they encountered by sending text messages to the doctors and nurses through the WeChat group, who provided feedback and encouraged them to cope with their situation, resulting in higher medication adherence and better pain management. Most of the patients included in this study had advanced cancer, and their pain changed as the disease progressed, for patients with frequent breakthrough pain, the nurse will remind them to return to the doctor, which is an effective way for a nurse to manage such patients, because, in China, nurses do not have the right to suggest drug adjustments to the patients. At the same time, this approach increases patients’ satisfaction with pain management in contrast to their old concept of simply bearing it. The present results show that the follow-up approach involving telephone calls combined with the booklet through WeChat can help to reduce opioids' related side effects of dizziness, nausea and vomiting, and constipation. By WeChat, patients learned to deal with some of the side effects themselves or find help from health-care providers who can give them suggestions on WeChat instead of coming back to the clinic.
Ethics approval from hospital committee
This study obtained approval from the Human Subjects Committee of Affiliated Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine. All subjects signed written informed consent forms.
Limitations
This is a quasi-experimental study to compare the effectiveness of nurse-led telephone calls combined with booklets through WeChat versus telephone calls only. In China, WeChat is very popular and is used in many areas, and it is a very easy method for message propagation. In this study, the WeChat platform was put in a public place in clinics, and patients could easily share it with other patients. It is hard to include patients randomly at the same time period, so we recruited patients at different time periods and divided them into two groups in order not to contaminate the data. We designed this study as a quasi-experimental study and not an RCT. We acknowledge that this is a weakness of the study.
Implications for practice
WeChat is a useful method to support patients with cancer pain to manage pain at home. The findings that WeChat does not only increase the knowledge of patients' self-management of the side effects, but also provides a suggestion of medication adjustment by the health-care providers. Accessing the WeChat platform resulted in improvements in pain management, side effects and medication adherence.
Although this research has provided insight regarding WeChat for pain management and opioid-related symptom management, and the results showed that it is a worthwhile tool for patients with mild pain; however, for patients with moderate or severe pain further research is needed into interventions delivered to patients with cancer pain by WeChat.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, telephone calls combined with booklets through WeChat are effective interventions that can potentially decrease pain level and lessen side effects. It is an acceptable and convenient way to help patients follow health-care providers’ guidance. However, this was only a quasi-experimental study and lacked variety in outcome measurements or validated instruments. Although the telephone calls combined with the booklet sent through WeChat were valued by patients, additional research should address these study design and outcome measurement issues to establish statistical significance.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Hangzhou Health Science & Technology Plan Project (grant no. 2018A87) and Zhejiang Province Science and Technology Hall Project (grant no. LGF18G030001).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Breitbart W, Park J, Katz AM. Psycho-Oncology.
2. Gupta N, Patel FD, Kapoor R, Sharma SC. Pain management in cancer. Internet J Pain Sympt Control Palliat Care. 2007;5(1):83–89.
3. Sayed D. The interdisciplinary management of cancer pain. Tech Reg Anesthesiol Pain Manag. 2013;17(4):163–167. doi:10.1053/j.trap.2014.07.003
4. O’Brien T, Kane CM. Pain services and palliative medicine: an integrated approach to pain management in the cancer patient. Br J Pain. 2014;8(4):163–171. doi:10.1177/2049463714548768
5. Smith TJ, Staats PS, Deer T, et al. Randomized clinical trial of an implantable drug delivery system compared with comprehensive medical management for refractory cancer pain: impact on pain, drug-related toxicity, and survival. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(19):4040–4049. doi:10.1200/JCO.2002.02.118
6. Smith TJ, Coyne PJ. Implantable drug delivery systems (IDDS) after failure of comprehensive medical management (CMM) can palliate symptoms in the most refractory cancer pain patients. J Palliat Med. 2005;8(4):736–742. doi:10.1089/jpm.2005.8.736
7. Wong FKY, Ho MM, Yeung S. Effects of a health-social partnership transitional programme on hospital readmission: a randomized controlled trial. Soc Sci Med. 2011;73:960–969. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2011.06.036
8. Naylor MD, Brooten DA, Campbell RL, et al. Transitional care of older adults hospitalized with heart failure: a randomized, controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52:675–684. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52202.x
9. Wong FKY, Chow SKY, Chan TMF, et al. Comparison of effects between home visits with telephone calls and telephone calls only for transitional discharge support: a randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing. 2014;43:91–97. doi:10.1093/ageing/aft123
10. McEwan A, Billings L. Past use of and current satisfaction with a nurse-led hospital cardiac helpline. Br J Cardiac Nurs. 2009;4:372–377. doi:10.12968/bjca.2009.4.8.43491
11. Stacey D, Chambers SK, Jacobsen MJ, Dunn J. Overcoming barriers to cancer-helpline professionals providing decision support for callers: an implementation study. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2008;35:961–969. doi:10.1188/08.ONF.961-969
12. Zhang JE, Wong FKY, You LM, Zheng MC. A qualitative study exploring the nurse telephone follow-up of patients returning home with a colostomy. J Clin Nurs. 2011;21:1407–1415. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2702.2011.03824.x
13. Jensen BT, Kristensen SA, Christensen SV, Borre M. Efficacy of tele-nursing consultations in rehabilitation after radical prostatectomy: a randomised controlled trial study. Int J Urol Nursing. 2011;5:123–130. doi:10.1111/ijun.2011.5.issue-3
14. Puszkiewicz P, Roberts AL, Smith L, Wardle J, Fisher A. Assessment of cancer survivors’ experiences of using publicly available physical activity mobile application. JMIR Cancer. 2011;2:1–19.
15. Feng S, Liang Z, Zhang R, et al. Effects of mobile phone WeChat services improve adherence to corticosteroid nasal spray treatment for chronic rhinosinusitis after functional endoscopic sinus surgery: a 3-month follow-up study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;274:1477–1485. doi:10.1007/s00405-016-4371-0
16. Li X, Liu W. Effects of WeChat intervention on medication adherence and pain intensity in cancer patients. Chin J Nurs. 2015;50(12):1454–1457.
17. Mayer RE, Moreno RA. A cognitive theory of multimedia learning: implications for design principles; 1998: 1–11. Available from:
18. Mayer RE. Multimedia Learning. New York: Cambridge University Press; 2009.
19. Jordi P, Sara O, Emmanouil R, Manuel B, Yoram S. The McGill University Health Centre Cancer Pain Clinic: a retrospective analysis of an interdisciplinary approach to cancer pain management. Pain Res Manage. 2016;1–7.
20. Wang XS, Mendoza TR, Gao SZ, Cleeland CS. The Chinese version of the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI-C): its development and use in a study of cancer pain. Pain. 1996;67:407–416.
21. Hjermstad MJ, Fayers PM, Haugen DF, et al. Studies comparing numerical rating scales, verbal rating scales and visual analogue scales for assessment of pain intensity in adults: a systematic literature review. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2011;41:1073–1093. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2010.08.016
22. Lindsey D, Sarah H, Bradley M. A Palliative Care Clinic's Experience with Medication Adhrence to Neuropathic Pain Medications. J Palliat Med. 2018;21(2):245–248. doi:10.1089/jpm.2015.0230
23. Caro JJ, Ishak KJ, Huybrechts KF, Raggio G, Naujoks C. The impact of compliance with osteoporosis therapy on fracture rates in actual practice. Osteoporosis Int. 2004;15(12):1003–1008. doi:10.1007/s00198-004-1652-z
24. Van Den Beuken-van Everdingen MH, De Rijke JM, Kessels AG, Schouten HC, Van Kleef M, Patijn J. Prevalence of pain in patients with cancer: a systematic review of the past 40 years. Ann Oncol. 2007;18(9):1437–1449. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdm056
25. Banna GL, Collova E, Gebbia V, et al. Anticancer oral therapy: emerging related issues. Cancer Treat Rev. 2010;36(8):595–605. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.04.005
26. Bordonaro S, Romano F, Lateri E, et al. Effect of a structured, active, home-based cancer-treatment program for the management of patients on oral chemotherapy. Patient Preferences Adherence. 2014;8:917–923. doi:10.2147/PPA.S62666
27. Mistiaen P, Poot E. Telephone follow-up, initiated by a hospital-based health professional, for postdischarge problems in patients discharged from hospital to home. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;4:CD004510.
28. Schilder CM, Seynaeve C, Linn SC, et al. Cognitive functioning of postmenopausal breast cancer patients before adjuvant systemic therapy, and its association with medical and psychological factors. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2010;76(2):133–141. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2009.11.001
29.
30. Liu X, Luo H, Zhang L, et al. Telephone-based re-education on the day before colonoscopy improves the quality of bowel preparation and the polyp detection rate: a prospective, colonoscopist-blinded, randomised, controlled study. Gut. 2014;63:125–130. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2012-304292
31. Li W, Han LQ, Guo YJ, Sun J. Using WeChat official accounts to improve malaria health literacy among Chinese expatriates in Niger: an intervention study. Malar J. 2016;15:567. doi:10.1186/s12936-016-1621-y
32. Bedard G, Zeng L, Zhang L, et al. Minimal clinically important differences in the edmonton symptom assessment system in patients with advanced cancer. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2013;46(2):192–200. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2012.07.022
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
