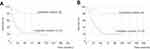Back to Journals » Clinical and Experimental Gastroenterology » Volume 12
Number of positive lymph nodes and lymphatic invasion are significant prognostic factors after pancreaticoduodenectomy for distal cholangiocarcinoma
Authors Suzuki S , Shimoda M, Shimazaki J, Maruyama T , Oshiro Y , Nishida K, Kuroda J, Miyoshi K, Koike N, Harada N
Received 2 March 2019
Accepted for publication 2 May 2019
Published 6 June 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 255—262
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CEG.S207333
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Anastasios Koulaouzidis
Shuji Suzuki,1 Mitsugi Shimoda,1 Jiro Shimazaki,1 Tsunehiko Maruyama,1 Yukio Oshiro,1 Kiyotaka Nishida,1 Jun Kuroda,1 Kenta Miyoshi,1 Nobusada Koike,2 Nobuhiko Harada2
1Department of Gastroenterological Surgery, Ibaraki Medical Center, Tokyo Medical University, Ibaraki 300-0395, Japan; 2Department of Surgery, Hachioji Digestive Disease Hospital, Tokyo 192-0903, Japan
Background: Early recurrence of distal cholangiocarcinoma (DCC) may result in a poorer prognosis. This study aimed to evaluate the clinicopathological factors that predict survival and recurrence in patients with DCC.
Methods: Fifty-five patients with DCC who underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy between 2005 and 2015 were studied retrospectively. The following clinicopathological parameters were analyzed as predictors of disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS): sex, age, body mass index, presence of biliary tract decompression, macroscopic type, histological type, tumor size, TNM classification, lymph node metastasis ratio, number of positive lymph nodes (PLNs), lymphatic invasion, venous invasion, perineural invasion, proximal bile duct margin, dissected margin, portal system invasion, arterial system invasion, stage, and residual tumor.
Results: Univariate analysis showed that contiguous extension of the primary tumor, PLN, lymphatic invasion, venous invasion, perineural invasion, and stage were significant prognostic factors for DFS and OS. Multivariate analysis revealed that PLN and lymphatic invasion were prognostic for DFS and OS (P<0.001). Significant differences in OS and DFS were found in analyses stratified by PLN (0, 1, 2 vs ≥3) and lymphatic invasion (0 vs 1, 2, 3).
Conclusion: Among the clinicopathological parameters analyzed, PLN and lymphatic invasion were confirmed as prognostic factors for DCC.
Keywords: number of positive lymph nodes, lymphatic invasion, prognostic factor, distal cholangiocarcinoma
Introduction
Distal cholangiocarcinoma (DCC) is a relatively rare epithelial malignancy, constituting approximately 30% of all cholangiocarcinomas.1 Moreover, the incidence of this cancer is increasing worldwide.2 Surgical resection by pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) remains the only definitively curative therapy for the long-term survival of DCC patients. However, the reported 5-year survival rates after surgical curative resection for DCC range from only 18%–47.1%.3–5 Moreover, early recurrence of DCC results in a poorer prognosis.6 To date, the prognostic factors for DCC following surgical resections have been reported to be perineural invasion,7 lymph node metastasis,4,6 resection margin,8 T stage according to TNM classification,5 and tumor differentiation.3,6
The recent Japanese classification of biliary tract cancers principally adopted the 7th edition of the staging system developed by the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) and the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC).9 However, several pathological points are described in detail in the revised Japanese classification system, which retains the classification of site-specific surgical margin status.10 Prior to this time, pathological factors of DCC meeting the recent Japanese classification of biliary tract cancers had not been discussed. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the clinicopathological factors that could predict survival and recurrence for patients with DCC.
Materials and methods
Fifty-five DCC patients who underwent PD between 2005 and 2015 were examined retrospectively at our center and its associated hospitals. Regional lymph node dissection was performed routinely for DCC, and dissection of the regional lymph nodes, including nodes along the common hepatic artery, nodes in the hepatoduodenal ligament, and anterior or posterior pancreatoduodenal nodes, was performed in most patients by only four surgeons. The following clinicopathological parameters were analyzed as predictors of disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS): sex, age, body mass index (BMI), presence of biliary tract decompression, macroscopic type, histological type, tumor size, TNM classification, number of retrieved lymph nodes (DLNs), lymph node metastasis ratio (LMR), number of positive lymph nodes (PLNs), lymphatic invasion, venous invasion, perineural invasion, proximal bile duct margin, dissected margin, portal system invasion, arterial system invasion, stage, and residual tumor. Pathological factors were defined in accordance with the 3rd English edition of the Japanese classification of biliary tract cancers.9 For distant metastasis (M), the following categories were applied: M0, no distant metastasis, and M1, distant metastasis specified as PUL (pulmonary), MAR (bone marrow), OSS (osseous), PLE (pleura), HEP (hepatic), PER (peritoneum), BRA (brain), ADR (adrenals), LYM (lymph nodes), SKI (skin), or OTH (other) metastases. For proximal bile duct margin (HM), the following categories were applied: HM0, no involvement of the proximal ductal margin; HM1, microscopic, but not macroscopic, involvement of the proximal bile duct margin, and HM2, macroscopic and microscopic involvement of the proximal bile duct margin. For dissected margin (EM), the following categories were applied: EM0, no involvement of the dissected margin; EM1, microscopic, but not macroscopic, involvement of the dissected margin, and EM2, macroscopic and microscopic involvement of the dissected margin. For residual tumor (R), the following categories were applied: R0, no residual tumor; R1, microscopic residual tumor, and R2, macroscopic residual tumor.9 The R factor was included in both the proximal bile duct margin and dissected margin factors. All patients had pathologically confirmed DCC and underwent PD via duct-to-mucosa pancreaticojejunostomy, without a stenting tube.
Statistical analysis
The chi-squared test was used to evaluate differences in categorical data. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were generated and compared using log-rank tests. P-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant. Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to perform the multivariate analyses for factors with significance (P<0.05) identified by univariate analysis. The SPSS statistical software package, version 24.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA), was used for the statistical analysis.
Ethics statement
The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Ibaraki Medical Center, Tokyo Medical University (acceptance number 16–37). All procedures in this study involving human participants were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration. Written informed consent was not required, as the study was retrospective, and patients were not identifiable. This article does not contain any animal studies performed by any of the authors.
Results
The mean patient age was 69.8 (range, 54–86) years, and the study cohort included 41 men (74.5%) and 14 women (25.5%). All patients had pathologically confirmed DCC. The following UICC stages were observed: Ia, seven patients (12.7%); Ib, five patients (9.1%); IIa, 18 patients (32.7%); IIb, 23 patients (41.8%), and IV, two patients (3.6%). In addition, 36, 17, and two patients achieved R0, R1, and R2 status, respectively. R1 cases comprised three cases of HM1 and seven cases of EM1. Median DFS was 31.4 months, and DFS rates at 1, 3, and 5 years were 67.3%, 41.4%, and 39.5%, respectively. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival and median survival time for OS were 90.9%, 52.4%, and 37.9%, and 42 months, respectively. Univariate analysis showed that T, PLN, lymphatic invasion, venous invasion, perineural invasion, and stage were significant prognostic factors for DFS and OS (Tables 1 and 2). Multivariate analysis revealed that PLN and lymphatic invasion were prognostic for DFS and OS (Tables 1 and 2). Significant differences in OS and DFS were found in survival analyses stratified by PLN (0, 1, 2 vs ≥3) and lymphatic invasion (0 vs 1, 2, 3) (Figure 1A and B) (Figure 2A and B).
 | Table 1 Univariate and multivariste analyses of relationship between various clinicopathological factors and disease-free survival (DFS) |
 | Table 2 Univariate and multivatiate analyses of relationship between various clinicopathological factors and overall survival (OS) |
Discussion
DCC is a relatively uncommon disease, accounting for approximately 30% of all cholangiocarcinomas, and is reported to occur more frequently in Japan than in Western countries.3,4 Several previous studies have reported significant prognostic factors for DCC, including histopathological findings evaluated according to the UICC and AJCC staging systems. We investigated DCC in Japan, using the 7th edition of the Japanese classification of biliary tract cancers staging system.
Periampullary tumors are differentiated as an inhomogeneous set of lesions with very different long-term survival rates following PD, despite having a common embryological origin.11 Furthermore, cholangiocarcinomas, a heterogeneous group depending on site of origin, may show different tendencies in the invasion of bordering structures, which affect both the role of surgery and long-term outcome.12 Operative procedures are determined by the location and extent of the tumor; therefore, PD, in terms of lymph node dissection, is the radical resection performed for DCC patients with complete tumor resection.13 In our study, this surgery was performed for DCC patients.
Previous studies have reported median DFS of 14.6–36 months.6,14,15 In the present study, median DFS was 31.4 months. In previous reports, the estimated cumulative probabilities of recurrence at 5 years have ranged from 41.1%–67.0%.5,6,14,15 The most common distant metastasis location was the liver, followed by the peritoneum and isolated locoregional recurrences.14,15 Previous studies have reported several prognostic factors for DFS, such as nodal status, histological differentiation, microvascular invasion, perineural invasion, and pancreatic invasion.6,14,15 In the current study, the best prognostic factors for DFS were PLN and lymphatic invasion, as shown by multivariate analysis. These factors are related to local recurrence and lymph node metastasis, and they could be used to classify postoperative recurrence after tumor resection.
Several prognostic factors for OS after resection of DCC have been reported, including nodal status, perineural invasion, histological differentiation, R status, T category, resection margin, vascular invasion, pancreatic invasion, and portal vein invasion.3–8,12,15–18 In the current study, PLN and lymphatic invasion were confirmed to be prognostic factors for OS. In a meta-analysis, Wellner et al found that resection margin status is an influential prognostic factor for 5-year survival.16 Sasaki et al reported that invasive carcinoma at the ductal resection margins in DCC appears to have a significant relation to local recurrence.17 In a review article, Wakai et al reported that patients with residual carcinoma in situ at the ductal resection margins for DCC may have late local recurrence, whereas residual invasive ductal lesions cause early local recurrence.18 However, in our study, margin status did not affect the mode of recurrence, although patients with >3 positive lymph nodes and positive lymphatic invasion status demonstrated significantly more recurrences and poorer prognoses in the multivariate analysis.
The LMR has been reported to be an effective prognostic factor for several cancers;19,20 however, its prognostic utility remains controversial for DCC.21 Kiriyma et al reported that the poor survival of patients with higher LMRs could be explained by the presence of many involved nodes in DCC.4 However, differences between the numbers of lymph nodes that are dissected at different institutions present an obstacle to the use of LMR as a prognostic factor. In cases of colorectal cancer, higher numbers of evaluated lymph nodes per case have been associated with better prognoses.22 The AJCC has endorsed a “12-node minimum” for DCC to prevent inadequate staging. In the current study, the overall number of evaluated lymph nodes per patient (mean ± standard error) was 16.11±1.34. Therefore, we regard the evaluation of lymph node dissections in this study as being adequate. Our analysis revealed that PLN ≤2 and negative lymphatic invasion status were significant and independent predictors of good prognosis without LMR. This study revealed that lymphatic system invasion was the most important prognostic factor for DCC.
Hernandez et al concluded that aggressive operative resection and application of adjuvant therapy should be used to treat all patients with cholangiocarcinoma without evidence of distant disease, even when an R0 resection has been performed.23 Evaluating a randomized trial with 108 perihilar cases and 117 distal cases, Ebata et al reported that the survival probability was not significantly different between a gemcitabine adjuvant chemotherapy group and an observation group.24 In a systematic review, a beneficial effect of adjuvant therapy was not evident in the overall analysis, but was observed in subgroups formed according to lymph node involvement and recommended adjuvant chemotherapy in node-positive disease following resection.25 The review reported that adjuvant chemotherapy was beneficial for patients with LN-positive or R1 disease.25 Adequate lymph node dissection may, therefore, improve prognosis in DCC patients.
The present study has several limitations: first, it was retrospective, although the DCC patients were consecutively recruited; second, it included only a small number of cases because of the relative rarity of DCC. Hence, additional multicenter investigations involving larger patient populations are needed before definitive conclusions can be drawn.
Conclusion
A wide range of clinicopathological parameters were analyzed in this study, which confirmed that PLN and lymphatic invasion are prognostic for DFS and OS following radical resection of DCC. Therefore, adequate lymph node dissection may be an effective strategy for improving the curability and prognosis of patients with DCC.
Acknowledgment
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Launois B, Reding R, Lebeau G, Buard JL. Surgery for hilar cholangiocarcinoma: french experience in a collective survey of 552 extrahepatic bile duct cancers. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2000;7(2):128–134.
2. Von Hahn T, Ciesek S, Wegener G, et al. Epidemiological trends in incidence and mortality of hepatobiliary cancers in Germany. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011;46(9):1092–1098. doi:10.3109/00365521.2011.589472
3. Andrianello S, Paiella S, Allegrini V, et al. Pancreaticoduodenectomy for distal cholangiocarcinoma: surgical results, prognostic factors, and long–term follow–up. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2015;400(5):623–628. doi:10.1007/s00423-015-1320-0
4. Kiriyama M, Ebata T, Aoba T, et al. Nagoya Surgical Oncology Group. Prognostic impact of lymph node metastasis in distal cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Surg. 2015;102(4):399–406. doi:10.1002/bjs.9752
5. Kim YS, Hwang IG, Park SE, et al. Role of adjuvant therapy after R0 resection for patients with distal cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016;77(5):979–985. doi:10.1007/s00280-016-2970-5
6. Choi SB, Park SW, Kim KS, Choi JS, Lee WJ. The survival outcome and prognostic factors for middle and distal bile duct cancer following surgical resection. J Surg Oncol. 2009;99(6):335–342. doi:10.1002/jso.v99:6
7. Tan X, Xiao K, Liu W, Chang S, Zhang T, Tang H. Prognostic factors of distal cholangiocarcinoma after curative surgery: a series of 84 cases. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013;60(128):1892–1895.
8. Qiao QL, Zhang TP, Guo JC, et al. Prognostic factors after pancreatoduodenectomy for distal bile duct cancer. Am Surg. 2011;77(11):1445–1448.
9. Miyazaki M, Ohtsuka M, Miyakawa S, et al. Classification of biliary tract cancers established by the Japanese society of hepato–biliary–pancreatic surgery: 3rd English edition. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015;22(3):181–196. doi:10.1002/jhbp.223
10. Ohtsuka M, Miyakawa S, Nagino M, Takada T, Miyazaki M. Revision concepts and distinctive points of the new Japanese classification for biliary tract cancers in comparison with the 7(th) edition of the Union For International Cancer Control and the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015;22(3):197–201. doi:10.1002/jhbp.223
11. Androulakis J, Colborn GL, Skandalakis PN, Skandalakis LJ, Skandalakis JE. Embryologic and anatomic basis of duodenal surgery. Surg Clin North Am. 2000;80(1):171–199. doi:10.1016/S0039-6109(05)70401-1
12. Ercolani G, Dazzi A, Giovinazzo F, et al. Intrahepatic, peri–hilar and distal cholangiocarcinoma: three different locations of the same tumor or three different tumors? Eur J Surg Oncol. 2015;41(9):1162–1169. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2015.05.013
13. Kwon HJ, Kim SG, Chun JM, Lee WK, Hwang YJ. Prognostic factors in patients with middle and distal bile duct cancers. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(21):6658–6665. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6658
14. Courtin–Tanguy L, Rayar M, Bergeat D, et al. The true prognosis of resected distal cholangiocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2016;113(5):575–580. doi:10.1002/jso.24165
15. Komaya K, Ebata T, Shirai K, et al. Nagoya surgical oncology group. recurrence after resection with curative intent for distal cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Surg. 2017;104(4):426–433. doi:10.1002/bjs.10452
16. Wellner UF, Shen Y, Keck T, Jin W, Xu Z. The survival outcome and prognostic factors for distal cholangiocarcinoma following surgical resection: a meta–analysis for the 5–year survival. Surg Today. 2017;47(3):271–279. doi:10.1007/s00595-016-1362-0
17. Sasaki R, Takeda Y, Funato O, et al. Significance of ductal margin status in patients undergoing surgical resection for extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Surg. 2007;31(9):1788–1796. doi:10.1007/s00268-007-9102-7
18. Wakai T, Sakata J, Katada T, et al. Surgical management of carcinoma in situ at ductal resection margins in patients with extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2018;2(5):359–366. doi:10.1002/ags3.12196
19. Rosenberg R, Friederichs J, Schuster T, et al. Prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer is associated with lymph node ratio: a single-center analysis of 3026 patients over a 25-year time period. Ann Surg. 2008;248(6):968–978. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181855718
20. Schiffman SC, McMasters KM, Scoggins CR, Martin RC, Chagpar AB. Lymph node ratio: a proposed refinement of current axillary staging in breast cancer patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;213(1):45–52. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2011.04.024
21. Kawai M, Tani M, Kobayashi Y, et al. The ratio between metastatic and examined lymph nodes is an independent prognostic factor for patients with resectable middle and distal bile duct carcinoma. Am J Surg. 2010;199(4):447–452. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2009.01.019
22. Schrembs P, Martin B, Anthuber M, Schenkirsch G, Märkl B. The prognostic significance of lymph node size in node–positive colon cancer. PLoS One. 2018;12(8):e0201072. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0201072
23. Hernandez J, Cowgill SM, Al–Saadi S, et al. An aggressive approach to extrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas is warranted: margin status does not impact survival after resection. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15(3):807–814. doi:10.1245/s10434-007-9756-2
24. Ebata T, Hirano S, Konishi M, et al. Bile Duct Cancer Adjuvant Trial (BCAT) study group. Randomized clinical trial of adjuvant gemcitabine chemotherapy versus observation in resected bile duct cancer. Br J Surg. 2018;105(3):192–202. doi:10.1002/bjs.10776
25. Horgan AM, Amir E, Walter T, Knox JJ. Adjuvant therapy in the treatment of biliary tract cancer: a systematic review and meta–analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(16):1934–1940. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.40.5381
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.