Back to Journals » International Journal of General Medicine » Volume 13
Major miRNA Involved in Insulin Secretion and Production in Beta-Cells
Authors Aghaei M, Khodadadian A, Elham KN , Nazari M , Babakhanzadeh E
Received 9 February 2020
Accepted for publication 3 March 2020
Published 10 March 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 89—97
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S249011
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Mohsen Aghaei,1 Ali Khodadadian,1 Karimi-Nazari Elham,2 Majid Nazari,1 Emad Babakhanzadeh1,3
1Department of Medical Genetics, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran; 2Nutrition and Food Security Research Center, School of Public Health, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran; 3Medical Genetics Research Center, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran
Correspondence: Emad Babakhanzadeh Email [email protected]
Abstract: Insulin is implicated as a leading factor in glucose homeostasis and an important theme in diabetes mellitus (DM). Numerous proteins are involved in insulin signaling pathway and their dysregulation contributes to DM. microRNAs (miRNAs) as single-strand molecules have a critical effect on gene expression at post-transcriptional levels. Intensive investigation done by DM researchers disclosed that miRNAs have a significant role in insulin secretion by direct targeting numerous proteins engaged in insulin signaling pathway; so, their dysregulation contributes to DM. In this review, we presented some major miRNAs engaged in the insulin production and secretion.
Keywords: insulin, diabetes mellitus, microRNAs, insulin signaling pathway
Introduction
Insulin, as an endocrine hormone, serves as a mediator in glucose metabolism and energy storage. This spherical miniprotein hormone (5.8 kDa) is derived from the intermolecular disulfide bridge (CysA7-CysB7 and CysA20-CysB19) between peptide chains of the A-chain (Ins-A, 21 amino acid residues) that contains an intramolecular disulfide bridge (CysA6-CysA11) and B-chain (Ins-B, 30 amino acid residues).1 Pancreatic islets in mammals are rich in beta-cells and are assumed as the only source of circulating insulin.2 Freshly synthesized insulin in beta-cells is initially produced as the prohormone proinsulin. Later, it is converted into mature insulin by the prohormone convertase action (PC1, PC2, encoded by Pcsk1 and Pcsk2, respectively) during shuttling by the secretory pathway.1 Active insulin is kept in condensed core secretory granules (5–10,000 per cell),3 while each of these granules contains 300,000 or more molecules of insulin.2 According to the literature, changes in insulin secretion are one of the main reasons for the beginning of diabetes mellitus (DM).4 In the current research, we introduced the major pathways involved in insulin granule fusion, focused on most important miRNAs that contributed to insulin production and secretion, and finally discussed miRNA-therapy as a novel approach to alleviate diseases such as DM.
Proteins Involved in Docking and Fusion
High-affinity interaction between SNAREs, as highly conserved proteins, which are soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor, has a significant effect on insulin granule docking, priming, and fusion. These proteins include synaptobrevin-2 (VAMP), stx-1, and SNAP-25 (25-kDa synaptosomal-associated protein): Stx-1 and SNAP25 are plasma membrane proteins and are named t-SNAREs (target SNAREs); VAMP exists in the vesicle or granule membrane and is often called v-SNAREs (vesicle SNAREs), in this protein as a homologous SNARE motif is composed of 60–70 amino acids. The four SNARE motifs (stx-1 has one SNARE motif, VAMP has a separate SNARE motif, while SNAP 25 has two SNARE motives) combine together to establish a ternary complex that has a significant effect on insulin granules’ fusion with the plasma membrane.5
The cAMP Role in Insulin Granule Exocytosis
The regulator activity of cAMP in various cellular functions of various cell types has changed cAMP into an important universal intracellular messenger.6 The cAMP generation from ATP is catalyzed by adenylyl cyclases (ACs) and 10 members of this enzyme family have been identified while their expressions in islet cell were proved.7 In insulin secretion, it has been long known that cAMP action is mediated by protein kinase A (PKA)8 of proteins associated with the secretory process through phosphorylation.
ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channel
The ATP-sensitive potassium channel (KATP channel) is a metabolic sensor, which is able to couple a cell’s metabolic status with electrical activity and adjusts various cellular functions. In pancreatic beta-cells, KATP channels regulate the secretion of insulin.9 With regard to structure, KATP channels, as large hetero-octameric complexes include four regulatory sulphonylurea receptors (SURx) and four pore-forming (Kir6.x) (via cytoplasmic domains bind to ATP) subunits, which are encoded by ABCC8 and KCNJ11, respectively.10,11 Considering the KATP channel activity, the membrane is held at a hyperpolarized level that results in voltage-gated Ca2+ channels’ closure.12 A rise in the serum glucose triggers the pancreatic beta-cell to uptake glucose through glucose transporter GLUT2. Later, glucose converts into ATP via subsequent mechanisms.10 By binding to Kir6.2, ATP closes the KATP channel; this closure can be facilitated by Epac2, which binds with the channel’s SUR1 subunit.13,14 As a result, a membrane depolarization is created that opens channels of the voltage-gated Ca2+ and initiates the beta-cell electrical activity as well as Ca2+ influx. Subsequently, increase in [Ca2+] stimulates the insulin release.12
G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR)
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), as versatile, seven-transmembrane-domain proteins, are responsible for regulating various intracellular signaling arrays cascade in response to hormones, neurotransmitters, and ions.15 In this regard, G proteins include heterotrimer proteins consisting of the α, β, and γ subunits. Although G proteins differ basically in amino acid with regard to their sequence of the α-subunit, such as Gs, Gi, and Gq, many of them can couple with the GPCRs. Gs makes the adenylate cyclase active and increases production of cAMP and activates protein kinase A (PKA) and the Epac (exchange proteins that are activated by cAMP directly) family of cAMP-regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Both PKA and Epac contain multiple downstream effectors in insulin secretion. Gi is responsible for inhibiting the adenylate cyclase and stimulating the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). In order to produce inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG), Gq stimulates PLC-β. Finally, IP3 stimulates the Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum, while DAG makes protein kinase C active.16
MicroRNAs are introduced as a class of gene expression negative regulators involved in developing endocrine pancreas and regulating insulin secretion.17
Biogenesis and Maturation of miRNA
The miRNA genes, transcribed by RNA polymerase II (Pol II), are controlled by RNA Pol II-associated transcription factors and epigenetic regulators. In this regard, long primary transcript (pri-miRNA) that span over 1kb has a local hairpin structure, which contains miRNA sequences.18 The nuclear RNase III Drosha and DGCR8 create a complex: Microprocessor. This Microprocessor copies the stem–loop and initiates the maturation process in order to release a small hairpin-shaped RNA of ~65 nucleotides in length (pre-miRNA).19 After this export, pre-miRNA is cleaved next to the terminal loop by Dicer and liberates a small RNA duplex consisting of a passenger and guide strand.20 Subsequently, this RNA duplex forms the effector complex of RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) after loading onto an AGO protein.21 Following the above-mentioned process, the pre-RISC (in which AGO proteins are associated with RNA duplexes) eliminates the passenger strand quickly and generates a mature RISC that performs gene silencing (Figure 1).22 Following miRNA duplex loading, the pre-RISC (in which AGO proteins associate with RNA duplexes) quickly removes the passenger strand to generate a mature RISC that performs gene silencing.23 In this review, we tried to introduce better miRNAs involved in insulin secretion and production (Table 1), Figure 2.
 |
Table 1 Selected miRNAs Involved in Insulin Secretion |
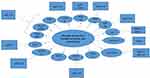 |
Figure 2 A summary of the major miRNAs involved in production and secretion of insulin and their interaction with targets. |
miR-7
MiR-7, as an intronic miRNA, is mapped to the initial intron of heterogenous ribonuclear protein K gene on chromosome 9.24 MiR-7 has been evolutionarily conserved and has recently emerged as a prototypical neuroendocrine miRNA. Among the neurons and neuroendocrine organs most significantly enriched in miR-7 the endocrine pancreas, pituitary, and adrenal glands can be mentioned.25,26
The mTOR, as a serine/threonine kinase, acts as a growth regulator as well as nutrient sensor. It exists as part of two functionally and biochemically distinct complexes: mTOR complex1 (mTORC1) and mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2).27 The mTORC2 was found to mediate the phosphorylation of Akt/PKB at ser47. Phosphorylation Akt at ser 473 activates Akt for further phosphorylation in catalytic domain at Thr 308. Akt and 3-phosphoinositide –dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) trigger full activation of Akt, which is very important for glucose uptake.28 Furthermore, it was found that miR-7 down-regulated Akt, mTOR, and P70S6K transcription, which are considered as the major components of PI3K/Akt pathway.29
miR-9
MiR-9 is produced by mapping three genes of miR-9-1, miR-9-2, and miR-9-3 in the human genome to chromosomes 1, 5, and 15, respectively.30 MiR-9 mediate insulin exocytosis in insulin-producing cells through direct targeting Onecut-2 (OC-2) mRNA. As a result, decreased expression of the OC-2 can increase the Granuphilin levels, as its target gene. Additionally, it is well known that Granuphilin acts as a negative regulator of insulin secretion.31
The sirtuins family of proteins are NAD-dependent protein deacetylases involved in numerous physiological processes, such as apoptosis, cell growth, stress response, and energy metabolism.32–34 This family has been found to have seven members involving Sirt 1‑7. Mammalian Sirt1 is widely expressed in mammalian tissues and functions as a nuclear protein. As its main characteristic, mammalian Sirt1 can deacetylate histones’ co-regulators in a NAD-dependent manner and transcription factors.35–38 As a member of the mitochondrial inner membrane proteins, UCP2 has been implicated to promote proton leakage across the mitochondrial. In this way, UCP2 through decreasing ATP synthesis reduces insulin secretion. It is also of great importance that Sirt1 binds to the UCP2 promoter and abolishes UCP2 transcriptional activation. In this manner, Sirt1 regulates insulin secretion.39 Furthermore, recent investigations have introduced mir-9 as a key factor in modulating Sirt1 expression in the living organism. As Saunders et al40 reported, mir-9 targets Sirt1 in embryonic stem cells of rats. However, the intensive investigation conducted by Ramachandran et al41 showed that the above-mentioned process (mir-9 targeting of Sirt1) is a significant physiological process in insulin-secreting cells.
miR-29
The miR-29 family includes four mature members including miR-29a, miR-29b1, miR-29b2, and miR-29c. These members are encoded by two gene clusters of miR-29b2/miR-29c (mapped on chromosome 1q32) and miR-29b1/miR-29a (mapped on chromosome 7q32).42 Heterodimer-type (Class I) PI3Ks consists of a regulatory subunit that is at least encoded by three distinct genes (85α, p85β, p55γ) and a p110 catalytic subunit.43 The p85α is the most frequently expressed regulatory isoform of PI3K, which encodes two minor alternative splicing isoforms of p55a and p50a additionally.44 It also binds to tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins, like Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 (IRS-1), and activates PI3K activity of the pll0 subunit in insulin signaling.45 The miR-29 targets p85α directly and affects insulin signaling. Furthermore, miR-29 develops gluconeogenesis by aiming at hepatic p85α and enhancing expression of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK).46
As we mentioned previously, syntaxin-1a (Stx-1a) is an important factor in insulin granule fusion with the plasma membrane. An experimental study conducted by Bagge et al47 over INS-1E cells disclosed that miR-29a targeted the Stx-1a transcript directly and decreased Stx-1a mRNA and protein levels.
miR-34a
Among the mammalians, the family of miR-34 includes three processed miRNAs that reside in two various genes of miR-34a and miR-34b/c, which are located on 1p36 and 11q23, respectively.48 The researchers found that miR-34a affects the hepatic insulin signaling by targeting Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1).49
miR-124a
MiR-124a family, which is mainly expressed in the brain and pancreas, includes three processed miRNAs, which are encoded by three various genes of miR-124a1, miR-124a2, and miR-124a3, which are located on chromosome 14, chromosome 3, and chromosome 2, respectively.50,51 Forkhead box A2 (FOXA2)/Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 3β (HNF3β) is a member of the forkhead box family and belongs to the liver transcription factors including FOXA1 and FOXA3 (or HNF3α, HNF3γ).52 We should also consider these factors’ conserved DNA binding domain and binding (as monomers) to the DNA elements that are homologous with the consensus sequence 5′- T(G/A)TTT(A/G)(C/T)T-3′.53,54 Different levels of FOXA2 expression (high and low) are observed in the liver and other tissues, respectively.55 FOXA2, as a transcriptional activator of Pdx-1, Sur1, preproinsulin, and Kir6.2 has been implicated in pancreatic beta-cell. So, FOXA2 protein over-production triggers the up-regulation of Kir6.2, Pdx-1, Sur-1, and preproinsulin mRNA expression.51,56 Recent investigations demonstrated that miR-124a2 had a crucial effect on insulin secretion by targeting at Foxa2 gene, which regulates insulin secretion.17
miR-143
The miR-143 has a highly conserved sequence belongs to the miR-143/145 family. It was also found that miR-143 was mapped to chromosome 5.57 The oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) as well as OSBP-related proteins (ORPs) form a large family of genes that include sterol/lipid transportations and regulatory activities.58 ORP8 is located on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by its C-terminal transmembrane span and is bound to 25-hydroxycholesterol, which has changed it into a new ER oxysterol-binding protein. According to the literature, ORP8 was most highly expressed in the liver, macrophages, spleen, kidney, and brain and functioned in insulin signaling.59 Moreover, PIP2 concentration was considered as a phospholipase C (PLC) substrate that hydrolyzes PIP2 to PIP3 and is modulated by ORP8. As a result of binding IP3 to IP3R in the ER, Ca2+ releases to the cytosol.60 A recent study showed that miR-143 plays an important role in insulin secretion by targeting oxysterol-binding-protein-related protein 8 (ORP8).61
miR-153
Two copies of miR-153 have been known: A) miR-153-1, which is mapped to a highly conserved region in the intron 19 of IA-2 on chromosome 2 and B) miR-153-2, which resides in a highly conserved intronic region between exon 19 and 20 of IA-2β on chromosome 7. As mentioned previously, SNAP-25 and VAMP-2 are required for insulin granule fusion. Recent investigations disclosed that miR-153 played a crucial role in insulin secretion by targeting SNAP-25 and VAMP-2 directly.62
miR-187
Homeodomain-interacting protein kinases (HIPK1, HIPK2, HIPK3) can interact with the homeobox transcription factors Nkx-1.2.63 HIPK3 acts as a novel positive regulator of pdx-1 abundance through phosphorylation of pdx-1 (positive regulator of insulin biosynthesis).64 It is also a direct target of miR-187 with down-regulated expression levels in pancreatic islets of patients with type 2 diabetes.65
miR-204
MiR-204, as a highly beta-cell-enriched microRNA, is localized within large intron 6 of TRPM3 and mapped to chromosome 9q21.12.66 Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), as a GPCR, is composed of seven transmembrane domains.67 Increased dosage of GLP1R was reported in pancreatic beta-cells. It also has an important effect on the GLP-1, as the main incretin created in intestinal L-cells and pancreatic islet alpha cells.68,69 Food-stimulated GLP-1 secretion and its binding to the GLP1R triggers glucose-induced beta-cell insulin secretion via elevation of cAMP concentration.70 Jo et al discovered that the 3ʹUTR of GLP1R was a direct target for miR-204 in the beta-cell-derived rat INS-1 cell line as well as the primary mouse and human islets; thereby, the expression was down-regulated. In this manner, miR-204 acts as a negative regulator in insulin secretion.70
miR-375
Structural organization of MiR-375 gene on human chromosome 2 shows an intergenic spacer between CRYBA2 and CCDC108 genes.71 Pdx-1 is a homeodomain protein with a critical role in pancreatic β-cell function and development.72,73 Furthermore, insulin transcription activation resulted from Pdx-1, which is bound to the conserved AT-rich A3 box (−201/-196 bp). However, this protein acts as a repressor in other gene contexts.74 At low glucose concentrations (1–2mM) in β cells, the nuclear periphery is the main location of Pdx-1. Following the insulin secretion stimulation, Pdx-1 shuttles into the nucleus as a consequence of its phosphorylation. Atypical protein kinase C isoforms, p38/stress-activated protein kinase, glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) kinase, and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) are among the main signaling pathways that adjust shuttling of the nucleo-cytoplasmic and adjust the Pdx-1 transactivation potential.75 Furthermore, it was disclosed that the Pdx-1 interaction with different transcriptional coregulators was mediated by glucose. Additionally, it was approved that expression of insulin gene under low and non-insulin stimulating glucose concentrations decreased by association of Pdx-1 with the histone deacetylases HDAC-1 and HDAC-2.76 Furthermore, Pdx-1 SUMOylation regulates its localization and stability. It is also associated with increased activity of insulin promoter.77 In addition, SUMOylation of Pdx-1 increases its nuclear localization as well as its protein stability and is correlated with an increase in insulin promoter activity.78 Finally, Pdx-1 is composed of at least two sites of O-GlcNAcylation, which promote its DNA activity of binding.79,80 A research indicated that miR-375 regulated insulin secretion by targeting Pdx-1.81
Myotrophin with ankyrin repeats mediates the protein–protein interactions in other proteins. Myotrophin functions to remodel F-actin filaments and secretory granules exocytosis.82 Furthermore, the literature found that miR-375 targets myotrophin mRNA.83
NeuroD1/Beta2 is a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor that binds with the ubiquitously expressed E-box proteins at the conserved insulin E1 (−100/-91bp) site in a complex.84 O-GlcNAcylation of NeuroD185 as a crucial factor for its translocation to the nucleus is mediated by high glucose levels. It was disclosed that miR-375 targets NeuroD1 mRNA.81
Conclusion
Insulin secretion plays an important role in preventing hyper- and hypo-glycemic states and its defect develops diabetes mellitus. The miRNAs, which have a significant impact on various disease processes, emerged as important players of gene regulation. Deregulated expression of miRNA has been widely implicated in the insulin-secreting pancreatic beta-cell of patients with type-2 diabetes. As a result, impaired insulin secretion is a major factor in disease progression. So, a more in-depth understanding of the interplay between miRNAs and protein involved in insulin production and secretion may afford valuable insights and novel therapeutic strategies to treat diabetes.
Abbreviations
miRNA, microRNA; DM, diabetes mellitus; PC, prohormone convertase; AC, adenylyl cyclase; SUR, sulphonylurea receptor; GPCR, G protein-coupled receptors; PKA, protein kinase A; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; IP3, produce inositol 1, 4, 5-triphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; Stx-1a, syntaxin-1a; FOXA2, Forkhead box A2; HNF3β, Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 3β; OSBP: oxysterol-binding protein; HIPK, Homeodomain-interacting protein kinases; GLP1R, Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Dr. S. Mirjalili, Dr. Montazeri, and Mr. Heydarian for their valuable support.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to data analysis, drafting and revising the article, gave final approval of the version to be published, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Liu M, Weiss MA, Arunagiri A, et al. Biosynthesis, structure, and folding of the insulin precursor protein. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20:28–50. doi:10.1111/dom.13378
2. Rutter GA, Pullen T, Hodson D, et al. Pancreatic β-cell identity, glucose sensing and the control of insulin secretion. Biochem J. 2015;466(2):203–218. doi:10.1042/BJ20141384
3. Fava E, Dehghany J, Ouwendijk J, et al. Novel standards in the measurement of rat insulin granules combining electron microscopy, high-content image analysis and in silico modelling. Diabetologia. 2012;55(4):1013–1023. doi:10.1007/s00125-011-2438-4
4. Fernández-Real J, Pickup J. Innate immunity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2012;55(2):273–278. doi:10.1007/s00125-011-2387-y
5. Yin P. Architecture and Function of the Insulin Granule Secretion Machinery. Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis; 2018.
6. Seino S, Takahashi H, Fujimoto W, et al. Roles of cAMP signalling in insulin granule exocytosis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009;11(s4):180–188. doi:10.1111/dom.2009.11.issue-s4
7. Roger B, Papin J, Vacher P, et al. Adenylyl cyclase 8 is central to glucagon-like peptide 1 signalling and effects of chronically elevated glucose in rat and human pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetologia. 2011;54(2):390–402. doi:10.1007/s00125-010-1955-x
8. Sonoda N, Imamura T, Yoshizaki T, et al. β-arrestin-1 mediates glucagon-like peptide-1 signaling to insulin secretion in cultured pancreatic β cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2008;105(18):6614–6619. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710402105
9. Quan Y, Barszczyk A, Feng Z-P, et al. Current understanding of K ATP channels in neonatal diseases: focus on insulin secretion disorders. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011;32(6):765. doi:10.1038/aps.2011.57
10. Stuhlmann T, Planells-Cases R, Jentsch TJ. LRRC8/VRAC anion channels enhance β-cell glucose sensing and insulin secretion. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1974. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-04353-y
11. Real J, Miranda C, Olofsson CS, et al. Lipophilicity predicts the ability of nonsulphonylurea drugs to block pancreatic beta‐cell KATP channels and stimulate insulin secretion; statins as a test case. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2018;1(2):e00017. doi:10.1002/edm2.2018.1.issue-2
12. Ashcroft F. KATP Channels and Insulin Secretion: A Key Role in Health and Disease. Portland Press Limited; 2006.
13. Trapp S, Tucker SJ, Ashcroft FM. Activation and inhibition of K-ATP currents by guanine nucleotides is mediated by different channel subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94(16):8872–8877. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.16.8872
14. Ozaki N, Shibasaki T, Kashima Y, et al. cAMP-GEFII is a direct target of cAMP in regulated exocytosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2(11):805. doi:10.1038/35041046
15. Hilger D, Masureel M, Kobilka BK. Structure and dynamics of GPCR signaling complexes. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018;25(1):4. doi:10.1038/s41594-017-0011-7
16. Ahrén B. Islet G protein-coupled receptors as potential targets for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8(5):369. doi:10.1038/nrd2782
17. Sebastiani G, Mancarella F, Ventriglia G, Nigi L, Valentini M, Grieco GE. MicroRNA miR-124a, a negative regulator of insulin secretion, is hyperexpressed in human pancreatic islets of type 2 diabetic patients. RNA Dis. 2015;2(2).
18. Ha M, Kim VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(8):509. doi:10.1038/nrm3838
19. Han J, Lee Y, Yeom KH, Kim YK, Jin H, Kim VN. The Drosha-DGCR8 complex in primary microRNA processing. Genes Dev. 2004;18(24):3016–3027. doi:10.1101/gad.1262504
20. Yi R, Qin Y, Macara IG, Cullen BR. Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of pre-microRNAs and short hairpin RNAs. Genes Dev. 2003;17(24):3011–3016. doi:10.1101/gad.1158803
21. Ketting RF, Fischer SE, Bernstein E, Sijen T, Hannon GJ, Plasterk RH. Dicer functions in RNA interference and in synthesis of small RNA involved in developmental timing in C. elegans. Genes Dev. 2001;15(20):2654–2659. doi:10.1101/gad.927801
22. Hammond SM, Boettcher S, Caudy AA, Kobayashi R, Hannon GJ. Argonaute2, a link between genetic and biochemical analyses of RNAi. Science. 2001;293(5532):1146–1150. doi:10.1126/science.1064023
23. Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, et al. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(3):228. doi:10.1038/ncb0309-228
24. Reddy SDN, Ohshiro K, Rayala SK, et al. MicroRNA-7, a homeobox D10 target, inhibits p21-activated kinase 1 and regulates its functions. Cancer Res. 2008;68(20):8195–8200. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2103
25. Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell. 2007;129(7):1401–1414. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.040
26. Joglekar MV, Joglekar VM, Hardikar AA. Expression of islet-specific microRNAs during human pancreatic development. Gene Expr Patterns. 2009;9(2):109–113. doi:10.1016/j.gep.2008.10.001
27. Yoon M-S, Choi CS. The role of amino acid-induced mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling in insulin resistance. Exp Mol Med. 2017;48(1):e201. doi:10.1038/emm.2015.93
28. Zoncu R, Efeyan A, Sabatini DM. mTOR: from growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12(1):21. doi:10.1038/nrm3025
29. Fang Y, Xue J-L, Shen Q, et al. MicroRNA‐7 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the phosphoinositide 3‐kinase/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2012;55(6):1852–1862. doi:10.1002/hep.25576
30. Cekaite L, Rantala JK, Bruun J. et al. MiR-9, -31, and −182 deregulation promote proliferation and tumor cell survival in colon cancer. Neoplasia. 2012;14(9):868–879. doi:10.1593/neo.121094
31. Kato T, Shimano H, Yamamoto T, et al. Granuphilin is activated by SREBP-1c and involved in impaired insulin secretion in diabetic mice. Cell Metab. 2006;4(2):143–154. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2006.06.009
32. Finkel T, Deng CX, Mostoslavsky R. Recent progress in the biology and physiology of sirtuins. Nature. 2009;460(7255):587–591. doi:10.1038/nature08197
33. K.P. Bagul, S. K Banerjee, Insulin resistance, oxidative stress and cardiovascular complications: role of sirtuins. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(32):5663–5677.
34. Chen YR, Lai Y-L, Lin S-D, et al. SIRT1 interacts with metabolic transcriptional factors in the pancreas of insulin-resistant and calorie-restricted rats. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40(4):3373–3380. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-2412-3
35. Langley E, Pearson M, Faretta M, et al. Human SIR2 deacetylates p53 and antagonizes PML/p53‐induced cellular senescence. EMBO J. 2002;21(10):2383–2396. doi:10.1093/emboj/21.10.2383
36. Vaquero A, Scher M, Lee D, et al. Human SirT1 interacts with histone H1 and promotes formation of facultative heterochromatin. Mol Cell. 2004;16(1):93–105. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.08.031
37. Vaquero A, Scher M, Erdjument-Bromage H, et al. SIRT1 regulates the histone methyl-transferase SUV39H1 during heterochromatin formation. Nature. 2007;450(7168):440–444. doi:10.1038/nature06268
38. Wang RH, Kim H-S, Xiao C, et al. Hepatic Sirt1 deficiency in mice impairs mTorc2/Akt signaling and results in hyperglycemia, oxidative damage and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(11). doi:10.1172/JCI46243
39. Bordone L, Motta MC, Picard F, et al. Sirt1 regulates insulin secretion by repressing UCP2 in pancreatic β cells. PLoS Biol. 2005;4(2):e31. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040031
40. Saunders LR, Sharma AD, Tawney J, et al. miRNAs regulate SIRT1 expression during mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation and in adult mouse tissues. Aging (Albany NY). 2010;2(7):415. doi:10.18632/aging.v2i7
41. Ramachandran D, Roy U, Garg S, et al. Sirt1 and mir‐9 expression is regulated during glucose‐stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic β‐islets. FEBS J. 2011;278(7):1167–1174. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08042.x
42. Mazzoccoli L, Robaina MC, Apa AG, et al. MiR-29 silencing modulates the expression of target genes related to proliferation, apoptosis and methylation in Burkitt lymphoma cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018;144(3):483–97.
43. Pons S, Asano T, Glasheen E, et al. The structure and function of p55PIK reveal a new regulatory subunit for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15(8):4453–4465. doi:10.1128/MCB.15.8.4453
44. Fruman DA, Cantley LC, Carpenter CL. Structural organization and alternative splicing of the murine phosphoinositide 3-kinase p85α gene. Genomics. 1996;37(1):113–121. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0527
45. Suzuki H, Terauchi Y, Fujiwara M, Aizawa S, Yazaki Y, Kadowaki T, Koyasu S. Xid-like immunodeficiency in mice with disruption of the p85α subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Science. 1999;283(5400):390–392. doi:10.1126/science.283.5400.390
46. Pandey AK, Verma G, Vig S, et al. miR-29a levels are elevated in the db/db mice liver and its overexpression leads to attenuation of insulin action on PEPCK gene expression in HepG2 cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011;332(1):125–133. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2010.10.004
47. Bagge A, Dahmcke CM, Dalgaard LT. Syntaxin-1a is a direct target of miR-29a in insulin-producing β-cells. Horm Metab Res. 2013;45(06):463–466. doi:10.1055/s-00000025
48. Hermeking H. The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17(2):193. doi:10.1038/cdd.2009.56
49. Lee J, Padhye A, Sharma A, et al. A pathway involving farnesoid X receptor and small heterodimer partner positively regulates hepatic sirtuin 1 levels via microRNA-34a inhibition. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(17):12604–12611. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.094524
50. Baroukh NN, Van Obberghen E. Function of microRNA‐375 and microRNA‐124a in pancreas and brain. FEBS J. 2009;276(22):6509–6521. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07353.x
51. Baroukh N, Ravier MA, Loder MK, et al. MicroRNA-124a regulates Foxa2 expression and intracellular signaling in pancreatic β-cell lines. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(27):19575–19588. doi:10.1074/jbc.M611841200
52. Friedman J, Kaestner K. The Foxa family of transcription factors in development and metabolism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006;63(19):2317–2328. doi:10.1007/s00018-006-6095-6
53. Overdier DG, Porcella A, Costa RH. The DNA-binding specificity of the hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/forkhead domain is influenced by amino-acid residues adjacent to the recognition helix. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14(4):2755–2766. doi:10.1128/MCB.14.4.2755
54. Rada-Iglesias A, Wallerman O, Koch C, et al. Binding sites for metabolic disease related transcription factors inferred at base pair resolution by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genomic microarrays. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14(22):3435–3447. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddi378
55. Kaestner KH, Hiemisch H, Luckow B, et al. The HNF-3 gene family of transcription factors in mice: gene structure, cDNA sequence, and mRNA distribution. Genomics. 1994;20(3):377–385. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1191
56. Lantz KA, Vatamaniuk MZ, Brestelli JE, et al. Foxa2 regulates multiple pathways of insulin secretion. J Clin Invest. 2004;114(4):512–520. doi:10.1172/JCI21149
57. Li B, Fan J, Chen N. A novel regulator of type II diabetes: microRNA-143. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018;29(6):380–388. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2018.03.019
58. Charman M, Colbourne TR, Pietrangelo A, et al. Oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP)-related protein 4 (ORP4) is essential for cell proliferation and survival. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(22):15705–15717. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.571216
59. Yan D, Mäyränpää MI, Wong J, et al. OSBP-related protein 8 (ORP8) suppresses ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux from macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(1):332–340. doi:10.1074/jbc.M705313200
60. Pulli I, Lassila T, Pan G, et al. Oxysterol-binding protein related-proteins (ORPs) 5 and 8 regulate calcium signaling at specific cell compartments. Cell Calcium. 2018;72:62–69. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2018.03.001
61. Jordan SD, Krüger M, Willmes DM, et al. Obesity-induced overexpression of miRNA-143 inhibits insulin-stimulated AKT activation and impairs glucose metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(4):434–446. doi:10.1038/ncb2211
62. Mandemakers W, Abuhatzira L, Xu H, et al. Co-regulation of intragenic microRNA miR-153 and its host gene Ia-2β: identification of miR-153 target genes with functions related to IA-2β in pancreas and brain. Diabetologia. 2013;56(7):1547–1556. doi:10.1007/s00125-013-2901-5
63. van der Laden J, Soppa U, Becker W. Effect of tyrosine autophosphorylation on catalytic activity and subcellular localisation of homeodomain-interacting protein kinases (HIPK). Cell Commun Signal. 2015;13(1):3. doi:10.1186/s12964-014-0082-6
64. Shojima N, Hara K, Fujita H, et al. Depletion of homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 3 impairs insulin secretion and glucose tolerance in mice. Diabetologia. 2012;55(12):3318–3330. doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2711-1
65. Locke J, da Silva Xavier G, Dawe HR, et al. Increased expression of miR-187 in human islets from individuals with type 2 diabetes is associated with reduced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetologia. 2014;57(1):122–128. doi:10.1007/s00125-013-3089-4
66. Mikhaylova O, Stratton Y, Hall D, et al. VHL-regulated MiR-204 suppresses tumor growth through inhibition of LC3B-mediated autophagy in renal clear cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2012;21(4):532–546. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.019
67. Thorens B. Expression cloning of the pancreatic beta cell receptor for the gluco-incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1992;89(18):8641–8645. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.18.8641
68. Lamont BJ, Li Y, Kwan E, et al. Pancreatic GLP-1 receptor activation is sufficient for incretin control of glucose metabolism in mice. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(1):388–402. doi:10.1172/JCI42497
69. Mondal P, Song W-J, Li Y, et al. Increasing β-cell mass requires additional stimulation for adaptation to secretory demand. Mol Endocrinol. 2015;29(1):108–120. doi:10.1210/me.2014-1265
70. Jo S, Chen J, Xu G, et al. miR-204 controls glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor expression and agonist function. Diabetes. 2018;67(2):256–264. doi:10.2337/db17-0506
71. Chakraborty C, Doss CGP, Bandyopadhyay S, et al. Influence of miRNA in insulin signaling pathway and insulin resistance: micro‐molecules with a major role in type‐2 diabetes. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014;5(5):697–712. doi:10.1002/wrna.1240
72. Stoffers DA, Thomas MK, Habener JF. Homeodomain protein IDX-1: a master regulator of pancreas development and insulin gene expression. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1997;8(4):145–151. doi:10.1016/S1043-2760(97)00008-8
73. Jonsson J, Ahlgren U, Edlund T, Edlund H. IPF1, a homeodomain protein with a dual function in pancreas development. Int J Dev Biol. 2003;39(5):789–798.
74. Wang H, Maechler P, Ritz-Laser B, et al. Pdx1 level defines pancreatic gene expression pattern and cell lineage differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(27):25279–25286. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101233200
75. Vanderford NL, Cantrell JEL, Popa GJ, et al. Multiple kinases regulate mafA expression in the pancreatic beta cell line MIN6. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008;480(2):138–142. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2008.10.001
76. Mosley AL, Özcan S. The pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1 protein (Pdx-1) interacts with histone deacetylases Hdac-1 and Hdac-2 on low levels of glucose. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(52):54241–54247. doi:10.1074/jbc.M410379200
77. Mosley AL, Özcan S. Glucose regulates insulin gene transcription by hyperacetylation of histone h4. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(22):19660–19666. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212375200
78. Kishi A, Nakamura T, Nishio Y, et al. Sumoylation of Pdx1 is associated with its nuclear localization and insulin gene activation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003;284(4):. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00390.2002
79. Gao Y, Miyazaki JI, Hart GW. The transcription factor PDX-1 is post-translationally modified by O-linked N-acetylglucosamine and this modification is correlated with its DNA binding activity and insulin secretion in min6 β-cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2003;415(2):155–163. doi:10.1016/S0003-9861(03)00234-0
80. Kebede M, Ferdaoussi M, Mancini A, et al. Glucose activates free fatty acid receptor 1 gene transcription via phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-dependent O-GlcNAcylation of pancreas-duodenum homeobox-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2012;109(7):2376–2381. doi:10.1073/pnas.1114350109
81. Keller DM, McWeeney S, Arsenlis A, et al. Characterization of pancreatic transcription factor Pdx-1 binding sites using promoter microarray and serial analysis of chromatin occupancy. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(44):32084–32092. doi:10.1074/jbc.M700899200
82. Poy MN, Eliasson L, Krutzfeldt J, et al. A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. Nature. 2004;432(7014):226. doi:10.1038/nature03076
83. Ghelani HS, Rachchh MA, Gokani RH. MicroRNAs as newer therapeutic targets: a big hope from a tiny player. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2012;3(3):217. doi:10.4103/0976-500X.99416
84. Naya FJ, Huang H-P, Qiu Y, et al. Diabetes, defective pancreatic morphogenesis, and abnormal enteroendocrine differentiation in BETA2/neuroD-deficient mice. Genes Dev. 1997;11(18):2323–2334. doi:10.1101/gad.11.18.2323
85. Andrali SS, Qian Q, Özcan S. Glucose mediates the translocation of NeuroD1 by O-linked glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(21):15589–15596. doi:10.1074/jbc.M701762200
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.