Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 8
Linagliptin: from bench to bedside
Authors Doupis J
Received 20 December 2013
Accepted for publication 20 February 2014
Published 5 May 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 431—446
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S59523
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
John Doupis
Iatriko Palaiou Falirou Medical Center, Division of Diabetes, Athens, Greece
Purpose: The nature of biomedical research affords a broad range of investigational topics at the preclinical stage, not all of which may be explored in subsequent clinical studies. To provide a comprehensive perspective on the physiologic effects of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor linagliptin, this review will discuss the results of both preclinical and clinical research, summarizing data describing outcomes associated with its use.
Summary: Clinical studies demonstrate an overall favorable safety profile, low risk for hypoglycemia, weight neutrality, primarily nonrenal clearance, and efficacy for glycosylated hemoglobin reduction, typically ranging from 0.6% to 0.8% depending on baseline levels. In addition to these characteristics, preclinical research on linagliptin has yielded several interesting findings such as improved wound healing, reduced hepatic fat content, decreased infarct size following myocardial infarction or intracranial stroke, and improved vascular function with decreased oxidative stress. In accordance with its preclinical profile, linagliptin is unique among available dipeptidyl peptidase-4 compounds because it does not require dose adjustment when used in patients with renal dysfunction. Reduction of albuminuria with linagliptin on top of inhibitors of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system in both preclinical and post hoc clinical analysis serves as the foundation for ongoing clinical trials.
Conclusion: In addition to its efficacy for glycemic control, current literature points to other potential opportunities associated with linagliptin therapy. These results warrant further investigation and underscore the importance of translational study based on findings from preclinical research. Moving forward, we can expect that future research on linagliptin and other incretin-based therapies will continue to expand their applications beyond the maintenance of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, linagliptin, type 2 diabetes
Introduction
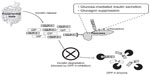
Inhibitors of the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) enhance the effects of the incretin hormones glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and gastric inhibitory peptide-1 (GIP-1). These hormones are secreted by epithelial cells of the distal ileum and colon in response to ingestion of a meal (Figure 1).1 Following absorption into the hepatic portal circulation, GLP-1 then binds to receptors in various tissues, including pancreatic α- and β-cells. This action sensitizes pancreatic tissue to intracellular glucose concentrations, leading to enhanced secretion of insulin in the presence of elevated plasma glucose.2 The enzyme DPP-4 is a serine protease present in various body tissues, and as an integral component of incretin-mediated signaling serves to terminate the actions of the gastric hormones GLP-1 and GIP-1.3,4 Thus, by preventing the degradation of incretin hormones, DPP-4 inhibitors prolong the physiologic effects of these molecules.5,6 Extended GLP-1 signaling that results from DPP-4 inhibition leads to enhanced, physiologically regulated insulin secretion based on plasma glucose concentration.2,4,7
Linagliptin is a DPP-4 inhibitor approved in the US and elsewhere for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.8 Like others in the class, linagliptin is a competitive, reversible inhibitor of DPP-4.2,9 In contrast to other agents in the class,7 however, early studies in animal models demonstrated that linagliptin is almost completely (99%) bound to plasma proteins (mainly the DPP-4 enzyme) at the 5 mg therapeutic concentration, perhaps because of its high binding affinity and nonpolar surface area.9,10 Likely by virtue of its extensive binding characteristics, in human studies it was determined that linagliptin is cleared mainly by hepatobiliary mechanisms.2,9,10 A key clinical consequence of this property is that linagliptin can be used without dose reduction in patients with declining renal function. This paper will review the results of preclinical and clinical research on linagliptin, summarizing data describing its efficacy and safety profile, tolerability, effects on body weight, potential use in patients with renal dysfunction, putative effects on wound healing, and changes in cardiovascular markers.
Methods
PubMed searches were conducted for published studies of linagliptin in either humans or animal models. The following terms and their derivatives were used to search among English language publication titles for specific topics in the PubMed database: linagliptin [ti] AND (weight [ti] OR mass [ti] OR BMI [ti]); linagliptin [ti] AND (myocardial OR cardiovascular OR lipid* OR cholesterol OR triglyceride* OR pressure); linagliptin [ti] AND (renal OR kidney OR filtration OR GFR OR creatinine); linagliptin [ti] AND (age* OR elder*). When needed, results were restricted to clinical trials for targeted searches or expanded to title/abstract using the available PubMed limiters to increase the number of results. No date restrictions were specified. Abstracts were qualitatively reviewed and individually selected based on their relevance to the specific topics covered in this manuscript. Literature articles considered relevant based on abstract assessment were obtained and further evaluated, with attention given to references cited in these articles to broaden the scope of the review.
Results
Preclinical pharmacology
Chemistry
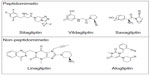
DPP-4 inhibitors are synthesized from unrelated chemical scaffolds, resulting in unique pharmacologic properties for each agent (Figure 2). Linagliptin is an inhibitor of DPP-4 derived by chemical coupling of xanthine and quinazoline derivatives.8 The chemical name for linagliptin is 1H-purine-2,6-dione, 8-[(3R)-3-amino-1-piperidinyl]-7-(2-butyn-1-yl)-3,7-dihydro-3-methyl-1-[(4-methyl-2-quinazolinyl)methyl]-, the structural formula is C25H28N8O2, and the molecular weight is 472.54 g/mol.2
Pharmacokinetics
Initial preclinical pharmacokinetic studies suggested that linagliptin can be characterized by low bioavailability. Roughly 15% to 51% of the dose administered to Wistar rats appeared in the plasma.3,11 This limited bioavailability is due to bioabsorption of linagliptin via transport by intestinal P-glycoprotein channels. For example, one study demonstrated that inhibition of P-glycoprotein-mediated transport with zosuquidar increased the linagliptin maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) from 26 to 348 nmol/L in healthy Wistar rats.12 Although P-glycoprotein transport accounts for low bioavailability of linagliptin, importantly, only minor fluctuations in inter- and intraindividual absorption were observed.12 Similarly, linagliptin exposure increased from 147 to 309 nmol · h/L following P-glycoprotein inhibition. Once absorbed into the bloodstream, linagliptin is predominantly bound to protein (mostly the target enzyme DPP-4).2 This binding explains the primarily enterohepatic mechanism of clearance without significant metabolism. Approximately 12%, 28%, and 49% of linagliptin when administered as supraclinical intravenous doses to Wistar rats was eliminated as the unchanged parent compound via gut, urine, and bile, respectively.12
Pharmacodynamics
Findings from rodent and murine models show that linagliptin is a selective and potent inhibitor of DPP-4, leading to increases of intact GLP-1 for up to 24 hours after a single dose.13,14 In a diabetic rodent model, the effect of linagliptin on GLP-1 levels was sustained with multiple once-daily dosing.14 These results support a GLP-1–mediated mechanism for the use of once-daily linagliptin for treatment of diabetes. In vitro data show that linagliptin has the highest potency for inhibiting DPP-4 among the available DPP-4 inhibitors, with an inhibitory concentration (IC50) of approximately 1 nM (compared with 24 nM for alogliptin, 19 nM for sitagliptin, 50 nM for saxagliptin, and 62 nM for vildagliptin).13 Moreover, the disassociation of linagliptin from the DPP-4 enzyme is approximately 10-fold slower than that of vildagliptin, which contributes to the long duration of action and once-daily dosing profile of linagliptin.13
Selectivity
Potential for inhibition of other enzymes in the DPP family by agents that target DPP-4 is an important research topic. Using animal models and in vitro experiments, Thomas et al investigated the potential for off-target inhibition of DPP family member enzymatic activity by linagliptin.13 In this study, measurement of the linagliptin half-maximal IC50 of various enzymes were 1 nM (DPP-4), 100,000 nM (DPP-2), 40,000 nM (DPP-8), 10,000 nM (DPP-9), and 89 nM (fibroblast activation protein). Given that linagliptin Cmax following the therapeutic 5 mg dose is known to be approximately 9 nM, clinically significant inhibition of other off-target DPP family enzymes was not expected in clinical trials.
Clinical pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
Results from Phase I and II studies of linagliptin in healthy volunteers and patients with type 2 diabetes were consistent with the pharmacologic findings from preclinical studies.2,15 In accordance with animal studies, linagliptin has a low absolute bioavailability of approximately 30%.2 The apparent volume of distribution V(d) after administration of a single 5 mg intravenous infusion in healthy male volunteers is 1,110 L,15 compared with approximately 70–580 L for most other available DPP-4 inhibitors.16 The large V(d) of linagliptin indicates extensive tissue distribution.
As in preclinical studies, binding of linagliptin to blood proteins in humans explains enterohepatic clearance from the body without significant metabolism.17 Following intravenous 5 mg infusion of radiolabeled drug in healthy human volunteers, Cmax of the main linagliptin metabolite was only 34 nmol · h/L compared with 356 nmol · h/L for unmetabolized linagliptin.17 In addition, approximately 31% of the intravenous administered dose was eliminated in urine versus 58% in feces.12,17 Compared with 5 mg intravenous administration, the approved 5 mg oral dose results in lower plasma concentrations. Perhaps because of its lower bioavailability and through desaturation of binding proteins, these lower plasma concentrations lead to a greater shift in the proportion of linagliptin eliminated in urine/feces. For example, in a 12-day study of 5 mg daily oral linagliptin therapy in participants with type 2 diabetes, Heise et al reported mean Cmax and steady state exposure values of 8.32 nmol/L and 158 nmol · h/L, respectively.10 Here, the corresponding fraction eliminated in urine was <7%. In comparison, the renal excretion of parent compound or metabolite is ≥60% for other available DPP-4 inhibitors (Figure 3).2,7,18–20 Thus, linagliptin is unique among available compounds because it does not require dose adjustment or drug-related kidney monitoring when used in patients with renal dysfunction. Because of the predominantly nonrenal route of elimination of linagliptin, an open-label Phase I study evaluated the pharmacokinetics of linagliptin in healthy subjects (n=8) and participants with mild (n=8), moderate (n=9), or severe (n=8) hepatic impairment.21 No increase in linagliptin exposure occurred after single or multiple 5 mg doses in participants with varying degrees of hepatic impairment compared with healthy controls. Therefore, dose adjustment is not required in patients with liver dysfunction.
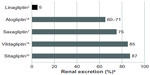  | Figure 3 Percentage renal excretion of available dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors.2,7,18–20 |
Pharmacodynamics
The underlying physiologic changes associated with linagliptin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes result from increased levels of GLP-1 and GIP-1.22 Over the course of a 28-day study, the lowering of blood glucose following treatment with linagliptin was associated with mean placebo-corrected, two- to three-fold increases in intact GLP-1 (+18.1 pmol · h/L) and GIP-1 (+91.4 pmol · h/L). Importantly, a decrease in plasma glucagon was also observed (−18.7 pg · h/L), which may suggest the potential for modulation of hepatic glucose production.22 Glucagon levels or hepatic glucose production have not yet been fully described in most published clinical studies of linagliptin; this, therefore, may offer an interesting topic for future research.
Efficacy for improvement in glycosylated hemoglobin
Investigation of the effects of a new molecular entity in animal models of a disease of interest precedes clinical trials, with additional preclinical studies examining other off-target effects. Consistent with this drug development paradigm, one study evaluated the effect of linagliptin administered before an oral glucose tolerance test to mice and Zucker fatty rats.13 The glucose excursion was decreased by approximately 30%–50% when linagliptin was administered 30–45 minutes before the challenge in both species, and by 20%–30% when administered 16 hours before the challenge in rats. The efficacy of linagliptin for lowering of blood glucose was evaluated in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice.14 In this study, after 27 days of treatment with linagliptin, mean postprandial glucose concentrations significantly decreased by approximately 10%, and mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) decreased by approximately 1.0%. These studies indicate a β-cell–independent effect of linagliptin on overall glucose control in this model. Recently, results from an in vitro study of human islet cells exposed to diabetic conditions showed that linagliptin restored β-cell proliferation and survival after glucotoxicity, lipotoxicity, and cytokine toxicity.23 In addition to these investigations, published animal studies of linagliptin describe its effect on incretin physiology,13,14 body weight,24 or other extraglycemic effects such as stroke25 and wound healing.26–28
After confirmation of glycemic benefits in preclinical studies, the clinical trial program for linagliptin commenced and filing for a US new drug application occurred in July 2010 (Figure 4).29 Phase I and II trials established the clinical dosage of linagliptin 5 mg once daily that was used in the Phase III program.29 Clinical studies of linagliptin included a range of patient populations with regard to disease severity and duration. As is standard for a type 2 diabetes clinical development program, the first trials established the safety and efficacy of the drug when used as monotherapy. With increasing duration of type 2 diabetes, patients tend to experience a progressive decline in the ability to maintain adequate glycemic control with antidiabetic therapies, thus necessitating an escalation in medication doses over time (using agents for which this is an option). When maximum effective dose is reached, a combination regimen must then be selected in an attempt to control blood glucose. Clinical trials therefore evaluate the efficacy of new antidiabetic therapies not only as monotherapy, but in the setting of other concomitant treatments as well. Approval of linagliptin in May 2011 was based on monotherapy and combination therapy trials with other commonly used glucose-lowering agents.29
  | Figure 4 Overview of linagliptin trials from bench to bedside showing the stage of development for select outcomes. |
Treatment with linagliptin monotherapy alone is associated with significant improvement in glycemic control (Table 1). For example, an 18-week study of linagliptin monotherapy in patients for whom metformin was contraindicated or not well tolerated (n=227) demonstrated a placebo-corrected HbA1c change of −0.60% (P<0.0001; baseline, 8.1%).30 This result was consistent with the larger, double-blind, placebo-controlled, pivotal Phase III trial that evaluated the safety and efficacy of linagliptin monotherapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.31,32 In this trial, more than 500 participants (mean baseline, HbA1c 8.0%) were randomized to receive placebo or linagliptin 5 mg/day for 24 weeks. At the end of the study, the mean placebo-adjusted HbA1c change from baseline was −0.69% (P<0.0001). In patients with baseline HbA1c ≥9.0%, mean reduction from baseline was −1.01%, consistent with the greater magnitude of HbA1c reduction that has been observed in other studies of patients with high baseline values.
Addition of linagliptin to ongoing treatment with metformin also leads to similar improvement in HbA1c compared with linagliptin monotherapy. For example, a 12-week randomized study in 333 patients with type 2 diabetes showed that addition of linagliptin to an existing regimen of metformin was associated with a placebo-adjusted HbA1c reduction from baseline (8.5%) of −0.73% after 12 weeks.33 Similarly, a pivotal Phase III trial showed that linagliptin add-on therapy in participants with inadequate glycemic control receiving metformin was associated with a placebo-corrected HbA1c reduction from baseline (8.1%) of −0.64% after 24 weeks of therapy.34 Moreover, results from a 24-week pivotal study of 1,058 patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on maximum doses of metformin and sulfonylurea (SU) showed that addition of linagliptin as a third agent was associated with a placebo-corrected HbA1c reduction from baseline (8.15) of −0.62%.35
As recommended in most treatment algorithms, initiation or progression of antidiabetic pharmacotherapies usually involves the prescription of a single new agent. However, given the prevalent need to progress therapy, alternative strategies involving the initiation or progression of treatment with more than one agent have often been investigated. A 24-week placebo-controlled study explored the comparative efficacy of this approach, randomizing patients to monotherapy with linagliptin or metformin, or alternatively to linagliptin administered as initial combination therapy with metformin.36 Results demonstrated that initial combination therapy was associated with greater HbA1c reduction compared with either agent given as monotherapy.36 For example, patients randomized to receive 1,000 mg twice-daily metformin monotherapy demonstrated a placebo-adjusted HbA1c reduction of −1.2% (baseline, 8.5%), whereas patients receiving a lower dose of metformin (500 mg twice daily) in combination with linagliptin experienced an adjusted HbA1c reduction of −1.3% (baseline, 8.7%). Patients given linagliptin with metformin 1,000 mg twice daily exhibited the greatest improvement in glycemic control, with a mean HbA1c reduction of −1.7% (baseline, 8.7%). The results of this trial formed the basis for the January 2012 US approval37 of the fixed-dose combination of linagliptin and metformin in a single tablet for twice-daily treatment of type 2 diabetes in adults. In addition to the metformin trial of initial combination therapy, another pivotal trial examined linagliptin administered initially in combination with pioglitazone versus pioglitazone alone; linagliptin was associated with a mean adjusted HbA1c reduction from baseline (8.6%) of −0.51% (P<0.0001).38 Comparable HbA1c reductions were seen in studies evaluating the addition of linagliptin to ongoing therapy with a SU or insulin.39,40 In an 18-week placebo-controlled study that combined linagliptin with an SU, the addition of linagliptin was associated with a placebo-adjusted mean HbA1c change from baseline (8.6%) of −0.47% (P<0.0001).39 In a 24-week placebo-controlled study of 1,261 patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on basal insulin alone or with oral therapy, the addition of linagliptin (with or without metformin and/or pioglitazone) provided a placebo-adjusted mean HbA1c change from baseline (8.3%) of −0.65% (P<0.0001).2,40
Thus, these studies demonstrate that comparable improvements in glycemic control can be achieved with linagliptin administered either as monotherapy or as part of combination regimens. In placebo-controlled clinical trials of linagliptin, which usually recruited participants with baseline HbA1c values between 8% and 9%, the efficacy of HbA1c improvement generally ranges from −0.6% to −0.8% (Table 1). Additionally, linagliptin improved markers of β-cell function, such as the homeostasis model assessment for β-cell function and the disposition index, in several clinical trials that assessed these parameters.32,34,35,38,41
Safety and tolerability
Preclinical evaluations of safety typically focus on the effects of a drug on fertility, cancer incidence, and mutagenesis and occur early in the drug development process. Linagliptin did not increase the incidence of tumors after 2 years of exposure in rats or mice at doses that substantially exceed the clinical dose based on area under the curve exposure.2 In vitro testing showed that linagliptin was not mutagenic or clastogenic.2
Further investigation revealed no safety signals within the concentration range of the therapeutic dose in a dose-ranging study in healthy human volunteers that tested single oral administration of linagliptin tablets up to 600 mg.42 As a class, clinical studies have demonstrated that DPP-4 inhibitors are characterized by a favorable safety/tolerability profile. Individual clinical trials of linagliptin have demonstrated results consistent with this observation, with overall adverse event (AE) rates typically comparable between linagliptin and placebo groups. A recent meta-analysis of data from eight Phase III clinical trials of linagliptin (n=3,572 patients with type 2 diabetes) has quantitatively evaluated AEs reported in published studies of linagliptin.43 AEs in patients receiving linagliptin versus placebo were pooled across studies, and the resulting overall AE rates were similar in both groups (55.0%, linagliptin; 55.8%, placebo). Serious AEs were also comparable: 2.8% versus 2.7% in the linagliptin and placebo groups, respectively. AE rates in the pooled linagliptin group were also comparable to (or less than) those in patients receiving placebo for upper respiratory tract infection, headache, urinary tract infection, blood and lymphatic disorders, hypersensitivity reactions, elevated hepatic enzymes, increased serum creatinine, nasopharyngitis, and cough. In this pooled analysis, the incidence of hypoglycemia was 8.2% for linagliptin and 5.1% for placebo due to a higher incidence among those receiving SU background therapy (20.7% and 13.3%, respectively).43 A low rate of hypoglycemia (≤1%) was observed in studies where SU background therapy was not permitted. One case of chronic pancreatitis was reported in a patient receiving linagliptin; no cases of acute pancreatitis were reported.43
Overall in the clinical trial program, pancreatitis was reported in 15.2 cases per 10,000 patient-year exposure to linagliptin compared with 3.7 cases per 10,000 patient-year exposure to comparator (placebo and active comparator), with three additional cases reported after the last administered dose.2 Acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis, has been reported in postmarketing experience.2 Use of linagliptin has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis.2 It is unknown whether patients with such a history are at an increased risk for the development of pancreatitis while using a DPP-4 inhibitor.2,7
Durability
Because the natural history of type 2 diabetes typically spans many decades, the long-term durability of antidiabetic therapies is an important subject of clinical research. While studies on this timescale are infeasible in animal models of type 2 diabetes (and pose a significant challenge in clinical study as well), trials of up to 1–2 years duration are considered long-term evaluation of the safety and efficacy of antidiabetic therapies.
Clinical research studies with follow-up periods of up to 2 years support the long-term safety and efficacy of linagliptin therapy.30,40,44 The longest published study of linagliptin was a randomized 2-year prospective noninferiority study in more than 1,500 patients comparing linagliptin with glimepiride added to metformin.44 In the full analysis set (n=1,519), the mean HbA1c reductions with linagliptin and glimepiride were −0.16% and −0.36%, respectively; the treatment difference of 0.20% (97.5% confidence interval [CI], 0.09–0.30) met the noninferiority criterion. There was a significantly lower rate of hypoglycemia in linagliptin-treated patients (7% versus 36%). In patients who completed the study (n=504), mean HbA1c reductions were −0.56% and −0.63%, respectively (Figure 5). Although of short duration for assessment of cardiovascular outcomes, one observation made in this study was a lower incidence of cardiovascular events (linagliptin, n=12; glimepiride, n=26; relative risk, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.23–0.91), mainly due to fewer nonfatal strokes in patients treated with linagliptin (n=3) versus glimepiride (n=11). To further assess the risk–benefit of linagliptin for individuals, an exploratory analysis evaluated patient achievement of the target HbA1c (<7.0%) without hypoglycemia or weight gain.45 Among those who completed the trial without rescue medication, this composite endpoint was achieved by 54.1% of the linagliptin group compared with 22.9% of the glimepiride group (odds ratio, 3.86; 95% CI, 2.63–5.68; P<0.0001).
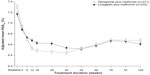  | Figure 5 Change in glycosylated hemoglobin from 2-year comparative trial of linagliptin compared with glimepiride. |
A second long-term study recruited patients who had participated in one of four pivotal 24-week trials of linagliptin studied as monotherapy32 or as add-on to pioglitazone,38 metformin,34 or metformin plus SU.35 These patients continued to a 102-week evaluation of safety, tolerability, and efficacy.46 Participants receiving placebo in the parent studies were switched to linagliptin 5 mg/day and analyzed as a comparator group. The mean HbA1c change from baseline to week 102 was −0.8%, comparable to the improvements in HbA1c seen in the pivotal parent trials. The rate of treatment-related AEs in participants receiving linagliptin throughout the 102-week study period was low and comparable to participants switching to linagliptin from 24 weeks of treatment with placebo (14.4% versus 14.1%). Whereas hypoglycemia occurred in 13.6% and 14.6% of participants, respectively, the incidence of hypoglycemia was mainly associated with the use of SU. Participants continuing from the parent study evaluating linagliptin in combination with metformin plus SU had rates of 10.9% (linagliptin continuation) and 11.4% (placebo switch to linagliptin); however, rates of hypoglycemia in participants continuing from any other trial only ranged from 0.1% to 2.4%.
Weight and organ fat content
Management of body weight is an integral component of type 2 diabetes treatment, and some therapies indicated for treatment of type 2 diabetes can lead to increases in weight.47 Research efforts have focused on development of effective type 2 diabetes therapies that do not cause weight gain, including animal models investigating the effects of linagliptin on body weight. Vickers et al studied the effects of linagliptin and exenatide on body fat content and total body weight in obese Wistar rats.24 In a comprehensive study design, animals were treated with linagliptin alone, exenatide alone, linagliptin and exenatide in combination, exenatide alone followed by a switch to linagliptin, or vehicle. Linagliptin alone did not significantly change body weight versus vehicle. However, in animals withdrawn from exenatide, switching to linagliptin was associated with greater subsequent weight maintenance (mean, −4.6% baseline weight versus controls; P<0.05) compared with switching to vehicle (−3.3% versus controls). Thus, in this study linagliptin reduced weight regain following withdrawal of exenatide. Another animal study showed that linagliptin administered for 6 weeks was associated with a significant reduction in hepatic fat content.48 Wistar rats were fed a high-fat diet to induce obesity, followed by administration of linagliptin, the appetite suppressant sibutramine, or vehicle. At baseline and after 6 weeks of treatment, animals were weighed, and magnetic resonance spectroscopy was used to quantify hepatic and intramyocellular fat content. Linagliptin-treated animals did not have significant changes in total body fat, subcutaneous fat, or visceral fat; however, at the end of treatment, the mean vehicle-corrected change from baseline in hepatic fat content was −59.0% (P=0.015) for linagliptin and −54.3% (P=0.027) for sibutramine. In addition, an assessment of intramyocellular lipid content also showed significant vehicle-corrected reductions from baseline: −62.1% (P=0.073) and −72.4% (P=0.044) for linagliptin and sibutramine, respectively. These results were consistent with another study demonstrating a dose-dependent reduction in hepatic fat content in animals treated with linagliptin.49
Body weight is included as an endpoint in clinical trials of type 2 diabetes therapies. Findings from a meta-analysis of trials of linagliptin, sitagliptin, and saxagliptin have generally demonstrated a mean weight change from baseline within ±1% of baseline body weight.50 Therefore, in clinical practice, DPP-4 inhibitors are generally considered weight neutral. In pivotal 24-week studies of linagliptin, mean weight changes (versus placebo) from baseline to end of study were +0.2 with linagliptin versus −0.7 kg with placebo administered as monotherapy,36 −0.4 versus −0.5 kg in combination with metformin,34 and +0.3 versus −0.1 kg as add-on to metformin plus SU.35 At the end of the 2-year comparative add-on to metformin study, mean body weight decreased with linagliptin and increased with glimepiride (−1.4 versus +1.3 kg), with a treatment difference of −2.7 kg (P<0.0001).44
Potential in patients with renal dysfunction
One of the complications of type 2 diabetes is loss of renal function over time. Improving glycemic control with type 2 diabetes treatment may slow the progression of microvascular disease and reduce the risk of chronic kidney disease.51 Some glucose-lowering therapies may require dose reduction in type 2 diabetes patients with reduced renal function, whereas others are not recommended or are contraindicated for use in this population. Linagliptin does not require dose adjustment in patients with impaired renal function2 and therefore is a good candidate for additional study regarding potential renal properties.
The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of alogliptin, linagliptin, and sitagliptin were evaluated in a rat model of chronic renal failure.52 This same investigation also assessed the effects of linagliptin on biomarkers of cardiac and renal fibrosis. Results demonstrated no effect of DPP-4 inhibitor treatment on estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). The pharmacokinetics of linagliptin were unaffected by renal impairment, whereas exposure to sitagliptin and alogliptin increased significantly in 5 of 6 nephrectomized rats. Although all DPP-4 inhibitors decreased levels of osteopontin (associated with diabetic nephropathy53), linagliptin was the only compound not associated with increases in biomarkers of glomerular or tubular injury. Moreover, linagliptin treatment normalized the mRNA expression of markers associated with uremic cardiomyopathy and levels of B-type natriuretic peptide, a marker of heart failure.
A study in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy demonstrated a synergistic benefit of combining linagliptin with the angiotensin receptor blocker telmisartan.54 Mice were genetically engineered to delete the endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene (leading to nephropathy) and then treated with streptozotocin to induce diabetes. Animals then received telmisartan, linagliptin, both agents combined, or vehicle. Compared with mice that did not receive streptozotocin (nondiabetic controls), combination therapy significantly reduced albuminuria (71.7 mcg/d versus 170.8 mcg/d; P=0.017). Although neither agent used alone had a statistically significant effect on albuminuria, linagliptin administered alone was associated with lower levels of kidney malondialdehyde immune reactivity (a marker of oxidative stress), and linagliptin in combination with telmisartan significantly reduced plasma osteopontin levels and decreased histologic evidence of glomerulosclerosis.
These preclinical findings, as well as conflicting reports regarding the effects of DPP-4 inhibitors on blood pressure,55 warranted further investigation of concomitant renin–angiotensin–aldosterone therapies and linagliptin. Of note, a small clinical study suggested that DPP-4 inhibitor treatment with sitagliptin attenuated the hypotensive effect of maximal angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition via the activation of the sympathetic nervous system.56 A preclinical study in male Wistar rats with hypertension induced by stenosis of the renal artery was undertaken to examine the effects of linagliptin, administered alone and with angiotensin receptor blocker therapy, on blood pressure, renal function, and oxidative stress.57 Results demonstrated that linagliptin administered in combination with telmisartan-normalized blood pressure and reduced oxidative stress.
Given the importance of renal disease therapy considerations for type 2 diabetes, the linagliptin clinical program included a pharmacokinetic study in individuals with renal impairment,58 a long-term evaluation of the safety and efficacy of linagliptin in participants with type 2 diabetes and severe renal impairment,59 and a trial in individuals with moderate to severe renal impairment.60 Graefe-Mody et al published the results of a trial assessing the pharmacokinetics of linagliptin in participants with and without type 2 diabetes with varying degrees of renal impairment, categorized according to creatinine clearance (CrCl) as mild (CrCl >50 to ≤80 mL/min), moderate (CrCl >30 to ≤50 mL/min), or severe (CrCl ≤30 mL/min).58 Participants with end-stage renal disease were included and evaluated using a single dose, whereas all other participants received linagliptin for 7–10 days to achieve steady state. In all groups, the renal excretion of linagliptin was <7% of the administered dose. Thus, this study demonstrated that linagliptin exposure did not increase by more than two-fold in the presence of renal impairment (compared with healthy participants who had normal renal function).
A long-term study included more than 130 patients with eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 who were randomized to receive placebo or linagliptin 5 mg daily.59 After 12 weeks of therapy, the mean placebo-adjusted HbA1c change from baseline (primary endpoint) was −0.60% (P<0.0001); further improvement in HbA1c was seen after 1 year (−0.72%; P<0.0001). As a further measure of efficacy for glycemic control in this study, patients concomitantly taking insulin demonstrated an insulin-sparing effect in the linagliptin group. Mean insulin doses were decreased by −6.2 and −0.3 units in the linagliptin and placebo groups, respectively. After 1 year of therapy, the overall incidence of AEs was 94.1% in patients receiving linagliptin versus 92.3% in the placebo group.
In another 1-year double-blind trial, individuals with type 2 diabetes and moderate to severe renal impairment were randomized to receive linagliptin 5 mg daily (n=113) or placebo (n=122).60 Those receiving placebo switched to glimepiride (1–4 mg daily) at week 12 and continued treatment during a 40-week extension. The mean placebo-adjusted HbA1c change from baseline to week 12 (primary endpoint) was −0.42% (P<0.0001). During the 40-week extension, linagliptin treatment provided lower HbA1c values, a lower incidence of treatment-related AEs, and a lower rate of hypoglycemia compared with glimepiride.
Reduction of albuminuria with linagliptin added to telmisartan in the preclinical model of renal damage54 provided a foundation for evaluating its effects on albuminuria in a pooled post hoc analysis of data from four linagliptin pivotal trials.32,34–36 This analysis included participants (n=217) with diabetic nephropathy (urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio 30–3,000 mg/g creatinine) who received angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers.61 Linagliptin treatment provided significant reductions in albuminuria, with a 32% reduction in the urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio in the linagliptin group compared with 6% in the placebo group (between-group difference, 28%; P=0.04). A prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical trial to evaluate effects of linagliptin on albuminuria when added to the current standard therapy for diabetic nephropathy is underway (MARLINA-T2D™ [efficacy, safety & Modification of Albuminuria in type 2 diabetes subjects with Renal disease With LINAgliptin], NCT01792518).62
Wound healing
One emerging feature that makes incretin therapies of relevance to the elderly diabetic population is the potential for improvement in wound healing. Several studies have shown that the underlying physiology of wound healing is altered in diabetic/obese animal models.26,27,63,64 Because possible mechanisms may be related to hyperglycemia, altered levels of signaling hormones (eg, insulin, glucagon, or others) or the effects that these conditions may have on inflammation and cellular remodeling, the precise etiology remains unclear.28 However, data exist to answer the clinical question of whether treatment with antidiabetic therapies can influence the healing of wounds in patients with diabetes. For example, linagliptin effectively inhibited abnormally elevated levels of DPP-4 in wounds of obese C57BL/6J mice, and this inhibition was associated with an improvement in molecular and cellular markers of wound healing.26
Up to now, no clinical data on the effect of linagliptin on wound healing exist. One clinical study has reported a beneficial effect of DPP-4 inhibition on the healing of diabetes-related ulcers.65 Patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic (>3 months) full-thickness, nonhealing diabetic foot ulcers were randomized to receive open-label vildagliptin (n=53) or treatment with non-DPP-4 antidiabetic therapies (n=53) for 3 months. At the end of the study, more patients receiving vildagliptin (16/53) experienced complete ulcer healing compared with controls (8/53). In addition, fewer patients treated with vildagliptin required ulcer surgery (4/53) versus controls (8/53), and fewer vildagliptin-treated patients had ulcer-related AEs such as infection, cellulitis, or osteomyelitis. A comprehensive biochemical investigation of ulcer biopsies in this study suggested that promotion of angiogenesis might have been a mechanism by which vildagliptin-treated patients experienced significantly better outcomes than patients not receiving therapy with a DPP-4 inhibitor. Clearly, more data are needed in this area of clinical research.
Cardiovascular effects
Improvement in cardiovascular outcomes with current type 2 diabetes therapy has proved elusive, with promising findings from animal studies not always reproducible in clinical trials, as was the case with rosiglitazone.66 Based on the knowledge that GLP-1 receptors are present in the heart, preclinical studies have investigated the role of incretin therapies in mediating cardiovascular effects.66 Studies in animal models suggest that DPP-4 inhibition may improve postmyocardial infarction outcomes. For instance, improved outcomes have been observed in Wistar rats treated with linagliptin prior to inducing cardiac ischemia through ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery.67 When evaluated for 7 days and for 8 weeks after ligation-induced cardiac ischemia, animals pretreated with linagliptin showed significantly smaller infarct size versus vehicle-treated controls (P<0.05). Furthermore, animal models have also identified the potential for improvement in poststroke outcomes. In one study, stroke was induced by cerebral artery occlusion in healthy mice and in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes.25 Healthy C57B1 mice treated with linagliptin showed significantly lower brain infarct volume versus vehicle-treated animals. In the type 2 diabetes mouse model (C57B1 mice with diet-induced diabetes), there was an apparent trend toward lower infarct size, although the difference versus vehicle was not significant.
Preclinical studies suggest that DPP-4 inhibitors have antioxidant, vasodilatory, and anti-inflammatory properties that may provide cardiovascular opportunities.68–70 Linagliptin treatment normalized vascular function and decreased oxidative stress after lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis in rats.70 These effects were independent of its glucose-lowering properties.70
Data from preclinical models provide insight into potential mechanisms of cardiovascular effects of linagliptin observed in clinical trials. As per recent US Food and Drug Administration guidance, cardiovascular events were monitored prospectively in the linagliptin Phase III clinical trial program.71 Recently, data from eight published trials of linagliptin were pooled and assessed for cardiovascular events (n=5,239 patients, with 34 primary cardiovascular events).72 When evaluated as a composite primary endpoint of cardiovascular death, stroke, myocardial infarction, or hospitalization for unstable angina, analysis showed that there were significantly fewer events in patients treated with linagliptin versus comparator therapies (hazard ratio 0.34; 95% CI, 0.16–0.70). An updated meta-analysis of independently adjudicated cardiovascular events from 19 double-blind randomized trials (n=9,459 patients) showed a lower composite event rate for linagliptin (13.4 per 1,000 patient years) versus comparators (18.9 per 1,000 patient years) for a hazard ratio of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.55–1.12; P= not significant).73 As the pooled trials were not individually powered to study cardiovascular outcomes associated with linagliptin therapy, these results are hypothesis-generating and should not be considered as definitive evidence of any effect on cardiovascular outcomes.
To address this question, CAROLINA®: Cardiovascular Outcome Study of Linagliptin Versus Glimepiride in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes is ongoing (NCT01243424).74,75 This study has recruited 6,000 participants with type 2 diabetes who are at increased risk for cardiovascular events. The study will evaluate a primary composite outcome of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, and hospitalization for unstable angina pectoris. With 400-week duration (7.7 years), the study is expected to be complete in 2018. In addition, CARMELINA®: CArdiovascular safety and Renal Microvascular outcomE with LINAgliptin in patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at High Vascular Risk has commenced (NCT01897532).76 This long-term, placebo-controlled study will investigate cardiovascular and renal microvascular outcomes in adults with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk defined by albuminuria and previous macrovascular disease and/or impaired renal function.
Discussion
With an overall favorable safety profile, low risk for hypoglycemia, and weight neutrality, DPP-4 inhibitors have a broad therapeutic potential. From a safety perspective, a key feature of DPP-4 inhibitors is a low risk for hypoglycemia. This is the result of the underlying physiologic changes resulting from inhibition of the DPP-4 enzyme, which initially leads to elevated levels of incretin hormones, the downstream effect being an increase of cyclic adenosine monophosphate production within the pancreatic β-cell.77–80 Given that cyclic adenosine monophosphate promotes the release of insulin in the presence of elevated blood glucose, incretin hormones thus sensitize the β-cell to insulin secretion using native glucose-sensing mechanisms, which most likely explains the low risk for hypoglycemia associated with incretin-based therapies. Rates of hypoglycemia in clinical trials of linagliptin were comparable to placebo when administered as monotherapy32 and when combined with other agents such as metformin33,34 and pioglitazone,38 although a higher rate of hypoglycemic events (versus placebo) was observed when linagliptin was given in combination with metformin plus SU (16.7% versus 10.3%).35 This effect is a well-known feature of the class; prescribing information for each agent indicates that a reduced dose of SU or insulin is needed when used in combination with DPP-4 inhibitors.2,4,7 On this basis, the placement of DPP-4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes has been compared with SUs. Despite the greater HbA1c-lowering potential of SUs when given as monotherapy, DPP-4 inhibitor efficacy for HbA1c reduction may be comparable to SU as add-on therapy,81 whereas SUs are associated with higher risks of weight gain and hypoglycemia. The overall cardiovascular safety profile of SUs is an area of uncertainty. The CAROLINA® study is the only prospective cardiovascular outcomes study to directly compare major adverse cardiovascular events of a DPP-4 inhibitor (linagliptin) with a SU (glimepiride).75 Given these considerations, it has been suggested that DPP-4 inhibitors may assume a comparable role in therapy as the SUs,82,83 particularly as additional cardiovascular data on DPP-4 become available. Results from the SAVOR-TIMI (Saxagliptin Assessment of Vascular Outcomes Recorded in patients with diabetes mellitus–Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction, NCT01107886) study showed that treatment with saxagliptin did not increase or decrease the risk of overall cardiovascular events compared with placebo when added to usual diabetes care.84
One feature relevant to clinical application is that linagliptin is cleared primarily via the hepatobiliary system, which has important implications for its use in patients with diabetic kidney disease, considering that linagliptin does not require dose reduction in patients with declining renal function.2 Kidney disease is a frequent comorbidity associated with diabetes, with an estimated prevalence rate of 40% for chronic kidney disease in patients with diabetes. Diabetes is associated with a higher risk of kidney disease than obesity, hypertension, or cardiovascular disease, with an odds ratio for developing renal impairment potentially as high as 4.1.85 Accordingly, diabetes constitutes a major contributing factor to the development of end-stage renal disease, with more than half of end-stage renal disease cases in 2007 occurring in diabetic patients.86 Some antidiabetic therapies are not suitable for use in the presence of kidney dysfunction, and physicians may not consider the prevalence of low-level renal impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes, particularly in the absence of renal function assessment (ie, CrCl, eGFR).87 Because of these factors, there is a need for both increased awareness of renal status as well as antidiabetic medications that can be used in this setting. Therefore, availability of antidiabetic medications that can be used in patients with this condition is a key medical need.
A second population for which the characteristics of linagliptin may be of relevance is elderly patients with type 2 diabetes. Management of type 2 diabetes in elderly patients is challenging, given the convergence of multiple considerations associated with both advanced age and disease duration. For example, elderly patients with type 2 diabetes are more likely to take multiple medications and have reduced β-cell function, more advanced micro- and macrovascular complications (including an age-related decline in renal function), and altered drug metabolism. In addition, hypoglycemia can be characterized by altered counter-regulatory mechanisms in the elderly and may not be as readily recognized, thus leading to more serious consequences (ie, falls, fractures). Given their low risk of hypoglycemia, the American Diabetes Association and the American Geriatrics Society suggest that DPP-4 inhibitors may be of benefit for elderly patients.88 Recently reported results of a 24-week, double-blind, randomized study in elderly individuals (≥70 years) with type 2 diabetes showed that linagliptin (n=162) was efficacious in lowering glucose when added to current therapy, with a placebo-corrected mean change in HbA1c from baseline of −0.64% (95% CI, −0.81 to −0.48; P<0.0001; baseline, 8.7%), and a safety profile similar to placebo (n=79).89
In continuation of the translational research that has brought linagliptin to approval for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, other aspects of preclinical data that have not yet been investigated in humans might be further explored. The implications of research in animal models regarding the effects of incretin therapies on hepatic fat content and myocardial and brain infarct physiology are of particular interest, and some of these issues are being studied with other incretin agents in the clinical setting.28,63,64 For example, one study showed a relatively smaller area of damaged cardiac tissue following myocardial infarction in patients receiving exenatide versus placebo.5 Other studies have implicated the role of incretin therapies in the reduction of hepatic fat content.90–94 Because these topics are under investigation, the current body of literature points toward a potential benefit and underscores the importance of translational study based on findings from preclinical research. Moving forward, we can expect that future research on DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists will continue to expand their application beyond the maintenance of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Acknowledgments
The author was fully responsible for all content and editorial decisions, was involved at all stages of manuscript development, and has approved the final version of the review that reflects the author’s interpretation and conclusions. Medical writing assistance, supported financially by Boehringer Ingelheim, was provided by Michael P Bennett, PhD, and Marissa Buttaro, MPH, of Envision Scientific Solutions during the preparation of this review. Boehringer Ingelheim was given the opportunity to check the data used in the manuscript for factual accuracy only.
Disclosure
The author has declared no potential conflicts of interest.
References
Ohlsson L, Alsalim W, Carr RD, et al. Glucose-lowering effect of the DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin after glucose and non-glucose macronutrient ingestion in non-diabetic subjects. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15(6):531–537. | |
Tradjenta (linagliptin) [prescribing information]. Ingelheim am Rhein, Germany; Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc.; 2013. Available from: http://bidocs.boehringer-ingelheim.com/BIWebAccess/ViewServlet.ser?docBase=renetnt&folderPath=/Prescribing+Information/PIs/Tradjenta/Tradjenta.pdf. Accessed July 23, 2013. | |
Eckhardt M, Langkopf E, Mark M, et al. 8-(3-(R)-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7- but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-(4-methyl-quinazolin-2-ylme thyl)-3,7-dihydropurine-2,6-dione (BI 1356), a highly potent, selective, long-acting, and orally bioavailable DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J Med Chem. 2007;50(26):6450–6453. | |
Januvia (sitagliptin) [prescribing information]. Whitehouse Station, NJ; Merck and Co, Inc.; 2013. Available from: http://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/j/januvia/januvia_pi.pdf. Accessed July 23, 2013. | |
Koliaki C, Doupis J. Incretin-based therapy: a powerful and promising weapon in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2011;2(2):101–121. | |
Doupis J, Veves A. DPP4 inhibitors: a new approach in diabetes treatment. Adv Ther. 2008;25(7):627–643. | |
Onglyza (saxagliptin) [prescribing information]. New York, NY; Bristol-Myers Squibb; 2013. Available from: http://packageinserts.bms.com/pi/pi_onglyza.pdf. Accessed June 14, 2013. | |
Agrawal R, Jain P, Dikshit SN. Linagliptin: a novel methylxanthin based approved dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor. Curr Drug Targets. 2012;13(7):970–983. | |
Fuchs H, Tillement JP, Urien S, Greischel A, Roth W. Concentration-dependent plasma protein binding of the novel dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor BI 1356 due to saturable binding to its target in plasma of mice, rats and humans. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009;61(1):55–62. | |
Heise T, Graefe-Mody EU, Hüttner S, Ring A, Trommeshauser D, Dugi KA. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and tolerability of multiple oral doses of linagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in male type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009;11(8):786–794. | |
Eckhardt M, Hauel N, Himmelsbach F, et al. 3,5-Dihydro-imidazo[4,5-d]pyridazin-4-ones: a class of potent DPP-4 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008;18(11):3158–3162. | |
Fuchs H, Runge F, Held HD. Excretion of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor linagliptin in rats is primarily by biliary excretion and P-gp-mediated efflux. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2012;45(5):533–538. | |
Thomas L, Eckhardt M, Langkopf E, Tadayyon M, Himmelsbach F, Mark M. (R)-8-(3-amino-piperidin-1-yl)-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-(4-methyl-quinazolin-2-ylmethyl)-3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione (BI 1356), a novel xanthine-based dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, has a superior potency and longer duration of action compared with other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;325(1):175–182. | |
Thomas L, Tadayyon M, Mark M. Chronic treatment with the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor BI 1356 [(R)-8-(3-amino-piperidin-1-yl)-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-(4-methyl-quinazolin-2-ylmethyl)-3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione] increases basal glucagon-like peptide-1 and improves glycemic control in diabetic rodent models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;328(2):556–563. | |
Retlich S, Duval V, Ring A, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of single rising intravenous doses (0.5 mg-10 mg) and determination of absolute bioavailability of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor linagliptin (BI 1356) in healthy male subjects. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010;49(12):829–840. | |
Golightly LK, Drayna CC, McDermott MT. Comparative clinical pharmacokinetics of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012;51(8):501–514. | |
Blech S, Ludwig-Schwellinger E, Gräfe-Mody EU, Withopf B, Wagner K. The metabolism and disposition of the oral dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, linagliptin, in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010;38(4):667–678. | |
Christopher R, Covington P, Davenport M, et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tolerability of single increasing doses of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor alogliptin in healthy male subjects. Clin Ther. 2008;30(3):513–527. | |
He H, Tran P, Yin H, et al. Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of [14C]vildagliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009;37(3):536–544. | |
Vincent SH, Reed JR, Bergman AJ, et al. Metabolism and excretion of the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor [14C]sitagliptin in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2007;35(4):533–538. | |
Graefe-Mody U, Rose P, Retlich S, et al. Pharmacokinetics of linagliptin in subjects with hepatic impairment. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;74(1):75–85. | |
Rauch T, Graefe-Mody U, Deacon CF, et al. Linagliptin increases incretin levels, lowers glucagon, and improves glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2012;3(1):10. | |
Shah P, Ardestani A, Dharmadhikari G, et al. The DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin restores beta-cell function and survival in human isolated islets through GLP-1 stabilization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(7):E1163–E1172. | |
Vickers SP, Cheetham SC, Birmingham GD, et al. Effects of the DPP-4 inhibitor, linagliptin, in diet-induced obese rats: a comparison in naive and exenatide-treated animals. Clin Lab. 2012;58(7–8):787–799. | |
Darsalia V, Ortsäter H, Olverling A, et al. The DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin counteracts stroke in the normal and diabetic mouse brain: a comparison with glimepiride. Diabetes. 2013;62(4):1289–1296. | |
Schurmann C, Linke A, Engelmann-Pilger K, et al. The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor linagliptin attenuates inflammation and accelerates epithelialization in wounds of diabetic ob/ob mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012;342(1):71–80. | |
Goren I, Müller E, Pfeilschifter J, Frank S. Severely impaired insulin signaling in chronic wounds of diabetic ob/ob mice: a potential role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Am J Pathol. 2006;168(3):765–777. | |
Eming SA, Krieg T, Davidson JM. Inflammation in wound repair: molecular and cellular mechanisms. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127(3):514–525. | |
US Food and Drug Administration. Center For Drug Evaluation and Research. Application Number: 201280Orig1s000. Summary Review. Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2011/201280Orig1s000SumR.pdf. Accessed April 18, 2013. | |
Barnett AH, Patel S, Harper R, et al. Linagliptin monotherapy in type 2 diabetes patients for whom metformin is inappropriate: an 18-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial with a 34-week active-controlled extension. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(12):1145–1154. | |
Del Prato S. Linagliptin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011;12(17):2759–2762. | |
Del Prato S, Barnett AH, Huisman H, Neubacher D, Woerle HJ, Dugi KA. Effect of linagliptin monotherapy on glycaemic control and markers of beta-cell function in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13(3):258–267. | |
Forst T, Uhlig-Laske B, Ring A, et al. Linagliptin (BI 1356), a potent and selective DPP-4 inhibitor, is safe and efficacious in combination with metformin in patients with inadequately controlled Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2010;27(12):1409–1419. | |
Taskinen MR, Rosenstock J, Tamminen I, et al. Safety and efficacy of linagliptin as add-on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13(1):65–74. | |
Owens DR, Swallow R, Dugi KA, Woerle HJ. Efficacy and safety of linagliptin in persons with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by a combination of metformin and sulphonylurea: a 24-week randomized study. Diabet Med. 2011;28(11):1352–1361. | |
Haak T, Meinicke T, Jones R, Weber S, von Eynatten M, Woerle HJ. Initial combination of linagliptin and metformin improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(6):565–574. | |
US Food and Drug Administration. CDER Drug and Biologic Calendar Year Approvals as of December 31, 2012. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/developmentapprovalprocess/howdrugsaredevelopedandapproved/drugandbiologicapprovalreports/ucm342732.pdf. Accessed March 18, 2014. | |
Gomis R, Espadero RM, Jones R, Woerle HJ, Dugi KA. Efficacy and safety of initial combination therapy with linagliptin and pioglitazone in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13(7):653–661. | |
Lewin AJ, Arvay L, Liu D, Patel S, von Eynatten M, Woerle HJ. Efficacy and tolerability of linagliptin added to a sulfonylurea regimen in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus: an 18-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Ther. 2012;34(9):1909–1919.e15. | |
Yki-Järvinen H, Rosenstock J, DurÁn-Garcia S, et al. Effects of adding linagliptin to basal insulin regimen for inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes. A ≥52-week randomized, double-blind study. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(12):3875–3881. | |
Kawamori R, Inagaki N, Araki E, et al. Linagliptin monotherapy provides superior glycaemic control versus placebo or voglibose with comparable safety in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, placebo and active comparator-controlled, double-blind study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(4):348–357. | |
Hüttner S, Graefe-Mody EU, Withopf B, Ring A, Dugi KA. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of single oral doses of BI 1356, an inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase 4, in healthy male volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;48(10):1171–1178. | |
Schernthaner G, Barnett AH, Emser A, et al. Safety and tolerability of linagliptin: a pooled analysis of data from randomized controlled trials in 3572 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(5):470–478. | |
Gallwitz B, Rosenstock J, Rauch T, et al. 2-year efficacy and safety of linagliptin compared with glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: a randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2012;380(9840):475–483. | |
Gallwitz B, Rosenstock J, Emser A, von Eynatten M, Woerle HJ. Linagliptin is more effective than glimepiride at achieving a composite outcome of target HbA1c <7% with no hypoglycaemia and no weight gain over 2 years. Int J Clin Pract. 2013;67(4):317–321. | |
Gomis R, Owens DR, Taskinen MR, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of linagliptin as monotherapy or in combination with other oral glucose-lowering agents in 2121 subjects with type 2 diabetes: up to 2 years exposure in 24-week phase III trials followed by a 78-week open-label extension. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66(8):731–740. | |
Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach: position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2012;35(6):1364–1379. | |
Klein T, Niessen HG, Ittrich C, et al. Evaluation of body fat composition after linagliptin treatment in a rat model of diet-induced obesity: a magnetic resonance spectroscopy study in comparison with sibutramine. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(11):1050–1053. | |
Kern M, Klöting N, Niessen HG, et al. Linagliptin improves insulin sensitivity and hepatic steatosis in diet-induced obesity. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38744. | |
Monami M, Iacomelli I, Marchionni N, Mannucci E. Dipeptydil peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2010;20(4):224–235. | |
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes – 2013. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(Suppl 1):S11–S66. | |
Chaykovska L, von Websky K, Rahnenfuhrer J, et al. Effects of DPP-4 inhibitors on the heart in a rat model of uremic cardiomyopathy. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27861. | |
Nicholas SB, Liu J, Kim J, et al. Critical role for osteopontin in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2010;77(7):588–600. | |
Alter ML, Ott IM, von Websky K, et al. DPP-4 inhibition on top of angiotensin receptor blockade offers a new therapeutic approach for diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2012;36(1):119–130. | |
Hocher B, Reichetzeder C, Alter ML. Renal and cardiac effects of DPP4 inhibitors – from preclinical development to clinical research. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2012;36(1):65–84. | |
Marney A, Kunchakarra S, Byrne L, Brown NJ. Interactive hemodynamic effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibition and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in humans. Hypertension. 2010;56(4):728–733. | |
Chaykovska L, Alter ML, von Websky K, et al. Effects of telmisartan and linagliptin when used in combination on blood pressure and oxidative stress in rats with 2-kidney-1-clip hypertension. J Hypertens. 2013;31(11):2290–2298; discussion 2299. | |
Graefe-Mody U, Friedrich C, Port A, et al. Effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor linagliptin(*). Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13(10):939–946. | |
McGill JB, Sloan L, Newman J, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of linagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and severe renal impairment: a 1-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(2):237–244. | |
Laakso M, Rosentstock J, Groop PH, et al. Linagliptin vs placebo followed by glimepiride in type 2 diabetes patients with moderate to severe renal impairment. Diabetes. 2013;62(Suppl 1):A281–A282. Abstract. | |
Groop P-H, Cooper ME, Perkovic V, Emser H, Woerle HJ, von Eynatten M. Linagliptin lowers albuminuria on top of recommended standard treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal dysfunction. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(11):3460–3468. | |
Boehringer Ingelheim. MARLINA – T2D™: efficacy, safety & Modification of Albuminuria in type 2 diabetes subjects with Renal disease With LINAgliptin. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01792518?term=MARLINA&rank=1. NLM identifier: NCT01792518. Accessed June 19, 2013. | |
Lan CC, Wu CS, Huang SM, Wu IH, Chen GS. High-glucose environment enhanced oxidative stress and increased interleukin-8 secretion from keratinocytes: new insights on impaired diabetic wound healing. Diabetes. 2013;62(7):2530–2538. | |
Blakytny R, Jude E. The molecular biology of chronic wounds and delayed healing in diabetes. Diabet Med. 2006;23(6):594–608. | |
Marfella R, Sasso FC, Rizzo MR, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibition may facilitate healing of chronic foot ulcers in patients with type 2 diabetes. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012;2012:892706. | |
Ban K, Hui S, Drucker DJ, Husain M. Cardiovascular consequences of drugs used for the treatment of diabetes: potential promise of incretin-based therapies. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2009;3(4):245–259. | |
Hocher B, Sharkovska Y, Mark M, Klein T, Pfab T. The novel DPP-4 inhibitors linagliptin and BI 14361 reduce infarct size after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(1):87–93. | |
Takasawa W, Ohnuma K, Hatano R, Endo Y, Dang NH, Morimoto C. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 regulates microvascular endothelial growth induced by inflammatory cytokines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;401(1):7–12. | |
Ferreira L, Teixeira-de-Lemos E, Pinto F, et al. Effects of sitagliptin treatment on dysmetabolism, inflammation, and oxidative stress in an animal model of type 2 diabetes (ZDF rat). Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010:592760. | |
Kröller-Schön S, Knorr M, Hausding M, et al. Glucose-independent improvement of vascular dysfunction in experimental sepsis by dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 inhibition. Cardiovasc Res. 2012;96(1):140–149. | |
US Department of Health and Human Services. Guidance for Industry: Diabetes Mellitus--Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk in New Antidiabetic Therapies to Treat Type 2 Diabetes. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/ucm071627.pdf. Accessed May 30, 2013. | |
Johansen OE, Neubacher D, von Eynatten M, Patel S, Woerle HJ. Cardiovascular safety with linagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a pre-specified, prospective, and adjudicated meta-analysis of a phase 3 programme. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012;11:3. | |
Johansen OE, Neubacher D, Seck T, Patel S, Woerle HJ. Cardiovascular (CV) safety of linagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D): a pooled comprehensive analysis of prospectively adjudicated CV events in phase 3 studies. Diabetes. 2013;62(Suppl 1):A96. Abstract. | |
Boehringer Ingelheim. CAROLINA®: Cardiovascular Outcome Study of Linagliptin versus Glimepiride in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01243424?term=linagliptin&rank=12. NLM identifier: NCT01243424. Accessed June 7, 2013. | |
Rosenstock J, Marx N, Kahn SE, et al. Cardiovascular outcome trials in type 2 diabetes and the sulphonylurea controversy: Rationale for the active-comparator CAROLINA trial. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2013;10(4):289–301. | |
Boehringer Ingelheim. CARMELINA®: Cardiovascular and Renal Microvascular Outcome Study With Linagliptin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at High Vascular Risk. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01897532?term=CARMELINA&rank=1. NLM identifier: NCT01897532. Accessed August 21, 2013. | |
Huypens P, Ling Z, Pipeleers D, Schuit F. Glucagon receptors on human islet cells contribute to glucose competence of insulin release. Diabetologia. 2000;43(8):1012–1019. | |
Moens K, Heimberg H, Flamez D, et al. Expression and functional activity of glucagon, glucagon-like peptide I, and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide receptors in rat pancreatic islet cells. Diabetes. 1996;45(2):257–261. | |
Schuit FC, Huypens P, Heimberg H, Pipeleers DG. Glucose sensing in pancreatic beta-cells: a model for the study of other glucose-regulated cells in gut, pancreas, and hypothalamus. Diabetes. 2001;50(1):1–11. | |
Drucker DJ, Philippe J, Mojsov S, Chick WL, Habener JF. Glucagon-like peptide I stimulates insulin gene expression and increases cyclic AMP levels in a rat islet cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84(10):3434–3438. | |
Scheen AJ. DPP-4 inhibitors in the management of type 2 diabetes: a critical review of head-to-head trials. Diabetes Metab. 2012;38(2):89–101. | |
Ahrén B. Are sulfonylureas less desirable than DPP-4 inhibitors as add-on to metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes? Curr Diab Rep. 2011;11(2):83–90. | |
Gallwitz B, Häring HU. Future perspectives for insulinotropic agents in the treatment of type 2 diabetes-DPP-4 inhibitors and sulphonylureas. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010;12(1):1–11. | |
Scirica BM, Bhatt DL, Braunwald E, et al; for the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Steering Committee and Investigators. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(14):1317–1326. | |
United States Renal Data System. 2013 USRDS Annual Data Report: Chronic Kidney Disease in the General Population. Available from: http://www.usrds.org/2013/pdf/v1_ch1_13.pdf. Accessed March 19, 2014. | |
United States Renal Data System. USRDS 2009 Annual Data Report. Available from: http://www.usrds.org/2009/pdf/V2_02_INC_PREV_09.pdf. Accessed June 7, 2013. | |
Meyers JL, Candrilli SD, Kovacs B. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment in a large outpatient electronic medical records database: rates of diagnosis and antihyperglycemic medication dose adjustment. Postgrad Med. 2011;123(3):133–143. | |
Kirkman M, Briscoe VJ, Clark N, et al. Diabetes in older adults: a consensus report. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60(12):2342–2356. | |
Barnett AH, Huisman H, Jones R, von Eynatten M, Patel S, Woerle HJ. Linagliptin for patients aged 70 years or older with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with common antidiabetes treatments: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2013;383(9902):1413–1423. | |
Cuthbertson DJ, Irwin A, Gardner CJ, et al. Improved glycaemia correlates with liver fat reduction in obese, type 2 diabetes, patients given glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50117. | |
Forst T, Uhlig-Laske B, Ring A, Ritzhaupt A, Graefe-Mody U, Dugi KA. The oral DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin significantly lowers HbA1c after 4 weeks of treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13(6):542–550. | |
Itou M, Kawaguchi T, Taniguchi E, Oriishi T, Sata M. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor improves insulin resistance and steatosis in a refractory nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patient: a case report. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2012;6(2):538–544. | |
Ross SA, Rafeiro E, Meinicke T, Toorawa R, Weber-Born S, Woerle HJ. Efficacy and safety of linagliptin 2.5 mg twice daily versus 5 mg once daily in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Curr Med Res Opin. 2012;28(9):1465–1474. | |
Sathyanarayana P, Jogi M, Muthupillai R, Krishnamurthy R, Samson SL, Bajaj M. Effects of combined exenatide and pioglitazone therapy on hepatic fat content in type 2 diabetes. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2011;19(12):2310–2315. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.