Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 13
Intraocular Lens Implantation In The Ciliary Sulcus: Challenges And Risks
Received 5 August 2019
Accepted for publication 5 November 2019
Published 27 November 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 2317—2323
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S205148
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Rajvi Mehta, Ahmad A Aref
Illinois Eye and Ear Infirmary, Chicago, IL, USA
Correspondence: Ahmad A Aref
Illinois Eye and Ear Infirmary, 1855 W. Taylor Street, M/C 648, Chicago, IL 60612, USA
Tel +1312-996-7030
Fax +1312-413-8574
Email [email protected]
Purpose: This article reviews the current literature on the risks and challenges associated with intraocular lens (IOL) implantation in the ciliary sulcus.
Recent findings: The development of IOLs designed specifically for placement in the ciliary sulcus continues to be an area of interest for the ophthalmic industry. Currently the one-piece PMMA (polymethylmethacrylate) lens or a three-piece IOL are the best available options for IOL placement in the ciliary sulcus space. Single piece acrylic (SPA) IOLs are not designed for sulcus placement and there is growing evidence of chronic complications related to their use in the ciliary sulcus. Many of these eyes ultimately require surgical intervention, including lens exchange. Endoscopic imaging and ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) have enabled a better understanding of ciliary sulcus anatomy and measurements in the living eye.
Summary: When the capsular bag is compromised, IOL placement in the ciliary sulcus is a reasonable option. In these circumstances, appropriate choice of IOL, knowledge of the sulcus anatomy, and correct technique can improve results and reduce postoperative complications.
Keywords: ciliary sulcus, capsule rupture, intraocular lens, complications, surgical technique
Introduction
The anatomic zone for optimal placement of intraocular lens (IOL) implantation is within the capsular bag. This provides the greatest IOL stability and places the IOL closer to the nodal point of the original crystalline lens, resulting in better image resolution.1 This position also keeps the foreign lens material away from the anterior chamber, thus preventing complications involving the endothelium and anterior chamber angle.1 However, when the IOL cannot be securely placed within the capsular bag, an alternative positioning and fixation is required. In cases of posterior capsule rupture, zonular laxity, lens subluxation with absent capsule, or planned piggyback IOL placement, IOL placement in the ciliary sulcus is preferred.1,2 Surgeons must be familiar with the anatomy and indications for IOL placement in this space in order to maximize chances of visual rehabilitation and decrease risk of vision threatening complications.
Ciliary Sulcus Anatomy
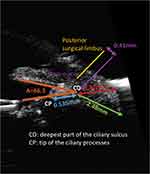
Ciliary sulcus anatomy and measurements have been reported in cadaver eyes and more recently in the living eye using endoscopic imaging and ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM). The exact sulcus-to-sulcus distance cannot be measured, but it is estimated to be approximately 11.0–12.5 mm based on anatomic findings of the ciliary body, corneal diameter, and white-to-white measurement.3 The ciliary sulcus is wider than the posterior surgical limbus, with the total mean limbus-ciliary sulcus distance noted to be 0.9 mm accounting for both sides.4 These measurements indicate that placement of the haptics of an IOL with an adequate diameter of 12.5 mm or more in the ciliary sulcus would provide stable haptic fixation by generating outward tension.2,5
Based on measurements in living eyes using UBM (Figure 1), the mean angle of the ciliary sulcus is 66.3±20.0 degrees, the mean distance from the deepest part of the ciliary sulcus to the tip of the ciliary processes is 0.535±0.137 mm, the mean length of a perpendicular line drawn from the deepest part of the ciliary sulcus to the sclera is 1.52±0.197 mm, and the mean length of a line drawn parallel to the posterior iris surface from the deepest part of the ciliary sulcus to the scleral surface is 2.48±0.305 mm.3,6 Based on these images, the Schlemm canal was noted to be reachable with a perpendicular incision from the posterior surgical limbus (the point of intersection on the sclera of a line perpendicular to the sclera passing through an area presumed to be Schlemm canal). The distance between the posterior surgical limbus and the perpendicular line drawn from the deepest part of the ciliary sulcus to the sclera (AC) was measured as 0.41 mm.3 These measurements indicate that the distance between the point of emergence on the sclera of the needle inserted in the deepest part of the ciliary sulcus and the posterior surgical limbus in ab interno ciliary sulcus suture fixation of an IOL would be expected to be 2.37 mm (0.41 mm+1.96 mm).3
The total length of the pars plicata, which contains the ciliary processes, is approximately 2.0 mm, and the distance from the posterior surgical limbus to the ciliary sulcus is 0.41 mm on each side. Therefore, the end of the pars plicata should be located at 2.41 mm (0.41 mm+2.00 mm) from the posterior surgical limbus. This is an important landmark because major bleeding can occur if a needle is inserted closer than 2.41 mm from the posterior surgical limbus.3 The pars plicata bleeds easily because of the presence of a capillary network originating from the circulus arteriosus iridis major. Also, in cases requiring pars plana suture fixation, the IOL haptics would be fixated over the ciliary processes and may get lodged obliquely in the valleys between the tips of the ciliary processes, resulting in significant and irreversible IOL tilt and decentration.3
Endoscopic visualization of the ciliary sulcus showed that the ciliary sulcus is formed by the two surfaces, with the posterior iris forming the upper surface, and the lower surface being formed by the fused ciliary processes. The absence of chasms in the lower surface of the ciliary sulcus indicates that it is feasible to place the haptics at this site.3
Indications For Sulcus IOL Implantation
- Capsular Rupture
Three situations of capsular damage are:
- Anterior capsular tear without extension: The IOL can usually be placed in the bag and a single-piece acrylic IOL would be a good option in this case because the soft acrylic haptics oriented 90 degrees away from the tear, create little tension on the bag, and minimize risk of extension of tear.1,2 However, the disadvantage of placing this IOL in the bag is that if the radial tear advances to the posterior capsule during insertion, the IOL needs to be removed and exchanged for a 3-piece IOL suitable for sulcus placement.7
- Anterior capsular tear extending to posterior capsule: When both anterior and posterior capsules are torn, the area is sealed off with viscoelastic and IOL is placed in the sulcus.7
- Posterior capsular tear with intact anterior capsule: There are two options for sulcus placement and one for in-the-bag placement—one sulcus option is to place the entire IOL in the sulcus and the other option is to place the haptics in the sulcus and gently prolapse the optic in the bag with a well centered anterior capsulotomy. With the optic in the bag, no IOL power adjustment is needed, and the optic capture is stable and seals off vitreous from the anterior chamber. For stable posterior capsule tears or those completed with a posterior capsulorrhexis, a single-piece acrylic IOL can be placed in the bag.2
If there is a defect in the posterior capsule, the haptics should be oriented 90 degrees away from the defect to prevent the haptic from sliding into the area of concern.4
Contraindications To Sulcus IOL Implantation
- Lack of Anterior Capsular Support
When the anterior capsule is not adequate, alternative fixation techniques need to be used. If there is no capsule support, iris fixation, scleral fixation, or an anterior chamber intraocular lens (ACIOL) can be used, although the latter should be avoided in patients with shallow anterior chamber and compromised corneas.10 For patients who have undergone pars plana vitrectomy and have no capsule support, scleral fixation, ACIOL, and iris-fixated Artisan-Ophtec aphakic IOL are options, but iris fixation should be avoided due to iridodinesis postvitrectomy.10,11
IOLs
The best options for ciliary sulcus placement are a one-piece PMMA lens or a three-piece IOL with posteriorly angulated and thin looped haptics, which displace the optic away from the iris (Figure 2). The optic surface should be smooth with round edges and have an optic diameter of at least 6mm. The diameter from one haptic edge to the other across the optic should be at least 13mm for adequate tension on the sulcus and IOL centration in the visual axis. The large optic is forgiving of mild decentration and permits a better view of the peripheral retina.2
- 3-piece IOL options: acrylic IOL and silicone IOL
 |
Figure 2 High-frequency ultrasound biomicroscopic image demonstrating a well positioned 3-piece intraocular lens in the ciliary sulcus space. |
The IOL with Acrylic optic and square anterior edge has wide haptics (13mm) and a large yet injectable 6.5mm optic. While this lens can be used in patients who have undergone vitrectomy, the haptic length may be too small for larger eyes and the square anterior edge may rub against the pupil.2 While the 3-piece IOL with the silicon optic and rounded anterior edges has a longer haptic (13.5mm) which is great for larger eyes, it injects relatively quickly and silicone is not good if vitrectomy is required because of the possible use of silicone oil which deposits on silicone lenses causing opacification.2 Acrylic IOLs are preferred over silicone IOLs for sulcus implantation because patients with capsular trauma are at risk for retinal detachment and possible use of silicone oil.1,2
1-piece PMMA IOLs have fallen out of favor as the primary IOL implant because of the large 6–7mm incision size required for insertion but their thin haptic design makes these IOLs compatible with both capsular and sulcus placement. When placed in the sulcus, these rigid non-foldable lenses with their thin haptic design allow the optic to be displaced away from the iris.1
Single piece foldable acrylic lenses are a poor choice for ciliary sulcus placement because the square-edged optic design, thick haptics, and unpolished side walls cause friction at the edges of the lens.10 The overall diameter of these lenses, while ideal for capsular fixation, is undersized for the ciliary sulcus. Even when optic capture is possible, these lenses are not well suited for sulcus fixation. They have minimal to no posterior angulation and the optic may be more likely to prolapse anteriorly, increasing the risk of pupillary capture. The adherent surface of the acrylic IOL and the bulkier single-piece haptics promote iris chafing, increasing the risk for pigment dispersion syndrome, uveitis-glaucoma-hyphema (UGH) syndrome, iridocyclitis, and increased intraocular pressure (IOP).10
Adjustment Of Lens Power
When placed entirely within the ciliary sulcus, the IOL sits 0.5 mm more anterior than if it were placed within the capsular bag.2 The A constant should be lowered by about 0.80 diopters (D) in these cases and because lenses only come in half-diopter steps, despite the fact that a 11D and 16D lens are not the same, the amount of change needed when the lens is moved forward into the sulcus is about a half-diopter less for both lenses.
The power of the sulcus based IOL usually needs to be decreased by 0.50–1.00D to provide the same refractive outcome for an average eye. For larger, myopic eyes the IOL needs to be reduced by less than 0.50D, while for small, hyperopic eyes it may need to be reduced by 1.50D.9 The exact adjustment of IOL power can be calculated if the sulcus position is known but the “rule of 9s” method is a reasonable approximation (Table 1).10,11
 |
Table 1 Adjustment Of IOL Power Based On “Rule Of 9s” Method2,10,11 |
In cases where the anterior capsular rim is intact and there is a centered appropriately sized capsulorhexis, the haptics can be placed in the ciliary sulcus and the optic can be pushed posteriorly and captured behind the capsulorhexis. This approach gives better stability and minimally affects lens power calculations.10
Techniques
- 3-piece foldable IOL entirely in the sulcus
The key for sulcus IOL placement is to avoid vitreous prolapse. The incision should be large enough for the 3-piece IOL injector to be easily inserted without much force; if pushed too hard, viscoelastic may be lost with risk for vitreous prolapse.2 Dispersive viscoelastic creates space between the iris and the anterior capsule to compartmentalize the eye and better allow the leading haptic into the sulcus. A bolus of viscoelastic through the posterior capsule break serves to tamponade the vitreous and create a barrier.15
The IOL should then be placed gently in the sulcus. Manual forceps delivery of the IOL requires a large incision and care should be taken to avoid damaging the trailing haptic during insertion of the 3-piece IOL.1,15 The larger Monarch B (Alcon, Inc., Fort Worth, TX) cartridge can be used to insert the optic with the trailing haptic placed to the side of the knob on the cartridge to protect the haptic from the advancing plunger.1 The leading haptic is placed under the iris and in the sulcus with the trailing haptic outside the eye or over the iris until the leading haptic is correctly positioned in the sulcus. The trailing haptic can then be placed in the sulcus with forceps or rotated in position with a Kuglen hook.1
Viscoelastic should be removed from the anterior chamber carefully with the understanding that it is better to leave a little viscoelastic within the eye than to risk vitreous prolapse.2 Dispersive OVD causes fewer pressure spikes if left behind and coats tissue better.15
In cases where there is an area of weakness like a defect in the posterior capsule or weak zonules, the sulcus lens haptic should be placed away from the area of concern.1,2 Suture fixation of sulcus IOL is not commonly performed unless the lens is clearly not stable because of loss of zonules or lack of anterior capsular support.15 The sulcus IOL may be sutured in place to the back of the iris or sclera. However sometimes the sutured lenses can torque resulting in cystoid macular edema, and a sutured one-piece lens has been reported to cause iris chafing and secondary pigment glaucoma so this should be avoided.1,15
An intact capsulorhexis of appropriate dimensions allows the optic to be captured through it like a buttonhole. This allows for better stability than placing the IOL entirely in the sulcus.1
In cases with an intact anterior capsule but large or peripheral posterior capsule tear and loss of capsular bag support, optic capture through an anterior continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis (CCC) ensures fixation and centration of IOL while minimizing risk of haptic and/or optic chafing of uveal tissues. The capsulorhexis should be well centered with an opening that is at least 1.0–2.0mm smaller than the optic diameter.1 Any prolapsed vitreous is removed with anterior vitrectomy and an ophthalmic viscosurgical device is placed in the anterior chamber and the ciliary sulcus. The IOL is then placed in the ciliary sulcus and the edges of the optic are placed through the capsulorhexis with gentle pressure on one side and then the other side of the anterior surface of the IOL, 90 degrees away from the haptic-optic junctions.1,16 The haptics remain in the sulcus.
If a large anterior capsule tear is present extending to the equator, optic capture through a posterior CCC is an option. The IOL is positioned in the ciliary sulcus and the optic is captured posteriorly through the anterior and posterior capsule openings. This maintains IOL centration and prevents formation of Elschnig’s pearl and visual axis opacification posterior to the IOL.1,2
Finally, the haptics are placed in the sulcus with IOL optic capture through a membrane opening for secondary procedures. These secondary procedures include (1) repositioning of decentered IOLs from poor initial positioning (one haptic in the sulcus and other in the bag) or because of asymmetric contraction of capsular bag, (2) fixating replacement IOLs (when in-the-bag IOLs need to be replaced because of optical degradation because of calcification or opacification), or (3) for secondary IOL placement in aphakic eyes (such as in infant cataract surgery).1 One piece PMMA IOLs and three-piece foldable IOLs can be captured this way.16 This technique is particularly useful if the IOL being repositioned has an overall length that is appropriate for the capsular bag but not for the sulcus or if the haptics are crimped and no longer suitable for sulcus placement.2,15
Complications And Outcomes
Most severe complications related to sulcus IOL placement arise from poor choice of IOL, particularly patients with single-piece acrylic (SPA) IOL implantation in the ciliary sulcus have been reported to develop secondary pigment dispersion (83%), elevated IOP (33%) and secondary pigmentary glaucoma, intraocular hemorrhage (23%), and iris transillumination defects (TIDs) (80%).17–20 Analysis of several sulcus-fixated single piece acrylic IOLs that were explanted because of pigment dispersion syndrome revealed that the most common histopathologic finding was pigment granules on the anterior surface of the IOL.10 This accumulation was greatest on the haptic but also appeared on the peripheral optic and haptic–optic junction. These findings are consistent with posterior iris chafing caused by the optic and the relatively thick flexible haptics, all of which have squared edges and unpolished side walls.10 Iris chafing results in TIDs, and secondary pigment dispersion can result in krukenberg spindle formation and hyperpigmentation of the trabecular meshwork.21
Other complications from sulcus placement of single-piece IOLs may include recurrent iridocyclitis, uveitis-glaucoma-hyphema (UGH) syndrome, vitreous hemorrhage, cystoid macular edema, and, most commonly, lens decentration resulting in symptomatic edge glare.10,21–25 The contact of the sharp IOL edges with the posterior iris vasculature can also predispose the eye to chronic uveal inflammation and recurrent microhyphemas that can impair vision and abruptly raise the IOP. Many of these eyes (93%) ultimately require surgical intervention, including IOL exchange (83%).10,25
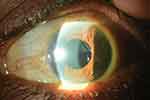
Despite increasing reports of postoperative complications associated with SPA IOL placement in the sulcus, the use of this IOL remains controversial. Two studies at the same center by Taskapili et al26,27 supported implantation of a single-piece acrylic IOL in the sulcus because it maintains the advantages of a small incision surgery with good postoperative visual results and few complications or decentered IOLs. Another interventional case series by Uy et al28 followed 20 eyes which had undergone hydrophobic acrylic IOL (HAIOL) implantation in the ciliary sulcus after developing posterior capsule rupture during phacoemulsification. Four of 20 eyes (20%) exhibited transient IOP rise (-CBrk-25 mm Hg), seven eyes (35%) exhibited pigment release, of which three eyes developed secondary glaucoma requiring IOP-lowering treatment including filtering surgery (Figure 3). The mean duration to onset of secondary glaucoma was 13.0±9.6 months. Even with these complications, postoperative best-corrected visual acuity was 20/40 or better in all eyes, and none of the HAIOLs was decentered or dislocated.
When the question of whether a SPA IOL should be placed in the ciliary sulcus was presented at the Spotlight on Cataract Complications Symposium at the 2008 American Academy of Ophthalmology annual meeting, 47% of the respondents said “never”, 40% said “yes, if capsule support was adequate”, 2% said “yes, if suture fixated”, and 11% said “yes, if no other PC IOL was available”.10
Chang et al10 then conducted a large retrospective survey of patients referred to six members of the American Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgery (ASCRS) Cataract Clinical Committee for chronic complications associated with SPA IOLs implanted in the ciliary sulcus. Thirty patients (30 eyes) were evaluated, 29 of 30 IOLs were single piece acrylic IOLs, and posterior capsule rupture with IOL decentration occurred in two-thirds of the eyes. The mean IOP was 22.1 mmHg, and one-third of the patients were taking at least one IOP lowering medication. Complications other than posterior capsule rupture were analyzed, with the most common being pigment dispersion and iris transillumination defects followed by IOL edge symptoms and elevated IOP (maximum IOP >22 mm Hg); intraocular hemorrhage and cystoid macular edema were relatively infrequent.10
Although there is no information on how many eyes have had sulcus SPA IOL implantation without complications, several case reports and large case series have shared SPA IOLs induced postoperative chronic problems. These complications are consistent with and predicted by the design of SPA IOLs which are made for capsular placement and are not compatible with sulcus placement. The development, investigation, and supply of IOLs specifically for placement in eyes lacking adequate capsule bag support continues to be an unmet need for the ophthalmic industry.
Conclusions
IOL placement in the ciliary sulcus is rarely a matter of choice. When capsular placement is not a possibility, sulcus placement of the IOL serves as a viable alternative. The correct choice of IOL, understanding of the ciliary sulcus anatomy, and proper technique can enable better outcomes and minimize complications.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Randleman JB, Ahmed IIK, Editors. Intraocular Lens Surgery. New York: Thieme medical publishers; 2016:
2. Kim T, DelMonte DW, Gupta PK, Chang DF, Editors. Curbside Consultation in Cataract Surgery.
3. Sugiura T, Kaji Y, Tanaka Y. Anatomy of the ciliary sulcus and the optimum site of needle passage for intraocular lens suture fixation in the living eye. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2018;44:1247–1253. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2018.07.017
4. Kawamorita T, Uozato H, Kamiya K, Shimizu K. Relationship between ciliary sulcus diameter and anterior chamber diameter and corneal diameter. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36(4):617–624. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2009.11.017
5. Pop M, Payette Y, Mansour M. Predicting sulcus size using ocular measurements. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001;27:1033–1038. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(00)00830-0
6. Oh J, Shin HH, Kim JH, Kim HM, Song JS. Direct measurement of the ciliary sulcus diameter by 35-megahertz ultrasound biomicroscopy. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:1685–1688.
7. Moshirfar M, Skanchy DF, Shah T. Intraoperative management of anterior capsular tear. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2007;28:42–48. doi:10.1097/ICU.0000000000000325
8. Tribus C, Alge CS, Haritoglou C, et al. Indications and clinical outcome of capsular tension ring (CTR) implantation: a review of 9528 cataract surgeries. Clin Ophthalmol. 2007;1(1):65–69.
9. Abdelghany AA, Alio JL. Surgical options for correction of refractive error following cataract surgery. Eye Vis (Lond). 2014;1:2. doi:10.1186/s40662-014-0002-2
10. Chang DF, Masket S, Miller KM, et al. Complications of sulcus placement of single-piece acrylic intraocular lenses: recommendations for backup IOL implantation following posterior capsule rupture. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35(8):1445–1458. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2009.04.027
11. Negretti GS, Lai M, Petrou P, Walker R, Charteris D. Anterior chamber lens implantation in vitrectomised eyes. Eye (Lond). 2018;32(3):597–601. doi:10.1038/eye.2017.261
12. Bayramlar H, Hepsen IF, Yilmaz H. Myopic shift from the predicted refraction after sulcus fixation of PMMA posterior chamber intraocular lenses. Can J Ophthalmol. 2006;41:78–82. doi:10.1016/S0008-4182(06)80072-4
13. Suto C, Hori S, Fukuyama E, Akura J. Adjusting intraocular lens power for sulcus fixation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003;29:1913–1917.
14. Suto C. Sliding scale of IOL power for sulcus fixation using computer simulation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004;30:2452–2454. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2004.08.041
15. Brazitikos PD, Balidis MO, Tranos P, et al. Sulcus implantation of a 3-piece, 6.0mm optic, hydrophobic foldable acrylic intraocular lens in phacoemulsification complicated by posterior capsule rupture. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002;28:1618–1622. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(02)01211-7
16. Gimbel HV, DeBroff BM. Intraocular lens optic capture. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004;30:200–206. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2003.11.035
17. Kohnen T, Kook D. Solving intraocular lens–related pigment dispersion syndrome with repositioning of primary sulcus implanted single-piece IOL in the capsular bag. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35(8):1459–1463. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2009.05.005
18. Kristianslund O, Raen M, Ostern AE, Drolsum L. Glaucoma and intraocular pressure in patients operated for late in-the-bag intraocular lens dislocation: a randomized clinical trial. Am J Ophthalmol. 2017;176:219–227. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2017.01.026
19. Wagoner MD, Cox TA, Ariyasu RG, Jacobs DS, Karp CL. Intraocular lens implantation in the absence of capsular support: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2003;110(4):840–859. doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(02)02000-6
20. Ali HM, Dikopf SM, Aref AA. Late complications of single-piece intraocular lens implantation in the ciliary sulcus. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018;136(7):825–826. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.6050
21. Micheli T, Cheung LM, Sharma S, et al. Acute haptic-induced pigmentary glaucoma with an AcrySof intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002;28:1869–1872.
22. LeBoyer RM, Werner L, Snyder ME, Mamalis N, Riemann CD, Augsberger JJ. Acute haptic-induced ciliary sulcus irritation associated with single-piece AcrySof intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31:1422–1427. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2004.12.056
23. Toma HS, DiBernardo C, Schein OD, Adams NA. Recurrent vitreous hemorrhage secondary to haptic-induced chafing. Can J Ophthalmol. 2007;42:312–313. doi:10.3129/canjophthalmol.i07-018
24. Wintle R, Austin M. Pigment dispersion with elevated intraocular pressure after AcrySof intraocular lens implantation in the ciliary sulcus. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001;27:642–644. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(00)00792-6
25. Amino K, Yamakawa R. Long-term results of out-of-the-bag intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:266–270. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(99)00345-4
26. Taskapili M, Engin G, Kaya G, Kucuksahin H, Kocabora MS, Yilmazli C. Single-piece foldable acrylic intraocular lens implantation in the sulcus in eyes with posterior capsule tear during phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31:1593–1597. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2005.01.029
27. Taskapili M, Gulkilik G, Kocabora MS, et al. Comparison of sulcus implantation of single-piece hydrophilic foldable acrylic and polymethylmethacrylate intraocular lenses in eyes with posterior capsule tear during phacoemulsification surgery. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2007;17:595–600. doi:10.1177/112067210701700418
28. Uy HS, Chan PST. Pigment release and secondary glaucoma after implantation of single-piece acrylic intraocular lenses in the ciliary sulcus. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;142:330–332. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2006.02.033
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.